Introduction to RTL. Horácio Neto, Paulo Flores INESC-ID/IST. Design Complexity
|
|
|
- Neil Stewart
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to RTL INESC-ID/IST 1 Design Complexity How to manage the complexity of a digital design with logic gates? Abstraction simplify system model Consider only specific features for the given abstraction-level Ignore unnecessary detail E.g. at gate-level consider only logic values, 0 or 1, and fixed gate delays. Register Transfer Level Represent the digital system as a sequence of data processing/transfers between registers 2
2 Abstraction Hierarchy Set of representation levels that describe the system with more or less detail Higher-level Level 1 Less detail Level i Level i+1 Transformation Lower-level Level N More detail 3 Abstraction Levels Abstraction Representation in Level Behavioral Domain Structural Domain Processor Algorithm Microprocessor, or Chip RAM, ASICs... Register Data Flow Register, ALU, Counter, MUX,... Gate Boolean equations AND,OR,XOR,FF,... Circuit Differential equations Transistor, R, L, C Layout IC Masks 4
3 Design Flow Behavioral Domain Structural Domain Processor Register-Transfer Level RTL Algorithm Data Flow Behavioral The system is described by defining the relationship between the input and output signals Gate Circuit Layout Logic Transistors Masks Structural The system is described as an set of interconnections (netlist) of lower-level components 5 Main Design Tasks Synthesis Transform system representation from higher to lower abstraction level, (or from behavioral to structural domain) Placement and Routing Obtain final circuit layout Verification Check functionality and performance (timing) Testing Detect physical defects after circuit manufacture 6
4 Synthesis The outcome of a synthesis process is a circuit structural description at the lower (same) abstraction level High-level (Architectural) synthesis RT level synthesis Gate level synthesis Technology mapping 7 Design Space The designer must establish a tradeoff between: Area region of acceptable designs faster design (61ns, 394) speed area (cost!) power testability smaller design (78ns, 272) Delay 8
5 Verification Simulation cannot prove absence of errors not exhaustive depends on designer testbench. post P&R simulation may be very computation intensive Timing analysis (static) checks delay may be pessimistic 9 Algorithm to hardware? Example: y = ⅛ (a x 2 + b x + c) calculate 2 nd order polynomial divide by 8 round the result y = ⅛ ((a x + b) x + c) 10
6 Direct dataflow implementation? res <= r1 when p4(2) = '1' else r0; r1 <= r0 + 1; r0 <= "000" & p4(p4'high downto 3); p4 <= p3 + c ; p3 <= p2 * x ; p2 <= p1 + b ; p1 <= a * x ; -- c + x *(b + a*x) -- x *(b + a*x) -- (b + a*x) -- a * x 11 Datapath with intermediate regs Intermediate registers reduce critical path and may support pipelining (for streaming applications) y = ⅛ ((a x + b) x + c)
7 Problems with direct implementation Can only be used to implement simple algorithms Not flexible Resources cannot be shared Difficult to map algorithms where the number of operations (and/or their order of execution) is not fixed 13 Register-Transfer Level Methodology RTL: The digital system is represented as a sequence of data processing/transfers between registers Use registers to store (intermediate) data Use a datapath to implement all required operations between registers Use a control unit (FSM) to specify the order of execution of the operations FSMD = Finite-State Machine with Datapath 14
8 Basic RT Operation R dest f ( R src1, R src2,, R srcn ) At the rising edge of the clock, the values stored in registers R src are available The values are processed by a combinational circuit that implements f (...) At the next rising edge of the clock, the result is stored into R dest 15 Datapath Example (1) y = ⅛ (a x 2 + b x + c) y = ⅛ ((a x + b) x + c) Sequence of RT operations R 2 R A * R X R 2 R 2 + R B R 2 R 2 * R X R 2 R 2 + R C R 2 ⅛ * R 2 16
9 Control Unit Use a FSM to control the RT operations States transition is on clock-by-clock basis FSM enforces order of execution selects MUX paths selects ALU operations enables/disables registers FSM allows branches on execution sequence 17 Example (1) FSM controls sequence of RT operations New value of R 2 becomes available at the end of the corresponding execution state. x = 2 a = 3 b = 4 c = 5 y = ⅛ ((a x + b) x + c) = 3 18
10 Datapath Example (2) y = ⅛ ((a x + b) x + c) Sequence of RT operations R 2 R A * R X + R B R 2 ⅛ (R 2 * R X + R C ) 19
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Contents. System Development Models and Methods. Design Abstraction and Views. Synthesis. Control/Data-Flow Models. System Synthesis Models
 System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
System-on. on-chip Design Flow. Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems. jouni.tomberg@tut.
