3D Viewing Pipeline. Instructor Stephen J. Guy
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Stephany O’Connor’
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3D Viewing Pipeline Instructor Stephen J. Guy 1
2 Overview Review Linear s & Homogeneous coordinates Scene Graph 3D Polygon rendering Graphics Pipeline Viewing 2
3 Overview Review Linear s & Homogeneous coordinates Scene Graph 3D Polygon rendering Graphics Pipeline Viewing 3
4 Reviewing Transforms Linear s Scale Rotate Shear Mirror 4
5 Review Homogeneous Coordinates Use 3 coordinates for a 2D point (4 coord. for 3D point) (x,y,w) represents (x,y,0) represents (0,0,0) a point at (x/w, y/w) a point at infinity not allowed! (2,1,1) or (4,2,2,) or (6,3,3) 5
6 Review Translating and More Basic 2D s as 3x3 6
7 Review 3D Transforms Homogenous coordinates (x,y,z,w) 4x4 transformation matrix 7
8 Review Basic 3D Transforms 8
9 Review 3D Rotations 9
10 Review Hierarchies Successively applied matrixes Stored in a DAG == Scene Graph Examples Robot Arm Articulated Characters Complex Scenes 10
11 Transform Example - Robot Arms 11
12 Example Humanoid Character 12
13 Example Complex Scenes 13
14 Example Complex Scene Graph 14
15 Ray Casting with Hierarchies 15
16 Overview Review Linear s & Homogeneous coordinates Scene Graph 3D Polygon rendering Graphics Pipeline Viewing 16
17 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications make use if 3D polygons with direct illumination 17
18 3D Polygon Rendering - Examples 18 Quake II (Id Software)
19 3D Polygon Rendering - Examples Architectural Walkthrough 19
20 Ray Casting Revisiting For each sample Construct ray though pixel Find first surface intersected by ray through pixel Compute color of sample based on surface radiance More Efficient Algorithms Utilize Spatial Coherence! 20
21 3D Polygon Rendering What steps are necessary to utilize spatial coherence while drawing polygons on a 2D image? 21
22 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing A pipelined sequence of operations to draw a 3D primitive onto a 2D image Projection Clipping Scan Conversion 22 Image
23 OpenGL Example Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Clipping Scan Conversion glbegin(gl_polygon); glvertex3f(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); glvertex3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glvertex3f(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glvertex3f(0.0, 1.0, 1.0); glend(); OpenGL runs the 3D rendering pipeline for each polygon 23 Image
24 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Transform in 3D word coordinate system Lighting Viewing Projection Clipping Scan Conversion 24 Image
25 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Viewing Projection Clipping Scan Conversion 25 Image
26 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Projection Clipping Scan Conversion 26 Image
27 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion 27 Image
28 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Clip primitives outside camera s view Scan Conversion 28 Image
29 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion Clip primitives outside camera s view Draw Pixels (also texturing, hidden surface, ) 29 Image
30 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion Clip primitives outside camera s view Draw Pixels (also texturing, hidden surface, ) 30 Image
31 3D Rendering Pipeline (direct illumination only) 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion Clip primitives outside camera s view Draw Pixels (also texturing, hidden surface, ) 31 Image
32 s p(x,y,z) Modeling 3D World Coordinates Viewing Projection Window-to-Viewport 32 p'(x,y ) 3D Object Coordinates 3D Camera Coordinates 2D Screen Coordinates 2D Image Coordinates s map points from one coordinate system to another 3D World Coordinates 3D Camera Coordinates 3D Object Coordinates
33 Viewing s p(x,y,z) 3D Object Coordinates Modeling 3D World Coordinates Viewing Projection Window-to-Viewport 33 p'(x,y ) 3D Camera Coordinates 2D Screen Coordinates 2D Image Coordinates Viewing s
34 Camera Coordinates Canonical coordinate system Convention is right-handed (looking down z-axis) Convenient for projection, clipping, etc 34
35 Viewing Mapping from world to camera coordinates Eye position maps to origin Right vector maps to X-axis Up vector maps to Y-axis Back vector maps to Z-axis 35
36 Finding the Viewing We have the camera (in world coordinates) We want T taking objects from world to camera P c = T * P W Trick: Find T-1 taking objects from camera to world P W = T * P c 36
37 Finding the Viewing 37
38 Viewing s p(x,y,z) 3D Object Coordinates Modeling 3D World Coordinates Viewing Projection Window-to-Viewport 38 p'(x,y ) 3D Camera Coordinates 2D Screen Coordinates 2D Image Coordinates Viewing s
39 Projection General definition: Transform points in n-space to m-space (m<n) In computer graphics Map 3D camera coordinates to 2D screen coordinates 39
40 Taxonomy of Projections 40
41 Taxonomy of Projections 41
42 Parallel Projection Center of projection is at infinity Direction of Projection (DOP) is same for all points 42
43 Orthographic Projection DOP Parallel to View Plane 43
44 Oblique Projection DOP not perpendicular to view plane 44
