THE ADVANTAGES OF COMBINING LOW PIN COUNT TEST WITH SCAN COMPRESSION OF VLSI TESTING
|
|
|
- Aubrey Clarke
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zbornik radova 56. Konferencije za ETRAN, Zlatibor, juna Proc. 56th ETRAN Conference, Zlatibor, June 11-14, 2012 THE ADVANTAGES OF COMBINING LOW PIN COUNT TEST WITH SCAN COMPRESSION OF VLSI TESTING Dragan Topisirović, Regional center for talents Niš, Niš, Serbia, Abstract Currently produced digital systems are being of exceptionally high performance and demand testing of VLSI or VVLSI (Very-Very Large Scale Integration) circuit at rates of Gbps. In recent years, we are witnessing significantly fast growth of new techniques for testing of VLSI circuits and systems, which give high quality and fast testing times. Testing at Gbps rates is necessary to overcome traditional techniques, which rely extensively an ATE, and the technology improvements in ICs and their high clock rates [1]. This requires radical changes in the organization of the test as well as innovative and practical solutions to the support equipment. These changes have a profound impact on many aspects of the existing test techniques. Low Pin Count Test (LPCT) is a technique which reduces the cost of the test by minimizing the pin requirements of a device when tested on an ATE. When applying LPCT, devices can be easily tested on structural DFT(Design for Testability) testers at high reduced costs, while meeting the low pin count requirements of device and design flow. Combining LPCT with test compression further extends the test capabilities to allow application of all necessary fault models using low-cost testers that are seriously pin-limited. The techniques which are described in this paper represent reduces of test interface and cost of testing and also enable gains in test coverage with less application time and minimal effects on design and test overhead [2]. 1. INTRODUCTION Today's economy and the rising role of new technologies, and expending costs for development of new products, are forcing the electronic industry to reexamine the existing approaches to design and test. For new product, the development of new technological enviroments promises to provide productivity increases and the fastest time to market, while keeping costs under control. Although, testing and debugging of these devices represent very difficult problems; the new economy and modern industry recognizes that the costs of testing are escalating faster than the other costs which are related to the development phase. 1.1 Testing at Gbps rates For example, allowing high transfer rates among channels and functional units, such as in the I/O definition of a SoC, requires readressing the implication of data format and communication within a serial mode. This contains feature into a shell, that physical phenomenon, such as the jitter, which becomes very relevant to tester operation. It is today s focus on all of these issues which make multigigahertz testing a challenging problem in today's test technology. The manufacturing test process for ICs is increasing in cost and effort in order to keep up with rigorous quality standards, complexity of newer designs and process nodes, narrower time-to-market windows, and demand to reduce the test pins. High density, core-based ICs have significant popularity, although the complexity of these chips can slowdown the development and the increase cost, rather than enable high performance and profit margins in manufacturing. DFT engineers are using the advanced fault models to improve the test quality. However, the increasing of test time and volume, which translates into increased cost, is forcing many companies to apply the necessary tests in fewer test cycles and with fewer pins, if possible. Low Pin Count Test (LPCT) is a technique which reduces the cost of the test by minimizing the pin requirements of a device under test, when tested on an ATE. When applying LPCT, devices can be easily tested on structural DFT testers at dramatically reduced costs while meeting the low pin count requirements of the device and the design flow. Combining of LPCT with the test compression further extends the test capabilities to allow application of all necessary fault models using low-cost testers that are seriously pin-limited. The LPCT techniques enable gains in test coverage with less application time and minimal effects on design and test overhead. 1.2 Automated test equipment, ATE Interface The economics of the test, especially in a case of need test equipment in particular, has received a significant attention from many vendors and ATE manufacturers, customers of ATE and the research community at large. The general block scheme of ATE is shown in Fig. 1 [3-4-5]. Computer control of the testing kontrola Timing Test signal processing DC signals Formating Probe and companion electronics Fig.1. Architecture of a electronic tester, ATE The increasing cost of the ATE increases the price of the product. The features, such as multisite organization, architecture arization, and the increased presence of inexpensive testers such as those included in techniques ( - Built In Self Test), are some of the significant developments in recent years. As one possible alternative for speeding up the test application time occurs a combination of and ATE [4]. D U T EL
2 The rigorous quality standards for manufacturing test of ICs, the complexity of newer technology nodes, and narrower time-to-market windows are increasing the cost and the effort to test the manufactured parts. To improve the test quality, the DFT engineers are using advanced fault models, such as transition, path-delay, multiple-detect, bridging, etc., which intention is the catching of the additional defects, which are missed by the conventional stuck-at fault model. There are two areas contributing to the increasing costs: the growing test data volume and the cost of the automatic test equipment (ATE). Each of these advanced fault models requires complex test sets, which are much bigger in size when compared to a conventional stuck-at pattern test set. The growing circuit size and support for other fault models increases the test data volume that has to be stored inside a tester and the test application time, which is directly proportional to the volume of test data shifted into the circuit via scan chains. In order to extend life of the existing testers which are limited in the number of pins they support, a smaller tester interface is needed. This is achieved through reduction of dedicated pins required for test as well as functional pins that must be controlled and observed during test application. Specific test pins include tester scan channels, test control signals such as scan enable, and test clocks. Reducing the test and functional I/O pin interface to the tester, enables the use of cheaper testers that do not support large number of pins. This approach also simplifies design and manufacture of tester heads which can be very costly. 