Lab 7: VHDL 16-Bit Shifter
|
|
|
- Rolf Conley
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 7: VHDL 16-Bit Shifter Objectives : Design a 16-bit shifter which need implement eight shift operations: logic shift right, logic shift left, arithmetic shift right, arithmetic shift left, rotate right, rotate left rotate left with carry, rotate left with carry. 16-Bit Shifter specification: 16 4 S A C H To C 16 Figure 1. Symbol Figure 2. Logic diagram 1
2 S 1 S 0 Shift Operation 0 0 Logic Shift 0 1 Arithmetic shift 1 0 Rotate 1 1 Rotate with carry S 3 S 2 Shift direction 0 0 Parallel Load 0 1 Shift Right with I L 1 0 Shift Left with I R 1 1 No Change In the above logic diagram, for the unit 16-bit basic shifter design you may refer to the available code for the Universal Shift Register with parallel load(three different style codes are given). Universal Shifter Register with parallel Load Figure 3. Universal Shift Register Symbol S 1 S 0 Next State after Description rising_edge of clk 0 0 Q[3..0] <=Q[3..0] No Change 0 1 Q[3..0] <=I[3..0] Parallel Load 1 0 Q[3..1]<=Q[2..0], Q[0]<=I R Shift Left with I R 1 1 Q[3]<=I L, Q[2..0]<=Q[3..1] Shift Right with I L 1. Universal shift register using array slicing and concatenation method. LISTING 1: Save as Filename= univ_shiftreg1.vhd USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL; USE IEEE.NUMERIC_BIT.ALL; 2
3 ENTITY univ_shiftreg1 IS PORT(clk, il, ir : IN BIT; s: IN BIT_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0); i : IN BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0); q : OUT BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0)); END univ_shiftreg1; ARCHITECTURE beh1 OF univ_shiftreg1 IS SIGNAL qtmp : BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0); PROCESS(clk) IF (clk = '1' AND clk'event) THEN CASE s IS WHEN "00" => qtmp <= qtmp; WHEN "01" => qtmp <= i; WHEN "10" => qtmp<=qtmp(2 DOWNTO 0) & ir; WHEN "11" => qtmp<=il & qtmp(3 DOWNTO 1); WHEN OTHERS => NULL; END CASE; END IF; END PROCESS; q <= qtmp; END beh1; 2. Universal shift register using shifting operators: sll, srl. LISTING 2: Save as Filename= univ_shiftreg2.vhd library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.numeric_bit.all; entity univ_shiftreg2 is port(clk,il,ir :in bit; s :in bit_vector(1 downto 0); i : in bit_vector(3 downto 0); q : out bit_vector(3 downto 0)); end univ_shiftreg2; architecture beh2 of univ_shiftreg2 is signal qtmp: bit_vector(5 downto 0); begin process(clk) begin if (clk = '1' and clk'event) then case s is when "00" => qtmp <= qtmp; 3
4 end beh2; when others => null; end case; end if; end process; q<=qtmp(4 downto 1); when "01" => qtmp <=il&i&ir; when "10" => qtmp <= (il&qtmp(4 downto 1)&ir) sll 1; when "11" => qtmp<= (il&qtmp(4 downto 1)&ir) srl 1 ; 3. Universal shift register using structural modelling. Figure 4. Universal Shift Register Implementation. MUX_sel NEXT STATE after rising_edge of clk S1S0 Q3 Q2 Q1 Q0 Operation 00 Q3 Q2 Q1 Q0 No Change 01 I3 I2 I1 I0 Parallel Load 10 Q2 Q1 Q0 IR Shift left 11 IL Q3 Q2 Q1 Shift right Write a vhdl code to model (entity and architecture) a four to one multiplexer called MUX41. LISTING 3: Save as Filename= univ_shiftreg3.vhd ENTITY MUX41 IS PORT (i3, i2, i1, i0 : IN BIT; 4
5 s: IN BIT_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0); o: OUT BIT); END MUX41; ARCHITECTURE arch_mux41 OF MUX41 IS PROCESS(i3, i2, i1, i0, s) CASE s IS WHEN "00" => o <= i0; WHEN "01" => o <= i1; WHEN "10" => o <= i2; WHEN "11" => o <= i3; WHEN OTHERS => NULL; END CASE; END PROCESS; END arch_mux41 Write a vhdl code to model (entity and architecture) d flip-flop called DFF. ENTITY DFF IS PORT(d, clk : IN BIT; q, qb : OUT BIT); END DFF; ARCHITECTURE arch_dff OF DFF IS PROCESS(clk) VARIABLE q_temp : BIT; IF(clk'EVENT AND clk='1')then q_temp := d; END IF; q <= q_temp; qb <= NOT q_temp; END PROCESS; END arch_dff; Using DFF and MUX41 components, generates the structural model of the univ_shiftreg. That is, show the port map for each of the components shown in Fig 2. ENTITY univ_shiftreg3 IS PORT(clk, il, ir : IN BIT; s: IN BIT_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0); i : IN BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0); q : OUT BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0)); END univ_shiftreg3; ARCHITECTURE struct OF univ_shiftreg3 IS COMPONENT MUX41 PORT (i3, i2, i1, i0 : IN BIT; s: IN BIT_VECTOR(1 DOWNTO 0); o: OUT BIT); END COMPONENT; COMPONENT DFF PORT(d, clk : IN BIT; 5
