О.С. Істер. Алгебра 8 клас. Вправи Самостійні роботи Тематичні контрольні роботи Завдання для експрес-контролю. Видання третє, доповнене
|
|
|
- Зинаида Харченко
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ОС Істер Алгебра 8 клас Вправи Самостійні роботи Тематичні контрольні роботи Завдання для експрес-контролю Видання третє, доповнене ТЕРНОПІЛЬ НАВЧАЛЬНА КНИГА БОГДАН
2 УДК 511(0753) ББК 1я7 І89 І89 Істер ОС Алгебра 8 клас: Вправи Самостійні роботи Тематичні контрольні роботи Завдання для експрес-контролю Вид 3-є, доповн Тернопіль: Навчальна книга Богдан, с ISBN У посібнику запропонована повна добірка матеріалів з алгебри 8-го класу відповідно до шкільної програми: вправи, рівневі самостійні роботи, тематичні контрольні роботи та завдання для експрес-контролю знань Призначений для вчителів, методистів та учнів загальноосвітніх навчальних закладів Охороняється законом про авторське право Жодна частина цього видання не може бути відтворена в будь-якому вигляді без дозволу автора чи видавництва ISBN Навчальна книга Богдан, майнові права, 011 ББК 1я7 Передмова Посібник містить дидактичні матеріали з курсу алгебри 8-го класу: 764 вправи, 13 рівневих самостійних робіт, кожна з яких подана у 6 варіантах (три рівні у двох рівноцінних варіантах); 8 тематичних контрольних робіт, кожна з яких подана у двох рівноцінних варіантах, та 7 наборів завдань для проведення рівневого експрес-контролю знань (кожен у двох варіантах) Назви розділів та пунктів посібника відповідають назвам тем програми, тому посібник легко адаптується до підручників: ОС Істер «Алгебра 8», ГП Бевз, ВГ Бевз «Алгебра 8», АГ Мерзляк та ін «Алгебра 8», ГМ Янченко та ін «Алгебра 8» Для зручності користування посібником у назві кожної самостійної роботи, тематичної контрольної роботи чи завдання для експрес-контролю знань відбито їхню тематику У кінці посібника наведено відповіді та вказівки до більшості вправ До самостійних, тематичних контрольних робіт та завдань для експрес-контролю знань відповіді відсутні Тому вчитель, придбавши посібник на весь клас (або один примірник на парту), може використовувати його під час будь-якого уроку (закріплення нових знань, перевірки знань, експрес-контролю знань тощо) Нижче розглянемо деякі особливості посібника та роботи з ним 1 Вправи Посібник містить вправи для класних і домашніх робіт Вправи, рекомендовані для домашнього виконання, відзначені (номери вправ подані на темному фоні) Задачі, позначені кружечком ( ), відповідають початковому та середньому рівням навчальних досягнень; задачі без цієї позначки достатньому та високому рівням навчальних досягнень Достатня кількість вправ дасть змогу вчителю використовувати посібник практично на кожному уроці та давати з нього домашні зав дання Самостійні роботи У посібнику подано добірку рівневих самостійних робіт Вони позначені буквою С з відповідним номером Після номера вказано одну з літер А, Б або В (наприклад, С-Б) відповідно до рівня цієї роботи:
3 4 Передмова Передмова 5 А самостійна робота, що відповідає початковому та середньому рівням навчальних досягнень; Б самостійна робота, що відповідає достатньому рівню навчальних досягнень; В самостійна робота, що відповідає високому рівню навчальних досягнень Для кожного рівня подано два рівноцінні варіанти Кожна самостійна робота містить 3 завдання і розрахована на хв (залежно від теми) Самостійні роботи мають, як правило, навчальний характер і не призначені для оцінювання знань учнів Якщо вчитель захоче оцінити роботу, то кожне завдання рівня А автор пропонує оцінювати у бали, рівня Б в 3 бали, рівня В в 4 бали Таким чином, максимальна оцінка за роботу рівня А 6 балів, рівня Б 9 балів, рівня В 1 балів При оцінюванні кожного завдання вчитель може застосовувати систему, що подана нижче (для оцінювання тематичної контрольної роботи) Рівень самостійної роботи, що виконує учень, як правило, визначає вчитель 3 Тематичні контрольні роботи (надалі ТКР) Кожна ТКР містить як завдання, що відповідають початковому та середньому рівням навчальних досягнень (вони позначені кружечками), так і завдання, що відповідають достатньому та високому рівням навчальних досягнень Усі завдання оцінено в балах таким чином, що максимально оцінка за ТКР дорівнює 1 балам Кожна ТКР розрахована на один урок (40 45 хв) Звичайно, вчитель може збільшити або зменшити як кількість ТКР, так і кількість завдань у кожній ТКР, змінивши при цьому оцінювання в балах таким чином, щоб сума балів дорівнювала 1 Автор пропонує на першому етапі вести оцінювання кожного завдання у звичній для вчителя математики системі «плюс-мінус»: «+» (плюс) учень повністю розв язав завдання; «±» (плюс-мінус) хід розв язування завдання правильний, але допущено помилки логічного або обчислювального характеру, які привели до неправильної відповіді; (мінус-плюс) завдання не закінчено, але учень суттєво наблизився до повного розв язання, виконавши не менше його половини; (мінус) учень почав розв язувати правильно (наприклад, зробив малюнок, записав фрагмент розв язання), але виконав завдання менше ніж наполовину; «0» (нуль) учень не починав завдання або почав неправильно На другому етапі вчитель переводить оцінку із системи «плюсмінус» у бали Пропонується наступна шкала Максимальний бал