REC FPGA Seminar IAP Seminar Format
|
|
|
- Silas Burke
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REC FPGA Seminar IAP 1998 Session 1: Architecture, Economics, and Applications of the FPGA Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Seminar Format Four 45 minute open sessions two on Wed. January 21st, two on Fri. January 23rd session 1: Architecture, Economics, and Applications of FPGAs session 2: Design tools, Configuration and Practical Considerations session 3: Advanced FPGA design techniques, Optimizations, and Tricks session 4: Future Directions and Applications of FPGAs Hands-on session (preregistered only) starts on Mon. January 26th in lab, continues through the week three 45 minute orientations for design tools and RHP4K board one basic lab and one advanced lab assignment cylon lab pong, the video game plus two days open lab time for your own project Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
2 Seminar Goals Teach practical FPGA knowledge From design concept to finished product When to use FPGAs Which one to use How to integrate them into your circuit Impart the ability to implement design solutions to real world problems in FPGAs Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Genesis Field Programmable Gate Array Name belies genesis and original purpose Gate arrays are a kind of ASIC ASIC types include CBIC, GA, and FC GA: moderately fast-turn, cost effective, volume ASIC Mfg. bakes a set of wafers with only transistor diffusions (first half of fabrication time and cost) User specifies metalization layers for device application Saves on NRE (fewer mask sets to make) Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
3 Architecture: Genesis (gate array structure) Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Genesis Industry generally considers FPGA to be a kind of ASIC extremely fast turn, low volume ASIC sold as a completed chip in package FPGA has a sea of gates structure with user-defineable interconnections fuses, antifuses, or pass gates target market: low volume, fast turn operations higher cost per device countered by lower NRE cost many FPGA vendors make OTP devices because they are cheaper per device (Actel s anti-fuse) Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
4 Architecture: Varieties FPGA architectures are market-driven Primary classifications for FPGAs configuration method granularity routing architecture Other practical considerations density speed cost design tools vertical migration Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Varieties EPAC Electrically Programmable Analog Circuit Contains programmable gain amplifiers, comparators, multiplexers, DACs, track-and-hold, filtering components Made by imp Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
5 Architecture: Configuration Configuration method In-circuit programmable methods SRAM based (Xilinx 2K/3K/4K, Altera 8K/10K, Lucent Orca) volatile, but fast configuration times must reprogram on every power-up some architectures offer partial reconfiguration (Atmel) most expensive in terms of area and timing costs standard CMOS process EEPROM based (Altera 7K/9K) nonvolatile, slow config; sometimes requires extra voltages for programming and erasing special silicon processing required Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Configuration Configuration method (cont d) Pre-assembly programmable methods Antifuse based (Actel, Quicklink FPGAs) nonvolatile, very fast links permanent configuration (OTP) smallest link size (lower cost) special silicon processing technology required (E)EPROM based (Altera 5K, 7K, Xilinx 7200, 7300) nonvolatile, moderate performance reprogrammable after special erase cycle medium-sized link special silicon processing technology required Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
6 Granularity Architecture: Granularity Defined as ratio of logic per cell versus routing Very fine-grained architectures Partial set of n-input boolean functions per cell Roughly 6-1 ratio of logic inputs to registers per cell Atmel, Actel Fine-grained architectures Full set of n-input boolean functions per cell Sometimes multiple n-input boolean functions per cell Roughly 8-1 ratio of logic inputs to registers per cell Well-suited for state machines, simple arithmetic, pipelined applications Xilinx 3K/4K, Altera 8K/10K Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Granularity Granularity (cont d) Coarse-grained architectures PLD-style product term arrays Roughly 32-1 ratio of logic inputs to registers per cell Well-suited for address decoding, complicated arithmetic operations, datapath operators, complex state machines Poorly suited for pipelined applications and simple operations Altera 5K/7K, Xilinx 7K Dual-grained architectures or heirarchical architectures Combines coarse and fine-grained features Often exhibit separate local and global routing resources Lucent Orca, Altera 9K Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
7 Routing method Architecture: Routing Fine-grained Short hops (1 to 8 logic cells spanned per track) Path-dependant timing Exhibits high density Flexible switch matrices Less logic placement constraints Coarse-grained Tracks span entire chip Fixed timing regardless of logic placement Lower density Logic placement constrained by routing availability Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Routing Routing method (cont d) Heirarchical routing Local, fine-grained routing between cells Global, coarse-grained routing between groups of cells Usually path-dependant timing Best of both worlds, but can be difficult to utilize efficiently Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
