Chapter 10. Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing
|
|
|
- Ashley Lindsey
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 10 Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 1 1
2 Outline Introduction Digital Boundary Scan (1149.1) Boundary Scan for Advanced Networks (1149.6) Embedded Core Test Standard (1500) Comparison between and 1500 VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 2 2
3 Boundary Scan Original objective: board-level digital testing Now also apply to: MCM and FPGA Analog circuits and high-speed networks Verification, debugging, clock control, power management, chip reconfiguration, etc. History: Mid-1980: JETAG 1988: JTAG 1990: First boundary scan standard VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 3 3
4 Boundary Scan Family No Main target Digital chips and interconnects among chips Extended digital serial interface Direct access testability interface Mixed-signal test bus Standard module test and maintenance (MTM) bus High-speed network interface Status Std Discontinue Discontinue Std Std (not endorsed by IEEE since 2003) Std VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 4 4
5 Core-Based SOC Design ADC RAM RAM ROM GLUE LOGIC PLL DAC BUS & INTERCONNECT ASIC 1 IP 1 DSP CPU ASIC 2 IP 2 RAM ROM ASIC DSP ALU ASIC VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 5 5
6 Digital Boundary Scan Basic concepts Overall test architecture & operations Hardware components Instruction register & instruction set Boundary scan description language On-chip test support Board/system-level control architectures VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 6 6
7 Basic Idea of Boundary Scan Boundary-scan cell Internal Logic VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 7 7
8 A Board Containing 4 IC s s with Boundary Scan Boundary-scan cell Boundary-scan chain Serial Data in Internal Logic Internal Logic Serial Data out Internal Logic Internal Logic System interconnect 8 VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 8
9 Boundary-Scan Architecture Boundary-Scan Register (consists of boundary Scan cells) Test Data In (TDI) 1 1 Internal Logic Internal Registers Bypass Register Miscellaneous Register Instruction Register Test Data Out (TDO) Test Mode Select (TMS) Test Clock (TCK) TAP Controller Test Reset (TRST*) (optional) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
10 Hardware Components of A test access port (TAP) consisting of : 4 mandatory pins: Test data in (TDI), Test data out (TDO), Test mode select (TMS), Test clock (TCK), and 1 optional pin: Test reset (TRST) A test access port controller (TAPC) An instruction register (IR) Several test data registers A boundary scan register (BSR) consisting of boundary scan cells (BSCs) A bypass register (BR) Some optional registers (Device-ID register, designspecified registers such as scan registers, LFSRs for BIST, etc.) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
11 Basic Operations 1. Instruction sent (serially) through TDI into instruction register. 2. Selected test circuitry configured to respond to the instruction. 3. Test pattern shifted into selected data register and applied to logic to be tested 4. Test response captured into some data register 5. Captured response shifted out; new test pattern shifted in simultaneously 6. Steps 3-5 repeated until all test patterns are applied. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
12 Boundary-Scan Circuitry in A Chip Design-Spec. Reg. Data Register TDO TDI TRST* TMS TCK T A P T A P C Device-ID Reg. Boundary Scan Reg. Bypass Reg. (1-bit) 3 ClockDR, ShiftDR, UpdateDR Reset* ClockIR, ShiftIR, UpdateIR 3 Instruction Register M U X IR decode 0 1 Select M U X 1D TCK EN Enable VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
13 Data registers Boundary scan register: consists of boundary scan cells Bypass register: a one-bit register used to pass test signal from a chip when it is not involved in current test operation Device-ID register: for the loading of product information (manufacturer, part number, version number, etc.) Other user-specified data registers (scan chains, LFSR for BIST, etc.) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
14 A Typical Boundary-Scan Cell (BSC) Operation modes Normal: IN OUT (Mode = 0) Shift: TDI... IN OUT... TDO (ShiftDR = 1, ClockDR) Capture: IN R1, OUT driven by IN or R2 (ShiftDR = 0, ClcokDR) Update: R1 OUT (Mode_Control = 1, UpdateDR) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
15 TAP Controller A finite state machine with 16 states Input: TCK, TMS Output: 9 or 10 signals included ClockDR, UpdateDR, ShiftDR, ClockIR, UpdateIR, ShiftIR, Select, Enable, TCK and TRST* (optional). VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
16 State Diagram of TAP Controller VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
17 Main functions of TAP controller Providing control signals to Reset BS circuitry Load instructions into instruction register Perform test capture operation Perform test update operation Shift test data in and out VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