за завдання Оцінки в системі плюс-мінус Переведення в бали + ± 1 1 0,5 0,5 0 1,5 1 0,5 3 3,5 1 1,5 0, Природним є те, що оцінкою роботи є сума балів, отримана учнем за виконання кожного завдання окремо Якщо сумою є не ціле число (а саме це число має п ять десятих), то кори с тує мося звичним правилом округлювання (наприклад, 9,5 10) 4 Завдання для експрес-контролю ( надалі ЕК) Якщо учень пропустив урок, на якому проводилася ТКР, йому можна запропонувати рівневі завдання для ЕК Автор пропонує вчителю спочатку визначити середню поточну оцінку учня, яка враховує відповіді біля дошки, ведення зошита тощо; а потім запропонувати учневі завдання ЕК на один рівень вищий за рівень середньої поточної оцінки Кожен із рівнів, що відповідає рівням навчальних досягнень (середньому, достатньому та високому), містить завдання, сума балів яких дорівнює 3 Кожне завдання вчитель оцінює у системі плюс-мінус, а потім переводить у бали (див табл вище) Якщо під час ЕК учень бездоганно виконав завдання на середній чи достатній рівень, то вчитель може запропонувати йому завдання більш високого рівня Сума середньої поточної оцінки та балів, набраних під час ЕК, може враховуватися вчителем при виставленні оцінки за тему як оцінка, отримана іншими учнями під час ТКР, або якимось іншим чином на розсуд учителя
4 П е р е д м о в а д о т р е т ь о г о видання З моменту виходу першого видання автор отримав чимало відгуків Деякі з них містили пропозиції, спрямовані на покращення посібника Враховуючи ці поради, автор значно розширив розділ відповідей та вказівок до вправ Крім того, в тексті посібника були виправлені друкарські та авторські помилки Автор щиро дякує всім своїм учням та, особливо, своєму синові Дмитру Істеру, які брали участь в апробації першого видання посібника Друге видання посібника перероблено відповідно до чинної програми, у третє видання автор вніс правки до деяких завдань Відвідайте наші сторінки в Інтернеті і Бажаємо успіхів! Вправи I Повторення матерiалу за курс алгебри 7 класу Цiлi вирази Перетворення цiлого виразу у многочлен 1 Спростіть вираз: (3x 5) + ( x); ) (5m 10) (4 m); 3) (3x + ( 3x x ); 4) (10n 1n ) (n 3 n + 6) Спростіть вираз: (7m 8) + (m 4); ) (5x ) ( 3x ); 3) (4x ) + (4 x 4x ); 4) (7 4m 3 ) ( m 4m 3 ) 3 Подайте у вигляді степеня вираз: (m ) 3 ; ) ( x ) 4 ; 3) a 3 a 4 ; 4) ((t ) 3 ) 7 ; 5) (b 8 ) 3 (b 4 ) 7 ; 6) (a 4 ) 8 : (a ) 16 4 Подайте у вигляді степеня вираз: (c 4 ) ; ) ( m ) 3 ; 3) ( b 3 ) ( b 5 ); 4) ((x 3 ) 4 ) 5 ; 5) (c 3 ) 5 (c ) 9 ; 6) (c 3 ) 6 :(c 9 ) 5 Подайте у вигляді многочлена: 3m (m 5); ) 0,4c(5 c); 3) 7t(t t + 7); 4) (t + ) (t 7); 5) (5x (4x + ); 6) (c ) (c c + 3) 6 Спростіть вираз: 3(x 8) + 4(3 4x); ) 6m(m 3m) 3m(m 6m); 3) (3x (x + 7) 6x ; 4) 1y 3 (4y ) (3y + 5) 7 Подайте у вигляді многочлена вираз: 8x (x 7x + 6); ) (4m )(5m + 3); 3) (x 3)(x + x 8); 4) 5y(y 3y) 3y(y 5y);
5 8 Вправи Повторення матерiалу за курс алгебри 7 класу 9 5) (7y )(8y + 3) 56y ; 6) 6m 4 (m 3)(3m 3 + ) 8 Подайте у вигляді многочлена: (m 5)(m + 5); ) (7 + x)(x 7); 3) (5z 3)(3 + 5z ); 4) (m + ) ; 5) (9 x) ; 6) (4m ; 7) (8 + 3c ) ; 8) (5m 4n) ; 9) (x + )(x x + 4); 10) (a 3)(a + 3a + 9) 9 Подайте вираз у вигляді многочлена: (c + 3)(3 c); ) (7m 4)(4 + 7m ); 3) (x ; 4) (4 + 5c ) ; 5) (x 3y) ; 6) (5c + m 3 ) ; 7) (x (x + x + ; 8) (t + 5)(t 5t + 5) 10 Спростіть вираз: (y + 3)(y 7) + 4y(1 y); ) (x )(x + 3) (x + 3)(x 7); 3) (x 3y)(3x + y) + (6x y)(6y x); 4) (7a + 5x)(a 3 x) a 3 (7a + 5x) 11 Подайте вираз у вигляді многочлена: (5m 3n)(5m + 3n) + (3m 5n)(3m + 5n); ) (y 3) + (y ) (y + ); 3) (4x 3y)(3y + 4x) (4x y) ; 4) (x )(x + 3) + (x + ) (5 x)(5 + x); 5) 7x(x 3)(3 + x) (1 3x) + 7(3x + )( 3x); 6) 8(x ) (x + ) 5(x + 7)(x 1 Спростіть вираз: (3x 5m)(3m x) + (x m)(3x 15m); ) (3b + 4)(b 3 x) 3b 3 (5 + b ); 3) (m + (3m 4)(4 + 3m); 4) (y )(y + ) (y 8) ; 5)7x(x )(x + ) 4x(x 3) ; 6) (m 3) (m + 3) (m 3)(m 7) 13 Доведіть, що значення виразу (x )(x + 6) 4(x 8) при будьякому значенні x набуває додатних значень 14 Доведіть, що при будь-якому цілому значенні m значення виразу (m 8) m(m 16) + 3m кратне 3 15 При якому значенні a многочлен стандартного вигляду, тотожно рівний добутку (y + y 3) (y a), не містить y? Розкладання многочленів на множники 16 Подайте многочлен у вигляді добутку: 7a 1; ) 5m mn; 3) 7ax 7ay; 4) y 3y; 5) 4x 1xy; 6) 3m m; 7) m 6 + m ; 8) 9m 3 3m 5 ; 9) 18a b 6ab; 10) 49x y + 56xy ; 1 8m m 4 ; 14x 9 1x 7 17 Розкладіть на множники: 8m 4; ) 7x xy; 3) 8mn 16mx; 4) m 3 4m; 5) c 8 c 6 ; 6) 5x 8 30x 6 ; 7) 7xy 3xy ; 8) 8c 3 n + 1cn 3 ; 9) 9c c 7 18 Розкладіть на множники: 5x 7 15x 9 + 5x 3 ; ) 8mn 3 1m n 4 m n ; 3) 9m 7 1m 6 n + 18m 5 ; 4) 10ab c 3 15a b c 0a 3 bc 19 Подайте у вигляді добутку многочлен: ax 3a + bx 3b ) x ax + bx ab; 3) 5m + 5n xm xn; 4) 7t tx 7 + x; 5) m 3 m + 5m 5; 6) 10a b 5a + ab a 0 Розкладіть на множники: by 5b 5x + xy; ) y my ny + mn; 3) 8m am 16 + a; 4) 1mb 3b + 4bm b 1 Розкладіть на множники: 3b 4 4b 3 y 6b + 8y; ) 3m 3 b 3m + m b m; 3) a b mb + ma t b + at ; 4) xm xn + yn + zn zm ym Розкладіть на множники: m 9; ) 36a 1; 3) 0,49 0,64t ; 4) mn ; 16 5) m 8 n ; 6) 0,16b 8 0,64c Подайте у вигляді добутку: 16 c ; ) 1 0,64p ; 3) 81 8 p c ; 4) m 049, n Розкладіть на множники: с 8 b 4 ; ) 81t 4 c 16 ;
