Revision on Basic Transistor Amplifiers
|
|
|
- Lisa O’Connor’
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Circuits Revision on Basic Transistor Amplifiers Contents Biasing Amplification principles Small-signal model development for BJT
2 Aim of this chapter To show how transistors can be used to amplify a signal. amplifier 2
3 Basic idea Step 1: Set the transistor at a certain DC level biasing Step 2: Inject a small signal to the input and get a bigger output coupling 0.6V amplifier 7V 3
4 Biasing the transistor To set the transistor to a certain DC level = To set V CE and I C R B V BE V CC =10V I B I C V CE Suppose we want the following biasing condition: I C = 10 ma and V CE = 5 V Find R B and Start with V BE 0.7 V. Then, I B = (10 V BE )/ R B = (10 0.7)/ R B I C = βi B = 100 (10 0.7)/ R B = 10 ma So, R B = 94kΩ Transistor: β = 100 Also, V CE = 10 I C Hence, 5 = So, = 0.5kΩ 4
5 β dependent biasing bad biasing V CC =10V Now, let s go to the lab and try using R B = 94kΩ and = 0.5kΩ, and see if we get what we want. R B I C totally wrong! We don t get I C = 10mA and V CE = 5V V BE I B Transistor: β = 100 V CE This is not a good biasing circuit! because it relies on the accuracy of β, but β can be ±50% different from what is given in the databook. 5
6 A slightly better biasing method V CC =10V Again, our objective is to find the resistors such that I C = 10mA and V CE = 5V. First, if I B is small, we can approximately write R B1 R B2 I B V BE I C V CE Suppose we get I C = 10mA. Then = 0.5kΩ. We can start with R B1 = 940Ω and R B2 = 60Ω. Such resistors will make sure I B is much smaller than the current flowing down R B1 and R B2, which is consistent with the assumption. What we need in practice is to fine tune R B1 or R B2 such that V CE is exactly 5V. 6
7 A much better biasing method emitter degeneration V CC =10V Again, our objective is to find the resistors such that I C = 10mA and V CE = 5V. R B1 R B2 I B V E I C V CE R E Set V E = 2V, say. Then, R E = 2V/10mA = 0.2kΩ. Surely, = 0.3kΩ in order to get V CE = 5V. Finally, we have V B = V E 0.6. Therefore, if I B is small compared to I RB1 and I RB2, we have Hence, R B1 = 740Ω and R B1 = 260Ω. NOTE: β is never used in calculation!! 7
8 Stable (good) biasing V CC =10V Summary of biasing with emitter degeneration: Choose V E, I C and V CE. R B1 I C V B R B2 I B V E V CE R E R E Use V BE 0.6 to get V B. Then use to choose R B1 and R B2 such that I B is much smaller the current flowing in R B1 and R B2. 8
9 Terminology The following are the same: Biasing point Quiescent point Operating point (OP) DC point 9
10 Alternative view of biasing V CC V BE I C V CE V CC I C V R V CE I C Load line Slope=1/ operating point V CC V CE 10
11 What controls the operating point? V CC I C V BE I C V CE Load line Slope=1/ operating point a bigger V BE a smaller V CC V CE CONCLUSION: V BE or I B controls the OP also controls the OP 11
12 What happens if V BE dances up and down? V CC V BE I C V CE I C Load line Slope=1/ a bigger V BE = 0.65 a smaller V BE = 0.6 V CC V CE The OP also dances up and down along the load line. V CE also moves up and down. Typically, when V BE moves a little bit, V CE moves a lot! THIS IS CALLED AMPLICATION. 12
13 Derivation of voltage gain Question: what is? V CC Clearly, Ohm s law says that V BE I C V CE Then, what relates I C and V BE? Last lecture: transconductance Hence, 13
14 Common-emitter amplifier The one we have just studied is called COMMON-EMITTER amplifier. V CC SUMMARY: R B1 R B2 v BE v CE I C Small-signal voltage gain = g m That means we can increase the gain by increasing g m and/or. Output waveform is antiphase. 14
15 How do we inject signal into the amplifier? V CC R B1 I C ±20mV? R B2 V BE v CE = V CE v CE or v CE 15
16 Note on symbols = Total signal a v CE = V CE v CE DC point A total signal (large signal) operating point or DC value or quiescent point small signal or ac signal Small signal a or a 16
17 Solution: Add the same biasing DC level Exactly the same biasing V BE R B1 V CC I C But, it is impossible to find a voltage source which is equal to the exact biasing voltage across B-E. ±20mV R B2 v BE v CE V BE could actually be V, which is determined by the network RB1, RB2 and the transistor characteristic!! How to apply the exact V BE? 17
18 The wonderful voltage source: capacitor V CC The capacitor voltage is exactly equal to V BE because DC current must be zero V C 0A R B1 R B2 V BE I C V CE 18
