From ead to oe. Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation
|
|
|
- Abel Gilbert
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science) began in 1981 with a grant from the National Science Foundation. The non-profit AIMS Education Foundation publishes hands-on instructional materials that build conceptual understanding. The foundation also sponsors a national program of professional development through which educators may gain expertise in teaching math and science. Copyright 1986, 2010, 2013 by the AIMS Education Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this book or associated digital media may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means except as noted below. A person purchasing this AIMS publication is hereby granted permission to make unlimited copies of any portion of it (or the files on the accompanying disc), provided these copies will be used only in his or her own classroom. Sharing the materials or making copies for additional classrooms or schools or for other individuals is a violation of AIMS copyright. For a workshop or conference session, presenters may make one copy of any portion of a purchased activity for each participant, with a limit of five activities or up to one-third of a book, whichever is less. All copies must bear the AIMS Education Foundation copyright information. Modifications to AIMS pages (e.g., separating page elements for use on an interactive white board) are permitted only for use within the classroom for which the pages were purchased, or by presenters at conferences or workshops. Interactive white board files may not be uploaded to any third-party website or otherwise distributed. AIMS artwork and content may not be used on non-aims materials. Digital distribution rights may be purchased for users who wish to place AIMS materials on secure servers for school- or district-wide use. Contact us or visit the AIMS website for complete details. AIMS Education Foundation 1595 S. Chestnut Ave., Fresno, CA aimsedu.org ISBN Printed in the United States of America FROM HEAD TO TOE 2010 AIMS Education Foundation
2 H From ead to oe T Table of Contents How to Assemble Rubber Band Books... 4 Our Amazing Bodies... 5 Nervous System A Mind of Your Own... 7 The Nervous System You ve Got Some Nerve Circulatory System A Heart-felt Model Heart Strings Ya Gotta Have Heart! How Does Your Heart Rate? Isn t It Interesting: Heart Smart Respiratory System Breathe In, Breathe Out Take a Breather Digestive System Reader s Digestion Digestion Details The Adventures of PB & J Chyme Chemistry The Food Tube Down the Tubes Casing the System Isn t It Interesting: It Takes Guts Musculoskeletal System Dem Bones Bone Biopsy Many Muscles Hands and Fingers, Muscles and Bones Winging It! Isn t It Interesting: Musclebound Sensory Organs Touchy Feely Skin Deep Sensitive Skin Here s to Ears In Your Ear Eye See Sight-Seeing No Goal in Sight Getting It Together The Nose Knows Tasty Tidbits TrickyTastes Culminating Activities System Overlay Construction Human Body Hunt Urinary System Take Me to the Cleaners FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
3 Topic Digestive system Key Question What is the length of your digestive tract? Learning Goals Students will: determine the lengths of their digestive tracts, and model their tracts on outlines of their bodies. Guiding Documents Project 2061 Benchmarks For the body to use food for energy and building materials, the food must first be digested into molecules that are absorbed and transported to cells. Like other animals, human beings have body systems for obtaining and providing energy, defense, reproduction, and the coordination of body functions. Length can be thought of as unit lengths joined together, area as a collection of unit squares, and volume as a set of unit cubes. NRC Standard The human organism has systems for digestion, respiration, reproduction, circulation, excretion, movement, control, and coordination, and for protection from disease. These systems interact with one another. NCTM Standards 2000* Understand such attributes as length, area, weight, volume, and size of angle and select the appropriate type of unit for measuring each attribute Select and apply appropriate standard units and tools to measure length, area, volume, weight, time, temperature, and the size of angles Math Measurement length Estimation Computation Proportional reasoning Science Life science human body digestive system Integrated Processes Observing Collecting and recording data Comparing and contrasting Generalizing Materials Bulletin board paper Crepe paper streamers Metric tape measures Glue Construction paper Scissors Student pages Background Information The digestive tract is the body s passageway through which food moves and digests. The digestive tract, also called the alimentary canal, is a continuous muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the anus. