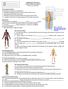
General Body and Directional Terms
|
|
|
- Irma Watson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Body and Directional Terms Course Anatomy & Physiology Unit I Orientation to the Human Body Essential Question What common terminology is used to describe human anatomy? TEKS (c) 2A 6A, 6B 10A Prior Student Learning None Estimated time 2-4 hours Rationale Healthcare professionals must have a comprehensive medical vocabulary in order to communicate effectively with other health professionals. Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, the learner should be able to: Define and decipher common terms associated with the structural organization of the body Identify the body cavities and distinguish the organs contained within those cavities List and define the terms related to positions, directions and planes of the body Engage Place several markings on a student volunteer s body. Have three other students write down how they would describe where the marks are located on the student volunteer. Then have each of the three students read aloud what they have written. Explain that by using medical terms to describe the locations of the marks, we can be more exact and this will help whomever is reading the report understand the true location of injuries, anomalies or incisions. Key Points I. Branches of Science that study the human body a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other 3. Dissection is used to study the structure of the human body b. Biology - Study of all forms of life and living things c. Embryology 1. Study of the origin and development of an organism 2. Covers from 2 nd to the 8 th week after conception, the embryonic state 3. After eight weeks, the developing organism is known as a fetus. d. Histology 1. Study of the body microscopically 2. Studies the minute structures and their composition, plus the functions of normal cells, tissue and organs. e. Pathology 1. Study of the changes in the human body which are caused
2 by disease 2. Study changes due to disease that alter the function of the body f. Physiology - Studies the normal activity and functions of the body II. III. Body in General a. Cells are the basic unit of life b. Cells that perform similar functions join together, or group together, to form tissue. c. Groups of different types of tissue join together to form an organ d. Groups of organs work together to perform a complex function, for a body system e. Trillions of cells that vary in size and shape according to their purpose or function f. Specialized cells are responsible for the functions of growth, secretions, excretions, nutrition, and reproduction g. Mechanical, chemical and nervous stimulation activate the cells Cells a. Epithelial cells 1. Skin cells 2. May be square and flat b. Fat cells - contain large vacant spaces for fat storage c. Muscle cells - long and slender d. Nerve cells - may be long and have fingerlike extensions, which carry impulses IV. Tissues a. Connective tissue 1. Supports and encases body structures. 2. Most widespread kind of tissue throughout the body 3. Holds organs in place and connects body parts to each other 4. Main types of connective tissue: (a) Bone that supports the body (b) Cartilage which is firm but bendable (c) Dense fibrous: makes up the tendons and ligaments (d) Loose that connects adjoining structures (e) Adipose that pads and protects, stores fat, and insulates the body against heat loss b. Epithelial tissue 1. Found in the skin and in the lining of blood vessels 2. Makes up the outer covering of external and internal body surfaces and the lining of the digestive, respiratory, and Page 2 of 25
3 urinary tracts c. Muscle tissue 1. Provides movement 2. The main function is to contract d. Nerve tissue 1. Conducts impulses to and from the brain 2. Is composed of nerve cells called neurons 3. Needs more oxygen and nutrients than any other body tissue V. Organs a. When two or more kinds of tissue work together to perform a specific function, you have an organ b. Although organs act as units, they do not function alone c. Several organs join together to form a system and perform a body function d. Each system has a special function VI. Systems a. Cardiovascular system 1. Includes the heart and blood vessels 2. Carries the blood throughout the body b. Digestive or gastrointestinal system 1. Includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and the small and large intestines 2. Digests and absorbs food and excretes waste c. Endocrine system 1. Made up of a variety of glands 2. Manufactures and distributes hormones d. Integumentary system 1. Includes the hair, skin, nails, sweat glands and oil glands 2. Helps protect the body e. Lymphatic system 1. Works with the cardiovascular system 2. Helps protect the body against disease-causing organisms f. Musculoskeletal system 1. Composed of bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments 2. Provides the framework for the body 3. Supports organs 4. Permits movement in the body g. Reproductive system 1. Includes the uterus, ovaries, testes, and prostate 2. Provides for reproduction h. Respiratory system 1. Includes the trachea, lungs, and bronchi 2. Provides for the exchange of gases 3. Absorbs oxygen Page 3 of 25
