MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
|
|
|
- Horace Gray
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Glycine Serine does have a chiral α-carbon. Go back and review the different amino acids to find the one that is achiral. Proline does have a chiral α-carbon. Go back and review the different amino acids to find the one that is achiral. Alanine does have a chiral α-carbon. Go back and review the different amino acids to find the one that is achiral. D. Correct! Glycine does not have a chiral α-carbon. Its α-carbon has two hydrogens bonded to it. (1) Recall the structures of the amino acids. Alpha-amino acids all have the same general structure (where R is the individual side chains): H 2 N R * H H The carbon marked with a star is the α-carbon. In 19 of the 20 α-amino acids, the α-carbon is bonded to four different groups making it a stereocenter. For one amino acid, however, R is a hydrogen making its α-carbon achiral. The achiral amino acid is glycine. (2) Read each choice and choose the correct answer. Therefore, the correct answer is (D).
2 Question No. 2 of 10 Question 2. Which amino acid has the one letter code of K? Question #02 (A) Lysine (B) Phenylalanine (C) Valine (D) Threonine A. Correct! Lysine was given the one letter code of K. Phenylalanine has the one letter code of F. Go back and review the codes given all the amino acids. Valine has the one letter code of V. Go back and review the codes given all the amino acids. Threonine has the one letter code of T. Go back and review the codes given all the amino acids. (1) Recall the letter codes for amino acids. There are two systems of letter codes for amino acids. ne system uses three letter abbreviations for each amino acid and the other uses just one letter abbreviations. The question asked about the one letter code of K. As with the structures of the amino acids, the three letter code system and the one letter code systems have to be memorized. You are likely to be asked about either system so you should be familiar with both. The one letter code of K corresponds to the amino acid lysine. Therefore, the correct answer is (A).
3 Question No. 3 of 10 Question 3. What is the name of the amino acid shown? H H 2 N C C H CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 NH Question #03 C NH NH 2 (A) Asparagine (B) Histidine (C) Arginine (D) Lysine Asparagine contains an amide in its side chain. Go back and review the structure of the amino acids. Histidine has an imidazole ring in its side chain. Go back and review the structure of the amino acids. C. Correct! Arginine has a guanidino group in its side chain making it one of the basic amino acids. Lysine has an amino group in its side chain. Go back and review the structure of the amino acids. (1) Recall the different amino acid structures. The amino acid shown is arginine. It is the only amino acid with a guanidino group in its side chain. There are a number of things regarding amino acids you should know prior to taking the MCAT. You need to know the structure of all 20 amino acids, what category the side chain is a part of (aliphatic, acidic, basic, etc.), the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid and the one letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Putting this information of flash cards is usually very helpful to students. Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
4 Question No. 4 of 10 Question 4. Which statement about amino acids is incorrect? Question #04 (A) All amino acids incorporated into proteins are in the D-form. (B) There are twenty α-amino acids. (C) In a neutral solution, amino acids are zwitterionic, with a positive charge on the amino group and a negative charge on the carboxylic acid group. (D) The amino acids each have a unique side chain that varies in several ways including size, shape, hydrogen bonding capacity and affinity for water. A. Correct! All amino acids incorporated into proteins are in the L-form. (Carbohydrates used in the body are in the D-form.) There are twenty α-amino acids though humans can synthesize only about half of them. Go back and review the information on amino acids in the tutorial. The amino and carboxylic acid groups in amino acids can protonated or deprotonated respectively while in solution. This process leads to a zwitterion in neutral solution where the amino group is positively charged and the acid group is negatively charged. Go back and review the information on amino acids in the tutorial. Each of the amino acids side chains are unique and vary in many ways including size, shape, hydrogen bonding capacity, and their affinity for water. Go back and review the information on amino acids in the tutorial. (1) Recall the infomation on amino acids in the tutorial. All amino acids incorporated into proteins are in the L form. There are twenty α-amino acids. The amino acids each have a unique side chain that varies in several ways including size, shape, hydrogen bonding capacity and affinity for water. And in a neutral aqueous solution, amino acids are zwitterionic, with a positive charge on the amino group and a negative charge on the carboxylic acid group. (2) Read each statement carefully and choose the one that incorrect. Therefore, the correct answer is (A).
