Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
|
|
|
- Damian Hart
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the food you eat. But a bite of sandwich can t travel through your blood and get to your cells in its original form. The organs of the digestive system get the nutrients in food into a form your cells can use. The Parts of Your Digestive System You can think of your digestive system as a long, twisting tube inside your body. Several different organs make up the tube and each organ has its own job. At one end (your mouth) food enters and at the other end (your anus) waste goes out. In between, your teeth grind your food, muscles knead it, and chemicals turn it into forms your cells can use. Word Connection The word digest means to break down. T Think About It! How do you think nutrients from food get to your muscle cells? What needs to happen to these nutrients for them to get to your cells? 81
2 82 Chapter 9 Human Body Fact Your small intestine is so long feet that when you pat your stomach you are probably patting your small intestine. This picture of the digestive system shows the organs that connect to each other to form the digestive tube. These organs include the mouth, esophagus (i-sahf-uh-guhs), stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Looking at the picture, start at the mouth and pass your finger over each of these organs. This is the path that food takes as it moves through the digestive system. Some other important organs are attached to this tube. The salivary glands, liver, and pancreas (pan-kree-us) produce important substances, called digestive juices. The gall bladder stores the digestive juices the liver produces. Mouth Salivary Glands Esophagus Liver Gall Bladder Small Intestine Stomach Pancreas Large Intestine Rectum
3 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System 83 The Teamwork of Cells Your body has special cells that help with digestion. Chief cells, in your stomach, produce an enzyme that breaks down proteins. This enzyme only works when an acid is present. Parietal cells are found next to chief cells in your stomach. They produce an acid that turns on the enzymes from the chief cells. Parietal cells A group of chief cells How Is Food Broken Down? Food is broken down in the digestive system in two ways: Chemical digestion Special chemicals, called enzymes, change the food into forms that are simple enough to pass into your blood. There are enzymes in saliva, in fluids in your stomach (called gastric juices), and in your small intestine. Human Body Fact A normal meal stays in the stomach for about 2 3 hours. A really big meal may stay in your stomach for 5 hours or more.
4 84 Chapter 9 T Think About It! When you chew food, you end up with many small pieces instead of one large piece. Why do you think this helps the enzymes do their work? (Hint: Enzymes work on the exposed parts of the food pieces. Does one large piece of food or many small pieces of food have more surfaces exposed?) Physical digestion Muscles in the digestive system break down food into smaller pieces. This also mixes in the enzymes. In your mouth, your teeth and jaw muscles begin this process when you chew your food. Further down, the muscles of your stomach and small intestine squeeze the food in a back-and-forth motion similar to kneading dough. These two processes work together. Physical digestion breaks food into smaller pieces and mixes in the enzymes. Chemical digestion breaks the food into forms that can pass into the blood. A Sandwich s Journey How does eating a sandwich at lunch help you run a race hours later? How do the nutrients in it get to the muscles in your legs? How do these nutrients help your muscles work hard to carry you across the finish line? What s in a Turkey Sandwich? Carbohydrates (mostly in bread) Vitamins and minerals (in vegetables, meat, and bread) Fats (in spreads, meat, and bread) Protein (mostly in meat)
5 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System 85 What Happens When You Eat a Turkey Sandwich? 1. Mouth: Teeth grind food up into small pieces. 2. Salivary Glands: Saliva flows from these glands into your mouth. Enzymes in the saliva start breaking down carbohydrates. 3. Esophagus: The swallowed ball of food is squeezed from behind to push it towards the stomach. 4. Stomach: Stomach enzymes, turned on by acids, began breaking down proteins. Strong muscles knead the food, mixing in the enzymes and turning the food to mush. Liver Gall Bladder 5. Small Intestine: More enzymes and digestive juices are added to the mush (some of these come from the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas). Fats and the remaining proteins and carbohydrates are digested into simpler forms. The food is now in a form small and simple enough to pass into the blood. Pancreas 6. Large Intestine: Undigested food (such as fiber) becomes a stool as water is absorbed from it and passed to the blood. 7. Rectum: The stool is stored here until it s time to go to the bathroom. What Happens to the Food Our Bodies Can t Use? Your large intestine helps you get rid of the parts of food your body can t use. How does it do this? Any food that hasn t been broken down passes into your large intestine. As the undigested food moves through the large intestine, water and minerals are pulled from it and passed to the blood. By the time the remains reach the end of the large intestine, enough water has been removed that a firm stool has formed. This stool is stored in your rectum until it is ready to be passed out through the anus. Human Body Facts An adult s large intestine is around 25 feet long! It takes 18 hours to 2 days for food to travel through the large intestine.