45 Oblique Projection Examples Oblique Cabinet Cavalier Fortification Diagrams 45
46 Orthographic Perspective in Games Common in pre-hardware card Graphics 46
47 Parallel Projection View Volume 47
48 Orthographic Project Matrix Straight on projection throw away Z What does the matrix look like? 48
49 Parallel Projection Matrix 49
50 Taxonomy of Projections 50
51 Perspective Projection 51
52 Perspective View Volume 52
53 Camera to Screen Remember: Object -> Camera -> Screen Just like raytracer screen is the z=d plane for some constant d Origin of screen coordinate is (0,0,d) Its x and y axes are parallel to the x and y axes of the eye coordinate system All these coordinates are in camera space 53
54 Overhead view of our screen 54
55 The Perspective Matrix This division by z can be accomplished by a 4x4 matrix too! What happens to the point (x,y,z,1) What s this in non-homogenous coordinates? 55
56 What s Next? 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion Clip primitives outside camera s view Draw Pixels (also texturing, hidden surface, ) 56 Image
57 What s Next? 3D Geometric Primitives Modeling Lighting Viewing Projection Transform in 3D word coordinate system Illuminate according to lighting and reflectance Transform into 3D camera coordinate system Transform into 2D screen coordinate system Clipping Scan Conversion Clip primitives outside camera s view Draw Pixels (also texturing, hidden surface, ) 57 Image
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Sample Exam Questions 2007
 Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Image Processing and Computer Graphics. Rendering Pipeline. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 torsten@sfu.ca www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 torsten@sfu.ca www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Basic Problem: Map a 3D object to a 2D display surface. Analogy - Taking a snapshot with a camera
 3D Viewing Basic Problem: Map a 3D object to a 2D display surface Analogy - Taking a snapshot with a camera Synthetic camera virtual camera we can move to any location & orient in any way then create a
3D Viewing Basic Problem: Map a 3D object to a 2D display surface Analogy - Taking a snapshot with a camera Synthetic camera virtual camera we can move to any location & orient in any way then create a
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines
 Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines CS447 3-1 Mastering 2D & 3D Graphics Overview of 2D & 3D Pipelines What are pipelines? What are the fundamental
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines CS447 3-1 Mastering 2D & 3D Graphics Overview of 2D & 3D Pipelines What are pipelines? What are the fundamental
Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course :
 Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course : Computer Graphics (CSI-425) Course Coordinator : Mr. ISSA ALSMADI
Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course : Computer Graphics (CSI-425) Course Coordinator : Mr. ISSA ALSMADI
CPIT-285 Computer Graphics
 Department of Information Technology B.S.Information Technology ABET Course Binder CPIT-85 Computer Graphics Prepared by Prof. Alhasanain Muhammad Albarhamtoushi Page of Sunday December 4 0 : PM Cover
Department of Information Technology B.S.Information Technology ABET Course Binder CPIT-85 Computer Graphics Prepared by Prof. Alhasanain Muhammad Albarhamtoushi Page of Sunday December 4 0 : PM Cover
GUI GRAPHICS AND USER INTERFACES. Welcome to GUI! Mechanics. Mihail Gaianu 26/02/2014 1
 Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
3D Viewing. Chapter 7. Projections. 3D clipping. OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes
 3D Viewing Chapter 7 Projections 3D clipping OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes 1 Projections Parallel Perspective Coordinates are transformed along parallel lines Relative sizes are preserved
3D Viewing Chapter 7 Projections 3D clipping OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes 1 Projections Parallel Perspective Coordinates are transformed along parallel lines Relative sizes are preserved
Transformations in the pipeline
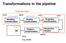 Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Computer Graphics. Introduction. Computer graphics. What is computer graphics? Yung-Yu Chuang
 Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: c@csie.ntu.edu.tw Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: c@csie.ntu.edu.tw Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
Geometric Camera Parameters
 Geometric Camera Parameters What assumptions have we made so far? -All equations we have derived for far are written in the camera reference frames. -These equations are valid only when: () all distances
Geometric Camera Parameters What assumptions have we made so far? -All equations we have derived for far are written in the camera reference frames. -These equations are valid only when: () all distances
2D Geometric Transformations
 2D Geometric Transformations (Chapter 5 in FVD) 2D Geometric Transformations Question: How do we represent a geometric object in the plane? Answer: For now, assume that objects consist of points and lines.
