PSPICE Demonstrations and Exercises (SET: 14)
|
|
|
- Erica Greer
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 1 of 7 ELEC ENG 2EI5 ELECTRONIC DEVICES and CIRCUITS I Term II, January April 2005 Instructor: Dr. M. Bakr Prepared by: Dr. M. Bakr and Anthony Bilinski Objective: To learn and use the PSpice model and its parameters for Bipolar Junction Transistors(BJT). To understand and explain the output and transfer characteristics of the BJT. Example 1) Sketch the common-emitter output characteristic for the npn Bipolar Junction transistor in the shown circuit for I B =10µA. Verify your result using a simulation in PSpice. Vary the collector-emitter voltage V CE between -5V and 10V with a step size of 10mV. Perform this sweep for base currents I B ={10µA, 30µA, 50µA}. Plot the resulting collector current waveforms. For the BJT the saturation current is I S =0.1fA Analysis: To determine the shape of the output characteristic calculate the collector current as a function of the collector-emitter voltage V CE. For V CE <0.2 (an assumed small voltage). The transistor is operating in the reverse-active region. I E =-β R I B =-50µA. I C =I E /α R =-60µA. For -0.2<V CE <0.2V the transistor is operating in the saturation region and appears as a closed switch with varying currents maintaining I B +I C -I E =0. For V CE >0.2 the transistor is operating in the forward active region. I C =β F I B and I E =I C /α F =260µA. The ±0.2V value is an assumed small voltage range around 0V. Collector Current ( µa) Common-emitter Output Characte risitic of the NPN transistor Voltage V CE (Volts)
2 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 2 of 7 Building the Circuit: The circuit consists of 3 components: A current source, voltage source and an npn BJT. The name of the generic model for the npn BJT is QBreakN. Similarly the pnp transistor is referred to as QBreakP. These devices can be found in the BREAKOUT library. Construct the circuit as shown. Q1 Qbreakn 0Vdc VCE IB 0Adc Rename the ground node to be 0. Now edit the PSpice model parameters for the npn transistor: Select the npn transistor by clicking on it and then from the edit menu click PSpice Model to load the model editor. The QBreak model for the BJT has many parameters. Some of them are summarized in the shown table. Symbol I S β F V AF r B β R Spice Name Is Bf VAf Rb Br Model Parameter Saturation Current Forward current gain Forward Early Voltage Base ohmic resistance Reverse current gain Default Value 0.1fA 100 0Ω 1 In the PSpice Model Editor change the forward and reverse Beta parameters to 25 and 5 respectively as given in the problem statement. Save the changes and return to the schematic editor.
3 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 3 of 7 View the netlist to see how PSpice represents the BJT in this format. Netlist: * source PSET14EXAMPLE1 Q_Q1 N00065 N Qbreakn V_VCE N Vdc I_IB 0 N00118 DC 0Adc The BJT statement begins with Q followed by a unique name. The nodes to which the element is connected are then listed in the order of those connected to the collector, base, and emitter. Take note that the collector current I C is the negative(-) of the current through the source V CE. Simulating the Circuit: To construct the common-emitter output characteristics for the npn transistor a DC Sweep simulation must be performed on V CE for each of the requested values of I B. Create a new simulation profile and for the analysis type select DC Sweep. Set up the primary sweep of VCE as shown. The model for the operation of the BJT transistor used in Jaeger is actually a simplified version of a more complex model called the Gummel-Poon Model. It is this complex model that forms the heart of the model used by PSpice for simulation. Calculations using the simplified model should not exhibit very much deviation from the more complex and accurate model used by Spice however the results may differ slightly. Select a Parametric Sweep as shown and set it up to sweep the current source I B for the values specified in the problem statement. Ensure the box beside the Parametric Sweep option contains a checkmark and click OK to complete the set-up and return to the schematic. Run the simulation.
4 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 4 of 7 The probe window appears. Click the Add traces Button and add a trace for the collector current I C which is given by the negative of the output variable I(VCE). The resulting graph is shown. 2.0mA 1.0mA To determine which curves corresponds to which value of the current I B click on a curve with the right mouse button and select information. A dialog will appear containing information about the state of the circuit when the simulation was performed. Thus the green curves corresponds to I B =10µA. 0A -1.0mA -5V 0V 5V 10V -I(VCE) V_VCE Labels can be added to each curve using the Text Label Button. Click the text label button and type I B =10uA. 2.0mA 1.0mA IB=50uA IB=30uA Click OK and stamp the label beside the green curve to which it corresponds. Repeat for the other two plots which correspond to 30µA and 50µA. IB=10uA 0A -1.0mA -5V 0V 5V 10V -I(VCE) V_VCE Notice that the collector current is higher when I B is higher. Note that in the reverse and forward active regions the collector current is virtually constant and does not depend on V CE but in the saturation region the current varies quite dramatically with small changes in V CE.
