Leakage Power Reduction Using Sleepy Stack Power Gating Technique
|
|
|
- Violet Melton
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Leakage Power Reduction Using Sleepy Stack Power Gating Technique M.Lavanya, P.Anitha M.E Student [Applied Electronics], Dept. of ECE, Kingston Engineering College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Kingston Engineering College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India ABSTRACT: The project presents the power gating techniques used for leakage power reduction.the rapid progress in semiconductor technology have led the feature sizes of transistor to be shrunk there by evolution of Deep Sub-Micron (DSM) technology; there by the extremely complex functionality is enabled to be integrated on a single chip. In the growing market of mobile hand-held devices used all over the world today, the battery-powered electronic system forms the backbone. To maximize the battery life, the tremendous computational capacity of portable devices such as notebook computers, personal communication devices (mobile phones, pocket PCs, PDAs), hearing aids and implantable pacemakers has to be realized with very low power requirements. Leakage power consumption is one of the major technical problem in DSM in CMOS circuit design. A comprehensive study and analysis of various leakage power minimization techniques have been presented in this paper a novel Leakage reduction technique is developed in Tanner EDA tool. KEYWORDS : Sleep Transistor,Stack Approach,Sleepy Keeper,Leakage Feedback I. INTRODUCTION Leakage power consumption of current CMOS technology is already a great challenge. ITRS projects that leakage power consumption may come to dominate total chip power consumption as the technology feature size shrinks. We propose a novel leakage reduction technique, named sleepy stack, which can be applied to general logic design. Our sleepy stack approach retains exact logic state making it better than traditional sleep and zigzag techniques while saving leakage power consumption. Unlike the stack approach (which saves state), the sleepy stack approach can work well with dual-vth technologies, reducing leakage by several orders of magnitude over the stack approach in single-vth technology. Unfortunately, the sleepy stack approach does have a area penalty (roughly %) as compared to stack technology; nonetheless, the sleepy stack approach occupies a nice where state-saving and extra low leakage is desired at a (potentially small) cost in terms of increased delay and area.in today s technology, the main contributer to static power consumption of a CMOS circuit is subthreshold leakage, i.e., source to drain current when gate voltage is smaller than the transistor threshold voltage. In this paper, we focus exclusively on reducing subthreshold leakage power. As introduced in Section 1, previously proposed work can be divided into techniques that either (i) preserve state or (ii) destroy state. State-destructive techniques (ii) cut off transistor (pull-up or pull-down or both) networks from supply voltage or ground using sleep transistors. These types of techniques are also called gated-vdd (note that a gated clock is generally used for dynamic power reduction). Motoh et al. propose a technique called multi-thresholdvoltage CMOS (MTCMOS), which adds high Vth sleep transistors between pullup networks and VDD and between pull-down networks and ground while logic 150 J.C. Park, V.J. Mooney, and P. Pfeiffenberger circuits use low Vth to maintain logic performance.the sleep transistor is turned off when the logic circuits are not in use. Powell et al. propose a gated-vdd cache technique called DRI cache, which dynamically changes cache size with gated-vdd transistors of dual or single Vth. Since the gated-vdd technique cuts off logic blocks from VDD and Gnd, time and energy for waking up are significant. The zigzag technique proposes the reduction of wake-up overhead by choosing a particular circuit state (e.g., corresponding to a reset ) and then, for the exact circuit state chosen, cutting off the pull-down network for each gate whose output is high while conversely cutting off the pull-up network for each gate whose output is low.although the zigzag technique can retain a particular state chosen prior to chip fabrication, any other arbitrary state during regular operation is lost in power-down mode. Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
2 Another technique to reduce leakage power is transistor stacking that exploits the stack effect, i.e., it turns out that two stacked and turned off transistors reduce subthreshold leakage current substantially due mainly to a reverse bias between the gate and source. A. Data-Driven Clock Gating II. RELATED WORK Clock enabling signals are very well understood at the system level and thus can effectively be defined and capture the periods where functional blocks and modules do not need to be clocked. Those are later being automatically synthesized into clock enabling signals at the gate level. In many cases, clock enabling signals are manually added for every FF as a part of a design methodology. Fig.1.Practical data-driven clock gating A FF finds out that its clock can be disabled in the next cycle by XORing its output with the present data input that will appear at its output in the next cycle. The outputs of k XOR gates are ORed to generate a joint gating signal for k FFs, which is then latched to avoid glitches. The combination of a latch with AND gate is commonly used by commercial tools and is called integrated clock gate (ICG). Such datadriven gating is used for a digital filter in an ultralow-power design. A single ICG is amortized over k FFs. Knowing the optimal group size k, the next step is to partition the FFs of a system into k-size sets such that the power savings will be maximized. Grouping FFs for joint clock gating as a part of the physical layout synthesis. Such tools are focusing on skew, power, and area minimization, but they are not aware of the toggling correlations of the underlying FFs, which this paper is focusing on. Fig.2.Activity similarity of FFs in a DSP core Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