6 86 Chapter 9 Eat Those Fruits and Vegetables! Most of the food that passes into your large intestine is fiber. Fiber comes from plant foods (fruits, vegetables, and grains). Your body needs fiber. It helps you have regular bowel movements so you can get rid of the parts of food your body can t use. Digestion and Exercise Why Do You Feel Hungry After You ve Been Active? Fitness Fact You can keep muscle fatigue from happening by building up endurance. The hearts and lungs of people who exercise regularly work better. And they get more oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to their muscles than people who don t exercise as often. Have you ever noticed how hungry you get when you play sports, ski, or hike? Your muscle cells need a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients to create the energy they need for these activities. While you re playing, your cells use nutrients they have stored up. Afterwards, your body needs to fill up on these stored nutrients. The feeling of hunger you have is your body s way of letting you know that it s time to get nutrients again. Why Do You Feel Thirsty During and After Exercise? You may have also noticed how your throat feels dry during a long run, or how welcome a tall glass of ice water is after a game of basketball. Active muscles use up your body s supply of water, as well as nutrients and oxygen. When water is in short supply your body sends you a message to drink up to replace the water your muscles have used.
7 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System 87 Why Do Your Muscles Feel Tired? Muscle fatigue is another sign that your muscle cells have used up your body s supplies of nutrients, oxygen, and water. Your muscles are giving you a signal that they don t have enough oxygen and nutrients to create the energy they need to keep contracting. Resting gives your muscles a chance to stock up again on the oxygen and nutrients they need to keep you moving. When the Body Can t Digest Food Some conditions prevent people from digesting certain foods properly. Lactose Intolerance You may know someone who can t eat milk or other dairy products. Milk has a sugar in it called lactose. Some people s bodies don t make enough of the enzyme (called lactase) that breaks down this sugar. When it isn t digested, lactose goes into the large intestine and gives people cramps and other problems. People with this problem can get lactose-free milk and dairy products. Next time you are at the grocery store see how many Lactose-Free food labels you notice.
8 88 Chapter 9 Celiac Disease This disease damages the small intestine so it can t pass some nutrients on to the blood. People with celiac disease often become malnourished (don t get the nutrition they need) and weak because the nutrients in the food they eat don t reach their cells. This happens because their bodies react to a protein (called gluten) that is found in wheat, rye, and barley. People with celiac disease need to avoid these foods to prevent more damage to their small intestines. They do this by shopping for foods labeled Gluten Free.
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
The Digestive System
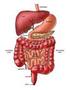 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]
![[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]](/thumbs/40/20967878.jpg) [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Managing Constipation
 Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Managing Constipation The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion
 Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestive System Simulation
 Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Reader s Theater. I AM the Most Important. (A Script about the human body systems. By Amy Bowden) Characters
 Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
Reader s Theater I AM the Most Important (A Script about the human body systems By Amy Bowden) Characters Judge (narrator) Digestive System Circulatory System Muscular System Respiratory System Nervous
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Dietary Fiber. Soluble fiber is fiber that partially dissolves in water. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water.