19 Solution insert coupling capacitor This is called a coupling capacitor DC voltage equal to exactly the same biasing V BE ±20mV R B1 R B2 V CC v BE v CE I C 19
20 Complete common emitter amplifier V CC R B1 I C R B2 v BE v CE coupling capacitors (large enough so that they become short-circuit at signal frequencies) 20
21 Can we simplify the analysis? We are mainly interested in the ac signals. The DC bias does not matter! Can we create a simple circuit just to look at ac signals? common emitter amplifier 21
22 Small-signal model Two basic questions: common emitter v?? in amplifier 1 2 What is the loading (resistance) seen here? What is the Thévenin or Norton equivalent circuit seen here? 22
23 Small-signal model of BJT: objectives To find: r in R o G m or r in R o A m r in R o r in R o G m A m Norton form Thévenin form 23
24 Derivation of the small-signal model Input side: i B v BE For small-signal, r π r π β/g m where g m is the BJT s transconductance 24
25 Derivation of the small-signal model Output side: VCC I C v CE = V CC I C For small-signal, g m v BE v CE v CE where g m is the BJT s transconductance 25
26 Derivation of the small-signal model Output side: V CC Including BJT s Early effect g m v BE r o v CE I C v CE where r o is the Early resistor of the BJT. Recall: r o = V A /I C, where V A is typically about 100V. A very rough approx. is r o =. 26
27 Initial small-signal model for BJT MUST REMEMBER Small-signal BJT parameters: v BE B r π g m v BE C r o v CE E BJT model 27
28 Initial small-signal model for FET Similar to BJT, but input resistance is. v GS G g m v GS S D r o v DS Small-signal FET parameters: FET model All amplifier configurations using BJT can be likewise constructed using FET. 28
29 Example: common-emitter amplifier Assume the coupling caps are large enough to be considered as short-circuit at signal frequency V CC B V CC is ac 0V. C R B1 R B2 v BE R B1 R B1 r π E g m v BE r o E 29
30 Complete model for common-emitter amplifier Complete model: R B1 R B1 v BE r π r o g m v BE Total input resistance R in = R B1 R B1 r π Simplified model: Total output resistance R o = r o R B1 R B1 r π v BE g m v BE r o Voltage gain 30
31 Alternative model for common-emitter amplifier Output in Thévenin form: r o Total input resistance R B1 R B1 r π v BE R in = R B1 R B1 r π Total output resistance g m ( r o ) v BE R o = r o Voltage gain 31
32 More about common-emitter amplifier Because the output resistance is quite large (equal to r o ), the common-emitter amplifier is a POOR voltage driver. That means, it is not a good idea to use such an amplifier for loads which are smaller than. This makes it not suitable to deliver current to load. 1kΩ, for example R B1 R B1 r π v BE r o practically no output!! 10Ω g m ( r o ) v BE 32
33 Bad idea wrong use of common-emitter amplifier 10V Transconductance g m = I C /(25mV) = 5/25 = 0.2 A/V R B1 5mA 1kΩ Expected gain = g m = (0.2)(1k) = 200 or 46dB But the output circuit is: R B2 v BE speaker 10Ω 200 1kΩ 10Ω The effective gain drops to 33
34 Proper use of common-emitter amplifier 10V The load must be much larger than. R B1 5mA 1kΩ Now the output circuit is: R B2 v BE nearly open circuit 10MΩ 200 1kΩ 10MΩ The effective gain is 34
35 How can we use the amplifier in practice? 10V How to connect the output to load? R B1 5mA 1kΩ? R B2 v BE speaker 10Ω 35
36 Emitter follower R B1 R B2 10V I C biased to 10mA V CE biased to 5V R E Biasing conditions: Base voltage 5.6V Emitter voltage 5V Collector current 10mA R E = 500Ω R B1 :R B2 44:56 Say, R B1 = 440kΩ R B2 = 560kΩ V E = V B 0.6 Thus, for small signal, V E = V B or = Gain = / = 1 36
37 Small-signal model of emitter follower 10V B C R B1 R B2 R E R B1 R B2 r π E R E g m v BE r o E 37
38 Small-signal model of emitter follower i B B C Input resistance is r r π g m v BE R B1 R B2 E E r o R E which is quite large (good)!! 38
39 Small-signal model of emitter follower B C Output resistance is r π g m v BE r o i m E E R E r out v m which is quite small (good)!! 39
40 Small-signal model of emitter follower Thevenin form: very large R E (1/g m ) very small r π (1β)R E 1 Large input resistance Small output resistance Voltage gain = 1 Draw no current from previous stage Good for any load 40