8 Architecture: Other Practical Density, speed and vertical migration Altera FLEX 8K is targetted at density-driven apps Altera MAX 7K is targetted at performance-driven apps Xilinx 4K series targets both speed and performance, with good vertical migration from 3K gates to 250K gates (Altera 10K is Xilinx 4K competitor) Xilinx 6200 series targets reconfigurable hardware applications Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Architecture: Design Tools Design tools - the other half of the equation FPGA is useless without good design tools Design tools slowly progressing to acceptable levels Entry methods include HDL, schematic Compilers are still slow (30 minutes - hours for any substantial design) Xilinx: Foundation Series / M1 technology Altera: MAXPLUS ][ Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
9 Architecture: Cost Cost formulas for FPGAs are complex OTP FPGAs tend to be cheaper Established lines are cheaper than new lines Cost increases exponentially with performance and density Some lines are targetted at cost-sensitive applications (Altera 7K) Not all speed grade-density combos available from manufacturers Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Fine-grained logic, SRAM based, with finegrained routing Array of CLBs embedded in single length / double length / quad length / longline routing resources + PSM CLB = Configurable Logic Block Two 4-input LUTs (LookUp Tables) and one 3-input LUT Two SR D-type flip flops Bypass paths and carry/cascade logic PSM = Programmable Switch Matrix 10 interconnect points per matrix Each interconnect contains six pass transistors for full connectivity between four directions Located at intersections of single and double length lines Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
10 Detail Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
11 Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
12 Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Configuration total (device) reconfiguration (no partial reconfig) several configuration modes available parallel and serial modes master and slave modes daisy chain ability device bitstreams between 50Kbits and 400Kbits config rate around 10 Mbit/sec max reconfig rate in a few tens of milliseconds typical reconfig in a couple of seconds Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
13 Detailed Architecture: Xilinx 4000E Other features distributed RAM CLB LUTs can function as a 32x1, 16x1, or 16x2 RAM synchronous RAM options available internal tri-state buffers global routing resources JTAG boundary scan configuration readback programmable slew rate and logic levels in IOBs common per-package pinout for all devices allows for easy vertical migration Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Applications Fast-turn, low volume ASIC (uninteresting) Reconfigurable Hardware Processors One-connector I/O solutions Rapid prototyping Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
14 Applications: RHP Direct implementation of algorithms in hardware circumvents instruction fetch, decode, issue overhead unrestricted parallelism disadvantage: little hardware abstraction, difficult to use RISC framework with reconfigurable instruction set user-defined instructions depending on process context prevents the MMX disease easier to use, more hardware abstraction, but lower performance Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Applications: RHP Optimal ISA compiler analyzes code and chooses an ISA optimal for the problem, and bundles the hardware description for the ISA with the code object Configurable memory management and caching useful for implementing special OS features VM paging schemes directly in hardware Ultimate RHP-one processor, any ISA In the future - possibly adaptive processors which automatically optimize their architecture per application Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
15 Applications: Direct Hardware Ideal for implementing simple, repetative operations (overhead operations) time synchronization on Novell networks CAM lookup tables for IP routing and neural nets encryption/decryption FEA (finite element analysis) Relaxation networks database searching higher peformance with special architectures (embedded RAM) Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Applications: I/O solutions One-connector I/O solutions use a single connector with any protocol desired ex: a DB-25 which can do SCSI, IEEE1284 parallel, serial ideal for space-limited applications Object oriented hardware devise a system such that a device plugged into the I/O port uploads the hardware configuration necessary to implement the communications protocol protocol upgrades are a cinch limited by electrical signalling compatibility issues drawback - can be confusing to users, potentially damaging to hardware Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
