1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
|
|
|
- Ellen Summers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo different processes in order to put resourceful nutrients to work and eliminate unnecessary waste products. In regards to utilizing nutrients from foods for the body, processes such as digestion and absorption are involved. Digestion is when foods are broken down into components, and absorption is when these products of digestion are moved through the small intestine walls and overall into circulation of the body. These processes correlate to everything we eat, which includes macronutrients. Macronutrients, in particular, are the nutrients in which a living organism needs in huge amounts for effective growth and development. The three main macronutrients consist of: lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lipids are one group of macronutrients. Lipids are a diverse class of molecules in which are insoluble in water, meaning that they do not dissolve in the presence of water. Fats, in particular, are one type of lipid. There are three different kinds of lipids found in foods: triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. In essence, the role of fat in our body is to provide energy and energy storage for later usage. The digestion and absorption of fats are not done easily as fats are insoluble, but these processes do happen primarily in the small intestine. The process of digestion for fats first starts off in the mouth, as salivary glands produce an enzyme called lingual lipase. This particular enzyme digests some triglycerides that can be found within the fats being ingested. As the food is swallowed, it moves along into the stomach. The intact food is then mixed and broken down into particles/fat droplets. The stomach also
2 releases gastric lipase, which aids in digesting some more triglycerides. At this point, however, a lot of digestion has not taken place. The gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine, and chyme (containing fat molecules) also passes slowly into the small intestine. The bile from the gallbladder helps to emulsify the fat, alongside pancreatic enzymes that derive from the pancreas. These pancreatic enzymes help to break triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids. Then, the spherical micelles found in the small intestine help to transport free fatty acids to the mucosal cells for absorption processes. Within these mucosal cells, a small amount of protein is involved, and is added to the lipids and this overall creates chylomicrons, which are lipoproteins produced by the cells that line the small intestine. Chylomicrons are considered to be the transport system that help remove fats and overall travel through the lymphatic system, along with being transported into the bloodstream. In order to get through these systems and cells, the triglycerides in the chylomicrons are once again broken down into two fatty acids and a monoglyceride with the help of lipoprotein lipase. Once entering the cell membrane, the broken down fatty acids and monoglyceride reform a triglyceride structure again. This is where the triglyceride can be utilized for the body, either for immediate energy use, to make lipid containing compounds, and/or for storage in the muscle and liver cells. The remaining fats can also be stored as adipose tissue (fat cells) within the body. As for elimination of waste products that involve fats, the undigested lipids move along to the large intestine.the intestinal bacteria in the large intestine helps to break down the undigested lipids into waste products (feces). Carbohydrates are another group of macronutrients that are mainly derived from plant foods (e.g. fruits, vegetables, and grains). In essence, carbohydrates can be classified as simple and complex. Within these two categories, there are many different types of carbohydrates involved. These various carbohydrates are digested and absorbed within the body through various steps. Carbohydrate digestion starts from the mouth and salivary amylase is produced from saliva. The salivary amylase starts off the
3 process by breaking down the starch (glucose molecules) into maltose, a disaccharide. Once the food is ingested, the produced maltose goes to the stomach. The acidic content of the stomach causes the maltose to become non functioning and shapeless. Although the content might go to the stomach, carbohydrates do not get digested via the stomach. Like lipid digestion, carbohydrate digestion also occurs mainly in the small intestine. The pancreas also helps by secreting pancreatic amylase into the small intestine, in order to break down starch found in the carbohydrates. As chyme enters the small intestine, the pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes starch into maltose effectively (unlike the stomach). The small intestine also helps to break down disaccharides into monosaccharides through certain enzymes. Then, these converted monosaccharides are all absorbed by the small intestine and overall enter the bloodstream. Through the bloodstream, these monosaccharides transfer over to the liver. The liver is where all the monosaccharides are then converted to glucose, and this glucose is spread out to different cells of the body for energy purposes. The remaining glucose, converted to glycogen, is then stored in the liver. Overall, the remaining (undigested) carbohydrates transport over to the large intestine. As we humans do not contain the bodily enzymes to digest fiber, the large intestine helps in breaking down some fiber structures. The large intestine contains intestinal bacteria that helps to break down the undigested carbohydrates, overall excreting it out of the body as feces. Proteins are the third type of macronutrients, and they are large and complex molecules that are made up of amino acids. Proteins are the primary source of nitrogen within our diets, and the digestion and absorption of proteins includes extensive steps as well as the other two macronutrients. The digestion of protein starts off in the mouth, where the proteins found in the food are broken down by salivary glands in saliva and chewing. This breakdown of food is then moved along to the stomach, where protein digestion essentially begins. The hydrochloric acid found in the stomach helps break down protein structure, also activating pepsin. Pepsin also helps to deconstruct proteins into single amino acids and smaller
4 polypeptides. The chyme overall moves along to the small intestine, where digestion continues, and pancreatic proteases help to digest the polypeptides into even smaller particles. The liver overall effectively digests the proteins, as the cells found in the wall of the small intestine complete breaking down polypeptides into single amino acids. The single amino acids then are transferred over to the liver, monitoring their metabolism and overall sending them out throughout the cells in the body as needed. The remaining dietary protein is eliminated by the help of the large intestine and its intestinal bacteria that helps to break down remaining proteins into feces. 2. Flowcharts of Digestion and Absorption processes of Macronutrients *The flowcharts of the macronutrients are found below in this order: Lipids (Fats) flowchart Carbohydrates flowchart Proteins flowchart
5
6
7
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
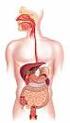
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Weds 5/20/15. Membranes - finish last lecture outline. Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system
 Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
OVERVIEW OF LIPID METABOLISM
 VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building [email protected] 9663286 *Please
VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building [email protected] 9663286 *Please
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm.
 Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
The Digestive System
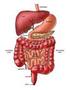 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
Lipid Metabolism. Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college
 Lipid Metabolism Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college Lipids - Heterogenous group of biomolecules - Water insoluble (hydrophobic) - Soluble in organic and non-polar solvents acetone,
Lipid Metabolism Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college Lipids - Heterogenous group of biomolecules - Water insoluble (hydrophobic) - Soluble in organic and non-polar solvents acetone,
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Physiology of Digestive system II
 Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Small Intestine Physiology of Digestive system II Motility of small intestine: Distention of the Small Intestine Elicits Mixing Contractions Called Segmentation Contractions. These are concentric contractions
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
NAME: DATE: Home Economics: The parts of the digestive system and their functions. Home Economics
 Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
17. The Digestion and Absorption of Food. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Processes
 chapter C H A P T E R 17 _ The Digestion and Overview: of the Gastrointestinal Organs Structure of the Gastrointestinal Tract Wall Digestion and Absorption Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamins Water and Minerals
chapter C H A P T E R 17 _ The Digestion and Overview: of the Gastrointestinal Organs Structure of the Gastrointestinal Tract Wall Digestion and Absorption Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamins Water and Minerals
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist
 Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion
 Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title
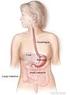 t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates
 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14
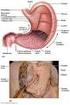 Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1. Lipids:
 (Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Classifying Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, p sphingolipids, p and cholesterol
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry
 NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
NSW Higher School Certificate Senior Science 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 Drug Solubility 9.2 Lifestyle Chemistry Section 5 ::: Drug Solubility 9.2.5 The solubility of drugs has an effect on the way
T F T F in childr T F
 T F T F in childr T F 108 Plant-derived energy nutrients 3 mon. 123 124. 110 Glucose is the preferred source of energy for the brain. What As noted earlier (in Chapter 1), carbohydrates are one of the
T F T F in childr T F 108 Plant-derived energy nutrients 3 mon. 123 124. 110 Glucose is the preferred source of energy for the brain. What As noted earlier (in Chapter 1), carbohydrates are one of the
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
 Overview of Lipid Metabolism Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture the students should be able to understand: Classification of Lipids The digestion, absorption and utilization of dietary lipids
Overview of Lipid Metabolism Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture the students should be able to understand: Classification of Lipids The digestion, absorption and utilization of dietary lipids
Module One: The Nature and Variety of Living Organisms. Human Nutrition. By the end of this lesson you should be able to
 Lesson Six Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to describe the chemical elements and structure of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, and the tests for glucose and starch identify sources
Lesson Six Aims By the end of this lesson you should be able to describe the chemical elements and structure of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, and the tests for glucose and starch identify sources
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
 Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Chemical Processes of Digestion
 Chemical Processes of Digestion Objective: To explain in short essays or diagrams how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are digested into end products that can be absorbed into the blood, at the level
Chemical Processes of Digestion Objective: To explain in short essays or diagrams how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are digested into end products that can be absorbed into the blood, at the level
Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c)
 Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c) Next lecture: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Ch. 19.2), Ketone Bodies (Ch. 19.3) and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (Ch. 19.4)
Lecture 6: Cholesterol (Ch. 9.1e, 9.2b, 19.7b,c) & Lipoproteins (Ch. 10.3*, 19.1, 19.7b,c) Next lecture: Fatty Acid Oxidation (Ch. 19.2), Ketone Bodies (Ch. 19.3) and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (Ch. 19.4)
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
Mammalian Physiology. Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption
 Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Mammalian Physiology Gastrointestinal System: Digestion and Absorption 1UNLV UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 33 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the digestive secretions
Lipids. Classifying Lipids
 (Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, sphingolipids, and cholesterol (together with proteins)
(Woods) Chem-131 Lec-19 09-4 Lipids 1 Lipids Triacylglycerols (triglycerides): a storage form of energy not required for immediate use. Phospholipids, sphingolipids, and cholesterol (together with proteins)
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS. (derived from Pancreatin USP) Sodium tauroglycocholate BPC 65mg (with sugar coating containing essential carminative oils)
 ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
Chapter 4. Carbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients
 hapter 4 arbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients hapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates,
hapter 4 arbohydrates: Bountiful Sources of Energy and Nutrients hapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Describe the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates,
