Ch22_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Delilah Charles
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch22_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A carbohydrate can be defined as a molecule A) composed of amine groups and carboxylic acid groups bonded to a carbon skeleton. B) composed mostly of hydrocarbons and soluble in non-polar solvents. C)whose name ends in "-ase". D) that is an aldehyde or ketone and that has more than one hydroxyl group. E) composed of carbon atoms bonded to water molecules. 1) 2) Classify the molecule shown according to the location of its carbonyl group and the number of carbon atoms. 2) A) ketotriose B) ketotetrose C) aldotetrose D) aldopentose E) aldotriose 3) Classify the molecule shown according to the location of its carbonyl group and the number of carbon atoms. 3) A) aldotetrose B) aldopentose C) aldotriose D) ketotriose E) ketotetrose 1
2 4) Classify the molecule shown according to the location of its carbonyl group and the number of carbon atoms. 4) A) ketotriose B) aldotriose C) aldotetrose D) aldopentose E) ketotetrose 5) Glucose can be classified as a(an) A) ketohexose. B) aldopentose. C) aldohexose. D) ketopentose. E) aldoketose. 5) 6) Ribose can be classified as a(an) A) ketohexose. B) aldohexose. C) ketopentose. D) aldopentose. E) aldoketose. 6) 7) Fructose can be classified as a(an) A) aldohexose. B) ketohexose. C) aldopentose. D) aldoketose. E) ketopentose. 7) 8) How many stereoisomers of an aldotetrose can exist? A) 16 B) 32 C)2 D) 4 E) 8 8) 9) How many stereoisomers of an aldopentose can exist? A) 2 B) 16 C)8 D) 32 E) 4 9) 10) Left- and right-handed mirror image molecules are known as A) structural isomers. B) enantiomers. C) diastereomers. D) anomers. E) cis-trans isomers. 10) 2
3 11) Molecules such as erythrose and threose, which are stereoisomers but not mirror images, are referred to as a pair of. D- and L-threose are mirror images and are referred to as a pair of. A) anomers; diastereomers B) diastereomers; anomers C) diastereomers; enantiomers D) enantiomers; diastereomers E) anomers; enantiomers 11) 12) Which molecule shown is D-glyceraldehyde? A) 12) B) C) D) E) 3
4 13) A sugar is classified as a D-isomer if the hydroxyl group A) on the chiral carbon nearest to the carbonyl points to the right. B) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl points to the left. C)on the end carbon farthest from the carbonyl points to the left. D) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl points to the right. E) on the chiral carbon nearest to the carbonyl points to the left. 13) 14) Which molecule shown is an L-isomer? A) 14) B) C) D) E) 4
5 15) Which molecule shown is a D-isomer? A) 15) B) C) D) 5
6 E) 16) Two isomeric sugars that are cyclic and only differ in the position of the -OH group attached to the hemiacetal carbon are called A) eneantiomers. B) anomers. C) diastereomers. D) mutarotations. E) epimers. 16) 17) Mutarotation is process where A) two glucose molecules react to form a disaccharide. B) glucose undergoes reaction to form an equilibrium mixture of anomers. C) glucose isomerizes to fructose. D) glucose reacts with an alcohol forming a cyclic acetal. E) the aldehyde group present in a sugar is converted to a hemiacetal. 17) 18) All of the statements concerning monosaccharides are correct except A) A molecule is classified as a D or L isomer by the position of the hydroxyl group on the chiral center farthest from the carbonyl group. B) Monosaccharides have the general formula Cn(H2O)n, but this only describes the number and kinds of atoms, not their structure. C)Monosaccharides with 5 or 6 carbon atoms exist in solution in cyclic form. D) The number of stereoisomers possible is 2n, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms in the molecule. E) The two different cyclic forms of a particular monosaccharide are called tautomers. 18) 19) The conversion of cyclic glucose between the alpha form and the beta form is called A) dimerization. B) hydrolysis. C) polymerization. D) cyclization. E) mutarotation. 19) 20) When a monosaccharide forms a ring by interaction of one of its hydroxyl groups with its aldehyde group, the bond is referred to as a(an) linkage. A) ester B) glycosidic C) hemiacetal D) acetal E) ether 20) 6
