CPSC 121: Models of Computation Lab #5: Flip-Flops and Frequency Division
|
|
|
- Grace Houston
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
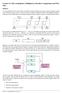
1 CPSC 121: Models of Computation Lab #5: Flip-Flops and Frequency Division Objectives In this lab, we will see the sequential circuits latches and flip-flops. Latches and flip-flops can be used to build circuits that remember information, and provide the last major component that we still needed in order to be able to design a circuit that implements a working computer. We will looking at clock frequencies, and how this can be used to make a circuit that counts. 1 Pre-lab 1.1 Counting We know from lecture the parallel between binary numbers and truth tables. And, we ve seen a pattern in both: the right-most column will be repeating (or FTFTFTFT), the one beside it repeats , the one beside that repeats like , and so on. In circuits, when we want to repeat a pattern like this, we use an electrical wave like the clock outputs you ve seen in the Magic Box, which regularly alternates between a value of 0 and 1. In the picture below, we have three waves: wave 0, wave 1, and wave 2. They re doing the same patterns we see in truth tables, and together we can use them to count up to 7 repeatedly: What differs between the three waves is their frequency: wave 0 is twice as frequent as wave 1, and wave 1 is twice as frequent as wave 2. If we want to be able to count to 15, all we need to do is add another wave, which is half as frequent as wave 2. Have a look at the animation at cs121/current/labs/lab5/counter.gif, which has such a wave. 1 TODO (pre-lab): If we wanted to add a fifth wave to the circuit in the animation so that we could count to 31, what wave frequency (in Hz) would we want? 1 Recall that 1 Hz means once every second; 2 Hz means twice every second, etc. 1
2 1.2 Sequential circuitry Here s another way of thinking about counting. Consider the mathematical formula: t n = t n where t 0 = 0. Here we re taking the previous value of t and using it to get the next one. For example, t 2 = t = (t 0 + 1) + 1 = (0 + 1) + 1 = 2. We can do this sort of thing with circuits, too. When we store and use the previous output of a circuit, we call it a sequential circuit. A latch is a type of sequential circuit, which works like this: If en=0, the latch s output (q) is its previous output (q prev ) If en=1, the latch s output (q) is its input d The latch allows us to remember a value; it is a simple form of memory. It looks like this: The truth table is a bit different than the ones you ve seen before: now we have a variable, q prev. It represents the q value that the latch had previously. en d q 0 0 q prev 0 1 q prev TODO (pre-lab): Answer the following questions: 1. Suppose we turned on the latch with en=1 and d=0. What would be the value of the latch s output q? 2. Now suppose we, after doing that step above, switched en=0. What value for q would the latch have? 3. And now, after that step, suppose we switched d=1. What value for q would the latch have? 4. Now after that step, suppose we switched en=1. What value for q would the latch have? 5. Lastly, after that, suppose we switched en=0. What value for q would the latch have? 2
3 1.3 Flip-Flops A flip-flop is another type of sequential circuit, and is very similar to a latch. However, when the flip-flop will take a new value is different. With the latch, we took in a new value whenever en was on so if we left en on, and flipped d on and off, we would see q go on and off in response. Flip-flops only take in a new value when en becomes on. Once en is on, nothing changes: we have to turn en off and then on again to load in a new value. Because of this, en is typically connected to a clock wave this allows it to regularly load in new values. A new value is loaded every time the clock wave becomes on; otherwise we hold onto the old value. We represent flip-flops with this symbol: Like for the latch, d is our input, and q is the value we re remembering. The > represents the clock input, replacing the en of the latch. TODO (pre-lab): What is the Q output? Look this up and cite your source 2. 2 Wiring a Counter In this section, you will wire up a 2-bit counter with two Magic Boxes: 1. Get a Magic Box for you and your partner, and find another team that has a Magic Box. 2. One team should set their Magic Box s clock frequency to 1 Hz, and the other team should set theirs to 2 Hz. See the Magic Box User s Manual page 6 for how this is done. 3. Remember to turn off the power to the Magic Box es while wiring them together. Leaving both of your original power and ground wires connected, connect the ground input of one Magic Box to the ground input of the other one. This gives the two circuits a common reference for voltages. Do not connect the power signals together. 4. Now connect the 2 Hz clock wave to the rightmost LED on your board (it is orange and labeled B0). 5. Connect the 1 Hz clock wave to the LED beside it (it is green and labeled B1). 6. Turn on your Magic Boxes and look at the number display. It should be counting over and over again. TODO: Once you have it counting to 3, show it to your TA. 2 If you are searching on the internet, it will help to look for a D Flip-Flop 3