18 States of TAP Controller Test-Logic-Reset: normal mode Run-Test/Idle: wait for internal test such as BIST Select-DR-Scan: initiate a data-scan sequence Capture-DR: load test data in parallel Shift-DR: load test data in series Exit1-DR: finish phase-1 shifting of data Pause-DR: temporarily hold the scan operation (e.g., allow the bus master to reload data) Exit2-DR: finish phase-2 shifting of data Update-DR: parallel load from associated shift registers Note: Controls for IR are similar to those for DR. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
19 Instruction Set BYPASS Bypass data through a chip SAMPLE Sample (capture) test data into BSR PRELOAD Shift-in test data and update BSR EXTEST Test interconnection between chips of board Optional INTEST, RUNBIST, CLAMP, IDCODE, USERCODE, HIGH-Z, etc. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
20 Execution of BYPASS Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
21 Execution of SAMPLE Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
22 Execution of PRELOAD Instruction Input PRELOAD R1 R2 M U X Internal Logic R1 R2 M U X Output TDI TDO VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
23 Execution of EXTEST Instruction (1/3) Shift-DR (Chip1) Internal Logic Internal Logic TDI Registers TDO TDI Registers TDO TAP controller TAP controller VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
24 Execution of EXTEST Instruction (2/3) Update-DR (Chip1) Capture-DR (Chip2) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
25 Execution of EXTEST Instruction (3/3) Shift-DR (Chip2) Internal Logic Internal Logic TDI Registers TDO TDI Registers TDO TAP controller TAP controller VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
26 Execution of INTEST Instruction (1/4) Shift-DR VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
27 Execution of INTEST Instruction (2/4) Update-DR VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
28 Execution of INTEST Instruction (3/4) Capture-DR Internal Logic TDI Registers TAP controller TDO VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
29 Execution of INTEST Instruction (4/4) Shift-DR Internal Logic TDI Registers TAP controller TDO VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
30 Boundary Scan Description Language (BSDL) Now a part of IEEE Purposes: Provide standard description language for BS devices. Simplify design work for BS automated synthesis is possible. Promote consistency throughout ASIC designers, device manufacturers, foundries, test developers and ATE manufacturers. Make it easy to incorporation BS into software tools for test generation, analysis and failure diagnosis. Reduce possibility of human error when employing boundary scan in a design. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
31 Features of BSDL Describes the testability features of BS devices that are compatible with S subset of VHDL. System-logic and the elements that are absolutely mandatory need not be specified. Examples: BYPASS register, TAP controller, etc. Commercial tools to synthesize BSDL exist. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
32 Scan and BIST Support with Boundary Scan VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
33 Bus Master for Chips with Boundary Scan (1/5) Ring architecture with shared TMS Application chips TDI TCK TMS TDO #1 Bus master TDI TDO TMS TCK TDI TCK TMS TDO #2 VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 33 TDI TCK TMS TDO #N 33
34 Bus Master for Chips with Boundary Scan (2/5) Ring architecture with separate TMS Application chips Bus master TDI TDO TMS1 TMS2 TMSN TCK TDI TCK TMS TDO TDI TCK TMS TDO #1 #2 TDI TCK TMS TDO VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 34 #N 34
35 Bus Master for Chips with Boundary Scan (3/5) Star architecture VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
36 Bus Master for Chips with Boundary Scan (4/5) Multi-drop architecture Multi-Drop Device Multi-Drop Device Multi-Drop Device Bus master TDI TMS TCK TDO Test Bus VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
37 Bus Master for Chips with Boundary Scan (5/5) Hierarchical architecture VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
38 Boundary scan for advanced networks Rationale Analog test receiver Digital driver logic Digital receiver logic Test access port for VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
39 Rationale Advanced signaling techniques are required for multiple-mega-per-second I/O. Differential or AC-coupling networks Coupling capacitor in AC-coupled networks blocks DC signals. DC-level applied during EXTEST may decay to undefined logic level. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
40 Capturing AC-Coupled Coupled Signal with C U C U TX Update-DR V T RX TX V H V L RX V H V L Capture-DR VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
41 Configuration for Differential Signaling C U C U TX RX VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
42 Analog Test Receiver Response to AC and DC-Coupled Coupled Signals VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
43 Digital Driver Logic Mission 0 Shift in ShiftDR 1 C U ClockDR Shift out UpdateDR Train/Pulse 0 1 AC Mode Bypass Extest Extest_Pulse 0 1 Mode Mode Data AC Test Signal Insertion, per driver AC Mode Train/Pulse 0 X X 1 0 X RTI State TCK D Q AC Test Signal (distributed to all AC drivers) Extest_Train AC Test Signal Generator (near TAP Controller) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
