Basic concepts of molecular biology and proteins I
|
|
|
- Cassandra Clarke
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basic concepts of molecular biology and proteins I
2 PROTEINS A large molecule composed of one or more chains of amino acids in a specific order; the order is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene coding for the protein. Proteins are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body s cells, tissues, and organs, and each protein has unique functions. Examples are hormones, enzymes, and antibodies.
3
4
5
6
7 A peptide bond. This covalent bond forms when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom (blue) from the amino group of a second amino acid. As indicated, a molecule of water is lost in this condensation reaction
8 Proteins are built up by amino acids that are linked by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. (a) Schematic diagram of an amino acid, A central carbon atom (Ca) is attached to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen atom (H), and a side chain (R). (b) In a polypeptide chain the carboxyl group of amino acid n has formed a peptide bond, C-N, to the amino group of amino acid n + 1. One water molecule is eliminated in this process. The repeating units, which are called residues, are divided into main-chain atoms and side chains. The main-chain part, which is identical in all residues, contains a central Ca atom attached to an NH group, a C'=O group, and an H atom. The side chain R, which is different for different residues, is bound to the Ca atom.
9
10 Condensation rxn (a water is lost) Opposite is hydrolysis rxn (a water is added)
11 Let us consider a macromolecule composed of n structural units along the backbone Ri= position vector for i Ri= Rxi Ryi Rzi { C i } = ith conformation { C } = { R1, R2, R3,..., Rn-1, Rn} Schematic representation of a chain of n backbone units. Bonds are labeled from 2 to n, and structural units from 1 to n. The location of the ith unit with respect to the laboratory-fixed frame OXYZ is indicated by the position vector Ri. R1 and R3 are explicitly shown.
12 Diagram showing a polypeptide chain where the main-chain atoms are represented as rigid peptide units, linked through the Ca atoms. Each unit has two degrees of freedom; it can rotate around two bonds, its Ca-C' bond and its N- Ca bond. The angle of rotation around the N-Ca bond is called phi (f) and that around the Ca- C' bond is called psi (y). The conformation of the main-chain atoms is therefore determined by the values of these two angles for each amino acid.
13 Looking down the H-Ca bond from the hydrogen atom, the L-form has CO, R and N substituents from Ca going from a clockwise direction (CORN)
14 Chiral molecules (except Gly)
15
16 Let us consider a macromolecule composed of n structural units along the backbone Ri= position vector for i Ri= Rxi Ryi Rzi { C i } = ith conformation { C } = { R1, R2, R3,..., Rn-1, Rn} Schematic representation of a chain of n backbone units. Bonds are labeled from 2 to n, and structural units from 1 to n. The location of the ith unit with respect to the laboratory-fixed frame OXYZ is indicated by the position vector Ri. R1 and R3 are explicitly shown.
17 { C } = { R1, R2, R3,..., Rn-1, Rn} If you know these variables, then you know the structure (3n variables since { Ri} = { Rix, Riy, Riz} Change of varaibles from R to internal coordinates
18 Can be used for representing the conformation of a protein
19
20 Schematic representation of a portion of the main chain of a macromolecule. l i is the bond vector between units i-1 and i, as shown. ϕ i denotes the torsional angle about bond i.
21 Spatial representation of the torsional mobility around the bond i+1. The torsional angle ϕi+1 of bond i+1 determines the position of the atom Ci+2 relative to Ci-1. C'i+2 and C"i+2 represent the locations of the atom i+2, when ϕi assumes the respective values 180 and 0, characteristic of the trans and cis rotameric states.
