Physics of Bipolar Junction Transistors
|
|
|
- Ruby Young
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUT Analog Circuits Physics of Bipolar Junction Transistors Prepared by: Siavash Kananian 1
2 Bipolar Transistor n the chapter, we will study the physics of bipolar transistor and derive large and small signal models. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 2
3 Voltage-Dependent Current Source A V V V out in KR L A voltage-dependent current source can act as an amplifier. f KR L is greater than 1, then the signal is amplified. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 3
4 Voltage-Dependent Current Source with nput Resistance Regardless of the input resistance, the magnitude of amplification remains unchanged. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 4
5 Exponential Voltage-Dependent Current Source A three-terminal exponential voltage-dependent current source is shown above. deally, bipolar transistor can be modeled as such. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 5
6 Structure and Symbol of Bipolar Transistor Bipolar transistor can be thought of as a sandwich of three doped Si regions. The outer two regions are doped with the same polarity, while the middle region is doped with opposite polarity. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 6
7 njection of Carriers Reverse biased PN junction creates a large electric field that sweeps any injected minority carriers to their majority region. This ability proves essential in the proper operation of a bipolar transistor. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 7
8 Forward Active Region Forward active region: V BE > 0, V BC < 0. Figure b) presents a wrong way of modeling figure a). Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 8
9 Accurate Bipolar Representation Collector also carries current due to carrier injection from base. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 9
10 Carrier Transport in Base Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 10
11 Collector Current C C S AE qdnn N W S E E B AE qdnn N W B 2 i V exp V BE T 2 i V exp V BE T 1 Applying the law of diffusion, we can determine the charge flow across the base region into the collector. The equation above shows that the transistor is indeed a voltage-controlled element, thus a good candidate as an amplifier. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 11
12 Parallel Combination of Transistors When two transistors are put in parallel and experience the same potential across all three terminals, they can be thought of as a single transistor with twice the emitter area. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 12
13 Simple Transistor Configuration Although a transistor is a voltage to current converter, output voltage can be obtained by inserting a load resistor at the output and allowing the controlled current to pass thru it. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 13
14 Constant Current Source deally, the collector current does not depend on the collector to emitter voltage. This property allows the transistor to behave as a constant current source when its base-emitter voltage is fixed. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 14
15 Base Current C B Base current consists of two components: 1) Reverse injection of holes into the emitter and 2) recombination of holes with electrons coming from the emitter. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 15
16 Emitter Current Applying Kirchoff s current law to the transistor, we can easily find the emitter current. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 16 B C C E B C E 1 1
17 Summary of Currents Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 17 1 exp 1 exp 1 exp T BE S E T BE S B T BE S C V V V V V V
18 Bipolar Transistor Large Signal Model A diode is placed between base and emitter and a voltage controlled current source is placed between the collector and emitter. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 18
19 Example: Maximum R L As R L increases, V x drops and eventually forward biases the collector-base junction. This will force the transistor out of forward active region. Therefore, there exists a maximum tolerable collector resistance. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 19
20 Characteristics of Bipolar Transistor Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 20
21 Example: V Characteristics Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 21
22 Transconductance g g g m m m d dv 1 V V T C T BE S V S exp V VBE exp V T BE T Transconductance, g m shows a measure of how well the transistor converts voltage to current. t will later be shown that g m is one of the most important parameters in circuit design. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 22
23 Visualization of Transconductance g m can be visualized as the slope of C versus V BE. A large C has a large slope and therefore a large g m. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 23
24 Transconductance and Area When the area of a transistor is increased by n, S increases by n. For a constant V BE, C and hence g m increases by a factor of n. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 24
25 Transconductance and c The figure above shows that for a given V BE swing, the current excursion around C2 is larger than it would be around C1. This is because g m is larger C2. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 25
26 Small-Signal Model: Derivation Small signal model is derived by perturbing voltage difference every two terminals while fixing the third terminal and analyzing the change in current of all three terminals. We then represent these changes with controlled sources or resistors. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 26
27 Small-Signal Model: V BE Change Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 27
28 Small-Signal Model: V CE Change deally, V CE has no effect on the collector current. Thus, it will not contribute to the small signal model. t can be shown that V CB has no effect on the small signal model, either. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 28
29 Small Signal Example g r m V g C T m Here, small signal parameters are calculated from DC operating point and are used to calculate the change in collector current due to a change in V BE. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 29
30 Small Signal Example n this example, a resistor is placed between the power supply and collector, therefore, providing an output voltage. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 30