 Dietary Fiber Introduction Fiber is a substance in plants. Dietary fiber is the kind of fiber you get from the foods you eat. Fiber is an important part of a healthy diet. Fiber helps get rid of excess
Dietary Fiber Introduction Fiber is a substance in plants. Dietary fiber is the kind of fiber you get from the foods you eat. Fiber is an important part of a healthy diet. Fiber helps get rid of excess
Lesson Title: Nutrient Wise
 Standards This lesson aligns with the OSPI Health and Fitness Standards. This lesson will address GLE 1.5.1 Applies nutrition goals based on dietary guidelines and individual activity needs. GLE 1.5.4
Standards This lesson aligns with the OSPI Health and Fitness Standards. This lesson will address GLE 1.5.1 Applies nutrition goals based on dietary guidelines and individual activity needs. GLE 1.5.4
From ead to oe. Developed and Published by. 2010 AIMS Education Foundation
 TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
Calcium. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nuf40101 Last reviewed: 02/19/2013 1
 Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
Calcium Introduction Calcium is a mineral found in many foods. The body needs calcium to maintain strong bones and to carry out many important functions. Not having enough calcium can cause many health
The Goat s Digestive System. Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County
 The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle:
 Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
Included in this download are printable puzzles to help you learn and label the main parts of the human body. Human Anatomy Magnetic Puzzle: Print out pages 3-7 on cardstock, then laminate with regular
HIGH FIBER DIET. (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003
 HIGH FIBER DIET (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003 Dietary fiber, found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes, is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation.
HIGH FIBER DIET (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003 Dietary fiber, found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes, is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation.
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Food and digestion. Background. Suggested teaching sequence. A pupil working at:
 1 of 5 Food and digestion Background A pupil working at: Level 4 can use scientific names for the main organs of the digestive system and can accurately locate them; can use scientific names for food groups.
1 of 5 Food and digestion Background A pupil working at: Level 4 can use scientific names for the main organs of the digestive system and can accurately locate them; can use scientific names for food groups.
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes?
 Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
simple steps give you for good bowel health
 simple steps give you for good bowel health This booklet contains simple steps you can take to help achieve good bowel health. This is important to everyone, as these small changes will help your digestive
simple steps give you for good bowel health This booklet contains simple steps you can take to help achieve good bowel health. This is important to everyone, as these small changes will help your digestive
MILK It does a body good
 MILK It does a body good September 2007 In the early 90 s an ad campaign began that reminded Americans of the benefits of drinking milk. Besides the obvious benefits of strong teeth and bones milk provides
MILK It does a body good September 2007 In the early 90 s an ad campaign began that reminded Americans of the benefits of drinking milk. Besides the obvious benefits of strong teeth and bones milk provides
First Grade The Human Body Assessment
 First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
First Grade The Human Body Assessment 1a. When we talk about the skeletal system we are talking about what part of our body? a. stomach b. bones 1b. How many bones in your skeleton? a. more than two hundred
Mini Medical School Lesson
 Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Mini Medical School Lesson The American Osteopathic Association s (AOA) Mini Medical School Lesson is designed to help educators teach children about health and fitness. This lesson is aimed towards elementary
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
High blood sugars caused by steroids
 High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist
 Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Three Day Preparatory Cleansing Program (Based on the teachings of Dr. John R. Christopher and Dr. Edward E. Shook) What you will need in brief:
 Three Day Preparatory Cleansing Program (Based on the teachings of Dr. John R. Christopher and Dr. Edward E. Shook) Supreme cleanliness is the first step towards a healthy body. Any accumulation of toxins
Three Day Preparatory Cleansing Program (Based on the teachings of Dr. John R. Christopher and Dr. Edward E. Shook) Supreme cleanliness is the first step towards a healthy body. Any accumulation of toxins
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. Normal bowel habits vary between people.
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. Normal bowel habits vary between people.