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and the anus. Contributing organs are the salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The task of the digestive system is the physical and chemical breakdown of food to supply the body with its energy and nutrient needs for growth and repair. There are several analogies that help us understand the digestive tract. One compares the digestive tract to a doughnut hole. The doughnut s hole is in the center and there is protective crust all around. Likewise, the digestive tract is a hole that runs from the mouth to the anus. The tube itself protects the body s interior from things external to it. There is no opening along the tube through which substances can enter the body. Substances can only enter the body when they are broken into pieces small enough that they can pass through the walls of the tube and enter the bloodstream. Another analogy is that of an assembly line. Along the digestive tract, teeth physically break down the food and muscles move it through the passage to different stations. Along the way, various stations of the digestive tract produce enzymes that aid in FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
4 the chemical breakdown of food. The food is finally absorbed and waste products are collected and expelled. The length of time involved in this assembly-line process varies from individual to individual. However, it is safe to say that the food must stay at each station along the way long enough for that station s job to be completed, whether that is the breakdown of carbohydrates, the breakdown of fats, the absorption of water, etc. Some approximate station times are: Mouth less than one minute; Esophagus a couple of seconds; Stomach two to four hours; Small Intestine one to four hours; Large Intestine 10 hours to several days. An adult s digestive tract is approximately nine meters (30 ft) in length, or about five times the adult s height. In this activity, students will gain an appreciation of the length of the digestive tract and, if appropriate, begin to understand why its great length is necessary. Management 1. Students will use traced body outlines on which to glue their digestive tracts. One outline per group is needed. 2. This activity is designed to be used at several levels. The simplest level is the measurement and placement of the digestive tract on the body cutout, and the identification of the major components. The most difficult level includes the placement, identification, and functional description of the components, including the contributing organs involved in the digestive process. You are encouraged to adapt this experience to meet your needs. 3. If the tracing of the students bodies presents a management problem in the classroom, send some bulletin board paper home with a student from each group along with parental instructions to trace around their child s body. 4. Because the crepe paper color tends to run when glued, it is advisable to use light-colored streamers such as pink or yellow. 5. Use a paper cutter or scissors to cut the crepe paper streamers in half. These narrower streamers represent the small intestine, mouth, and esophagus. Use the full width to represent the large intestine. 6. Metric tape measures (item number 1926) are available from AIMS. Procedure 1. Ask students how they think the food we eat nourishes our bodies. Discuss the fact that food must be broken down into a small enough size before it can be used by the body. Inform them that they will be exploring the digestive tract, or the passage the food takes from the moment it enters the mouth until it is excreted. 2. Have students get in groups of three. Distribute the bulletin board paper and have each group trace around one member s body. (See Management 3.) 3. Ask the Key Question. Write students responses on the board. 4. Distribute the student page and the materials. Encourage students to follow the instructions to determine the lengths of their digestive tracts and create their models. (Students will be amazed at how much they have to scrunch up the small intestine to fit it in the appropriate space. Use this as a teaching opportunity to discuss the reason for its long length.) 5. Distribute the appropriate information page describing the digestive tract. Discuss the parts of the digestive system and their functions. Connecting Learning 1. What is the function of the digestive system? 2. Approximately how long is your digestive tract? 3. About how many times longer is your digestive tract than your height? (You may want to have students cut a length of string equal to the length they have determined for their digestive tract. Using the string, they can concretely compare its length to the length of their body cutouts. Sample answers may be: My digestive tract is over four times as long as my height, but less than five times. or My digestive tract is four and three-fourths the length of my height. ) 4. How does the length of your digestive tract compare to that of another student s? How can you explain the difference? [The other student is taller (or shorter) than I am.] 5. What is the longest component of the digestive tract? [the small intestine] Why do you think it is called the small intestine? [Its diameter is less than that of the large intestine.] 6. How were you able to fit the small intestine into place? [by wrinkling it up] 7. Why do you think the small intestine is so long? 8. How is this model like the real thing? How is it different? 9. What are you wondering now? Extensions 1. Correlate the various digestive enzymes with the organs that produce them. 2. Have students determine the average ratio of their heights to the length of their digestive tracts. Have them apply this ratio to a professional basketball player whose height they know. * Reprinted with permission from Principles and Standards for School Mathematics, 2000 by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. All rights reserved. FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