2. THE ECONOMICS OF TEST The cost of an ATE is non-linearly proportional to the number of pins it can support, operating frequency, pin electronics, and memory per pin. As the operating frequency of the devices increases, packages become more complex, the demand for scan memory keeps on rising, and the infrastructure cost to support test increases exponentially, affecting the profit of a product. A purchase price of one tester can be calculated by using the following formula C b ( m x) (1) where C represents the cost, and the representations of the other values can be viewed in Table I. This also requires adding of costs of a tester s life cycle, such as amortization and obsolescence, maintenance, costs of work (energy, replacable components and similar) [5]. Today, many producers of testing devices exist. Depending on configuration one tester of high performance may cost a couple of millions dollar and more [6]. High quality probe and catcher, cost up to half milion dollar. This has forced many companies to move from the fullbandwidth, at-speed functional testing to low-pin-interface structural test. In such cases, the ATE is able to perform structural testing effectively by using a scan for control and observability and internal PLLs for high-frequency clocking, but cannot perform functional testing. To overcome this limitation, sufficient testing must be incorporated into the device to ensure high fault coverage for structural testing and to ensure test quality, so that functional tests can be reduced drastically. One of the common considerations for the Low Pin Count Test (LPCT) is a top-level chip routing, which can cause congestion in ar designs. The applying of the high quality test to each block, using as few as 1 or 2 channels, significantly reduces routing congestion. Other common test techniques for wafer and multi-site testing also benefit greatly from LPCT. Tester and design pin limitations can also limit the number of available pins for the test, thus mandating a low pin count test approach. Possibilities of testers ASIC and μprocessor of high performances Systems with mixed signals TABLE I. THE PRICES OF TESTERS Basic price (b) Price by pin (m) k$ $ Number of pins (x) DfT Tester ASIC and μcontroller of low performances Memory chips RF 200+ ~ LOW PIN COUNT TEST SOLUTIONS The following section describes and summarizes several LPCT methodologies that have been implemented to meet various designs and test requirements. Even in some extreme LPCT applications, such as the 3- pin Tessent TestKompress methodology described in this paper, high data and test time compression ratios greater than 25x have been demonstrated with no impact on the test coverage. When functional pin access is provided by using boundary scan cells, higher test coverage of logic between the scan cells and the top-level pins can be achieved. The focus is on manufacturing test which requires high quality deterministic test patterns which can effectively identify manufacturing defects in silicon. Low Pin Count Testing provides an effective manufacturing test methodology, which means that those devices can be tested with high quality deterministic test patterns and in a cost effective manner. This is achieved by reducing the number of pins which come in contact with the tester during execution of structural test for the device. Various design and test requirements drive the need to reduce the number of pins in the tester interface. This includes scan and test control pins
3 and functional pins, in some cases. Many of the common motivations for LPCT are listed below Design Pin Limitations Corresponding electronics, that is a board for interface with device or circuit under test (DUT-CUT), DIB (Device Interface Board), represents electrical interface between ATE and DUT. There are various form and size of DIB, but their common functions are to provide reliable and uncomplicated separable electrical interface between DUT and electrical instruments of the tester. VLSI testers, that are available on the market, may satisfy different needs. In contrast to PCs, testers have no standard architecture. Every producer of testing equipment is trying to apply some unique performance in order to complete with rival producers. Different producers of testing equipment build their own S/W platform for testing. Moreover, test routines developed for one type of tester frequently are very difficulty to translate for use on other testers because of H/W optimization to testers. Fortunately, the majority of automatic tester has many common functions and features. Beyond the chip-level test interface, LPCT provides a significant value in reducing the chip top level routing and congestion. Today s ar design practices require a reduction to the number of connections between cores and top level pins. LPCT enables application of test data with very few pins while maintaining the ability to apply a high quality deterministic patterns to each core with minimal test interface routed to each I/O pin. Although designs continue to grow in size, package pins have not maintained the same growth rate. In fact, many applications require fewer pins despite the gate count increase. In addition, an increase in the number of required analogue pins is reducing the number of digital pins available for digital test. Similarly, mixed-signal designs with small digital content may have as few as three digital pins, thus greatly complicating scan test. 3.2 Wafer Test application One of the challenges of wafer test application is the number of contacts that the test head must make with each die on the wafer. Each additional contact point results in additional cost due to the required precision and accuracy and the risk of poor contact. There s also potential for damage to the die as a result of each contact. By minimizing the test and functional interface requirements, LPCT addresses these concerns and ensures that yield is not reduced as a result of wafer test. Designs with multiple test access interfaces can be configured with fewer pins for wafer test while still providing a full pin interface for package test. To avoid the one hours work of analyzing all failures, we developed a metodology to correlate electrical failures to particular process steps[7]. In this step, we used metodology that dedicated inline defectivity inspections during fabrication. Comparing the wafer imagines with the layout, we can use a third-party tool to identify abnormalities. 3.3 Multi-site Testing A smaller test interface is required for effective application of the same test patterns to multiple devices in parallel. This technique, called multi-site testing, multiplies the value of scan compression by simultaneous test data application and observation. Low pin count test increases the number of devices that can be tested in parallel, greatly reducing test application time and test cost. Although not limited to wafer test, multi-site testing is most commonly used during wafer test. 3.3 High Quality Test at Board and System Levels A common test methodology for board and system level test is Built-in Self-Test (), shown on Fig.2., which applies pseudorandom patterns to the device and compresses the circuit responses into a signature [6]. Outside NF Test of Equipment Logic Memory Subsystem Fig.2. Architecture of chip with built in self-test. However, some devices may not be suitable for and require in-system test patterns that target specific defect mechanisms deterministically. In order to apply deterministic patterns in system, a low pin count interface such as the standard IEEE 1149.x Test Access Port (TAP) is required. The 4 or 5 pin TAP interface standardized chip-level access across the board and is commonly used to apply tests at board and system test. 3.4 Low Channel Tessent TestKompress For many designs, Tessent TestKompress alone can meet the reduced pin count requirements by reducing the scan interface to the tester. The Tessent TestKompress decompressor (Fig. 3.) is uniquely capable of encoding significant data through very few scan channels, enabling it to achieve high compression of test data and test application time with very few scan channels. Using patented technology, the compactor expands this capability further in the presence of unknown (X) states. In order to reduce pin count in cores or chip level of designs, Tessent TestKompress can apply high quality deterministic test patterns with as few as 1 scan channel. This can greatly simplify top level routing for cores and simplify the tester interface for chip level, wafer, and package tests. Aggressive compression by using only 1 or 2 channels can be achieved with the dramatic results.
