BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
|
|
|
- Ashley Scott
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing body landmarks, directions, planes, and surfaces. Name the body cavities, and indicate important organs in each cavity. Understand serial sections and anatomical reconstruction Most of us are naturally curious about our bodies. This curiosity is apparent even in infants, when they gaze in fascination at their own waving hands or their mother's nose. Unlike the infant, however, an anatomy student must learn to identify body structures formally. This exercise presents some of the most important anatomical terms you will be using to describe the body and introduces you to gross anatomy, the study of body structures you can see with your naked eye. As you become familiar with this anatomical terminology, you will have a chance to examine the three-dimensional relationships of body structures using illustrations and models. Proper Anatomical Position When doctors refer to specific areas of the human body, they do so relative to a standard position called the anatomical position. In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with head and toes pointed forward and arms hanging at the sides with palms facing forward (see Figure 3). ACTIVITY 1 Demonstrating the Anatomical Position Stand, and assume the anatomical position. Notice that it is not particularly comfortable, because you must hold your hands unnaturally forward instead of allowing them to hang partially cupped toward your thighs. Surface Anatomy Body surfaces provide a number of visible landmarks that can be used to study the body. Several of these are described on the following pages. Locating Body Landmarks Anterior Body Landmarks Identify and use anatomical terms to correctly label the following regions on Figure 1: BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 1
2 Abdominal: The anterior body trunk region inferior to the ribs Antecubital: The anterior surface of the elbow Axillary: The armpit Brachial: The arm Buccal: The cheek Carpal: The wrist Cervical: The neck region Coxal: The hip Deltoid: The roundness of the shoulder caused by the underlying deltoid muscle Digital: The fingers or toes Femoral: The thigh Fibular: The side of the leg Inguinal: The groin Mammary: The breast Manus: The hand Nasal: The nose Oral: The mouth Orbital: The bony eye socket (orbit) Patellar: The anterior knee (kneecap) region Pelvic: The pelvis region Pubic: The genital region Sternal: The region of the breastbone Tarsal: The ankle Thoracic: The chest Umbilical: The navel Posterior Body Landmarks Identify and appropriately label the following body surface regions in Figure 1 b: Cephalic: The head Gluteal: The buttocks or rump Lumbar: The area of the back between the ribs and hips; the loin Occipital: The posterior aspect of the head or base of the skull Popliteal: The back of the knee Sacral: The area between the hips Scapular: The scapula or shoulder blade area Sural: The calf or posterior surface of the leg Vertebral: The area of the spinal column BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 2
3 Figure 1. Surface Anatomy. Left image is anterior, Right image is posterior Body Orientation and Direction Study the terms below, referring to Figure 2. Notice as you read that certain terms have a different meaning for a four-legged animal than they do for a human. Superior/inferior (above/below): These terms refer to the location of a structure along the long axis of the body. Superior structures appear above other structures, and inferior structures are always below other body parts. Anterior/posterior (frontlback): In humans the most anterior structures are those that are most forward-the face, chest, and abdomen. Posterior structures are those toward the backside of the body. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 3
4 Medial/lateral (toward the midline/away from the midline or median plane): Medial structures are closer to the body midline than are lateral structures. The terms described above assume the person is in the anatomical position. The next four pairs of terms are more absolute. They do not relate to a particular body position, and they have the same meaning in all vertebrate animals. Cephalad/caudad (caudal) (toward the head/toward the tail): In humans these terms are used interchangeably with superior and inferior. But in four-legged animals, they are synonyms of anterior and posterior, respectively. Figure 2. Anatomical terminology for orientation and direction Dorsal/ventral (backsidelbelly side): Meaning "back," the term dorsal refers to the animal's back or the backside of any other structures. The term ventral, meaning "belly," always refers to the belly side of animals. In humans the terms ventral and dorsal are used interchangeably with the terms anterior and posterior, but in four-legged animals ventral and dorsal mean inferior and superior, respectively. Proximal/distal (nearer the trunk or attached end/farther from the trunk or point of attachment): These terms locate various areas along the body limbs or an elongated organ such as the intestine. For example, the fingers are distal to the elbow; the knee is proximal to the toes. Superficial/deep (toward or at the body surface/away from the body surface or more internal): These terms locate body organs according to their relative closeness to the body surface. For example, the skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles. Practice Using Correct Anatomical Terminology Before continuing, use a human torso model, a skeleton, or your own body to specify the relationship between the following structures. 1. The wrist is to the hand. 2. The trachea (windpipe) is to the spine. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 4