7 21) A hemiacetal linkage consists of a A) carbon atom bonded to two -OH groups. B) carbon atom bonded to both an -OH and an -OR group. C)carbon atom that is bonded to an -OR group and an -NH2 group. D) carbonyl group that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group. E) carbonyl group that is also bonded to an ether linkage. 21) 22) A sugar is classified as an L-isomer if the hydroxyl group A) on the chiral carbon closest to the carbonyl group points to the right. B) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group points to the right. C)on the chiral carbon closest to the carbonyl group points to the left. D) on the end carbon farthest from the carbonyl points to the left. E) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group points to the left. 22) 23) All of the following are common monosaccharides of interest in human biochemistry except A) glucose. B) maltose. C) ribose. D) galactose. E) fructose. 23) 24) Fructose is similar to glucose and galactose in all of the following aspects except A) it forms a hemiacetal ring. B) it can undergo mutarotation from α to β anomers. C)its formula is C6 H12O6. D) it is a ketose. 24) 25) When a monosaccharide forms a cyclic hemiacetal, the carbon atom that contained the carbonyl group is identified as the carbon atom because A) D; the carbonyl group is drawn to the right. B) anomeric; its substituents can assume an α or a β position. C)L; the carbonyl group is drawn to the left. D) acetal; it forms bonds to an OR and an OR'. E) enantiomeric; depending on its position, the resulting ring can have a mirror image. 25) 26) reaction of a simple sugar with an alcohol produces a. A) a mixture of anomers B) cyclic acetal C) glycoside D) all of the above 26) 27) of glucose leads to gluconic acid. A) Reduction B) Oxidation C) Isomerization D) Esterification E) Glycosidation 27) 7
8 28) Common reducing reactions of monosaccharides are due to A) the presence of more than one hydroxyl group. B) the presence of at least one chiral carbon atom. C)the presence of at least one hydroxyl group. D) their cyclic structures. E) the presence of a carbonyl group, usually on the #1 carbon atom. 28) 29) Which molecule is not a reducing sugar? A) glucose B) galactose C) lactose D) sucrose E) maltose 29) 30) Which molecule is a reducing sugar? A) starch B) glycogen C) amylopectin D) maltose E) sucrose 30) 31) Ketoses can act as reducing sugars in basic solution because A) their carbonyl groups can readily be oxidized just as in aldoses. B) mutarotation makes the carbonyl group accessible to oxidizing agents. C) the large number of hydroxyl groups allows oxidation of the molecules. D) the ketone is converted to an aldehyde by keto-enol tautomerization. 31) 32) A glycosidic bond is A) a bond between any two carbohydrate molecules. B) a bond formed between an anomeric carbon atom and any OR group. C) a bond between anomeric carbon atoms on two separate monosaccharides. D) any bond that can be broken by reaction with water. 32) 33) All of the following are functions of modified carbohydrate molecules except A) As heparin they form a fibrous network in blood clots. B) As a component of hemoglobin they transport oxygen. C)As a receptor molecule on cell surfaces they assist in the functioning of the immune system. D) As a component of cartilage they provide support to joints. E) As chitin they act as a structural component of lobster shells. 33) 34) Cellulose is produced by, and its major function is. A) animals; energy storage B) plants; energy storage C) animals; as a structural component D) plants; as a structural component 34) 35) The reaction in which a disaccharide is broken down into its component monosaccharides is A) oxidation. B) hydrolysis. C) reduction. D) glycoside formation. E) enediol formation. 35) 8
9 36) Lactose result from reacting glucose at its carbon and galactose at its carbon. A) 6, 1 B) 4, 1 C)1, 1 D) 1, 4 E) 1, 6 36) 37) The bond connecting the two monosaccharides in maltose is a(an) linkage. A) 1,2 anomeric B) α-1,4 glycosidic C) β-1,6 glycosidic D) β-1,4 glycosidic E) α-1,6 glycosidic 37) 38) The bond connecting the two monosaccharides in sucrose is a(an) linkage. A) α-1,6 glycosidic B) α-1,4 glycosidic C) β-1,6 glycosidic D) b-1, 4 glycosidic E) 1,2 anomeric 38) 39) The molecular formula of the common disaccharides in human biochemistry is A) C12H22O11. B) C2(H2O)2. C) C12H24O12. D) CH2O. E) C6H12O6. 39) 40) Sucrose is not a reducing sugar because its A) disaccharide bond is a β-1,4 linkage. B) disaccharide bond is an α-1,4 linkage. C) hemiacetal groups cannot be converted to aldehyde groups. D) disaccharide bond is a 1,2 anomeric link. 40) 41) Glocoproteins are formed by bonding a oligosaccharide to a protein through a linkage. A) glucuronic B) ester C) ether D) glycosidic E) imine 41) 42) Starch is produced by, and its major function is. A) animals; energy storage B) animals; as a structural component C) plants; energy storage D) plants; as a structural component 42) 9