4 4. Expels carbon dioxide i. Sensory or special senses system 1. Made up of the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin and nerves 2. Acts as the body s external perception/alarm system by letting in light, sound, taste and touch (both pleasure and pain) j. Nervous System 1. Brain, spinal cord and nerves 2. Allows the body to act and respond k. Urinary system 1. Manufactures and excretes urine 2. Includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra VII. VIII. Cavities of the Body a. Abdominal cavity 1. Contains the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas, ureters, and kidneys 2. Ventral body cavity (located on the front of the body) b. Cranial cavity 1. The cavity inside the skull, or the cranium 2. Space within the skull containing the brain 3. Cranial means pertaining to the skull. 4. Dorsal body cavities (located on the back part of the body) c. Pelvic cavity 1. Contains the urinary bladder, urethra, uterus and vagina in the female, part of the large intestine and the rectum 2. Ventral body cavity (located on the front of the body) 3. Space below the abdomen d. Spinal cavity 1. Consist of the spinal column connecting to the cranial cavity 2. Space within the spinal column (backbone) containing the spinal cord 3. Dorsal body cavities (located on the back part of the body) e. Thoracic or chest cavity 1. Contains the esophagus, trachea, lungs, heart and aorta 2. Can be divided into two smaller areas (a) The pleural cavity surrounds the lungs (b) The mediastinum is the area between the lungs, containing the heart, aorta, trachea, esophagus and thymus gland 3. Ventral body cavity (located on the front of the body) f. Pleural cavity 1. Space around each lung Roots of Structures Page 4 of 25
5 Root What it Means Example term What it Means Cyt/o Cell Cytology Study of cells Epitheli/o Epithelium Epithelioma Tumor of the skin Fibr/o Fibrous Fibrosis Condition of the fibrous tissue Hist/o Tissue Histologist Physician who studies tissue Lip/o Fat Liposuction Removal of fat cells by suction Myo Muscle Myositis Enlargement of an organ Neur/o Nerve Neuropathy Condition of the nerve Organ/o Organ Organomegaly Enlargement of an organ Viscer/o Internal organs Viscera Internal organs IX. Structural Suffixes Suffix What it Means Example term What it Means -cyte Cell Erythrocyte Red blood cell -gen Agent that causes Carcinogen Agent causing cancer -genic Producing Carcinogenic Has cancercausing properties -oma Tumor or swelling Myoma Tumor in the muscle -osis Abnormal condition Cytosis Abnormal condition of cells -pathy Disease Neuropathy A disease of the nerves -plasm Growth or Neoplasm A new growth formation -sarcoma Malignant tumor Myosarcoma Malignant muscle tumor X. Directional Terms a. Used to pinpoint or specifically locate an area on the body. b. Anatomical position is the body standing, arms at each side, with palms facing forward and the feet side by side c. Anatomical plane 1. An imaginary flat plate or field 2. Provide further division of the body, to identify a specific location or area d. Frontal or coronal plane 1. A vertical plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior Page 5 of 25
6 portions 2. Anterior means front 3. Posterior refers to the back e. Mid-sagittal plane 1. A horizontal plane 2. Divides the body into right and left halves at the body s midpoint f. Sagittal plane 1. A vertical plane 2. Passes from front to back 3. Divides the body into right and left sides g. Transverse plane 1. A horizontal (cross-section) plane, parallel to the ground and through the waistline 2. Divides the body into upper and lower halves h. Ventral 1. Anterior 2. Refers to the front of the body i. Dorsal 1. Posterior 2. Refers to the back of the body j. Cephalad 1. Above the waistline 2. head or upward 3. Superior above k. Caudal 1. Below the waistline 2. Inferior, below l. Superior and inferior 1. Also used to describe body parts in relation to one another in general m. Lateral - sides of the body n. Medial refers to the middle o. Distal away from the point of origin 1. The foot would be the distal portion of the leg p. Proximal refers to nearest the point of origin, close proximity 1. The upper thigh would e the proximal portion of the leg q. Ipsilateral 1. Pertains to one side r. Mediolateral 1. Pertaining to the middle and one side XI. Root words that pertain to directional terms Page 6 of 25