6 q, qb : OUT BIT); END COMPONENT; FOR U1, U2, U3, U4: MUX41 USE ENTITY WORK.MUX41(arch_mux41); FOR U5, U6, U7, U8: DFF USE ENTITY WORK.DFF(arch_dff); SIGNAL o: BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0); SIGNAL qb: BIT_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0); SIGNAL qt:bit_vector(3 DOWNTO 0); U1:MUX41 PORT MAP(il,qt(2), i(3), qt(3), s, o(3)); U2:MUX41 PORT MAP(qt(3), qt(1), i(2), qt(2), s, o(2)); U3:MUX41 PORT MAP(qt(2), qt(0), i(1), qt(1), s, o(1)); U4:MUX41 PORT MAP(qt(1), ir, i(0), qt(0), s, o(0)); U5:DFF PORT MAP(o(3), clk, qt(3), qb(3)); U6:DFF PORT MAP(o(2), clk, qt(2), qb(2)); U7:DFF PORT MAP(o(1), clk, qt(1), qb(1)); U8:DFF PORT MAP(o(0), clk, qt(0), qb(0)); q <= qt; END struct; Combinatorial Implementation of Basic 4-bit Shifter* A combinatorial implementation of basic 4 bit shifter is given in Fig 5. Please expand it to 16 bit shifter and use it in the implementation of Figure 2 instead of universal shift register. (S is 2 bit selection signal, S= S 1 S 0 ) Figure 5. 4 bit shifter *NOTE: This is 4-bit shifter implementation to be used in the project 6
Digital Design with VHDL
 Digital Design with VHDL CSE 560M Lecture 5 Shakir James Shakir James 1 Plan for Today Announcement Commentary due Wednesday HW1 assigned today. Begin immediately! Questions VHDL help session Assignment
Digital Design with VHDL CSE 560M Lecture 5 Shakir James Shakir James 1 Plan for Today Announcement Commentary due Wednesday HW1 assigned today. Begin immediately! Questions VHDL help session Assignment
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z <= A; else Z <= B; end if; end process;
 if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
12. A B C A B C A B C 1 A B C A B C A B C JK-FF NETr
 2..,.,.. Flip-Flops :, Flip-Flops, Flip Flop. ( MOD)... -8 8, 7 ( ).. n Flip-Flops. n Flip-Flops : 2 n. 2 n, Modulo. (-5) -4 ( -), (-) - ( -).. / A A A 2 3 4 5 MOD-5 6 MOD-6 7 MOD-7 8 9 / A A A 2 3 4 5
2..,.,.. Flip-Flops :, Flip-Flops, Flip Flop. ( MOD)... -8 8, 7 ( ).. n Flip-Flops. n Flip-Flops : 2 n. 2 n, Modulo. (-5) -4 ( -), (-) - ( -).. / A A A 2 3 4 5 MOD-5 6 MOD-6 7 MOD-7 8 9 / A A A 2 3 4 5
Lenguaje VHDL. Diseño de sistemas digitales secuenciales
 Lenguaje VHDL Diseño de sistemas digitales secuenciales Flip-Flop D 1 entity d_ff is clk: in std_logic; d: in std_logic; q: out std_logic 2 end d_ff; P3 P1 5 Q D Q Q(t+1) 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 architecture
Lenguaje VHDL Diseño de sistemas digitales secuenciales Flip-Flop D 1 entity d_ff is clk: in std_logic; d: in std_logic; q: out std_logic 2 end d_ff; P3 P1 5 Q D Q Q(t+1) 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 architecture
ECE 3401 Lecture 7. Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design
 ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
VGA video signal generation
 A VGA display controller VGA video signal generation A VGA video signal contains 5 active signals: horizontal sync: digital signal, used for synchronisation of the video vertical sync: digital signal,
A VGA display controller VGA video signal generation A VGA video signal contains 5 active signals: horizontal sync: digital signal, used for synchronisation of the video vertical sync: digital signal,
Let s put together a Manual Processor
 Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
LAB #3 VHDL RECOGNITION AND GAL IC PROGRAMMING USING ALL-11 UNIVERSAL PROGRAMMER
 LAB #3 VHDL RECOGNITION AND GAL IC PROGRAMMING USING ALL-11 UNIVERSAL PROGRAMMER OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the basic elements of VHDL that are implemented in Warp. 2. Build a simple application using VHDL and