5 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 5 of 7 Using the cursor measure the collector current in the reverse and forward active regions to determine if our calculations were correct. Click the Toggle Cursor button to activate the cursor. Use cursor A1 and its controlling left mouse button to move the cursor to any point in the reverse active region on the curve corresponding to I B =10µA. the value is read from the second column as -60µA. This is exactly the value previously calculated. Now move the cursor to any point on the same plot in the forward active region. The value is again read from the second column as 250µA. The value calculated was 260µA and thus there is a minor and negligible difference between the two results. Example 2) Sketch the common-emitter transfer characteristic for the npn Bipolar Junction transistor for the case when V BC =0. The CE transfer characteristic shows the relationship between the collector current I C and the Base-emitter voltage V BE. Verify your result using a simulation in PSpice. Discuss the similarities between this characteristic and that of a pn junction diode. For the BJT the saturation current is I S =0.1fA Analysis: Since V BC =0 the equation for the collector current reduces V to BE I C = I S exp 1. This is exactly the formula for VT the diode current. Common-Emitter Transfer Characterisitic for the npn BJT 3.5 Collector Current (Amps) Base-Em itter Voltage (Volts)
6 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 6 of 7 Building the Circuit: The circuit is basically the same as that used in Example 1 above. Again a 0Vdc voltage source is used to function as an ammeter to monitor the collector current I C. The Circuit is shown to the right. Netlist: V_Ammeter-IC 0Vdc Q1 *source PSET14EXAMPLE2 Q_Q1 N00087 N Qbreakn V_VBE N Vdc V_V_Ammeter-IC N00007 N Vdc 0Vdc VBE Qbreakn Simulating the Circuit: Create a new simulation profile and set-up a DC Sweep for the voltage V BE as shown. Run the simulation and add a trace for the collector current which corresponds to the current through the 0Vdc ammeter voltage source. The resulting plot is shown below. 3.0A 2.0A 1.0A 0A 0V 0.2V 0.4V 0.6V 0.8V 1.0V I(V_Ammeter-IC) V_VBE
7 ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronic Devices and Circuits I Page: 7 of 7 View the semi log plot of the transfer characteristic by clicking the Log Y Axis button. The plot appears as a straight line. To find the slop of this line we use the cursor. Applying cursor 1 at approximately 100pA and cursor 2 at approximately 10µA account for 5 decades. Thus the voltage difference between these two points divided by 5 gives the voltage difference per decade. Voltage mV = = 59.5mV/decade 60mV/decade decade 5 decades An increase of only 60mV in the base-emitter voltage will increase the collector current by a factor of 10. Similar Circuits and Exercises: Problem 1) Sketch the common-base output characteristic for the npn Bipolar Junction transistor in the shown circuit for I E =0.2mA. Verify your result using a simulation in PSpice. Vary the collector-base voltage V CB between -0.85V and 5V with a step size of 10mV. Perform this sweep for emitter currents I E ={0.2mA, 0.6mA, 1mA}. Plot the resulting collector current waveforms. Problem 2) Sketch the common-emitter output characteristic for the pnp Bipolar Junction transistor in the shown circuit for I B =10µA. Verify your result using a simulation in PSpice. Vary the emitter-collector voltage V CE between -5V and 10V with a step size of 10mV. Perform this sweep for base currents I B ={10µA, 30µA, 50µA}. Plot the resulting collector current waveforms.
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics
 I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Lecture-7 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Part-I Continued
 1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
Lab 1: Introduction to PSpice
 Lab 1: Introduction to PSpice Objectives A primary purpose of this lab is for you to become familiar with the use of PSpice and to learn to use it to assist you in the analysis of circuits. The software
Lab 1: Introduction to PSpice Objectives A primary purpose of this lab is for you to become familiar with the use of PSpice and to learn to use it to assist you in the analysis of circuits. The software
Voltage Divider Bias
 Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
Transistor Biasing. The basic function of transistor is to do amplification. Principles of Electronics
 192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
05 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) basics
 The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime
 Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
CIRCUITS LABORATORY. In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
The basic cascode amplifier consists of an input common-emitter (CE) configuration driving an output common-base (CB), as shown above.
 Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
W04 Transistors and Applications. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
1Meg. 11.A. Resistive Circuit Nodal Analysis
 11. Creating and Using Netlists PART 11 Creating and Using Netlists For this entire text, we have created circuits schematically and then run simulations. Behind the scenes, Capture generates a netlist
11. Creating and Using Netlists PART 11 Creating and Using Netlists For this entire text, we have created circuits schematically and then run simulations. Behind the scenes, Capture generates a netlist
Lecture 17. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.
 Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
3 The TTL NAND Gate. Fig. 3.1 Multiple Input Emitter Structure of TTL
 3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
EE 242 EXPERIMENT 5: COMPUTER SIMULATION OF THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS USING PSPICE SCHEMATICS 1
 EE 242 EXPERIMENT 5: COMPUTER SIMULATION OF THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS USING PSPICE SCHEMATICS 1 Objective: To build, simulate, and analyze three-phase circuits using OrCAD Capture Pspice Schematics under balanced
EE 242 EXPERIMENT 5: COMPUTER SIMULATION OF THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS USING PSPICE SCHEMATICS 1 Objective: To build, simulate, and analyze three-phase circuits using OrCAD Capture Pspice Schematics under balanced
BJT Circuit Configurations
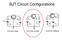 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
2N6387, 2N6388. Plastic Medium-Power Silicon Transistors DARLINGTON NPN SILICON POWER TRANSISTORS 8 AND 10 AMPERES 65 WATTS, 60-80 VOLTS
 2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
BJT Ebers-Moll Model and SPICE MOSFET model
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Amplifier Teaching Aid
 Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Common-Emitter Amplifier
 Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Bob York. Transistor Basics - BJTs
 ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I
 Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Qucs. A Tutorial. Getting Started with Qucs. Stefan Jahn Juan Carlos Borrás
 Qucs A Tutorial Getting Started with Qucs Stefan Jahn Juan Carlos Borrás Copyright c 2007 Stefan Jahn Copyright c 2007 Juan Carlos Borrás Permission is granted to
Qucs A Tutorial Getting Started with Qucs Stefan Jahn Juan Carlos Borrás Copyright c 2007 Stefan Jahn Copyright c 2007 Juan Carlos Borrás Permission is granted to
2N4921G, 2N4922G, 2N4923G. Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors 1.0 AMPERE GENERAL PURPOSE POWER TRANSISTORS 40 80 VOLTS, 30 WATTS
 ,, Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors These highperformance plastic devices are designed for driver circuits, switching, and amplifier applications. Features Low Saturation Voltage Excellent
,, Medium-Power Plastic NPN Silicon Transistors These highperformance plastic devices are designed for driver circuits, switching, and amplifier applications. Features Low Saturation Voltage Excellent
Vdc. Vdc. Adc. W W/ C T J, T stg 65 to + 200 C
 2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA1020
 2SA12 TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA12 Power Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications Unit: mm Low Collector saturation voltage: V CE (sat) =.5 V (max) (I C
2SA12 TOSHIBA Transistor Silicon PNP Epitaxial Type (PCT Process) 2SA12 Power Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications Unit: mm Low Collector saturation voltage: V CE (sat) =.5 V (max) (I C
Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis
 Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Theory & Introduction Lab #9: AC Steady State Analysis Goals for Lab #9 The main goal for lab 9 is to make the students familar with AC steady state analysis, db scale and the NI ELVIS frequency analyzer.
Years after 2000. US Student to Teacher Ratio 0 16.048 1 15.893 2 15.900 3 15.900 4 15.800 5 15.657 6 15.540
 To complete this technology assignment, you should already have created a scatter plot for your data on your calculator and/or in Excel. You could do this with any two columns of data, but for demonstration
To complete this technology assignment, you should already have created a scatter plot for your data on your calculator and/or in Excel. You could do this with any two columns of data, but for demonstration
Figure 1: Common-base amplifier.