6 Самостійні роботи 119 Самостійні роботи С-1 Повторення матеріалу за курс алгебри 7 класу I варіант С 1А 1 Спростіть вираз: (6y + (y 3) y(4 + 3y); ) (3x (3x + (x + 7) Розкладіть на множники: a 18; ) x 10x + 5; 3) xy + x + 5y + 5 x + y = 6, 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь 3x y = 13 С 1Б 1 Спростіть вираз: (5x 3x)(x + 5x (x ); ) (7m n) (7m + n) (5m n) Розкладіть на множники: 3m 3 n 1mn; ) 5x x + 45x; 3) m n + n mn m 3 5( x + y) + 4( x y) = 6, 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь ( x + 3) 3 = 3( y ) С 1В 1 Спростіть вираз: (3x + (9x 3x + + (9x 5)(7 3x ); ) (6p + q 3 )( q 3 + 6p ) 9(p + q 3 ) Розкладіть на множники: 3m ; ) 3m 3 n + 1mn 4 + 1m n 3 ; 3) p 3 pq 7p + 7q 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь y( y+ 4x) ( y ) = 4x( y 4, x y 7x 5x 7y + = ІІ варіант С 1А 1 Спростіть вираз: (4x + (x 3) x(5 + x); ) (m (m + (m + 5) Розкладіть на множники: 3a 1; ) x 6x + 9; 3) ab + a + b + x y = 7, 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь x + 3y = 19 С 1Б 1 Спростіть вираз: (3x x)(x + 3x (x 4); ) (3y p)(3y + p) (y p) Розкладіть на множники: x 3 y 18xy; ) 4x x + 144x; 3) a 3 + ab a b b ( x y) + 3( x + y) = 3, 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь 3( x + 18 = ( y 4) С 1В 1 Спростіть вираз: (x (4x + x + + (x 3)(5 4x ); ) (4m 3 + n )( n + 4m 3 ) 4(m 3 + n ) Розкладіть на множники: x 4 + 3; ) x 4 y + 18x y 3 + 1x 3 y ; 3) m 3 mn 4m + 4n 3 Розв яжіть систему рівнянь x y 5x + 1 7x 11y + =, x( x + y) ( x = y( x 1
7 146 Тематичні контрольні роботи Тематичні контрольні роботи 147 Тематичні контрольні роботи ТКР-1 Алгебраїчні дроби Основна властивість дробу Додавання і віднімання дробів І варіант 1 ( бали) При яких значеннях змінної має зміст вираз: 5 x 4 ; ) x 1 x x +? ( ) ( бали) Скоротіть дріб: 5x y 5 ; ) 4 xy 8 y ; 6 5xy 1y 3) 5 a 10 ; 4) m a m 1 3 ( бали) Виконайте дію: 7 3 a 4 + a 4 + a ; ) b b 4 (4 бали) Спростіть вираз: a a a a ; ) 8 b x 4b ; b 5a 1 4 c c 3) + ; 4) + + y 5a 5a y c c c c 5 ( бали) При яких натуральних значеннях m дріб m + 3 m + 4 m набуває натуральних значень? ІІ варіант 1 ( бали) При яких значеннях змінної має зміст вираз: 4 x + ; ) x + 3 x x 1? ( ) ( бали) Скоротіть дріб: 8 5 x y 4 7x y ; ) 3 ab 9 b ; 15b 3) 4 t 1 ; 4) y t y ( бали) Виконайте дію: b b 5 + b ; ) a a 4 (4 бали) Спростіть вираз: b b b b ; ) 9 a y 3a ; 3a 4t 1 5 x x 5 3) + ; 4) + + m 16t 4t m x 5x x 5 x 5 ( бали) При яких натуральних значеннях m дріб m + 4 m + 6 m набуває натуральних значень?
8 16 Завдання для експрес-контролю знань Завдання для експрес-контролю знань 163 З а в д а н н я для експрес-контролю знань Середній рівень ЕК-1 Алгебраїчні дроби Основна властивість дробу Додавання і віднімання дробів І варіант 1 (1 бал) Скоротіть дріб 7y-y y 49 ( бали) При яких значеннях змінної дріб x x : x + 3 не має змісту; ) дорівнює нулю? Достатній рівень 1 (1 бал) Скоротіть дріб 3 x + 8 x + 4x + 4 ( бали) Спростіть вираз a a 4a y a y + a+ y + + y 4a Високий рівень 1 (1 бал) При яких значеннях змінної дріб x + 3 x : x 3 не має змісту; ) дорівнює нулю? ( бали) Знайдіть значення a і b, при яких для будь-яких допустимих значень x рівність є тотожністю: a b x x + + x = x 9 ІІ варіант Середній рівень 1 (1 бал) Скоротіть дріб m 5m 5 m ( бали) При яких значеннях змінної дріб x 3 x : x + не має змісту; ) дорівнює нулю? Достатній рівень 1 (1 бал) Скоротити дріб y 6y+ 9 3 y 7 ( бали) Спростіть вираз m + 9b 3b 3b + + m 9b m+ 3b 3b m Високий рівень 1 (1 бал) При яких значеннях змінної дріб x x : x не має змісту; ) дорівнює нулю? ( бали) Знайдіть значення a і b, при яких для будь-яких допустимих значень x рівність є тотожністю: a b x x = x + x 4
Problem A. Nanoassembly
 Problem A. Nanoassembly 2.5 seconds One of the problems of creating elements of nanostructures is the colossal time necessary for the construction of nano-parts from separate atoms. Transporting each of
Problem A. Nanoassembly 2.5 seconds One of the problems of creating elements of nanostructures is the colossal time necessary for the construction of nano-parts from separate atoms. Transporting each of
Programming the Microchip Pic 16f84a Microcontroller As a Signal Generator Frequencies in Railway Automation
 988 Programming the Microchip Pic 16f84a Microcontroller As a Signal Generator Frequencies in Railway Automation High School of Transport "Todor Kableshkov" 1574 Sofia, 158 Geo Milev str. Ivan Velev Abstract
988 Programming the Microchip Pic 16f84a Microcontroller As a Signal Generator Frequencies in Railway Automation High School of Transport "Todor Kableshkov" 1574 Sofia, 158 Geo Milev str. Ivan Velev Abstract
Using the ac Method to Factor
 4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
4.6 Using the ac Method to Factor 4.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine factorability 2. Use the results of the ac test 3. Completely factor a trinomial In Sections 4.2 and 4.3 we used the trial-and-error
The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping
 296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
296 CHAPTER 5 Factoring and Applications 5.1 The Greatest Common Factor; Factoring by Grouping OBJECTIVES 1 Find the greatest common factor of a list of terms. 2 Factor out the greatest common factor.
