Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
|
|
|
- Curtis Sydney Young
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Multiple Choice 1. An ac generator with peak voltage 100 volts is placed across a 10-Ω resistor. What is the average power dissipated? a. 100 W b. 150 W c. 500 W d W e W 2. An electric heater draws an average power of 1100 Watts when plugged into a 110 V-rms outlet. Calculate the resistance of the heater and the rms current. a. 11Ω, 10 A (rms) b. 110Ω, 10 A (rms) c. 10Ω, 11 A (rms) d. 10Ω, 110 A (rms) e..09ω, 11 A (rms) 3. An incandescent lightbulb is rated at 100 Watts when plugged into a 110 V-rms household outlet. Calculate the resistance of the filament and the rms current. a. 12.2Ω, 0.9A (rms) b. 10Ω, 1A (rms) c. 110Ω, 1A (rms) d. 122Ω, 0.9 A (rms) e. 11Ω, 1.1 A (rms) 4. A high-voltage powerline operates at 500,000 V-rms and carries an rms current of 500 A. If the resistance of the cable is.05ω/km, what is the resistive power loss in 200 km of the powerline? a. 250 kw b. 500 kw c. 1 Megawatt d. 2.5 Megawatts e. 250 Megawatts
2 2 Chapter A 230,000 V-rms powerline carries an average power P AV = 250 MW a distance of 200 km. If the total resistance of the cables is 10 ohms, what is the resistive power loss? a. 1.0 MW b. 2.5 MW c. 5.4 MW d MW e. 10 kw 6. Inductive reactance X L is given by a. Lω b. L/ω c. 1 /Lω d. ω/l e. ω 2 L 7. Capacitance reactance X C is given by a. 1/ωC b. ωc c. ω/c d. C/ω e. 1/ω 2 C 8. The total impedance Z of an RLC circuit driven by an ac voltage source at angular frequency ω is, a. R 2 + (ωl) 2 X C 2 b. R 2 + (X L X C ) 2 c. 1 R 2 + (X L X C ) 2 d. R 2 + (X L + X C ) 2 e. R 2 (X L + X C ) 2 9. At what frequency will a 12-µF capacitor have a reactance X C = 300Ω? a. 44 Hz b. 88 Hz c. 176 Hz d. 352 Hz e. 278 Hz 10. At what frequency will a 50-mH inductor have a reactance X L = 700Ω? a. 352 Hz b. 777 Hz c khz d khz e. 14 khz
3 Chapter A 2-µF capacitor in series with a 2-kΩ resistor is connected to a 60-Hz ac source. Calculate the impedance of the circuit. a ohms b ohms c ohms d ohms e ohms 12. A 10-µF capacitor is plugged into a 110 V-rms 60-Hz voltage source, with an ammeter in series. What is the rms value of the current through the capacitor? a A (rms) b A (rms) c A (rms) d A (rms) e A (rms) 13. A 0.5-H inductor is connected into a 110 V-rms 60-Hz voltage source, with an ammeter in series. What is the rms value of the current through the inductor? a A (rms) b A (rms) c A (rms) d A (rms) e A (rms) 14. An LC circuit is to have resonant oscillations at 5.0 MHz. Find the value of a capacitor which will work with a 1.0-mH inductor. a. 2 mf b. 1 µf c µf d. 1 pf e. 40 pf 15. The inductance of a tuning circuit of an AM radio is 4 mh. Find the capacitance of the circuit required for reception at 1200 khz. a. 2.1 pf b. 4.4 pf c pf d pf e pf 16. Find the resonant frequency for a series RLC circuit where R = 10Ω, C = 5 µf, and L = 2 mh. a. 998 Hz b khz c khz d khz e khz
4 4 Chapter The voltage 8 sin (400t) is applied to a series RLC circuit, with R = 200Ω, L = 0.1 H, and C = 1 µf. What are the impedance Z and the phase angle θ? a. 200 Ω, 37 b. 566 Ω, +87 c Ω, 85.4 d Ω, 88.8 e. 393 Ω, If an R = 1-kΩ resistor, a C = 1-µF capacitor, and an L = 0.2-H inductor are connected in series with a V = 150 sin (377t) volts source, what is the maximum current delivered by the source? a A b. 27 ma c. 54 ma d A e A 19. If the input to an RLC series circuit is V = V m cos ωt, then the current in the circuit is a. b. c. d. V m cos ωt R V m cos ωt R 2 + ω 2 L 2 V m sin ωt R 2 + (ωl + 1/ωC) 2 V m cos (ωt φ) R 2 + (ωl 1/ωC) 2 e. V m R ωl cos ωt ωc 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms, C = 25 µf, and L =.16 H. For what angular frequency of an ac voltage is the current flow maximum? a. 251 rad/s b. 500 rad/s c. 757 rad/s d. 884 rad/s e rad/s
