7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
|
|
|
- Ginger Lee
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit that implements most or all of the functions of a complete electronic system, which solves an embedded application. It is a heterogeneous system: may include hardware and software parts, control and data-processing functionality, digital and analog parts etc. Contains more than a single processor: memory modules, custom circuitry, I/O peripherals, A/D or D/A converters etc. 2
2 A typical SoC structure 3 Basic components of a SoC A microprocessor and its memory subsystem: Could be an 8-bit microcontroller core up to 64-bit RISC. The memory subsystem can be single or multi-levelled. A datapath with interfaces to the external system: The external interfaces can be bus drivers, Ethernet interfaces, A/D D/A converters, electro-mechanical converters etc. Blocks performing transformations on data received from the external systems: Could be implemented by custom hardware and/or by DSP cores. Interface logic to peripherals. 4
3 Basic components of a SoC (cont d) Programmable processor cores: Algorithms and protocols become increasingly complex, and this makes their implementation in hardware difficult Modern processors are fast as a result of their sophisticated design. Upgrading the software implementation is easy (flexibility). Custom hardware is still quite useful: High performance for time-critical task. Low energy consumption. 5 Typical SoC example SoC structure for the implementation of a typical wireless telecommunication application. 6
4 Why do we need System-on-Chips? System-on-chips now are technologically possible: today s chips can contain up to 100 million transistors (according to the Moores Law, approximately every 18 months the number of transistors on a single chip doubles). Higher performance: fast data transfer compared to board multi-chip designs. Lower energy consumption: multi-chip designs need additional drivers and interfaces for inter-chip and inter-board connections. Reduced size: components connected on a PCB can now be integrated onto a single chip. Lower cost. Increased reliability and design security. 7 Problems in SoC design Increased system complexity mainly due to the heterogeneity (analog along with digital parts, processors along with custom hardware, different memory types etc.), and due to the integrated nature. This creates problems to the design phase (expertise in different design areas is needed and the integration is a quite demanding task), and to the technology (several processes have to be incorporated onto a single die). Traditional hardware design methodologies does not work. Increased verification requirements. Design productivity vs. time-to-market pressure. Solutions to overcome complexity, low design productivity and time-to-market pressure is to use advanced SoC design methodologies and tools and mainly to re-use IP (Intellectual Property) blocks in our SoC design. 8
5 IP-based SoC design IP-based design is the process of composing a new system by reusing existing components. Possible IP blocks to be used: Microprocessors (ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, SPARC etc.) Interfaces (USB, PCI, UART etc.) Encoder and decoders (JPEG, MPEG, Viterbi etc.) Memories (SRAM, Flash etc.) Microcontrollers (HC11 etc.) DSPs (TI, Oak etc.) Transformers (FFT, IFFT etc.) Networking blocks (Ethernet, ATM etc.) Encryption blocks (DES, AES etc.). The increasing need of SoCs is forcing design houses and vendors to develop high-quality IP blocks (a new industry has been developed!). 9 IP-based SoC design (cont d) 10
6 SoC design productivity and cost 1200 Gates per day SoC 10% re -use 50% re -use M 1200 ~ 350 ~8.5K ~3M ~5M ~8M 11 Main issues in IP blocks design How to specify an IP block for a reuse library: functionality, timing information, interface properties, achieved speed, power consumption etc. Much effort has to be allocated for: Specification, simulation, estimation and exploration. Integration (interfaces definition and implementation). Verification and testing for many operating conditions and inputs. 12