The European Ombudsman
 Overview The European Ombudsman Е в р о п е й с к и о м б у д с м а н E l D e f e n s o r d e l P u e b l o E u r o p e o E v r o p s k ý v e ř e j n ý o c h r á n c e p r á v D e n E u r o p æ i s k e
Overview The European Ombudsman Е в р о п е й с к и о м б у д с м а н E l D e f e n s o r d e l P u e b l o E u r o p e o E v r o p s k ý v e ř e j n ý o c h r á n c e p r á v D e n E u r o p æ i s k e
1.4. Removing Brackets. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes. Learning Style
 Removing Brackets 1. Introduction In order to simplify an expression which contains brackets it is often necessary to rewrite the expression in an equivalent form but without any brackets. This process
Removing Brackets 1. Introduction In order to simplify an expression which contains brackets it is often necessary to rewrite the expression in an equivalent form but without any brackets. This process
Factoring Methods. Example 1: 2x + 2 2 * x + 2 * 1 2(x + 1)
 Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
Factoring Methods When you are trying to factor a polynomial, there are three general steps you want to follow: 1. See if there is a Greatest Common Factor 2. See if you can Factor by Grouping 3. See if
UNDERGRADUATE STUDY SKILLS GUIDE 2014-15
 SCHOOL OF SLAVONIC AND EAST EUROPEAN STUDIES UNDERGRADUATE STUDY SKILLS GUIDE 2014-15 ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS HISTORY LANGUAGES AND CULTURE POLITICS AND SOCIOLOGY 1 1. AN INTRODUCTION TO STUDY SKILLS 5
SCHOOL OF SLAVONIC AND EAST EUROPEAN STUDIES UNDERGRADUATE STUDY SKILLS GUIDE 2014-15 ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS HISTORY LANGUAGES AND CULTURE POLITICS AND SOCIOLOGY 1 1. AN INTRODUCTION TO STUDY SKILLS 5
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
 Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Factoring the trinomial ax 2 + bx + c when a = 1 A trinomial in the form x 2 + bx + c can be factored to equal (x + m)(x + n) when the product of m x n equals c and the sum of m + n equals b. (Note: the
Section 1. Finding Common Terms
 Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
Worksheet 2.1 Factors of Algebraic Expressions Section 1 Finding Common Terms In worksheet 1.2 we talked about factors of whole numbers. Remember, if a b = ab then a is a factor of ab and b is a factor
Russian Introductory Course
 Russian Introductory Course Natasha Bershadski Learn another language the way you learnt your own Succeed with the and learn another language the way you learnt your own Developed over 50 years, the amazing
Russian Introductory Course Natasha Bershadski Learn another language the way you learnt your own Succeed with the and learn another language the way you learnt your own Developed over 50 years, the amazing
Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c
 4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
4.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x 2 bx c 4.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor a trinomial of the form x 2 bx c 2. Factor a trinomial containing a common factor NOTE The process used to factor here is frequently
1.4. Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions 1.4 Introduction Just as one whole number divided by another is called a numerical fraction, so one algebraic expression divided by another is known as an algebraic fraction.
Arithmetic of Algebraic Fractions 1.4 Introduction Just as one whole number divided by another is called a numerical fraction, so one algebraic expression divided by another is known as an algebraic fraction.
Factoring - Grouping
 6.2 Factoring - Grouping Objective: Factor polynomials with four terms using grouping. The first thing we will always do when factoring is try to factor out a GCF. This GCF is often a monomial like in
6.2 Factoring - Grouping Objective: Factor polynomials with four terms using grouping. The first thing we will always do when factoring is try to factor out a GCF. This GCF is often a monomial like in
MARI-ENGLISH DICTIONARY
 MARI-ENGLISH DICTIONARY This project was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) 1, grant P22786-G20, and carried out at the Department of Finno-Ugric Studies 2 at the University of Vienna 3. Editors:
MARI-ENGLISH DICTIONARY This project was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) 1, grant P22786-G20, and carried out at the Department of Finno-Ugric Studies 2 at the University of Vienna 3. Editors:
How To Factor By Grouping
 Lecture Notes Factoring by the AC-method page 1 Sample Problems 1. Completely factor each of the following. a) 4a 2 mn 15abm 2 6abmn + 10a 2 m 2 c) 162a + 162b 2ax 4 2bx 4 e) 3a 2 5a 2 b) a 2 x 3 b 2 x
Lecture Notes Factoring by the AC-method page 1 Sample Problems 1. Completely factor each of the following. a) 4a 2 mn 15abm 2 6abmn + 10a 2 m 2 c) 162a + 162b 2ax 4 2bx 4 e) 3a 2 5a 2 b) a 2 x 3 b 2 x
IС A A RT 2013. Proceedings Volume 2. 5th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence. Barcelona, Spain 15-18 February, 2013
 «'.''«ИЧИЧГШ ИШ М Ш * /////>. л ъ и г ш я ш и ъ в т ъ т ', : 4 р * т Ъ ъ ^ Х 'Ш У Л *а * 1 ЛЧй==:й?й!^'ййй IС A A RT 2013. *»ф«ч>»д* 'И И в Я в З Г З г И Ж /а 1 * icw-ia & «:*>if E M e i i i i y. x '-
«'.''«ИЧИЧГШ ИШ М Ш * /////>. л ъ и г ш я ш и ъ в т ъ т ', : 4 р * т Ъ ъ ^ Х 'Ш У Л *а * 1 ЛЧй==:й?й!^'ййй IС A A RT 2013. *»ф«ч>»д* 'И И в Я в З Г З г И Ж /а 1 * icw-ia & «:*>if E M e i i i i y. x '-
Factoring a Difference of Two Squares. Factoring a Difference of Two Squares
 284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
284 (6 8) Chapter 6 Factoring 87. Tomato soup. The amount of metal S (in square inches) that it takes to make a can for tomato soup is a function of the radius r and height h: S 2 r 2 2 rh a) Rewrite this
FACTORING ax 2 bx c. Factoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1
 5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
5.7 Factoring ax 2 bx c (5-49) 305 5.7 FACTORING ax 2 bx c In this section In Section 5.5 you learned to factor certain special polynomials. In this section you will learn to factor general quadratic polynomials.
1.5. Factorisation. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes. Learning Style
 Factorisation 1.5 Introduction In Block 4 we showed the way in which brackets were removed from algebraic expressions. Factorisation, which can be considered as the reverse of this process, is dealt with
Factorisation 1.5 Introduction In Block 4 we showed the way in which brackets were removed from algebraic expressions. Factorisation, which can be considered as the reverse of this process, is dealt with
Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method
 6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
6.7 Factoring Trinomials: The ac Method 6.7 OBJECTIVES 1. Use the ac test to determine whether a trinomial is factorable over the integers 2. Use the results of the ac test to factor a trinomial 3. For
Nataliia ZARUDNA MODERN REQUIREMENTS FOR ACCOUNTING MANAGEMENT FOR PROVISION PROCESS
 444 JOURNAL Vol. 10 ( 4). December 2011 P u b l i c a t i o n o f T e r n o p i l N a t i o n a l E c o n o m i c U n i v e r s i t y Microeconomics Nataliia ZARUDNA MODERN REQUIREMENTS FOR ACCOUNTING
444 JOURNAL Vol. 10 ( 4). December 2011 P u b l i c a t i o n o f T e r n o p i l N a t i o n a l E c o n o m i c U n i v e r s i t y Microeconomics Nataliia ZARUDNA MODERN REQUIREMENTS FOR ACCOUNTING
FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c
 Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
Tallahassee Community College 55 FACTORING TRINOMIALS IN THE FORM OF ax 2 + bx + c This kind of trinomial differs from the previous kind we have factored because the coefficient of x is no longer "1".