LAB #3 VHDL RECOGNITION AND GAL IC PROGRAMMING USING ALL-11 UNIVERSAL PROGRAMMER OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the basic elements of VHDL that are implemented in Warp. 2. Build a simple application using VHDL and
VHDL programmering H2
 VHDL programmering H2 VHDL (Very high speed Integrated circuits) Hardware Description Language IEEE standard 1076-1993 Den benytter vi!! Hvornår blev den frigivet som standard første gang?? Ca. 1980!!
VHDL programmering H2 VHDL (Very high speed Integrated circuits) Hardware Description Language IEEE standard 1076-1993 Den benytter vi!! Hvornår blev den frigivet som standard første gang?? Ca. 1980!!
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits
 Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
Digital Logic Design Sequential circuits Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Rania.Swief E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Eng. Ahmed H. Madian Registers An n-bit register
! " # # $ '"() * #! +, # / $0123$
 ! " # # $ ##% "& & $# '"() * # +,(- *,. & #! +, # ( / $0123$ ( 1 - $# #4+,ENTITY4 ' 4 ) '! )( 5, # - 5 $ Contador_1s D #+ 6 CNT #+ 7( D 3 Contador_1s 2 Cnt ENTITY Contador_1s IS PORT ( D: IN BIT_VECTOR(2
! " # # $ ##% "& & $# '"() * # +,(- *,. & #! +, # ( / $0123$ ( 1 - $# #4+,ENTITY4 ' 4 ) '! )( 5, # - 5 $ Contador_1s D #+ 6 CNT #+ 7( D 3 Contador_1s 2 Cnt ENTITY Contador_1s IS PORT ( D: IN BIT_VECTOR(2
CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE. Ioan Lemeni
 CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE Ioan Lemeni Computer and Communication Engineering Department Faculty of Automation, Computers and Electronics University of Craiova 13, A.I. Cuza, Craiova,
CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE Ioan Lemeni Computer and Communication Engineering Department Faculty of Automation, Computers and Electronics University of Craiova 13, A.I. Cuza, Craiova,
Step : Create Dependency Graph for Data Path Step b: 8-way Addition? So, the data operations are: 8 multiplications one 8-way addition Balanced binary
 RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4
 An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4 Dave Galloway Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto March 2005 Introduction This document describes a simple
An Example VHDL Application for the TM-4 Dave Galloway Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto March 2005 Introduction This document describes a simple
Digital Systems Design. VGA Video Display Generation
 Digital Systems Design Video Signal Generation for the Altera DE Board Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 12-1 VGA Video Display Generation A VGA signal contains 5 active signals Two TTL compatible signals for
Digital Systems Design Video Signal Generation for the Altera DE Board Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 12-1 VGA Video Display Generation A VGA signal contains 5 active signals Two TTL compatible signals for
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
5 Combinatorial Components. 5.0 Full adder. Full subtractor
 5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS
 VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
Sprites in Block ROM
 Sprites in Block ROM 1 Example 37 Sprites in Block ROM In Example 36 we made a sprite by storing the bit map of three initials in a VHDL ROM. To make a larger sprite we could use the Core Generator to
Sprites in Block ROM 1 Example 37 Sprites in Block ROM In Example 36 we made a sprite by storing the bit map of three initials in a VHDL ROM. To make a larger sprite we could use the Core Generator to
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL
 Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
VHDL Reference Manual
 VHDL Reference Manual 096-0400-003 March 1997 Synario Design Automation, a division of Data I/O, has made every attempt to ensure that the information in this document is accurate and complete. Synario
VHDL Reference Manual 096-0400-003 March 1997 Synario Design Automation, a division of Data I/O, has made every attempt to ensure that the information in this document is accurate and complete. Synario
Rotary Encoder Interface for Spartan-3E Starter Kit