16 Applications: EA Evolutionary algorithms some research done on FPGAs already tone recognition application possibly requires intimate knowledge of FPGA hardware vendor licencsing issues EA apps do not map well into current FPGA architectures however, with the right FPGA EA could yield very interesting results Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP Applications: Rapid Prototyping FPGAs are a handy thing to have on the lab bench simple digital circuits no longer require wiring or order parts, etc modifying and duplicating existing designs is relatively easy with the right design tools, hardware design re-use is an additional benefit Robotics and Electronics Cooperative FPGA Seminar IAP
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic
 NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
NCNU_2013_DD_7_1 Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable Logic 71I 7.1 Introduction ti 7.2 Random Access Memory 7.3 Memory Decoding 7.5 Read Only Memory 7.6 Programmable Logic Array 77P 7.7 Programmable Array
NAND Flash FAQ. Eureka Technology. apn5_87. NAND Flash FAQ
 What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
What is NAND Flash? What is the major difference between NAND Flash and other Memory? Structural differences between NAND Flash and NOR Flash What does NAND Flash controller do? How to send command to
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Memory Basics. SRAM/DRAM Basics
 Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Reconfigurable Computing. Reconfigurable Architectures. Chapter 3.2
 Reconfigurable Architectures Chapter 3.2 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jürgen Teich Lehrstuhl für Hardware-Software-Co-Design Coarse-Grained Reconfigurable Devices Recall: 1. Brief Historically development (Estrin Fix-Plus
Reconfigurable Architectures Chapter 3.2 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jürgen Teich Lehrstuhl für Hardware-Software-Co-Design Coarse-Grained Reconfigurable Devices Recall: 1. Brief Historically development (Estrin Fix-Plus
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs
 Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS. A step change in speed
 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed NAME OF REPORT SECTION 3 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed Faster is more profitable in the front office
HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed NAME OF REPORT SECTION 3 HARDWARE ACCELERATION IN FINANCIAL MARKETS A step change in speed Faster is more profitable in the front office
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design. Accelerates PLD Development
 Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
Pre-tested System-on-Chip Design Accelerates PLD Development March 2010 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503) 268-8000 www.latticesemi.com 1 Pre-tested
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure
 Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure Micah Dowty University of Colorado at Boulder [email protected] March 26, 2004 Abstract Traditional software development
Test Driven Development of Embedded Systems Using Existing Software Test Infrastructure Micah Dowty University of Colorado at Boulder [email protected] March 26, 2004 Abstract Traditional software development
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs
 Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Embedded System Hardware - Processing (Part II)
 12 Embedded System Hardware - Processing (Part II) Jian-Jia Chen (Slides are based on Peter Marwedel) Informatik 12 TU Dortmund Germany Springer, 2010 2014 年 11 月 11 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts.
12 Embedded System Hardware - Processing (Part II) Jian-Jia Chen (Slides are based on Peter Marwedel) Informatik 12 TU Dortmund Germany Springer, 2010 2014 年 11 月 11 日 These slides use Microsoft clip arts.
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Implementation Details
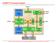 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
Hardware and Software
 Hardware and Software 1 Hardware and Software: A complete design Hardware and software support each other Sometimes it is necessary to shift functions from software to hardware or the other way around
Hardware and Software 1 Hardware and Software: A complete design Hardware and software support each other Sometimes it is necessary to shift functions from software to hardware or the other way around
Programming NAND devices
 Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
Technical Guide Programming NAND devices Kelly Hirsch, Director of Advanced Technology, Data I/O Corporation Recent Design Trends In the past, embedded system designs have used NAND devices for storing
With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as:
 Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
Memory Classification With respect to the way of data access we can classify memories as: - random access memories (RAM), - sequentially accessible memory (SAM), - direct access memory (DAM), - contents
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition
 RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
Memory. The memory types currently in common usage are:
 ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
ory ory is the third key component of a microprocessor-based system (besides the CPU and I/O devices). More specifically, the primary storage directly addressed by the CPU is referred to as main memory
In-System Programming Design TM. Guidelines for ispjtag Devices. Introduction. Device-specific Connections. isplsi 1000EA Family.