5 3. The brain is to the spinal cord. 4. The kidneys are to the liver. 5. The nose is to the cheekbones. 6. The chest is to the abdomen. 7. The skin is to the skeleton. Figure 3. Planes of the body Body Planes and Sections The body is three-dimensional. So, to observe its internal parts, it often helps to make use of a section, or cut made along an imaginary surface or line called a plane. There are three planes (Figure 3), or sections, that lie at right angles to one another. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 5
6 Sagittal plane: A plane that runs lengthwise or longitudinally down the length of the body, dividing it into right and left parts, is a sagittal plane. If it divides the body into equal parts, down the midline of the body, it is called a median, or midsagittal, plane. Frontal (coronal) plane: A longitudinal plane that divides the body (or an organ) into anterior and posterior parts. Transverse plane: A plane that runs horizontally, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts. These sections are also commonly called cross sections. As shown in Figure 4, a sagittal or frontal section of any nonspherical object, be it a banana or a body organ, provides quite a different view from a transverse section. Observing Sectioned Specimens Figure 4. Longitudial and transverse sections 1. Observe an entire (uncut) kidney and transversely and longitudinally cut kidneys. Pay close attention to the different structural details you can see in the samples. 2. Observe a sectioned gelatin-spaghetti mold (cooked spaghetti added to warm gelatin that is then allowed to gel.) You should see spaghetti strands that have been cut transversely (XS), longitudinally, and obliquely. Draw each of these spaghetti sections below. Body Cavities The axial portion of the body has two main cavities (Figure 5). Dorsal Body Cavity The dorsal body cavity consists of the cranial and spinal cavities. The cranial cavity, within the rigid skull, contains the brain. The spinal cavity, which runs within the bony vertebral column, protects the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a continuation of the brain, and the cavities containing them are continuous with each other. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 6
7 Ventral Body Cavity Like the dorsal cavity, the ventral body cavity is subdivided. The superior thoracic cavity is separated from the rest of the ventral cavity by the muscular diaphragm. The heart and lungs, located in the thoracic cavity, are protected by the bony rib cage. The cavity inferior to the diaphragm is the abdominopelvic cavity. Although there is no further physical separation of this part of the ventral cavity, some describe the abdominopelvic cavity in terms of a superior abdominal cavity, the area that houses the stomach, intestines, liver, and other organs, and an inferior pelvic cavity, which is partially enclosed by the bony pelvis and contains the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum. Notice that the pelvic cavity tips away from the abdominal cavity in a posterior direction (Figure 5). Figure 5. Body cavities Abdominopelvic Quadrants and Regions The abdominopelvic cavity is quite large and contains many organs, so it is helpful to divide it up into smaller areas for study. The medical scheme divides the abdominal surface (and the abdominopelvic cavity deep to it) into four approximately equal regions called quadrants, named according to their relative position-they are, right upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, and left lower quadrant (Figure 6). Another scheme, commonly used by anatomists, divides the abdominal surface and abdominopelvic cavity into nine separate regions by four planes, also shown in Figure 6. Although the names of these nine regions are unfamiliar to you now, with a little patience and study, they will become easier to remember. These regions are: BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 7
8 Umbilical region: The centermost region, which includes the umbilicus. Epigastric region: Immediately superior to the umbilical region; overlies most of the stomach. Hypogastric (pubic) region: Immediately inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area. Iliac regions: Lateral to the hypogastric region and overlying the superior parts of the hip bones. Lumbar regions: Between the ribs and the flaring portions of the hip bones; lateral to the umbilical region. Hypochondriac regions: Flanking the epigastric region laterally and overlying the lower ribs. ACTIVITY Read through the descriptions of these nine regions locate them in Figure 6. Be sure to notice the organs they contain. Figure 6. Abdominopelvic surface and cavity. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 8
9 Locate the regions of the abdominal surface on a torso model and on yourself before continuing. Looking at Two Dimensional and Three Dimensional Morphology Creating Serial Sections Figure 7. Long and short axis and meridian marks on hardboiled egg 1. Obtain a hardboiled egg and remove the shell from the egg. 2. Using a paper towel, dry the shelled egg. Mark the short and long axis meridians using a Flair (water soluble) type marker (Fig. 7) 3. Using the egg slicer, slice egg along its long axis (Fig. 8). 4. Arrange egg slices in order on a piece of paper (Fig. 9). You should create about 6 to 7 slices. 5. Place grid on the first slice and align axis marks with the x and y axis (0,0) 6. Draw the pattern seen in section one on the serial section grid labeled Section One on Figure 9. Please think about this: Seven slices should result in 6 serial sections. 7. Continue for each of the other serial sections. Keep the sections in order; label each in sequence. Figure 8. Hard-boiled egg in slicer along long axis Figure 9. Serial section arranged in order showing axis meridian marks BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 9
10 Figure 10. Serial sections through hardboiled egg BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 10