2D Geometric Transformations (Chapter 5 in FVD) 2D Geometric Transformations Question: How do we represent a geometric object in the plane? Answer: For now, assume that objects consist of points and lines.
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1.
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1. What is Computer Graphics? Synthesis of images User Computer Image Applications 2D Display Text User Interfaces (GUI) - web - draw/paint
Introduction to Computer Graphics Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1. What is Computer Graphics? Synthesis of images User Computer Image Applications 2D Display Text User Interfaces (GUI) - web - draw/paint
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su (sarasu@cs.tufts.edu) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su (sarasu@cs.tufts.edu) TA: Matt Menke
SkillsUSA 2014 Contest Projects 3-D Visualization and Animation
 SkillsUSA Contest Projects 3-D Visualization and Animation Click the Print this Section button above to automatically print the specifications for this contest. Make sure your printer is turned on before
SkillsUSA Contest Projects 3-D Visualization and Animation Click the Print this Section button above to automatically print the specifications for this contest. Make sure your printer is turned on before
Digital 3D Animation
 Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Elizabethtown Area School District Digital 3D Animation Course Number: 753 Length of Course: 1 semester 18 weeks Grade Level: 11-12 Elective Total Clock Hours: 120 hours Length of Period: 80 minutes Date
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
Lecture Notes. Fundamentals of Computer Graphics. Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University
 COMP 557 Winter 2015 Lecture Notes Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University NOTE: These lecture notes are dynamic. The initial version of the
COMP 557 Winter 2015 Lecture Notes Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University NOTE: These lecture notes are dynamic. The initial version of the
OpenGL & Delphi. Max Kleiner. http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22
 OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
Computer Applications in Textile Engineering. Computer Applications in Textile Engineering
 3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203.
 VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
2: Introducing image synthesis. Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system architecture Overview of OpenGL / GLU / GLUT
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
Geometric Transformation CS 211A
 Geometric Transformation CS 211A What is transformation? Moving points (x,y) moves to (x+t, y+t) Can be in any dimension 2D Image warps 3D 3D Graphics and Vision Can also be considered as a movement to
Geometric Transformation CS 211A What is transformation? Moving points (x,y) moves to (x+t, y+t) Can be in any dimension 2D Image warps 3D 3D Graphics and Vision Can also be considered as a movement to
Computer Graphics. Anders Hast
 Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010
 COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, kry@cs.mcgill.ca Course
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, kry@cs.mcgill.ca Course
Jan Köhnlein and Helmut Weberpals 01.12.99
 1 Graphics Primitives Graphics Primitives 3-dimensional point class Point3d 3-dimensional (directional) vector class Vector3d Class of 3-dimensional line segments LineArray 2 Modeling of 3D Objects Modeling
1 Graphics Primitives Graphics Primitives 3-dimensional point class Point3d 3-dimensional (directional) vector class Vector3d Class of 3-dimensional line segments LineArray 2 Modeling of 3D Objects Modeling
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins. Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections
 4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV
 Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1
 From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 History Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection in Computer Graphics Andries van Dam September 13, 2001 3D Viewing I 1/34
From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 History Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection in Computer Graphics Andries van Dam September 13, 2001 3D Viewing I 1/34
ICS : 435. Computer Graphics Applications. Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh
 ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph
 Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph Why a scene graph? What is stored in the scene graph? objects appearance camera lights Rendering with a scene graph Practical example 1 The 3D Rendering Pipeline (our version
Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph Why a scene graph? What is stored in the scene graph? objects appearance camera lights Rendering with a scene graph Practical example 1 The 3D Rendering Pipeline (our version
Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing
 Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing Helen H. Hu Westminster College, Salt Lake City, UT hhu@westminstercollege.edu Figure 1. Examples of student work. For fun, enthusiastic students
Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing Helen H. Hu Westminster College, Salt Lake City, UT hhu@westminstercollege.edu Figure 1. Examples of student work. For fun, enthusiastic students
Course Overview. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1. Administrative Issues Modeling Animation Rendering OpenGL Programming [Angel Ch.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
Geometry for Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics and Visualisation Geometry for Computer Graphics Student Notes Developed by F Lin K Wyrwas J Irwin C Lilley W T Hewitt T L J Howard Computer Graphics Unit Manchester Computing Centre
Computer Graphics and Visualisation Geometry for Computer Graphics Student Notes Developed by F Lin K Wyrwas J Irwin C Lilley W T Hewitt T L J Howard Computer Graphics Unit Manchester Computing Centre
Computer Graphics Labs
 Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Affine Transformations
 A P P E N D I X C Affine Transformations CONTENTS C The need for geometric transformations 335 C2 Affine transformations 336 C3 Matri representation of the linear transformations 338 C4 Homogeneous coordinates
A P P E N D I X C Affine Transformations CONTENTS C The need for geometric transformations 335 C2 Affine transformations 336 C3 Matri representation of the linear transformations 338 C4 Homogeneous coordinates
2D Geometrical Transformations. Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5
 2D Geometrical Transformations Fole & Van Dam, Chapter 5 2D Geometrical Transformations Translation Scaling Rotation Shear Matri notation Compositions Homogeneous coordinates 2D Geometrical Transformations
2D Geometrical Transformations Fole & Van Dam, Chapter 5 2D Geometrical Transformations Translation Scaling Rotation Shear Matri notation Compositions Homogeneous coordinates 2D Geometrical Transformations
Essential Mathematics for Computer Graphics fast
 John Vince Essential Mathematics for Computer Graphics fast Springer Contents 1. MATHEMATICS 1 Is mathematics difficult? 3 Who should read this book? 4 Aims and objectives of this book 4 Assumptions made
John Vince Essential Mathematics for Computer Graphics fast Springer Contents 1. MATHEMATICS 1 Is mathematics difficult? 3 Who should read this book? 4 Aims and objectives of this book 4 Assumptions made
3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4132 Rev. 0, 05/2010 3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4132 Rev. 0, 05/2010 3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX
Masters of Science in Software & Information Systems
 Masters of Science in Software & Information Systems To be developed and delivered in conjunction with Regis University, School for Professional Studies Graphics Programming December, 2005 1 Table of Contents
Masters of Science in Software & Information Systems To be developed and delivered in conjunction with Regis University, School for Professional Studies Graphics Programming December, 2005 1 Table of Contents
Vector Notation: AB represents the vector from point A to point B on a graph. The vector can be computed by B A.
 1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE. M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science. Friday 18 th January 2008.
 COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
Introduction Computer stuff Pixels Line Drawing. Video Game World 2D 3D Puzzle Characters Camera Time steps
 Introduction Computer stuff Pixels Line Drawing Video Game World 2D 3D Puzzle Characters Camera Time steps Geometry Polygons Linear Algebra NURBS, Subdivision surfaces, etc Movement Collisions Fast Distances
Introduction Computer stuff Pixels Line Drawing Video Game World 2D 3D Puzzle Characters Camera Time steps Geometry Polygons Linear Algebra NURBS, Subdivision surfaces, etc Movement Collisions Fast Distances
Scan-Line Fill. Scan-Line Algorithm. Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list
 Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph
 Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph Why a scene graph? What is stored in the scene graph? objects appearance camera lights Rendering with a scene graph Practical example 1 The 3D Rendering Pipeline (our version
Chapter 6 - The Scene Graph Why a scene graph? What is stored in the scene graph? objects appearance camera lights Rendering with a scene graph Practical example 1 The 3D Rendering Pipeline (our version
521493S Computer Graphics. Exercise 2 & course schedule change
 521493S Computer Graphics Exercise 2 & course schedule change Course Schedule Change Lecture from Wednesday 31th of March is moved to Tuesday 30th of March at 16-18 in TS128 Question 2.1 Given two nonparallel,
521493S Computer Graphics Exercise 2 & course schedule change Course Schedule Change Lecture from Wednesday 31th of March is moved to Tuesday 30th of March at 16-18 in TS128 Question 2.1 Given two nonparallel,
How to read Plans and Do Basic Drawings
 How to read Plans and Do Basic Drawings Workshop session W1 10.00 Site Orientation Exercise 10.10 Drawing Conventions 10.45 Can drawings Distort the Truth? 11.30 Summary + Coffee 11.45 Simple Drawing Techniques
How to read Plans and Do Basic Drawings Workshop session W1 10.00 Site Orientation Exercise 10.10 Drawing Conventions 10.45 Can drawings Distort the Truth? 11.30 Summary + Coffee 11.45 Simple Drawing Techniques
CIS 536/636 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Kansas State University. CIS 536/636 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 2 Lecture Outline Animation 2 of 3: Rotations, Quaternions Dynamics & Kinematics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre
2 Lecture Outline Animation 2 of 3: Rotations, Quaternions Dynamics & Kinematics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre
COMPUTER GRAPHICS IMPORTANT QUESTION AND ANSWERS. Computer graphics
 Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes:
 3 3.1 2D Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes: 1. Change coordinate frames (world, window, viewport, device, etc). 2. Compose objects
3 3.1 2D Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes: 1. Change coordinate frames (world, window, viewport, device, etc). 2. Compose objects
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 01 / 25 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Review the syllabus Review course policies Color CIE system chromaticity diagram color gamut, complementary colors, dominant
CS 325 Computer Graphics 01 / 25 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Review the syllabus Review course policies Color CIE system chromaticity diagram color gamut, complementary colors, dominant
Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC. Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar
 Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar Overview Introduction Android Tools Game Development OpenGL ES Marketing Summary Questions Introduction Disgruntled
Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar Overview Introduction Android Tools Game Development OpenGL ES Marketing Summary Questions Introduction Disgruntled
Computer Animation: Art, Science and Criticism
 Computer Animation: Art, Science and Criticism Tom Ellman Harry Roseman Lecture 12 Ambient Light Emits two types of light: Directional light, coming from a single point Contributes to diffuse shading.
Computer Animation: Art, Science and Criticism Tom Ellman Harry Roseman Lecture 12 Ambient Light Emits two types of light: Directional light, coming from a single point Contributes to diffuse shading.
DESIGNING A HIGH RESOLUTION 3D IMAGING DEVICE FOR FOOTPRINT AND TIRE TRACK IMPRESSIONS AT CRIME SCENES 1 TR-CIS-0416-12. Ruwan Egoda Gamage
 DESIGNING A HIGH RESOLUTION 3D IMAGING DEVICE FOR FOOTPRINT AND TIRE TRACK IMPRESSIONS AT CRIME SCENES 1 TR-CIS-0416-12 Ruwan Egoda Gamage Abhishek Joshi Jiang Yu Zheng Mihran Tuceryan A Technical Report
DESIGNING A HIGH RESOLUTION 3D IMAGING DEVICE FOR FOOTPRINT AND TIRE TRACK IMPRESSIONS AT CRIME SCENES 1 TR-CIS-0416-12 Ruwan Egoda Gamage Abhishek Joshi Jiang Yu Zheng Mihran Tuceryan A Technical Report
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
How To Learn To Program In Csc 406 Computer Graphics
 CSC 406 Computer Graphics Fall 2011 1 CSC 406 Computer Graphics Geometry, Modeling, and Animation Fall 2011 Lectures Tyler Hall, Room 052 Monday, 6:30-9:15 PM Professor Jean-Yves Hervé Tyler Hall, Room
CSC 406 Computer Graphics Fall 2011 1 CSC 406 Computer Graphics Geometry, Modeling, and Animation Fall 2011 Lectures Tyler Hall, Room 052 Monday, 6:30-9:15 PM Professor Jean-Yves Hervé Tyler Hall, Room