 The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Electronics. Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit. LD Physics Leaflets P4.2.1.1
 Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Features: Characteristic Symbol Rating Unit. Collector-Emitter Voltage V CEO 100 Collector-Base Voltage I C
 Designed for use in general purpose power amplifier and switching applications. Features: Collector-Emitter Sustaining Voltage V CEO(sus) = 100V (Minimum) - TIP35C, TIP36C DC Current Gain h FE = 25 (Minimum)
Designed for use in general purpose power amplifier and switching applications. Features: Collector-Emitter Sustaining Voltage V CEO(sus) = 100V (Minimum) - TIP35C, TIP36C DC Current Gain h FE = 25 (Minimum)
Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]
![Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57] Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]](/thumbs/40/21338705.jpg) Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Copyright 2011 Linear Technology. All rights reserved.
 Copyright. All rights reserved. LTspice IV Getting Started Guide 2 Benefits of Using LTspice IV Stable SPICE circuit simulation with Unlimited number of nodes Schematic/symbol editor Waveform viewer Library
Copyright. All rights reserved. LTspice IV Getting Started Guide 2 Benefits of Using LTspice IV Stable SPICE circuit simulation with Unlimited number of nodes Schematic/symbol editor Waveform viewer Library
MJD112 (NPN), MJD117 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors. DPAK For Surface Mount Applications
 MJD (NPN), MJD7 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors For Surface Mount Applications Designed for general purpose power and switching such as output or driver stages in applications such as
MJD (NPN), MJD7 (PNP) Complementary Darlington Power Transistors For Surface Mount Applications Designed for general purpose power and switching such as output or driver stages in applications such as
BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-40. Amplifier Transistors. PNP Silicon. These are Pb Free Devices* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS
 BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-4 Amplifier Transistors PNP Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 45 Vdc CollectorEmitter Voltage
BC327, BC327-16, BC327-25, BC327-4 Amplifier Transistors PNP Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 45 Vdc CollectorEmitter Voltage
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 Apr 23 2001 Oct 10 FEATURES High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V). APPLICATIONS Audio and video amplifiers. PINNING
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 Apr 23 2001 Oct 10 FEATURES High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V). APPLICATIONS Audio and video amplifiers. PINNING
2N2222A. Small Signal Switching Transistor. NPN Silicon. MIL PRF 19500/255 Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV. http://onsemi.com.
 Small Signal Switching Transistor NPN Silicon Features MILPRF19/ Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV COLLECTOR MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Small Signal Switching Transistor NPN Silicon Features MILPRF19/ Qualified Available as JAN, JANTX, and JANTXV COLLECTOR MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
TIP31, TIP32 High Power Bipolar Transistor
 Features: Collector-Emitter sustaining voltage - V CEO(sus) = 60V (Minimum) - TIP31A, TIP32A = 100V (Minimum) - TIP31C,. Collector-Emitter saturation voltage - V CE(sat) = 1.2V (Maximum) at I C = 3.0A.
Features: Collector-Emitter sustaining voltage - V CEO(sus) = 60V (Minimum) - TIP31A, TIP32A = 100V (Minimum) - TIP31C,. Collector-Emitter saturation voltage - V CE(sat) = 1.2V (Maximum) at I C = 3.0A.
OrCAD Capture with PSpice and Allegro DE CIS with AMS Simulator. Describes how to create a PSpice Archive File with Capture
 Title: Product: Summary: Creating a Project Archive OrCAD Capture with PSpice and Allegro DE CIS with AMS Simulator Describes how to create a PSpice Archive File with Capture Author/Date: Wei Ling / 03.08.2009
Title: Product: Summary: Creating a Project Archive OrCAD Capture with PSpice and Allegro DE CIS with AMS Simulator Describes how to create a PSpice Archive File with Capture Author/Date: Wei Ling / 03.08.2009
Lecture 12: DC Analysis of BJT Circuits.
 Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
Whites, 320 Lecture 12 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 12: D Analysis of JT ircuits. n this lecture we will consider a number of JT circuits and perform the D circuit analysis. For those circuits with an active mode
3. On the top menu bar, click on File > New > Project as shown in Fig. 2 below: Figure 2 Window for Orcad Capture CIS
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of North Texas Denton, TX. 76207 EENG 2920 Quickstart PSpice Tutorial Tutorial Prepared by Oluwayomi Adamo 1. To run the PSpice program, click on Start >
Department of Electrical Engineering University of North Texas Denton, TX. 76207 EENG 2920 Quickstart PSpice Tutorial Tutorial Prepared by Oluwayomi Adamo 1. To run the PSpice program, click on Start >
Figure 1. Diode circuit model
 Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
BD238. Low voltage PNP power transistor. Features. Applications. Description. Low saturation voltage PNP transistor
 Low voltage PNP power transistor Features Low saturation voltage PNP transistor Applications Audio, power linear and switching applications Description The device is manufactured in planar technology with
Low voltage PNP power transistor Features Low saturation voltage PNP transistor Applications Audio, power linear and switching applications Description The device is manufactured in planar technology with
Peak Atlas DCA. Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55. User Guide
 GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
GB55-7 Peak Atlas DCA Semiconductor Component Analyser Model DCA55 User Guide Peak Electronic Design Limited 2000/2007 In the interests of development, information in this guide is subject to change without
2N4401. General Purpose Transistors. NPN Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
 General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc Emitter
General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc Emitter
http://users.ece.gatech.edu/~mleach/ece3050/notes/feedback/fbexamples.pdf
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors
 TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors Designed for use in general purpose amplifier and switching applications. Features
TIP41, TIP41A, TIP41B, TIP41C (NPN); TIP42, TIP42A, TIP42B, TIP42C (PNP) Complementary Silicon Plastic Power Transistors Designed for use in general purpose amplifier and switching applications. Features
2N6056. NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor DARLINGTON 8 AMPERE SILICON POWER TRANSISTOR 80 VOLTS, 100 WATTS
 NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
PHOTOTRANSISTOR OPTOCOUPLERS
 MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
MCT2 MCT2E MCT20 MCT27 WHITE PACKAGE (-M SUFFIX) BLACK PACKAGE (NO -M SUFFIX) DESCRIPTION The MCT2XXX series optoisolators consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode driving a silicon phototransistor
TIP140, TIP141, TIP142, (NPN); TIP145, TIP146, TIP147, (PNP) Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors
 TIP140, TIP141, TIP142, (); TIP145, TIP146, TIP147, () Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors Designed for generalpurpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High DC
TIP140, TIP141, TIP142, (); TIP145, TIP146, TIP147, () Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors Designed for generalpurpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High DC
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis
 Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
DATA SHEET. PBSS5540Z 40 V low V CEsat PNP transistor DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product data sheet Supersedes data of 2001 Jan 26. 2001 Sep 21.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET fpage M3D87 PBSS554Z 4 V low V CEsat PNP transistor Supersedes data of 21 Jan 26 21 Sep 21 FEATURES Low collector-emitter saturation voltage High current capability Improved
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET fpage M3D87 PBSS554Z 4 V low V CEsat PNP transistor Supersedes data of 21 Jan 26 21 Sep 21 FEATURES Low collector-emitter saturation voltage High current capability Improved
MPS2222, MPS2222A. NPN Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS MARKING DIAGRAMS THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
 , is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS CollectorEmitter Voltage CollectorBase Voltage Rating Symbol Value Unit
, is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS CollectorEmitter Voltage CollectorBase Voltage Rating Symbol Value Unit
Scatter Plots with Error Bars
 Chapter 165 Scatter Plots with Error Bars Introduction The procedure extends the capability of the basic scatter plot by allowing you to plot the variability in Y and X corresponding to each point. Each
Chapter 165 Scatter Plots with Error Bars Introduction The procedure extends the capability of the basic scatter plot by allowing you to plot the variability in Y and X corresponding to each point. Each
Document Contents Introduction Layout Extraction with Parasitic Capacitances Timing Analysis DC Analysis
 Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group rev S06 (convert to spectre simulator) Document Contents Introduction
Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group rev S06 (convert to spectre simulator) Document Contents Introduction
P2N2222ARL1G. Amplifier Transistors. NPN Silicon. These are Pb Free Devices* Features. http://onsemi.com
 Amplifier Transistors NPN Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = 25 C unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 4 CollectorBase
Amplifier Transistors NPN Silicon Features These are PbFree Devices* MAXIMUM RATINGS (T A = 25 C unless otherwise noted) Characteristic Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 4 CollectorBase
Table 1 Comparison of DC, Uni-Polar and Bi-polar Stepper Motors
 Electronics Exercise 3: Uni-Polar Stepper Motor Controller / Driver Mechatronics Instructional Laboratory Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Lab Director: I. Charles
Electronics Exercise 3: Uni-Polar Stepper Motor Controller / Driver Mechatronics Instructional Laboratory Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Lab Director: I. Charles
CONSTRUCTING A VARIABLE POWER SUPPLY UNIT
 CONSTRUCTING A VARIABLE POWER SUPPLY UNIT Building a power supply is a good way to put into practice many of the ideas we have been studying about electrical power so far. Most often, power supplies are
CONSTRUCTING A VARIABLE POWER SUPPLY UNIT Building a power supply is a good way to put into practice many of the ideas we have been studying about electrical power so far. Most often, power supplies are
DATA SHEET. BC875; BC879 NPN Darlington transistors DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS. Product specification Supersedes data of 1999 May 28.