11 Figure 11. Serial sections through hardboiled egg (continued) Visualizing a section in the 90 degree plane: Reconstruction The sections you have just drawn are in a plane known as longitudinal. You will now use these sections to create a cross section. For this assignment you should choose a plane crossing each of your sections in which there is some of the egg yolk present. For instance, suppose you are going to draw the cross section at grid line 5 as shown in Figure 12. From each section at grid line 5 you would transfer the data to that section line in Figure 12. When you are done, you smoothly connect the dots and reconstruct the unknown cross section. Try this with your serial sections and reconstruct a 90 degree cross section in Figure 10. Figure 12. Reconstruction of 90 degree cross section from serial section data. Dots are data from single serial sections. BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 11
12 Figure 13. Reconstruction of 90 degree cross section of hardboiled egg BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 12
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Body cavities. Body Planes
 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112)
 Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
Name: Period: Date: Body Planes & Directions Anatomic Reference Systems (Unit 6, pp. 110-112) The Anatomic Position In the anatomic position, the individual is: 1. Standing up/sitting down (circle one)
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY
 THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
THE LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY Know all the terms identified in these sections of this exercise: Correct anatomical position: When the body is erect, with feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointing forward,
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Outline Introduction Characteristics of Living Things 1. Organization 2. Responsiveness 3. Growth & Differentiation 4. Reproduction 5. Movement
Concepts of the. Human Body. chapter outline. 1 The Human Body and Disease. The Study of the. Human Body. Organization of the.
 1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
1 UNIT 1 The Human Body and Disease Concepts of the Human Body chapter outline The Study of the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Body Cavities, Regions, and Quadrants Anatomical Terminology LifeS
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Define anatomy and physiology Identify the levels of organization in organisms from simplest to most complex Identify the organ systems of the human
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
General Body and Directional Terms
 General Body and Directional Terms Course Anatomy & Physiology Unit I Orientation to the Human Body Essential Question What common terminology is used to describe human anatomy? TEKS 130.206 (c) 2A 6A,
General Body and Directional Terms Course Anatomy & Physiology Unit I Orientation to the Human Body Essential Question What common terminology is used to describe human anatomy? TEKS 130.206 (c) 2A 6A,
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Characteristics of most living organisms include the ability to A) repair and completely restore itself during any type
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program
 Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
Supporting Adults through Vocational Education (S.A.V.E) EMT Program The S.A.V.E. EMT Program prepares adult students to become certified emergency medical technicians and to work in the EMT field where
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General this course emphasizes the elationship between anatomy and physiology More conceptual approach, interactions stressed! need some of both to truly understand how the body
Human Anatomy & Physiology General this course emphasizes the elationship between anatomy and physiology More conceptual approach, interactions stressed! need some of both to truly understand how the body
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD
 1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
1 CHINESE QI GONG EXERCISES TAUGHT BY JAKE PAUL FRATKIN, OMD Doctor of Oriental Medicine MORNING ROUTINE SUMMATION 1. Joint Opening Exercises 2. Meridian Stretching Exercises 3. Qi Circulation Exercises
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and
 A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
 In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
In: Recent Advances in Equine Theriogenology, B.A. Ball (Ed.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org) Ultrasonographic Determination of Equine Fetal Gender (31 Mar 2000)
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
6. Pig Dissection I. BI102. B.K. Penney
 6. Pig Dissection I BACKGROUND To study the anatomy of vertebrates, we will be dissecting fetal pigs. Material for these labs is essentially from Term 1. The context for BI02 is that I want you to understand
6. Pig Dissection I BACKGROUND To study the anatomy of vertebrates, we will be dissecting fetal pigs. Material for these labs is essentially from Term 1. The context for BI02 is that I want you to understand
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins
 Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
What is Acupuncture? 1 Summary of Acupoint Indications. 1.1 Head
 What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it gained recognition as a valid treatment for chronic or long-standing pain. Using the PAIN GONE on acupoints
What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it gained recognition as a valid treatment for chronic or long-standing pain. Using the PAIN GONE on acupoints
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Unit 1 Levels of Organization 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Learning Outcomes After studying this chapter, you should be able to do the following: A wooden toe on an ancient Egyptian mummy
Unit 1 Levels of Organization 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Learning Outcomes After studying this chapter, you should be able to do the following: A wooden toe on an ancient Egyptian mummy
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest. Exercise 2: Pelvic Tilt. Exercise 3: Hip Rolling. Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface.
 Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Qigong. Ba Duan Jin. The Eight Pieces of Brocade
 Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
Qigong Ba Duan Jin The Eight Pieces of Brocade by Col and g Hamilton Yiheyuan Martial Arts Contents Page Introduction 2 Preparation 2 1. Hold up the Sky 3 2. The Archer 4 3. Join Heaven and Earth 5 4a.
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
SPINE. Postural Malalignments 4/9/2015. Cervical Spine Evaluation. Thoracic Spine Evaluation. Observations. Assess position of head and neck
 SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
SPINE Observations Body type Postural alignments and asymmetries should be observed from all views Assess height differences between anatomical landmarks Figure 25-9 Figure 25-10 Figure 25-11 & 12 Postural
How To Improve Drainage
 Rehabilitation Home Program Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may
Rehabilitation Home Program Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe
 No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
No Equipment Agility/Core/Strength Program for Full Body No Equip Trainer: Rick Coe Introduction Program designed to be performed in a circuit. Perform exercises in sequence without rest 2-3 times. Increase
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
This week. CENG 732 Computer Animation. Challenges in Human Modeling. Basic Arm Model
 CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 8 Modeling and Animating Articulated Figures: Modeling the Arm, Walking, Facial Animation This week Modeling the arm Different joint structures Walking
CENG 732 Computer Animation Spring 2006-2007 Week 8 Modeling and Animating Articulated Figures: Modeling the Arm, Walking, Facial Animation This week Modeling the arm Different joint structures Walking
Low Back Pain: Exercises
 Low Back Pain: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise if you
Low Back Pain: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise if you
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Massage and Movement
 Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
Massage and Movement Incorporating Movement into Massage Part One: Theory and Technique in Prone With Lee Stang, LMT NCBTMB #450217-06 1850 West Street Southington, CT 06489 860.747.6388 www.bridgestohealthseminars.com
CHAPTER 3: BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES. Standing Quad Stretch Athletic Edge - www.athleticedge.biz - (650) 815-6552
 CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
CHAPTER : BACK & ABDOMINAL STRETCHES Standing Quad Stretch ) Stand and grasp right ankle with same hand, use a wall or chair to Lower maintain Back balance with left hand. Maintain an upright Stretches
7) Which of these regions are NOT associated with the ventral (anterior) portion of the head: 7) A) oral B) orbital C) buccal D) nasal E) occiptal
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A section that divides the body on the longitudinal plane into equal right and left parts
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A section that divides the body on the longitudinal plane into equal right and left parts
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Sheet 1A. Treating short/tight muscles using MET. Pectorals. Upper trapezius. Levator scapula
 Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
Sheet 1A Treating short/tight muscles using MET Pectorals Once daily lie at edge of bed holding a half-kilo can, arm out sideways. Raise arm and hold for 10 seconds, then allow arm to hang down, stretching
by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman
 10 Yoga Poses for Low Back Pain Prevention by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman Introduction This series of poses is designed to prevent future back pain and also to relieve back pain that you may
10 Yoga Poses for Low Back Pain Prevention by Ellen Saltonstall and Dr. Loren Fishman Introduction This series of poses is designed to prevent future back pain and also to relieve back pain that you may
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca
 www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
www.healthyworkplaceweek.ca A Stretch-Break Program for Your Workplace! Why is stretching at work important? Sitting at a desk or computer; or standing at your work station for extended periods of time
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength
 EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength Two sets of 40 repetitions each. Stand with your feet pointed straight and hip-width apart. Place your fingertips
EGOSCUE CLINIC PAIN/POSTURE STRETCHES 1. Standing Arm Circles: Helps Restore Upper Body Strength Two sets of 40 repetitions each. Stand with your feet pointed straight and hip-width apart. Place your fingertips
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
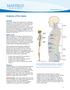 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Babies. Home treatment information sheet 1
 Home treatment information sheet 1 Babies Given out by (practice/practitioner): Recommended treatment: x per day/per week for. Dear parents, With these recommendations for treatment at home you will be
Home treatment information sheet 1 Babies Given out by (practice/practitioner): Recommended treatment: x per day/per week for. Dear parents, With these recommendations for treatment at home you will be
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
Anatomical perfection
 Is this winged lion a flight of fancy? Not really: if you understand the anatomy of an animal, any creature you make will be believable TIPS & TRICKS Anatomical perfection Getting under the skin of an
Is this winged lion a flight of fancy? Not really: if you understand the anatomy of an animal, any creature you make will be believable TIPS & TRICKS Anatomical perfection Getting under the skin of an
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK
 HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
stretches and exercises
 stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
stretches and exercises The enclosed sheets contain stretches and exercises which can be used to delay and minimise the development of contractures and deformities occurring in children with Duchenne muscular
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Coccydynia. (Coccyx Pain) Information for patients. Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312
 Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