Hardware design for ray tracing
 Hardware design for ray tracing Jae-sung Yoon Introduction Realtime ray tracing performance has recently been achieved even on single CPU. [Wald et al. 2001, 2002, 2004] However, higher resolutions, complex
Hardware design for ray tracing Jae-sung Yoon Introduction Realtime ray tracing performance has recently been achieved even on single CPU. [Wald et al. 2001, 2002, 2004] However, higher resolutions, complex
L 2 : x = s + 1, y = s, z = 4s + 4. 3. Suppose that C has coordinates (x, y, z). Then from the vector equality AC = BD, one has
 The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
How To Teach Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Traditional Drawing Tools
 Engineering Drawing Traditional Drawing Tools DRAWING TOOLS DRAWING TOOLS 1. T-Square 2. Triangles DRAWING TOOLS HB for thick line 2H for thin line 3. Adhesive Tape 4. Pencils DRAWING TOOLS 5. Sandpaper
Engineering Drawing Traditional Drawing Tools DRAWING TOOLS DRAWING TOOLS 1. T-Square 2. Triangles DRAWING TOOLS HB for thick line 2H for thin line 3. Adhesive Tape 4. Pencils DRAWING TOOLS 5. Sandpaper
Fundamentals of Computer Animation
 Fundamentals of Computer Animation Quaternions as Orientations () page 1 Visualizing a Unit Quaternion Rotation in 4D Space ( ) = w + x + y z q = Norm q + q = q q [ w, v], v = ( x, y, z) w scalar q =,
Fundamentals of Computer Animation Quaternions as Orientations () page 1 Visualizing a Unit Quaternion Rotation in 4D Space ( ) = w + x + y z q = Norm q + q = q q [ w, v], v = ( x, y, z) w scalar q =,
TEXTURE AND BUMP MAPPING
 Department of Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences University of Cantabria UC-CAGD Group COMPUTER-AIDED GEOMETRIC DESIGN AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS: TEXTURE AND BUMP MAPPING Andrés Iglesias e-mail:
Department of Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences University of Cantabria UC-CAGD Group COMPUTER-AIDED GEOMETRIC DESIGN AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS: TEXTURE AND BUMP MAPPING Andrés Iglesias e-mail:
Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications. Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University Presentation Outline What is computer graphics? 3D graphics pipeline Programming
Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University Presentation Outline What is computer graphics? 3D graphics pipeline Programming
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell
 Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
Triangle Scan Conversion using 2D Homogeneous Coordinates
 Triangle Scan Conversion using 2D Homogeneous Coordinates Marc Olano 1 Trey Greer 2 University of North Carolina Hewlett-Packard ABSTRACT We present a new triangle scan conversion algorithm that works
Triangle Scan Conversion using 2D Homogeneous Coordinates Marc Olano 1 Trey Greer 2 University of North Carolina Hewlett-Packard ABSTRACT We present a new triangle scan conversion algorithm that works
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 12 (Part 1) Curves. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Instructor: Longfei Li Math 43 Lecture Notes.5 Equations of Lines and Planes What do we need to determine a line? D: a point on the line: P 0 (x 0, y 0 ) direction (slope): k 3D: a point on the line: P
Lecture 2: Homogeneous Coordinates, Lines and Conics
 Lecture 2: Homogeneous Coordinates, Lines and Conics 1 Homogeneous Coordinates In Lecture 1 we derived the camera equations λx = P X, (1) where x = (x 1, x 2, 1), X = (X 1, X 2, X 3, 1) and P is a 3 4
Lecture 2: Homogeneous Coordinates, Lines and Conics 1 Homogeneous Coordinates In Lecture 1 we derived the camera equations λx = P X, (1) where x = (x 1, x 2, 1), X = (X 1, X 2, X 3, 1) and P is a 3 4
Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL
 Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL Tony Parisi Beijing Cambridge Farnham Köln Sebastopol Tokyo Table of Contents Preface ix Part I. Foundations 1. Introduction 3 HTML5: A New Visual Medium
Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL Tony Parisi Beijing Cambridge Farnham Köln Sebastopol Tokyo Table of Contents Preface ix Part I. Foundations 1. Introduction 3 HTML5: A New Visual Medium
How To Fuse A Point Cloud With A Laser And Image Data From A Pointcloud
 REAL TIME 3D FUSION OF IMAGERY AND MOBILE LIDAR Paul Mrstik, Vice President Technology Kresimir Kusevic, R&D Engineer Terrapoint Inc. 140-1 Antares Dr. Ottawa, Ontario K2E 8C4 Canada paul.mrstik@terrapoint.com