41 A better emitter follower 10V Input resistance is very LARGE because R E =. R B1 Output resistance is 1/g m. R B2 I E 1/g m Gain = 1. This circuit is also called CLASS A output stage. Details to be studied in second year EC2. 41
42 Common-emitter amplifier with emitter follower as buffer 10V R B1 emitter follower (unit gain) R B2 v BE common-emitter amplifier (high gain) I E 1 g m speaker 10Ω 42
43 FET amplifiers (similar to BJT amplifiers) 10V R G1 source follower (unit gain) R G2 v GS common-source amplifier (high gain = g m ) I S 1 g m speaker 10Ω 43
44 Further thoughts Will the biasing resistors affect the gain? Seems not, because R bias Gain = g m which does not depend on R bias. However, a realistic voltage source has finite internal resistance. This will affect the gain. 44
45 Input source with finite resistance The input has a voltage divider network. R bias R s Therefore, the gain decreases to assuming r o very large. R s R bias v BE r π g m v BE r o 45
46 Example 10V 94kΩ 5mA 1kΩ By how much does the gain drop? 50Ω 50Ω 600Ω R bias v BE 94k 600 = 596Ω r π g m = 5mA/25mV = 0.2A/V r π = β/g m = 100/0.2 = 500Ω Voltage divider attenuation = Hence, the gain is reduced to 0.845(g m ) =
47 Further thoughts Recall that the best biasing scheme should be β independent. 10V 84kΩ 16kΩ 5mA 1kΩ 200Ω One good scheme is emitter degeneration, i.e., using R E to fix biasing current directly. Here, since V B is about 1.6V, as fixed by the base resistor divider, V E is about 1V. Therefore, I C V E /R E = 5mA (no β needed!) Question: Will this biasing scheme affect the gain? 47
48 Common-emitter amplifier with emitter degeneration V CC R B1 Exercise: Find the small-signal gain of this amplifier. Answer: R B2 R E The gain is MUCH smaller. We have a good biasing, but a poor gain! Can we improve the gain? 48
49 Common-emitter amplifier with emitter by-pass V CC Add C E such that the effective emitter resistance becomes zero at signal frequency. R B1 R B2 R E C E So, this circuit has good biasing, and the gain is still very high! Gain = g m which is unaffected by R E because effectively R E is shorted at signal frequency. C E is called bypass capacitor. 49
50 Summary Basic BJT model (small-signal ac model): B C v BE r π g m v BE r o E E 50
51 Summary Basic FET model (small-signal ac model): Similar to the BJT model, but with infinite input resistance. Therefore, the FET can be used in the same way as amplifiers. G S v GS g m v GS r o D S 51
52 Summary Common-emitter (CE) amplifier small-signal ac model: R bias R bias v BE r π g m v BE r o Gain = g m Input resistance = R bias r π (quite large desirable) Output resistance = r o (large undesirable) 52
53 Summary Emitter follower (EF) small-signal ac model: R bias R E v BE r π g m v BE R bias R E Gain = 1 Input resistance = R bias [r π (1β)R E ] Output resistance = R E (1/g m ) (quite large desirable) (small desirable) 53
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier
 Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Common Base BJT Amplifier Common Collector BJT Amplifier Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Configuration Common Base Configuration Small Signal Analysis Design Example Amplifier Input and Output Impedances
Common-Emitter Amplifier
 Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Common-Emitter Amplifier A. Before We Start As the title of this lab says, this lab is about designing a Common-Emitter Amplifier, and this in this stage of the lab course is premature, in my opinion,
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
BJT AC Analysis. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Oct. 20, 2001, rev Aug. 31, 2008 Introduction This note will discuss AC analysis using the beta, re transistor model shown in Figure 1 for the three types of amplifiers: common-emitter,
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers
 BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
BJT Characteristics and Amplifiers Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2002 Lab Section 003 April 2, 2006 Abstract As a basic component in amplifier design, the properties of the Bipolar Junction Transistor
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
The 2N3393 Bipolar Junction Transistor Common-Emitter Amplifier Aaron Prust Abstract The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a non-linear electronic device which can be used for amplification and switching.