4 Fig.3. Tessent TestKompress Architecture For ar designs with several implementations of low channel Tessent TestKompress logic, a significant reduction in top level routing and block interface can be achieved. Additionally, identical blocks can share inputs that broadcast the test stimuli and further reduce test pins. Another key requirement for manufacturing test is effective and accurate diagnosis. Tessent TestKompress patterns can be diagnosed during manufacturing with the same accuracy of uncompressed patterns using Tessent Diagnosis. This enables online diagnosis of failing devices on the manufacturing floor without the need for offline application of bypass patterns. 3.5 Functional Pin Access through TAP A standard scan methodology requires the tester to connect to all device pins in order to apply scan data through the scan I/O, drive values on the functional primary input pins and to observe circuit responses on the functional primary output pins. The basis of ideas that allows the implementation of these requirements is to add cell shift register with each input/output interface components. The structure of the system that was designed to BS concept, it should contain at least four additional connections per PCB or chip, which is related to the signals TDI(Test Data In), TDO(Test data Out), TMS(Test Mode Select) and TCK(Test clock). The topological and functional, these signals must be processed before they lead to very "cells." This set of connections is required and is known as Test Access Port or TAP for short. Of course, as we have seen, the topological and functional, these signals must be processed before they lead to very "cells". When we say topology, we mean the fact that the TDI takes a serial input of BSR, taken as a TDO serial output. On the other hand, however, the TCK(Clock) and TMS are conducted in parallel to each BSC. When we say functional, we mean the fact that on the basis of signals generated by other (Update-DR, for example). For this reason, the TAP complex is accompanied by a digital circuit whose name according to the standard, followed by TAP kontroler. Thus, the TAP controller is a sequential machine with 16 states that, in fact, acts as a protocol for the implementation of testing. Fig.4. Boundary Scan Access to Functional I/O Pins For example, consider this, compared BS concept and consideration in this paper, Fig. 4 depicts the basic configuration for this approach which eliminates the need for the tester to connect to the primary input and output pins directly. In order to enable the use of the TAP controller and facilitate functional pin access through the Boundary Scan Register (BSR), certain modifications are necessary in the BSR. In this test mode, the TAP controller is placed in the Shift-DR (Data Register) state, and the control signals for the boundary scan cells are bypassed. As a result, the signals for shifting and updating data on the boundary scan registers are generated by the tester. In this manner, the boundary scan cells can be fully controlled, regardless of the controller s state. This greatly simplifies manufacture testing by using boundary scan cells since they will act as standard scan cells without continuously manipulating the TAP state machine pin TAP Only Tessent TestKompress This low pin count test strategy utilizes the 4 or 5-pin TAP interface to control all scan hardware as well as the functional I/O pins using the techniques described in the previous section. Fig.5. Design using only TAP port to control Tessent TestKompress and boundary scan logic The ability to test the design deterministically using only the TAP ports makes it possible to test CUT or DUT that the design on board and in system as well as on the ATE.