44 Digital Receiver Logic Optional, Required for Observe-and-Control Capabilty on Single-Ended Inputs Only 0 Boundary Register Cell Shift In 1 0 ShiftDR Capture FF Shift Out Update FF 1 EXTEST: TCK TAP State Init_Memory Clock_DR Capture-DR Shift_DR Test Receiver Pad EXTEST_PULSE or EXTEST_TRAIN Selected R F AC DC C F V T V Hyst V Hyst ClockDR UpdateDR D Set Hyst Mem Clear Init_Memory (common to all test receivers) EXTEST_PULSE, EXTEST_TRAIN: Latch Q Init_Memory NOTE: The generated clock (Init_Memory) shown is suitable for rising edge-sensitive behavior only. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 44 TCK TAP State TMS May be located near TAP controller Q Q SET Q CLR D LG Exit*-DR Update_DR Capture-DR EXTEST EXTEST_TRAIN EXTEST_PULSE TMS Exit1-DR Exit2-DR TCK 44
45 Example of Modification on TAP Driver Behavior During EXTEST_PULSE Pulse Width TCK (TAP State) Test-Logic Reset Update-xR Run-Test/Idle Select-DR Capture-DR AC Test Signal Update Point Capture Point AC Pin Driver Data Inverted Data Data VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
46 Embedded Core Test Standard SOC test problems Overall architecture Wrapper components and functions Instruction set Core test language Core test supporting and system test configurations Hierarchical test control and plug & play VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
47 SOC Test Problems/Requirements (1/2) Mixing technologies: logic, processor, memory, analog Need various DFT/BIST/other techniques Deeply embedded cores Need Test Access Mechanism Hierarchical core reuse Need hierarchical test management Different core providers and SOC test developers Need standard for test integration IP protection/test reuse Need core test standard/documentation VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
48 SOC Test Problems/Requirements (2/2) Higher-performance core pins than SOC pins Need on-chip, at-speed testing External ATE inefficiency Need on-chip ATE Long test application time Need parallel testing or test scheduling Test power must be considered Need lower power design or test scheduling Testable design automation Need new testable design tools and flow VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
49 A System Overview of IEEE 1500 Standard VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
50 Test Interface of A Core Wrapper Wrapper Parallel Input WPI Wrapper Parallel Control WPC Optional W rapper Parallel Port (W PP) Wrapper Parallel Output WPO Core WSI Wrapper Serial Input Required W rapper Serial Port (WSP) Wrapper WSC Wrapper Serial Control WSO Wrapper Serial Output VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
51 Serial Test Circuitry of 1500 for a Core VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
52 Wrapper Components Wrapper series port (WSP) Wrapper series input (WSI), Wrapper series output (WSO), Wrapper series control (WSC) Wrapper parallel port (WPP) (optional) Wrapper parallel input (WPI), Wrapper parallel output (WPO), wrapper parallel control (WPC) Wrapper instruction register (WIR) Wrapper bypass regiester (WBY) Wrapper data register (WBR) Consists of wrapper boundary cells (WBC s) Core data register (CDR) (optional) VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
53 Wrapper Series Control (WSC) signals WRCK: wrapper clock terminal AUXCKn: Optional auxiliary clocks, where n is the number of the clocks. WRSTN: wrapper reset SelectWIR: determine whether WIR is selected CaptureWR: enable Capture operation ShiftWR: enable Shift operation UpdateWR: enable Update operation TransferDR: enable Transfer operation VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
54 Wrapper Instruction Register VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
55 Wrapper Boundary Register (WBR) Consists of Wrapper boundary cells (WBC s) WBC Terminals: Cell functional input (CFI), cell functional output (CFO), cell test input (CTI), cell test output (CTO) Functional modes: Normal, inward facing, outward facing, nonhazardous (safe). Operation events: Shift, capture, update, transfer, apply. VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
56 Events of WBR (WBC) Shift: data advance one-bit forward on WBR s shift path Capture: data on CFI or CFO are captured and stored in WBC Update: data stored in WBC s shift path storage are loaded into an off-shift-path storage of the WBC Transfer: move data to the storage closest to CTI or one bit closer to CTO Apply: a derivative event inferred from other events to apply data to functional inputs of cores or functional outputs of WBR VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
57 Four Symbols Used in Bubble Diagrams for WBC s Storage element Data path Decision point Data paths from a source VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
58 Some Typical WBC s Represented by Bubble Diagrams VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
59 Example WIR Interface of WBY, WBR WDR(s) ) and CDR(s) SelectWIR {SelectWIR, WRCK, WRSTN, CaptureWR, ShiftWR, UpdateWR} WIR Circuitry Core_Cntrl WDR_Cntrl CDR_Cntrl DR_Select[n:0] WBR_Cntrl WBY_Cntrl WBR CDR k WDR k WIR_WSO DR_Select[n:0] DR_WSO WSO WSI WBY VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