7 Types of IP blocks Hard IP blocks: Fully designed, placed and routed by the supplier. It is offered as a completely validated layout with definite timing characteristics and offers fast integration but low flexibility. Reusability Flexibility Integration effort Firm IP blocks: Technology-mapped gatelevel netlist and offers flexibility during place and route, but with lower predictability. Soft IP blocks: Synthesizable RTL or behavioral descriptions. Require much effort for integration/verification, but offers maximal flexibility. Predictability Performance, Cost Supplier effort 13 Players in IP blocks design Author: creator of the IP block Foundry: manufacturer Catalog: enables customers to find and select the IP bock. Integrator: designs the SoC for the customer. 14
8 IP block life cycle 15 IP block life cycle (cont d) Authoring: Find the idea, create a model, perform high-level validation, create simulation models to be delivered with the IP block. Implementation: create hard of firm IP blocks. Delivery: Extract design characteristics (functionality, interfacing, timing, power consumption, technology-related aspects, compatibility aspects etc.) and put the block in an IP catalog containing adequate search mechanisms. Integration: instantiate the block, build interfaces (interface logic synthesis), verify (by simulation). Manufacturing: Fabrication and testing of the integrated circuit composed by the implemented IP blocks. Note, that IP-based design is also a solution for improving software design productivity. Reuse techniques and libraries of predefined software modules (classes, functions) are not new in software. 16
9 SoC design flow 17 Example: Wireless LAN SoC Flexible architecture to implement the digital part of the physical layer functionality of two wireless LAN standards (5 GHz band): HIPERLAN/2, IEEE a. Implements the operations CL and ΜΑC/DLC of the HIPERLAN/2 and the lower-mac layer of the IEEE a standard. Contains two embedded microprocessors: ARM946E-S for the implementation of the high layers of the HIPERLAN/2 standard. ARM7TDMI for the implementation of the lower-mac layer of the HIPERLAN/2 standard and for controlling the baseband modem (transmitter/receiver) of the system. Also, includes a MAC hardware accelerator (custom block) that implements critical functionality of the MAC layer of the IEEE a. Various peripherals: test and debug controller, power controller, Ethernet and PCI interfaces, SDRAM controller, DMA controller, UARTs. 18
10 Example: Wireless LAN SoC (cont d) FLASH SDRAM PCI Controller ETHERNET Controller Timers Watchdog Interrupt Controller ARM 946ES core with 16KB Cache Memory DMA Controller SDRAM & FLASH Controller PCI Interface ETHERNET Interface UART AMBA AHB (primary bus) Test Port Test and debug Controller Power Management Dual-port SRAM Bus Bridge Secondary bus ARM 7TDMI core SRAM UART MAC Hardware Accelerator (IEEE a) MAC/PHY Interface (HIPERLAN/2) Baseband Modem RF Controller Analog & RF front-end 19 Example: Wireless LAN SoC (cont d) Design Fabrication 20
11 Second example: Audio processing SoC Audio processing SoC (Siemens): 16-bit DSP Custom logic: 15,000 gates SRAM, ROM memory modules 1 Mbit DRAM 21 Prototyping platforms Prototyping platforms are used after the simulation (or as an alternative to the simulation) in order to prototype the SoC design into an FPGA-based board, before its fabrication. Main characteristics of prototyping platforms: Offer an accurate representation of the design since they are actual implementations and not just simulations. Faster than simulations: they can reproduce a problem after several seconds of execution, while in HDL simulation environments things are much slower. However, they are not exact replicas of the final SoC, and they cannot run at the same frequency with the real silicon SoC. The design can be mapped relatively quickly (hours or days). Debugging support is usually included. However, tasks such as design partitioning (to the available FPGAs), clock tree routing, bus handling and memory mapping are complex and difficult. Can be expensive for large designs, and sometimes they can lead to resource bottleneck (a group have to wait for another group to finish using the platform). 22
12 Example: ARM integrator platform Contains a system board and up to 5 modules. The system board provide the AMBA bus and other system functionality. Core modules allows the presence of ARM cores in the prototype and logic modules provide user programmable logic elements (FPGAs). ARM Core module System board Logic module 23 ARM integrator platform: System board Major features of the system board: System control FPGA which implements: System bus interface to core and logic modules. System bus arbiter. Interrupt controller. Peripheral input and output controllers. Timers. Reset controller. System status and control registers. Clock generator. 32MB flash memory. Boot ROM. SRAM. System expansion, supporting core and logic modules (up to 5 in total). PCI bus interface. 24