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Bipolar Junction Transistors
 Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Bipolar Junction Transistors Physical Structure & Symbols NPN Emitter (E) n-type Emitter region p-type Base region n-type Collector region Collector (C) B C Emitter-base junction (EBJ) Base (B) (a) Collector-base
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design
 Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Common Emitter BJT Amplifier Design Current Mirror Design 1 Some Random Observations Conditions for stabilized voltage source biasing Emitter resistance, R E, is needed. Base voltage source will have finite
Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 2005 Bipolar Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to construct a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must
Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems This document contains
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
LAB VII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW You need to first identify the physical
Transistors. NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
 Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
Transistors They are unidirectional current carrying devices with capability to control the current flowing through them The switch current can be controlled by either current or voltage ipolar Junction
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
Voltage Divider Bias
 Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
Voltage Divider Bias ENGI 242 ELEC 222 BJT Biasing 3 For the Voltage Divider Bias Configurations Draw Equivalent Input circuit Draw Equivalent Output circuit Write necessary KVL and KCL Equations Determine
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
LAB VIII. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab, you will study the DC characteristics of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). 2. OVERVIEW In this lab, you will inspect the
BJT Amplifier Circuits
 JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
JT Amplifier ircuits As we have developed different models for D signals (simple large-signal model) and A signals (small-signal model), analysis of JT circuits follows these steps: D biasing analysis:
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 2
 Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
Small Signal Analysis of a PMOS transistor Consider the following PMOS transistor to be in saturation. Then, 1 I SD = µ pcox( VSG Vtp)^2(1 + VSDλ) 2 From this equation it is evident that I SD is a function
MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP
 MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP Op-Amp Circuits: Bias, in an electronic circuit, describes the steady state operating characteristics with no signal being applied. In an op-amp circuit, the operating characteristic
MAS.836 HOW TO BIAS AN OP-AMP Op-Amp Circuits: Bias, in an electronic circuit, describes the steady state operating characteristics with no signal being applied. In an op-amp circuit, the operating characteristic
Objectives The purpose of this lab is build and analyze Differential amplifiers based on NPN transistors (or NMOS transistors).
 1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
1 Lab 03: Differential Amplifiers (BJT) (20 points) NOTE: 1) Please use the basic current mirror from Lab01 for the second part of the lab (Fig. 3). 2) You can use the same chip as the basic current mirror;
VI. Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads.
 Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION
 11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION The properties of an amplifying circuit using an op-amp depend primarily on the characteristics of the feedback network rather than on those of the op-amp itself. A
11: AUDIO AMPLIFIER I. INTRODUCTION The properties of an amplifying circuit using an op-amp depend primarily on the characteristics of the feedback network rather than on those of the op-amp itself. A
Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers. EE 3120 Microelectronics II
 1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FT are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly. Then, similar FT
LM 358 Op Amp. If you have small signals and need a more useful reading we could amplify it using the op amp, this is commonly used in sensors.
 LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38. The r e Transistor model. Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE
 BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38 The r e Transistor model Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE BJT AC Analysis 2 of 38 Three amplifier configurations, Common Emitter Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Common Base BJT
BJT AC Analysis 1 of 38 The r e Transistor model Remind Q-poiint re = 26mv/IE BJT AC Analysis 2 of 38 Three amplifier configurations, Common Emitter Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Common Base BJT
Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720. Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment.
 Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720 Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment. This assignment will take you through the simulation and basic characterization of a simple operational
Op-Amp Simulation EE/CS 5720/6720 Read Chapter 5 in Johns & Martin before you begin this assignment. This assignment will take you through the simulation and basic characterization of a simple operational
Figure 1: Common-base amplifier.