7 Root word Anter/o Caud/o Cephal/o Dist/o Dors/o Infer/o Later/o Medi/o Poster/o Proxim/o Super/o Ventr/o What it means Front Tail or downward Head or upward Away from (distant) the point of origin Back Below Side Middle Back or behind Near to (proximity) the point of origin Above Front or belly XII. Regions of the body a. Anatomical divisions of the abdomen b. Used to describe the regions in which organs and structures are found c. Used to diagnose abdominal problems with greater accuracy 1. Hypochondriac region (a) Upper lateral regions beneath the ribs 2. Epigastric region (a) Region of the stomach 3. Lumbar region (a) Two middle lateral regions 4. Umbilical region (a) Region of the navel or umbilicus 5. Inguinal (iliac) region (a) Lower lateral regions 6. Hypogastric region (a)lower middle region, below the umbilicus XIII. Quadrants a. Right upper quadrant 1. RUQ 2. Contains the right lobe of the liver, gallbladder, and parts of the small and large intestines. b. Left upper quadrant 1. LUQ 2. Contains the left lobe of the liver, stomach, pancreas, spleen, and parts of the small and large intestines c. Right lower quadrant 1. RLQ 2. Contains parts of the small and large intestines, appendix, right ureters, right ovary, and fallopian tube. d. Left lower quadrant Page 7 of 25
8 XIV. 1. LLQ 2. Contains parts of the small and large intestines, left ureters, left ovary, and fallopian tube Divisions of the back Division Abbreviation Location Cervical C Neck region. There are 7 cervical vertebrae (C1-C7). Thoracic T or D (D = dorsal) Chest region. There are 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12). Each bone is joined to a rib Lumbar L Loin or flank region (between the ribs and the hip bone). There are 5 lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5). Sacral D Five bones (S1-S5) are fused to form one bone, the sacrum. Coccygeal (none) The coccyx (tailbone) is a small bone composed of 4 fused pieces. XV. Other body regions Region Auricular region Axillary Buccal Clavicular Infraorbital Infrascapular Lumbar Mammary Mental Orbital Pubic Sacral Sternal Submental Supraclavicular Where it is Around the ears Axillae (armpits) Cheeks of the face On each side of the sternum (breastbone) Below the eyes On each side of the chest down to the last rib Below the infrascapular area Breast area Region of the chin Around the eyes Above the hypogastric region (above the pubis) Area over the sacrum Over the sternum Below the chin Above the clavicles XVI. Positions a. Erect a standing position b. Lateral recumbent lying on left side with right thigh and knee drawn up to chest c. Prone lying face down d. Supine lying flat on your back Page 8 of 25
9 e. Sims position 1. Semi-prone side position 2. Lying on the left side with the right thigh and knee sharply flexed; left leg straight 3. The lower arm (left) is behind the person 4. Pillow is under the person s head and shoulder 5. Usually not comfortable for older persons f. Fowler s position 1. Semi-sitting 2. The head of the bed is raised between 45 and 60 degrees 3. Spine is straight 4. Head is supported with a small pillow Activity I. In pairs, create a stick-like figure, with a head, trunk, arms, and legs using play dough. As the terms are discussed, the student will use a toothpick to designate the area. After all the terms are discussed, cut the figure into the planes. II. In pairs, identify the following areas on partner: Area distal to the knee. Area proximal to the elbow. Lateral to the big toe. Anterior side of the body. Posterior side of the body. Area that is medial to the shoulder. Area that is superior to the lungs. Area that is inferior to the heart. III. Complete Body and Directional Terms Worksheet. IV. Complete Color the Cavities and Color the Abdominal Regions activity. V. Complete the Body Planes and Directions activity. VI. Develop a Short Story describing best date or worst nightmare using anatomical terms. VII. Show students copies of CT-scans and quiz them on which body plane is being used. Assessment Successful completion of the activities Writing Rubric Body Orientation Quiz and Key Materials Assorted colors of clay Crayons Colored toothpicks Paper plates Rulers Bananas Page 9 of 25
10 Permanent markers - atlas of the human body Data projector Computer Utah State Office of Education, (2005). Medical Anatomy and Physiology Teacher Resource CD. Utah. Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the student will practice terms using flash cards. For enrichment, the student will choose 20 general body and directional terms and create a crossword puzzle National and State Education Standards National Healthcare Foundation Standards and Accountability Criteria: Foundation Standard 2: Communications 2.21 Use roots, prefixes, and suffixes to communicate information 2.22 Use medical abbreviations to communicate information TEKS (c)(2)(a) know the definition of science and understand that it has limitations, as specified in subsection (b)(2) of this section; (c)(6)(a) investigate and describe the integration of the chemical and physical processes, including equilibrium, temperature, ph balance, chemical reactions, passive transport, active transport, and biofeedback, that contribute to homeostasis; (c)(6)(b) determine the consequences of the failure to maintain homeostasis; and (c)(10)(A) analyze the relationships between the anatomical structures and physiological functions of systems, including the integumentary, nervous, skeletal, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, endocrine, and reproductive. Texas College and Career Readiness Standards English and Language Arts Understand new vocabulary and concepts and use them accurately in reading, speaking, and writing 1. Identify new words and concepts acquired through study of their relationships to other words and concepts 2. Apply knowledge of roots and suffixes to infer the meanings of new words 3. Use reference guides to confirm the meanings of new words or concepts Cross-Disciplinary Standards Page 10 of 25
11 I. Key Cognitive Skills D. Academic Behavior: 1. Self-monitor learning needs and seek assistance when needed; 3. Strive for accuracy and precision; 4. Persevere to complete and master task E. Work habits: 1. Work independently 2. Work collaboratively II. Foundation Skills A. 2. Use a variety of strategies to understand the meaning of new words 4. Identify the key information and supporting details Page 11 of 25
12 Body and Directional Terms Root What it Means Example term What it Means Cyt/o Cytology Epitheli/o Epithelioma Fibr/o Fibrosis Hist/o Histologist Lip/o Liposuction Myo Myositis Neur/o Neuropathy Organ/o Organomegaly Viscer/o Viscera Root word Anter/o Caud/o Cephal/o Dist/o Dors/o Infer/o Later/o Medi/o Poster/o Proxim/o Super/o Ventr/o What it means Suffix What it Means Example term What it Means -cyte Erythrocyte -gen Carcinogen -genic Carcinogenic -oma Myoma -osis Cytosis -pathy Neuropathy -plasm Neoplasm -sarcoma Myosarcoma Division Abbreviation Location Cervical C Thoracic T or D (D = dorsal) Lumbar L Sacral D Medical Terminology Page 12 of 25
13 Body and Directional Terms Region Auricular region Axillary Buccal Clavicular Infraorbital Infrascapular Lumbar Mammary Mental Orbital Pubic Sacral Sternal Submental Supraclavicular Where it is afferent efferent anterior posterior central deep superficial distal proximal inferior superior lateral medial supine prone Frontal plane Sagittal plane Transverse plane Page 13 of 25
14 KEY - Medical Terminology Body and Directional Terms Root What it Means Example term What it Means Cyt/o Cell Cytology Study of cells Epitheli/o Epithelium Epithelioma Tumor of the skin Fibr/o Fibrous Fibrosis Condition of the fibrous tissue Hist/o Tissue Histologist Physician who studies tissue Lip/o Fat Liposuction Removal of fat cells by suction Myo Muscle Myositis Enlargement of an organ Neur/o Nerve Neuropathy Condition of the nerve Organ/o Organ Organomegaly Enlargement of an organ Viscer/o Internal organs Viscera Internal organs Root word Anter/o Caud/o Cephal/o Dist/o Dors/o Infer/o Later/o Medi/o Poster/o Proxim/o Super/o Ventr/o What it means Front Tail or downward Head or upward Away from (distant) the point of origin Back Below Side Middle Back or behind Near to (proximity) the point of origin Above Front or belly Suffix What it Means Example term What it Means -cyte Cell Erythrocyte Red blood cell -gen Agent that Carcinogen Agent causing cancer causes -genic Producing Carcinogenic Has cancer-causing properties -oma Tumor or Myoma Tumor in the muscle swelling -osis Abnormal Cytosis Abnormal condition of cells condition -pathy Disease Neuropathy A disease of the nerves -plasm Growth or Neoplasm A new growth formation -sarcoma Malignant tumor Myosarcoma Malignant muscle tumor Page 14 of 25
15 Division Abbreviation Location Cervical C Neck region. There are 7 cervical vertebrae (C1-C7). Thoracic T or D (D = dorsal) Chest region. There are 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12. Each bone is joined to a rib Lumbar L Loin or flank region (between the ribs and the hip bone). There are 5 lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5). Sacral D Five bones (S1-S5) are fused to form one bone, the sacrum. Coccygeal (none) The coccyx (tailbone) is a small bone composed of 4 fused pieces. Region Auricular region Axillary Buccal Clavicular Infraorbital Infrascapular Lumbar Mammary Mental Orbital Pubic Sacral Sternal Submental Supraclavicular afferent efferent anterior posterior central deep superficial distal proximal inferior superior lateral medial supine prone Where it is Around the ears Axillae (armpits) Cheeks of the face On each side of the sternum (breastbone) Below the eyes On each side of the chest down to the last rib Below the infrascapular area Breast area Region of the chin Around the eyes Above the hypogastric region (above the pubis) Area over the sacrum Over the sternum Below the chin Above the clavicles Conducting toward a structure. Conducting away from a structure. Front of the body (ventral). Back of the body (dorsal). Pertaining to the center. Away from the surface. Near the surface. Away from the beginning of a structure; away from the center. Pertaining to the beginning of a structure Away from the head; below another structure (caudal). Toward the head; above another structure (cephalic). Pertaining to the side. Pertaining to the middle. Lying on the back Lying on the belly Page 15 of 25