5 Question No. 5 of 10 Question 5. How many peptide bonds are in the peptide chain shown? Question #05 H 2 N CH C CH 3 (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 N H CH C CH 2 H N H CH C H CH H CH 3 There is more than one peptide bond in this tripeptide. Go back and review the structure and formation of peptide bonds. B. Correct! There are three amino acids in this tripeptide that are bonded together with peptide bonds (amide linkages). There are two peptide bonds in the structure. Remember, the number of peptide bonds is always one less than the number of amino acids in the chain. There are less than 3 peptide bonds in this tripeptide. Go back and review the structure and formation of peptide bonds. There are less than 4 peptide bonds in this tripeptide. Go back and review the structure and formation of peptide bonds. (1) Determine the number of peptide bonds in the molecule. You can approach this problem two ways. In the first, you can count the number of amino acid residues that are present in the peptide. There are three amino acids. You learned in the tutorial that the number of peptide bonds is one less than the number of amino acid residues present so that must mean there are 2 peptide bonds in this molecule. In the second approach, you can count the number of amide bonds in the molecule because all a peptide bond is, is a bond between a carbonyl group and an amine. We have seen this before when studying the functional group of amides. Therefore, the correct answer is (B).
6 Question No. 6 of 10 Question 6. What is the name of the process shown? H H 2 N CH C H + H 2 N CH C H H 2 N CH C N CH C H + H 2 CH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 SH SH Question #06 (A) reductive amination (B) hydrolysis (C) amidation (D) amino acid synthesis Reductive amination is the process of taking a carbonyl compound and transforming it to an amine. Go back and review the reactions of peptides. Hydrolysis is the process of adding water to an amide to reform the carboxylic acid and the amine. Hydrolysis is the reverse process of the one shown. Go back and review the reactions of peptides. C. Correct! Amidation is the process of substituting an amine onto a carboxylic acid to form an amide. Amino acid synthesis is the making of amino acids. Here the amino acids are being joined together in a different process. Go back and review the reactions of peptides. (1) Look at the equation and determine the process that is occurring. In the above equation, a new peptide bond is being formed between the acid group of one amino acid and the amine group of the second amino acid. (2) Recall the types of reactions listed as choices. Reductive amination is the process of taking a carbonyl compound, like a ketone, forming the imine and then reducing the imine to give an amine as the final product. We learned this synthesis of amines in the amine tutorial. Hydrolysis is the process of deconstructing a molecule usually by its reaction with water. Hydrolysis of a peptide occurs when the peptide bonds are broken to give an acid and amine as the final products. Amino acid synthesis involves constructing amino acids. Amination is the process of substituting an amine onto a carboxylic acid to form an amide. That is the process occurring in this reaction. Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
7 Question No. 7 of 10 Question 7. How many amino acids are in an oligopeptide? Question #07 (A) 1-10 (B) (C) (D) more than 30 Peptide chains that consist of 1-10 amino acids are often named using numerical prefixes followed by the word peptide. Example: A chain of 3 amino acids is called a tripeptide. B. Correct! ligopeptides (oligo is from the Greek for little/few) consist of amino acids. Most peptide chains that consist of 20 or more amino acids are often called polypeptides. Go back and review the classification of peptides. Most peptide chains that consist of 20 or more amino acids are often called polypeptides. Go back and review the classification of peptides. (1) Recall the definition of oligopeptide. An oligopeptide is a peptide consisting of between amino acids. (2) Read each choice and choose the correct one. Therefore, the correct answer is (B).
8 Question No. 8 of 10 Question 8. Which statement regarding the common peptide structural motif shown is incorrect? Question #08 (A) This motif is representative of the α-helix, a secondary structure element in peptides. (B) The helical structure is due to hydrogen bond formation between the carbonyl and NH groups on amino acids that are three residues apart. (C) Each end of the coil will have an unbound amine group on it. (D) There is a handedness to the coil s configuration (it is chiral). This drawing is a representation of an α-helix which comprises secondary structure in peptides. Go back and review different types of protein structure. Hydrogen bond formation is responsible for the helical structure found in many peptides. The hydrogen bonds form between carbonyls and amine groups in the next turn of the coil. Go back and review the secondary structure of proteins. C. Correct! ne end of the helix will have an unbound amine group but the opposite end will have an unbound carboxylic acid group on it. An α-helix is chiral and appears to look like thread on a right handed screw. Go back and review the secondary structure of proteins. (1) Recognize the peptide structural motif. It is an α-helix. (2) Recall the theory behind α-helices. Alpha-helices are a secondary structural element in peptides. ne end of the helix has an unbound amine group on it while the other end will have an unbound carboxylic acid group on it. The helical structure is due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between residues. Usually they occur between a carbonyl group and a NH group on amino acids that are three residues apart. There is a handedness to the coil making α-helices chiral. (3) Read each statement carefully and choose the statement that is incorrect. Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
9 Question No. 9 of 10 Question 9. Which level of protein structure describes the complete 3-D structure of polypeptide units of a given protein? Question #09 (A) Primary structure (B) Secondary structure (C) Tertiary structure (D) Quaternary structure Primary structure is the linear order and number of amino acids present. Go back and review protein structure. Secondary structure is the regular conformational forms conferred on the protein by hydrogen bond formation between residues. Go back and review protein structure. C. Correct! Tertiary structure is the complete 3-D structure of a polypeptide. Quaternary structure describes proteins containing several distinct polypeptide chains along with nonprotein groups. Go back and review protein structure. (1) Recall the four level of protein structure. Primary structure is the linear order and number of amino acids present. Secondary structure is the regular conformational forms conferred on the protein by hydrogen bond formation between residues. Tertiary structure is the complete 3-D structure of the polypeptide units of a protein. And lastly, quaternary structure describes proteins containing several distinct polypeptide chains along with nonprotein groups. (2) Re-read the question carefully and choose the correct answer. Therefore, the correct answer is (C).