13 ARM integrator platform: Core module The major components on the core module are as follows: ARM core (7 or 9 family). FPGA which implements: SDRAM controller. System bus bridge. Reset controller. Interrupt controller. Status & control registers. SSRAM (256KB) and plugged SDRAM. SSRAM controller. Clock generator. System bus connectors. Debugging connectors. ARM 25 ARM integrator platform: Logic module The logic module comprises of: Xilinx or Altera FPGA. Configuration PLD and flash Memory for storing FPGA configurations. 1MB SSRAM. Clock generators and reset sources. Switches. LEDs. Prototyping grid. Debug connectors. System bus connectors to a system board or other modules. 26
14 Wireless LAN System-on-Chip prototyping Core Modules A to D and D to A conversion board Antenna Top Logic Module Bottom Logic Module IF board ARM Integrator Motherboard RF board Two ARM7TDMI core modules (one implementing the upper layers of the protocol and the second controlling the baseband modem and implementing the lower MAC protocol layer). Two logic modules with XILINX Virtex E 2000 FPGAs implementing the baseband modem functionality. The average FPGA utilization was 87%. 27 Second example: Carmen platform Major components: ARM processor (7 or 9) FPGA (XILINX Virtex XCV2000E or ALTERA APEX20K1000). 30 MHz system clock. 64MB SRAM, expandable SDRAM up to 256MB. 8Mbyte FLASH and 2MB high-speed SRAM. Multiple I/O interfaces: PCMCIA, PCI, USB RS232 etc. AMBA bus components. RAM & FLASH controllers. Timers. UART. Interrupt controller. ARM CARMEN platform by SIDSA 28
15 Second example: Carmen platform (cont d) 29 Conclusions With the current technology and in the context of increasingly complex applications and strong market pressure, system-on-chip is a natural approach for several embedded applications. Programmable components provide the necessary flexibility and custom hardware is needed for time-critical tasks implementation and for low power consumption. The real bottleneck in SoC design is productivity. Solutions are the IP-based design (blocks reuse), and the improvement of existing design methodologies and tools. Prototyping platforms (e.g. ARM Integrator, Carmen) are used after the co-simulation (or as an alternative to the simulation) in order to prototype and test the SoC design into an FPGA-based board, before its fabrication. 30
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview
 EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email: [email protected] Feb. 2013 Course Overview
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email: [email protected] Feb. 2013 Course Overview
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
Custom design services
 Custom design services Your partner for electronic design services and solutions Barco Silex, Barco s center of competence for micro-electronic design, has established a solid reputation in the development
Custom design services Your partner for electronic design services and solutions Barco Silex, Barco s center of competence for micro-electronic design, has established a solid reputation in the development
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications
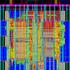 System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications N. Izeboudjen, K. Kaci, S. Titri, L. Sahli, D. Lazib, F. Louiz, M. Bengherabi, *N. Idirene Centre de Développement des Technologies
System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications N. Izeboudjen, K. Kaci, S. Titri, L. Sahli, D. Lazib, F. Louiz, M. Bengherabi, *N. Idirene Centre de Développement des Technologies
Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik
 Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik Contents Überblick: Aufbau moderner FPGA Einblick: Eigenschaften
Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik Contents Überblick: Aufbau moderner FPGA Einblick: Eigenschaften
System-on. on-chip Design Flow. Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems. jouni.tomberg@tut.
 System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON. SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY. Chapter-1L07: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
White Paper. S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com.