5 Fig. 5 shows a high-level view of how a single Tessent TestKompress scan channel and boundary scan register are controlled through the TAP ports. The test patterns which are normally applied to the primary I/O of the device can now be compressed as part of the scan patterns stored on the tester. In this configuration, Tessent TestKompress provides a dramatic compression of the test data and the application time, while the TAP interface eliminates the need for functional I/O access. Using this technique on sub-block and/or core applications, large amounts of test data can be delivered to the core in a small amounts of time and with few connections to chip-level pins pin Only Tessent TestKompress Test pattern generation typically requires the test structures and the test control pins which are controlled during the test. Typically, these test control pins such as scan enabler, scan clock and resets are available at the top level for ATPG to control. When running the Tessent TestKompress, two additional test control pins are required (edt_update and edt_clock). In some situations, however, there are fewer than required top level pins that exist for the test purposes. In order to run ATPG, these control signals need to be driven by some internal logic block to ensure that the generated patterns are valid and accurate. The basis of ideas that allows the implementation of these requirements is to add cell shift register with each input/output interface components. BSC are memory elements that are distributed across the edge of the integrated circuit. Primary input signal must pass through a BSC to arrive a system of logic. Also, the signal from the output of the system logic must pass through a BSC to reach the primary outputs, as shown in Figure 6. BS cell has two data inputs, four control inputs and two outputs. At the same input Scan In-TDI and Out-scan output TDO are serial, and when excluding the first and last BS cells, information are transported through the BSR. Other inputs and outputs are parallel. This means, for example, that the control signals CLK A, Test mode select, Shift / Load and CLK B common for all BS cells. The requirements for using only 3 digital pins (scan in, scan out, clock) with the Tessent Test Kompress are to maintain high compression, provide an X tolerant solution, maintain the same high stuck-at and transition fault coverage, and maintain diagnosis capability of compressed patterns. The appearance of a BSC is shown in Fig. 6. All of these requirements can be met using a test controller that generates all necessary signals internally. Mod Signal In Shift/Load Scan In CLK A Scan Out D Q D Q CLK B Fig.6. Boundary scan cell Signal Out The original hardware implementation for the 3-pin test controller was done as a custom block, which addressed the stated requirements while reducing test application time and test data volume by 25x. The test controller implementation flow is now being fully automated in the Tessent TestKompress and will be generated as a part of the standard logic when specified by the user. 4. CONCLUSION Research results shown are related to the problem of testing and diagnosis of digital electronic circuits. Problems related to short transition times were discussed first. Then impact on testing technology was considered including the ATE performance for different types of circuits under test. Accordingly, new design architectures were discussed enabling design for testability with low pin count testing is an effective solution for reducing structural costs in the IC manufacturing environment. By combining LPCT with test compression, extend the capabilities of manufacturing testing to allow application of at-speed test patterns using low-cost testers which are very pin-limited. Using the Tessent TestKompress with LPCT enables improvements in test coverage and application time with minimal impact on design and test overhead. REFERENCES [1] D. Topisirović, Advances in VLSI Testing at MultiGb per Second Rates, Serbian Journal of Electrical Engineering, Volume 2, No. 1, May 2005., pp [2] Silicon Test & Yield Analysis: Combining Low Pin Count Test with Scan Compression, february 2010., [3] V. B. Litovski, "CAD of electronic circuits, DIGP Nova Jugoslavija, Vranje, 2000 [4] Mark Baker, "Demystifying Mixed- Signal Test Methods", An imprint of Elsevier Science, USA, [5] Vančo B. Litovski, Osnovi testiranja elektronskih kola, Printed by Unigraf Niš, [6] Mark Burns, Gordon W. Roberts, "An Introduction to Mixed-Signal IC Test and Measurement", Oxford University Press, New York, [7] C. Hora et al., An Effective Diagnosis Method to Support Yield Improvment Proc. int l Test Conf. (ITC 03), IEEE, Press, 2002, pp
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
JTAG Applications. Product Life-Cycle Support. Software Debug. Integration & Test. Figure 1. Product Life Cycle Support
 JTAG Applications While it is obvious that JTAG based testing can be used in the production phase of a product, new developments and applications of the IEEE-1149.1 standard have enabled the use of JTAG
JTAG Applications While it is obvious that JTAG based testing can be used in the production phase of a product, new developments and applications of the IEEE-1149.1 standard have enabled the use of JTAG
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990
 Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990 ABSTRACT Mechanical and chemical process challenges initially limited acceptance of surface mount technology (SMT). As those challenges
Non-Contact Test Access for Surface Mount Technology IEEE 1149.1-1990 ABSTRACT Mechanical and chemical process challenges initially limited acceptance of surface mount technology (SMT). As those challenges
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course. Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
Introduction to VLSI Testing 李 昆 忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Introduction to VLSI Testing.1 Problems to Think A 32 bit adder A
The Boundary Scan Test (BST) technology
 The Boundary Scan Test () technology J. M. Martins Ferreira FEUP / DEEC - Rua Dr. Roberto Frias 42-537 Porto - PORTUGAL Tel. 35 225 8 748 / Fax: 35 225 8 443 ([email protected] / http://www.fe.up.pt/~jmf) Objectives
The Boundary Scan Test () technology J. M. Martins Ferreira FEUP / DEEC - Rua Dr. Roberto Frias 42-537 Porto - PORTUGAL Tel. 35 225 8 748 / Fax: 35 225 8 443 ([email protected] / http://www.fe.up.pt/~jmf) Objectives
Objective. Testing Principle. Types of Testing. Characterization Test. Verification Testing. VLSI Design Verification and Testing.