5 Chapter Determine the rms voltage for the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 99 V (rms) b. 140 V (rms) c. 196 V (rms) d. 70 V (rms) e. 110 V (rms) 22. Determine the impedance for the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 600 Ω b Ω c Ω d Ω e Ω 23. Determine the rms current for the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 55 ma b. 77 ma c. 99 ma d A e. 61 ma
6 6 Chapter Determine the resonant frequency of the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 159 Hz b. 32 Hz c. 5 Hz d. 500 Hz e Hz 25. Determine the rms voltage drop across the resistor in the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 55 V b. 77 V c. 9.9 V d. 5.5 V e. 61 V 26. Determine the rms voltage drop across the inductor in the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 11 V b V c. 33 V d V e V
7 Chapter Determine the rms voltage drop across the capacitor in the circuit. 1 kω V = 140 sin (500 t) 1 Η 1 µf a. 55 V b. 77 V c. 110 V d. 154 V e. 198 V 28. A current I = 3 sin (400 t) amperes flows in a series RL circuit in which L = 1 mh and R = 100Ω. What is the average power loss? a. 225 W b. 450 W c. 980 W d kw e. 900 W 29. What is the average power dissipation in a series RC circuit if R = 5 kω, C = 2 µf, and V = 170 cos (300t)? a W b W c W d. 157 W e W 30. What is the average power dissipation in an RLC series circuit with R = 10Ω, L = 0.1 H, C = 10 µf when driven at resonance by a 100 V-rms source? a. 100 W b. 500 W c W d. 2 kw e. 700 W 31. A series RLC circuit has an impedance of 120Ω and a resistance of 64Ω. What average power is delivered to this circuit when V rms = 90 volts? a. 36 W b. 100 W c. 192 W d. 360 W e. 12 W
8 8 Chapter A transformer is to be designed to increase the 30 kv-rms output of a generator to the transmission-line voltage of 345 kv-rms. If the primary winding has 80 turns, how many turns must the secondary have? a. 6 b. 70 c. 920 d e The primary winding of an electric train transformer has 400 turns and the secondary has 50. If the input voltage is 120V(rms) what is the output voltage? a. 15 V (rms) b. 30 V (rms) c. 60 V (rms) d. 2.4 V (rms) e. 960 V (rms) 34. A step-up transformer has an input voltage of 110V(rms). There are 100 turns on the primary and 1500 on the secondary. What is the output voltage? a V (max) b V (rms) c V (max) d. 165 kv (rms) e. 7.3 V (rms) 35. A primary current of 6 A exists in an ideal iron-core transformer at a primary voltage of 100 volts. If the current in the secondary is.75 A, calculate the output voltage. a V b. 40 V c. 400 V d. 800 V e. 200 V 36. An ideal step-down transformer has 200 primary turns and 50 secondary turns. If 440 volts (rms) is placed across the primary, what is the current in the secondary if the load resistance is 7 ohms? a. 3.6 A (rms) b. 7.3 A (rms) c A (rms) d A (rms) e A (rms)
9 Chapter Calculate V out /V in for the circuit if R = 2 kω, C = 0.02 µf and V = 140V sin(50,000t) R V in C Vout a b c. 0.8 d e The impedance of the parallel RLC circuit shown is given by V 0 sin ωt R L C a. b. c. 1 R + 1 ωl + ωc 1 R 2 + ωc 1 ωl 1 R + 1 ωl 1 ωc 2 1/2 d. R ωl ωc e. 1 R 2 + ωc 1 ωl 39. The rms current from the voltage source is 2 V 0 sin ωt R L C a. V rms Z b. V rms /Z c. V rms /R d. V rms /(R +X L X C ) e. V rms /(2Z)
10 10 Chapter The phase angle between V and I is V 0 sin ωt R L C a. tan 1 R R X C X L b. tan 1 R X C X L c. tan 1 X C X L R d. tan 1 R R 2 + (X L X C ) 2 e. tan 1 R 2 + (X L X C ) For driving voltage V = V m sin t, the current through the resistor is V 0 sin ωt R L C a. V m sin (ωt + φ) b. V m cos (ωt + φ) c. d. e. V m R V m sin (ωt + φ) sin (ωt + φ) Z V m sin ωt R 42. If R = 10 ohms, L = 0.1 henry, C = 10 µf, what is the resonant frequency for the parallel RLC-circuit? a Hz b. 333 Hz c. 159 Hz d. 53 Hz e. 500 Hz Conceptual Problems 43. Suppose the circuit parameters in a series RLC circuit are: L = 1.0 µh, C = 10.0 nf, R = 100Ω, and the source voltage is 22 V. Determine the resonant frequency of the circuit and the amplitude of the current at resonance.