22 GENERALIZED COORDINATES FOR DEFINING THE INTERNAL CONFORMATION If you eliminate translation and rotation => 3(n-2) variables will be left li = ri - ri-1 is the bond vector connecting the units i-1 and i, pointing from i-1 to i An alternative representation, change of coordinate system: ri is the position vector in the new frame. r1= 0 (removes translational degrees of freedom) if you choose the first bond along x axis, You remove the rotational degrees of freedom y2=z2=z3=0
23 The remaining 3n-6 coordinates { x2,x3,y3,x4,y4,z4,... xn,yn,zn } define the internal configuration of the molecule The position of the ith unit with respect to original frame can be expressed in terms of the internal position vectors ri as T1 is the transformation matrix for the passage from the frame O1X1Y1Z1 into the laboratory-fixed frame OXYZ. (first atom is used as a reference)
24 Note: cis vs trans state: Not all torsional angles are equally probable Some torsional angles, referred to as rotational isomeric states (RIS), are more frequent than others, these being favored by the intrinsic torsional energies of the particular bonds. Rotational energy as a function of dihedral angle for a threefold symmetric torsional potential (dashed curve) and a three-state potential with a preference for the trans isomer (ϕ = 180 ) over the gauche isomers (60 and 300 ) (solid curve), and the cis (0 ) state being most unfavorable.
25 Trans (180) gauche- (60) gauche+ (300) Cis (0, 360) Rotational isomeric states for the central bond in a segment of four backbone atoms. Large blue spheres show backbone atoms. They are indexed from 1 to 4. The small spheres show side groups; they are labeled by the indices of the backbone atoms to which they are affixed (with a prime sign).
26 The staggered conformations are the most energetically favored conformations of two tetrahedrally coordinated carbon atoms. (a) A view along the C-C bond in ethane (CH 3 CH 3 ) showing how the two carbon atoms can rotate so that their hydrogen atoms are either not staggered (aligned) or staggered.three indistinguishable staggered conformations are obtained by a rotation of 120 degrees around the C-C bond. (b-d) Similar views as in (a) of valine. The three staggered conformations are different for valine because the three groups attached to C β are different. The first staggered conformation (b) is less crowded and energetically most favored because the two methyl groups bound to C b are both close to the small H atom bound to C a.
27 360 Psi 0 0 phi 360 Ramachandran plots showing allowed combinations of the conformational angles phi and psi Psi Psi phi phi 360
28
29 Proteins may assume infinitely many conformations. Fixed bond lengths (l) Fixed bond angles (θ) Variable torsional angles (φ) 0º < φ < 360º 0º < θ < 180º But just one of them is the native (tertiary structure) This process is almost reversible (native <-> non-native)
30 Back to the protein science from protein structure Refolding of a denatured protein.
31
32 Non-covalent bonds C-C bond has an energy of 83 kcal/mol E N...H-O (a water is lost) O...H-N Each has an energy of 5 kcal/mol Although they are very weak, many of them form to create a strong bonding arrangement KK
33
34 Disulfide bonds. This diagram illustrates how covalent disulfide bonds form between adjacent cysteine side chains. As indicated, these cross-linkages can join either two parts of the same polypeptide chain or two different polypeptide chains. Since the energy required to break one covalent bond is much larger than the energy required to break even a whole set of noncovalent bonds, a disulfide bond can have a major stabilizing effect on a protein. Small proteins need more S-S bonds
35 The disulfide is usually the end product of air oxidation according to the following schematic reaction scheme: 2 -CH 2 SH + 1/2 O 2 ï -CH 2 -S-S-CH 2 + H 2 O
36 The binding of a protein to another molecule is highly selective. Many weak bonds are needed to enable a protein to bind tightly to a second molecule (a ligand). The ligand must therefore fit precisely into the protein's binding site, like a hand into a glove, so that a large number of noncovalent bonds can be formed between the protein and the ligand
37 Interior of proteins is hydrophobic Hydrophobic core Hydrophilic surface Proteins have alpha helices and beta- sheets as their secondary structures
38 Secondary structures: α-helices n th n th n+4 th n+4 th Mostly right-handed in proteins Linus Pauling (1951) first desciribed them Phi and psi angles are and consecutively H bonds between the C=O of residue n and NH of residue n+4. ~10 residues long (4-to-more than 40 residues)
39 All the H bonds point in the same direction So helices have dipoles Negatively charged groups such as phosphate ions frequently bind to the amino ends of a helices. The dipole moment of an a helix as well as the possibility of hydrogen-bonding to free NH groups at the end of the helix favors binding.