3 FFs are paired only if they share same pre-enabled clock signal. Undesirable pairs are Encircled. Notice that different pre-enabled clock signals may have a different duration m of enabled window.as expected, the activity similarity is very high, mostly due to the very low FFs toggling during their enabled clock window.still, highly active and uncorrelated FF pairs exist and are encircled. A good FFs grouping algorithm should avoid putting the FFs of an encircled pair into the same group. Data-driven clock gating is shown to achieve savings of more than 10% of the total dynamic power consumed by the clock tree. Data driven clock gating for digita filters achieves 20% power savings.the gating logic is tailored to the structure of the filter, whereas the approach discussed in this paper is more general and applies to large scale and a wide range of designs. Fig.3.Distribution of the number of FFs sharing a common pre-enabled clock signal of a DSP core A.Power Gating Technique III. PROPOSED MODEL New low power solutions for Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) are proposed. Especially, we focus on leakage power reduction. Although neglected at 0.18u technology and above, leakage power is nearly equal to dynamic power consumption in nanoscale technology, e.g., 0.07u. We present a novel circuit structure, we call it sleepy stack, which is a combination of two well-known low-leakage techniques: the forced stack and sleeptransistortechniques. B.Sleep approach Sleep approach is used for reduction of gate oxide and sub threshold leakage current in DSM technology.sleep approach is used to rail off the circuit from Vdd to ground, so we insert a PMOS transistor above pull up network and Vdd and NMOS transistor below pull down Network and GND.During standby mode a sleep transistor turns off turn off and rail from Vdd and reduces the leakage current.during active mode we ON the sleep transistor and direct connection of circuit with Vdd, so increase the performance of the circuit and Reduces the leakage power efficiently.unlike the forced stack technique, the sleepy stack technique can utilize high-vth transistors without incurring a large delay increase. Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
4 C.Stack Approach Fig.4. Sleep Approach NAND Gate Force stack is another approach for further leakage reduction, in this approach we provide the stacking of the transistor, we divide pull up and pull down network into two half size. The dividing of the transistor will not affect the W/L ratio of the circuit, The W/L ratio of the circuit is maintained after dividing of the circuit. For better Leakage saving we divide pull up PMOS network which provide the stacking of the transistor, same process of dividing is also done in pulldown network serially. Also, unlike the sleep transistor technique, the sleepy stack technique can retain exact logic state while achieving similar leakage power savings. In short, our sleepy stack structure achieves ultra-low leakage power consumption while retaining logic state. We apply the sleepy stack technique to both generic logic circuits as well as SRAM. At 0.07u technology, the sleepy stack logic circuits achieves up to 200X leakage reduction compared the forced stack technique with small (under 7%) delay variations and 51~118% area overheads. The sleepy stack SRAM cell with 1.5xVth achieves 5X leakage reduction with 32% delay increase or 2.49X leakage reduction without delay increase compared to the high-vth SRAM cell. As such, the sleepy stack technique can be applicable to a design that requires ultra-low leakage power with quick response time while paying area and delay cost. Fig.5.Stack Approach based 2 input NAND gate Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
5 We achieve 20.43% processor dynamic energy savings with 4.14% execution cycle increase using 2-stage low-vdd LPPC. Furthermore, we apply LPPC to the sleepy stack SRAM. The sleepy stack pipelined SRAM achieves 17X leakage power reduction while increasing execution time by 4% on average. Although this combined technique increases active power consumption by 33%, this technique is well suited for the system that spends most of its time in sleep mode. Static power consumption is a major concern in nanometer technologies. Along with technology scaling down and higher operating speeds of CMOS VLSI circuits, the leakage power is getting enhanced. As process geometries are becoming smaller, device density increases and threshold voltage as well as oxide thickness decrease to keep pace with performance. D.Leakage Feedback Approach Another Leakage reduction technique is leakage feedback approach; In this approach we use two parallel PMOS transistor above pull up network and Vdd. To provide the inverting output of the circuit we connect inverter at the output, an inverter provides the proper logic feedback to both pull down NMOS(S') and pull up PMOS(S) sleep transistor. This two transistor enhance the circuit performance and maintain the proper logic of the circuit during standby mode. In standby mode one of the transistor of parallel sleep transistor turn off both NMOS