11 Chapter A 10-Ω resistor, 10-mH inductor, and 10-µF capacitor are connected in series with a 10-kHz voltage source. The rms current through the circuit is 0.20 A. Find the voltage drop across each of the 3 elements. 45. An ac power generator produces 50 A (rms) at 3600 V. The voltage is stepped up to 100,000 V by an ideal transformer and the energy is transmitted through a long distance power line which has a resistance of 100 ohms. What percentage of the power delivered by the generator is dissipated as heat in the long-distance power line? 46. An alternating current circuit has resistance R, inductance L and capacitance C in series with a voltage source. Which statement is correct? a. The voltage across the capacitor leads the voltage across the inductor by 90. b. The voltage across the inductor leads the voltage across the capacitor by 90. c. The voltage across the capacitor leads the voltage across the inductor by 180. d. The voltage across the inductor leads the voltage across the capacitor by 180. e. Both voltages lead the voltage across the resistor by In a series ac LRC circuit a. capacitors and inductors act as short circuits at high frequencies. b. capacitors and inductors act as open circuits at low frequencies. c. a capacitor acts as an open circuit at low frequencies and as a short circuit at high frequencies. d. an inductor acts as an open circuit at low frequencies and as a short circuit at high frequencies. e. a capacitor acts as a short circuit at high frequencies and an inductor acts as a short circuit at low frequencies. 48. The power output, Pout, of a step-up transformer that receives power input, Pin, and which has N1turns in the primary and N2 turns in the secondary coil is given by a. P out = P in b. P out = N 2 N 1 P in. c. P out = N 1 P N in. 2 d. P out = N 2 N 1 e. P out = N 1 N 2 2 Pin. 2 Pin. 49. In a typical transmission line, the current I is very small and the voltage V is very large. A unit length of line has resistance R. For a power line that supplies power to 10,000 households, we can conclude that a. IV = I 2 R. b. I = V/R. c. IV<I 2 R. d. IV>I 2 R. e. I 2 R = 0.
12 12 Chapter Whenever the alternating current frequency in a series RLC circuit is halved, a. the inductive reactance is doubled and the capacitive reactance is halved. b. the inductive reactance is doubled and the capacitive reactance is doubled. c. the inductive reactance is halved and the capacitive reactance is halved. d. the inductive reactance is halved and the capacitive reactance is doubled. e. the reactance of the circuit remains the same. 51. The average power input to a series alternating current circuit is minimum when a. there are only a resistor and capacitor in the circuit. b. there are only a resistor and inductor in the circuit. c. there is only a resistor in the circuit d. X L = X C and the circuit contains a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor. e. there is only a capacitor in the circuit.