4 3 A Flip-Flop Connect up a 74LS175 Quad D Flip-Flop chip to power and ground, and power the Clear input in the lower left corner of the chip. Clear can be read as not Clear and often the complement or inversion of a signal is written with a line overtop. For one of the four flip-flops in the circuit, connect 1D to a switch, 1Q and 1Q to LEDs, and CLOCK to a connection in the clock output box. Figure 1: The clock output box of a Magic Box Unlike in lab #1 where we used a clock wave that was generated by the Magic Box, here we want to use a manual clock there is a white button above the clock output that you can press (it s at the top of the figure above). Each time you press it, a new clock cycle begins (the clock begins outputting a value of 1); when you release it, the clock cycle is complete (the output of the clock again becomes 0). For how to switch to manual clocking, see the Magic Box User s Manual, page 6. TODO: Determine a truth table for this circuit. For some entries, you may want to define and use variables like q prev, or describe what happens in English. D Clock button Q Q 0 is pressed 1 is pressed 0 is not pressed 1 is not pressed 4
5 4 Shift Registers Flip flops can be connected together, so that their states can be passed down such a chain. This is called a shift register. Using your D Flip-Flop, connect 1Q to 2D, and 2Q to 3D, to connect three flip-flops in a chain. Also connect 1Q, 2Q and 3Q to green, yellow and red LEDs, respectively. Keep the clock connected to the clock button, and 1D connected to a switch. Figure 2 shows a diagram of the circuit you have just implemented. Figure 2: Three flip-flops connected in series. TODO: Test your circuit to see what happens. Play with different values for 1D and see what happens as you clock the circuit manually. What happens? 5 Frequency Division and Counting Our Magic Boxes only have one clock wave generator each: if we want to make a counter with one Magic Box, we need to be able to get multiple clock wave frequencies out of one generator. We accomplish this by making a frequency divider. It is a circuit which takes in a wave, and outputs a wave that is half as frequent: We can make a frequency divider with one flip-flop, like so 3 : 3 Thanks to the physics of these integrated circuits, no D input is needed to get the circuit to work. 5
6 If you connect both your clock signal, and the output of your frequency divider, to your number display, you should get it counting repeatedly. Check to see that s what happens. To get your circuit to count upwards, invert your original clock signal: You should be seeing it count repeatedly we call this a 2-bit counter. TODO: Show your 2-bit counter to your TA. Now, build a second frequency divider with a different LS175 chip. Verify it works. You can now build a circuit that repeatedly counts to 7, using both of your frequency dividers. You will want to figure out how you want to connect the two together on paper beforehand, since you will have to figure out which inputs and outputs go together! If you get stuck, ask your TAs for help! TODO: Show your 3-bit counter to your TA once you have it working. 6 Further Analysis Questions TODO (further analysis): Because sequential circuits take their outputs as an input, they typically start off having an undetermined state. For a flip-flop, why is that, and when does it have a determined state? What could some problems of this be? 6
7 7 End of Lab Survey TODO: To help us improve these labs both this term and for future offerings, complete the survey at A Challenge Problem TODO (challenge): Build a synchronous circuit in Logisim that acts as a traffic light controller. The traffic light controller cycles between 4 states that are outlined in the image below. For example in state 1, light 1 should be red (R1 = 1, A1 = 0, G1= 0) and light 2 should be green (R2 = 0, A2 = 0, G2 = 1). The circuit should change state on each rising clock edge. B Marking scheme All labs are out of ten marks. Two marks for pre-labs, and eight marks are for in-lab work: Two marks - Pre-lab questions Five marks - In-lab questions one mark per TODO:. In this lab, it is 1 point for Section 2, 1 point for Section 3 (Flip-Flop), 1 point for Section 4 (Shift Registers) and 2 points for Section 5 (Counters/Frequency Dividers). Two marks - Further analysis. One mark - End of lab survey. TAs may at their discretion award one bonus mark, such as for completing a challenge problem. 7
Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop.
 Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits
 CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
CS311 Lecture: Sequential Circuits Last revised 8/15/2007 Objectives: 1. To introduce asynchronous and synchronous flip-flops (latches and pulsetriggered, plus asynchronous preset/clear) 2. To introduce
To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC.
 8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
Decimal Number (base 10) Binary Number (base 2)
 LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
The components. E3: Digital electronics. Goals:
 E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
Design: a mod-8 Counter
 Design: a mod-8 Counter A mod-8 counter stores a integer value, and increments that value (say) on each clock tick, and wraps around to 0 if the previous stored value was 7. So, the stored value follows
Design: a mod-8 Counter A mod-8 counter stores a integer value, and increments that value (say) on each clock tick, and wraps around to 0 if the previous stored value was 7. So, the stored value follows
Counters and Decoders
 Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops
 Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
Lesson 12 Sequential Circuits: Flip-Flops 1. Overview of a Synchronous Sequential Circuit We saw from last lesson that the level sensitive latches could cause instability in a sequential system. This instability
Lecture-3 MEMORY: Development of Memory:
 Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D.
 BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine
 The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems
 Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Lecture 8: Synchronous Digital Systems The distinguishing feature of a synchronous digital system is that the circuit only changes in response to a system clock. For example, consider the edge triggered
Digital Electronics Detailed Outline
 Digital Electronics Detailed Outline Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and Digital Electronics (32 Total Days) Lesson 1.1: Foundations and the Board Game Counter (9 days) 1. Safety is an important concept
Digital Electronics Detailed Outline Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and Digital Electronics (32 Total Days) Lesson 1.1: Foundations and the Board Game Counter (9 days) 1. Safety is an important concept
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. 6.002 Electronic Circuits Spring 2007
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.002 Electronic Circuits Spring 2007 Lab 4: Audio Playback System Introduction In this lab, you will construct,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.002 Electronic Circuits Spring 2007 Lab 4: Audio Playback System Introduction In this lab, you will construct,
Digital circuits make up all computers and computer systems. The operation of digital circuits is based on
 Digital Logic Circuits Digital circuits make up all computers and computer systems. The operation of digital circuits is based on Boolean algebra, the mathematics of binary numbers. Boolean algebra is
Digital Logic Circuits Digital circuits make up all computers and computer systems. The operation of digital circuits is based on Boolean algebra, the mathematics of binary numbers. Boolean algebra is
COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits
 Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to
 Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to 1. Demonstrate safety of the individual, class, and overall environment of the classroom/laboratory, and understand that electricity, even at the nominal
Upon completion of unit 1.1, students will be able to 1. Demonstrate safety of the individual, class, and overall environment of the classroom/laboratory, and understand that electricity, even at the nominal
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Module 3: Floyd, Digital Fundamental
 Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : [email protected] Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
Module 3: Lecturer : Yongsheng Gao Room : Tech - 3.25 Email : [email protected] Structure : 6 lectures 1 Tutorial Assessment: 1 Laboratory (5%) 1 Test (20%) Textbook : Floyd, Digital Fundamental
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS
 CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
CHAPTER 11 LATCHES AND FLIP-FLOPS This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 11.1 Introduction 11.2 Set-Reset Latch 11.3 Gated D Latch 11.4 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop 11.5 S-R Flip-Flop
So far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs.
 equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
equential Logic o far we have investigated combinational logic for which the output of the logic devices/circuits depends only on the present state of the inputs. In sequential logic the output of the
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1.
 File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters
 LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
Design Example: Counters. Design Example: Counters. 3-Bit Binary Counter. 3-Bit Binary Counter. Other useful counters:
 Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
Design Eample: ers er: a sequential circuit that repeats a specified sequence of output upon clock pulses. A,B,C,, Z. G, O, T, E, R, P, S,!.,,,,,,,7. 7,,,,,,,.,,,,,,,,,,,. Binary counter: follows the binary
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. Block diagram. Flip Flop. S-R Flip Flop. Block Diagram. Circuit Diagram
 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/sequential_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com The combinational circuit does not use any memory. Hence the previous
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/sequential_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com The combinational circuit does not use any memory. Hence the previous
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Sequential Logic: Clocks, Registers, etc.
 ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design
 Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuit Design ECE 52 Winter 22 Reading ssignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7.5 T Flip-Flop 7.5. Configurable Flip-Flops 7.6
Contents COUNTER. Unit III- Counters
 COUNTER Contents COUNTER...1 Frequency Division...2 Divide-by-2 Counter... 3 Toggle Flip-Flop...3 Frequency Division using Toggle Flip-flops...5 Truth Table for a 3-bit Asynchronous Up Counter...6 Modulo
COUNTER Contents COUNTER...1 Frequency Division...2 Divide-by-2 Counter... 3 Toggle Flip-Flop...3 Frequency Division using Toggle Flip-flops...5 Truth Table for a 3-bit Asynchronous Up Counter...6 Modulo
ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006. Homework 5. Due back in class on Friday, April 28.
 ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006 Homework 5 Due back in class on Friday, April 28. 1. Fill up the function table (truth table) for the following latch. How is this latch related to those described in the lectures
ENEE 244 (01**). Spring 2006 Homework 5 Due back in class on Friday, April 28. 1. Fill up the function table (truth table) for the following latch. How is this latch related to those described in the lectures
Digital Fundamentals. Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications
 Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0 B. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003). Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008). Bradbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications Name: Date: Objectives:
Richland College Engineering Technology Rev. 0 B. Donham Rev. 1 (7/2003). Horne Rev. 2 (1/2008). Bradbury Digital Fundamentals CETT 1425 Lab 8 Asynchronous Counter Applications Name: Date: Objectives:
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
Digital Controller for Pedestrian Crossing and Traffic Lights
 Project Objective: - To design and simulate, a digital controller for traffic and pedestrian lights at a pedestrian crossing using Microsim Pspice The controller must be based on next-state techniques
Project Objective: - To design and simulate, a digital controller for traffic and pedestrian lights at a pedestrian crossing using Microsim Pspice The controller must be based on next-state techniques
3-Digit Counter and Display
 ECE 2B Winter 2007 Lab #7 7 3-Digit Counter and Display This final lab brings together much of what we have done in our lab experiments this quarter to construct a simple tachometer circuit for measuring
ECE 2B Winter 2007 Lab #7 7 3-Digit Counter and Display This final lab brings together much of what we have done in our lab experiments this quarter to construct a simple tachometer circuit for measuring
Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor
 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra
 Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
Latches, the D Flip-Flop & Counter Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters and a Simple Processor 7. Basic Latch 7.2 Gated SR Latch 7.2. Gated SR
Lab 11 Digital Dice. Figure 11.0. Digital Dice Circuit on NI ELVIS II Workstation
 Lab 11 Digital Dice Figure 11.0. Digital Dice Circuit on NI ELVIS II Workstation From the beginning of time, dice have been used for games of chance. Cubic dice similar to modern dice date back to before
Lab 11 Digital Dice Figure 11.0. Digital Dice Circuit on NI ELVIS II Workstation From the beginning of time, dice have been used for games of chance. Cubic dice similar to modern dice date back to before
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
DIGITAL COUNTERS. Q B Q A = 00 initially. Q B Q A = 01 after the first clock pulse.
 DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
DIGITAL COUNTERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/digital_counters.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Counter is a sequential circuit. A digital circuit which is used for a counting
Take-Home Exercise. z y x. Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science. The University of Texas at Dallas
 Take-Home Exercise Assume you want the counter below to count mod-6 backward. That is, it would count 0-5-4-3-2-1-0, etc. Assume it is reset on startup, and design the wiring to make the counter count
Take-Home Exercise Assume you want the counter below to count mod-6 backward. That is, it would count 0-5-4-3-2-1-0, etc. Assume it is reset on startup, and design the wiring to make the counter count
Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain
 Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
Chapter 3 Counters & Shift Registers Chapter 8 of R.P Jain Counters & Shift Registers Counters, Syllabus Design of Modulo-N ripple counter, Up-Down counter, design of synchronous counters with and without
Asynchronous Counters. Asynchronous Counters
 Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
ELEC 2210 - EXPERIMENT 1 Basic Digital Logic Circuits
 Objectives ELEC - EXPERIMENT Basic Digital Logic Circuits The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to digital electronic circuits. You will learn how to use the IDL-00 Bit
Objectives ELEC - EXPERIMENT Basic Digital Logic Circuits The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to digital electronic circuits. You will learn how to use the IDL-00 Bit
Combinational Logic Design Process
 Combinational Logic Design Process Create truth table from specification Generate K-maps & obtain logic equations Draw logic diagram (sharing common gates) Simulate circuit for design verification Debug
Combinational Logic Design Process Create truth table from specification Generate K-maps & obtain logic equations Draw logic diagram (sharing common gates) Simulate circuit for design verification Debug
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY
 DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
WEEK 8.1 Registers and Counters. ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers
 ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
ETEC 23 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 9 Latches, Flip-Flops, and Timers Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 27 by Janna B. Gallaher Latches A temporary
2 : BISTABLES. In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blocks of electronic counting circuits.