 In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
In-System Design TM February 2002 Introduction In-system programming (ISP ) has often been billed as a direct replacement for configuring a device through a programmer. The idea that devices can simply
We r e going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! "Answers:" "Questions:" - 1 -
 . (0 pts) We re going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! Associate the following answers with the appropriate question. (You are given the "answers": Pick the "question" that goes best with each "answer".)
. (0 pts) We re going to play Final (exam) Jeopardy! Associate the following answers with the appropriate question. (You are given the "answers": Pick the "question" that goes best with each "answer".)
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization
 Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
Lecture 5: Gate Logic Logic Optimization MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 5 1 Overview Reading McCluskey, Logic Design Principles- or any text in boolean algebra Introduction We could design at the level of irsim
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
In-System Programmability
 In-System Programmability in MAX Devices September 2005, ver. 1.5 Application Note 95 Introduction Features & Benefits MAX devices are programmable logic devices (PLDs), based on the Altera Multiple Array
In-System Programmability in MAX Devices September 2005, ver. 1.5 Application Note 95 Introduction Features & Benefits MAX devices are programmable logic devices (PLDs), based on the Altera Multiple Array
Design Cycle for Microprocessors
 Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Cycle for Microprocessors Raúl Martínez Intel Barcelona Research Center Cursos de Verano 2010 UCLM Intel Corporation, 2010 Agenda Introduction plan Architecture Microarchitecture Logic Silicon ramp Types
Atmel s Self-Programming Flash Microcontrollers
 Atmel s Self-Programming Flash Microcontrollers By Odd Jostein Svendsli, Marketing Manager Summary The third-generation Flash microcontrollers from Atmel are now available. These microcontrollers offer
Atmel s Self-Programming Flash Microcontrollers By Odd Jostein Svendsli, Marketing Manager Summary The third-generation Flash microcontrollers from Atmel are now available. These microcontrollers offer
A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic
 A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic Shawki Areibi Abstract Present industry practice has created a high demand for systems designers with knowledge and experience in using
A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic Shawki Areibi Abstract Present industry practice has created a high demand for systems designers with knowledge and experience in using
VON BRAUN LABS. Issue #1 WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS VON BRAUN LABS. State Machine Technology
 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS WWW.VONBRAUNLABS.COM Issue #1 VON BRAUN LABS WE PROVIDE COMPLETE SOLUTIONS ULTRA LOW POWER STATE MACHINE SOLUTIONS State Machine Technology IoT Solutions Learn
Enhancing High-Speed Telecommunications Networks with FEC
 White Paper Enhancing High-Speed Telecommunications Networks with FEC As the demand for high-bandwidth telecommunications channels increases, service providers and equipment manufacturers must deliver
White Paper Enhancing High-Speed Telecommunications Networks with FEC As the demand for high-bandwidth telecommunications channels increases, service providers and equipment manufacturers must deliver
NVM memory: A Critical Design Consideration for IoT Applications
 NVM memory: A Critical Design Consideration for IoT Applications Jim Lipman Sidense Corp. Introduction The Internet of Things (IoT), sometimes called the Internet of Everything (IoE), refers to an evolving
NVM memory: A Critical Design Consideration for IoT Applications Jim Lipman Sidense Corp. Introduction The Internet of Things (IoT), sometimes called the Internet of Everything (IoE), refers to an evolving
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Chapter 2 Basic Structure of Computers Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Functional Units Basic Operational Concepts Bus Structures Software
Developing Embedded Applications with ARM Cortex TM -M1 Processors in Actel IGLOO and Fusion FPGAs. White Paper
 Developing Embedded Applications with ARM Cortex TM -M1 Processors in Actel IGLOO and Fusion FPGAs White Paper March 2009 Table of Contents Introduction......................................................................