 System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
FSMD and Gezel. Jan Madsen
 FSMD and Gezel Jan Madsen Informatics and Mathematical Modeling Technical University of Denmark Richard Petersens Plads, Building 321 DK2800 Lyngby, Denmark [email protected] Processors Pentium IV General-purpose
FSMD and Gezel Jan Madsen Informatics and Mathematical Modeling Technical University of Denmark Richard Petersens Plads, Building 321 DK2800 Lyngby, Denmark [email protected] Processors Pentium IV General-purpose
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Digital Design Verification
 Digital Design Verification Course Instructor: Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Dept of Computer Sc. and Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Even Semester Course No: CS 676 1 Verification??? What is meant
Digital Design Verification Course Instructor: Debdeep Mukhopadhyay Dept of Computer Sc. and Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Even Semester Course No: CS 676 1 Verification??? What is meant
Chapter 13: Verification
 Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
ESP-CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation
 Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745. Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation
 Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
Fault Modeling. Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults. Transistor faults Summary
 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Step : Create Dependency Graph for Data Path Step b: 8-way Addition? So, the data operations are: 8 multiplications one 8-way addition Balanced binary
 RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
Computer organization
 Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs
 High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
Undergraduate Major in Computer Science and Engineering
 University of California, Irvine 2015-2016 1 Undergraduate Major in Computer Science and Engineering On This Page: Overview Admissions Requirements for the B.S. in Computer Science and Engineering Sample
University of California, Irvine 2015-2016 1 Undergraduate Major in Computer Science and Engineering On This Page: Overview Admissions Requirements for the B.S. in Computer Science and Engineering Sample
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS
 VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
Computer Systems Design and Architecture by V. Heuring and H. Jordan
 1-1 Chapter 1 - The General Purpose Machine Computer Systems Design and Architecture Vincent P. Heuring and Harry F. Jordan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado - Boulder
1-1 Chapter 1 - The General Purpose Machine Computer Systems Design and Architecture Vincent P. Heuring and Harry F. Jordan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado - Boulder
Design Cycle for Microprocessors
 Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
CLASS: Combined Logic Architecture Soft Error Sensitivity Analysis
 CLASS: Combined Logic Architecture Soft Error Sensitivity Analysis Mojtaba Ebrahimi, Liang Chen, Hossein Asadi, and Mehdi B. Tahoori INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING
CLASS: Combined Logic Architecture Soft Error Sensitivity Analysis Mojtaba Ebrahimi, Liang Chen, Hossein Asadi, and Mehdi B. Tahoori INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING
IL2225 Physical Design
 IL2225 Physical Design Nasim Farahini [email protected] Outline Physical Implementation Styles ASIC physical design Flow Floor and Power planning Placement Clock Tree Synthesis Routing Timing Analysis Verification
IL2225 Physical Design Nasim Farahini [email protected] Outline Physical Implementation Styles ASIC physical design Flow Floor and Power planning Placement Clock Tree Synthesis Routing Timing Analysis Verification
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS. IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE
 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
Introducción. Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
 Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
ECE 3401 Lecture 7. Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization
 Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU is the heart and brain It interprets and executes machine level instructions Controls data transfer from/to Main Memory (MM) and CPU Detects any errors In the following
Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU is the heart and brain It interprets and executes machine level instructions Controls data transfer from/to Main Memory (MM) and CPU Detects any errors In the following
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course. Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
AES1. Ultra-Compact Advanced Encryption Standard Core. General Description. Base Core Features. Symbol. Applications
 General Description The AES core implements Rijndael encoding and decoding in compliance with the NIST Advanced Encryption Standard. Basic core is very small (start at 800 Actel tiles). Enhanced versions
General Description The AES core implements Rijndael encoding and decoding in compliance with the NIST Advanced Encryption Standard. Basic core is very small (start at 800 Actel tiles). Enhanced versions
Implementation Details
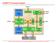 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design
 Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
Computer Architecture Lecture 2: Instruction Set Principles (Appendix A) Chih Wei Liu 劉 志 尉 National Chiao Tung University [email protected].