 Rotary Encoder Interface for Spartan-3E Starter Kit Ken Chapman Xilinx Ltd 2 th February 26 Rev.2 With thanks to Peter Alfke (Xilinx Inc.) Limitations Limited Warranty and Disclaimer. These designs are
Rotary Encoder Interface for Spartan-3E Starter Kit Ken Chapman Xilinx Ltd 2 th February 26 Rev.2 With thanks to Peter Alfke (Xilinx Inc.) Limitations Limited Warranty and Disclaimer. These designs are
SELECT INPUTS STROBE OUTPUTS
 1 9. 1. I SN74153. 4x1 U1 74153 2 21 22 23 1. SN74153 ( ), ogic Is-MUs MUX. SEET DT INPUTS STROE OUTPUT INPUTS 1 2 3 G Y X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X 1. SN74153. : SEET INPUTS
1 9. 1. I SN74153. 4x1 U1 74153 2 21 22 23 1. SN74153 ( ), ogic Is-MUs MUX. SEET DT INPUTS STROE OUTPUT INPUTS 1 2 3 G Y X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X 1. SN74153. : SEET INPUTS
CHAPTER IX REGISTER BLOCKS COUNTERS, SHIFT, AND ROTATE REGISTERS
 CHAPTER IX-1 CHAPTER IX CHAPTER IX COUNTERS, SHIFT, AN ROTATE REGISTERS REA PAGES 249-275 FROM MANO AN KIME CHAPTER IX-2 INTROUCTION -INTROUCTION Like combinational building blocks, we can also develop
CHAPTER IX-1 CHAPTER IX CHAPTER IX COUNTERS, SHIFT, AN ROTATE REGISTERS REA PAGES 249-275 FROM MANO AN KIME CHAPTER IX-2 INTROUCTION -INTROUCTION Like combinational building blocks, we can also develop
16-bit ALU, Register File and Memory Write Interface
 CS M152B Fall 2002 Project 2 16-bit ALU, Register File and Memory Write Interface Suggested Due Date: Monday, October 21, 2002 Actual Due Date determined by your Lab TA This project will take much longer
CS M152B Fall 2002 Project 2 16-bit ALU, Register File and Memory Write Interface Suggested Due Date: Monday, October 21, 2002 Actual Due Date determined by your Lab TA This project will take much longer
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS. IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE
 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
(1) D Flip-Flop with Asynchronous Reset. (2) 4:1 Multiplexor. CS/EE120A VHDL Lab Programming Reference
 VHDL is an abbreviation for Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Description Language, and is used for modeling digital systems. VHDL coding includes behavior modeling, structure modeling and dataflow
VHDL is an abbreviation for Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Description Language, and is used for modeling digital systems. VHDL coding includes behavior modeling, structure modeling and dataflow
VHDL Test Bench Tutorial
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory VHDL Test Bench Tutorial Purpose The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to automate
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory VHDL Test Bench Tutorial Purpose The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to automate
Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher
 International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
Layout of Multiple Cells
 Layout of Multiple Cells Beyond the primitive tier primitives add instances of primitives add additional transistors if necessary add substrate/well contacts (plugs) add additional polygons where needed
Layout of Multiple Cells Beyond the primitive tier primitives add instances of primitives add additional transistors if necessary add substrate/well contacts (plugs) add additional polygons where needed
Asynchronous & Synchronous Reset Design Techniques - Part Deux
 Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
Sequential Logic. (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements )
 Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
Sequential Logic (Materials taken from: Principles of Computer Hardware by Alan Clements ) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits Combinatorial circuits: their outputs are computed entirely from their present
CPE 462 VHDL: Simulation and Synthesis
 CPE 462 VHDL: Simulation and Synthesis Topic #09 - a) Introduction to random numbers in hardware Fortuna was the goddess of fortune and personification of luck in Roman religion. She might bring good luck