5 Key Question What is the length of your digestive tract? Learning Goals Students will: determine the lengths of their digestive tracts, and model their tracts on outlines of their bodies. FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
6 How long is your digestive tract? You need: Body outline Glue Scissors Construction paper Metric tape measure Crepe paper streamers (narrow and wide) Key Mouth = 10 cm Esophagus = 25 cm Stomach = 15 cm Small intestine = Height x 3 Large intestine = Height + 15 cm Do this: 1. Find and record the height of your group s model. 2. Use the key to calculate the length of the digestive tract from the mouth to the top of the stomach. Cut a length of narrow crepe paper that is this long. 3. Cut a stomach from construction paper that is the right size. Glue the mouth, esophagus, and stomach in place on the body outline. 4. Calculate the length of the digestive tract so far (from the mouth to the end of the stomach). 5. Determine the length of the small intestine. Cut a length of narrow crepe paper that is this long. 6. Determine the length of the large intestine to the anus. Cut a length of wide crepe paper that is this long. 7. Glue the small and large intestine in place on the body outline. Use the diagram to help you. 8. Find the total length of the digestive tract. 9. On your body cutout, label the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. How many times longer is the digestive tract than your model s height? cm cm cm cm cm On the back of this paper, explain how you determined this. FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
7 Mouth The teeth physically break the food into smaller bits. The tongue helps to move the food particles into a ball that is then swallowed. Esophagus Once the food has been swallowed, it moves down the throat into the esophagus. The esophagus is lined with muscles that help to mix the food and push it down toward the stomach. Stomach The stomach is a J-shaped expansion of the digestive tube that can hold two to four liters of food! The stomach stores food. Its muscles knead the food, breaking it down even more. The stomach adds chemicals to the food that turn the food into a soupy liquid. Small Intestine The soupy liquid moves into the small intestine, a narrow tube (two to four cm in diameter) the longest portion of the digestive tract. Here the food is broken down into small enough particles that it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large Intestine Undigested food is passed into the large intestine. Water and salt are absorbed by the large intestine. The undigested food, dead cells, and dead bacteria left in the large intestine are called feces. Muscles in the large intestine move the feces on toward the anus. Anus The anus is the exit point for the feces. The anus has strong muscles that, when relaxed, allow the body to get rid of its solid waste. FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
8 Mouth The teeth physically break the food into smaller bits. The tongue helps to move the food particles into a ball that is then swallowed. Esophagus Once the food has been swallowed, it moves down the throat into the esophagus. The esophagus is lined with muscles that help to mix the food and push it down toward the stomach. Stomach The stomach is a J-shaped expansion of the digestive tube that can hold two to four liters of food! The stomach stores food. Its muscles knead the food, breaking it down even more. The stomach adds chemicals to the food that turns the food into a soupy liquid. Small Intestine The soupy liquid moves into the small intestine, a narrow tube (two to four cm in diameter) the longest portion of the digestive tract. Here the food is broken down into small enough particles that it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large Intestine Undigested food is passed on into the large intestine. Water and salt is absorbed by the large intestine. The undigested food, dead cells, and dead bacteria left in the large intestine are called feces. Muscles in the large intestine move the feces on toward the anus. Anus The anus is the exit point for the feces. The anus has strong muscles that, when relaxed, allow the body to get rid of its solid waste. Salivary Glands The salivary glands produce saliva that starts the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates. Saliva also moistens the food making it easier to swallow. Liver The liver is an organ about the size of a football. It removes harmful substances and waste products from the blood. The liver produces bile that acts like a detergent in breaking up fats. The liver stores the fats and carbohydrates we use for energy along with iron and other vitamins. It regulates the blood sugar levels in the body. Pancreas The pancreas produces chemicals that help in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It also produces a chemical that helps to neutralize the stomach acids. Gallbladder The gallbladder stores the bile that was produced by the liver. The gallbladder releases the bile into the small intestine where it helps to break down the fats we have eaten. FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