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
 Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
The Basics of Nutrition: Understanding Nutrition Facts, Servings Sizes, & Adequate Portions
 The Basics of Nutrition: Understanding Nutrition Facts, Servings Sizes, & Adequate Portions K AT I E L. H O W E H E A LT H E D U C AT O R D I V I S I O N O F S T U D E N T A F FA I R S U S C U P S TAT
The Basics of Nutrition: Understanding Nutrition Facts, Servings Sizes, & Adequate Portions K AT I E L. H O W E H E A LT H E D U C AT O R D I V I S I O N O F S T U D E N T A F FA I R S U S C U P S TAT
TRACKS Lesson Plan. Calcium Calcium Counts Grades 5-8
 TRACKS Lesson Plan Calcium Calcium Counts Grades 5-8 I. Lesson Objectives: A. Students will describe the importance of calcium in their diet. B. Students will recognize a variety of foods that contain
TRACKS Lesson Plan Calcium Calcium Counts Grades 5-8 I. Lesson Objectives: A. Students will describe the importance of calcium in their diet. B. Students will recognize a variety of foods that contain
Gateways to Science SAMPLE. STAAR Edition. Teacher Edition
 Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
Maintaining Proper Bowel Elimination
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal. Index of Topics. You and Your Heart Activity 1: How Your Heart Functions.2 Activity 2: Break the Heart Code..
 This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
This is your LOVE MY HEART Journal Use this workbook to learn about your heart and ways to keep your heart healthy. Talk with your family about the things that you do and learn in this book! Have fun!
1. (U4C1L4:G9) T or F: The human body is composed of 60 to 70 percent water. 2. (U4C1L4:G13) Another name for fiber in a diet is.
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C1L4:G9) T or F: The human body is composed of 60 to 70 percent water. A) True B) False 2. (U4C1L4:G13) Another name for fiber in a diet is. A) vegetables B) laxative C) fruit D)
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C1L4:G9) T or F: The human body is composed of 60 to 70 percent water. A) True B) False 2. (U4C1L4:G13) Another name for fiber in a diet is. A) vegetables B) laxative C) fruit D)
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
The Digestive System
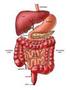 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Food Allergies and. Food allergies and the immune system. Food allergies and the immune system
 Food Allergies and Intolerances Food allergies and the immune system Food allergies and True allergies involve an adverse reaction/ response by the body s immune system to a usually harmless substance
Food Allergies and Intolerances Food allergies and the immune system Food allergies and True allergies involve an adverse reaction/ response by the body s immune system to a usually harmless substance
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Importance of water for weight loss
 Importance of water for weight loss Most people do not drink enough water; one reason for this is because they have gotten out of the habit. If you are trying to lose weight, drinking plenty of water is
Importance of water for weight loss Most people do not drink enough water; one reason for this is because they have gotten out of the habit. If you are trying to lose weight, drinking plenty of water is
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
Juice Cleanse 2014. Why do a juice cleanse?
 Why do a juice cleanse? Our world has become a toxic place, not only from our environment but also through the food and substances we put in our body. These toxins enter our body, accumulate over time,
Why do a juice cleanse? Our world has become a toxic place, not only from our environment but also through the food and substances we put in our body. These toxins enter our body, accumulate over time,
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
VIDEO WORKSHEET. Review: #300007. Name: Hour:
 #300007 Name: Hour: Review: VIDEO WORKSHEET After watching each segment of Obesity in a Bottle II: How to Pick Healthy Beverages, answer the following questions. How to Choose Healthy Beverages 1. What
#300007 Name: Hour: Review: VIDEO WORKSHEET After watching each segment of Obesity in a Bottle II: How to Pick Healthy Beverages, answer the following questions. How to Choose Healthy Beverages 1. What
Gestational diabetes. Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy. What is gestational diabetes?
 Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
Gestational diabetes Information to help you stay healthy during your pregnancy What is gestational diabetes? How gestational diabetes can affect my baby How to take care of myself and my baby during pregnancy
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment).
 2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
2. Provide the scoring guide/rubric for the culminating task (summative assessment). Criteria Oral Presentation- Group project Poster Presentation display/ visual aids 1 - Attempts the standard use the
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
You may continue to use your old manuals by writing in the detailed changes below:
 STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test
 Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people
 Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