60 Example Schematic Diagram of WBC WC_SD2_CIO CTI SHIFT XFER WRCK D1 MODE CFI CAPT CFO D2 CTO IO_FACE WRCK VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
61 WS_BYPASS Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
62 WS_EXTEST Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
63 WP_EXTEXT Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
64 WS_SAFE Instruction Disabled Safe States W B R FI FO Core FO FI W B R Safe States WSI Bypass WIR WSO WSC VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
65 WS_PRELOAD Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
66 WP_PRELOAD Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
67 WS_CLAMP Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
68 WS_INTEST Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
69 WS_INTEST_SCAN Instruction VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
70 General Parallel TAM Structure VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
71 Multiplexed TAM Architectures VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
72 Daisy chained TAM Architecture VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
73 Direct Access TAM Architectures VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
74 Local Controller TAM Architectures VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
75 Core Access Switch (CAS) Architecture VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
76 Different Functional Modes of CAS VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
77 Various Types of Test Supporting Using CAS Structure VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
78 A Hierarchical Test Architecture Supporting Plug & Play Feature VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
79 Detailed I/O and CTC of The Hierarchical Test Architecture VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
80 A Hierarchical Test Architecture with I/Os Compatible to VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P
81 Comparison between and 1500 Purpose Parallel Mode Extra Data/Control I/Os FSM Transfer Mode Latency between operations Mandatory Instructions Board-level No Mandatory: TDI, TDO, TMS, TCK Optional: TRST Yes No Yes EXTEST, BYPASS, SAMPLE, PRELOAD 1500 Core-based VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 81 Yes Mandatory: WSI, WSO, 6 WSC Optional: TransferDR, WPP, AUXCKn(s) No Yes No WS_EXTEST, WS_BYPASS, one Wx_INTEST, WS_PRELOAD (cond. required) 81
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
The Boundary Scan Test (BST) technology
 The Boundary Scan Test () technology J. M. Martins Ferreira FEUP / DEEC - Rua Dr. Roberto Frias 42-537 Porto - PORTUGAL Tel. 35 225 8 748 / Fax: 35 225 8 443 ([email protected] / http://www.fe.up.pt/~jmf) Objectives
The Boundary Scan Test () technology J. M. Martins Ferreira FEUP / DEEC - Rua Dr. Roberto Frias 42-537 Porto - PORTUGAL Tel. 35 225 8 748 / Fax: 35 225 8 443 ([email protected] / http://www.fe.up.pt/~jmf) Objectives
TABLE OF CONTENTS. xiii List of Tables. xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules. xix Preface to the First Edition. xxi Preface to the Second Edition
 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures xiii List of Tables xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules xix Preface to the First Edition xxi Preface to the Second Edition xxiii Acknowledgement xxv 1 Boundary-Scan Basics
TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures xiii List of Tables xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules xix Preface to the First Edition xxi Preface to the Second Edition xxiii Acknowledgement xxv 1 Boundary-Scan Basics
Boundary-Scan Tutorial
 See the ASSET homepage on the World Wide Web at http://www.asset-intertech.com ASSET and the ASSET logo are registered trademarks of ASSET InterTech, Inc. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft
See the ASSET homepage on the World Wide Web at http://www.asset-intertech.com ASSET and the ASSET logo are registered trademarks of ASSET InterTech, Inc. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft
Primer. Semiconductor Group
 Primer 1997 Semiconductor Group IEEE Std 1149.1 (JTAG) Testability Primer i IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any semiconductor
Primer 1997 Semiconductor Group IEEE Std 1149.1 (JTAG) Testability Primer i IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any semiconductor
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Boundary Scan. Boundary Scan.1
 Boundary Scan! Objectives! History! Family of 49! Architecture! Bus Protocol! Boundary scan cell! TAP controller! Instruction set! Boundary Scan Description Language Boundary Scan. Objectives! Standards
Boundary Scan! Objectives! History! Family of 49! Architecture! Bus Protocol! Boundary scan cell! TAP controller! Instruction set! Boundary Scan Description Language Boundary Scan. Objectives! Standards
A STUDY OF INSTRUMENT REUSE AND RETARGETING IN P1687
 A STUDY OF INSTRUMENT REUSE AND RETARGETING IN P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Erik Larsson Linköping University Gunnar Carlsson Ericsson ABSTRACT Modern chips may contain a large number
A STUDY OF INSTRUMENT REUSE AND RETARGETING IN P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Erik Larsson Linköping University Gunnar Carlsson Ericsson ABSTRACT Modern chips may contain a large number
Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990
 Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990 ABSTRACT Mechanical and chemical process challenges initially limited acceptance of surface mount technology (SMT). As those challenges
Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990 ABSTRACT Mechanical and chemical process challenges initially limited acceptance of surface mount technology (SMT). As those challenges
REUSING AND RETARGETING ON-CHIP INSTRUMENT ACCESS PROCEDURES IN IEEE P1687
 REUSING AND RETARGETING ON-CHIP INSTRUMENT ACCESS PROCEDURES IN IEEE P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Erik Larsson Linköping University Gunnar Carlsson Ericsson ABSTRACT Modern chips may contain
REUSING AND RETARGETING ON-CHIP INSTRUMENT ACCESS PROCEDURES IN IEEE P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Erik Larsson Linköping University Gunnar Carlsson Ericsson ABSTRACT Modern chips may contain
The Advanced JTAG Bridge. Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09
 The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production
 Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production Hogeschool van Arnhem en Nijmegen 6 June 23 Rob Staals JTAG Technologies [email protected] Copyright 23, JTAG Technologies juni 3 The importance
Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production Hogeschool van Arnhem en Nijmegen 6 June 23 Rob Staals JTAG Technologies [email protected] Copyright 23, JTAG Technologies juni 3 The importance
Reusing and Retargeting On-Chip Instrument Access Procedures in IEEE P1687
 Reusing and Retargeting On-Chip Instrument Access Procedures in IEEE P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Gunnar Carlsson and Erik Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this
Reusing and Retargeting On-Chip Instrument Access Procedures in IEEE P1687 Farrokh Ghani Zadegan, Urban Ingelsson, Gunnar Carlsson and Erik Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this
Implementation Details
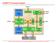 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Section 33. Programming and Diagnostics
 Section 33. and Diagnostics HGHLGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 33.1 ntroduction... 33-2 33.2 n-ircuit Serial (SP )... 33-2 33.3 Enhanced n-ircuit Serial... 33-3 33.4 JTAG
Section 33. and Diagnostics HGHLGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 33.1 ntroduction... 33-2 33.2 n-ircuit Serial (SP )... 33-2 33.3 Enhanced n-ircuit Serial... 33-3 33.4 JTAG
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
JTAG Applications. Product Life-Cycle Support. Software Debug. Integration & Test. Figure 1. Product Life Cycle Support
 JTAG Applications While it is obvious that JTAG based testing can be used in the production phase of a product, new developments and applications of the IEEE-1149.1 standard have enabled the use of JTAG
JTAG Applications While it is obvious that JTAG based testing can be used in the production phase of a product, new developments and applications of the IEEE-1149.1 standard have enabled the use of JTAG
G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo. Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip
 G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip December 2005 Preface Fast innovation in VLSI technologies makes possible the integration a complete system into a single chip (System-on-Chip,
G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip December 2005 Preface Fast innovation in VLSI technologies makes possible the integration a complete system into a single chip (System-on-Chip,
Analysis of Hardware and Software Approaches to Embedded In-Circuit Emulation of Microprocessors
 Analysis of Hardware and Software Approaches to Embedded In-Circuit Emulation of Microprocessors Hsin-Ming Chen, Chung-Fu Kao and Ing-Jer Huang Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen
Analysis of Hardware and Software Approaches to Embedded In-Circuit Emulation of Microprocessors Hsin-Ming Chen, Chung-Fu Kao and Ing-Jer Huang Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen
Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs
 Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs AN-628-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the Agilent 3070 test system to achieve faster programming
Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs AN-628-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the Agilent 3070 test system to achieve faster programming
Octal T1/E1/J1 Line Interface Unit
 Octal T/E/J Line Interface Unit CS6884 Features Industrystandard Footprint Octal E/T/J Shorthaul Line Interface Unit Low Power No external component changes for 00 Ω/20 Ω/75 Ω operation. Pulse shapes can
Octal T/E/J Line Interface Unit CS6884 Features Industrystandard Footprint Octal E/T/J Shorthaul Line Interface Unit Low Power No external component changes for 00 Ω/20 Ω/75 Ω operation. Pulse shapes can
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter
 Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
In-System Programming Design TM. Guidelines for ispjtag Devices. Introduction. Device-specific Connections. isplsi 1000EA Family.