16 Frontal plane Sagittal plane Transverse plane Vertical plane dividing the body or structure into an anterior and posterior portion. Vertical plane dividing the body or structure into right and left portions. Horizontal plane dividing the body or structure into upper and lower portions. Page 16 of 25
17 Color the Cavities Using a diagram of the human body, label and color code each of the following. Ventral Cavity Thoracic Cavity Pleural Cavities Pelvic Cavity Mediastinum Pericardial Cavity Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Page 17 of 25
18 Color the Cavities Using a diagram of the human body, label and color code each of the following. Dorsal cavity Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity Cranial Cavity Page 18 of 25
19 Color the Abdominal Regions A. Color the following drawing using the body regions: 1. Right iliac- purple 2. Epigastric- red 3. Left lumbar- blue 4. Right hypochondriac- yellow 5. Umbilical- orange 6. Left iliac- pink 7. Right lumbar-green 8. Hypogastric- brown 9. Left hypochondriac- leave blank B. Using a black marker label the 4 abdominal quadrants. Page 19 of 25
20 Body Planes and Directions Activity Planes and directions are practiced using fruit and toothpicks. Be careful with the surgical instruments. Read and follow the instructions very carefully. Materials: Knives Marker Colored toothpicks Bananas Rulers Banana: Cut the banana with a transverse plane. Stick a blue toothpick in the superior end of the banana. Place red toothpick in the most distal point on the right inferior piece. Make a 3cm midsagittal incision on the posterior inferior portion of your banana. Place a yellow toothpick at the anterior superior medial section of the banana. With a maker place a (X) on the left posterior superior lateral section on your banana. Page 20 of 25
21 Short Story Incorporate the following terms into a story describing your describing your worst nightmare. Underline the term(s) in the story. Superior Inferior Anterior Abdominal Cavity Dorsal Pelvic Cavity Medial Oral Cavity Lateral Proximal Distal Superficial Deep Skeletal System Cardiovascular System Page 21 of 25
22 Body Orientation Quiz 1. Describe how a body would be divided by each of the following types of planes: A. Frontal (Coronal) B. Midsagittal C. Sagittal D. Transverse 2. Identify the correct directional term to complete the following statements. A. The liver is to the diaphragm. B. Fingers are located to the wrist bones. C. The skin on the dorsal surface of your body is said to be located on your surface. D. The great (big) toe is to the little toe. E. The skin on your leg is to the muscle tissue in your leg. F. When you float face down in a pool, you are lying on your surface. G. The lungs and the heart are located to the abdominal organs. 3. Identify which cavity each of the following organs are in: A. Heart G. Lungs B. Liver H. Spleen C. Intestines I. Kidneys D. Spinal Cord J. Stomach E. Brain K. Urinary Bladder F. Sex Organs L. Pancreas 4. Fill in the blank completing the analogy. A. anterior is to ventral as posterior is to B. superficial is to external as deep is to C. cranial is to caudal as superior is to D. medial is to lateral as proximal is to Page 22 of 25
23 5. Match the organs with the cavity they are in. CAVITY 1. cranial cavity 2. spinal cavity 3. thoracic cavity 4. abdominal cavity 5. pelvic cavity ORGAN A. stomach B. reproductive organs C. brain D. small intestines E. urinary bladder F. spinal cord G. liver, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen H. lung 6. Match the abdominal region with the descriptive term: 1. Iliac/ingiuinal A. above the stomach 2. Epigastric B. near the belly button 3. Lumbar/lateral C. below the stomach 4. hypochondriac D. below the ribs 5. Umbilical E. near the large bones of spinal cord 6. hypogastric/ pelvic F. near the groin ("Medical anatomy and," 2005) Page 23 of 25