40 Some amino acids are favored in helices: Ala, Glu, Leu, and Met Pro, Gly, Tyr, and Ser are very unfavored
41 The helical wheel or spiral 3.6 amino acids per turn, so the angle between two consecutive aa is 100 0
42 Secondary structures: β-sheets Proteins formed by strands are rigid
43 5-to-10 residues long Residues are fully extended Phi and psi are range in the upper left quadrant
44 Two types of beta sheet structures. (A) Antiparallel beta sheet (B) Parallel beta sheet. Both of these structures are common. The structure of a coiled-coil. Amphipathic: one side hydrophilic other side hydrophobic
45 A collection of protein molecules, selected to show a range of sizes and shapes. Each protein is shown as a space-filling model, represented at the same scale.
46 Collagen and elastin. (A) Collagen is a triple helix formed by three extended protein chains that wrap around one another. Many rodlike collagen molecules are cross-linked together in the extracellular space to form unextendable collagen fibrils (top) that have the tensile strength of steel. The striping on the collagen fibril is caused by the regular repeating arrangement of the collagen molecules within the fibril. (B) Elastin polypeptide chains are cross-linked together to form rubberlike, elastic fibers. Each elastin molecule uncoils into a more extended conformation when the fiber is stretched and will recoil spontaneously as soon as the stretching force is relaxed.
47 HW1: The coordinates of a polypeptide with the following sequence are provided as follows: ATOM 1 N THR N ATOM 2 CA THR C ATOM 3 C THR C ATOM 8 N VAL N ATOM 9 CA VAL C ATOM 10 C VAL C ATOM 15 N ALA N ATOM 16 CA ALA C ATOM 17 C ALA C ATOM 20 N TYR N ATOM 21 CA TYR C ATOM 22 C TYR C ATOM 32 N ILE N ATOM 33 CA ILE C ATOM 34 C ILE C ATOM 40 N ALA N ATOM 41 CA ALA C ATOM 42 C ALA C ATOM 45 N ILE N ATOM 46 CA ILE C ATOM 47 C ILE C ATOM 53 N AGLY N ATOM 55 CA AGLY C ATOM 57 C AGLY C ATOM 61 N ASER N ATOM 63 CA ASER C ATOM 65 C ASER C ATOM 73 N AASN N ATOM 75 CA AASN C ATOM 77 C AASN C
48 Ignore the fisrt two columns, third column gives the type of the atom of the backbone chain. The fourth column gives the residue type, fifth column lists the residue numbers, the sixth-to to-eighth columns gives the x, y,z of the atom. Calculate the phi, psi and omega angles of one of the residues. Theta angle of that residue and the bond vectors. Dou you think your residue is a part of a helix, a beta strand or a loop, (refer to the ramachandran map)
49 Summary Protein interiors are hydrophobic Proteins are made of secondary structures Secondary structure elements are connected to form simple motifs Protein molecules are organized in a structural hierarchy Large polypeptide chains fold into several domains
50 Two a helices that are connected by a short loop region in a specific geometric arrangement constitute a helix-turn-helix motif. Two such motifs are shown: the DNA-binding motif (a), which is further discussed in Chapter 8, and the calcium-binding motif (b), which is present in many proteins whose function is regulated by calcium.
51 Schematic diagrams of the calcium-binding motif.
52
53 The hairpin motif is very frequent in b sheets and is built up from two adjacent b strands that are joined by a loop region. Two examples of such motifs are shown. (a) Schematic diagram of the structure of bovine trypsin inhibitor. The hairpin motif is colored red. (b) Schematic diagram of the structure of the snake venom erabutoxin. The two hairpin motifs within the b sheet are colored red and green.