REAL TIME 3D FUSION OF IMAGERY AND MOBILE LIDAR Paul Mrstik, Vice President Technology Kresimir Kusevic, R&D Engineer Terrapoint Inc. 140-1 Antares Dr. Ottawa, Ontario K2E 8C4 Canada paul.mrstik@terrapoint.com
SimFonIA Animation Tools V1.0. SCA Extension SimFonIA Character Animator
 SimFonIA Animation Tools V1.0 SCA Extension SimFonIA Character Animator Bring life to your lectures Move forward with industrial design Combine illustrations with your presentations Convey your ideas to
SimFonIA Animation Tools V1.0 SCA Extension SimFonIA Character Animator Bring life to your lectures Move forward with industrial design Combine illustrations with your presentations Convey your ideas to
ENG4BF3 Medical Image Processing. Image Visualization
 ENG4BF3 Medical Image Processing Image Visualization Visualization Methods Visualization of medical images is for the determination of the quantitative information about the properties of anatomic tissues
ENG4BF3 Medical Image Processing Image Visualization Visualization Methods Visualization of medical images is for the determination of the quantitative information about the properties of anatomic tissues
William Paterson University of New Jersey Department of Computer Science College of Science and Health Course Outline
 William Paterson University of New Jersey Department of Computer Science College of Science and Health Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: Computer Graphics, CS 461, Credits: 3, (Major
William Paterson University of New Jersey Department of Computer Science College of Science and Health Course Outline 1. TITLE OF COURSE AND COURSE NUMBER: Computer Graphics, CS 461, Credits: 3, (Major
Graphics Input Primitives. 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL. String Choice/Selection Valuator
 4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
Thin Lenses Drawing Ray Diagrams
 Drawing Ray Diagrams Fig. 1a Fig. 1b In this activity we explore how light refracts as it passes through a thin lens. Eyeglasses have been in use since the 13 th century. In 1610 Galileo used two lenses
Drawing Ray Diagrams Fig. 1a Fig. 1b In this activity we explore how light refracts as it passes through a thin lens. Eyeglasses have been in use since the 13 th century. In 1610 Galileo used two lenses
Section 2.4: Equations of Lines and Planes
 Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary TERM DEFINITION GEOMETRIC FIGURE. Cannot be defined by using other figures.
 Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
Geometry: Unit 1 Vocabulary 1.1 Undefined terms Cannot be defined by using other figures. Point A specific location. It has no dimension and is represented by a dot. Line Plane A connected straight path.
GRAFICA - A COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEACHING ASSISTANT. Andreas Savva, George Ioannou, Vasso Stylianou, and George Portides, University of Nicosia Cyprus
 ICICTE 2014 Proceedings 1 GRAFICA - A COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEACHING ASSISTANT Andreas Savva, George Ioannou, Vasso Stylianou, and George Portides, University of Nicosia Cyprus Abstract This paper presents
ICICTE 2014 Proceedings 1 GRAFICA - A COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEACHING ASSISTANT Andreas Savva, George Ioannou, Vasso Stylianou, and George Portides, University of Nicosia Cyprus Abstract This paper presents
Interactive Computer Graphics
 Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach Using OpenGL FIFTH EDITION EDWARD ANGEL UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore
Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach Using OpenGL FIFTH EDITION EDWARD ANGEL UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore
Basic Understandings
 Activity: TEKS: Exploring Transformations Basic understandings. (5) Tools for geometric thinking. Techniques for working with spatial figures and their properties are essential to understanding underlying
Activity: TEKS: Exploring Transformations Basic understandings. (5) Tools for geometric thinking. Techniques for working with spatial figures and their properties are essential to understanding underlying
Rendering Microgeometry with Volumetric Precomputed Radiance Transfer
 Rendering Microgeometry with Volumetric Precomputed Radiance Transfer John Kloetzli February 14, 2006 Although computer graphics hardware has made tremendous advances over the last few years, there are
Rendering Microgeometry with Volumetric Precomputed Radiance Transfer John Kloetzli February 14, 2006 Although computer graphics hardware has made tremendous advances over the last few years, there are