 The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
The Common-Base Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of a single stage common-base amplifier. The object is to solve for the small-signal voltage gain, input resistance, and output
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier
 Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
Chapter 12: The Operational Amplifier 12.1: Introduction to Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are very high gain dc coupled amplifiers with differential inputs; they are used
Field Effect Transistors and Noise
 Physics 3330 Experiment #8 Fall 2005 Field Effect Transistors and Noise Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors. We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct
Physics 3330 Experiment #8 Fall 2005 Field Effect Transistors and Noise Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors. We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
LABORATORY 2 THE DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how to amplify weak (small) signals in the presence of noise. 1. To understand how a differential amplifier rejects noise and common
COMMON-SOURCE JFET AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT 04 Objectives: Theory: 1. To evaluate the common-source amplifier using the small signal equivalent model. 2. To learn what effects the voltage gain. A self-biased n-channel JFET with an AC
EXPERIMENT 04 Objectives: Theory: 1. To evaluate the common-source amplifier using the small signal equivalent model. 2. To learn what effects the voltage gain. A self-biased n-channel JFET with an AC
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-2 Transistor
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
CHAPTER 10 OPERATIONAL-AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS Chapter Outline 10.1 The Two-Stage CMOS Op Amp 10.2 The Folded-Cascode CMOS Op Amp 10.3 The 741 Op-Amp Circuit 10.4 DC Analysis of the 741 10.5 Small-Signal Analysis
Objective. To design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors.
 ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
ascode Amplifier Design. Objective. o design and simulate a cascode amplifier circuit using bipolar transistors. Assignment description he cascode amplifier utilises the advantage of the common-emitter
Transistor Biasing. The basic function of transistor is to do amplification. Principles of Electronics
 192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
192 9 Principles of Electronics Transistor Biasing 91 Faithful Amplification 92 Transistor Biasing 93 Inherent Variations of Transistor Parameters 94 Stabilisation 95 Essentials of a Transistor Biasing
Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW 6.1 THE MOSFET AMPLIFIER
 C H A P T E R 6 Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits containing these
C H A P T E R 6 Basic FET Ampli ers 6.0 PREVIEW In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits containing these
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
W04 Transistors and Applications. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç Gören
 W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
W04 Transistors and Applications W04 Transistors and Applications ELK 2018 - Contents W01 Basic Concepts in Electronics W02 AC to DC Conversion W03 Analysis of DC Circuits (self and condenser) W04 Transistors
Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers
 Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers The operational amplifier, or op-amp, is a basic building block of modern electronics. Op-amps date back to the early days of vacuum tubes, but they only became common
Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers The operational amplifier, or op-amp, is a basic building block of modern electronics. Op-amps date back to the early days of vacuum tubes, but they only became common
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits LTSpice LTSpice is a free circuit simulator based on Berkeley
Differential Amplifier Offset. Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset R C
 ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
ESE39 ntroduction to Microelectronics Differential Amplifier Offset Causes of dc voltage and current offset Modeling dc offset mismatch S mismatch β mismatch transistor mismatch dc offsets in differential
Electronics. Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit. LD Physics Leaflets P4.2.1.1
 Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
Electronics Operational Amplifier Internal design of an operational amplifier LD Physics Leaflets Discrete assembly of an operational amplifier as a transistor circuit P4.2.1.1 Objects of the experiment
CIRCUITS LABORATORY. In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low
 CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT 6 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS 6.1 ABSTRACT In this experiment, the output I-V characteristic curves, the small-signal low frequency equivalent circuit parameters, and the
Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
The basic cascode amplifier consists of an input common-emitter (CE) configuration driving an output common-base (CB), as shown above.
 Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Cascode Amplifiers by Dennis L. Feucht Two-transistor combinations, such as the Darlington configuration, provide advantages over single-transistor amplifier stages. Another two-transistor combination
Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]
![Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57] Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]](/thumbs/40/21338705.jpg) Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
g fs R D A V D g os g os
 AN12 JFET Biasing Techniques Introduction Engineers who are not familiar with proper biasing methods often design FET amplifiers that are unnecessarily sensitive to device characteristics. One way to obtain
AN12 JFET Biasing Techniques Introduction Engineers who are not familiar with proper biasing methods often design FET amplifiers that are unnecessarily sensitive to device characteristics. One way to obtain
Amplifier Teaching Aid
 Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
Amplifier Teaching Aid Table of Contents Amplifier Teaching Aid...1 Preface...1 Introduction...1 Lesson 1 Semiconductor Review...2 Lesson Plan...2 Worksheet No. 1...7 Experiment No. 1...7 Lesson 2 Bipolar
3.4 - BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
 BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
BJT Differential Amplifiers (6/4/00) Page 1 3.4 BJT DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Define and characterize the differential amplifier.) Show the
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 INTRODUCTION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS The student will be introduced to the application and analysis of operational amplifiers in this laboratory experiment. The student will apply circuit analysis techniques
INTRODUCTION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS The student will be introduced to the application and analysis of operational amplifiers in this laboratory experiment. The student will apply circuit analysis techniques
Bipolar Junction Transistor Basics
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 29, 2001, rev 1 Introduction A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three layer semiconductor device with either NPN or PNP construction. Both constructions have the identical
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin
 TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin (Updated 7/19/08 to delete sine wave output) I constructed the 1 MHz square wave generator shown in the Appendix. This
TESTS OF 1 MHZ SIGNAL SOURCE FOR SPECTRUM ANALYZER CALIBRATION 7/8/08 Sam Wetterlin (Updated 7/19/08 to delete sine wave output) I constructed the 1 MHz square wave generator shown in the Appendix. This
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS
 LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
LAB 7 MOSFET CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS Objective In this experiment you will study the i-v characteristics of an MOS transistor. You will use the MOSFET as a variable resistor and as a switch. BACKGROUND
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
CHAPTER 3 BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS A bipolar junction transistor, BJT, is a single piece of silicon with two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back
Notes about Small Signal Model. for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits
 Notes about Small Signal Model for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits 1. Model the MOSFET Transistor For a MOSFET transistor, there are NMOS and PMOS. The examples shown here would be for NMOS. Figure
Notes about Small Signal Model for EE 40 Intro to Microelectronic Circuits 1. Model the MOSFET Transistor For a MOSFET transistor, there are NMOS and PMOS. The examples shown here would be for NMOS. Figure
Lecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Lecture 22: Class C Power Amplifiers
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Class B Amplifier (Push-Pull Emitter Follower) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
CHAPTER 2 POWER AMPLIFIER
 CHATER 2 OWER AMLFER 2.0 ntroduction The main characteristics of an amplifier are Linearity, efficiency, output power, and signal gain. n general, there is a trade off between these characteristics. For
CHATER 2 OWER AMLFER 2.0 ntroduction The main characteristics of an amplifier are Linearity, efficiency, output power, and signal gain. n general, there is a trade off between these characteristics. For
Lecture 39: Intro to Differential Amplifiers. Context
 Lecture 39: Intro to Differential Amplifiers Prof J. S. Smith Context Next week is the last week of lecture, and we will spend those three lectures reiewing the material of the course, and looking at applications
Lecture 39: Intro to Differential Amplifiers Prof J. S. Smith Context Next week is the last week of lecture, and we will spend those three lectures reiewing the material of the course, and looking at applications
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies
 Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Operational Amplifier - IC 741
 Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
Operational Amplifier - IC 741 Tabish December 2005 Aim: To study the working of an 741 operational amplifier by conducting the following experiments: (a) Input bias current measurement (b) Input offset
http://users.ece.gatech.edu/~mleach/ece3050/notes/feedback/fbexamples.pdf