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring
 1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
1.3 Polynomials and Factoring Polynomials Constant: a number, such as 5 or 27 Variable: a letter or symbol that represents a value. Term: a constant, variable, or the product or a constant and variable.
Factoring Polynomials: Factoring by Grouping
 OpenStax-CNX module: m21901 1 Factoring Polynomials: Factoring by Grouping Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m21901 1 Factoring Polynomials: Factoring by Grouping Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX. The study of dissolution kinetics of drugs with riboxinum (inosine)
 Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Der Pharma Chemica, 2016, 8(1):412-416 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) The study of dissolution kinetics of drugs
Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Der Pharma Chemica, 2016, 8(1):412-416 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) The study of dissolution kinetics of drugs
15.1 Factoring Polynomials
 LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
LESSON 15.1 Factoring Polynomials Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. Also A.SSE.3? ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you use the greatest common factor to factor polynomials? EXPLORE
By reversing the rules for multiplication of binomials from Section 4.6, we get rules for factoring polynomials in certain forms.
 SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
SECTION 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques 317 5.4 Special Factoring Techniques OBJECTIVES 1 Factor a difference of squares. 2 Factor a perfect square trinomial. 3 Factor a difference of cubes. 4 Factor
7-6. Choosing a Factoring Model. Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable IN T RO DUC E T EACH. Standards for Mathematical Content
 7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
7-6 Choosing a Factoring Model Extension: Factoring Polynomials with More Than One Variable Essential question: How can you factor polynomials with more than one variable? What is the connection between
The course of understanding British and American prose and poetry by future managers
 4. Полат Е. С. Новые педагогические и информационные технологии в системе образования. М.: Просвещение, 2000. 5. Гальцова Н. П., Мезенцева Т. И., Швадленко И. А. Использование электронных информационно-образовательных
4. Полат Е. С. Новые педагогические и информационные технологии в системе образования. М.: Просвещение, 2000. 5. Гальцова Н. П., Мезенцева Т. И., Швадленко И. А. Использование электронных информационно-образовательных
FACTORING POLYNOMIALS
 296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
296 (5-40) Chapter 5 Exponents and Polynomials where a 2 is the area of the square base, b 2 is the area of the square top, and H is the distance from the base to the top. Find the volume of a truncated
Tool 1. Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
 Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
Chapter 4: Factoring Review Tool 1 Greatest Common Factor (GCF) This is a very important tool. You must try to factor out the GCF first in every problem. Some problems do not have a GCF but many do. When
BEGINNING ALGEBRA ACKNOWLEDMENTS
 BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
BEGINNING ALGEBRA The Nursing Department of Labouré College requested the Department of Academic Planning and Support Services to help with mathematics preparatory materials for its Bachelor of Science
COMPLIANCE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING WHEN USING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES
 Margaryta I. Skrypnyk, Mykola M. Matiukha COMPLIANCE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING WHEN USING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES The article studies the correspondence of management accounting structure when using of
Margaryta I. Skrypnyk, Mykola M. Matiukha COMPLIANCE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING WHEN USING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES The article studies the correspondence of management accounting structure when using of
( ) FACTORING. x In this polynomial the only variable in common to all is x.
 FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
FACTORING Factoring is similar to breaking up a number into its multiples. For example, 10=5*. The multiples are 5 and. In a polynomial it is the same way, however, the procedure is somewhat more complicated
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials
 Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
Operations with Algebraic Expressions: Multiplication of Polynomials The product of a monomial x monomial To multiply a monomial times a monomial, multiply the coefficients and add the on powers with the
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation
 CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
CM2202: Scientific Computing and Multimedia Applications General Maths: 2. Algebra - Factorisation Prof. David Marshall School of Computer Science & Informatics Factorisation Factorisation is a way of
Factoring - Factoring Special Products
 6.5 Factoring - Factoring Special Products Objective: Identify and factor special products including a difference of squares, perfect squares, and sum and difference of cubes. When factoring there are
6.5 Factoring - Factoring Special Products Objective: Identify and factor special products including a difference of squares, perfect squares, and sum and difference of cubes. When factoring there are
Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Our goal in this chapter is to solve non-linear equations by breaking them down into a series of linear equations that we can solve. To do this,
Sect 6.1 - Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Our goal in this chapter is to solve non-linear equations by breaking them down into a series of linear equations that we can solve. To do this,
Polynomials. Key Terms. quadratic equation parabola conjugates trinomial. polynomial coefficient degree monomial binomial GCF
 Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Polynomials 5 5.1 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials and Polynomial Functions 5.2 Multiplication of Polynomials 5.3 Division of Polynomials Problem Recognition Exercises Operations on Polynomials
Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder).
 Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
Math 50, Chapter 8 (Page 1 of 20) 8.1 Common Factors Definitions 1. A factor of integer is an integer that will divide the given integer evenly (with no remainder). Find all the factors of a. 44 b. 32
FUNCTIONS OF THE MODAL VERBS IN ENGLISH (MODAL VERBS ANALOGIES IN THE RUSSIAN LANGUAGE) Сompiled by G.V. Kuzmina
 FUNCTIONS OF THE MODAL VERBS IN ENGLISH (MODAL VERBS ANALOGIES IN THE RUSSIAN LANGUAGE) Сompiled by G.V. Kuzmina Москва Издательство Российского университета дружбы народов 2002 FUNCTIONS OF THE MODAL
FUNCTIONS OF THE MODAL VERBS IN ENGLISH (MODAL VERBS ANALOGIES IN THE RUSSIAN LANGUAGE) Сompiled by G.V. Kuzmina Москва Издательство Российского университета дружбы народов 2002 FUNCTIONS OF THE MODAL
Limits and Continuity
 Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture Limits and Continuity Slide Review of Limit. Side limits and squeeze theorem. Continuous functions of 2,3 variables. Review: Limits Slide 2 Definition Given a function
Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture Limits and Continuity Slide Review of Limit. Side limits and squeeze theorem. Continuous functions of 2,3 variables. Review: Limits Slide 2 Definition Given a function
2. SALESMATERIALSStudentswithorwithoutsmartphonesareabletofacilitatethesalewiththesales materialsprovidedintheirstarterkit,aswelasonourwebsite.