10 43) Glycogen is produced by, and its major function is. A) plants; as a structural component B) animals; as a structural component C) plants; energy storage D) animals; energy storage 43) 44) Starch is composed of two polymers,, which is an unbranched chain, and, which is a branched polymer. A) amylase; amylose B) amylose; amylase C) amylopectin; amylose D) amylose; amylopectin E) amylase; amylopectin 44) 45) Which of the following statements comparing amylopectin and glycogen is false? A) Both are polymers of α-d-glucose. B) Both serve as energy storage molecules. C) Glycogen is more highly branched than amylopectin. D) Glycogen molecules are generally larger than amylopectin molecules. 45) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 46) Explain why cows and other grazing animals can eat grass and benefit from its nutritive value, but humans cannot. 46) MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following. 47) enantiomers 48) diastereomers 49) anomers 50) galactose 51) ribose 52) fructose A) a monosaccharide that is sweeter than sucrose and found in honey and fruits B) an aldopentose that is a component of nucleic acids C) stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other D) a monosaccharide which is a component of milk sugar E) mirror-image forms of chiral molecules 47) 48) 49) 50) 51) 52) F) isomers of cyclic sugars that exist in the position of the hydroxyl group at the hemiacetal carbon atom 10
11 53) glucose 54) reducing sugar 55) polysaccharide 56) sucrose 57) maltose 58) lactose 59) disaccharide 60) amylose 61) cellulose 62) glycogen A) a monosaccharide that functions as the transport form of carbohydrates in blood B) a polysaccharide composed of glucose units joined by β-1,4 linkages C) a disaccharide composed of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose D) a disaccharide composed of two molecules of glucose E) a very highly branched polysaccharide composed of glucose units F) a component of starch composed of glucose units joined by β-1,4 linkages G) a carbohydrate that yields two monosaccharides upon hydrolysis 53) 54) 55) 56) 57) 58) 59) 60) 61) 62) H) a carbohydrate composed of a large number of monosaccharides chemically combined I) a carbohydrate that can be oxidized to produce an acid molecule or its corresponding anion J) a disaccharide composed of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose 11
12 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 1) D 2) C 3) E 4) D 5) C 6) D 7) B 8) D 9) C 10) B 11) C 12) A 13) D 14) D 15) E 16) B 17) B 18) E 19) E 20) C 21) B 22) E 23) B 24) D 25) B 26) D 27) B 28) E 29) D 30) D 31) D 32) B 33) B 34) D 35) B 36) B 37) B 38) E 39) A 40) D 41) D 42) C 43) D 44) D 45) E 46) Humans do not have the enzyme that breaks the β-1,4-linkages in cellulose. Grazing animals and some insects have bacteria in their digestive systems that produce an enzyme that hydrolyzes these linkages. Therefore these animals can digest and metabolize cellulose. 47) E 48) C 12
13 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 49) F 50) D 51) B 52) A 53) A 54) I 55) H 56) J 57) D 58) C 59) G 60) F 61) B 62) E 13
3) How many monosaccharides are connected to each other in a disaccharide? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
CHEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) Page 1
 CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
I. Chapter 5 Summary. II. Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. III. Lipids
 I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates
 The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES OF LIFE C A R B O H Y D R A T E S, L I P I D S, P R O T E I N S, A N D N U C L E I C A C I D S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 115, Page 1 of 29) Carbon
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
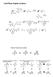 Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1
 CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
Catalysis by Enzymes. Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction.
 Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2
 Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Elements in Biological Molecules
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Qualitative Testing for Carbohydrates
 R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids
 VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids Grades 10 - College 25mins Teacher Notes by Sue Wright, B. Sc., Dip. Ed. Produced by VEA Pty Ltd
VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Macromolecules 1 Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids Grades 10 - College 25mins Teacher Notes by Sue Wright, B. Sc., Dip. Ed. Produced by VEA Pty Ltd
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Organic Compounds. Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for?