and PMOS, the output of the circuit is pass through inverter which keep ON one of the sleep transistor which is connected parallel by providing the proper feedback approach. Hence circuit is active in standby mode, we mitigate the various leakage current which flow during standby mode and increase the performance of the circuit. E.Sleepy Keeper Approach Above all this approach the most efficient approach for leakage power reduction is the sleepy keeper approach. In this approach combination of PMOS and NMOS transistor which is connected paralleled inserted between pull up network and Vdd and pull down and GND, NMOS transistor of pull up sleep transistor connected PMOS pull down sleep transistor. As NMOS sleep transistor which rail off the path from Vdd to GND is connected to GND and PMOS transistor which is connected to Vdd, NMOS transistor is not turn ON that s why it will not efficiently pass Vdd, this problem can be overcome by maintaining output value 1 in sleep mode by connecting NMOS to Vdd. PMOS transistor which is connected to the pull up NMOS transistor and GND which is parallel to NMOS sleep transistor, to maintain output value equal to 0 in sleep mode.this approach reduces the leakage power efficiently and maintains the proper logic of the circuit with lesser area. Fig.6. Sleepy keeper Approach based 2 input NAND gate Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
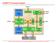
6 IV. SIMULATION RESULTS Fig.7.Power Gating Circuit Fig.8.Waveform of Power Gating Circuit Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
7 IV. CONCLUSION In nanometer scale CMOS technology, subthreshold leakage power consumption is a great challenge. Although previous approaches are effective in some ways, no perfect solution for reducing leakage power consumption is yet known. Therefore, designers choose techniques base upon technology and design criteria. Our novel sleepy stack, which combines the sleep and the stack approaches, is proposed as a new choice for logic designers. Furthermore, the sleepy stack is applicable to single and multiple threshold voltages. In conclusion, the sleepy stack combine some of the advantages of sleep transistors most notably the effective use of dual-vth technology with some of the advantages of the stack approach most notably the ability to save state. As such, the sleepy stack approach represents a new weapon in the VLSI designer s repertoire. REFERENCES [1] J. Kwong and A. P. Chandrakasan, Variation-driven device sizing for minimum energy sub-threshold circuits, in Proc. Int. Symp. Low Power Electron. Design, Oct. 2006, pp [2]N. Verma, J. Kwong, and A. P. Chandrakasan, Nanometer MOSFET variation in minimum energy subthreshold circuits, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 55, no. 1, pp , Jan [3]D. Bol, R. Ambroise, D. Flandre, and J. D. Legat, Analysis and minimization of practical energy in 45 nm subthreshold logic circuits, in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Design, Oct. 2008, pp [4]Y. Pu, J. P. de Gyvez, H. Corporaal, and Y. Ha, An ultra low energy/frame multi-standard JPEG co processor in 65 nm CMOS with sub/nearthreshold power supply, in IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits Conf. Dig. Tech. Papers, Feb. 2009, pp [5]V. G. Oklobdzija, Digital System Clocking High-Performance And Low- Power Aspects. New York, NyUsa: Wiley, Copyright to IJAREEIE DOI: /ijareeie
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology
 Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Low leakage and high speed BCD adder using clock gating technique
 Low leakage and high speed BCD adder using clock gating technique Mr. Suri shiva 1 Mr K.R.Anudeep Laxmikanth 2 Mr. Naveen Kumar.Ch 3 Abstract The growing market of mobile, battery powered electronic systems
Low leakage and high speed BCD adder using clock gating technique Mr. Suri shiva 1 Mr K.R.Anudeep Laxmikanth 2 Mr. Naveen Kumar.Ch 3 Abstract The growing market of mobile, battery powered electronic systems
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system
 Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications
 Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India
 Power reduction on clock-tree using Energy recovery and clock gating technique S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India Abstract Power consumption of
Power reduction on clock-tree using Energy recovery and clock gating technique S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India Abstract Power consumption of
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN
 TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units
 Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Slides adapted from: N. Weste,. Harris, CMOS VLSI esign, Addison-Wesley, 3/e, 24 Introduction Integrated Circuits: many transistors on one chip Very Large Scale Integration
Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Slides adapted from: N. Weste,. Harris, CMOS VLSI esign, Addison-Wesley, 3/e, 24 Introduction Integrated Circuits: many transistors on one chip Very Large Scale Integration
ECE 410: VLSI Design Course Introduction
 ECE 410: VLSI Design Course Introduction Professor Andrew Mason Michigan State University Spring 2008 ECE 410, Prof. A. Mason Lecture Notes Page i.1 Age of electronics microcontrollers, DSPs, and other
ECE 410: VLSI Design Course Introduction Professor Andrew Mason Michigan State University Spring 2008 ECE 410, Prof. A. Mason Lecture Notes Page i.1 Age of electronics microcontrollers, DSPs, and other
Introduction to VLSI Programming. TU/e course 2IN30. Prof.dr.ir. Kees van Berkel Dr. Johan Lukkien [Dr.ir. Ad Peeters, Philips Nat.