 Computer Architecture Lecture 2: Instruction Set Principles (Appendix A) Chih Wei Liu 劉 志 尉 National Chiao Tung University [email protected] Review Computers in mid 50 s Hardware was expensive
Computer Architecture Lecture 2: Instruction Set Principles (Appendix A) Chih Wei Liu 劉 志 尉 National Chiao Tung University [email protected] Review Computers in mid 50 s Hardware was expensive
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques
 Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus
 EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2014 Course Objectives Simply, a computer is a set of components (Processor, Memory and Storage, Input/Output Devices)
EE361: Digital Computer Organization Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2014 Course Objectives Simply, a computer is a set of components (Processor, Memory and Storage, Input/Output Devices)
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
Asynchronous & Synchronous Reset Design Techniques - Part Deux
 Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
A Second Undergraduate Course in Digital Logic Design: The Datapath+Controller-Based Approach
 A Second Undergraduate Course in Digital Logic Design: The Datapath+Controller-Based Approach Mitchell A. Thornton 1 and Aaron S. Collins 2 Abstract A second undergraduate course in digital logic design
A Second Undergraduate Course in Digital Logic Design: The Datapath+Controller-Based Approach Mitchell A. Thornton 1 and Aaron S. Collins 2 Abstract A second undergraduate course in digital logic design
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
e.g. τ = 12 ps in 180nm, 40 ps in 0.6 µm Delay has two components where, f = Effort Delay (stage effort)= gh p =Parasitic Delay
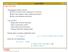 Logic Gate Delay Chip designers need to choose: What is the best circuit topology for a function? How many stages of logic produce least delay? How wide transistors should be? Logical Effort Helps make
Logic Gate Delay Chip designers need to choose: What is the best circuit topology for a function? How many stages of logic produce least delay? How wide transistors should be? Logical Effort Helps make
IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR
 International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
Introduction ABOUT THIS CHAPTER CHAPTER
 CHAPTER Introduction 1 Charles E. Stroud Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama Laung-Terng (L.-T.) Wang SynTest Technologies, Inc., Sunnyvale, California Yao-Wen Chang National Taiwan University, Taipei,
CHAPTER Introduction 1 Charles E. Stroud Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama Laung-Terng (L.-T.) Wang SynTest Technologies, Inc., Sunnyvale, California Yao-Wen Chang National Taiwan University, Taipei,
University of Texas at Dallas. Department of Electrical Engineering. EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design
 University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
CAD TOOLS FOR VLSI. FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING
 FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING Floorplanning: taking layout information into account at early stages of the design process. BEHAVIORAL D. STRUCTURAL D. Systems Algorithms Processors Register transfers
FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING Floorplanning: taking layout information into account at early stages of the design process. BEHAVIORAL D. STRUCTURAL D. Systems Algorithms Processors Register transfers
Embedded Systems. introduction. Jan Madsen
 Embedded Systems introduction Jan Madsen Informatics and Mathematical Modeling Technical University of Denmark Richard Petersens Plads, Building 321 DK2800 Lyngby, Denmark [email protected] Wireless Sensor
Embedded Systems introduction Jan Madsen Informatics and Mathematical Modeling Technical University of Denmark Richard Petersens Plads, Building 321 DK2800 Lyngby, Denmark [email protected] Wireless Sensor
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial. Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research
 PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research Derek Lockhart, Berkin Ilbeyi, Christopher Batten Computer Systems Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer
PyMTL and Pydgin Tutorial Python Frameworks for Highly Productive Computer Architecture Research Derek Lockhart, Berkin Ilbeyi, Christopher Batten Computer Systems Laboratory School of Electrical and Computer
Hunting Asynchronous CDC Violations in the Wild
 Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180B Lab 7: MISP Processor Design Spring 1995
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B Lab 7: MISP Processor Design Spring 1995 Objective: In this lab, you will complete the design of the MISP processor,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B Lab 7: MISP Processor Design Spring 1995 Objective: In this lab, you will complete the design of the MISP processor,
EE411: Introduction to VLSI Design Course Syllabus
 : Introduction to Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2008 Course Overview This is an introductory course which covers basic theories and techniques of digital VLSI design in CMOS technology.
: Introduction to Course Syllabus Dr. Mohammad H. Awedh Spring 2008 Course Overview This is an introductory course which covers basic theories and techniques of digital VLSI design in CMOS technology.