Developing Embedded Applications with ARM Cortex TM -M1 Processors in Actel IGLOO and Fusion FPGAs White Paper March 2009 Table of Contents Introduction......................................................................
Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic devices Implementing logic with PLDs Static hazards
 Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Points ddressed in this Lecture Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Professor Peter Cheung Department of EEE, Imperial College London Read-only memory Implementing logic with ROM Programmable logic
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Microprocessor or Microcontroller?
 Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Router Architectures
 Router Architectures An overview of router architectures. Introduction What is a Packet Switch? Basic Architectural Components Some Example Packet Switches The Evolution of IP Routers 2 1 Router Components
Router Architectures An overview of router architectures. Introduction What is a Packet Switch? Basic Architectural Components Some Example Packet Switches The Evolution of IP Routers 2 1 Router Components
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA CARD IN CONTENT FILTERING SOLUTIONS FOR SECURING COMPUTER NETWORKS. Received May 2010; accepted July 2010
 ICIC Express Letters Part B: Applications ICIC International c 2010 ISSN 2185-2766 Volume 1, Number 1, September 2010 pp. 71 76 IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA CARD IN CONTENT FILTERING SOLUTIONS FOR SECURING COMPUTER
ICIC Express Letters Part B: Applications ICIC International c 2010 ISSN 2185-2766 Volume 1, Number 1, September 2010 pp. 71 76 IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA CARD IN CONTENT FILTERING SOLUTIONS FOR SECURING COMPUTER
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
FPGA Music Project. Matthew R. Guthaus. Department of Computer Engineering, University of California Santa Cruz http://vlsida.soe.ucsc.
 Department of Computer Engineering, University of California Santa Cruz http://vlsida.soe.ucsc.edu Biographic Info 2006 PhD, University of Michigan in Electrical Engineering 2003-2005 Statistical Physical
Department of Computer Engineering, University of California Santa Cruz http://vlsida.soe.ucsc.edu Biographic Info 2006 PhD, University of Michigan in Electrical Engineering 2003-2005 Statistical Physical
NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications
 NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications 1 Sheetal Bhoyar, 2 Dr. D. V. Padole 1 Research Scholar, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur, India 2 Professor, G. H.
NIOS II Based Embedded Web Server Development for Networking Applications 1 Sheetal Bhoyar, 2 Dr. D. V. Padole 1 Research Scholar, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur, India 2 Professor, G. H.
Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances
 Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances Hiroki Matsutani, Ryuji Wakikawa, Koshiro Mitsuya and Jun Murai Faculty of Environmental Information, Keio University Graduate
Performance Oriented Management System for Reconfigurable Network Appliances Hiroki Matsutani, Ryuji Wakikawa, Koshiro Mitsuya and Jun Murai Faculty of Environmental Information, Keio University Graduate
Contents. System Development Models and Methods. Design Abstraction and Views. Synthesis. Control/Data-Flow Models. System Synthesis Models
 System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
System Development Models and Methods Dipl.-Inf. Mirko Caspar Version: 10.02.L.r-1.0-100929 Contents HW/SW Codesign Process Design Abstraction and Views Synthesis Control/Data-Flow Models System Synthesis
FPGA. AT6000 FPGAs. Application Note AT6000 FPGAs. 3x3 Convolver with Run-Time Reconfigurable Vector Multiplier in Atmel AT6000 FPGAs.
 3x3 Convolver with Run-Time Reconfigurable Vector Multiplier in Atmel AT6000 s Introduction Convolution is one of the basic and most common operations in both analog and digital domain signal processing.