 Organic Compounds Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for? Aristotle: Francesco Redi: What do we already know? Spontaneous
Organic Compounds Essential Questions: What is Organic? What are the 4 major Organic Compounds? How are they made? What are they used for? Aristotle: Francesco Redi: What do we already know? Spontaneous
Carbon-organic Compounds
 Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins
 Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Worksheet 13.1. Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary
 Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. Carbohydrates. Organic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R.
 hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbon The element of life! All living things contain the element carbon. Organic means it contains carbon The reason for this is because of carbon s ability
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbon The element of life! All living things contain the element carbon. Organic means it contains carbon The reason for this is because of carbon s ability
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Ch24_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch24_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Substances originating in plant or animal material and soluble in non-polar organic solvents
Ch24_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Substances originating in plant or animal material and soluble in non-polar organic solvents
II. Chemistry of Sugars
 II. Chemistry of Sugars Sugars-or saccharides- are the most abundant bio-molecule on the planet. They are important in a number of biological roles. Most obviously you will know them as a major component
II. Chemistry of Sugars Sugars-or saccharides- are the most abundant bio-molecule on the planet. They are important in a number of biological roles. Most obviously you will know them as a major component
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which molecule is a carboxylic acid? A) 1) B) C) D) E) CH3 CH2 CH2 NH2 2) Which molecule
Ch17_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which molecule is a carboxylic acid? A) 1) B) C) D) E) CH3 CH2 CH2 NH2 2) Which molecule
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates
 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles
 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
WATER CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" POLARITY HYDROGEN BONDING
 CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" WATER Compare the body of the jellyfish with our own bodies. The jellyfish will die if it is removed from its water environment, yet we can live in the
CHAPTER 3 - BIOCHEMISTRY "THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE" WATER Compare the body of the jellyfish with our own bodies. The jellyfish will die if it is removed from its water environment, yet we can live in the
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Water. Definition: A mole (or mol ) Water can IONIZE transiently. NONpolar covalent molecules do not dissolve in water + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
 Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
The Molecules of Life - Overview. The Molecules of Life. The Molecules of Life. The Molecules of Life
 The Molecules of Life - Overview The Molecules of Life The Importance of Carbon Organic Polymers / Monomers Functions of Organic Molecules Origin of Organic Molecules The Molecules of Life Water is the
The Molecules of Life - Overview The Molecules of Life The Importance of Carbon Organic Polymers / Monomers Functions of Organic Molecules Origin of Organic Molecules The Molecules of Life Water is the
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
 Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein
 Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
 Enzymes Essential Questions: What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work? What are the properties of enzymes? How do they maintain homeostasis for the body? What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
Enzymes Essential Questions: What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work? What are the properties of enzymes? How do they maintain homeostasis for the body? What happens to the food we eat? It gets broken down!
BIOMOLECULES. reflect
 reflect A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnifi cent structures. The elaborate city scene to the right is made of small, simple
reflect A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnifi cent structures. The elaborate city scene to the right is made of small, simple
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids
 Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids Outline Fats and Oils Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Biodiesel Homework We hear quite a lot about the place of fats and oils in human nutrition. Foods high in fat are at the
Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids Outline Fats and Oils Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Biodiesel Homework We hear quite a lot about the place of fats and oils in human nutrition. Foods high in fat are at the
3120-1 - Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which series is arranged in correct order according to decreasing size of structures? A) DNA, nucleus, chromosome, nucleotide, nitrogenous base B) chromosome, nucleus, nitrogenous base, nucleotide,
Name: 1) Which series is arranged in correct order according to decreasing size of structures? A) DNA, nucleus, chromosome, nucleotide, nitrogenous base B) chromosome, nucleus, nitrogenous base, nucleotide,
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch
 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Digestive Physiology: Amylase hydrolysis of starch Introduction Enzymes are proteins composed of amino acid building blocks. Enzymes catalyze or increase the rate of metabolic
Molecule Projections
 Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
Lipids. There are 2 types of lipids; those that contain the structural component of a fatty acid; and
 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. named for the Greek word lipos, which means fat. extracted from cells using
Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. named for the Greek word lipos, which means fat. extracted from cells using
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Compounds with the -OH group attached to a saturated alkane-like carbon are known as A)
Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Compounds with the -OH group attached to a saturated alkane-like carbon are known as A)
Photosynthesis and Sucrose Production
 Photosynthesis and Sucrose Production 2 Starch and sucrose, key substrates for the development of dental caries, are exclusively synthesized by plants. They are made in plant leaves by a process called
Photosynthesis and Sucrose Production 2 Starch and sucrose, key substrates for the development of dental caries, are exclusively synthesized by plants. They are made in plant leaves by a process called
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
IR Applied to Isomer Analysis
 DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Prerequisites: Course Description: Textbook: CHM 212 Organic
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Prerequisites: Course Description: Textbook: CHM 212 Organic
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Chemistry 201. Practical aspects of buffers. NC State University. Lecture 15
 Chemistry 201 Lecture 15 Practical aspects of buffers NC State University The everyday ph scale To review what ph means in practice, we consider the ph of everyday substances that we know from experience.
