Outline. Synthesis Of VHDL Code. Computability. Big-O notation. Computation complexity. 1. Fundamental limitation of EDA software
|
|
|
- Justin Lindsey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline Synthesis Of VHDL Code 1. Fundamental limitation of EDA software 2. Realization of VHDL operator 3. Realization of VHDL data type 4. VHDL synthesis flow 5. Timing consideration RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 1 RTL Hardware Design Chapter Fundamental limitation of EDA software Can C-to-hardware be done? EDA tools: Core: optimization algorithms Shell: wrapping What does theoretical computer science say? Computability Computation complexity RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 3 Computability A problem is computable if an algorithm exists. E.g., halting problem : can we develop a program that takes any program and its input, and determines whether the computation of that program will eventually halt? any attempt to examine the meaning of a program is uncomputable RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 4 Computation complexity How fast an algorithm can run (or how good an algorithm is)? Interferences in measuring execution time: types of CPU, speed of CPU, compiler etc. Big-O notation f(n) is O(g(n)): if n 0 and c can be found to satisfy: f(n) < cg(n) for any n, n > n 0 g(n) is simple function: 1, n, log 2 n, n 2, n 3, 2 n Following are O(n 2 ): RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 5 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 6 1
2 Interpretation of Big-O E.g., Filter out the interference : constants and less important terms n is the input size of an algorithm The scaling factor of an algorithm: What happens if the input size increases RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 7 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 8 Theoretical limitation Intractable problems: algorithms with O(2 n ) Not realistic for a larger n Frequently tractable algorithms for suboptimal solution exist Many problems encountered in synthesis are intractable Synthesis software does not know your intention Synthesis software cannot obtain the optimal solution Synthesis should be treated as transformation and a local search in the design space Good VHDL code provides a good starting point for the local search RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 9 RTL Hardware Design Chapter Realization of VHDL operator What is the fuss about: hardware-software co-design? SystemC, HardwareC, SpecC etc.? Logic operator Simple, direct mapping Relational operator =, /= fast, simple implementation exists >, < etc: more complex implementation, larger delay Addition operator Other arith operators: support varies RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 11 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
3 Operator with two constant operands: Simplified in preprocessing No hardware inferred Good for documentation E.g., Operator with one constant operand: Can significantly reduce the hardware complexity E.g., adder vs. incrementor E.g y <= rotate_right(x, y); -- barrel shifter y <= rotate_right(x, 3); -- rewiring y <= x(2 downto 0) & x(7 downto 3); E.g., 4-bit comparator: x=y vs. x=0 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 13 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 14 An example 0.55 um standard-cell CMOS implementation 3. Realization of VHDL data type Use and synthesis of Z Use of - RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 15 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 16 Use and synthesis of Z Tri-state buffer: Output with high-impedance Not a value in Boolean algebra Need special output circuitry (tri-state buffer) Major application: Bi-directional I/O pins Tri-state bus VHDL description: y <= 'Z' when oe='1' else a_in; Z cannot be used as input or manipulated f <= 'Z' and a; y <= data_a when in_bus='z' else data_b; RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 17 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
4 Separate tri-state buffer from regular code: Less clear: with sel select y <= 'Z' when "00", '1' when "01" "11", '0' when others; better: with sel select tmp <= '1' when "01" "11", '0' when others; y <= 'Z' when sel="00" else tmp; Bi-directional i/o pins RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 19 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 20 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 21 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 22 Tri-state bus RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 23 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
5 Problem with tri-state bus Difficult to optimize, verify and test Somewhat difficult to design: parking, fighting Alternative to tri-state bus: mux Use of - In conventional logic design - as input value: shorthand to make table compact E.g., RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 25 RTL Hardware Design Chapter as output value: help simplification E.g., - assigned to 1: a + b - assigned to 0: a b + ab Use - in VHDL As input value (against our intuition): Wrong: RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 27 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 28 Fix #1: Wrong: Fix #2: Fix: RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 29 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
6 - as an output value in VHDL May work with some software 4. VHDL Synthesis Flow Synthesis: Realize VHDL code using logic cells from the device s library a refinement process Main steps: RT level synthesis Logic synthesis Technology mapping RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 31 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 32 RT level synthesis Realize VHDL code using RT-level components Somewhat like the derivation of the conceptual diagram Limited optimization Generated netlist includes regular logic: e.g., adder, comparator random logic: e.g., truth table description RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 33 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 34 Module generator regular logic can be replaced by predesigned module Pre-designed module is more efficient Module can be generated in different levels of detail Reduce the processing time Logic Synthesis Realize the circuit with the optimal number of generic gate level components Process the random logic Two categories: Two-level synthesis: sum-of-product format Multi-level synthesis RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 35 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