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 May 28 2004 Nov 05 FEATURES High DC current gain (min. 1000) High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET book, halfpage M3D186 Supersedes data of 1999 May 28 2004 Nov 05 FEATURES High DC current gain (min. 1000) High current (max. 1 A) Low voltage (max. 80 V) Integrated
45 V, 100 ma NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor
 Rev. 4 18 February 29 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor pair in a very small SOT363 (SC-88) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package.
Rev. 4 18 February 29 Product data sheet 1. Product profile 1.1 General description NPN/PNP general-purpose transistor pair in a very small SOT363 (SC-88) Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package.
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Plots, Curve-Fitting, and Data Modeling in Microsoft Excel
 Plots, Curve-Fitting, and Data Modeling in Microsoft Excel This handout offers some tips on making nice plots of data collected in your lab experiments, as well as instruction on how to use the built-in
Plots, Curve-Fitting, and Data Modeling in Microsoft Excel This handout offers some tips on making nice plots of data collected in your lab experiments, as well as instruction on how to use the built-in
Diodes and Transistors
 Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15. Instruction Manual ELENCO
 POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15 Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2013 by Elenco Electronics, Inc. REV-A 753020 All rights reserved. No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying,
POWER SUPPLY MODEL XP-15 Instruction Manual ELENCO Copyright 2013 by Elenco Electronics, Inc. REV-A 753020 All rights reserved. No part of this book shall be reproduced by any means; electronic, photocopying,
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET BC856; BC857; BC858
 DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET Supersedes data of 23 Apr 9 24 Jan 16 FEATURES Low current (max. 1 ma) Low voltage (max. 65 V). APPLICATIONS General purpose switching and amplification. PINNING PIN
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS DATA SHEET Supersedes data of 23 Apr 9 24 Jan 16 FEATURES Low current (max. 1 ma) Low voltage (max. 65 V). APPLICATIONS General purpose switching and amplification. PINNING PIN
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of rectifier and Zener diodes in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn to recognize
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of rectifier and Zener diodes in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn to recognize
BD241A BD241C. NPN power transistors. Features. Applications. Description. NPN transistors. Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors
 BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
BD241A BD241C NPN power transistors Features. NPN transistors Applications Audio, general purpose switching and amplifier transistors Description The devices are manufactured in Planar technology with
Differential transistor amplifiers
 Differential transistor amplifiers This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Differential transistor amplifiers This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
AB07 Common Collector PNP Transistor Characteristics. Analog lab Experiment board. Ver 1.0
 Common Collector PNP Transistor Characteristics Analog lab Experiment board Ver 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by
Common Collector PNP Transistor Characteristics Analog lab Experiment board Ver 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by
2N3906. General Purpose Transistors. PNP Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS
 2N396 General Purpose Transistors PNP Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V
2N396 General Purpose Transistors PNP Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* COLLECTOR 3 MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V
2N3903, 2N3904. General Purpose Transistors. NPN Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* Features. http://onsemi.com MAXIMUM RATINGS
 N393, General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc CollectorBase Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc EmitterBase
N393, General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc CollectorBase Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc EmitterBase
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
 SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
OrCAD Flow Tutorial. Product Version 10.0 Februaruy 2004
 OrCAD Flow Tutorial Product Version 10.0 Februaruy 2004 2003-2004 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. Cadence Design Systems, Inc., 555 River Oaks
OrCAD Flow Tutorial Product Version 10.0 Februaruy 2004 2003-2004 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. Cadence Design Systems, Inc., 555 River Oaks
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY. Fig. 8.1a Fig 8.1b
 DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
Bipolar transistor biasing circuits
 Bipolar transistor biasing circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Bipolar transistor biasing circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
2N3903, 2N3904. General Purpose Transistors. NPN Silicon. Features Pb Free Package May be Available. The G Suffix Denotes a Pb Free Lead Finish
 N393, N393 is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Package May be Available. The GSuffix Denotes a PbFree Lead Finish MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter
N393, N393 is a Preferred Device General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Package May be Available. The GSuffix Denotes a PbFree Lead Finish MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit CollectorEmitter