 White Paper FPGA Prototyping of System-on-Chip Designs The Need for a Complete Prototyping Platform for Any Design Size, Any Design Stage with Enterprise-Wide Access, Anytime, Anywhere S2C Inc. 1735 Technology
White Paper FPGA Prototyping of System-on-Chip Designs The Need for a Complete Prototyping Platform for Any Design Size, Any Design Stage with Enterprise-Wide Access, Anytime, Anywhere S2C Inc. 1735 Technology
System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components
 FEATURE ARTICLE Thomas Anderson System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components Here in the Recycling Age, designing for reuse may sound like a great idea. But with increasing requirements and chip sizes,
FEATURE ARTICLE Thomas Anderson System-on-Chip Design with Virtual Components Here in the Recycling Age, designing for reuse may sound like a great idea. But with increasing requirements and chip sizes,
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Concept Engineering Adds JavaScript-based Web Capabilities to Nlview at DAC 2016
 KAL - Large IP Cores: Memory Controllers: SD/SDIO 2.0/3.0 Controller SDRAM Controller DDR/DDR2/DDR3 SDRAM Controller NAND Flash Controller Flash/EEPROM/SRAM Controller Dear , Concept Engineering
KAL - Large IP Cores: Memory Controllers: SD/SDIO 2.0/3.0 Controller SDRAM Controller DDR/DDR2/DDR3 SDRAM Controller NAND Flash Controller Flash/EEPROM/SRAM Controller Dear , Concept Engineering
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor
 Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Qsys and IP Core Integration
 Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Qsys and IP Core Integration Prof. David Lariviere Columbia University Spring 2014 Overview What are IP Cores? Altera Design Tools for using and integrating IP Cores Overview of various IP Core Interconnect
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design. Accelerates PLD Development
 Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
ZigBee Technology Overview
 ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
ZigBee Technology Overview Presented by Silicon Laboratories Shaoxian Luo 1 EM351 & EM357 introduction EM358x Family introduction 2 EM351 & EM357 3 Ember ZigBee Platform Complete, ready for certification
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers
 ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
ARM Microprocessor and ARM-Based Microcontrollers Nguatem William 24th May 2006 A Microcontroller-Based Embedded System Roadmap 1 Introduction ARM ARM Basics 2 ARM Extensions Thumb Jazelle NEON & DSP Enhancement
How To Design A Single Chip System Bus (Amba) For A Single Threaded Microprocessor (Mma) (I386) (Mmb) (Microprocessor) (Ai) (Bower) (Dmi) (Dual
 Architetture di bus per System-On On-Chip Massimo Bocchi Corso di Architettura dei Sistemi Integrati A.A. 2002/2003 System-on on-chip motivations 400 300 200 100 0 19971999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Transistors
Architetture di bus per System-On On-Chip Massimo Bocchi Corso di Architettura dei Sistemi Integrati A.A. 2002/2003 System-on on-chip motivations 400 300 200 100 0 19971999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Transistors
Model-based system-on-chip design on Altera and Xilinx platforms
 CO-DEVELOPMENT MANUFACTURING INNOVATION & SUPPORT Model-based system-on-chip design on Altera and Xilinx platforms Ronald Grootelaar, System Architect [email protected] Agenda 3T Company profile Technology
CO-DEVELOPMENT MANUFACTURING INNOVATION & SUPPORT Model-based system-on-chip design on Altera and Xilinx platforms Ronald Grootelaar, System Architect [email protected] Agenda 3T Company profile Technology
System-on-a-Chip with Security Modules for Network Home Electric Appliances
 System-on-a-Chip with Security Modules for Network Home Electric Appliances V Hiroyuki Fujiyama (Manuscript received November 29, 2005) Home electric appliances connected to the Internet and other networks
System-on-a-Chip with Security Modules for Network Home Electric Appliances V Hiroyuki Fujiyama (Manuscript received November 29, 2005) Home electric appliances connected to the Internet and other networks
Getting Started with Embedded System Development using MicroBlaze processor & Spartan-3A FPGAs. MicroBlaze
 Getting Started with Embedded System Development using MicroBlaze processor & Spartan-3A FPGAs This tutorial is an introduction to Embedded System development with the MicroBlaze soft processor and low
Getting Started with Embedded System Development using MicroBlaze processor & Spartan-3A FPGAs This tutorial is an introduction to Embedded System development with the MicroBlaze soft processor and low
Implementation Details
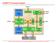 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
VON BRAUN LABS. Issue #1 WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS VON BRAUN LABS. State Machine Technology
 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System
 Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
The Motherboard Chapter #5
 The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