CPE 462 VHDL: Simulation and Synthesis Topic #09 - a) Introduction to random numbers in hardware Fortuna was the goddess of fortune and personification of luck in Roman religion. She might bring good luck
Computer organization
 Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION
 Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
State Machines in VHDL
 State Machines in VHDL Implementing state machines in VHDL is fun and easy provided you stick to some fairly well established forms. These styles for state machine coding given here is not intended to
State Machines in VHDL Implementing state machines in VHDL is fun and easy provided you stick to some fairly well established forms. These styles for state machine coding given here is not intended to
A CPLD VHDL Introduction
 Application Note: CPLD R XAPP105 (v2.0) August 30, 2001 Summary This introduction covers the fundamentals of VHDL as applied to Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs). Specifically included are those
Application Note: CPLD R XAPP105 (v2.0) August 30, 2001 Summary This introduction covers the fundamentals of VHDL as applied to Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs). Specifically included are those
Memory Elements. Combinational logic cannot remember
 Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
Memory Elements Combinational logic cannot remember Output logic values are function of inputs only Feedback is needed to be able to remember a logic value Memory elements are needed in most digital logic
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters
 LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
LAB #4 Sequential Logic, Latches, Flip-Flops, Shift Registers, and Counters LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Introduction to latches and the D type flip-flop 2. Use of actual flip-flops to help you understand sequential
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
MICROPROCESSOR. Exclusive for IACE Students www.iace.co.in iacehyd.blogspot.in Ph: 9700077455/422 Page 1
 MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
Combinational-Circuit Building Blocks
 May 9, 24 :4 vra6857_ch6 Sheet number Page number 35 black chapter 6 Combinational-Circuit Building Blocks Chapter Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Commonly used combinational subcircuits
May 9, 24 :4 vra6857_ch6 Sheet number Page number 35 black chapter 6 Combinational-Circuit Building Blocks Chapter Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Commonly used combinational subcircuits
Lecture-3 MEMORY: Development of Memory:
 Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Lecture-3 MEMORY: It is a storage device. It stores program data and the results. There are two kind of memories; semiconductor memories & magnetic memories. Semiconductor memories are faster, smaller,
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques
 Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
WEEK 8.1 Registers and Counters. ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
WEEK 8.1 egisters and Counters ECE124 igital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Additional schematic FF symbols Active low set and reset signals. S Active high set and reset signals. S ECE124 igital Circuits
NOT COPY DO NOT COPY DO NOT COPY DO NOT COPY DO NOT COPY DO NOT COPY
 Section 8. Counters HOW MUCH Once you understand the capabilities of different Ps, you might ask, Why not ES I COS? just always use the most capable P available? For example, even if a circuit fits in
Section 8. Counters HOW MUCH Once you understand the capabilities of different Ps, you might ask, Why not ES I COS? just always use the most capable P available? For example, even if a circuit fits in
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users
 Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Printed Circuit Board Design with HDL Designer
 Printed Circuit Board Design with HDL Designer Tom Winkert Teresa LaFourcade NASNGoddard Space Flight Center 301-286-291 7 NASNGoddard Space Flight Center 301-286-0019 tom.winkert8 nasa.gov teresa. 1.