 T GA Tym wamcm mk y!wm,wy Wyykb, mw: 1 PREENTATIONAPPwmqwyymk wwmtmmmbb FBLAby,yw,y m 2 ALEMATERIALwwmbw mk,wwb 3 GOALETTINGHEETEb Tm,mkyyw 4 REVENUECALCULATORM ybywm w mbwb 5 INTRUCTIONALWEBINARP AMCM
T GA Tym wamcm mk y!wm,wy Wyykb, mw: 1 PREENTATIONAPPwmqwyymk wwmtmmmbb FBLAby,yw,y m 2 ALEMATERIALwwmbw mk,wwb 3 GOALETTINGHEETEb Tm,mkyyw 4 REVENUECALCULATORM ybywm w mbwb 5 INTRUCTIONALWEBINARP AMCM
Algebra (Expansion and Factorisation)
 Chapter10 Algebra (Expansion and Factorisation) Contents: A B C D E F The distributive law Siplifying algebraic expressions Brackets with negative coefficients The product (a + b)(c + d) Geoetric applications
Chapter10 Algebra (Expansion and Factorisation) Contents: A B C D E F The distributive law Siplifying algebraic expressions Brackets with negative coefficients The product (a + b)(c + d) Geoetric applications
With content marketing, you can move beyond measuring success in terms of impressions, awareness, or perception.
 L k m k?j SHSMD y! A m k b mm y SHSMD b y k w y y m. Byj 4 000 mm y SHSMDm mb y w x b y y j bm y : F w b m y x A w m m w b b T w m Am H A R b w S b B b m k A m m m! V www. m. /b. Sy H Sy Mk Dm P Mk P V
L k m k?j SHSMD y! A m k b mm y SHSMD b y k w y y m. Byj 4 000 mm y SHSMDm mb y w x b y y j bm y : F w b m y x A w m m w b b T w m Am H A R b w S b B b m k A m m m! V www. m. /b. Sy H Sy Mk Dm P Mk P V
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 256 Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2011 Mar-Apr;139(3-4):256-261 ПРЕГЛЕД ЛИТЕРАТУРЕ / REVIEW ARTICLE DOI: 10.2298/SARH1104256B Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Snežana Brkić, Slavica Tomić, Maja Ružić, Daniela Marić Hospital
256 Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2011 Mar-Apr;139(3-4):256-261 ПРЕГЛЕД ЛИТЕРАТУРЕ / REVIEW ARTICLE DOI: 10.2298/SARH1104256B Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Snežana Brkić, Slavica Tomić, Maja Ružić, Daniela Marić Hospital
Chapter 5. Rational Expressions
 5.. Simplify Rational Expressions KYOTE Standards: CR ; CA 7 Chapter 5. Rational Expressions Definition. A rational expression is the quotient P Q of two polynomials P and Q in one or more variables, where
5.. Simplify Rational Expressions KYOTE Standards: CR ; CA 7 Chapter 5. Rational Expressions Definition. A rational expression is the quotient P Q of two polynomials P and Q in one or more variables, where
expression is written horizontally. The Last terms ((2)( 4)) because they are the last terms of the two polynomials. This is called the FOIL method.
 A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
A polynomial of degree n (in one variable, with real coefficients) is an expression of the form: a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 where a n, a n 1, a n 2, a 2, a 1, a 0 are
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions
 Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
Section 6.1 Factoring Expressions The first method we will discuss, in solving polynomial equations, is the method of FACTORING. Before we jump into this process, you need to have some concept of what
How To Factor By Gcf In Algebra 1.5
 7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
7-2 Factoring by GCF Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(w + 1) 2. 3x(x 2 4) 2w + 2 3x 3 12x Find the GCF of each pair of monomials. 3. 4h 2 and 6h 2h 4. 13p and 26p
Factoring. Factoring Monomials Monomials can often be factored in more than one way.
 Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Factoring Factoring is the reverse of multiplying. When we multiplied monomials or polynomials together, we got a new monomial or a string of monomials that were added (or subtracted) together. For example,
Student Outcomes. Lesson Notes. Classwork. Discussion (10 minutes)
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 5 8 Student Outcomes Students know the definition of a number raised to a negative exponent. Students simplify and write equivalent expressions that contain
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 5 8 Student Outcomes Students know the definition of a number raised to a negative exponent. Students simplify and write equivalent expressions that contain
#6 Opener Solutions. Move one more spot to your right. Introduce yourself if needed.
 1. Sit anywhere in the concentric circles. Do not move the desks. 2. Take out chapter 6, HW/notes #1-#5, a pencil, a red pen, and your calculator. 3. Work on opener #6 with the person sitting across from
1. Sit anywhere in the concentric circles. Do not move the desks. 2. Take out chapter 6, HW/notes #1-#5, a pencil, a red pen, and your calculator. 3. Work on opener #6 with the person sitting across from
Simplifying Algebraic Fractions
 5. Simplifying Algebraic Fractions 5. OBJECTIVES. Find the GCF for two monomials and simplify a fraction 2. Find the GCF for two polynomials and simplify a fraction Much of our work with algebraic fractions
5. Simplifying Algebraic Fractions 5. OBJECTIVES. Find the GCF for two monomials and simplify a fraction 2. Find the GCF for two polynomials and simplify a fraction Much of our work with algebraic fractions
tegrals as General & Particular Solutions
 tegrals as General & Particular Solutions dy dx = f(x) General Solution: y(x) = f(x) dx + C Particular Solution: dy dx = f(x), y(x 0) = y 0 Examples: 1) dy dx = (x 2)2 ;y(2) = 1; 2) dy ;y(0) = 0; 3) dx
tegrals as General & Particular Solutions dy dx = f(x) General Solution: y(x) = f(x) dx + C Particular Solution: dy dx = f(x), y(x 0) = y 0 Examples: 1) dy dx = (x 2)2 ;y(2) = 1; 2) dy ;y(0) = 0; 3) dx
THE INFLUENCE OF POLITICAL ADVERTISING ON STUDENTS PREFERENCES AND THEIR POLITICAL CHOICE
 UDK 159.94 Garkavets S.A., Zhadan O.А., Kushnarenko V. I. THE INFLUENCE OF POLITICAL ADVERTISING ON STUDENTS PREFERENCES AND THEIR POLITICAL CHOICE The article considers the features of influence political
UDK 159.94 Garkavets S.A., Zhadan O.А., Kushnarenko V. I. THE INFLUENCE OF POLITICAL ADVERTISING ON STUDENTS PREFERENCES AND THEIR POLITICAL CHOICE The article considers the features of influence political
How To Solve Factoring Problems
 05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
05-W4801-AM1.qxd 8/19/08 8:45 PM Page 241 Factoring, Solving Equations, and Problem Solving 5 5.1 Factoring by Using the Distributive Property 5.2 Factoring the Difference of Two Squares 5.3 Factoring
Factoring Special Polynomials
 6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
6.6 Factoring Special Polynomials 6.6 OBJECTIVES 1. Factor the difference of two squares 2. Factor the sum or difference of two cubes In this section, we will look at several special polynomials. These
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions
 6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
6.1 Add & Subtract Polynomial Expression & Functions Objectives 1. Know the meaning of the words term, monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial, degree, coefficient, like terms, polynomial funciton, quardrtic
Factoring - Greatest Common Factor
 6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
6.1 Factoring - Greatest Common Factor Objective: Find the greatest common factor of a polynomial and factor it out of the expression. The opposite of multiplying polynomials together is factoring polynomials.