System Design Issues in Embedded Processing
 System Design Issues in Embedded Processing 9/16/10 Jacob Borgeson 1 Agenda What does TI do? From MCU to MPU to DSP: What are some trends? Design Challenges Tools to Help 2 TI - the complete system The
System Design Issues in Embedded Processing 9/16/10 Jacob Borgeson 1 Agenda What does TI do? From MCU to MPU to DSP: What are some trends? Design Challenges Tools to Help 2 TI - the complete system The
SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT. Nicholas Wieder
 SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT by Nicholas Wieder A thesis submitted to the faculty of The University of North Carolina at Charlotte in partial fulfillment of
SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT by Nicholas Wieder A thesis submitted to the faculty of The University of North Carolina at Charlotte in partial fulfillment of
Network connectivity controllers
 Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design
 Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design MITCHELL MYJAK Senior Research Engineer Pacific Northwest National Laboratory PNNL-SA-93202 31 January 2013 1 About Me Biography BSEE, University of Portland, 2002
Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design MITCHELL MYJAK Senior Research Engineer Pacific Northwest National Laboratory PNNL-SA-93202 31 January 2013 1 About Me Biography BSEE, University of Portland, 2002
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs
 High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
ADM5120 HOME GATEWAY CONTROLLER. Product Notes
 HOME GATEWAY CONTROLLER Product Notes ADMtek.com.tw Information in this document is provided in connection with ADMtek products. ADMtek may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any
HOME GATEWAY CONTROLLER Product Notes ADMtek.com.tw Information in this document is provided in connection with ADMtek products. ADMtek may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
Chapter 2 Features of Embedded System
 Chapter 2 Features of Embedded System Abstract This chapter will introduce the basic elements of embedded systems (or dedicated systems). The integrated control systems represent one of the areas of modern
Chapter 2 Features of Embedded System Abstract This chapter will introduce the basic elements of embedded systems (or dedicated systems). The integrated control systems represent one of the areas of modern
Product Development Flow Including Model- Based Design and System-Level Functional Verification
 Product Development Flow Including Model- Based Design and System-Level Functional Verification 2006 The MathWorks, Inc. Ascension Vizinho-Coutry, [email protected] Agenda Introduction to Model-Based-Design
Product Development Flow Including Model- Based Design and System-Level Functional Verification 2006 The MathWorks, Inc. Ascension Vizinho-Coutry, [email protected] Agenda Introduction to Model-Based-Design
AN FPGA FRAMEWORK SUPPORTING SOFTWARE PROGRAMMABLE RECONFIGURATION AND RAPID DEVELOPMENT OF SDR APPLICATIONS
 AN FPGA FRAMEWORK SUPPORTING SOFTWARE PROGRAMMABLE RECONFIGURATION AND RAPID DEVELOPMENT OF SDR APPLICATIONS David Rupe (BittWare, Concord, NH, USA; [email protected]) ABSTRACT The role of FPGAs in Software
AN FPGA FRAMEWORK SUPPORTING SOFTWARE PROGRAMMABLE RECONFIGURATION AND RAPID DEVELOPMENT OF SDR APPLICATIONS David Rupe (BittWare, Concord, NH, USA; [email protected]) ABSTRACT The role of FPGAs in Software
Design Cycle for Microprocessors
 Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Codesign: The World Of Practice
 Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
Simplifying Embedded Hardware and Software Development with Targeted Reference Designs
 White Paper: Spartan-6 and Virtex-6 FPGAs WP358 (v1.0) December 8, 2009 Simplifying Embedded Hardware and Software Development with Targeted Reference Designs By: Navanee Sundaramoorthy FPGAs are becoming
White Paper: Spartan-6 and Virtex-6 FPGAs WP358 (v1.0) December 8, 2009 Simplifying Embedded Hardware and Software Development with Targeted Reference Designs By: Navanee Sundaramoorthy FPGAs are becoming
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications. Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global
 CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Chapter 02: Computer Organization. Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures
 Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
1. Introduction to Embedded System Design
 1. Introduction to Embedded System Design Lothar Thiele ETH Zurich, Switzerland 1-1 Contents of Lectures (Lothar Thiele) 1. Introduction to Embedded System Design 2. Software for Embedded Systems 3. Real-Time
1. Introduction to Embedded System Design Lothar Thiele ETH Zurich, Switzerland 1-1 Contents of Lectures (Lothar Thiele) 1. Introduction to Embedded System Design 2. Software for Embedded Systems 3. Real-Time
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller
 Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
Introduction to System-on-Chip