13 Chapter 33 1 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1. Answer: c 2. Answer: a 3. Answer: d 4. Answer: d 5. Answer: d 6. Answer: a 7. Answer: a 8. Answer: b 9. Answer: a 10. Answer: d 11. Answer: d 12. Answer: b 13. Answer: c 14. Answer: d 15. Answer: b 16. Answer: b 17. Answer: c 18. Answer: c 19. Answer: d 20. Answer: b 21. Answer: a 22. Answer: c 23. Answer: a
14 2 Chapter Answer: a 25. Answer: a 26. Answer: b 27. Answer: c 28. Answer: b 29. Answer: b 30. Answer: c 31. Answer: a 32. Answer: c 33. Answer: a 34. Answer: b 35. Answer: d 36. Answer: d 37. Answer: b 38. Answer: b 39. Answer: b 40. Answer: a 41. Answer: e 42. Answer: c 43. Answer: 1.59 MHz, 0.22 A 44. Answer: 2.0 V, V, V 45. Answer: 0.18% 46. Answer: d 47. Answer: e 48. Answer: a 49. Answer: d
15 Chapter Answer: d 51. Answer: e
16 4 Chapter 33
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Physics 6C, Summer 2006 Homework 2 Solutions
 Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Chapter 35 Alternating Current Circuits
 hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
Inductors in AC Circuits
 Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
Inductors in AC Circuits Name Section Resistors, inductors, and capacitors all have the effect of modifying the size of the current in an AC circuit and the time at which the current reaches its maximum
Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
hapter 9 Alternating-urrent ircuits onceptual Problems A coil in an ac generator rotates at 6 Hz. How much time elapses between successive emf values of the coil? Determine the oncept Successive s are
RLC Series Resonance
 RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
RLC Series Resonance 11EM Object: The purpose of this laboratory activity is to study resonance in a resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) circuit by examining the current through the circuit as a function
45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 1500-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across?
 PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
PHYS Practice Problems hapters 8- hapter 8. 45. The peak value of an alternating current in a 5-W device is 5.4 A. What is the rms voltage across? The power and current can be used to find the peak voltage,
Chapter 12 Driven RLC Circuits
 hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter Driven ircuits. A Sources... -. A ircuits with a Source and One ircuit Element... -3.. Purely esistive oad... -3.. Purely Inductive oad... -6..3 Purely apacitive oad... -8.3 The Series ircuit...
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam
 The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
The W5JCK Guide to the Mathematic Equations Required for the Amateur Extra Class Exam This document contains every question from the Extra Class (Element 4) Question Pool* that requires one or more mathematical
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 3
 PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
Diodes have an arrow showing the direction of the flow.
 The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
The Big Idea Modern circuitry depends on much more than just resistors and capacitors. The circuits in your computer, cell phone, Ipod depend on circuit elements called diodes, inductors, transistors,
Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering
 Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering 2. A circular coil has a 10.3 cm radius and consists of 34 closely wound turns of wire. An externally produced magnetic field of
Homework #11 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering 2. A circular coil has a 10.3 cm radius and consists of 34 closely wound turns of wire. An externally produced magnetic field of
Transformer circuit calculations
 Transformer circuit calculations This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Transformer circuit calculations This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks. Valentin Todorow, December, 2009
 Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide
 Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Test (CTT) Study Guide 1 05/2014 Study Guide for Pacific Gas & Electric Company Apprentice Telecommunications Technician Qualifying Test (CTT) About the Test The
Alternating-Current Circuits
 hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
hapter 1 Alternating-urrent ircuits 1.1 A Sources... 1-1. Simple A circuits... 1-3 1..1 Purely esistive load... 1-3 1.. Purely Inductive oad... 1-5 1..3 Purely apacitive oad... 1-7 1.3 The Series ircuit...
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Experiment #11: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept: circuits Time: 30 m SW Interface: 750 Windows file: RLC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage
Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7
 CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Autumn Examinations 2012 Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7 Module Code: ELEC7007 School: School of Mechanical, Electrical and Process
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Autumn Examinations 2012 Module Title: Electrotechnology for Mech L7 Module Code: ELEC7007 School: School of Mechanical, Electrical and Process
Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill. Presented by Scott Peele PE
 Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill Presented by Scott Peele PE Understanding Power Factor Definitions kva, kvar, kw, Apparent Power vs. True Power Calculations Measurements
Understanding Power Factor and How it Affects Your Electric Bill Presented by Scott Peele PE Understanding Power Factor Definitions kva, kvar, kw, Apparent Power vs. True Power Calculations Measurements
ε: Voltage output of Signal Generator (also called the Source voltage or Applied
 Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
Experiment #10: LR & RC Circuits Frequency Response EQUIPMENT NEEDED Science Workshop Interface Power Amplifier (2) Voltage Sensor graph paper (optional) (3) Patch Cords Decade resistor, capacitor, and
IF Transformer. V2 is 2Vp-p sinusoidal