 Introduction to VLSI Programming TU/e course 2IN30 Prof.dr.ir. Kees van Berkel Dr. Johan Lukkien [Dr.ir. Ad Peeters, Philips Nat.Lab] Introduction to VLSI Programming Goals Create silicon (CMOS) awareness
Introduction to VLSI Programming TU/e course 2IN30 Prof.dr.ir. Kees van Berkel Dr. Johan Lukkien [Dr.ir. Ad Peeters, Philips Nat.Lab] Introduction to VLSI Programming Goals Create silicon (CMOS) awareness
LOW POWER DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS USING ENERGY RECOVERY CLOCKING AND CLOCK GATING
 LOW POWER DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS USING ENERGY RECOVERY CLOCKING AND CLOCK GATING A thesis work submitted to the faculty of San Francisco State University In partial fulfillment of the requirements for
LOW POWER DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS USING ENERGY RECOVERY CLOCKING AND CLOCK GATING A thesis work submitted to the faculty of San Francisco State University In partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Class 11: Transmission Gates, Latches
 Topics: 1. Intro 2. Transmission Gate Logic Design 3. X-Gate 2-to-1 MUX 4. X-Gate XOR 5. X-Gate 8-to-1 MUX 6. X-Gate Logic Latch 7. Voltage Drop of n-ch X-Gates 8. n-ch Pass Transistors vs. CMOS X-Gates
Topics: 1. Intro 2. Transmission Gate Logic Design 3. X-Gate 2-to-1 MUX 4. X-Gate XOR 5. X-Gate 8-to-1 MUX 6. X-Gate Logic Latch 7. Voltage Drop of n-ch X-Gates 8. n-ch Pass Transistors vs. CMOS X-Gates
Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating
 Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating S.Nandhini 1, T.G.Dhaarani 2, P.Kokila 3, P.Premkumar 4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Nandha Engineering College, Erode,
Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating S.Nandhini 1, T.G.Dhaarani 2, P.Kokila 3, P.Premkumar 4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Nandha Engineering College, Erode,
A Survey on Sequential Elements for Low Power Clocking System
 Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-3, February 10, 2012 A Survey on Sequential Elements for Low Power Clocking System Bhuvana S ECE Department, Avinashilingam University
Journal of Computer Applications ISSN: 0974 1925, Volume-5, Issue EICA2012-3, February 10, 2012 A Survey on Sequential Elements for Low Power Clocking System Bhuvana S ECE Department, Avinashilingam University
SRAM Scaling Limit: Its Circuit & Architecture Solutions
 SRAM Scaling Limit: Its Circuit & Architecture Solutions Nam Sung Kim, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison SRAM VCC min Challenges
SRAM Scaling Limit: Its Circuit & Architecture Solutions Nam Sung Kim, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison SRAM VCC min Challenges
DRG-Cache: A Data Retention Gated-Ground Cache for Low Power 1
 DRG-Cache: A Data Retention Gated-Ground Cache for Low Power 1 ABSTRACT In this paper we propose a novel integrated circuit and architectural level techniue to reduce leakage power consumption in high
DRG-Cache: A Data Retention Gated-Ground Cache for Low Power 1 ABSTRACT In this paper we propose a novel integrated circuit and architectural level techniue to reduce leakage power consumption in high
Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells
 Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells Sushil B. Bhaisare 1, Sonalee P. Suryawanshi 2, Sagar P. Soitkar 3 1 Lecturer in Electronics Department, Nagpur University, G.H.R.I.E.T.W. Nagpur,
Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells Sushil B. Bhaisare 1, Sonalee P. Suryawanshi 2, Sagar P. Soitkar 3 1 Lecturer in Electronics Department, Nagpur University, G.H.R.I.E.T.W. Nagpur,
Test Solution for Data Retention Faults in Low-Power SRAMs
 Test Solution for Data Retention Faults in Low-Power SRAMs L. B. Zordan 1 A. Bosio 1 L. Dilillo 1 P. Girard 1 A. Todri 1 A. Virazel 1 N. Badereddine 2 1 LIRMM - Université Montpellier II / CNRS 161, rue
Test Solution for Data Retention Faults in Low-Power SRAMs L. B. Zordan 1 A. Bosio 1 L. Dilillo 1 P. Girard 1 A. Todri 1 A. Virazel 1 N. Badereddine 2 1 LIRMM - Université Montpellier II / CNRS 161, rue
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING
 DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 14 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 50% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem
 A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits
 IEE5049 - Spring 2012 數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits Course Overview Professor Wei Hwang 黃 威 教 授 Department of Electronics Engineering National Chiao Tung University [email protected] Wei
IEE5049 - Spring 2012 數 位 積 體 電 路 Digital Integrated Circuits Course Overview Professor Wei Hwang 黃 威 教 授 Department of Electronics Engineering National Chiao Tung University [email protected] Wei
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers
 High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers Mehta Shantanu Sheetal #1, Vigneswaran T. #2 # School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers Mehta Shantanu Sheetal #1, Vigneswaran T. #2 # School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures
 McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
Power consumption is now the major technical
 COVER FEATURE Leakage Current: Moore s Law Meets Static Power Microprocessor design has traditionally focused on dynamic power consumption as a limiting factor in system integration. As feature sizes shrink
COVER FEATURE Leakage Current: Moore s Law Meets Static Power Microprocessor design has traditionally focused on dynamic power consumption as a limiting factor in system integration. As feature sizes shrink
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
CMOS Thyristor Based Low Frequency Ring Oscillator
 CMOS Thyristor Based Low Frequency Ring Oscillator Submitted by: PIYUSH KESHRI BIPLAB DEKA 4 th year Undergraduate Student 4 th year Undergraduate Student Electrical Engineering Dept. Electrical Engineering
CMOS Thyristor Based Low Frequency Ring Oscillator Submitted by: PIYUSH KESHRI BIPLAB DEKA 4 th year Undergraduate Student 4 th year Undergraduate Student Electrical Engineering Dept. Electrical Engineering
A true low voltage class-ab current mirror
 A true low voltage class-ab current mirror A. Torralba, 1a) R. G. Carvajal, 1 M. Jiménez, 1 F. Muñoz, 1 and J. Ramírez-Angulo 2 1 Departamento de Ingeniería Electrónica, Escuela Superior de Ingenieros,
A true low voltage class-ab current mirror A. Torralba, 1a) R. G. Carvajal, 1 M. Jiménez, 1 F. Muñoz, 1 and J. Ramírez-Angulo 2 1 Departamento de Ingeniería Electrónica, Escuela Superior de Ingenieros,
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic
 Infineon Page 1 CHES 2006 - Yokohama Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic L. Giancane, R. Luzzi, A. Trifiletti {marco.bucci, raimondo.luzzi}@infineon.com {giancane, trifiletti}@die.mail.uniroma1.it Summary
Infineon Page 1 CHES 2006 - Yokohama Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic L. Giancane, R. Luzzi, A. Trifiletti {marco.bucci, raimondo.luzzi}@infineon.com {giancane, trifiletti}@die.mail.uniroma1.it Summary
Fault Modeling. Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults. Transistor faults Summary
 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
NEW adder cells are useful for designing larger circuits despite increase in transistor count by four per cell.
 CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1
 ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Chip level timing Have discussed some issues related to timing analysis. Talked briefly about longest combinational path for a combinational circuit. Talked briefly
ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems Page 1 Chip level timing Have discussed some issues related to timing analysis. Talked briefly about longest combinational path for a combinational circuit. Talked briefly
A 1.62/2.7/5.4 Gbps Clock and Data Recovery Circuit for DisplayPort 1.2 with a single VCO
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.13, NO.3, JUNE, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.3.185 A 1.62/2.7/5.4 Clock and Data Recovery Circuit for DisplayPort 1.2 with a single VCO
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.13, NO.3, JUNE, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.3.185 A 1.62/2.7/5.4 Clock and Data Recovery Circuit for DisplayPort 1.2 with a single VCO
Model-Based Synthesis of High- Speed Serial-Link Transmitter Designs
 Model-Based Synthesis of High- Speed Serial-Link Transmitter Designs Ikchan Jang 1, Soyeon Joo 1, SoYoung Kim 1, Jintae Kim 2, 1 College of Information and Communication Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University,
Model-Based Synthesis of High- Speed Serial-Link Transmitter Designs Ikchan Jang 1, Soyeon Joo 1, SoYoung Kim 1, Jintae Kim 2, 1 College of Information and Communication Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University,
Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization. TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu
 Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu 1 Outline Introduction Engineering Change Order (ECO) Voltage drop (IR-DROP) New design
Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu 1 Outline Introduction Engineering Change Order (ECO) Voltage drop (IR-DROP) New design
Low latency synchronization through speculation
 Low latency synchronization through speculation D.J.Kinniment, and A.V.Yakovlev School of Electrical and Electronic and Computer Engineering, University of Newcastle, NE1 7RU, UK {David.Kinniment,Alex.Yakovlev}@ncl.ac.uk
Low latency synchronization through speculation D.J.Kinniment, and A.V.Yakovlev School of Electrical and Electronic and Computer Engineering, University of Newcastle, NE1 7RU, UK {David.Kinniment,Alex.Yakovlev}@ncl.ac.uk
CHARGE pumps are the circuits that used to generate dc
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND TOOLS FOR CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 1, JUNE 2011 27 A Charge Pump Circuit by using Voltage-Doubler as Clock Scheme Wen Chang Huang, Jin Chang Cheng,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND TOOLS FOR CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS, VOL. 1, NO. 1, JUNE 2011 27 A Charge Pump Circuit by using Voltage-Doubler as Clock Scheme Wen Chang Huang, Jin Chang Cheng,
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
CMOS, the Ideal Logic Family
 CMOS, the Ideal Logic Family INTRODUCTION Let s talk about the characteristics of an ideal logic family. It should dissipate no power, have zero propagation delay, controlled rise and fall times, and have
CMOS, the Ideal Logic Family INTRODUCTION Let s talk about the characteristics of an ideal logic family. It should dissipate no power, have zero propagation delay, controlled rise and fall times, and have
An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing
 2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
Semiconductor Memories
 Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
Semiconductor Memories Semiconductor memories array capable of storing large quantities of digital information are essential to all digital systems Maximum realizable data storage capacity of a single
NAME AND SURNAME. TIME: 1 hour 30 minutes 1/6
 E.T.S.E.T.B. MSc in ICT FINAL EXAM VLSI Digital Design Spring Course 2005-2006 June 6, 2006 Score publication date: June 19, 2006 Exam review request deadline: June 22, 2006 Academic consultancy: June
E.T.S.E.T.B. MSc in ICT FINAL EXAM VLSI Digital Design Spring Course 2005-2006 June 6, 2006 Score publication date: June 19, 2006 Exam review request deadline: June 22, 2006 Academic consultancy: June
STRATEGIES & METHODOLOGIES FOR LOW POWER VLSI DESIGNS: A REVIEW
 Abstract STRATEGIES & METHODOLOGIES FOR LOW POWER VLSI DESIGNS: A REVIEW Kanika Kaur 1 and Arti Noor 2 1 KIIT College of Engineering, Gurgaon, India [email protected] 2 Centre for Development of Advanced
Abstract STRATEGIES & METHODOLOGIES FOR LOW POWER VLSI DESIGNS: A REVIEW Kanika Kaur 1 and Arti Noor 2 1 KIIT College of Engineering, Gurgaon, India [email protected] 2 Centre for Development of Advanced
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution
 Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
CMOS Power Consumption and C pd Calculation
 CMOS Power Consumption and C pd Calculation SCAA035B June 1997 1 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any semiconductor product or
CMOS Power Consumption and C pd Calculation SCAA035B June 1997 1 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any semiconductor product or
True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique
 True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique Priyanka Sharma ME (ECE) Student NITTTR Chandigarh Rajesh Mehra Associate Professor Department of ECE NITTTR Chandigarh