3x3 Convolver with Run-Time Reconfigurable Vector Multiplier in Atmel AT6000 s Introduction Convolution is one of the basic and most common operations in both analog and digital domain signal processing.
Handout 17. by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal. Memory Unit and Read Only Memories
 Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
Handout 17 by Dr Sheikh Sharif Iqbal Memory Unit and Read Only Memories Objective: - To discuss different types of memories used in 80x86 systems for storing digital information. - To learn the electronic
CMS Level 1 Track Trigger
 Institut für Technik der Informationsverarbeitung CMS Level 1 Track Trigger An FPGA Approach Management Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. h.c. J. Becker Prof. Dr.-Ing. Eric Sax Prof. Dr. rer. nat. W. Stork KIT University
Institut für Technik der Informationsverarbeitung CMS Level 1 Track Trigger An FPGA Approach Management Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. h.c. J. Becker Prof. Dr.-Ing. Eric Sax Prof. Dr. rer. nat. W. Stork KIT University
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE
 8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems. 2008 Chapter-1L03: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin
 BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
Spacecraft Computer Systems. Colonel John E. Keesee
 Spacecraft Computer Systems Colonel John E. Keesee Overview Spacecraft data processing requires microcomputers and interfaces that are functionally similar to desktop systems However, space systems require:
Spacecraft Computer Systems Colonel John E. Keesee Overview Spacecraft data processing requires microcomputers and interfaces that are functionally similar to desktop systems However, space systems require:
- Nishad Nerurkar. - Aniket Mhatre
 - Nishad Nerurkar - Aniket Mhatre Single Chip Cloud Computer is a project developed by Intel. It was developed by Intel Lab Bangalore, Intel Lab America and Intel Lab Germany. It is part of a larger project,
- Nishad Nerurkar - Aniket Mhatre Single Chip Cloud Computer is a project developed by Intel. It was developed by Intel Lab Bangalore, Intel Lab America and Intel Lab Germany. It is part of a larger project,
Cryptographic Rights Management of FPGA Intellectual Property Cores
 Cryptographic Rights Management of FPGA Intellectual Property Cores Tom Kean Algotronix Ltd. PO Box 23116 Edinburgh EH8 8YB United Kingdom [email protected] ABSTRACT As the capacity of FPGA s increases
Cryptographic Rights Management of FPGA Intellectual Property Cores Tom Kean Algotronix Ltd. PO Box 23116 Edinburgh EH8 8YB United Kingdom [email protected] ABSTRACT As the capacity of FPGA s increases
SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC
 SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC Tim Armbruster [email protected] HIC for FAIR, Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und February 2011 Visit http://spadic.uni-hd.de 1. Introduction
SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC Tim Armbruster [email protected] HIC for FAIR, Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und February 2011 Visit http://spadic.uni-hd.de 1. Introduction
FPGA Implementation of Boolean Neural Networks using UML
 FPGA Implementation of Boolean Neural Networks using UML Roman Kohut,, Bernd Steinbach, Dominik Fröhlich Freiberg University of Mining and Technology Institute of Computer Science Freiberg (Sachs), Germany
FPGA Implementation of Boolean Neural Networks using UML Roman Kohut,, Bernd Steinbach, Dominik Fröhlich Freiberg University of Mining and Technology Institute of Computer Science Freiberg (Sachs), Germany
Delay Characterization in FPGA-based Reconfigurable Systems
 Institute of Computer Architecture and Computer Engineering University of Stuttgart Pfaffenwaldring 47 D 70569 Stuttgart Master s Thesis Nr. 3505 Delay Characterization in FPGA-based Reconfigurable Systems
Institute of Computer Architecture and Computer Engineering University of Stuttgart Pfaffenwaldring 47 D 70569 Stuttgart Master s Thesis Nr. 3505 Delay Characterization in FPGA-based Reconfigurable Systems
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
LatticeXP2 Configuration Encryption and Security Usage Guide
 April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1142 Unlike a volatile FPGA, which requires an external boot-prom to store configuration data, the LatticeXP2 devices are non-volatile and have on-chip configuration