 2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
Counters. Present State Next State A B A B 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
 ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
ounter ounters ounters are a specific type of sequential circuit. Like registers, the state, or the flip-flop values themselves, serves as the output. The output value increases by one on each clock cycle.
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 3 PART 1
 UNIT 22: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 3 PART 1 This work covers part of outcome 3 of the Edexcel standard module: Outcome 3 is the most demanding
UNIT 22: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 3 PART 1 This work covers part of outcome 3 of the Edexcel standard module: Outcome 3 is the most demanding
FORDHAM UNIVERSITY CISC 3593. Dept. of Computer and Info. Science Spring, 2011. Lab 2. The Full-Adder
 FORDHAM UNIVERSITY CISC 3593 Fordham College Lincoln Center Computer Organization Dept. of Computer and Info. Science Spring, 2011 Lab 2 The Full-Adder 1 Introduction In this lab, the student will construct
FORDHAM UNIVERSITY CISC 3593 Fordham College Lincoln Center Computer Organization Dept. of Computer and Info. Science Spring, 2011 Lab 2 The Full-Adder 1 Introduction In this lab, the student will construct
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute. 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1 4. LECTURE: COUNTERS AND RELATED 1. Counters,
Registers & Counters
 Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots
 Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
ENGI 241 Experiment 5 Basic Logic Gates
 ENGI 24 Experiment 5 Basic Logic Gates OBJECTIVE This experiment will examine the operation of the AND, NAND, OR, and NOR logic gates and compare the expected outputs to the truth tables for these devices.
ENGI 24 Experiment 5 Basic Logic Gates OBJECTIVE This experiment will examine the operation of the AND, NAND, OR, and NOR logic gates and compare the expected outputs to the truth tables for these devices.
Figure 8-1 Four Possible Results of Adding Two Bits
 CHPTER EIGHT Combinational Logic pplications Thus far, our discussion has focused on the theoretical design issues of computer systems. We have not yet addressed any of the actual hardware you might find
CHPTER EIGHT Combinational Logic pplications Thus far, our discussion has focused on the theoretical design issues of computer systems. We have not yet addressed any of the actual hardware you might find
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 4 Bit Binary Ripple Counter (Up-Down Counter) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
4 Bit Binary Ripple Counter (Up-Down Counter) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Robot Board Sub-System Testing. Abstract. Introduction and Theory. Equipment. Procedures. EE 101 Spring 2006 Date: Lab Section # Lab #6
 EE 101 Spring 2006 Date: Lab Section # Lab #6 Name: Robot Board Sub-System Testing Partner: No Lab partners this time! Abstract The ECEbot robots have a printed circuit board (PCB) containing most of the
EE 101 Spring 2006 Date: Lab Section # Lab #6 Name: Robot Board Sub-System Testing Partner: No Lab partners this time! Abstract The ECEbot robots have a printed circuit board (PCB) containing most of the
Wiki Lab Book. This week is practice for wiki usage during the project.
 Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Wiki Lab Book Use a wiki as a lab book. Wikis are excellent tools for collaborative work (i.e. where you need to efficiently share lots of information and files with multiple people). This week is practice
Digital Logic Elements, Clock, and Memory Elements
 Physics 333 Experiment #9 Fall 999 Digital Logic Elements, Clock, and Memory Elements Purpose This experiment introduces the fundamental circuit elements of digital electronics. These include a basic set
Physics 333 Experiment #9 Fall 999 Digital Logic Elements, Clock, and Memory Elements Purpose This experiment introduces the fundamental circuit elements of digital electronics. These include a basic set
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 2. LECTURE: ELEMENTARY SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS: FLIP-FLOPS 1st year BSc course 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 2. LECTURE: ELEMENTARY SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS: FLIP-FLOPS 1st year BSc course 2nd (Spring) term 2012/2013 1
Basics of Digital Recording
 Basics of Digital Recording CONVERTING SOUND INTO NUMBERS In a digital recording system, sound is stored and manipulated as a stream of discrete numbers, each number representing the air pressure at a
Basics of Digital Recording CONVERTING SOUND INTO NUMBERS In a digital recording system, sound is stored and manipulated as a stream of discrete numbers, each number representing the air pressure at a
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
Experiment 8 : Pulse Width Modulation
 Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Experiment 8 : Pulse Width Modulation Laboratory Outline In experiment 5 we learned how to control the speed of a DC motor using a variable resistor. This week, we will learn
Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Experiment 8 : Pulse Width Modulation Laboratory Outline In experiment 5 we learned how to control the speed of a DC motor using a variable resistor. This week, we will learn
Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts)
 Dr. Greg Tumbush, [email protected] Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
Dr. Greg Tumbush, [email protected] Lab #5: Design Example: Keypad Scanner and Encoder - Part 1 (120 pts) Objective The objective of lab assignments 5 through 9 are to systematically design and implement
A Digital Timer Implementation using 7 Segment Displays
 A Digital Timer Implementation using 7 Segment Displays Group Members: Tiffany Sham u2548168 Michael Couchman u4111670 Simon Oseineks u2566139 Caitlyn Young u4233209 Subject: ENGN3227 - Analogue Electronics
A Digital Timer Implementation using 7 Segment Displays Group Members: Tiffany Sham u2548168 Michael Couchman u4111670 Simon Oseineks u2566139 Caitlyn Young u4233209 Subject: ENGN3227 - Analogue Electronics
MATERIALS. Multisim screen shots sent to TA.
 Page 1/8 Revision 0 9-Jun-10 OBJECTIVES Learn new Multisim components and instruments. Conduct a Multisim transient analysis. Gain proficiency in the function generator and oscilloscope. MATERIALS Multisim
Page 1/8 Revision 0 9-Jun-10 OBJECTIVES Learn new Multisim components and instruments. Conduct a Multisim transient analysis. Gain proficiency in the function generator and oscilloscope. MATERIALS Multisim
Table 1 Comparison of DC, Uni-Polar and Bi-polar Stepper Motors
 Electronics Exercise 3: Uni-Polar Stepper Motor Controller / Driver Mechatronics Instructional Laboratory Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Lab Director: I. Charles
Electronics Exercise 3: Uni-Polar Stepper Motor Controller / Driver Mechatronics Instructional Laboratory Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Lab Director: I. Charles
Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence.
 Counters Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence. They can count up, count down, or count through other fixed sequences. Two distinct types are in common usage:
Counters Counters are sequential circuits which "count" through a specific state sequence. They can count up, count down, or count through other fixed sequences. Two distinct types are in common usage:
Lab 1: Study of Gates & Flip-flops
 1.1 Aim Lab 1: Study of Gates & Flip-flops To familiarize with circuit implementations using ICs and test the behavior of different logic gates and Flip-flops. 1.2 Hardware Requirement a. Equipments -
1.1 Aim Lab 1: Study of Gates & Flip-flops To familiarize with circuit implementations using ICs and test the behavior of different logic gates and Flip-flops. 1.2 Hardware Requirement a. Equipments -
Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals
 ELET 3156 DL - Laboratory #6 Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals There is no pre-lab work required for this experiment. However, be sure to read through the assignment completely prior to starting
ELET 3156 DL - Laboratory #6 Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals There is no pre-lab work required for this experiment. However, be sure to read through the assignment completely prior to starting
7. Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
Chapter 7 Latches and Flip-Flops Page 1 of 18 7. Latches and Flip-Flops Latches and flip-flops are the basic elements for storing information. One latch or flip-flop can store one bit of information. The