True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique Priyanka Sharma ME (ECE) Student NITTTR Chandigarh Rajesh Mehra Associate Professor Department of ECE NITTTR Chandigarh
Area 3: Analog and Digital Electronics. D.A. Johns
 Area 3: Analog and Digital Electronics D.A. Johns 1 1970 2012 Tech Advancements Everything but Electronics: Roughly factor of 2 improvement Cars and airplanes: 70% more fuel efficient Materials: up to
Area 3: Analog and Digital Electronics D.A. Johns 1 1970 2012 Tech Advancements Everything but Electronics: Roughly factor of 2 improvement Cars and airplanes: 70% more fuel efficient Materials: up to
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption
 Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed VLSI
 International Journal of Advances in Engineering Science and Technology 225 www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaest/ and www.ijaestonline.com ISSN: 2319-1120 Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed
International Journal of Advances in Engineering Science and Technology 225 www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaest/ and www.ijaestonline.com ISSN: 2319-1120 Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed
Evaluating Embedded Non-Volatile Memory for 65nm and Beyond
 Evaluating Embedded Non-Volatile Memory for 65nm and Beyond Wlodek Kurjanowicz DesignCon 2008 Sidense Corp 2008 Agenda Introduction: Why Embedded NVM? Embedded Memory Landscape Antifuse Memory evolution
Evaluating Embedded Non-Volatile Memory for 65nm and Beyond Wlodek Kurjanowicz DesignCon 2008 Sidense Corp 2008 Agenda Introduction: Why Embedded NVM? Embedded Memory Landscape Antifuse Memory evolution
A New Low Power Dynamic Full Adder Cell Based on Majority Function
 World Applied Sciences Journal 4 (1): 133-141, 2008 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2008 A New Low Power Dynamic Full Adder Cell Based on Majority Function 1 Vahid Foroutan, 2 Keivan Navi and 1 Majid
World Applied Sciences Journal 4 (1): 133-141, 2008 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2008 A New Low Power Dynamic Full Adder Cell Based on Majority Function 1 Vahid Foroutan, 2 Keivan Navi and 1 Majid
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design
 Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
Curriculum for a Master s Degree in ECE with focus on Mixed Signal SOC Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview The VLSI Design program is part of two tracks in the department:
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER
 A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
A MULTILEVEL INVERTER FOR SYNCHRONIZING THE GRID WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES BY IMPLEMENTING BATTERY CUM DC-DC CONERTER 1 KARUNYA CHRISTOBAL LYDIA. S, 2 SHANMUGASUNDARI. A, 3 ANANDHI.Y 1,2,3 Electrical
CO2005: Electronics I (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1
 CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
NAND Flash FAQ. Eureka Technology. apn5_87. NAND Flash FAQ
 What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
Yaffs NAND Flash Failure Mitigation
 Yaffs NAND Flash Failure Mitigation Charles Manning 2012-03-07 NAND flash is one of very few types of electronic device which are knowingly shipped with errors and are expected to generate further errors
Yaffs NAND Flash Failure Mitigation Charles Manning 2012-03-07 NAND flash is one of very few types of electronic device which are knowingly shipped with errors and are expected to generate further errors
Subthreshold Real-Time Counter.
 Subthreshold Real-Time Counter. Jonathan Edvard Bjerkedok Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2013 Supervisor: Snorre Aunet, IET Co-supervisor: Øivind Ekelund, Energy Micro AS Norwegian
Subthreshold Real-Time Counter. Jonathan Edvard Bjerkedok Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2013 Supervisor: Snorre Aunet, IET Co-supervisor: Øivind Ekelund, Energy Micro AS Norwegian
A 10,000 Frames/s 0.18 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory
 Presented at the 2001 International Solid State Circuits Conference February 5, 2001 A 10,000 Frames/s 0.1 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory Stuart Kleinfelder, SukHwan Lim, Xinqiao
Presented at the 2001 International Solid State Circuits Conference February 5, 2001 A 10,000 Frames/s 0.1 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory Stuart Kleinfelder, SukHwan Lim, Xinqiao
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC
 10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected] P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected]
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected] P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected]
PFP Technology White Paper
 PFP Technology White Paper Summary PFP Cybersecurity solution is an intrusion detection solution based on observing tiny patterns on the processor power consumption. PFP is capable of detecting intrusions
PFP Technology White Paper Summary PFP Cybersecurity solution is an intrusion detection solution based on observing tiny patterns on the processor power consumption. PFP is capable of detecting intrusions
Here we introduced (1) basic circuit for logic and (2)recent nano-devices, and presented (3) some practical issues on nano-devices.