 Introduction to System-on-Chip COE838: Systems-on-Chip Design http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/coe838/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
Introduction to System-on-Chip COE838: Systems-on-Chip Design http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/coe838/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
Applying the Benefits of Network on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design
 Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
3 Software Defined Radio Technologies
 3 Software Defined Radio Technologies 3-1 Software Defined Radio for Next Generation Seamless Mobile Communication Systems In this paper, the configuration of the newly developed small-size software defined
3 Software Defined Radio Technologies 3-1 Software Defined Radio for Next Generation Seamless Mobile Communication Systems In this paper, the configuration of the newly developed small-size software defined
ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654
 ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654 Features ARM Cortex-A8 processor, 800MHz Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA expands vision processing capabilities Dual MIPI CSI-2 CMOS camera ports,
ARM Cortex -A8 SBC with MIPI CSI Camera and Spartan -6 FPGA SBC1654 Features ARM Cortex-A8 processor, 800MHz Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA expands vision processing capabilities Dual MIPI CSI-2 CMOS camera ports,
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems. 2008 Chapter-1L03: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter
 Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Defining Platform-Based Design. System Definition. Platform Based Design What is it? Platform-Based Design Definitions: Three Perspectives
 Based Design What is it? Question: How many definitions of Based Design are there? Defining -Based Design Answer: How many people to you ask? What does the confusion mean? It is a definition in transition
Based Design What is it? Question: How many definitions of Based Design are there? Defining -Based Design Answer: How many people to you ask? What does the confusion mean? It is a definition in transition
Fondamenti su strumenti di sviluppo per microcontrollori PIC
 Fondamenti su strumenti di sviluppo per microcontrollori PIC MPSIM ICE 2000 ICD 2 REAL ICE PICSTART Ad uso interno del corso Elettronica e Telecomunicazioni 1 2 MPLAB SIM /1 MPLAB SIM is a discrete-event
Fondamenti su strumenti di sviluppo per microcontrollori PIC MPSIM ICE 2000 ICD 2 REAL ICE PICSTART Ad uso interno del corso Elettronica e Telecomunicazioni 1 2 MPLAB SIM /1 MPLAB SIM is a discrete-event
Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada
 Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada BIOGRAPHY Yves Théroux, a Project Engineer with BAE Systems Canada (BSC) has eight years of experience in the design, qualification,
Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada BIOGRAPHY Yves Théroux, a Project Engineer with BAE Systems Canada (BSC) has eight years of experience in the design, qualification,
SDR Architecture. Introduction. Figure 1.1 SDR Forum High Level Functional Model. Contributed by Lee Pucker, Spectrum Signal Processing
 SDR Architecture Contributed by Lee Pucker, Spectrum Signal Processing Introduction Software defined radio (SDR) is an enabling technology, applicable across a wide range of areas within the wireless industry,
SDR Architecture Contributed by Lee Pucker, Spectrum Signal Processing Introduction Software defined radio (SDR) is an enabling technology, applicable across a wide range of areas within the wireless industry,
SBC8600B Single Board Computer
 SBC8600B Single Board Computer 720MHz TI s Sitara AM3359 ARM Cortex-A8 Microprocessor Onboard 512MByte DDR3 SDRAM and 512MByte NAND Flash UARTs, 2*USB Host and 1*OTG, 2*Ethernet, CAN, RS485, LCD/TSP, Audio,
SBC8600B Single Board Computer 720MHz TI s Sitara AM3359 ARM Cortex-A8 Microprocessor Onboard 512MByte DDR3 SDRAM and 512MByte NAND Flash UARTs, 2*USB Host and 1*OTG, 2*Ethernet, CAN, RS485, LCD/TSP, Audio,
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Quartus II 1
 (DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
(DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
Software engineering for real-time systems
 Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Designing Systems-on-Chip Using Cores
 Designing Systems-on-Chip Using Cores Reinaldo A. Bergamaschi 1, William R. Lee 2 1 IBM T. J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, NY, 2 IBM Microelectronics, Raleigh, NC [email protected], [email protected]
Designing Systems-on-Chip Using Cores Reinaldo A. Bergamaschi 1, William R. Lee 2 1 IBM T. J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, NY, 2 IBM Microelectronics, Raleigh, NC [email protected], [email protected]
NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications
 NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications 1 Sheetal Bhoyar, 2 Dr. D. V. Padole 1 Research Scholar, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur, India 2 Professor, G. H.
NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications 1 Sheetal Bhoyar, 2 Dr. D. V. Padole 1 Research Scholar, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur, India 2 Professor, G. H.
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board
 Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
USB 3.0 Connectivity using the Cypress EZ-USB FX3 Controller
 USB 3.0 Connectivity using the Cypress EZ-USB FX3 Controller PLC2 FPGA Days June 20, 2012 Stuttgart Martin Heimlicher FPGA Solution Center Content Enclustra Company Profile USB 3.0 Overview What is new?
USB 3.0 Connectivity using the Cypress EZ-USB FX3 Controller PLC2 FPGA Days June 20, 2012 Stuttgart Martin Heimlicher FPGA Solution Center Content Enclustra Company Profile USB 3.0 Overview What is new?
Low Cost System on Chip Design for Audio Processing
 Low Cost System on Chip Design for udio Processing 1 yas Kanta Swain, 2 Kamala Kanta Mahapatra bstract System-on-Chip (SoC) design is an integration of multi million transistors in a single chip for alleviating
Low Cost System on Chip Design for udio Processing 1 yas Kanta Swain, 2 Kamala Kanta Mahapatra bstract System-on-Chip (SoC) design is an integration of multi million transistors in a single chip for alleviating
Developing an Application on Core8051s IP-Based Embedded Processor System Using Firmware Catalog Drivers. User s Guide
 Developing an Application on Core8051s IP-Based Embedded Processor System Using Firmware Catalog Drivers User s Guide Developing an Application on Core8051s IP-Based Embedded Processor System Using Firmware
Developing an Application on Core8051s IP-Based Embedded Processor System Using Firmware Catalog Drivers User s Guide Developing an Application on Core8051s IP-Based Embedded Processor System Using Firmware
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION
 EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
December 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 285. This document describes the Excalibur web server demonstration design and includes the following topics:
 Excalibur Web Server Demonstration December 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 285 Introduction This document describes the Excalibur web server demonstration design and includes the following topics: Design
Excalibur Web Server Demonstration December 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 285 Introduction This document describes the Excalibur web server demonstration design and includes the following topics: Design
FPGAs in Next Generation Wireless Networks
 FPGAs in Next Generation Wireless Networks March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 FPGAs in Next Generation
FPGAs in Next Generation Wireless Networks March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 FPGAs in Next Generation
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs
 Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
Products. CM-i586 Highlights. Página Web 1 de 5. file://c:\documents and Settings\Daniel\Os meus documentos\humanoid\material_o...