 In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
SPI Flash Programming and Hardware Interfacing Using ispvm System
 March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
THE ADVANTAGES OF COMBINING LOW PIN COUNT TEST WITH SCAN COMPRESSION OF VLSI TESTING
 Zbornik radova 56. Konferencije za ETRAN, Zlatibor, 11-14. juna 2012. Proc. 56th ETRAN Conference, Zlatibor, June 11-14, 2012 THE ADVANTAGES OF COMBINING LOW PIN COUNT TEST WITH SCAN COMPRESSION OF VLSI
Zbornik radova 56. Konferencije za ETRAN, Zlatibor, 11-14. juna 2012. Proc. 56th ETRAN Conference, Zlatibor, June 11-14, 2012 THE ADVANTAGES OF COMBINING LOW PIN COUNT TEST WITH SCAN COMPRESSION OF VLSI
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention
 MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention March 2006, ver 1.0 Application Note 410 Introduction MAX II devices support the real-time in-system mability (ISP) feature that allows you
MAX II ISP Update with I/O Control & Register Data Retention March 2006, ver 1.0 Application Note 410 Introduction MAX II devices support the real-time in-system mability (ISP) feature that allows you
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected]. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
512K x 18, 256K x 36 9Mb SCD/DCD Sync Burst SRAMs
 9- and 65-Bump BGA Industrial Temp 52K x 8, 256K x 36 9Mb SCD/DCD Sync Burst SRAMs GS8828/36C(B/D)-xxxIV 25 MHz 5 MHz.8 V or 2.5 V V DD.8 V or 2.5 V I/O Features FT pin for user-configurable flow through
9- and 65-Bump BGA Industrial Temp 52K x 8, 256K x 36 9Mb SCD/DCD Sync Burst SRAMs GS8828/36C(B/D)-xxxIV 25 MHz 5 MHz.8 V or 2.5 V V DD.8 V or 2.5 V I/O Features FT pin for user-configurable flow through
MICROPROCESSOR. Exclusive for IACE Students www.iace.co.in iacehyd.blogspot.in Ph: 9700077455/422 Page 1
 MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1 9NJ, UK. *[email protected]
 Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban. Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering
 Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering 11-11-2014 2 zero-defect quality impossible to produce zero-defect boards early involvement services (Design
Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering 11-11-2014 2 zero-defect quality impossible to produce zero-defect boards early involvement services (Design
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs
 Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
XMC Modules. XMC-6260-CC 10-Gigabit Ethernet Interface Module with Dual XAUI Ports. Description. Key Features & Benefits
 XMC-6260-CC 10-Gigabit Interface Module with Dual XAUI Ports XMC module with TCP/IP offload engine ASIC Dual XAUI 10GBASE-KX4 ports PCIe x8 Gen2 Description Acromag s XMC-6260-CC provides a 10-gigabit
XMC-6260-CC 10-Gigabit Interface Module with Dual XAUI Ports XMC module with TCP/IP offload engine ASIC Dual XAUI 10GBASE-KX4 ports PCIe x8 Gen2 Description Acromag s XMC-6260-CC provides a 10-gigabit
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview
 EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email: [email protected] Feb. 2013 Course Overview
EEM870 Embedded System and Experiment Lecture 1: SoC Design Overview Wen-Yen Lin, Ph.D. Department of Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University Email: [email protected] Feb. 2013 Course Overview
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ
 nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada
 Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada BIOGRAPHY Yves Théroux, a Project Engineer with BAE Systems Canada (BSC) has eight years of experience in the design, qualification,
Open Architecture Design for GPS Applications Yves Théroux, BAE Systems Canada BIOGRAPHY Yves Théroux, a Project Engineer with BAE Systems Canada (BSC) has eight years of experience in the design, qualification,
How To Design A Single Chip System Bus (Amba) For A Single Threaded Microprocessor (Mma) (I386) (Mmb) (Microprocessor) (Ai) (Bower) (Dmi) (Dual
 Architetture di bus per System-On On-Chip Massimo Bocchi Corso di Architettura dei Sistemi Integrati A.A. 2002/2003 System-on on-chip motivations 400 300 200 100 0 19971999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Transistors
Architetture di bus per System-On On-Chip Massimo Bocchi Corso di Architettura dei Sistemi Integrati A.A. 2002/2003 System-on on-chip motivations 400 300 200 100 0 19971999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Transistors
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Computer organization
 Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
Computer organization Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
21555 Non-Transparent PCI-to- PCI Bridge
 21555 Non-Transparent PCI-to- PCI Bridge Specification Update December 2002 Notice: The 21555 may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may cause the 21555 s behavior
21555 Non-Transparent PCI-to- PCI Bridge Specification Update December 2002 Notice: The 21555 may contain design defects or errors known as errata. Characterized errata that may cause the 21555 s behavior
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design. Accelerates PLD Development
 Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
8 Gbps CMOS interface for parallel fiber-optic interconnects
 8 Gbps CMOS interface for parallel fiberoptic interconnects Barton Sano, Bindu Madhavan and A. F. J. Levi Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, California