7 E.g., Technology mapping Map generic gates to device-dependent logic cells The technology library is provided by the vendors who manufactured (in FPGA) or will manufacture (in ASIC) the device RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 37 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 38 E.g., mapping in standard-cell ASIC Device library Cost: 31 vs. 17 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 39 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 40 E.g., mapping in FPGA With 5-input LUT (Look-Up-Table) cells Effective use of synthesis software Logic operators: software can do a good job Relational/Arith operators: manual intervention needed layout and routing structure : Silicon chip is 2-dimensional square rectangular or tree-shaped circuit is easier to optimize RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 41 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
8 5. Timing consideration Propagation delay Synthesis with timing constraint Hazards Delay-sensitive design RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 43 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 44 Propagation delay E.g. Delay: time required to propagate a signal from an input port to a output port Cell level delay: most accurate Simplified model: The impact of wire becomes more dominant RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 45 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 46 System delay The longest path (critical path) in the system The worst input to output delay E.g., False path may exists: RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 47 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
9 Synthesis with timing constraint RT level delay estimation: Difficult if the design is mainly random logic Critical path can be identified if many complex operators (such adder) are used in the design. Multi-level synthesis is flexible It is possible to reduce by delay by adding extra logic Synthesis with timing constraint 1. Obtain the minimal-area implementation 2. Identify the critical path 3. Reduce the delay by adding extra logic 4. Repeat 2 & 3 until meeting the constraint RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 49 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 50 E.g., Area-delay trade-off curve RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 51 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 52 Improvement in architectural level design (better VHDL code to start with) Timing Hazards Propagation delay: time to obtain a stable output Hazards: the fluctuation occurring during the transient period Static hazard: glitch when the signal should be stable Dynamic hazard: a glitch in transition Due to the multiple converging paths of an output port RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 53 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
10 E.g., static-hazard (sh=ab +bc; a=c=1) E.g., dynamic hazard (a=c=d=1) RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 55 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 56 Dealing with hazards Some hazards can be eliminated in theory E.g., Eliminating glitches is very difficult in reality, and almost impossible for synthesis Multiple inputs can change simultaneously (e.g., 1111=>0000 in a counter) How to deal with it? Ignore glitches in the transient period and retrieve the data after the signal is stabilized RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 57 RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 58 Delay sensitive design and its danger Boolean algebra the theoretical model for digital design and most algorithms used in synthesis process algebra deals with the stabilized signals Delay-sensitive design Depend on the transient property (and delay) of the circuit Difficult to design and analyze E.g., hazard elimination circuit: ac term is not needed E.g., edge detection circuit (pulse=a a ) RTL Hardware Design Chapter 6 59 RTL Hardware Design Chapter
11 What s can go wrong: E.g., pulse <= a and (not a); During logic synthesis, the logic expressions will be rearranged and optimized. During technology mapping, generic gates will be re-mapped During placement & routing, wire delays may change It is bad for testing verification If delay-sensitive design is really needed, it should be done manually, not by synthesis RTL Hardware Design Chapter
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745. Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation
 Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla (kalla@ece.utah.edu) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla (kalla@ece.utah.edu) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS
 VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
ECE 3401 Lecture 7. Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1.
 File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
Contents. System Development Models and Methods. Design Abstraction and Views. Synthesis. Control/Data-Flow Models. System Synthesis Models
 System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization
 Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain firstname.lastname@tut.fi Department of Computer
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Step : Create Dependency Graph for Data Path Step b: 8-way Addition? So, the data operations are: 8 multiplications one 8-way addition Balanced binary
 RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk How to go
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course. Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
System-on. on-chip Design Flow. Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems. jouni.tomberg@tut.