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Objective VLSI Testing Mohammad Tehranipoor Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Need to understand Types of tests performed at different stages
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Objective VLSI Testing Mohammad Tehranipoor Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Need to understand Types of tests performed at different stages
Figure 1 FPGA Growth and Usage Trends
 White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
TABLE OF CONTENTS. xiii List of Tables. xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules. xix Preface to the First Edition. xxi Preface to the Second Edition
 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures xiii List of Tables xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules xix Preface to the First Edition xxi Preface to the Second Edition xxiii Acknowledgement xxv 1 Boundary-Scan Basics
TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures xiii List of Tables xviii List of Design-for-Test Rules xix Preface to the First Edition xxi Preface to the Second Edition xxiii Acknowledgement xxv 1 Boundary-Scan Basics
A New Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications
 Vol. 6, o., April, 011 A ew Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications Jee-Youl Ryu 1, Sung-Woo Kim 1, Jung-Hun Lee 1, Seung-Hun Park 1, and Deock-Ho Ha 1 1 Dept. of Information and Communications
Vol. 6, o., April, 011 A ew Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications Jee-Youl Ryu 1, Sung-Woo Kim 1, Jung-Hun Lee 1, Seung-Hun Park 1, and Deock-Ho Ha 1 1 Dept. of Information and Communications
Implementation Details
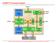 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
In-System Programming Design TM. Guidelines for ispjtag Devices. Introduction. Device-specific Connections. isplsi 1000EA Family.
 In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
Encounter DFT Architect
 Full-chip, synthesis-based, power-aware test architecture development Cadence Encounter DFT Architect addresses and optimizes multiple design and manufacturing objectives such as timing, area, wiring,
Full-chip, synthesis-based, power-aware test architecture development Cadence Encounter DFT Architect addresses and optimizes multiple design and manufacturing objectives such as timing, area, wiring,
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
Design Verification & Testing Design for Testability and Scan
 Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview esign for testability (FT) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit Reduce the cost and time associated with test development Reduce the execution time of performing
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1 9NJ, UK. *[email protected]
 Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
Serial Wire Debug and the CoreSight TM Debug and Trace Architecture Eddie Ashfield, Ian Field, Peter Harrod *, Sean Houlihane, William Orme and Sheldon Woodhouse ARM Ltd 110 Fulbourn Road, Cambridge, CB1
FPGA Prototyping Primer
 FPGA Prototyping Primer S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com What is FPGA prototyping? FPGA prototyping is the methodology
FPGA Prototyping Primer S2C Inc. 1735 Technology Drive, Suite 620 San Jose, CA 95110, USA Tel: +1 408 213 8818 Fax: +1 408 213 8821 www.s2cinc.com What is FPGA prototyping? FPGA prototyping is the methodology
G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo. Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip
 G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip December 2005 Preface Fast innovation in VLSI technologies makes possible the integration a complete system into a single chip (System-on-Chip,
G. Squillero, M. Rebaudengo Test Techniques for Systems-on-a-Chip December 2005 Preface Fast innovation in VLSI technologies makes possible the integration a complete system into a single chip (System-on-Chip,
Test Resource Partitioning and Reduced Pin-Count Testing Based on Test Data Compression
 Test esource Partitioning and educed Pin-Count Testing Based on Test Data Compression nshuman Chandra and Krishnendu Chakrabarty Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University, Durham,
Test esource Partitioning and educed Pin-Count Testing Based on Test Data Compression nshuman Chandra and Krishnendu Chakrabarty Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University, Durham,
PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes
 nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
AEHR TEST SYSTEMS. Worldwide Leader in Burn-in and Test Equipment
 AEHR TEST SYSTEMS Worldwide Leader in Burn-in and Test Equipment MB Electronique www.mbelectronique.com What is Burn-in? Burn-in is the process of stressing and exercising electrical devices to ensure
AEHR TEST SYSTEMS Worldwide Leader in Burn-in and Test Equipment MB Electronique www.mbelectronique.com What is Burn-in? Burn-in is the process of stressing and exercising electrical devices to ensure
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip
 Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip By Raja Narayanasamy, Product Apps Manager Sr, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is
Designing an efficient Programmable Logic Controller using Programmable System On Chip By Raja Narayanasamy, Product Apps Manager Sr, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is
Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production
 Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production Hogeschool van Arnhem en Nijmegen 6 June 23 Rob Staals JTAG Technologies [email protected] Copyright 23, JTAG Technologies juni 3 The importance
Testing and Programming PCBA s during Design and in Production Hogeschool van Arnhem en Nijmegen 6 June 23 Rob Staals JTAG Technologies [email protected] Copyright 23, JTAG Technologies juni 3 The importance
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Digital Circuit Design
 Test and Diagnosis of of ICs Fault coverage (%) 95 9 85 8 75 7 65 97.92 SSL 4,246 Shawn Blanton Professor Department of ECE Center for Silicon System Implementation CMU Laboratory for Integrated Systems
Test and Diagnosis of of ICs Fault coverage (%) 95 9 85 8 75 7 65 97.92 SSL 4,246 Shawn Blanton Professor Department of ECE Center for Silicon System Implementation CMU Laboratory for Integrated Systems
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
These help quantify the quality of a design from different perspectives: Cost Functionality Robustness Performance Energy consumption
 Basic Properties of a Digital Design These help quantify the quality of a design from different perspectives: Cost Functionality Robustness Performance Energy consumption Which of these criteria is important
Basic Properties of a Digital Design These help quantify the quality of a design from different perspectives: Cost Functionality Robustness Performance Energy consumption Which of these criteria is important
Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines
 Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines Mircea Popa Abstract: The paper approaches the problem of control and selecting possibilities offered by the PC parallel
Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines Mircea Popa Abstract: The paper approaches the problem of control and selecting possibilities offered by the PC parallel
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs
 Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs Today s mobile communications systems demand higher communication quality, higher data rates, higher operation, and more channels per unit bandwidth.