Printed Circuit Board Design with HDL Designer Tom Winkert Teresa LaFourcade NASNGoddard Space Flight Center 301-286-291 7 NASNGoddard Space Flight Center 301-286-0019 tom.winkert8 nasa.gov teresa. 1.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
Implementation of Web-Server Using Altera DE2-70 FPGA Development Kit
 1 Implementation of Web-Server Using Altera DE2-70 FPGA Development Kit A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT OF FOR THE DEGREE IN Bachelor of Technology In Electronics and Communication
1 Implementation of Web-Server Using Altera DE2-70 FPGA Development Kit A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT OF FOR THE DEGREE IN Bachelor of Technology In Electronics and Communication
Lab 1: Introduction to Xilinx ISE Tutorial
 Lab 1: Introduction to Xilinx ISE Tutorial This tutorial will introduce the reader to the Xilinx ISE software. Stepby-step instructions will be given to guide the reader through generating a project, creating
Lab 1: Introduction to Xilinx ISE Tutorial This tutorial will introduce the reader to the Xilinx ISE software. Stepby-step instructions will be given to guide the reader through generating a project, creating
Floating point package user s guide By David Bishop ([email protected])
 Floating point package user s guide By David Bishop ([email protected]) Floating-point numbers are the favorites of software people, and the least favorite of hardware people. The reason for this is because
Floating point package user s guide By David Bishop ([email protected]) Floating-point numbers are the favorites of software people, and the least favorite of hardware people. The reason for this is because
Coding Guidelines for Datapath Synthesis
 Coding Guidelines for Datapath Synthesis Reto Zimmermann Synopsys July 2005 Abstract This document summarizes two classes of RTL coding guidelines for the synthesis of datapaths: Guidelines that help achieve
Coding Guidelines for Datapath Synthesis Reto Zimmermann Synopsys July 2005 Abstract This document summarizes two classes of RTL coding guidelines for the synthesis of datapaths: Guidelines that help achieve
Modeling Registers and Counters
 Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC.
 8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
8.1 Objectives To design digital counter circuits using JK-Flip-Flop. To implement counter using 74LS193 IC. 8.2 Introduction Circuits for counting events are frequently used in computers and other digital
A Platform for Visualizing Digital Circuit Synthesis with VHDL
 A Platform for Visualizing Digital Circuit Synthesis with VHDL Abdulhadi Shoufan [email protected] Zheng Lu [email protected] Technische Universität Darmstadt Dept. of Computer Science
A Platform for Visualizing Digital Circuit Synthesis with VHDL Abdulhadi Shoufan [email protected] Zheng Lu [email protected] Technische Universität Darmstadt Dept. of Computer Science
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language
 Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Start Active-HDL by double clicking on the Active-HDL Icon (windows).