Chemistry 201 Lecture 15 Practical aspects of buffers NC State University The everyday ph scale To review what ph means in practice, we consider the ph of everyday substances that we know from experience.
Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a benzene ring.
 Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
Photo Cell Resp Practice. A. ATP B. oxygen C. DNA D. water. The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants.
 Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
CHEM 121. Chapter 19, Name: Date:
 CHEM 121. Chapter 19, Name: Date: 1. A lipid is any substance of biochemical origin that is A) soluble in water but insoluble in nonpolar solvents B) insoluble in both water and nonpolar solvents C) insoluble
CHEM 121. Chapter 19, Name: Date: 1. A lipid is any substance of biochemical origin that is A) soluble in water but insoluble in nonpolar solvents B) insoluble in both water and nonpolar solvents C) insoluble
Lab 2 Biochemistry. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Lipid Structure and Role in Food. The lab has the following learning objectives.
 1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End!
 Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
lt\ Nutrition a-glncose www.cambridge.org in this web service Cambridge University Press Glucose+ fructose Glucose+ galactose
 P. T. Marshall and G. M. ughes 1 Nutrition 1.1 The basic biochemistry of mammalian metabolites The mammals are heterotrophic, that is to say they derive their essential nutrients, via food chains, from
P. T. Marshall and G. M. ughes 1 Nutrition 1.1 The basic biochemistry of mammalian metabolites The mammals are heterotrophic, that is to say they derive their essential nutrients, via food chains, from
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Fourteen 1
 An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
3Reactions of Sugars. Introduction. Mutarotation
 3eactions of Sugars Introduction 35 Mutarotation 35 xidation of Sugars 39 Glycoside Formation 40 Acid atalyzed Sugar eactions 42 Alkaline-atalyzed Sugar eactions 43 Summary 45 Vocabulary 47 eferences 47
3eactions of Sugars Introduction 35 Mutarotation 35 xidation of Sugars 39 Glycoside Formation 40 Acid atalyzed Sugar eactions 42 Alkaline-atalyzed Sugar eactions 43 Summary 45 Vocabulary 47 eferences 47
Preliminary MFM Quiz
 Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
Preliminary MFM Quiz 1. The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is: A) adenosine monophosphate B) adenosine diphosphate C) adenosine trisphosphate D) guanosine trisphosphate E) carbamoyl phosphate
a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler units
 Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7. Alcohols, Ethers and More
 Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Topic 3: Nutrition, Photosynthesis, and Respiration
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line-bond (Lewis) structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed structural
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT
 EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below:
 CHEM 3311 Exam #1 Name Dr. Minger June 8, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received
CHEM 3311 Exam #1 Name Dr. Minger June 8, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received
Macromolecules in my food!!
 Macromolecules in my food!! Name Notes/Background Information Food is fuel: All living things need to obtain fuel from something. Whether it is self- made through the process of photosynthesis, or by ingesting
Macromolecules in my food!! Name Notes/Background Information Food is fuel: All living things need to obtain fuel from something. Whether it is self- made through the process of photosynthesis, or by ingesting
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1. Lipids:
 (Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Fatty Acids carboxylic acids
 Triglycerides (TG) should actually be called triacylglycerols (TAG). TG or TAG are molecules with a glycerol (a carbohydrate) backbone to which are attached three acyl groups. They represent a concentrated
Triglycerides (TG) should actually be called triacylglycerols (TAG). TG or TAG are molecules with a glycerol (a carbohydrate) backbone to which are attached three acyl groups. They represent a concentrated
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Carbohydrate Analysis: Column Chemistries and Detection
 Carbohydrate Analysis: Column Chemistries and Detection Joe Romano Waters Corporation Carbohydrates in Feeds Methodology Forum AOAC 2007 Annual Meeting Anaheim, CA September 18, 2007 2007 Waters Corporation
Carbohydrate Analysis: Column Chemistries and Detection Joe Romano Waters Corporation Carbohydrates in Feeds Methodology Forum AOAC 2007 Annual Meeting Anaheim, CA September 18, 2007 2007 Waters Corporation