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Feedback Amplifiers CollectionofSolvedProblems A collection of solved
Cancellation of Load-Regulation in Low Drop-Out Regulators
 Cancellation of Load-Regulation in Low Drop-Out Regulators Rajeev K. Dokania, Student Member, IEE and Gabriel A. Rincόn-Mora, Senior Member, IEEE Georgia Tech Analog Consortium Georgia Institute of Technology
Cancellation of Load-Regulation in Low Drop-Out Regulators Rajeev K. Dokania, Student Member, IEE and Gabriel A. Rincόn-Mora, Senior Member, IEEE Georgia Tech Analog Consortium Georgia Institute of Technology
Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2010, 2011 and 2012
 1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
1 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding of proper
Use and Application of Output Limiting Amplifiers (HFA1115, HFA1130, HFA1135)
 Use and Application of Output Limiting Amplifiers (HFA111, HFA110, HFA11) Application Note November 1996 AN96 Introduction Amplifiers with internal voltage clamps, also known as limiting amplifiers, have
Use and Application of Output Limiting Amplifiers (HFA111, HFA110, HFA11) Application Note November 1996 AN96 Introduction Amplifiers with internal voltage clamps, also known as limiting amplifiers, have
EE 330 Lecture 21. Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifier
 EE 330 Lecture 21 Small Signal Analsis Small Signal Analsis of BJT Amplifier Review from Last Lecture Comparison of Gains for MOSFET and BJT Circuits IN (t) A B BJT CC 1 R EE OUT I R C 1 t If I D R =I
EE 330 Lecture 21 Small Signal Analsis Small Signal Analsis of BJT Amplifier Review from Last Lecture Comparison of Gains for MOSFET and BJT Circuits IN (t) A B BJT CC 1 R EE OUT I R C 1 t If I D R =I
Scaling and Biasing Analog Signals
 Scaling and Biasing Analog Signals November 2007 Introduction Scaling and biasing the range and offset of analog signals is a useful skill for working with a variety of electronics. Not only can it interface
Scaling and Biasing Analog Signals November 2007 Introduction Scaling and biasing the range and offset of analog signals is a useful skill for working with a variety of electronics. Not only can it interface
Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers
 Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers By: Gary A. Ybarra Christopher E. Cramer Duke University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Durham, NC. Purpose The purpose of this lab is to examine the properties
Lab 5 Operational Amplifiers By: Gary A. Ybarra Christopher E. Cramer Duke University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Durham, NC. Purpose The purpose of this lab is to examine the properties
Diodes and Transistors
 Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
Diodes What do we use diodes for? Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double input voltage)
How To Calculate The Power Gain Of An Opamp
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 8 p. 1/23 EE 42/100 Lecture 8: Op-Amps ELECTRONICS Rev C 2/8/2012 (9:54 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 8 p. 1/23 EE 42/100 Lecture 8: Op-Amps ELECTRONICS Rev C 2/8/2012 (9:54 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley
BJT Circuit Configurations
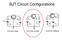 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
Lab 1: DC Circuits. Student 1, student1@ufl.edu Partner : Student 2, student2@ufl.edu
 Lab Date Lab 1: DC Circuits Student 1, student1@ufl.edu Partner : Student 2, student2@ufl.edu I. Introduction The purpose of this lab is to allow the students to become comfortable with the use of lab
Lab Date Lab 1: DC Circuits Student 1, student1@ufl.edu Partner : Student 2, student2@ufl.edu I. Introduction The purpose of this lab is to allow the students to become comfortable with the use of lab
Field Effect Transistors
 506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
506 19 Principles of Electronics Field Effect Transistors 191 Types of Field Effect Transistors 193 Principle and Working of JFET 195 Importance of JFET 197 JFET as an Amplifier 199 Salient Features of
Measurement of Capacitance
 Measurement of Capacitance Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor:. A capacitor is used to store. 2. What is the SI unit for capacitance? 3. A capacitor basically consists of two
Measurement of Capacitance Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor:. A capacitor is used to store. 2. What is the SI unit for capacitance? 3. A capacitor basically consists of two
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices
 Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
Theory of Transistors and Other Semiconductor Devices 1. SEMICONDUCTORS 1.1. Metals and insulators 1.1.1. Conduction in metals Metals are filled with electrons. Many of these, typically one or two per
Analog Signal Conditioning
 Analog Signal Conditioning Analog and Digital Electronics Electronics Digital Electronics Analog Electronics 2 Analog Electronics Analog Electronics Operational Amplifiers Transistors TRIAC 741 LF351 TL084
Analog Signal Conditioning Analog and Digital Electronics Electronics Digital Electronics Analog Electronics 2 Analog Electronics Analog Electronics Operational Amplifiers Transistors TRIAC 741 LF351 TL084
Equivalent Circuit. Operating Characteristics at Ta = 25 C, V CC = ±34V, R L = 8Ω, VG = 40dB, Rg = 600Ω, R L : non-inductive load STK4181V