 V2 is 2Vp-p sinusoidal Purpose and Function These transformers are specially designed tuned circuit in RFI-tight groundable metal packages for narrow bandwith IF application. 1 Theory and Design C30 and
V2 is 2Vp-p sinusoidal Purpose and Function These transformers are specially designed tuned circuit in RFI-tight groundable metal packages for narrow bandwith IF application. 1 Theory and Design C30 and
Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 Arecibo, a large radio telescope in Puerto Rico, gathers electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves. These long wavelengths pass through obscuring dust clouds, allowing astronomers to create
Arecibo, a large radio telescope in Puerto Rico, gathers electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves. These long wavelengths pass through obscuring dust clouds, allowing astronomers to create
AC Power. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Voltage Waveform Consider the
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
AC Generators. Basic Generator
 AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
AC Generators Basic Generator A basic generator consists of a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes and a resistive load. The magnetic field is usually an electromagnet. An armature is any number
Chapter 25 Alternating Currents
 Physics Including Human Applications 554 Chapter 25 Alternating Currents GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each
Physics Including Human Applications 554 Chapter 25 Alternating Currents GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each
Single Transistor FM Transmitter Design
 Single Transistor FM Transmitter Design In telecommunications, frequency modulation (FM) conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its frequency. FM is commonly used at VHF radio frequencies for
Single Transistor FM Transmitter Design In telecommunications, frequency modulation (FM) conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its frequency. FM is commonly used at VHF radio frequencies for
Properties of electrical signals
 DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
DC Voltage Component (Average voltage) Properties of electrical signals v(t) = V DC + v ac (t) V DC is the voltage value displayed on a DC voltmeter Triangular waveform DC component Half-wave rectifier
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 1 Spring 2015
 ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz Spring 205 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE ALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for numbers that appear without justification.
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz Spring 205 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE ALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for numbers that appear without justification.
2. A conductor of length 2m moves at 4m/s at 30 to a uniform magnetic field of 0.1T. Which one of the following gives the e.m.f. generated?
 Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
Extra Questions - 2 1. A straight length of wire moves through a uniform magnetic field. The e.m.f. produced across the ends of the wire will be maximum if it moves: a) along the lines of magnetic flux
Chapter 11. Inductors ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
CHAPTER 31. E max = 15.1 V
 CHAPTER 31 Note: Unless otherwise indicated, the symbols I, V, E, and P denote the rms values of I, V, and E and the average power. 1* A 00-turn coil has an area of 4 cm and rotates in a magnetic field
CHAPTER 31 Note: Unless otherwise indicated, the symbols I, V, E, and P denote the rms values of I, V, and E and the average power. 1* A 00-turn coil has an area of 4 cm and rotates in a magnetic field
Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum
 WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS. December 2011
 AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
AM 5-202 BASIC ELECTRONICS AC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS December 2011 DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for Pubic Release. Distribution is unlimited. DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY MILITARY AUXILIARY RADIO SYSTEM FORT
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits
 Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering)
 Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Z PRACTICAL WORK BOOK For The Course EE-113 Basic Electrical Engineering For First Year (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Name of Student: Class: Batch : Discipline: Class Roll No.: Examination Seat
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
Germanium Diode AM Radio
 Germanium Diode AM Radio LAB 3 3.1 Introduction In this laboratory exercise you will build a germanium diode based AM (Medium Wave) radio. Earliest radios used simple diode detector circuits. The diodes
Germanium Diode AM Radio LAB 3 3.1 Introduction In this laboratory exercise you will build a germanium diode based AM (Medium Wave) radio. Earliest radios used simple diode detector circuits. The diodes
DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4
 DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
DOE-HDBK-1011/3-92 JUNE 1992 DOE FUNDAMENTALS HANDBOOK ELECTRICAL SCIENCE Volume 3 of 4 U.S. Department of Energy Washington, D.C. 20585 FSC-6910 Distribution Statement A. Approved for public release;
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESISTANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
CURRENT ELECTRICITY INTRODUCTION TO RESI STANCE, CAPACITANCE AND INDUCTANCE P R E A M B L E This problem is adapted from an on-line knowledge enhancement module for a PGCE programme. It is used to cover
SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS
 Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Name: Date: Course and Section: Instructor: EXPERIMENT 1 SERIES-PARALLEL DC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVES 1. Test the theoretical analysis of series-parallel networks through direct measurements. 2. Improve skills
Application Note. So You Need to Measure Some Inductors?