Optimizing VCO PLL Evaluations & PLL Synthesizer Designs Today s mobile communications systems demand higher communication quality, higher data rates, higher operation, and more channels per unit bandwidth.
Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service. Industrial Ethernet: The key advantages of SERCOS III
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service profile Drive & Control Industrial Ethernet: The key advantages of SERCOS III SERCOS III is the open,
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service profile Drive & Control Industrial Ethernet: The key advantages of SERCOS III SERCOS III is the open,
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops
 Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
Sequential Logic Design Principles.Latches and Flip-Flops Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Bistable Elements Latches and Flip-Flops S-R Latch
The Evolution of ICT: PCB Technologies, Test Philosophies, and Manufacturing Business Models Are Driving In-Circuit Test Evolution and Innovations
 The Evolution of ICT: PCB Technologies, Test Philosophies, and Manufacturing Business Models Are Driving In-Circuit Test Evolution and Innovations Alan J. Albee Teradyne Inc. North Reading, Massachusetts
The Evolution of ICT: PCB Technologies, Test Philosophies, and Manufacturing Business Models Are Driving In-Circuit Test Evolution and Innovations Alan J. Albee Teradyne Inc. North Reading, Massachusetts
SuperIOr Controller. Digital Dynamics, Inc., 2014 All Rights Reserved. Patent Pending. Rev: 5-16-14 1
 SuperIOr Controller The SuperIOr Controller is a game changer in the world of high speed embedded control. The system combines incredible speed of both control and communication with revolutionary configurable
SuperIOr Controller The SuperIOr Controller is a game changer in the world of high speed embedded control. The system combines incredible speed of both control and communication with revolutionary configurable
High-Speed SERDES Interfaces In High Value FPGAs
 High-Speed SERDES Interfaces In High Value FPGAs February 2009 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 High-Speed SERDES
High-Speed SERDES Interfaces In High Value FPGAs February 2009 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 High-Speed SERDES
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs
 Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs AN-628-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the Agilent 3070 test system to achieve faster programming
Using the Agilent 3070 Tester for In-System Programming in Altera CPLDs AN-628-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the Agilent 3070 test system to achieve faster programming
DEDICATED TO EMBEDDED SOLUTIONS
 DEDICATED TO EMBEDDED SOLUTIONS RELIABILITY IN SUBSEA ELECTRONICS TECHNIQUES TO OBTAIN HIGH RELIABILITY STIG-HELGE LARSEN KARSTEN KLEPPE DATA RESPONS 2012-10-16 AGENDA Introduction Analysis and Design
DEDICATED TO EMBEDDED SOLUTIONS RELIABILITY IN SUBSEA ELECTRONICS TECHNIQUES TO OBTAIN HIGH RELIABILITY STIG-HELGE LARSEN KARSTEN KLEPPE DATA RESPONS 2012-10-16 AGENDA Introduction Analysis and Design
Designing VM2 Application Boards
 Designing VM2 Application Boards This document lists some things to consider when designing a custom application board for the VM2 embedded controller. It is intended to complement the VM2 Datasheet. A
Designing VM2 Application Boards This document lists some things to consider when designing a custom application board for the VM2 embedded controller. It is intended to complement the VM2 Datasheet. A
Design Considerations for DVT and Manufacturing Test of Wireless Devices
 WHITEPAPER Design Considerations for DVT and Manufacturing Test of Wireless Devices 2015 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Introduction Wireless devices are being deployed for a wide
WHITEPAPER Design Considerations for DVT and Manufacturing Test of Wireless Devices 2015 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Introduction Wireless devices are being deployed for a wide
Jitter Transfer Functions in Minutes
 Jitter Transfer Functions in Minutes In this paper, we use the SV1C Personalized SerDes Tester to rapidly develop and execute PLL Jitter transfer function measurements. We leverage the integrated nature
Jitter Transfer Functions in Minutes In this paper, we use the SV1C Personalized SerDes Tester to rapidly develop and execute PLL Jitter transfer function measurements. We leverage the integrated nature
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
DC to 30GHz Broadband MMIC Low-Power Amplifier
 DC to 30GHz Broadband MMIC Low-Power Amplifier Features Integrated LFX technology: Simplified low-cost assembly Drain bias inductor not required Broadband 45GHz performance: Good gain (10 ± 1.25dB) 14.5dBm
DC to 30GHz Broadband MMIC Low-Power Amplifier Features Integrated LFX technology: Simplified low-cost assembly Drain bias inductor not required Broadband 45GHz performance: Good gain (10 ± 1.25dB) 14.5dBm
Hardware Trojans Detection Methods Julien FRANCQ
 DEFENDING WORLD SECURITY Hardware Trojans Detection Methods Julien FRANCQ 2013, December the 12th Outline c 2013 CASSIDIAN CYBERSECURITY - All rights reserved TRUDEVICE 2013, December the 12th Page 2 /
DEFENDING WORLD SECURITY Hardware Trojans Detection Methods Julien FRANCQ 2013, December the 12th Outline c 2013 CASSIDIAN CYBERSECURITY - All rights reserved TRUDEVICE 2013, December the 12th Page 2 /
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Switched Interconnect for System-on-a-Chip Designs
 witched Interconnect for ystem-on-a-chip Designs Abstract Daniel iklund and Dake Liu Dept. of Physics and Measurement Technology Linköping University -581 83 Linköping {danwi,dake}@ifm.liu.se ith the increased
witched Interconnect for ystem-on-a-chip Designs Abstract Daniel iklund and Dake Liu Dept. of Physics and Measurement Technology Linköping University -581 83 Linköping {danwi,dake}@ifm.liu.se ith the increased
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330. Microcontrollers
 Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
1.Introduction. Introduction. Most of slides come from Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by Michael Quirk and Julian Serda.