9 Connecting Learning CONNECTING CONNECTING LEARNING LEARNING 1. What is the function of the digestive system? 2. Approximately how long is your digestive tract? 3. About how many times longer is your digestive tract than your height? 4. How does the length of your digestive tract compare to that of another student s? 5. What is the longest component of your digestive tract? Why do you think it is called the small intestine? FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
10 Connecting Learning CONNECTING CONNECTING LEARNING LEARNING 6. How were you able to fit the small intestine into place? 7. Why do you think the small intestine is so long? 8. How is this model like the real thing? How is it different? 9. What are you wondering now? FROM HEAD TO TOE AIMS Education Foundation
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
The Digestive System
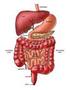 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist
 Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title
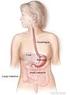 t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Grade 5
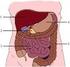 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE The Digestive System Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE The Digestive System Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]
![[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]](/thumbs/40/20967878.jpg) [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Outline Digestive System
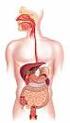 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle:
 Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Gateways to Science SAMPLE. STAAR Edition. Teacher Edition
 Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Surface Area and Absorption
 7 LESSON Surface Area and Absorption INTRODUCTION Have you ever built a campfire? Did you start with logs or twigs? Even though you will eventually need logs to keep the fire burning, you have to use twigs
7 LESSON Surface Area and Absorption INTRODUCTION Have you ever built a campfire? Did you start with logs or twigs? Even though you will eventually need logs to keep the fire burning, you have to use twigs
AIMS Education Foundation
 Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science) began in 1981 with a
Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science) began in 1981 with a
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
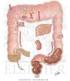 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
LESSON PLANS : The Body Curriculum Unit (Early Childhood)
 LESSON PLANS : The Body Curriculum Unit (Early Childhood) Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify body differences. Students will discover that the body is unique by exploring movement and
LESSON PLANS : The Body Curriculum Unit (Early Childhood) Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify body differences. Students will discover that the body is unique by exploring movement and
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
The Digestive System
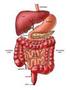 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Hypnotic. Gastric Band. Paul McKenna
 Hypnotic Gastric Band Paul McKenna Hypnotic Gastric Band The Amazing Truth About A Hypnotic Gastric Band A Gastric Band is a radical, surgical operation that reduces the available space in your stomach
Hypnotic Gastric Band Paul McKenna Hypnotic Gastric Band The Amazing Truth About A Hypnotic Gastric Band A Gastric Band is a radical, surgical operation that reduces the available space in your stomach
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry
 NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
How To Understand The Human Body
 Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
Introduction to Biology and Chemistry Outline I. Introduction to biology A. Definition of biology - Biology is the study of life. B. Characteristics of Life 1. Form and size are characteristic. e.g. A
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
NAME: DATE: Home Economics: The parts of the digestive system and their functions. Home Economics
 Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
The Goat s Digestive System. Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County
 The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Mini Medical School Lesson
 Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Digestive System Simulation
 Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
4 Weeks to Healthy Digestion
 4 Weeks to Healthy Digestion A Harvard Doctor s Proven Plan for Reducing Symptoms of Diarrhead Constipation Heartburn and More Norton J. Greenberger, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical
4 Weeks to Healthy Digestion A Harvard Doctor s Proven Plan for Reducing Symptoms of Diarrhead Constipation Heartburn and More Norton J. Greenberger, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical
Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology
 Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