8 Gbps CMOS interface for parallel fiberoptic interconnects Barton Sano, Bindu Madhavan and A. F. J. Levi Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, California
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition
 RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor
 Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
Designing a System-on-Chip (SoC) with an ARM Cortex -M Processor A Starter Guide Joseph Yiu November 2014 version 1.02 27 Nov 2014 1 - Background Since the ARM Cortex -M0 Processor was released a few years
POCKET SCOPE 2. The idea 2. Design criteria 3
 POCKET SCOPE 2 The idea 2 Design criteria 3 Microcontroller requirements 3 The microcontroller must have speed. 3 The microcontroller must have RAM. 3 The microcontroller must have secure Flash. 3 The
POCKET SCOPE 2 The idea 2 Design criteria 3 Microcontroller requirements 3 The microcontroller must have speed. 3 The microcontroller must have RAM. 3 The microcontroller must have secure Flash. 3 The
System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications
 System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications N. Izeboudjen, K. Kaci, S. Titri, L. Sahli, D. Lazib, F. Louiz, M. Bengherabi, *N. Idirene Centre de Développement des Technologies
System on Chip Platform Based on OpenCores for Telecommunication Applications N. Izeboudjen, K. Kaci, S. Titri, L. Sahli, D. Lazib, F. Louiz, M. Bengherabi, *N. Idirene Centre de Développement des Technologies
Memory Testing. Memory testing.1
 Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
Memory Testing Introduction Memory Architecture & Fault Models Test Algorithms DC / AC / Dynamic Tests Built-in Self Testing Schemes Built-in Self Repair Schemes Memory testing.1 Memory Market Share in
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:16 min)
 Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller
 Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
PLL frequency synthesizer
 ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 Lab 4: PLL frequency synthesizer 1.1 Goal The goals of this lab exercise are: - Verify the behavior of a and of a complete PLL - Find capture
ANALOG & TELECOMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS LABORATORY EXERCISE 4 Lab 4: PLL frequency synthesizer 1.1 Goal The goals of this lab exercise are: - Verify the behavior of a and of a complete PLL - Find capture
ADS9850 Signal Generator Module
 1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 1, 07/2014 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 1, 07/2014 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ARM Webinar series. ARM Based SoC. Abey Thomas
 ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
ARM Webinar series ARM Based SoC Verification Abey Thomas Agenda About ARM and ARM IP ARM based SoC Verification challenges Verification planning and strategy IP Connectivity verification Performance verification
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
RoHS Compliant Copper Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver for Gigabit Ethernet
 RoHS Compliant Copper Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver for Gigabit Ethernet Features Compatible with specifications for IEEE 802.3ab/Gigabit Ethernet Compliant with MSA specifications for
RoHS Compliant Copper Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver for Gigabit Ethernet Features Compatible with specifications for IEEE 802.3ab/Gigabit Ethernet Compliant with MSA specifications for
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine
 The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Design Verification & Testing Design for Testability and Scan
 Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19
 Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide
 MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 80 Document Version: 1.1 Document Date: July 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
MasterBlaster Serial/USB Communications Cable User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 80 Document Version: 1.1 Document Date: July 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
Section 33. Programming and Diagnostics
 Section 33. Programming and Diagnostics HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 33.1 Introduction... 33-2 33.2 Operation... 33-3 33.3 Interrupts... 33-13 33.4 Operation in
Section 33. Programming and Diagnostics HIGHLIGHTS This section of the manual contains the following topics: 33.1 Introduction... 33-2 33.2 Operation... 33-3 33.3 Interrupts... 33-13 33.4 Operation in
Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure
 Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure Micah Dowty University of Colorado at Boulder [email protected] March 26, 2004 Abstract Traditional software development
Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure Micah Dowty University of Colorado at Boulder [email protected] March 26, 2004 Abstract Traditional software development
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems. 2008 Chapter-1L03: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
PCI Express: The Evolution to 8.0 GT/s. Navraj Nandra, Director of Marketing Mixed-Signal and Analog IP, Synopsys
 PCI Express: The Evolution to 8.0 GT/s Navraj Nandra, Director of Marketing Mixed-Signal and Analog IP, Synopsys PCIe Enterprise Computing Market Transition From Gen2 to Gen3 Total PCIe instances. 2009