31 Early Effect The claim that collector current does not depend on V CE is not accurate. As V CE increases, the depletion region between base and collector increases. Therefore, the effective base width decreases, which leads to an increase in the collector current. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 31
32 Early Effect llustration With Early effect, collector current becomes larger than usual and a function of V CE. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 32
33 Early Effect Representation Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 33
34 Early Effect and Large-Signal Model Early effect can be accounted for in large-signal model by simply changing the collector current with a correction factor. n this mode, base current does not change. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 34
35 Early Effect and Small-Signal Model r o V CE C S VA V exp V BE T V A C Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 35
36 Summary of deas 36 Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi
37 Bipolar Transistor in Saturation When collector voltage drops below base voltage and forward biases the collector-base junction, base current increases and decreases the current gain factor,. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 37
38 Large-Signal Model for Saturation Region Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 38
39 Overall /V Characteristics The speed of the BJT also drops in saturation. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 39
40 Example: Acceptable V CC Region V CC C R C ( V 400mV ) BE n order to keep BJT at least in soft saturation region, the collector voltage must not fall below the base voltage by more than 400mV. A linear relationship can be derived for V CC and R C and an acceptable region can be chosen. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 40
41 Deep Saturation n deep saturation region, the transistor loses its voltagecontrolled current capability and V CE becomes constant. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 41
42 PNP Transistor With the polarities of emitter, collector, and base reversed, a PNP transistor is formed. All the principles that applied to NPN's also apply to PNP s, with the exception that emitter is at a higher potential than base and base at a higher potential than collector. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 42
43 A Comparison between NPN and PNP Transistors The figure above summarizes the direction of current flow and operation regions for both the NPN and PNP BJT s. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 43
44 PNP Equations C B E S V exp V 1 S EB T S V exp V EB T V exp V EB T Early Effect C S V exp V EB T V 1 V EC A 44 Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi
45 Large Signal Model for PNP Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 45
46 PNP Biasing Note that the emitter is at a higher potential than both the base and collector. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 46
47 Small Signal Analysis Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 47
48 Small-Signal Model for PNP Transistor The small signal model for PNP transistor is exactly DENTCAL to that of NPN. This is not a mistake because the current direction is taken care of by the polarity of V BE. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 48
49 Small Signal Model Example Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 49
50 Small Signal Model Example Small-signal model is identical to the previous ones. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 50
51 Small Signal Model Example Since during small-signal analysis, a constant voltage supply is considered to be AC ground, the final small-signal model is identical to the previous two. Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 51
52 Small Signal Model Example V Physics of BJTs, Fundamentals of Microelectronics, B.Razavi 52
53 A little Frequency Response! Consider the common emitter circuit above. Derive the Vo-Vi characteristics for f=10hz. Oscilloscope Screen on right: Siavash Kananian Copyright 53
54 Raising the frequency and checking the screen again, give some unpredictable result! f = 1kHz f = 10kHz f = 100kHz Siavash Kananian Copyright 54
55 What happens? Do you remember from earlier experiments, the Lissajous Patterns? t seems that input and output at higher frequencies have some phase shift! Why on earth something like that would happen? s there a capacitor somewhere we don t see? The answer is yes! BJT internal capacitors is the key to the question. Siavash Kananian Copyright 55
56 BJT at high frequency At high frequency, capacitive effects come into play. C b represents the base charge, whereas C and C je are the junction capacitances. Since an integrated bipolar circuit is fabricated on top of a substrate, another junction capacitance exists between the collector and substrate, namely C CS. Siavash Kananian Copyright 56
57 Another look at Characteristics: SPCE Simulation f = 10Hz f = 1kHz f = 10kHz f = 100kHz Siavash Kananian Copyright 57
58 SPCE Code n case you want to discover new things yourself: Bc107_high_frequency.options spice vcc r k r k q bc107 v1 1 0 sin tran 100u 200m.probe v(3).model bc107 npn s=7.049f Xti=3 Eg=1.11 Vaf=116.3 Bf=375.5 se=7.049f Ne=1.281 kf=4.589 Nk=.5 Xtb=1.5 Br=2.611 sc=121.7p Nc=1.865 kr=5.313 Rc=1.464 Cjc=5.38p Mjc=.329 Vjc=.6218 Fc=.5 Cje=11.5p Mje=.2717 Vje=.5 Tr=10n Tf=451p tf=6.194 Xtf=17.43 Vtf=10.op.end Siavash Kananian Copyright 58
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
05 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) basics
 The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
The first bipolar transistor was realized in 1947 by Brattain, Bardeen and Shockley. The three of them received the Nobel prize in 1956 for their invention. The bipolar transistor is composed of two PN
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
BJT Ebers-Moll Model and SPICE MOSFET model
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler [email protected] EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
CIRCUITS LABORATORY. In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
Amplifier Teaching Aid
 Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
3.4 - BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
 BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
Lecture 17. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.
 Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT): Part 1 Qualitative Understanding - How do they work? Reading: Pierret 10.1-10.6, 11.1 Looks sort of like two diodes back to back pnp mnemonic: Pouring N Pot
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime
 Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Electronics. Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit. LD Physics Leaflets P4.2.1.1
 Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics
 I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
Common-Emitter Amplifier
 Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
BJT Circuit Configurations
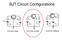 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier
 Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Diodes and Transistors
 Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Bob York. Transistor Basics - BJTs
 ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
ob York Transistor asics - JTs ipolar Junction Transistors (JTs) Key points: JTs are current-controlled devices very JT has a base, collector, and emitter The base current controls the collector current
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
Transistor Biasing. The basic function of transistor is to do amplification. Principles of Electronics
 192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720. Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment.
 Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720 Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment. This assignment will take you through the simulation and basic characterization of a simple operational
Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720 Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment. This assignment will take you through the simulation and basic characterization of a simple operational
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL
 TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
TWO PORT NETWORKS h-parameter BJT MODEL The circuit of the basic two port network is shown on the right. Depending on the application, it may be used in a number of different ways to develop different
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
Objectives The purpose of this lab is build and analyze Differential amplifiers based on NPN transistors (or NMOS transistors).
 1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
The basic cascode amplifier consists of an input common-emitter (CE) configuration driving an output common-base (CB), as shown above.
 Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 2
 Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
Content Map For Career & Technology
 Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices
 Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design
 Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
W04 Transistors and Applications. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
3. Diodes and Diode Circuits. 3. Diodes and Diode Circuits TLT-8016 Basic Analog Circuits 2005/2006 1
 3. Diodes and Diode Circuits 3. Diodes and Diode Circuits TLT-8016 Basic Analog Circuits 2005/2006 1 3.1 Diode Characteristics Small-Signal Diodes Diode: a semiconductor device, which conduct the current
3. Diodes and Diode Circuits 3. Diodes and Diode Circuits TLT-8016 Basic Analog Circuits 2005/2006 1 3.1 Diode Characteristics Small-Signal Diodes Diode: a semiconductor device, which conduct the current
Figure 1. Diode circuit model
 Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
Semiconductor Devices Non-linear Devices Diodes Introduction. The diode is two terminal non linear device whose I-V characteristic besides exhibiting non-linear behavior is also polarity dependent. The
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Differential Amplifier Offset. Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset R C
 ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME
 The national association for AMATEUR RADIO ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME This supplement is intended for use with the ARRL Morse Code Oscillator kit, sold separately.
The national association for AMATEUR RADIO ARRL Morse Code Oscillator, How It Works By: Mark Spencer, WA8SME This supplement is intended for use with the ARRL Morse Code Oscillator kit, sold separately.
Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 H2 - AC to DC Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits W04 Transistors and Applications (H-Bridge) W05 Op Amps
H2 - AC to DC Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits W04 Transistors and Applications (H-Bridge) W05 Op Amps
3 The TTL NAND Gate. Fig. 3.1 Multiple Input Emitter Structure of TTL
 3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
3 The TTL NAND Gate 3. TTL NAND Gate Circuit Structure The circuit structure is identical to the previous TTL inverter circuit except for the multiple emitter input transistor. This is used to implement
CONTENTS. Preface. 1.1.2. Energy bands of a crystal (intuitive approach)
 CONTENTS Preface. Energy Band Theory.. Electron in a crystal... Two examples of electron behavior... Free electron...2. The particle-in-a-box approach..2. Energy bands of a crystal (intuitive approach)..3.