 System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems jouni.tomberg@tut.fi 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems jouni.tomberg@tut.fi 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
Latch Timing Parameters. Flip-flop Timing Parameters. Typical Clock System. Clocking Overhead
 Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing What we covered thus far: Number representations Logic gates Boolean algebra Introduction to CMOS HW#2 due, HW#3 assigned
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing What we covered thus far: Number representations Logic gates Boolean algebra Introduction to CMOS HW#2 due, HW#3 assigned
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
Two-level logic using NAND gates
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Two and Multilevel logic implementation Tajana Simunic Rosing 1 Two-level logic using NND gates Replace minterm ND gates with NND gates Place
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Two and Multilevel logic implementation Tajana Simunic Rosing 1 Two-level logic using NND gates Replace minterm ND gates with NND gates Place
Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra
 Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ Jan. 25 ǁ PP.9-4 Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA Chandrasekhar
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ Jan. 25 ǁ PP.9-4 Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA Chandrasekhar
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users
 Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Adder.PPT(10/1/2009) 5.1. Lecture 13. Adder Circuits
 Adder.T(//29) 5. Lecture 3 Adder ircuits Objectives Understand how to add both signed and unsigned numbers Appreciate how the delay of an adder circuit depends on the data values that are being added together
Adder.T(//29) 5. Lecture 3 Adder ircuits Objectives Understand how to add both signed and unsigned numbers Appreciate how the delay of an adder circuit depends on the data values that are being added together
2 : BISTABLES. In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blocks of electronic counting circuits.
 2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
2 : BITABLE In this Chapter, you will find out about bistables which are the fundamental building blos of electronic counting circuits. et-reset bistable A bistable circuit, also called a latch, or flip-flop,
VHDL-Testbench as Executable Specification
 VHDL- as Executable Specification Michael Pichler Zentrum für Mikroelektronik Aargau Fachhochschule Aargau, Steinackerstrasse 5, CH-5210 Windisch Web: www.zma.ch - E-mail: m.pichler@zma.ch Seite 1 Overview
VHDL- as Executable Specification Michael Pichler Zentrum für Mikroelektronik Aargau Fachhochschule Aargau, Steinackerstrasse 5, CH-5210 Windisch Web: www.zma.ch - E-mail: m.pichler@zma.ch Seite 1 Overview
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs
 Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electrostatic Discharge Output Buffer Tri-state Output Circuit Latch-Up Prevention of Latch-Up
Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electrostatic Discharge Output Buffer Tri-state Output Circuit Latch-Up Prevention of Latch-Up
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Codesign: The World Of Practice
 Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
e.g. τ = 12 ps in 180nm, 40 ps in 0.6 µm Delay has two components where, f = Effort Delay (stage effort)= gh p =Parasitic Delay
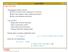 Logic Gate Delay Chip designers need to choose: What is the best circuit topology for a function? How many stages of logic produce least delay? How wide transistors should be? Logical Effort Helps make
Logic Gate Delay Chip designers need to choose: What is the best circuit topology for a function? How many stages of logic produce least delay? How wide transistors should be? Logical Effort Helps make
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs
 High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
Gates & Boolean Algebra. Boolean Operators. Combinational Logic. Introduction
 Introduction Gates & Boolean lgebra Boolean algebra: named after mathematician George Boole (85 864). 2-valued algebra. digital circuit can have one of 2 values. Signal between and volt =, between 4 and
Introduction Gates & Boolean lgebra Boolean algebra: named after mathematician George Boole (85 864). 2-valued algebra. digital circuit can have one of 2 values. Signal between and volt =, between 4 and
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots
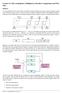 Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE
 CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
CHAPTER 10 FINITE STATE MACHINE: PRINCIPLE AND PRACTICE A finite state machine (FSM) is a sequential circuit with random next-state logic. Unlike the regular sequential circuit discussed in Chapters 8
Getting the Most Out of Synthesis
 Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
Computer organization
 Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Asynchronous & Synchronous Reset Design Techniques - Part Deux
 Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems cliffc@sunburst-design.com mills@lcdm-eng.com sgolson@trilobyte.com ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems cliffc@sunburst-design.com mills@lcdm-eng.com sgolson@trilobyte.com ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
design Synopsys and LANcity
 Synopsys and LANcity LANcity Adopts Design Reuse with DesignWare to Bring Low-Cost, High-Speed Cable TV Modem to Consumer Market What does it take to redesign a commercial product for a highly-competitive