CUBE-MAP DATA STRUCTURE FOR INTERACTIVE GLOBAL ILLUMINATION COMPUTATION IN DYNAMIC DIFFUSE ENVIRONMENTS
 ICCVG 2002 Zakopane, 25-29 Sept. 2002 Rafal Mantiuk (1,2), Sumanta Pattanaik (1), Karol Myszkowski (3) (1) University of Central Florida, USA, (2) Technical University of Szczecin, Poland, (3) Max- Planck-Institut
ICCVG 2002 Zakopane, 25-29 Sept. 2002 Rafal Mantiuk (1,2), Sumanta Pattanaik (1), Karol Myszkowski (3) (1) University of Central Florida, USA, (2) Technical University of Szczecin, Poland, (3) Max- Planck-Institut
3D Scanner using Line Laser. 1. Introduction. 2. Theory
 . Introduction 3D Scanner using Line Laser Di Lu Electrical, Computer, and Systems Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute The goal of 3D reconstruction is to recover the 3D properties of a geometric
. Introduction 3D Scanner using Line Laser Di Lu Electrical, Computer, and Systems Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute The goal of 3D reconstruction is to recover the 3D properties of a geometric
Computer Graphics and Image Processing Introduction
 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Introduction Part 1 Lecture 1 1 COMPSCI 373 Lecturers: A. Prof. Patrice Delmas (303.391) Week 1-4 Contact details: p.delmas@auckland.ac.nz Office: 303-391 (3 rd level
Computer Graphics and Image Processing Introduction Part 1 Lecture 1 1 COMPSCI 373 Lecturers: A. Prof. Patrice Delmas (303.391) Week 1-4 Contact details: p.delmas@auckland.ac.nz Office: 303-391 (3 rd level
COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics involves display, manipulation and storage of pictures and experimental data for proper visualization using a computer. Typical graphics system comprises of a host computer
COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics involves display, manipulation and storage of pictures and experimental data for proper visualization using a computer. Typical graphics system comprises of a host computer
VRayPattern also allows to curve geometry on any surface
 Introduction VrayPattern is a plug-in for 3dsmax and V-Ray VRayPattern allows to multiply geometry periodically without extra memory consumption. As a sample you can use any tiled geometry (or those with
Introduction VrayPattern is a plug-in for 3dsmax and V-Ray VRayPattern allows to multiply geometry periodically without extra memory consumption. As a sample you can use any tiled geometry (or those with
Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0 Basic Design
 Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
Introduction Datum features are non-solid features used during the construction of other features. The most common datum features include planes, axes, coordinate systems, and curves. Datum features do
The Geometry of Perspective Projection
 The Geometry o Perspective Projection Pinhole camera and perspective projection - This is the simplest imaging device which, however, captures accurately the geometry o perspective projection. -Rays o
The Geometry o Perspective Projection Pinhole camera and perspective projection - This is the simplest imaging device which, however, captures accurately the geometry o perspective projection. -Rays o
Relating Vanishing Points to Catadioptric Camera Calibration
 Relating Vanishing Points to Catadioptric Camera Calibration Wenting Duan* a, Hui Zhang b, Nigel M. Allinson a a Laboratory of Vision Engineering, University of Lincoln, Brayford Pool, Lincoln, U.K. LN6
Relating Vanishing Points to Catadioptric Camera Calibration Wenting Duan* a, Hui Zhang b, Nigel M. Allinson a a Laboratory of Vision Engineering, University of Lincoln, Brayford Pool, Lincoln, U.K. LN6
DIABLO VALLEY COLLEGE CATALOG 2014-2015
 ART DIGITAL MEDIA ARTDM Michael Almaguer, Dean Applied and Fine Arts Division Business and Foreign Language Building, Room 204 Possible career opportunities Digital media or graphic design jobs cover all
ART DIGITAL MEDIA ARTDM Michael Almaguer, Dean Applied and Fine Arts Division Business and Foreign Language Building, Room 204 Possible career opportunities Digital media or graphic design jobs cover all
QCD as a Video Game?
 QCD as a Video Game? Sándor D. Katz Eötvös University Budapest in collaboration with Győző Egri, Zoltán Fodor, Christian Hoelbling Dániel Nógrádi, Kálmán Szabó Outline 1. Introduction 2. GPU architecture
QCD as a Video Game? Sándor D. Katz Eötvös University Budapest in collaboration with Győző Egri, Zoltán Fodor, Christian Hoelbling Dániel Nógrádi, Kálmán Szabó Outline 1. Introduction 2. GPU architecture
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