CONTENTS Preface. Energy Band Theory.. Electron in a crystal... Two examples of electron behavior... Free electron...2. The particle-in-a-box approach..2. Energy bands of a crystal (intuitive approach)..3.
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis
 Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Fundamentals of Signature Analysis An In-depth Overview of Power-off Testing Using Analog Signature Analysis www.huntron.com 1 www.huntron.com 2 Table of Contents SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION... 7 PURPOSE...
Zero voltage drop synthetic rectifier
 Zero voltage drop synthetic rectifier Vratislav Michal Brno University of Technology, Dpt of Theoretical and Experimental Electrical Engineering Kolejní 4/2904, 612 00 Brno Czech Republic [email protected],
Zero voltage drop synthetic rectifier Vratislav Michal Brno University of Technology, Dpt of Theoretical and Experimental Electrical Engineering Kolejní 4/2904, 612 00 Brno Czech Republic [email protected],
Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV
 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV By Adam Zielinski (Posted at: http://wwwece.uvic.ca/~adam/) Version: August 22, 2002 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II - Tutorial
ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II Tutorial and Simulations for Micro-Cap IV By Adam Zielinski (Posted at: http://wwwece.uvic.ca/~adam/) Version: August 22, 2002 ELEC 380 Electronic Circuits II - Tutorial
Voltage Divider Bias
 Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Lecture-7 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Part-I Continued
 1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
1 Lecture-7 ipolar Junction Transistors (JT) Part-I ontinued 1. ommon-emitter (E) onfiguration: Most JT circuits employ the common-emitter configuration shown in Fig.1. This is due mainly to the fact that
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS IN ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
 CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor Study the characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage in the metal oxide semiconductor structure known
CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor Study the characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage in the metal oxide semiconductor structure known
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]
![Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57] Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]](/thumbs/40/21338705.jpg) Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
Vdc. Vdc. Adc. W W/ C T J, T stg 65 to + 200 C
 2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
2N6284 (NPN); 2N6286, Preferred Device Darlington Complementary Silicon Power Transistors These packages are designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. Features High
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
Semiconductors, diodes, transistors
 Semiconductors, diodes, transistors (Horst Wahl, QuarkNet presentation, June 2001) Electrical conductivity! Energy bands in solids! Band structure and conductivity Semiconductors! Intrinsic semiconductors!
Semiconductors, diodes, transistors (Horst Wahl, QuarkNet presentation, June 2001) Electrical conductivity! Energy bands in solids! Band structure and conductivity Semiconductors! Intrinsic semiconductors!
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I
 Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Lecture 22: Class C Power Amplifiers
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
AP331A XX G - 7. Lead Free G : Green. Packaging (Note 2)
 Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
Audio Power Amplifier Design Handbook
 Comments on Audio Power Amplifier Design Handbook by Douglas Self Samuel Groner February 13, 2011 1 Introduction Douglas Self s writing on audio power amplifiers provides the reader with invaluable information.
Comments on Audio Power Amplifier Design Handbook by Douglas Self Samuel Groner February 13, 2011 1 Introduction Douglas Self s writing on audio power amplifiers provides the reader with invaluable information.
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY. Fig. 8.1a Fig 8.1b
 DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15. BJT Structure and Fabrication
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
AN105. Introduction: The Nature of VCRs. Resistance Properties of FETs
 Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
Objective. To design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors.
 ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
2N6387, 2N6388. Plastic Medium-Power Silicon Transistors DARLINGTON NPN SILICON POWER TRANSISTORS 8 AND 10 AMPERES 65 WATTS, 60-80 VOLTS
 2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
2N6388 is a Preferred Device Plastic MediumPower Silicon Transistors These devices are designed for generalpurpose amplifier and lowspeed switching applications. Features High DC Current Gain h FE = 2500
ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012. A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742
 1.1. Differential Amplifiers ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012 A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742 Differential Amplifiers
1.1. Differential Amplifiers ENEE 307 Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory Spring 2012 A. Iliadis Electrical Engineering Department University of Maryland College Park MD 20742 Differential Amplifiers
CHAPTER 2 POWER AMPLIFIER
 CHATER 2 OWER AMLFER 2.0 ntroduction The main characteristics of an amplifier are Linearity, efficiency, output power, and signal gain. n general, there is a trade off between these characteristics. For
CHATER 2 OWER AMLFER 2.0 ntroduction The main characteristics of an amplifier are Linearity, efficiency, output power, and signal gain. n general, there is a trade off between these characteristics. For
Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers
 Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers By: Gary A. Ybarra Christopher E. Cramer Duke University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Durham, NC. Purpose The purpose of this lab is to examine the properties
Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers By: Gary A. Ybarra Christopher E. Cramer Duke University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Durham, NC. Purpose The purpose of this lab is to examine the properties
Field Effect Transistors
 506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
Log and AntiLog Amplifiers. Recommended Text: Pallas-Areny, R. & Webster, J.G., Analog Signal Processing, Wiley (1999) pp. 293-321
 Log and AntiLog Amplifiers Recommended Text: Pallas-Areny, R. & Webster, J.G., Analog Signal Processing, Wiley (999) pp. 93-3 ntroduction Log and Antilog Amplifiers are non-linear circuits in which the
Log and AntiLog Amplifiers Recommended Text: Pallas-Areny, R. & Webster, J.G., Analog Signal Processing, Wiley (999) pp. 93-3 ntroduction Log and Antilog Amplifiers are non-linear circuits in which the
Diode Circuits. Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode)
 Diode Circuits Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode) In may applications, operation in the reverse breakdown region is highly desirable. The reverse breakdown voltage is relatively insensitive
Diode Circuits Operating in the Reverse Breakdown region. (Zener Diode) In may applications, operation in the reverse breakdown region is highly desirable. The reverse breakdown voltage is relatively insensitive
Bipolar transistor biasing circuits
 Bipolar transistor biasing circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Bipolar transistor biasing circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies
 Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads.
 Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure
 The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
2N6056. NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor DARLINGTON 8 AMPERE SILICON POWER TRANSISTOR 80 VOLTS, 100 WATTS
 NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
NPN Darlington Silicon Power Transistor The NPN Darlington silicon power transistor is designed for general purpose amplifier and low frequency switching applications. High DC Current Gain h FE = 3000
2N4401. General Purpose Transistors. NPN Silicon. Pb Free Packages are Available* http://onsemi.com. Features MAXIMUM RATINGS THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
 General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc Emitter
General Purpose Transistors NPN Silicon Features PbFree Packages are Available* MAXIMUM RATINGS Rating Symbol Value Unit Collector Emitter Voltage V CEO 4 Vdc Collector Base Voltage V CBO 6 Vdc Emitter
Operational Amplifier - IC 741
 Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of rectifier and Zener diodes in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn to recognize
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of rectifier and Zener diodes in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn to recognize
Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits. http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf
 EE40 Lec 18 Diode Circuits Reading: Chap. 10 of Hambley Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf Slide 1 Diodes Circuits Load
EE40 Lec 18 Diode Circuits Reading: Chap. 10 of Hambley Supplement Reading on Diode Circuits http://www.inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/ edu/~ee40/fa09/handouts/ee40_mos_circuit.pdf Slide 1 Diodes Circuits Load
11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION
 11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION The properties of an amplifying circuit using an op-amp depend primarily on the characteristics of the feedback network rather than on those of the op-amp itself. A
11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION The properties of an amplifying circuit using an op-amp depend primarily on the characteristics of the feedback network rather than on those of the op-amp itself. A
Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS
 LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
Design of op amp sine wave oscillators
 Design of op amp sine wave oscillators By on Mancini Senior Application Specialist, Operational Amplifiers riteria for oscillation The canonical form of a feedback system is shown in Figure, and Equation
Design of op amp sine wave oscillators By on Mancini Senior Application Specialist, Operational Amplifiers riteria for oscillation The canonical form of a feedback system is shown in Figure, and Equation