 So You Need to Measure Some nductors? Take a look at the 1910 nductance Analyzer. Although specifically designed for production testing of inductors and coils, in addition to measuring inductance (L),
So You Need to Measure Some nductors? Take a look at the 1910 nductance Analyzer. Although specifically designed for production testing of inductors and coils, in addition to measuring inductance (L),
EEL303: Power Engineering I - Tutorial 4
 1. Determine the voltage at the generating station and the efficiency of the following system (Figure 1): Both transformers have ratio of 2kV/11kV. The resistance on LV side of both Figure 1: transformers
1. Determine the voltage at the generating station and the efficiency of the following system (Figure 1): Both transformers have ratio of 2kV/11kV. The resistance on LV side of both Figure 1: transformers
Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law
 Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law concept #1, 4, 5, 8, 13 Problem # 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 24, 23, 25, 31, 32a, 34, 37, 41, 43, 51, 61 Last chapter we saw that a current produces a magnetic
Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday s Law concept #1, 4, 5, 8, 13 Problem # 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 24, 23, 25, 31, 32a, 34, 37, 41, 43, 51, 61 Last chapter we saw that a current produces a magnetic
Phasors. Phasors. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department. ^ V cos (wt + θ) ^ V sin (wt + θ)
 V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
V cos (wt θ) V sin (wt θ) by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU, Page 1 Vector
Physics 102: Lecture 13 RLC circuits & Resonance
 Physics 102: Lecture 13 L circuits & esonance L Physics 102: Lecture 13, Slide 1 I = I max sin(2pft) V = I max sin(2pft) V in phase with I eview: A ircuit L V = I max X sin(2pft p/2) V lags I IE I V t
Physics 102: Lecture 13 L circuits & esonance L Physics 102: Lecture 13, Slide 1 I = I max sin(2pft) V = I max sin(2pft) V in phase with I eview: A ircuit L V = I max X sin(2pft p/2) V lags I IE I V t
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830
 APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: sales@pro-wave.com.tw URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: sales@pro-wave.com.tw URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02
 104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
Equipment: Power Supply, DAI, Variable resistance (8311), Variable inductance (8321)
 Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
Lab 4: 3-phase circuits. Objective: to study voltage-current relationships in 3-phase circuits; to learn to make delta and Y connections; to calculate and measure real, apparent, and reactive powers. Equipment:
Diode Applications. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008. This note illustrates some common applications of diodes.
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
GenTech Practice Questions
 GenTech Practice Questions Basic Electronics Test: This test will assess your knowledge of and ability to apply the principles of Basic Electronics. This test is comprised of 90 questions in the following
GenTech Practice Questions Basic Electronics Test: This test will assess your knowledge of and ability to apply the principles of Basic Electronics. This test is comprised of 90 questions in the following
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies
 Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
Rectifier circuits & DC power supplies Goal: Generate the DC voltages needed for most electronics starting with the AC power that comes through the power line? 120 V RMS f = 60 Hz T = 1667 ms) = )sin How
DRAFT. University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques
 University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques 1. Introduction. Students are often frustrated in their attempts to execute
University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques 1. Introduction. Students are often frustrated in their attempts to execute
Since any real component also has loss due to the resistive component, the average power dissipated is 2 2R
 Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
Quality factor, Q Reactive components such as capacitors and inductors are often described with a figure of merit called Q. While it can be defined in many ways, it s most fundamental description is: Q
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
 SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
SIMULATIONS OF PARALLEL RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 25 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and ORCAD Capture CIS to better
Power Supplies. 1.0 Power Supply Basics. www.learnabout-electronics.org. Module
 Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
Module 1 www.learnabout-electronics.org Power Supplies 1.0 Power Supply Basics What you ll learn in Module 1 Section 1.0 Power Supply Basics. Basic functions of a power supply. Safety aspects of working
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
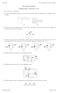 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
i( t) L i( t) 56mH 1.1A t = τ ln 1 = ln 1 ln 1 6.67ms
 Exam III PHY 49 Summer C July 16, 8 1. In the circuit shown, L = 56 mh, R = 4.6 Ω an V = 1. V. The switch S has been open for a long time then is suenly close at t =. At what value of t (in msec) will
Exam III PHY 49 Summer C July 16, 8 1. In the circuit shown, L = 56 mh, R = 4.6 Ω an V = 1. V. The switch S has been open for a long time then is suenly close at t =. At what value of t (in msec) will
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure
 The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
The Full-Wave Rectifier The full wave rectifier consists of two diodes and a resister as shown in Figure The transformer has a centre-tapped secondary winding. This secondary winding has a lead attached
7-41 POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
 POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
POWER FTOR CORRECTION INTRODUCTION Modern electronic equipment can create noise that will cause problems with other equipment on the same supply system. To reduce system disturbances it is therefore essential
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007
 [ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
[ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
GENERATOR SELECTION. a. Three phase - 120/208V, 3 phase, 4W wye; 277/408, 3 phase, 4W wye; * 120/240V 3 phase, 4W Delta
 GENERATOR SELECTION Generators must be sized to handle their load based on the continuous KW, kilowatt load, and KVA, kilovoltamp load, and the worst case starting load KW + KVA. They must be derated for
GENERATOR SELECTION Generators must be sized to handle their load based on the continuous KW, kilowatt load, and KVA, kilovoltamp load, and the worst case starting load KW + KVA. They must be derated for
12. Transformers, Impedance Matching and Maximum Power Transfer
 1 1. Transformers, Impedance Matching and Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than
1 1. Transformers, Impedance Matching and Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than
AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules
 Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Chapter 10. RC Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
L and C connected together. To be able: To analyse some basic circuits.
 circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and urrents Aims: To appreciate: Similarities between oscillation in circuit and mechanical pendulum. Role of energy loss mechanisms in damping. Why we study sinusoidal signals
VJ 6040 Mobile Digital TV UHF Antenna Evaluation Board
 VISHAY VITRAMON Multilayer Chip Capacitors Application Note GENERAL is a multilayer ceramic chip antenna designed for receiving mobile digital TV transmissions in the UHF band. The target application for
VISHAY VITRAMON Multilayer Chip Capacitors Application Note GENERAL is a multilayer ceramic chip antenna designed for receiving mobile digital TV transmissions in the UHF band. The target application for
Energy in Electrical Systems. Overview
 Energy in Electrical Systems Overview How can Potential Energy be stored in electrical systems? Battery Stored as chemical energy then transformed to electrical energy on usage Water behind a dam Water
Energy in Electrical Systems Overview How can Potential Energy be stored in electrical systems? Battery Stored as chemical energy then transformed to electrical energy on usage Water behind a dam Water
= V peak 2 = 0.707V peak
 BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
BASIC ELECTRONICS - RECTIFICATION AND FILTERING PURPOSE Suppose that you wanted to build a simple DC electronic power supply, which operated off of an AC input (e.g., something you might plug into a standard
CHAPTER 30: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits
 HAPTE 3: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and A ircuits esponses to Questions. (a) For the maximum value of the mutual inductance, place the coils close together, face to face, on the same axis.
HAPTE 3: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and A ircuits esponses to Questions. (a) For the maximum value of the mutual inductance, place the coils close together, face to face, on the same axis.
Tutorial 12 Solutions
 PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
Building the HVPS High Voltage Power Supply
 Introduction Building the HVPS High Voltage Power Supply Voltages higher than the LVPS provides kilovolts are needed in later experiments to get strong electric fields and to generate microwaves. The high-voltage
Introduction Building the HVPS High Voltage Power Supply Voltages higher than the LVPS provides kilovolts are needed in later experiments to get strong electric fields and to generate microwaves. The high-voltage
unit : mm With heat sink (see Pd Ta characteristics)
 Ordering number: EN1321E Monolithic Linear IC LA4261 3.5 W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Home Stereos and Music Centers Features. Minimum number of external parts required (No input capacitor, bootstrap
Ordering number: EN1321E Monolithic Linear IC LA4261 3.5 W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Home Stereos and Music Centers Features. Minimum number of external parts required (No input capacitor, bootstrap
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators
 Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators Technical Brief December 3 TB47. Author: Doug Mattingly Assumptions This Technical Brief makes the following assumptions:.
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE
 LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure 2. R. Figure 1.
 Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
Examples of Transient and RL Circuits. The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of Circuit. Let s examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure.
Aircraft Electrical System
 Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
Chapter 9 Aircraft Electrical System Introduction The satisfactory performance of any modern aircraft depends to a very great degree on the continuing reliability of electrical systems and subsystems.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the voltage at a point in space is zero, then the electric field must be A) zero. B) positive.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the voltage at a point in space is zero, then the electric field must be A) zero. B) positive.