 Ordering number: 2137B Thick Film Hybrid IC STK4181V AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply) (45W + 45W min, THD = 0.08%) Features Pin-compatible with the STK4102II series. The STK4101V series use the
Ordering number: 2137B Thick Film Hybrid IC STK4181V AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply) (45W + 45W min, THD = 0.08%) Features Pin-compatible with the STK4102II series. The STK4101V series use the
The BJT Differential Amplifier. Basic Circuit. DC Solution
 c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I
 Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
Lab 7: Operational Amplifiers Part I Objectives The objective of this lab is to study operational amplifier (op amp) and its applications. We will be simulating and building some basic op amp circuits,
2 Port Parameters I 1. ECE145A/218A Notes Set #4 1. Two-ways of describing device: A. Equivalent - Circuit-Model
 ECE45A/8A Notes et #4 Port Parameters Two-ways of describing device: A. Equivalent - Circuit-Model Physically based Includes bias dependence Includes frequency dependence Includes size dependence - scalability
ECE45A/8A Notes et #4 Port Parameters Two-ways of describing device: A. Equivalent - Circuit-Model Physically based Includes bias dependence Includes frequency dependence Includes size dependence - scalability
Power Amplifiers. Introduction to Power Amplifiers. Amplifiers. Module 5
 Module 5 Amplifiers Introduction to What you ll learn in Module 5. Section 5.0 Introduction to. Understand the Operation of. Section 5.1 Power Transistors & Heat Sinks. Power Transistor Construction. Power
Module 5 Amplifiers Introduction to What you ll learn in Module 5. Section 5.0 Introduction to. Understand the Operation of. Section 5.1 Power Transistors & Heat Sinks. Power Transistor Construction. Power
= V peak 2 = 0.707V peak
 BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
AN105. Introduction: The Nature of VCRs. Resistance Properties of FETs
 Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
Introduction: The Nature of s A voltage-controlled resistor () may be defined as a three-terminal variable resistor where the resistance value between two of the terminals is controlled by a voltage potential
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Fundamentals of Microelectronics H1 Why Microelectronics? H2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors H3 Diode ircuits H4 Physics of Bipolar ransistors H5 Bipolar Amplifiers H6 Physics of MOS ransistors H7 MOS
Transistor Models. ampel
 Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Transistor Models Review of Transistor Fundamentals Simple Current Amplifier Model Transistor Switch Example Common Emitter Amplifier Example Transistor as a Transductance Device - Ebers-Moll Model Other
Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers
 Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing: Creating the circuit to establish the desired DC oltages and currents for the operation of the amplifier Four common ways:. Biasing by fixing GS. Biasing by fixing
Biasing in MOSFET Amplifiers Biasing: Creating the circuit to establish the desired DC oltages and currents for the operation of the amplifier Four common ways:. Biasing by fixing GS. Biasing by fixing
EGR 278 Digital Logic Lab File: N278L3A Lab # 3 Open-Collector and Driver Gates
 EGR 278 Digital Logic Lab File: N278L3A Lab # 3 Open-Collector and Driver Gates A. Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to investigate: the operation of open-collector gates, including the
EGR 278 Digital Logic Lab File: N278L3A Lab # 3 Open-Collector and Driver Gates A. Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to investigate: the operation of open-collector gates, including the
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
LM1036 Dual DC Operated Tone/Volume/Balance Circuit
 LM1036 Dual DC Operated Tone/Volume/Balance Circuit General Description The LM1036 is a DC controlled tone (bass/treble), volume and balance circuit for stereo applications in car radio, TV and audio systems.
LM1036 Dual DC Operated Tone/Volume/Balance Circuit General Description The LM1036 is a DC controlled tone (bass/treble), volume and balance circuit for stereo applications in car radio, TV and audio systems.
PLL frequency synthesizer
 ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 Lab 4: PLL frequency synthesizer 1.1 Goal The goals of this lab exercise are: - Verify the behavior of a and of a complete PLL - Find capture
ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 Lab 4: PLL frequency synthesizer 1.1 Goal The goals of this lab exercise are: - Verify the behavior of a and of a complete PLL - Find capture
Operational Amplifiers
 Module 6 Amplifiers Operational Amplifiers The Ideal Amplifier What you ll learn in Module 6. Section 6.0. Introduction to Operational Amplifiers. Understand Concept of the Ideal Amplifier and the Need
Module 6 Amplifiers Operational Amplifiers The Ideal Amplifier What you ll learn in Module 6. Section 6.0. Introduction to Operational Amplifiers. Understand Concept of the Ideal Amplifier and the Need
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS IN ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
1. The early effect in a bipolar junction transistor is caused by (a) fast turn-on (c) large collector-base reverse bias (b)fast turn-off (d) large emitter-base forward bias 2. MOSFET can be used as a