 .Introduction If the automobile had followed the same development cycle as the computer, a Rolls- Royce would today cost $00, get one million miles to the gallon and explode once a year Most of slides
.Introduction If the automobile had followed the same development cycle as the computer, a Rolls- Royce would today cost $00, get one million miles to the gallon and explode once a year Most of slides
Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source
 Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source PCI Express () is a serial point-to-point interconnect standard developed by the Component Interconnect Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). lthough originally
Selecting the Optimum PCI Express Clock Source PCI Express () is a serial point-to-point interconnect standard developed by the Component Interconnect Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). lthough originally
ESP-CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation
 Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths
 An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
Simplifying System Design Using the CS4350 PLL DAC
 Simplifying System Design Using the CS4350 PLL 1. INTRODUCTION Typical Digital to Analog Converters (s) require a high-speed Master Clock to clock their digital filters and modulators, as well as some
Simplifying System Design Using the CS4350 PLL 1. INTRODUCTION Typical Digital to Analog Converters (s) require a high-speed Master Clock to clock their digital filters and modulators, as well as some
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology
 Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Abstract. Cycle Domain Simulator for Phase-Locked Loops
 Abstract Cycle Domain Simulator for Phase-Locked Loops Norman James December 1999 As computers become faster and more complex, clock synthesis becomes critical. Due to the relatively slower bus clocks
Abstract Cycle Domain Simulator for Phase-Locked Loops Norman James December 1999 As computers become faster and more complex, clock synthesis becomes critical. Due to the relatively slower bus clocks
VECTORAL IMAGING THE NEW DIRECTION IN AUTOMATED OPTICAL INSPECTION
 VECTORAL IMAGING THE NEW DIRECTION IN AUTOMATED OPTICAL INSPECTION Mark J. Norris Vision Inspection Technology, LLC Haverhill, MA [email protected] ABSTRACT Traditional methods of identifying and
VECTORAL IMAGING THE NEW DIRECTION IN AUTOMATED OPTICAL INSPECTION Mark J. Norris Vision Inspection Technology, LLC Haverhill, MA [email protected] ABSTRACT Traditional methods of identifying and
What s New in 2013. Mike Bailey LabVIEW Technical Evangelist. uk.ni.com
 What s New in 2013 Mike Bailey LabVIEW Technical Evangelist Building High-Performance Test, Measurement and Control Systems Using PXImc Jeremy Twaits Regional Marketing Engineer Automated Test & RF National
What s New in 2013 Mike Bailey LabVIEW Technical Evangelist Building High-Performance Test, Measurement and Control Systems Using PXImc Jeremy Twaits Regional Marketing Engineer Automated Test & RF National
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
Evaluating AC Current Sensor Options for Power Delivery Systems
 Evaluating AC Current Sensor Options for Power Delivery Systems State-of-the-art isolated ac current sensors based on CMOS technology can increase efficiency, performance and reliability compared to legacy
Evaluating AC Current Sensor Options for Power Delivery Systems State-of-the-art isolated ac current sensors based on CMOS technology can increase efficiency, performance and reliability compared to legacy
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs
 Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
Debug and Trace for Multicore SoCs How to build an efficient and effective debug and trace system for complex, multicore SoCs William Orme September 2008 Abstract As SoC designs become ever more complex
PARALLELS CLOUD STORAGE
 PARALLELS CLOUD STORAGE Performance Benchmark Results 1 Table of Contents Executive Summary... Error! Bookmark not defined. Architecture Overview... 3 Key Features... 5 No Special Hardware Requirements...
PARALLELS CLOUD STORAGE Performance Benchmark Results 1 Table of Contents Executive Summary... Error! Bookmark not defined. Architecture Overview... 3 Key Features... 5 No Special Hardware Requirements...