 Getting Started Using Aldec s Active-HDL This guide will give you a short tutorial in using the project mode of Active-HDL. This tutorial is broken down into the following sections 1. Part 1: Compiling
Getting Started Using Aldec s Active-HDL This guide will give you a short tutorial in using the project mode of Active-HDL. This tutorial is broken down into the following sections 1. Part 1: Compiling
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
Registers & Counters
 Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
Objectives This section deals with some simple and useful sequential circuits. Its objectives are to: Introduce registers as multi-bit storage devices. Introduce counters by adding logic to registers implementing
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises. Sept 14, 2007. James Barnes ([email protected])
 ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes ([email protected]) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
ECE 451 Verilog Exercises Sept 14, 2007 James Barnes ([email protected]) Organization These slides give a series of self-paced exercises. Read the specification of each exercise and write your
Decimal Number (base 10) Binary Number (base 2)
 LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
LECTURE 5. BINARY COUNTER Before starting with counters there is some vital information that needs to be understood. The most important is the fact that since the outputs of a digital chip can only be
FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE
 CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54
 Fall 2005 Instructor Texts University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54 Lab: Section 1: OSS LL14 Tuesday
Fall 2005 Instructor Texts University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54 Lab: Section 1: OSS LL14 Tuesday
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition
 RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
Study of 32-bit RISC Processor Architecture and VHDL FPGA Implementation 32-bitMatrix Manipulation
 Study of 32-bit RISC Processor Architecture and VHDL FPGA Implementation 32-bitMatrix Manipulation Vandana S. Shah Asstitant Professor, E&C Dept, SCET, Surat (India) ABSTRACT Present title discloses a
Study of 32-bit RISC Processor Architecture and VHDL FPGA Implementation 32-bitMatrix Manipulation Vandana S. Shah Asstitant Professor, E&C Dept, SCET, Surat (India) ABSTRACT Present title discloses a
COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
Two Binary Algorithms for Calculating the Jacobi Symbol and a Fast Systolic Implementation in Hardware
 Two Binary Algorithms for Calculating the Jacobi Symbol and a Fast Systolic Implementation in Hardware George Purdy, Carla Purdy, and Kiran Vedantam ECECS Department, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati,
Two Binary Algorithms for Calculating the Jacobi Symbol and a Fast Systolic Implementation in Hardware George Purdy, Carla Purdy, and Kiran Vedantam ECECS Department, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati,
Design of All Digital FM Receiver Circuit
 Design of All Digital FM Receiver Circuit Nursani Rahmatullah March 2005 Table of Contents Table of Contents...i Table of Figures...ii 1. Introduction...1 2. Architecture Description...1 2.1 Phase Detector...1
Design of All Digital FM Receiver Circuit Nursani Rahmatullah March 2005 Table of Contents Table of Contents...i Table of Figures...ii 1. Introduction...1 2. Architecture Description...1 2.1 Phase Detector...1
Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics!