10 Question No. 10 of 10 Question 10. What is the name of a protein whose quaternary structure consists of four identical polypeptide chains? Question #10 (A) Homotetramer (B) Heterotetramer (C) Homopentamer (D) Heterodimeric protein A. Correct! When a protein consists of four identical polypeptide subunits, it is considered to be a homotetramer. A heterotetramer is a protein that consists of 4 subunits that are not all identical. Go back and review the quaternary structure of proteins. A protein that consists of five identical polypeptide segments is called a homopentamer. Go back and review the quaternary structure of proteins. A protein that consists of two different sets of dimers is a heterodimeric protein. Go back and review the quaternary structure of proteins. (1) Recall the way quaternary structure is described in the tutorial. Proteins consisting of multiple polypeptide chains can be referred to in terms of the types and numbers of those chains present. Here we have four chains in the protein. The numerical prefix tetra- is placed with the suffix mer to form tetramer. Since the chains are identical, the structure is homogeneous so the prefix homo- is added to tetramer. If the chains had been different, it would have been called a heterotetramer. A homopentamer is a protein consisting of 5 polypeptide chains all of which are identical. A heterodimeric protein consists of two different dimers. Therefore the correct answer is (A).
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
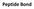 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
The peptide bond Peptides and proteins are linear polymers of amino acids. The amino acids are
 Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE. Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs,
 Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS
 UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS 11.1 Types of Lipids Lipids are also biochemical compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But lipids, unlike carbohydrates, share no common
UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS 11.1 Types of Lipids Lipids are also biochemical compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But lipids, unlike carbohydrates, share no common
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Structure and properties of proteins. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
CHAPTER 29 AMINO ACIDS, POLYPEPTIDES, AND PROTEINS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 22 Proteins
 hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers:
 Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
BOC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1. Calculating the charge of proteins
 BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í
 I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms
 In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012
 Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Exam 4 Outline CH 105 Spring 2012 You need to bring a pencil and your ACT card. Chapter 24: Lipids 1. Describe the properties and types of lipids a. All are hydrophobic b. Fatty acid-based typically contain
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display
 Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Combinatorial Biochemistry and Phage Display Prof. Valery A. Petrenko Director - Valery Petrenko Instructors Galina Kouzmitcheva and I-Hsuan Chen Auburn 2006, Spring semester COMBINATORIAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest
 Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS
 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS B 1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles. B. make copies of itself. C. join amino acids to each other.
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS B 1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles. B. make copies of itself. C. join amino acids to each other.
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
8/20/2012 H C OH H R. Proteins
 Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E.
 Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon
 Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
 Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
LECTURE-2. Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT. Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids
 LECTURE-2 Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT PREAMBLE Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids as the building blocks. There are 20 standard amino acids
LECTURE-2 Basics of Amino acids and Proteins HANDOUT PREAMBLE Proteins are the most complex and versatile macromolecules comprised of amino acids as the building blocks. There are 20 standard amino acids
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006. Lecture 16 March 10
 CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
Introduction to Chemical Biology
 Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
THE CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PEPTIDES
 TE EMIAL SYTESIS F PEPTIDES Peptides are the long molecular chains that make up proteins. Synthetic peptides are used either as drugs (as they are biologically active) or in the diagnosis of disease. Peptides
TE EMIAL SYTESIS F PEPTIDES Peptides are the long molecular chains that make up proteins. Synthetic peptides are used either as drugs (as they are biologically active) or in the diagnosis of disease. Peptides
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography
 Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Structures of Proteins. Primary structure - amino acid sequence
 Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
BNFO601 Introduction to Molecular Biology Protein
 BNFO601 Introduction to Molecular Biology Protein Outline: A. What can protein do? B. What are proteins? C. Structure and basis for catalysis D. Targeting protein E. Alteration of protein structure and
BNFO601 Introduction to Molecular Biology Protein Outline: A. What can protein do? B. What are proteins? C. Structure and basis for catalysis D. Targeting protein E. Alteration of protein structure and
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT
 EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein three-dimensional structure native state. native condition
 Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
Concluding lesson. Student manual. What kind of protein are you? (Basic)
 Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM
 AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
Worksheet 13.1. Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary
 Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7. Alcohols, Ethers and More
 Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Previous lecture: Today:
 Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Chemistry: Introduction to General, Organic & Biological Chemistry (Timberlake) Chapter 16: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 Chemistry: Introduction to General, Organic & Biological Chemistry (Timberlake) Chapter 16: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A)
Chemistry: Introduction to General, Organic & Biological Chemistry (Timberlake) Chapter 16: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A)
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chemistry 1110 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
 hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms
 ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
ROLE OF THE TRANSITION STATE Lecture 15: Enzymes & Kinetics Mechanisms Consider the reaction: H-O-H + Cl - H-O δ- H Cl δ- HO - + H-Cl Reactants Transition state Products Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Protein Structure and Function
 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI Protein Structure and Function SETI I APTE 2 APTE 3 Protein Structure Protein Function 27 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI 2 Protein Structure
Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI Protein Structure and Function SETI I APTE 2 APTE 3 Protein Structure Protein Function 27 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI 2 Protein Structure
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Acids and Bases. but we will use the term Lewis acid to denote only those acids to which a bond can be made without breaking another bond
 Acids and Bases. Brønsted acids are proton donors, and Brønsted bases are proton acceptors. Examples of Brønsted acids: HCl, HBr, H 2 SO 4, HOH, H 3 O +, + NH 4, NH 3, CH 3 CO 2 H, H CH 2 COCH 3, H C CH,
Acids and Bases. Brønsted acids are proton donors, and Brønsted bases are proton acceptors. Examples of Brønsted acids: HCl, HBr, H 2 SO 4, HOH, H 3 O +, + NH 4, NH 3, CH 3 CO 2 H, H CH 2 COCH 3, H C CH,
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins
 Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
 Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Name of mechanism...... (1) For Step 3, give the reagent, give a necessary condition and name the mechanism. Reagent... Condition...
 Q. A possible synthesis of the amino acid X is shown below. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for Step. Name of mechanism... Mechanism (5) (b) Give the IUPAC name of the product of Step.... () (c) For Step,
Q. A possible synthesis of the amino acid X is shown below. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for Step. Name of mechanism... Mechanism (5) (b) Give the IUPAC name of the product of Step.... () (c) For Step,
Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems.
![Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems. Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Key Concepts. Objectives See also posted Peptide/pH/Ionization practice problems.](/thumbs/25/5655226.jpg) Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 2, pp. 34-37 Practice problems (peptide ionization) [PDF]; problems in textbook: chapter 2, pp. 63-64,
Lecture 4: Peptides and Protein Primary Structure [PDF] Reading: Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer, Chapter 2, pp. 34-37 Practice problems (peptide ionization) [PDF]; problems in textbook: chapter 2, pp. 63-64,
Polypeptides and Proteins
 Polypeptides and Proteins These molecules are composed, at least in part, of chains of amino acids. Each amino acid is joined to the next one through an amide or peptide bond from the carbonyl carbon of
Polypeptides and Proteins These molecules are composed, at least in part, of chains of amino acids. Each amino acid is joined to the next one through an amide or peptide bond from the carbonyl carbon of
Provincial Exam Questions. 9. Give one role of each of the following nucleic acids in the production of an enzyme.
 Provincial Exam Questions Unit: Cell Biology: Protein Synthesis (B7 & B8) 2010 Jan 3. Describe the process of translation. (4 marks) 2009 Sample 8. What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis? A.
Provincial Exam Questions Unit: Cell Biology: Protein Synthesis (B7 & B8) 2010 Jan 3. Describe the process of translation. (4 marks) 2009 Sample 8. What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis? A.
Amides and Amines: Organic Nitrogen Compounds
 Chapter 25 Amides and Amines: Organic Nitrogen Compounds Nylon is one of the materials used to give these colorful sails their strength and durability. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry,
Chapter 25 Amides and Amines: Organic Nitrogen Compounds Nylon is one of the materials used to give these colorful sails their strength and durability. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry,
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
 Mass Spec - Fragmentation An extremely useful result of EI ionization in particular is a phenomenon known as fragmentation. The radical cation that is produced when an electron is knocked out of a neutral
Mass Spec - Fragmentation An extremely useful result of EI ionization in particular is a phenomenon known as fragmentation. The radical cation that is produced when an electron is knocked out of a neutral
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid.
 A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
I. Chapter 5 Summary. II. Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. III. Lipids
 I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