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders
 Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Fig1-1 2-bit asynchronous counter
 Digital electronics 1-Sequential circuit counters Such a group of flip- flops is a counter. The number of flip-flops used and the way in which they are connected determine the number of states and also
Digital electronics 1-Sequential circuit counters Such a group of flip- flops is a counter. The number of flip-flops used and the way in which they are connected determine the number of states and also
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: igital Circuits Chapter 7 Sequential Elements r. Curtis Nelson Sequential Elements In this chapter you will learn about: circuits that can store information; Basic cells, latches, and flip-flops;
Engr354: igital Circuits Chapter 7 Sequential Elements r. Curtis Nelson Sequential Elements In this chapter you will learn about: circuits that can store information; Basic cells, latches, and flip-flops;
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) LED Dimmer Circuit. Using a 555 Timer Chip
 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) LED Dimmer Circuit Using a 555 Timer Chip Goals of Experiment Demonstrate the operation of a simple PWM circuit that can be used to adjust the intensity of a green LED by varying
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) LED Dimmer Circuit Using a 555 Timer Chip Goals of Experiment Demonstrate the operation of a simple PWM circuit that can be used to adjust the intensity of a green LED by varying
Fig 3. PLC Relay Output
 1. Function of a PLC PLC Basics A PLC is a microprocessor-based controller with multiple inputs and outputs. It uses a programmable memory to store instructions and carry out functions to control machines
1. Function of a PLC PLC Basics A PLC is a microprocessor-based controller with multiple inputs and outputs. It uses a programmable memory to store instructions and carry out functions to control machines
Operating instructions Diffuse reflection sensor. OJ50xx 701396 / 01 07 / 2004
 Operating instructions Diffuse reflection sensor OJ50xx 7096 / 0 07 / 004 Contents Preliminary note. Symbols used Function and features Installation. Installation of the supplied mounting fixture 4 4 Electrical
Operating instructions Diffuse reflection sensor OJ50xx 7096 / 0 07 / 004 Contents Preliminary note. Symbols used Function and features Installation. Installation of the supplied mounting fixture 4 4 Electrical
DIGITAL TECHNICS II. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 5. LECTURE: REGISTERS AND RELATED
 DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 5. LECTURE: REGISTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 22/23 5. LECTURE: REGISTERS. Storage registers 2. Shift
DIGITAL TECHNICS II Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 5. LECTURE: REGISTERS AND RELATED 2nd (Spring) term 22/23 5. LECTURE: REGISTERS. Storage registers 2. Shift
Creating Relay Logic Diagrams
 This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Creating elay Logic Diagrams Chapter Outline 5. Introduction 5. elay Logic Diagrams 5.3 ules
This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Creating elay Logic Diagrams Chapter Outline 5. Introduction 5. elay Logic Diagrams 5.3 ules
Logic in Computer Science: Logic Gates
 Logic in Computer Science: Logic Gates Lila Kari The University of Western Ontario Logic in Computer Science: Logic Gates CS2209, Applied Logic for Computer Science 1 / 49 Logic and bit operations Computers
Logic in Computer Science: Logic Gates Lila Kari The University of Western Ontario Logic in Computer Science: Logic Gates CS2209, Applied Logic for Computer Science 1 / 49 Logic and bit operations Computers
ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME
 The national association for AMATEUR RADIO ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME This supplement is intended for use with the ARRL Morse Code Oscillator kit, sold separately.
The national association for AMATEUR RADIO ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME This supplement is intended for use with the ARRL Morse Code Oscillator kit, sold separately.
Digital Fundamentals
 igital Fundamentals with PL Programming Floyd Chapter 9 Floyd, igital Fundamentals, 10 th ed, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Summary Latches (biestables) A latch is a temporary storage
igital Fundamentals with PL Programming Floyd Chapter 9 Floyd, igital Fundamentals, 10 th ed, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved Summary Latches (biestables) A latch is a temporary storage
LAB4: Audio Synthesizer
 UC Berkeley, EECS 100 Lab LAB4: Audio Synthesizer B. Boser NAME 1: NAME 2: The 555 Timer IC SID: SID: Inductors and capacitors add a host of new circuit possibilities that exploit the memory realized by
UC Berkeley, EECS 100 Lab LAB4: Audio Synthesizer B. Boser NAME 1: NAME 2: The 555 Timer IC SID: SID: Inductors and capacitors add a host of new circuit possibilities that exploit the memory realized by
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:16 min)
 Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language
 Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