April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1142 Unlike a volatile FPGA, which requires an external boot-prom to store configuration data, the LatticeXP2 devices are non-volatile and have on-chip configuration
PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR USE IN REMOTELY OPERATED LABORATORIES
 PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR USE IN REMOTELY OPERATED LABORATORIES Carsten Wulff ([email protected]) Prof. Trond Ytterdal ([email protected]) Norwegian University of Science and Technology,
PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FOR USE IN REMOTELY OPERATED LABORATORIES Carsten Wulff ([email protected]) Prof. Trond Ytterdal ([email protected]) Norwegian University of Science and Technology,
Discovering Computers 2011. Living in a Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
FLASH TECHNOLOGY DRAM/EPROM. Flash. 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 Year Source: Intel/ICE, "Memory 1996"
 10 FLASH TECHNOLOGY Overview Flash memory technology is a mix of EPROM and EEPROM technologies. The term flash was chosen because a large chunk of memory could be erased at one time. The name, therefore,
10 FLASH TECHNOLOGY Overview Flash memory technology is a mix of EPROM and EEPROM technologies. The term flash was chosen because a large chunk of memory could be erased at one time. The name, therefore,
The Advanced JTAG Bridge. Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09
 The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
The Advanced JTAG Bridge Nathan Yawn [email protected] 05/12/09 Copyright (C) 2008-2009 Nathan Yawn Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19
 Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes
 nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
The Shortcut Guide to Balancing Storage Costs and Performance with Hybrid Storage
 The Shortcut Guide to Balancing Storage Costs and Performance with Hybrid Storage sponsored by Dan Sullivan Chapter 1: Advantages of Hybrid Storage... 1 Overview of Flash Deployment in Hybrid Storage Systems...
The Shortcut Guide to Balancing Storage Costs and Performance with Hybrid Storage sponsored by Dan Sullivan Chapter 1: Advantages of Hybrid Storage... 1 Overview of Flash Deployment in Hybrid Storage Systems...
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX
 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
Designing VM2 Application Boards
 Designing VM2 Application Boards This document lists some things to consider when designing a custom application board for the VM2 embedded controller. It is intended to complement the VM2 Datasheet. A
Designing VM2 Application Boards This document lists some things to consider when designing a custom application board for the VM2 embedded controller. It is intended to complement the VM2 Datasheet. A
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines
 Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines Mircea Popa Abstract: The paper approaches the problem of control and selecting possibilities offered by the PC parallel
Solutions for Increasing the Number of PC Parallel Port Control and Selecting Lines Mircea Popa Abstract: The paper approaches the problem of control and selecting possibilities offered by the PC parallel
Preventing Piracy and Reverse Engineering of SRAM FPGAs Bitstream
 Approche de conception d interface de communication pour les systèmes sur puce Preventing Piracy and Reverse Engineering of SRAM FPGAs Bitstream Lilian Bossuet 1, Guy Gogniat 1, Wayne Burleson 2 1 LESTER
Approche de conception d interface de communication pour les systèmes sur puce Preventing Piracy and Reverse Engineering of SRAM FPGAs Bitstream Lilian Bossuet 1, Guy Gogniat 1, Wayne Burleson 2 1 LESTER
ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT
 216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330. Microcontrollers
 Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT. Nicholas Wieder
 SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT by Nicholas Wieder A thesis submitted to the faculty of The University of North Carolina at Charlotte in partial fulfillment of
SYSTEM-ON-PROGRAMMABLE-CHIP DESIGN USING A UNIFIED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT by Nicholas Wieder A thesis submitted to the faculty of The University of North Carolina at Charlotte in partial fulfillment of
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller
 Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
Implementing a Digital Answering Machine with a High-Speed 8-Bit Microcontroller Zafar Ullah Senior Application Engineer Scenix Semiconductor Inc. Leo Petropoulos Application Manager Invox TEchnology 1.0