 Outline Here we introduced () basic circuit for logic and (2)recent nano-devices, and presented (3) some practical issues on nano-devices. Circuit Logic Gate A logic gate is an elemantary building block
Outline Here we introduced () basic circuit for logic and (2)recent nano-devices, and presented (3) some practical issues on nano-devices. Circuit Logic Gate A logic gate is an elemantary building block
1.1 Silicon on Insulator a brief Introduction
 Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgements Chapter 1: Overview 1.1 Silicon on Insulator a brief Introduction 1.2 Circuits and SOI 1.3 Technology and SOI Chapter 2: SOI Materials 2.1 Silicon on Heteroepitaxial
Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgements Chapter 1: Overview 1.1 Silicon on Insulator a brief Introduction 1.2 Circuits and SOI 1.3 Technology and SOI Chapter 2: SOI Materials 2.1 Silicon on Heteroepitaxial
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Analyzing Electrical Effects of RTA-driven Local Anneal Temperature Variation
 1 Analyzing Electrical Effects of RTA-driven Local Anneal Temperature Variation Vivek Joshi, Kanak Agarwal*, Dennis Sylvester, David Blaauw Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of Michigan,
1 Analyzing Electrical Effects of RTA-driven Local Anneal Temperature Variation Vivek Joshi, Kanak Agarwal*, Dennis Sylvester, David Blaauw Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of Michigan,
Interfacing 3V and 5V applications
 Authors: Tinus van de Wouw (Nijmegen) / Todd Andersen (Albuquerque) 1.0 THE NEED FOR TERFACG BETWEEN 3V AND 5V SYSTEMS Many reasons exist to introduce 3V 1 systems, notably the lower power consumption
Authors: Tinus van de Wouw (Nijmegen) / Todd Andersen (Albuquerque) 1.0 THE NEED FOR TERFACG BETWEEN 3V AND 5V SYSTEMS Many reasons exist to introduce 3V 1 systems, notably the lower power consumption
LOW POWER MULTIPLEXER BASED FULL ADDER USING PASS TRANSISTOR LOGIC
 LOW POWER MULTIPLEXER BASED FULL ADDER USING PASS TRANSISTOR LOGIC B. Dilli kumar 1, K. Charan kumar 1, M. Bharathi 2 Abstract- The efficiency of a system mainly depends on the performance of the internal
LOW POWER MULTIPLEXER BASED FULL ADDER USING PASS TRANSISTOR LOGIC B. Dilli kumar 1, K. Charan kumar 1, M. Bharathi 2 Abstract- The efficiency of a system mainly depends on the performance of the internal
Clock Distribution in RNS-based VLSI Systems
 Clock Distribution in RNS-based VLSI Systems DANIEL GONZÁLEZ 1, ANTONIO GARCÍA 1, GRAHAM A. JULLIEN 2, JAVIER RAMÍREZ 1, LUIS PARRILLA 1 AND ANTONIO LLORIS 1 1 Dpto. Electrónica y Tecnología de Computadores
Clock Distribution in RNS-based VLSI Systems DANIEL GONZÁLEZ 1, ANTONIO GARCÍA 1, GRAHAM A. JULLIEN 2, JAVIER RAMÍREZ 1, LUIS PARRILLA 1 AND ANTONIO LLORIS 1 1 Dpto. Electrónica y Tecnología de Computadores
An Ultra-low low energy asynchronous processor for Wireless Sensor Networks
 An Ultra-low low energy asynchronous processor for Wireless Sensor Networks.Necchi,.avagno, D.Pandini,.Vanzago Politecnico di Torino ST Microelectronics Wireless Sensor Networks - Ad-hoc wireless networks
An Ultra-low low energy asynchronous processor for Wireless Sensor Networks.Necchi,.avagno, D.Pandini,.Vanzago Politecnico di Torino ST Microelectronics Wireless Sensor Networks - Ad-hoc wireless networks
Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs
 Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electrostatic Discharge Output Buffer Tri-state Output Circuit Latch-Up Prevention of Latch-Up
Module 7 : I/O PADs Lecture 33 : I/O PADs Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electrostatic Discharge Output Buffer Tri-state Output Circuit Latch-Up Prevention of Latch-Up
Experimental Analysis of Batteries under Continuous and Intermittent Operations
 Experimental Analysis of Batteries under Continuous and Intermittent Operations S. Castillo, N. K. Samala, K. Manwaring, B. Izadi and D. Radhakrishnan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Experimental Analysis of Batteries under Continuous and Intermittent Operations S. Castillo, N. K. Samala, K. Manwaring, B. Izadi and D. Radhakrishnan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Design and Analysis of Parallel AES Encryption and Decryption Algorithm for Multi Processor Arrays
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 5, Issue, Ver. III (Jan - Feb. 205), PP 0- e-issn: 239 4200, p-issn No. : 239 497 www.iosrjournals.org Design and Analysis of Parallel AES
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 5, Issue, Ver. III (Jan - Feb. 205), PP 0- e-issn: 239 4200, p-issn No. : 239 497 www.iosrjournals.org Design and Analysis of Parallel AES
Tire pressure monitoring
 Application Note AN601 Tire pressure monitoring 1 Purpose This document is intended to give hints on how to use the Intersema pressure sensors in a low cost tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). 2 Introduction
Application Note AN601 Tire pressure monitoring 1 Purpose This document is intended to give hints on how to use the Intersema pressure sensors in a low cost tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS). 2 Introduction
Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop.
 Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
Objectives Having read this workbook you should be able to: recognise the arrangement of NAND gates used to form an S-R flip-flop. describe how such a flip-flop can be SET and RESET. describe the disadvantage
Optimization and Comparison of 4-Stage Inverter, 2-i/p NAND Gate, 2-i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort
 Optimization and Comparison of -Stage, -i/p NND Gate, -i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort Satyajit nand *, and P.K.Ghosh ** * Mody Institute of Technology & Science/ECE, Lakshmangarh,
Optimization and Comparison of -Stage, -i/p NND Gate, -i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort Satyajit nand *, and P.K.Ghosh ** * Mody Institute of Technology & Science/ECE, Lakshmangarh,
A 3.2Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit Without Reference Clock for a High-Speed Serial Data Link
 A 3.2Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit Without Reference Clock for a High-Speed Serial Data Link Kang jik Kim, Ki sang Jeong, Seong ik Cho The Department of Electronics Engineering Chonbuk National
A 3.2Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit Without Reference Clock for a High-Speed Serial Data Link Kang jik Kim, Ki sang Jeong, Seong ik Cho The Department of Electronics Engineering Chonbuk National
HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER
 HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER Sachin Kumar *1, Aman Kumar #2, Puneet Bansal #3 * Department of Electronic Science, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India # University Institute
HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER Sachin Kumar *1, Aman Kumar #2, Puneet Bansal #3 * Department of Electronic Science, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India # University Institute
Low Power and Reliable SRAM Memory Cell and Array Design
 Springer Series in Advanced Microelectronics 31 Low Power and Reliable SRAM Memory Cell and Array Design Bearbeitet von Koichiro Ishibashi, Kenichi Osada 1. Auflage 2011. Buch. XI, 143 S. Hardcover ISBN
Springer Series in Advanced Microelectronics 31 Low Power and Reliable SRAM Memory Cell and Array Design Bearbeitet von Koichiro Ishibashi, Kenichi Osada 1. Auflage 2011. Buch. XI, 143 S. Hardcover ISBN
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
Chapter 9 Semiconductor Memories Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Jin-Fu Li, EE, NCU 2 Outline Introduction
Implementation Details
 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems
 Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems DR.K.P.KALIYAMURTHIE 1, D.PARAMESWARI 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073 1 Asst. Prof. (SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
Load Balancing in Structured Peer to Peer Systems DR.K.P.KALIYAMURTHIE 1, D.PARAMESWARI 2 Professor and Head, Dept. of IT, Bharath University, Chennai-600 073 1 Asst. Prof. (SG), Dept. of Computer Applications,
ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT
 216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits
 Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING
 TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING BARIS TASKIN, JOHN WOOD, IVAN S. KOURTEV February 28, 2005 Research Objective Objective: Electronic design automation
TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING BARIS TASKIN, JOHN WOOD, IVAN S. KOURTEV February 28, 2005 Research Objective Objective: Electronic design automation
BURST-MODE communication relies on very fast acquisition
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 52, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 437 Instantaneous Clockless Data Recovery and Demultiplexing Behnam Analui and Ali Hajimiri Abstract An alternative
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 52, NO. 8, AUGUST 2005 437 Instantaneous Clockless Data Recovery and Demultiplexing Behnam Analui and Ali Hajimiri Abstract An alternative
FPGA Design of Reconfigurable Binary Processor Using VLSI
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
Class 18: Memories-DRAMs
 Topics: 1. Introduction 2. Advantages and Disadvantages of DRAMs 3. Evolution of DRAMs 4. Evolution of DRAMs 5. Basics of DRAMs 6. Basics of DRAMs 7. Write Operation 8. SA-Normal Operation 9. SA-Read Operation
Topics: 1. Introduction 2. Advantages and Disadvantages of DRAMs 3. Evolution of DRAMs 4. Evolution of DRAMs 5. Basics of DRAMs 6. Basics of DRAMs 7. Write Operation 8. SA-Normal Operation 9. SA-Read Operation
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Modeling SRAM Start-Up Behavior for Physical Unclonable Functions
 Modeling SRAM Start-Up Behavior for Physical Unclonable Functions Mafalda Cortez Apurva Dargar Said Hamdioui Delft University of Technology Faculty of EE, Mathematics and CS Mekelweg 4, 2628 CD Delft,
Modeling SRAM Start-Up Behavior for Physical Unclonable Functions Mafalda Cortez Apurva Dargar Said Hamdioui Delft University of Technology Faculty of EE, Mathematics and CS Mekelweg 4, 2628 CD Delft,
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor
 Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application
 Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Design of Four Input Buck-Boost DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Application A.Thiyagarajan Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Karpagam Institute of Technology
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