54 The Greek key motif is found in antiparallel b sheets when four adjacent b strands are arranged in the pattern shown as a topology diagram in (a). The motif occurs in many b sheets and is exemplified here by the enzyme Staphylococcus nuclease (b).
55 STRUCTURAL HIERARCHY Primary structure Arrangement of aa along the linear polypeptide chain Secondary structure helices and strands arrange themselves in simple motifs several motifs usually are combined to form compact globular structures called domains Tertiary structure Arrangement of motifs or domains in 3D space Quaternary structure Arrangement of monomeric proteins wrto each other in 3D space
56 Organization of polypeptide chains into domains. Small protein molecules like the epidermal growth factor, EGF, comprise only one domain. Others, like the serine proteinase chymotrypsin, are arranged in two domains that are require to form a functional unit. Many of the proteins that are involved in blood coagulation and fibrinolysis, such as urokinase, factor IX, and plasminogen, have long polypeptide chains tha comprise different combinations of domains homologous to EGF and serine proteinases and addition, calcium-binding domains and Kringle domains.
57 The fundemental unit of tertiary structure is the domain Domain; A polypeptide chain or a part of a polypeptide chain that can independently fold into a stable tertiary structure. Domains are units of functions
58 DOMAINS: Each domain can fold independently Elements of secondary structure such as alpha helices and beta sheets pack together into stable globular elements called domains. A typical protein molecule is built from one or more domains, often linked through relatively unstructured regions of polypeptide chain.
59 Different domain structures
60 Comparison of the conformations of two serine proteases. The backbone conformations of elastase and chymotrypsin. Although only those amino acids in the polypeptide chain shaded in green are the same in the two proteins, the two conformations are very similar nearly everywhere. The active site of each enzyme is circled in red; this is where the peptide bonds of the proteins that serve as substrates are bound and cleaved by hydrolysis. The serine proteases derive their name from the amino acid serine, whose side chain is part of the active site of each enzyme and directly participates in the cleavage reaction.
61 Motifs that are adjacent in the amino acid sequence are also usually adjacent in the three-dimensional structure. Triose-phosphate isomerase is built up from four β α β α motifs that are consecutive both in the amino acid sequence (a) and in the three-dimensional structure (b).
62 Schematic diagram showing the packing of hydrophobic side chains between the two α helices in a coiled-coil structure. Every seventh residue in both α helices is a leucine, labeled "d." Due to the heptad repeat, the d-residues pack against each other along the coiled-coil. Residues labeled "a" are also usually hydrophobic and participate in forming the hydrophobic core along the coiled-coil.
63 Salt bridges can stabilize coiled-coil structures and are sometimes important for the formation of heterodimeric coiled-coil structures. The residues labeled "e" and "g" in the heptad sequence are close to the hydrophobic core and can form salt bridges between the two α helices of a coiled-coil structure, the e-residue in one helix with the g-residue in the second and vice versa. (a) Schematic view from the top of a heptad repeat. (b) Schematic view from the side of a coiled-coil structure.
64 Proteins can be divided into three main classes Alpha domain proteins Alpha/beta structures Beta domain structures
65 Four-helix bundles frequently occur as domains in a proteins.
66 Alpha-Beta proteins
67 Alpha-Beta proteins
68 Alpha-Beta proteins In most a/b barrel structures the eight b starnds of the barrel enclose a tightly Packed hydrophobic core formed by the side chains from b-strands.