PCI Express: The Evolution to 8.0 GT/s Navraj Nandra, Director of Marketing Mixed-Signal and Analog IP, Synopsys PCIe Enterprise Computing Market Transition From Gen2 to Gen3 Total PCIe instances. 2009
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II
 CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
CSE2102 Digital Design II - Topics CSE2102 - Digital Design II 6 - Microprocessor Interfacing - Memory and Peripheral Dr. Tim Ferguson, Monash University. AUSTRALIA. Tel: +61-3-99053227 FAX: +61-3-99053574
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
MorphIO: An I/O Reconfiguration Solution for Altera Devices
 White Paper MorphIO: An I/O Reconfiguration Solution for Altera Devices Introduction Altera developed the MorphIO software to help designers use the I/O reconfiguration feature in Altera devices. It is
White Paper MorphIO: An I/O Reconfiguration Solution for Altera Devices Introduction Altera developed the MorphIO software to help designers use the I/O reconfiguration feature in Altera devices. It is
In-System Programmability
 In-System Programmability in MAX Devices September 2005, ver. 1.5 Application Note 95 Introduction Features & Benefits MAX devices are programmable logic devices (PLDs), based on the Altera Multiple Array
In-System Programmability in MAX Devices September 2005, ver. 1.5 Application Note 95 Introduction Features & Benefits MAX devices are programmable logic devices (PLDs), based on the Altera Multiple Array
C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course. Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia
 C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia Abstract In this paper, the utilization of the C8051F020 in an
C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia Abstract In this paper, the utilization of the C8051F020 in an
Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 0, 12/2013 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4836 Rev. 0, 12/2013 Single Phase Two-Channel Interleaved PFC Operating in CrM Using the MC56F82xxx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by Freescale
USB-Blaster Download Cable User Guide
 USB-Blaster Download Cable User Guide Subscribe UG-USB81204 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Introduction to USB-Blaster Download Cable...1-1 USB-Blaster Revision...1-1
USB-Blaster Download Cable User Guide Subscribe UG-USB81204 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents Introduction to USB-Blaster Download Cable...1-1 USB-Blaster Revision...1-1
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON. SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY. Chapter-1L07: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW. Renesas Technology America Inc.
 SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip
 Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip By Raja Narayanasamy, Product Apps Manager Sr, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is
Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip By Raja Narayanasamy, Product Apps Manager Sr, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops
 Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Tools For Debugging JTAG and Power Issues on DaVinci and OMAP devices. Ning Kang & Dr. Madhav Vij Texas Instruments Software Development Organization
 Tools For Debugging JTAG and Power Issues on DaVinci and OMAP devices Ning Kang & Dr. Madhav Vij Texas Instruments Software Development Organization Agenda JTAG Challenges for Multi-core Devices ICEPick
Tools For Debugging JTAG and Power Issues on DaVinci and OMAP devices Ning Kang & Dr. Madhav Vij Texas Instruments Software Development Organization Agenda JTAG Challenges for Multi-core Devices ICEPick
Web Site: www.parallax.com Forums: forums.parallax.com Sales: [email protected] Technical: [email protected]
 Web Site: www.parallax.com Forums: forums.parallax.com Sales: [email protected] Technical: [email protected] Office: (916) 624-8333 Fax: (916) 624-8003 Sales: (888) 512-1024 Tech Support: (888) 997-8267
Web Site: www.parallax.com Forums: forums.parallax.com Sales: [email protected] Technical: [email protected] Office: (916) 624-8333 Fax: (916) 624-8003 Sales: (888) 512-1024 Tech Support: (888) 997-8267
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs
 Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
Modeling Registers and Counters
 Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
Lab Workbook Introduction When several flip-flops are grouped together, with a common clock, to hold related information the resulting circuit is called a register. Just like flip-flops, registers may
ABB Drives. User s Manual HTL Encoder Interface FEN-31
 ABB Drives User s Manual HTL Encoder Interface FEN-31 HTL Encoder Interface FEN-31 User s Manual 3AUA0000031044 Rev B EN EFFECTIVE: 2010-04-06 2010 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety instructions
ABB Drives User s Manual HTL Encoder Interface FEN-31 HTL Encoder Interface FEN-31 User s Manual 3AUA0000031044 Rev B EN EFFECTIVE: 2010-04-06 2010 ABB Oy. All Rights Reserved. 5 Safety instructions
11. High-Speed Differential Interfaces in Cyclone II Devices
 11. High-Speed Differential Interfaces in Cyclone II Devices CII51011-2.2 Introduction From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) is the
11. High-Speed Differential Interfaces in Cyclone II Devices CII51011-2.2 Introduction From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) is the