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics! Part 2 A Simple Computer! Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode)
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 9 Computer Design Basics! Part 2 A Simple Computer! Charles Kime & Thomas Kaminski 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. (Hyperlinks are active in View Show mode)
Asynchronous Counters. Asynchronous Counters
 Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
Counters and State Machine Design November 25 Asynchronous Counters ENGI 25 ELEC 24 Asynchronous Counters The term Asynchronous refers to events that do not occur at the same time With respect to counter
Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Quartus II 1
 (DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
(DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
The components. E3: Digital electronics. Goals:
 E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
E3: Digital electronics Goals: Basic understanding of logic circuits. Become familiar with the most common digital components and their use. Equipment: 1 st. LED bridge 1 st. 7-segment display. 2 st. IC
(1) /30 (2) /30 (3) /40 TOTAL /100
 Your Name: SI Number: UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY BERKELEY AVIS IRVINE LOS ANGELES RIVERSIE SAN IEGO SAN FRANCISCO epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences SANTA BARBARA SANTA
Your Name: SI Number: UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY BERKELEY AVIS IRVINE LOS ANGELES RIVERSIE SAN IEGO SAN FRANCISCO epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences SANTA BARBARA SANTA
Clock Data Recovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni Guasti
 Application Note: Virtex and Spartan FPGA Families XAPP868 (v1.0) January 29, 2008 Clock Data ecovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni
Application Note: Virtex and Spartan FPGA Families XAPP868 (v1.0) January 29, 2008 Clock Data ecovery Design Techniques for E1/T1 Based on Direct Digital Synthesis Author: Paolo Novellini and Giovanni
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
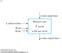 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
8254 PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER
 PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER Y Y Y Compatible with All Intel and Most Other Microprocessors Handles Inputs from DC to 10 MHz 8 MHz 8254 10 MHz 8254-2 Status Read-Back Command Y Y Y Y Y Six Programmable
PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER Y Y Y Compatible with All Intel and Most Other Microprocessors Handles Inputs from DC to 10 MHz 8 MHz 8254 10 MHz 8254-2 Status Read-Back Command Y Y Y Y Y Six Programmable
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses.
 Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: [email protected]
Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: [email protected]
Combining the ADS1202 with an FPGA Digital Filter for Current Measurement in Motor Control Applications
 Application Report SBAA094 June 2003 Combining the ADS1202 with an FPGA Digital Filter for Current Measurement in Motor Control Applications Miroslav Oljaca, Tom Hendrick Data Acquisition Products ABSTRACT
Application Report SBAA094 June 2003 Combining the ADS1202 with an FPGA Digital Filter for Current Measurement in Motor Control Applications Miroslav Oljaca, Tom Hendrick Data Acquisition Products ABSTRACT
Implementation of Modified Booth Algorithm (Radix 4) and its Comparison with Booth Algorithm (Radix-2)
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
Introduction to Simulink
 Introduction to Simulink MEEN 364 Simulink is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing dynamical systems. It supports linear and nonlinear systems, modeled in continuous time, sampled
Introduction to Simulink MEEN 364 Simulink is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing dynamical systems. It supports linear and nonlinear systems, modeled in continuous time, sampled
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots
 Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Using the HT46R46 I/O Ports to Implement Half-Duplex SPI Communication
 Using the HT46R46 I/O Ports to Implement Half-Duplex SPI Communication D/N: HA0150E Introduction This application explains how to use two I/O lines on the HT46R46 to implement half-duplex SPI communication.
Using the HT46R46 I/O Ports to Implement Half-Duplex SPI Communication D/N: HA0150E Introduction This application explains how to use two I/O lines on the HT46R46 to implement half-duplex SPI communication.
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano
 Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
The Designer's Guide to VHDL
 The Designer's Guide to VHDL Third Edition Peter J. Ashenden EDA CONSULTANT, ASHENDEN DESIGNS PTY. LTD. ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, ADELAIDE UNIVERSITY AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON m^^ yj 1 ' NEW
The Designer's Guide to VHDL Third Edition Peter J. Ashenden EDA CONSULTANT, ASHENDEN DESIGNS PTY. LTD. ADJUNCT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, ADELAIDE UNIVERSITY AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON m^^ yj 1 ' NEW
Chapter 7. Registers & Register Transfers. J.J. Shann. J. J. Shann
 Chapter 7 Registers & Register Transfers J. J. Shann J.J. Shann Chapter Overview 7- Registers and Load Enable 7-2 Register Transfers 7-3 Register Transfer Operations 7-4 A Note for VHDL and Verilog Users
Chapter 7 Registers & Register Transfers J. J. Shann J.J. Shann Chapter Overview 7- Registers and Load Enable 7-2 Register Transfers 7-3 Register Transfer Operations 7-4 A Note for VHDL and Verilog Users