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected]. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE
 CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON. SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY. Chapter-1L07: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter
 Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT
 216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems
 Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers
 ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
Elementary Logic Gates
 Elementary Logic Gates Name Symbol Inverter (NOT Gate) ND Gate OR Gate Truth Table Logic Equation = = = = = + C. E. Stroud Combinational Logic Design (/6) Other Elementary Logic Gates NND Gate NOR Gate
Elementary Logic Gates Name Symbol Inverter (NOT Gate) ND Gate OR Gate Truth Table Logic Equation = = = = = + C. E. Stroud Combinational Logic Design (/6) Other Elementary Logic Gates NND Gate NOR Gate
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution
 Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
Eastern Washington University Department of Computer Science. Questionnaire for Prospective Masters in Computer Science Students
 Eastern Washington University Department of Computer Science Questionnaire for Prospective Masters in Computer Science Students I. Personal Information Name: Last First M.I. Mailing Address: Permanent
Eastern Washington University Department of Computer Science Questionnaire for Prospective Masters in Computer Science Students I. Personal Information Name: Last First M.I. Mailing Address: Permanent
l C-Programming l A real computer language l Data Representation l Everything goes down to bits and bytes l Machine representation Language
 198:211 Computer Architecture Topics: Processor Design Where are we now? C-Programming A real computer language Data Representation Everything goes down to bits and bytes Machine representation Language
198:211 Computer Architecture Topics: Processor Design Where are we now? C-Programming A real computer language Data Representation Everything goes down to bits and bytes Machine representation Language
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
VHDL-Testbench as Executable Specification
 VHDL- as Executable Specification Michael Pichler Zentrum für Mikroelektronik Aargau Fachhochschule Aargau, Steinackerstrasse 5, CH-5210 Windisch Web: www.zma.ch - E-mail: [email protected] Seite 1 Overview
VHDL- as Executable Specification Michael Pichler Zentrum für Mikroelektronik Aargau Fachhochschule Aargau, Steinackerstrasse 5, CH-5210 Windisch Web: www.zma.ch - E-mail: [email protected] Seite 1 Overview
Programmable Logic Controllers Definition. Programmable Logic Controllers History
 Definition A digitally operated electronic apparatus which uses a programmable memory for the internal storage of instructions for implementing specific functions such as logic, sequencing, timing, counting,
Definition A digitally operated electronic apparatus which uses a programmable memory for the internal storage of instructions for implementing specific functions such as logic, sequencing, timing, counting,
Introduction to Functional Verification. Niels Burkhardt
 Introduction to Functional Verification Overview Verification issues Verification technologies Verification approaches Universal Verification Methodology Conclusion Functional Verification issues Hardware
Introduction to Functional Verification Overview Verification issues Verification technologies Verification approaches Universal Verification Methodology Conclusion Functional Verification issues Hardware
CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS
 TECHNICAL PAPER CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview...........................................................................1
TECHNICAL PAPER CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview...........................................................................1
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000. ILP Execution
 EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #11 Processor Architecture Stanford University Wednesday, 31 May 2000 Lecture #11: Wednesday, 3 May 2000 Lecturer: Ben Serebrin Scribe: Dean Liu ILP Execution
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION
 Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL
 IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: [email protected]
IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: [email protected]
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 [email protected] http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Sequential Circuit Design Lan-Da Van ( 倫 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2009 [email protected] http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/ Outlines
Verification of Triple Modular Redundancy (TMR) Insertion for Reliable and Trusted Systems
 Verification of Triple Modular Redundancy (TMR) Insertion for Reliable and Trusted Systems Melanie Berg 1, Kenneth LaBel 2 1.AS&D in support of NASA/GSFC [email protected] 2. NASA/GSFC [email protected]
Verification of Triple Modular Redundancy (TMR) Insertion for Reliable and Trusted Systems Melanie Berg 1, Kenneth LaBel 2 1.AS&D in support of NASA/GSFC [email protected] 2. NASA/GSFC [email protected]
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components
 FEATURE ARTICLE Thomas Anderson System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components Here in the Recycling Age, designing for reuse may sound like a great idea. But with increasing requirements and chip sizes,
FEATURE ARTICLE Thomas Anderson System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components Here in the Recycling Age, designing for reuse may sound like a great idea. But with increasing requirements and chip sizes,
YAML: A Tool for Hardware Design Visualization and Capture
 YAML: A Tool for Hardware Design Visualization and Capture Vivek Sinha, Frederic Doucet, Chuck Siska, Rajesh Gupta, Stan Liao, Abhijit Ghosh Center for Embedded Computer Systems, University of California,
YAML: A Tool for Hardware Design Visualization and Capture Vivek Sinha, Frederic Doucet, Chuck Siska, Rajesh Gupta, Stan Liao, Abhijit Ghosh Center for Embedded Computer Systems, University of California,
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