24 Quiz Key 1. Describe how a body would be divided by each of the following types of planes: A. Frontal (coronal) - divides body into anterior and posterior sections. B. Midsagittal - divides body into equal right and left sides. C. Sagittal - divides body into right and left sides. D. Transverse - divides body into superior and inferior sections. 2. Identify the correct directional term to complete the following statements. A. The liver is inferior to the diaphragm B. Fingers are located distal to the wrist bones. C. The skin on the dorsal surface of your body is said to be located on your posterior surface. D. The great(big) toe is medial to the little toe. E. The skin on your leg is superficial to the muscle tissue in your leg. F. When you float face down in a pool, you are lying on your anterior surface. G. The lungs and the heart are located superior to the abdominal organs. 3. Identify which cavity each of the following organs are in: A. Heart ventral/mediastinal G. Lungs ventral/pleural B. Liver abdominal H. Spleen abdominal C. Intestines abdominal I. Kidneys abdominal D. Spinal Cord vertebral J. Stomach abdominal E. Brain cranial K. Urinary Bladder pelvic F. Sex Organs pelvic L. Pancreas- abdominal 4. Fill in the blank completing the analogy. A. anterior is to ventral as posterior is to dorsal B. superficial is to external as deep is to internal C. cranial is to caudal as superior is to inferior D. medial is to lateral as proximal is to distal 5. Match the organs with the cavity they are in. CAVITY ORGAN 1. C cranial cavity A. stomach 2. F spinal cavity B. reproductive organs 3. H thoracic cavity C. brain 4. A, D, G abdominal cavity D. small intestines 5. B, E pelvic cavity E. urinary bladder F. spinal cord G. liver, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen H. lung Page 24 of 25
25 6. Match the abdominal region with the descriptive term: 1. F Iliac/ingiuinal A. above the stomach 2. A Epigastric B. near the belly button 3. E Lumbar/lateral C. below the stomach 4. D hypochondriac D. below the ribs 5. B Umbilical E. near the large bones of spinal cord 6. C hypogastric/ pelvic F. near the groin ("Medical Anatomy and," 2005) Page 25 of 25
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
Concepts of the. Human Body. chapter outline. 1 The Human Body and Disease. The Study of the. Human Body. Organization of the.
 1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
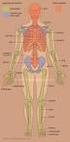
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II
 Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II An Overview of Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology CHAPTER 3 Good work is not accomplished in haste. Ancient Chinese Proverb HIGHLIGHTS Let s begin
Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology by Body Systems PART II An Overview of Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology CHAPTER 3 Good work is not accomplished in haste. Ancient Chinese Proverb HIGHLIGHTS Let s begin
Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112)
 Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Body cavities. Body Planes
 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
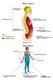
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program
 Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Application for a Medical Impairment Rating (MIR)
 STATE OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT Workers Compensation Division Medical Impairment Rating Program 220 French Landing Drive Nashville, TN 37243-1002 Phone (615) 253-1613 Fax
STATE OF TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND WORKFORCE DEVELOPMENT Workers Compensation Division Medical Impairment Rating Program 220 French Landing Drive Nashville, TN 37243-1002 Phone (615) 253-1613 Fax
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
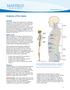 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Range of Injury Scale Values
 Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD
 1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Request for Designated Doctor Examination Type (or print in black ink) each item on this form
 Texas Department of Insurance Division of Workers Compensation 7551 Metro Center Drive, Suite 100 MS-603 Austin, TX 78744-1645 (512) 804-4380 phone (512) 804-4121 fax Complete, if known: DWC Claim # Carrier
Texas Department of Insurance Division of Workers Compensation 7551 Metro Center Drive, Suite 100 MS-603 Austin, TX 78744-1645 (512) 804-4380 phone (512) 804-4121 fax Complete, if known: DWC Claim # Carrier
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity)
 FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin integrity.
 Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Unit B Resident Care Skills Essential Standard NA5.00 Understand nurse aide s role in providing residents hygiene, grooming, and skin care. Indicator Understand nurse aide skills needed to promote skin
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Frog Dissection. Procedure
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
This is how quickly your brain forgets things
 Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