69
70 α/β barrel domain of an enzyme Hydrophilic hole
71 Enzyme pyruvate folds into several domains
72
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
The peptide bond Peptides and proteins are linear polymers of amino acids. The amino acids are
 Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon
 Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
 Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006. Lecture 16 March 10
 CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Proteins the primary biological macromolecules of living organisms
 Proteins the primary biological macromolecules of living organisms Protein structure and folding Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary structure of proteins Structure of Proteins Protein molecules adopt
Proteins the primary biological macromolecules of living organisms Protein structure and folding Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary structure of proteins Structure of Proteins Protein molecules adopt
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED
 Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms
 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
Hydrogen Bonds The electrostatic nature of hydrogen bonds
 Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
ENZYMES. Serine Proteases Chymotrypsin, Trypsin, Elastase, Subtisisin. Principle of Enzyme Catalysis
 ENZYMES Serine Proteases Chymotrypsin, Trypsin, Elastase, Subtisisin Principle of Enzyme Catalysis Linus Pauling (1946) formulated the first basic principle of enzyme catalysis Enzyme increase the rate
ENZYMES Serine Proteases Chymotrypsin, Trypsin, Elastase, Subtisisin Principle of Enzyme Catalysis Linus Pauling (1946) formulated the first basic principle of enzyme catalysis Enzyme increase the rate
Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Proteins. Proteins. Amino Acids. Most diverse and most important molecule in. Functions: Functions (cont d)
 Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012
 Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Invariant residue-a residue that is always conserved. It is assumed that these residues are essential to the structure or function of the protein.
 Chapter 6 The amino acid side chains have polar and nonpolar properties, and the relative hydrophobicity of the amino acid side chains is critical for the folding and stability of a protein. The more hydrophobic
Chapter 6 The amino acid side chains have polar and nonpolar properties, and the relative hydrophobicity of the amino acid side chains is critical for the folding and stability of a protein. The more hydrophobic
Structure and properties of proteins. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
8/20/2012 H C OH H R. Proteins
 Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
PROTEINS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (DR. TRAISH)
 Introduction to Proteins - Proteins are abundant and functionally diverse molecules - They participate in cell regulation at all levels - They share a common structural feature: all are linear polymers
Introduction to Proteins - Proteins are abundant and functionally diverse molecules - They participate in cell regulation at all levels - They share a common structural feature: all are linear polymers
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Introduction to Protein Folding
 Introduction to Protein Folding Chapter 4 Proteins: Three Dimensional Structure and Function Conformation - three dimensional shape Native conformation - each protein folds into a single stable shape (physiological
Introduction to Protein Folding Chapter 4 Proteins: Three Dimensional Structure and Function Conformation - three dimensional shape Native conformation - each protein folds into a single stable shape (physiological
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Conformational Properties of Polypeptide Chains
 Conformational Properties of Polypeptide Chains Levels of Organization Primary structure Amino acid sequence of the protein Secondary structure H bonds in the peptide chain backbone α helix and β sheets
Conformational Properties of Polypeptide Chains Levels of Organization Primary structure Amino acid sequence of the protein Secondary structure H bonds in the peptide chain backbone α helix and β sheets
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
 Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
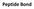 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
How To Understand The Chemistry Of An Enzyme
 Chapt. 8 Enzymes as catalysts Ch. 8 Enzymes as catalysts Student Learning Outcomes: Explain general features of enzymes as catalysts: Substrate -> Product Describe nature of catalytic sites general mechanisms
Chapt. 8 Enzymes as catalysts Ch. 8 Enzymes as catalysts Student Learning Outcomes: Explain general features of enzymes as catalysts: Substrate -> Product Describe nature of catalytic sites general mechanisms
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Structures of Proteins. Primary structure - amino acid sequence
 Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Elements in Biological Molecules
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond)
 Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
Non-Covalent Bonds (Weak Bond) Weak bonds are those forces of attraction that, in biological situations, do not take a large amount of energy to break. For example, hydrogen bonds are broken by energies
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
--not necessarily a protein! (all proteins are polypeptides, but the converse is not true)
 00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein three-dimensional structure native state. native condition
 Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms
 In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
CHM333 LECTURE 13 14: 2/13 15/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna
 INTRODUCTION TO ENZYMES Enzymes are usually proteins (some RNA) In general, names end with suffix ase Enzymes are catalysts increase the rate of a reaction not consumed by the reaction act repeatedly to
INTRODUCTION TO ENZYMES Enzymes are usually proteins (some RNA) In general, names end with suffix ase Enzymes are catalysts increase the rate of a reaction not consumed by the reaction act repeatedly to
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following?
 MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems.
![Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems. Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems.](/thumbs/25/5655226.jpg) Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 2, pp. 34-37 Practice problems (peptide ionization) [PDF]; problems in textbook: chapter 2, pp. 63-64,
Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 2, pp. 34-37 Practice problems (peptide ionization) [PDF]; problems in textbook: chapter 2, pp. 63-64,
Computational Systems Biology. Lecture 2: Enzymes
 Computational Systems Biology Lecture 2: Enzymes 1 Images from: David L. Nelson, Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, IV Edition, Freeman ed. or under creative commons license (search for images at http://search.creativecommons.org/)
Computational Systems Biology Lecture 2: Enzymes 1 Images from: David L. Nelson, Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, IV Edition, Freeman ed. or under creative commons license (search for images at http://search.creativecommons.org/)
Molecular Cell Biology
 Harvey Lodish Arnold Berk Paul Matsudaira Chris A. Kaiser Monty Krieger Matthew P. Scott Lawrence Zipursky James Darnell Molecular Cell Biology Fifth Edition Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations Copyright 2004
Harvey Lodish Arnold Berk Paul Matsudaira Chris A. Kaiser Monty Krieger Matthew P. Scott Lawrence Zipursky James Darnell Molecular Cell Biology Fifth Edition Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations Copyright 2004
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Introduction to Proteins and Enzymes
 Introduction to Proteins and Enzymes Basics of protein structure and composition The life of a protein Enzymes Theory of enzyme function Not all enzymes are proteins / not all proteins are enzymes Enzyme
Introduction to Proteins and Enzymes Basics of protein structure and composition The life of a protein Enzymes Theory of enzyme function Not all enzymes are proteins / not all proteins are enzymes Enzyme
CHM333 LECTURE 13 14: 2/13 15/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna
 INTRODUCTION TO ENZYMES Enzymes are usually proteins (some RNA) In general, names end with suffix ase Enzymes are catalysts increase the rate of a reaction not consumed by the reaction act repeatedly to
INTRODUCTION TO ENZYMES Enzymes are usually proteins (some RNA) In general, names end with suffix ase Enzymes are catalysts increase the rate of a reaction not consumed by the reaction act repeatedly to
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid.
 A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure
 FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Enzymes. Enzyme Structure. Enzyme Classification. CHEM464/Medh, J.D. Reaction Rate and Enzyme Activity
 Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts They are not consumed or altered during the reaction They do not change the equilibrium, just reduce the time required to reach equilibrium. They increase the rate
Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts They are not consumed or altered during the reaction They do not change the equilibrium, just reduce the time required to reach equilibrium. They increase the rate
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Some terms: An antigen is a molecule or pathogen capable of eliciting an immune response
 Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
Overview of the immune system We continue our discussion of protein structure by considering the structure of antibodies. All organisms are continually subject to attack by microorganisms and viruses.
K'NEX DNA Models. Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical Sciences Mount Sinai School of Medicine
 KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
LECTURE-2. Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT. Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids
 LECTURE-2 Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT PREAMBLE Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids as the building blocks. There are 20 standard amino acids
LECTURE-2 Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT PREAMBLE Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids as the building blocks. There are 20 standard amino acids
Papers listed: Cell2. This weeks papers. Chapt 4. Protein structure and function
 Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
Sickle cell anemia: Altered beta chain Single AA change (#6 Glu to Val) Consequence: Protein polymerizes Change in RBC shape ---> phenotypes
 Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE. Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs,
 Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Enzymes reduce the activation energy
 Enzymes reduce the activation energy Transition state is an unstable transitory combination of reactant molecules which occurs at the potential energy maximum (free energy maximum). Note - the ΔG of the
Enzymes reduce the activation energy Transition state is an unstable transitory combination of reactant molecules which occurs at the potential energy maximum (free energy maximum). Note - the ΔG of the
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