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups
 Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Measuring Impedance and Frequency Response of Guitar Pickups Peter D. Hiscocks Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com April 30, 2011 Introduction The CircuitGear
Modulation and Demodulation
 16 Modulation and Demodulation 16.1 Radio Broadcasting, Transmission and Reception 16. Modulation 16.3 Types of Modulation 16.4 Amplitude Modulation 16.5 Modulation Factor 16.6 Analysis of Amplitude Modulated
16 Modulation and Demodulation 16.1 Radio Broadcasting, Transmission and Reception 16. Modulation 16.3 Types of Modulation 16.4 Amplitude Modulation 16.5 Modulation Factor 16.6 Analysis of Amplitude Modulated
Series AMLDL-Z Up to 1000mA LED Driver
 FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
Slide 1 / 26. Inductance. 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
Slide 1 / 26 Inductance 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 26 Mutual Inductance If two coils of wire are placed near each other and have a current passing through them, they will each induce an emf on one
6 ELECTRICAL PARAMETERS
 6 ELECTRICAL PARAMETERS For power, low voltage and medium voltage cables, cross section nominal areas are calculated in taking into account several parameters as: permissible current carrying capacities
6 ELECTRICAL PARAMETERS For power, low voltage and medium voltage cables, cross section nominal areas are calculated in taking into account several parameters as: permissible current carrying capacities
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY. Fig. 8.1a Fig 8.1b
 DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
DIODE CIRCUITS LABORATORY A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the type,
LR Phono Preamps. Pete Millett ETF.13. pmillett@hotmail.com
 LR Phono Preamps Pete Millett ETF.13 pmillett@hotmail.com Agenda A bit about me Part 1: What is, and why use, RIAA? Grooves on records The RIAA standard Implementations of RIAA EQ networks and preamps
LR Phono Preamps Pete Millett ETF.13 pmillett@hotmail.com Agenda A bit about me Part 1: What is, and why use, RIAA? Grooves on records The RIAA standard Implementations of RIAA EQ networks and preamps
Current and Temperature Ratings
 Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
SWITCH-MODE POWER SUPPLY CONTROLLER PULSE OUTPUT DC OUTPUT GROUND EXTERNAL FUNCTION SIMULATION ZERO CROSSING INPUT CONTROL EXTERNAL FUNCTION
 SWITCH-MODE POWER SUPPLY CONTROLLER. LOW START-UP CURRENT. DIRECT CONTROL OF SWITCHING TRAN- SISTOR. COLLECTOR CURRENT PROPORTIONAL TO BASE-CURRENT INPUT REERSE-GOING LINEAR OERLOAD CHARACTERISTIC CURE
SWITCH-MODE POWER SUPPLY CONTROLLER. LOW START-UP CURRENT. DIRECT CONTROL OF SWITCHING TRAN- SISTOR. COLLECTOR CURRENT PROPORTIONAL TO BASE-CURRENT INPUT REERSE-GOING LINEAR OERLOAD CHARACTERISTIC CURE
Lecturer: James Grimbleby URL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email: j.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk
 AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
AC Circuit Analysis Module: SEEA5 Systems and Circuits Lecturer: UL: http://www.personal.rdg.ac.uk/~stsgrimb/ email:.b.grimbleby reading.ac.uk Number of Lectures: ecommended text book: David Irwin and
Frequency response: Resonance, Bandwidth, Q factor
 Frequency response: esonance, Bandwidth, Q factor esonance. Let s continue the exploration of the frequency response of circuits by investigating the series circuit shown on Figure. C + V - Figure The
Frequency response: esonance, Bandwidth, Q factor esonance. Let s continue the exploration of the frequency response of circuits by investigating the series circuit shown on Figure. C + V - Figure The
AN2866 Application note
 Application note How to design a 13.56 MHz customized tag antenna Introduction RFID (radio-frequency identification) tags extract all of their power from the reader s field. The tags and reader s antennas
Application note How to design a 13.56 MHz customized tag antenna Introduction RFID (radio-frequency identification) tags extract all of their power from the reader s field. The tags and reader s antennas
Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3
 Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3 Basics of Power systems Network topology Transmission and Distribution Load and Resource Balance Economic Dispatch Steady State System
Power System review W I L L I A M V. T O R R E A P R I L 1 0, 2 0 1 3 Basics of Power systems Network topology Transmission and Distribution Load and Resource Balance Economic Dispatch Steady State System
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Fundamentals of radio communication
 Fundamentals of radio communication This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Fundamentals of radio communication This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Step response of an RLC series circuit
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 5 Step response of an RLC series circuit 1 Introduction Objectives