Synopsys and LANcity LANcity Adopts Design Reuse with DesignWare to Bring Low-Cost, High-Speed Cable TV Modem to Consumer Market What does it take to redesign a commercial product for a highly-competitive
Hunting Asynchronous CDC Violations in the Wild
 Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
A s we saw in Chapter 4, a CPU contains three main sections: the register section,
 6 CPU Design A s we saw in Chapter 4, a CPU contains three main sections: the register section, the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU), and the control unit. These sections work together to perform the sequences
6 CPU Design A s we saw in Chapter 4, a CPU contains three main sections: the register section, the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU), and the control unit. These sections work together to perform the sequences
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
3.Basic Gate Combinations
 3.Basic Gate Combinations 3.1 TTL NAND Gate In logic circuits transistors play the role of switches. For those in the TTL gate the conducting state (on) occurs when the baseemmiter signal is high, and
3.Basic Gate Combinations 3.1 TTL NAND Gate In logic circuits transistors play the role of switches. For those in the TTL gate the conducting state (on) occurs when the baseemmiter signal is high, and
University of Texas at Dallas. Department of Electrical Engineering. EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design
 University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
5 Combinatorial Components. 5.0 Full adder. Full subtractor
 5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
Life Cycle of a Memory Request. Ring Example: 2 requests for lock 17
 Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI. Digital Systems Design. Digital Circuits Advanced Topics
 PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design
 ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Design and Development of Virtual Instrument (VI) Modules for an Introductory Digital Logic Course
 Session ENG 206-6 Design and Development of Virtual Instrument (VI) Modules for an Introductory Digital Logic Course Nikunja Swain, Ph.D., PE South Carolina State University swain@scsu.edu Raghu Korrapati,
Session ENG 206-6 Design and Development of Virtual Instrument (VI) Modules for an Introductory Digital Logic Course Nikunja Swain, Ph.D., PE South Carolina State University swain@scsu.edu Raghu Korrapati,
Finite State Machine. RTL Hardware Design by P. Chu. Chapter 10 1
 Finite State Machine Chapter 10 1 Outline 1. Overview 2. FSM representation 3. Timing and performance of an FSM 4. Moore machine versus Mealy machine 5. VHDL description of FSMs 6. State assignment 7.
Finite State Machine Chapter 10 1 Outline 1. Overview 2. FSM representation 3. Timing and performance of an FSM 4. Moore machine versus Mealy machine 5. VHDL description of FSMs 6. State assignment 7.
Boolean Algebra Part 1
 Boolean Algebra Part 1 Page 1 Boolean Algebra Objectives Understand Basic Boolean Algebra Relate Boolean Algebra to Logic Networks Prove Laws using Truth Tables Understand and Use First Basic Theorems
Boolean Algebra Part 1 Page 1 Boolean Algebra Objectives Understand Basic Boolean Algebra Relate Boolean Algebra to Logic Networks Prove Laws using Truth Tables Understand and Use First Basic Theorems
Sequential Logic: Clocks, Registers, etc.
 ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
ENEE 245: igital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 2 : Clocks, Registers, etc. ENEE 245: igital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 2 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To design
Modeling a GPS Receiver Using SystemC
 Modeling a GPS Receiver using SystemC Modeling a GPS Receiver Using SystemC Bernhard Niemann Reiner Büttner Martin Speitel http://www.iis.fhg.de http://www.iis.fhg.de/kursbuch/kurse/systemc.html The e
Modeling a GPS Receiver using SystemC Modeling a GPS Receiver Using SystemC Bernhard Niemann Reiner Büttner Martin Speitel http://www.iis.fhg.de http://www.iis.fhg.de/kursbuch/kurse/systemc.html The e
Memory Systems. Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Cell
 Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
Memory Systems This chapter begins the discussion of memory systems from the implementation of a single bit. The architecture of memory chips is then constructed using arrays of bit implementations coupled
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
CE4: Components and esign Techniques for igital ystems Tajana imunic osing ources: Where we are now What we ve covered so far (Chap -5, App. A& B) Number representations Boolean algebra OP and PO Logic
Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher
 International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Quartus II 1
 (DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
(DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Understanding Logic Design
 Understanding Logic Design ppendix of your Textbook does not have the needed background information. This document supplements it. When you write add DD R0, R1, R2, you imagine something like this: R1
Understanding Logic Design ppendix of your Textbook does not have the needed background information. This document supplements it. When you write add DD R0, R1, R2, you imagine something like this: R1
CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE. Ioan Lemeni
 CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE Ioan Lemeni Computer and Communication Engineering Department Faculty of Automation, Computers and Electronics University of Craiova 13, A.I. Cuza, Craiova,
CNC FOR EDM MACHINE TOOL HARDWARE STRUCTURE Ioan Lemeni Computer and Communication Engineering Department Faculty of Automation, Computers and Electronics University of Craiova 13, A.I. Cuza, Craiova,
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano
 Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes (miguel@di.uminho.pt) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes (miguel@di.uminho.pt) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language
 Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
Register File, Finite State Machines & Hardware Control Language Avin R. Lebeck Some slides based on those developed by Gershon Kedem, and by Randy Bryant and ave O Hallaron Compsci 04 Administrivia Homework
Karnaugh Maps. Circuit-wise, this leads to a minimal two-level implementation
 Karnaugh Maps Applications of Boolean logic to circuit design The basic Boolean operations are AND, OR and NOT These operations can be combined to form complex expressions, which can also be directly translated
Karnaugh Maps Applications of Boolean logic to circuit design The basic Boolean operations are AND, OR and NOT These operations can be combined to form complex expressions, which can also be directly translated
Basics of Simulation Technology (SPICE), Virtual Instrumentation and Implications on Circuit and System Design
 Basics of Simulation Technology (SPICE), Virtual Instrumentation and Implications on Circuit and System Design Patrick Noonan Business Development Manager National Instruments Electronics Workbench Group
Basics of Simulation Technology (SPICE), Virtual Instrumentation and Implications on Circuit and System Design Patrick Noonan Business Development Manager National Instruments Electronics Workbench Group
8-Bit Flash Microcontroller for Smart Cards. AT89SCXXXXA Summary. Features. Description. Complete datasheet available under NDA
 Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
Chapter 13: Verification
 Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Hardware/Software Co-Design of a Java Virtual Machine
 Hardware/Software Co-Design of a Java Virtual Machine Kenneth B. Kent University of Victoria Dept. of Computer Science Victoria, British Columbia, Canada ken@csc.uvic.ca Micaela Serra University of Victoria
Hardware/Software Co-Design of a Java Virtual Machine Kenneth B. Kent University of Victoria Dept. of Computer Science Victoria, British Columbia, Canada ken@csc.uvic.ca Micaela Serra University of Victoria
CpE358/CS381. Switching Theory and Logical Design. Class 4
 Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 4 1-122 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter 1) Binary codes, number systems, and arithmetic (Ch 1) Boolean algebra (Ch 2) Simplification
Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 4 1-122 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter 1) Binary codes, number systems, and arithmetic (Ch 1) Boolean algebra (Ch 2) Simplification
Karnaugh Maps & Combinational Logic Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 Karnaugh Maps & Combinational Logic Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 4 Optimized Implementation of Logic Functions 4. Karnaugh Map 4.2 Strategy for Minimization 4.2. Terminology
Karnaugh Maps & Combinational Logic Design ECE 52A Winter 22 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 4 Optimized Implementation of Logic Functions 4. Karnaugh Map 4.2 Strategy for Minimization 4.2. Terminology
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION
 Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Circuit Design
 Test and Diagnosis of of ICs Fault coverage (%) 95 9 85 8 75 7 65 97.92 SSL 4,246 Shawn Blanton Professor Department of ECE Center for Silicon System Implementation CMU Laboratory for Integrated Systems
Test and Diagnosis of of ICs Fault coverage (%) 95 9 85 8 75 7 65 97.92 SSL 4,246 Shawn Blanton Professor Department of ECE Center for Silicon System Implementation CMU Laboratory for Integrated Systems
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: cpatel2@cs.umbc.edu). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: cpatel2@cs.umbc.edu). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. EC262 Exam 1
 United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EC262 Exam 29 September 2. Do a page check now. You should have pages (cover & questions). 2. Read all problems in their entirety.
United States Naval Academy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EC262 Exam 29 September 2. Do a page check now. You should have pages (cover & questions). 2. Read all problems in their entirety.
Use of Reprogrammable FPGA on EUCLID mission
 19/05/2016 Workshop su Applicazioni FPGA in ambito Astrofisico Raoul Grimoldi Use of Reprogrammable FPGA on EUCLID mission Euclid mission overview EUCLID is a cosmology mission part of Cosmic Vision 2015-2025
19/05/2016 Workshop su Applicazioni FPGA in ambito Astrofisico Raoul Grimoldi Use of Reprogrammable FPGA on EUCLID mission Euclid mission overview EUCLID is a cosmology mission part of Cosmic Vision 2015-2025
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:16 min)
 Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Counters and Decoders
 Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
Physics 3330 Experiment #10 Fall 1999 Purpose Counters and Decoders In this experiment, you will design and construct a 4-bit ripple-through decade counter with a decimal read-out display. Such a counter