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING - Microprocessor Systems - Mitchell Aaron Thornton
 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS Mitchell Aaron Thornton, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Mississippi State University, PO Box 9571, Mississippi State, MS, 39762-9571, United States. Keywords:
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS Mitchell Aaron Thornton, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Mississippi State University, PO Box 9571, Mississippi State, MS, 39762-9571, United States. Keywords:
ATE for Manufacturing Test. Major ATE Companies: Teradyne, Credence, Agilent, Advantest, NPTest... Agilent 83K. Advantest T6682
 ATE for Manufacturing Test Major ATE Companies: Teradyne, Credence, Agilent, Advantest, NPTest... Agilent 83K Advantest T6682 1 Block Diagram for T6682 Block diagram for Advantest Model T6682 described
ATE for Manufacturing Test Major ATE Companies: Teradyne, Credence, Agilent, Advantest, NPTest... Agilent 83K Advantest T6682 1 Block Diagram for T6682 Block diagram for Advantest Model T6682 described
Maximizing UPS Availability
 Maximizing UPS Availability A comparative assessment of UPS designs and deployment configurations for the highavailability data center By Chris Loeffler Product Manager, BladeUPS & Data Center Applications
Maximizing UPS Availability A comparative assessment of UPS designs and deployment configurations for the highavailability data center By Chris Loeffler Product Manager, BladeUPS & Data Center Applications
A network is a group of devices (Nodes) connected by media links. A node can be a computer, printer or any other device capable of sending and
 NETWORK By Bhupendra Ratha, Lecturer School of Library and Information Science Devi Ahilya University, Indore Email: [email protected] Network A network is a group of devices (Nodes) connected by media
NETWORK By Bhupendra Ratha, Lecturer School of Library and Information Science Devi Ahilya University, Indore Email: [email protected] Network A network is a group of devices (Nodes) connected by media
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL
 FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
A NEW TEST STRATEGY FOR COMPLEX PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD ASSEMBLIES
 A NEW TEST STRATEGY FOR COMPLEX PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD ASSEMBLIES Stig Oresjo Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction The trend in Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) technology is towards higher complexity.
A NEW TEST STRATEGY FOR COMPLEX PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD ASSEMBLIES Stig Oresjo Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction The trend in Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) technology is towards higher complexity.
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Wafer Level Testing Challenges for Flip Chip and Wafer Level Packages
 Wafer Level Testing Challenges for Flip Chip and Wafer Level Packages by Lim Kok Hwa and Andy Chee STATS ChipPAC Ltd. 5 Yishun Street 23, Singapore 768442 [email protected]; [email protected]
Wafer Level Testing Challenges for Flip Chip and Wafer Level Packages by Lim Kok Hwa and Andy Chee STATS ChipPAC Ltd. 5 Yishun Street 23, Singapore 768442 [email protected]; [email protected]
VON BRAUN LABS. Issue #1 WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS VON BRAUN LABS. State Machine Technology
 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
PLC Based Liquid Filling and Mixing
 PLC Based Liquid Filling and Mixing 1 Mihir Panchal, 2 Aashish Panaskar. 3 Prof. Lalit Kumar KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: The objective of this paper is to design,
PLC Based Liquid Filling and Mixing 1 Mihir Panchal, 2 Aashish Panaskar. 3 Prof. Lalit Kumar KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: The objective of this paper is to design,
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture
 An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
An Introduction to the ARM 7 Architecture Trevor Martin CEng, MIEE Technical Director This article gives an overview of the ARM 7 architecture and a description of its major features for a developer new
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
Latch Timing Parameters. Flip-flop Timing Parameters. Typical Clock System. Clocking Overhead
 Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card)
 Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card) ISO 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, managed jointly by
Measurement and Analysis Introduction of ISO7816 (Smart Card) ISO 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, managed jointly by
AND8336. Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators. Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor. http://onsemi.
 Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Balun Parameter Definitions & Measurement May 2004
 Balun Parameter Definitions & Measurement May 2004 Differential circuits are becoming more widely used in RF circuits for the same reason that they have been used for years in lower frequency circuits.
Balun Parameter Definitions & Measurement May 2004 Differential circuits are becoming more widely used in RF circuits for the same reason that they have been used for years in lower frequency circuits.
MOSFET TECHNOLOGY ADVANCES DC-DC CONVERTER EFFICIENCY FOR PROCESSOR POWER
 MOSFET TECHNOLOGY ADVANCES DC-DC CONVERTER EFFICIENCY FOR PROCESSOR POWER Naresh Thapar, R.Sodhi, K.Dierberger, G.Stojcic, C.Blake, and D.Kinzer International Rectifier Corporation El Segundo, CA 90245.
MOSFET TECHNOLOGY ADVANCES DC-DC CONVERTER EFFICIENCY FOR PROCESSOR POWER Naresh Thapar, R.Sodhi, K.Dierberger, G.Stojcic, C.Blake, and D.Kinzer International Rectifier Corporation El Segundo, CA 90245.
SPI Flash Programming and Hardware Interfacing Using ispvm System
 March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
March 2005 Introduction Technical Note TN1081 SRAM-based FPGA devices are volatile and require reconfiguration after power cycles. This requires external configuration data to be held in a non-volatile
Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban. Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering
 Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering 11-11-2014 2 zero-defect quality impossible to produce zero-defect boards early involvement services (Design
Extended Boundary Scan Test breaching the analog ban Marcel Swinnen, teamleader test engineering 11-11-2014 2 zero-defect quality impossible to produce zero-defect boards early involvement services (Design
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Any-Rate Precision Clocks
 Any-Rate Precision Clocks Wireline Market Overview Analog Modems Large installed base and growth in embedded applications Voice Transition to VoIP to reduce service provider cost-of-ownership Timing Large,
Any-Rate Precision Clocks Wireline Market Overview Analog Modems Large installed base and growth in embedded applications Voice Transition to VoIP to reduce service provider cost-of-ownership Timing Large,
Chapter 10. Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing
 Chapter 10 Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch. 10 - Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 1 1 Outline Introduction Digital Boundary Scan (1149.1) Boundary
Chapter 10 Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch. 10 - Boundary Scan and Core-Based Testing - P. 1 1 Outline Introduction Digital Boundary Scan (1149.1) Boundary