Algebra 2 PreAP. Name Period
 Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Algebra 2 PreAP Name Period IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS!!! We understand that students come to Algebra II with different strengths and needs. For this reason, students have options for completing
Name Intro to Algebra 2. Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring
 Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Name Intro to Algebra 2 Unit 1: Polynomials and Factoring Date Page Topic Homework 9/3 2 Polynomial Vocabulary No Homework 9/4 x In Class assignment None 9/5 3 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Pg. 332
Factoring Flow Chart
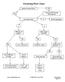 Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring Flow Chart greatest common factor? YES NO factor out GCF leaving GCF(quotient) how many terms? 4+ factor by grouping 2 3 difference of squares? perfect square trinomial? YES YES NO NO a 2 -b
Factoring. 472 Chapter 9 Factoring
 Factoring Lesson 9- Find the prime factorizations of integers and monomials. Lesson 9- Find the greatest common factors (GCF) for sets of integers and monomials. Lessons 9-2 through 9-6 Factor polynomials.
Factoring Lesson 9- Find the prime factorizations of integers and monomials. Lesson 9- Find the greatest common factors (GCF) for sets of integers and monomials. Lessons 9-2 through 9-6 Factor polynomials.
Tim Kerins. Leaving Certificate Honours Maths - Algebra. Tim Kerins. the date
 Leaving Certificate Honours Maths - Algebra the date Chapter 1 Algebra This is an important portion of the course. As well as generally accounting for 2 3 questions in examination it is the basis for many
Leaving Certificate Honours Maths - Algebra the date Chapter 1 Algebra This is an important portion of the course. As well as generally accounting for 2 3 questions in examination it is the basis for many
Math 432 HW 2.5 Solutions
 Math 432 HW 2.5 Solutions Assigned: 1-10, 12, 13, and 14. Selected for Grading: 1 (for five points), 6 (also for five), 9, 12 Solutions: 1. (2y 3 + 2y 2 ) dx + (3y 2 x + 2xy) dy = 0. M/ y = 6y 2 + 4y N/
Math 432 HW 2.5 Solutions Assigned: 1-10, 12, 13, and 14. Selected for Grading: 1 (for five points), 6 (also for five), 9, 12 Solutions: 1. (2y 3 + 2y 2 ) dx + (3y 2 x + 2xy) dy = 0. M/ y = 6y 2 + 4y N/
www.sakshieducation.com
 LENGTH OF THE PERPENDICULAR FROM A POINT TO A STRAIGHT LINE AND DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO PAPALLEL LINES THEOREM The perpendicular distance from a point P(x 1, y 1 ) to the line ax + by + c 0 is ax1+ by1+ c
LENGTH OF THE PERPENDICULAR FROM A POINT TO A STRAIGHT LINE AND DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO PAPALLEL LINES THEOREM The perpendicular distance from a point P(x 1, y 1 ) to the line ax + by + c 0 is ax1+ by1+ c
Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Algebra 1 Chapter 08 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the difference. 1. (4w 2 4w 8) (2w 2 + 3w 6)
Math 10C. Course: Polynomial Products and Factors. Unit of Study: Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address. Guiding Questions:
 Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Course: Unit of Study: Math 10C Polynomial Products and Factors Step 1: Identify the Outcomes to Address Guiding Questions: What do I want my students to learn? What can they currently understand and do?
Factoring Polynomials
 Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
Factoring a Polynomial Expression Factoring a polynomial is expressing the polynomial as a product of two or more factors. Simply stated, it is somewhat the reverse process of multiplying. To factor polynomials,
Manual for Vegetable Production in Botswana
 OF RESEARCH M V P Bw H R Pm V: W w w W Dm A R mm v x v vm v mv w M: W w x O m v vv w m mz v : Ev z Cv G mm W w v m mw v mv w vm V: W w v Cm Cm W w m mvm v v S O v q v w mm v m w w mv j m m Sv W x v m v
OF RESEARCH M V P Bw H R Pm V: W w w W Dm A R mm v x v vm v mv w M: W w x O m v vv w m mz v : Ev z Cv G mm W w v m mw v mv w vm V: W w v Cm Cm W w m mvm v v S O v q v w mm v m w w mv j m m Sv W x v m v
A COURSE IN MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY
 R. S. Ginzburg, S. S. Khidekel, G. Y. Knyazeva, A. A. Sankin A COURSE IN MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY SECOND EDITION Revised and Enlarged Допущено Министерством высшего и среднего специального образования
R. S. Ginzburg, S. S. Khidekel, G. Y. Knyazeva, A. A. Sankin A COURSE IN MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY SECOND EDITION Revised and Enlarged Допущено Министерством высшего и среднего специального образования
BES-III distributed computing status
 КОМПЬЮТЕРНЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ И МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЕ 2015 Т. 7 3 С. 469 473 СЕКЦИОННЫЕ ДОКЛАДЫ УДК: 004.75, 004.052.2, 004.052.32 BES-III distributed computing status S. Belov 1, Z. Deng 2, W. Li 2, T. Lin 2, I.
КОМПЬЮТЕРНЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ И МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЕ 2015 Т. 7 3 С. 469 473 СЕКЦИОННЫЕ ДОКЛАДЫ УДК: 004.75, 004.052.2, 004.052.32 BES-III distributed computing status S. Belov 1, Z. Deng 2, W. Li 2, T. Lin 2, I.
1. First-order Ordinary Differential Equations
 Advanced Engineering Mathematics 1. First-order ODEs 1 1. First-order Ordinary Differential Equations 1.1 Basic concept and ideas 1.2 Geometrical meaning of direction fields 1.3 Separable differential
Advanced Engineering Mathematics 1. First-order ODEs 1 1. First-order Ordinary Differential Equations 1.1 Basic concept and ideas 1.2 Geometrical meaning of direction fields 1.3 Separable differential
In the above, the number 19 is an example of a number because its only positive factors are one and itself.
 Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
Math 100 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping (Review) Factoring Definition: A factor is a number, variable, monomial, or polynomial which is multiplied by another number, variable, monomial,
MATH 10034 Fundamental Mathematics IV
 MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
MATH 0034 Fundamental Mathematics IV http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/0034/funmath4.pdf Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University January 2, 2009 ii Contents To the Instructor v Polynomials.
Unit 3: Day 2: Factoring Polynomial Expressions
 Unit 3: Day : Factoring Polynomial Expressions Minds On: 0 Action: 45 Consolidate:10 Total =75 min Learning Goals: Extend knowledge of factoring to factor cubic and quartic expressions that can be factored
Unit 3: Day : Factoring Polynomial Expressions Minds On: 0 Action: 45 Consolidate:10 Total =75 min Learning Goals: Extend knowledge of factoring to factor cubic and quartic expressions that can be factored
6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1.