 Página Web 1 de 5 The Home of the World's Best Computer-On-Module's Products Computer- On-Module's CM-X270 CM-X255 CM-iGLX CM-F82 CM-i686M CM-i686B CM-iVCF CM-i886 CM-i586 PC/104+ & ATX boards SBC-X270
Página Web 1 de 5 The Home of the World's Best Computer-On-Module's Products Computer- On-Module's CM-X270 CM-X255 CM-iGLX CM-F82 CM-i686M CM-i686B CM-iVCF CM-i886 CM-i586 PC/104+ & ATX boards SBC-X270
Outline. Introduction. Multiprocessor Systems on Chip. A MPSoC Example: Nexperia DVP. A New Paradigm: Network on Chip
 Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
Discovering Computers 2011. Living in a Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
HMI EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN AS A FUNCTION OF TECU
 HMI EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN AS A FUNCTION OF TECU Katrenčík J., Čupera J., Fajman M. Department of Technology and Automobile Transport, Faculty of Agronomy, Mendel University in Brno, Zemedelska 1, 613
HMI EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN AS A FUNCTION OF TECU Katrenčík J., Čupera J., Fajman M. Department of Technology and Automobile Transport, Faculty of Agronomy, Mendel University in Brno, Zemedelska 1, 613
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
on-chip and Embedded Software Perspectives and Needs
 Systems-on on-chip and Embedded Software - Perspectives and Needs Miguel Santana Central R&D, STMicroelectronics STMicroelectronics Outline Current trends for SoCs Consequences and challenges Needs: Tackling
Systems-on on-chip and Embedded Software - Perspectives and Needs Miguel Santana Central R&D, STMicroelectronics STMicroelectronics Outline Current trends for SoCs Consequences and challenges Needs: Tackling
WiSER: Dynamic Spectrum Access Platform and Infrastructure
 WiSER: Dynamic Spectrum Access Platform and Infrastructure I. Seskar, D. Grunwald, K. Le, P. Maddala, D. Sicker, D. Raychaudhuri Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey University of Colorado, Boulder
WiSER: Dynamic Spectrum Access Platform and Infrastructure I. Seskar, D. Grunwald, K. Le, P. Maddala, D. Sicker, D. Raychaudhuri Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey University of Colorado, Boulder
Design of a remote image monitoring system based on GPRS
 2009 International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing IPCSIT vol.3 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design of a remote image monitoring system based on GPRS Yongqiang Zhang 1, Guozhen Zhao
2009 International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing IPCSIT vol.3 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design of a remote image monitoring system based on GPRS Yongqiang Zhang 1, Guozhen Zhao
Configurable Sensor Nodes for AAL Applications
 Configurable Sensor Nodes for AAL Applications Peter Langendörfer Krzysztof Piotrowski, Anna Sojka, Frank Vater IHP Im Technologiepark 25 15236 Frankfurt (Oder) Germany IHP Im Technologiepark 25 15236
Configurable Sensor Nodes for AAL Applications Peter Langendörfer Krzysztof Piotrowski, Anna Sojka, Frank Vater IHP Im Technologiepark 25 15236 Frankfurt (Oder) Germany IHP Im Technologiepark 25 15236
System Considerations
 System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet MAC with Protocol Acceleration MAC-NET Core with Avalon Interface
 1 Introduction Ethernet is available in different speeds (10/100/1000 and 10000Mbps) and provides connectivity to meet a wide range of needs from desktop to switches. MorethanIP IP solutions provide a
1 Introduction Ethernet is available in different speeds (10/100/1000 and 10000Mbps) and provides connectivity to meet a wide range of needs from desktop to switches. MorethanIP IP solutions provide a
Computer System Design. System-on-Chip
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171000/ Computer System Design. System-on-Chip Description: The next generation of computer system designers will be less concerned
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171000/ Computer System Design. System-on-Chip Description: The next generation of computer system designers will be less concerned
SmartFusion csoc: Basic Bootloader and Field Upgrade envm Through IAP Interface
 Application Note AC372 SmartFusion csoc: Basic Bootloader and Field Upgrade envm Through IAP Interface Table of Contents Introduction................................................ 1 Introduction to Field
Application Note AC372 SmartFusion csoc: Basic Bootloader and Field Upgrade envm Through IAP Interface Table of Contents Introduction................................................ 1 Introduction to Field
A Mixed-Signal System-on-Chip Audio Decoder Design for Education
 A Mixed-Signal System-on-Chip Audio Decoder Design for Education R. Koenig, A. Thomas, M. Kuehnle, J. Becker, E.Crocoll, M. Siegel @itiv.uni-karlsruhe.de @ims.uni-karlsruhe.de
A Mixed-Signal System-on-Chip Audio Decoder Design for Education R. Koenig, A. Thomas, M. Kuehnle, J. Becker, E.Crocoll, M. Siegel @itiv.uni-karlsruhe.de @ims.uni-karlsruhe.de