![6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. 6 Commutators and the derived series. [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1.](/thumbs/19/254057.jpg) 6 Commutators and the derived series Definition. Let G be a group, and let x,y G. The commutator of x and y is [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. Note that [x,y] = e if and only if xy = yx (since x 1 y 1 = (yx) 1 ). Proposition
6 Commutators and the derived series Definition. Let G be a group, and let x,y G. The commutator of x and y is [x,y] = xyx 1 y 1. Note that [x,y] = e if and only if xy = yx (since x 1 y 1 = (yx) 1 ). Proposition
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages; Single-Family; indexed to the one-year Treasury Constant Maturity; 2 percent
 Pool Prefix Glossary Last Revised: July 6, 2015 *Shaded items are adjustable-rate products. 2I Conventional Intermediate-Term, Level-Payment Subordinate Mortgages; Single-Family; maturing or due in 15
Pool Prefix Glossary Last Revised: July 6, 2015 *Shaded items are adjustable-rate products. 2I Conventional Intermediate-Term, Level-Payment Subordinate Mortgages; Single-Family; maturing or due in 15
Mathematics Placement
 Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
Mathematics Placement The ACT COMPASS math test is a self-adaptive test, which potentially tests students within four different levels of math including pre-algebra, algebra, college algebra, and trigonometry.
A stochastic individual-based model for immunotherapy of cancer
 A stochastic individual-based model for immunotherapy of cancer Loren Coquille - Joint work with Martina Baar, Anton Bovier, Hannah Mayer (IAM Bonn) Michael Hölzel, Meri Rogava, Thomas Tüting (UniKlinik
A stochastic individual-based model for immunotherapy of cancer Loren Coquille - Joint work with Martina Baar, Anton Bovier, Hannah Mayer (IAM Bonn) Michael Hölzel, Meri Rogava, Thomas Tüting (UniKlinik
5.1 FACTORING OUT COMMON FACTORS
 C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
C H A P T E R 5 Factoring he sport of skydiving was born in the 1930s soon after the military began using parachutes as a means of deploying troops. T Today, skydiving is a popular sport around the world.
FINDING THE LEAST COMMON DENOMINATOR
 0 (7 18) Chapter 7 Rational Expressions GETTING MORE INVOLVED 7. Discussion. Evaluate each expression. a) One-half of 1 b) One-third of c) One-half of x d) One-half of x 7. Exploration. Let R 6 x x 0 x
0 (7 18) Chapter 7 Rational Expressions GETTING MORE INVOLVED 7. Discussion. Evaluate each expression. a) One-half of 1 b) One-third of c) One-half of x d) One-half of x 7. Exploration. Let R 6 x x 0 x
Abstract.Weproposetimed(nite)automatatomodelthebehaviorofrealtimesystemsovertime.Ourdenitionprovidesasimple,andyetpowerful,wayto
 ATheoryofTimedAutomata1 Abstract.Weproposetimed(nite)automatatomodelthebehaviorofrealtimesystemsovertime.Ourdenitionprovidesasimple,andyetpowerful,wayto ComputercienceDepartment,tanfordUniversity RajeevAlur2
ATheoryofTimedAutomata1 Abstract.Weproposetimed(nite)automatatomodelthebehaviorofrealtimesystemsovertime.Ourdenitionprovidesasimple,andyetpowerful,wayto ComputercienceDepartment,tanfordUniversity RajeevAlur2
MATH 289 PROBLEM SET 4: NUMBER THEORY
 MATH 289 PROBLEM SET 4: NUMBER THEORY 1. The greatest common divisor If d and n are integers, then we say that d divides n if and only if there exists an integer q such that n = qd. Notice that if d divides
MATH 289 PROBLEM SET 4: NUMBER THEORY 1. The greatest common divisor If d and n are integers, then we say that d divides n if and only if there exists an integer q such that n = qd. Notice that if d divides
Simplification of Radical Expressions
 8. Simplification of Radical Expressions 8. OBJECTIVES 1. Simplify a radical expression by using the product property. Simplify a radical expression by using the quotient property NOTE A precise set of
8. Simplification of Radical Expressions 8. OBJECTIVES 1. Simplify a radical expression by using the product property. Simplify a radical expression by using the quotient property NOTE A precise set of
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Academic Success Centre
 250) 960-6367 Factoring Polynomials Sometimes when we try to solve or simplify an equation or expression involving polynomials the way that it looks can hinder our progress in finding a solution. Factorization
250) 960-6367 Factoring Polynomials Sometimes when we try to solve or simplify an equation or expression involving polynomials the way that it looks can hinder our progress in finding a solution. Factorization
SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS
 40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
40 (8-8) Chapter 8 Powers and Roots 8. SIMPLIFYING SQUARE ROOTS In this section Using the Product Rule Rationalizing the Denominator Simplified Form of a Square Root In Section 8. you learned to simplify
Algebraic expressions are a combination of numbers and variables. Here are examples of some basic algebraic expressions.
 Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
Page 1 of 13 Review of Linear Expressions and Equations Skills involving linear equations can be divided into the following groups: Simplifying algebraic expressions. Linear expressions. Solving linear
STARTING SYSTEM OPERATION IN THE STARTER-GENERATOR
 International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization on TPE (IOTPE) ISSN 077-358 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com March 00
International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization on TPE (IOTPE) ISSN 077-358 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com March 00
INTEGRATING FACTOR METHOD
 Differential Equations INTEGRATING FACTOR METHOD Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module for learning to solve 1st order linear differential equations Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk
Differential Equations INTEGRATING FACTOR METHOD Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module for learning to solve 1st order linear differential equations Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk
6.3 FACTORING ax 2 bx c WITH a 1
 290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
290 (6 14) Chapter 6 Factoring e) What is the approximate maximum revenue? f) Use the accompanying graph to estimate the price at which the revenue is zero. y Revenue (thousands of dollars) 300 200 100
SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORS
 CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
CHAPTER 442 11 CHAPTER TABLE OF CONTENTS 11-1 Factors and Factoring 11-2 Common Monomial Factors 11-3 The Square of a Monomial 11-4 Multiplying the Sum and the Difference of Two Terms 11-5 Factoring the
SOCIAL-MEDIA PLATFORMS AND ITS EFFECT ON DIGITAL MARKETING ACTIVITIES
 УДК 339.138:659.1 Lesidrenska Svetlana, PhD., Associate Professor, Head of the Economics and Management Department at Technical University of Varna, (Bulgaria); Dicke Philipp, Ph.D. Student at University
УДК 339.138:659.1 Lesidrenska Svetlana, PhD., Associate Professor, Head of the Economics and Management Department at Technical University of Varna, (Bulgaria); Dicke Philipp, Ph.D. Student at University
Factoring Polynomials
 UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
UNIT 11 Factoring Polynomials You can use polynomials to describe framing for art. 396 Unit 11 factoring polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has variables that represent numbers. A number can
Pipe fittings plant in Kolpino, Leningrad Regions
 1 Pipe fittings plant in Kolpino, Leningrad Regions ROOST Group of companies is a fast growing association with a long history. Synergy of the ROOST Group companies gives an opportunity to keep leading
1 Pipe fittings plant in Kolpino, Leningrad Regions ROOST Group of companies is a fast growing association with a long history. Synergy of the ROOST Group companies gives an opportunity to keep leading
