Lecture Notes, CEng 477
|
|
|
- Job Thompson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477
2 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make such pictures, software and hardware, input/output devices. the whole field of study that involves these tools and the pictures they produce. Use of computer to define, store, manipulate, interrogate and present pictorial output.
3 How pictures are represented in computer graphics? How pictures are prepared for presentation? How interaction within the picture is accomplished?
4 Computer Graphics Applications Art, entertainment, and publishing movie production, animation, special effects computer games World Wide Web Book, magazine design, photo editing CG and Image processing (syntesis vs. analysis) Simulations (education, training) CAD architectural, circuit design etc. Scientific analysis and visualization Graphical User Interfaces
5 Display (Video Display Most CG on video monitors Device) Still most popular: Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Other popular display types: Liquid Crystal Display Plasma display Field Emission Displays Digital Meromirror Devices Light Emitting Diodes 3D display devices (hologram or page scan methods)
6 CRT 3. when electron beams contact screen phosphor emits light 1. cathode rays emitted by the electron gun 2. focusing and deflection 4. light fades, redraw required in a small period (refresh)
7 CRT types Direct View Storage Tubes (not CRT, no need for refresh, pictures stored as a permanent charge on phosphor screen) Calligraphic refresh CRT (line drawing or vector random scan, need refreshing) Raster scan (point by point refreshing) Refresh rate: # of complete images (frames) drawn on the screen in 1 second. Frames/sec. Frame time: reciprocal of the refresh rate, time between each complete scan. sec/frame
8 Vector Scan Picture definition is stored as a set of line drawing commands in a refresh buffer. to display a picture, the system cycles through the set of commands in the buffer Designed for line drawing applications (CAD)
9 Raster Scan Screen is a regular grid of samples called pixels (picture element) Screen is refreshed line by line non-interlaced interlaced, cycle 1 interlaced, cycle 2 interlaced, 2 cycles Interlacing: Avoid flickering affect for small refresh rates. interlaced 50Hz: actually 25Hz
10 resolution: a 2D term that measures the number of scanlines and the number of pixels on each line (maximum number of points that can be displayed without overlap on a CRT) black and white display only binary pixels. intensity of a pixel can be achieved by the force of electron beam (gray scale) color display?
11 Color Displays Beam penetration method: special phosphors emitting different colors for different intensity of electron. Slow, limited colors. Shadow mask method: 3 electron guns + a shadow mask grid. Intensities of 3 colors result in an arbitrary color pixel. (most TVs and monitors)
12 black and white: 1 bit per pixel. gray scale: 1 byte per pixel (256 gray levels) true color: 3 bytes=24pits per pixel (2 24 colors) indexed color frame buffer: each pixel uses 1 byte, an index entry in a colormap table matching the color to the actual color.
13 Vector vs Raster Scan raster scan monitors: inexpensive filled areas, patterns refresh process is independent (constant for any complex scene) vector scan monitors: Smooth lines. no need for scan conversion: lines to pixels. (raster scan solution antialiasing) sometimes memory and CPU efficient 1000 lines: Vector scan: 2000 endpoints and 1000 operations Raster scan: whole frame buffer 1000 scan conversions.
14 LCD Displays Thinner and lighter. No tube and electron beams. Blocking/unblocking light through polarized crystals. A matrix of LC cells one for each pixel. No refresh unless the screen changes. Color 3 cells per pixel.
15 Simple Raster Display System Frame buffer: stored pixel map of screen Video controller just refreshes the frame buffer on the monitor periodically. CPU Peripheral Devices System Bus System Frame Memory Buffer Video Controller Monitor
16 Inexpensive Scan conversion of output primitives (lines, rectangles etc.) done by the CPU. Slow. As refresh cycle increases, memory cycles used by the video controller increases. Memory is less available to CPU. Solution: Graphics Display Processor
17 Graphics Display Processor Scan conversion, output primitives, raster operations (double buffering) Separete frame buffer CPU Peripheral Devices System Bus Display Processor System Memory D. Proc. memory. Frame Buffer Video Controller Monitor
18 Computer Graphics Software Rendering Primitives Models are composed of, or can be converted to, a large number of geometric primitives. Typical rendering primitives directly supported in hardware include: Points (single pixels) Line segments Polygons (perhaps simple, triangle, rectangle)
19 Modeling primitives include these, but also Piecewise polynomial (spline) curves Piecewise polynomial (spline) surfaces Implicit surfaces (quadrics, blobbies, etc.) Other... Software renderer may support modeling primitives directly, or may convert them into polygonal or linear approximations for hardware rendering
20 Algorithms A number of basic algorithms are needed: Transformation: Convert representations of models/primitives from one coordinate system to another Clipping/Hidden surface removal: remove primitives and part of primitives that are not visible on the display Rasterization: Convert a projected screen space primitive to a set of pixels.
21 Advanced algorithms: Picking: select a 3D obejct by clicking an input device over a pixel location. Shading and illumination: Simulate the interaction of light with a scene. Animation: Simulate movement by rendering a sequence of frames.
22 Application Programming Interfaces X11: 2D rasterization Postscript, PDF: 2D transformations, 2D rasterization Phigs+, GL, OpenGL, Direct3D: 3D pipeline APIs provide access to rendering hardware via conceptual model. APIs abstract the hardware implementations and algorithms in standard software calls.
23 For 3D interactive applications, we might modify the scene or a model directly or just the change the attributes like viewing information. We need to interface to input devices in an event driven, asynchronous and device independent fashion. APIs and toolkits are also defined for this task. GLUT, Qt, GTK, MFC, DirectX, Motif, Tcl/Tk.
24 Graphics Rendering Pipeline Rendering: conversion from scene to image 3D Scene Render 2D Image Scene is represented as a model composed of primitives. Model is generated by a program or input by a user. Image is drawn on an output device: monitor, printer, memory, file, video frame. Device independence.
25 Typically rendering process is divided into steps called the graphics pipeline. Some steps are implemented by graphics hardware. Programmable graphics accelerator, GPU: programmable pipelines in graphics hardware
26 The basic forward projection pipeline: Model Model Modeling Transformations M1 M2 3D World Scene Viewing Transformations V 3D View Scene Model M3 MCS WCS VCS P Clip Normalize 2D/3D Device Scene Rasterization Projection NDCS 2D Image DCS SCS
Comp 410/510. Computer Graphics Spring 2016. Introduction to Graphics Systems
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2016 Introduction to Graphics Systems Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware (PC with graphics card)
Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays
 Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
Display technology Graphical displays are generally of two types: vector displays and raster displays. Vector displays Vector displays generally display lines, specified by their endpoints. Vector display
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
Computer Graphics. Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer
 Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
Computer Graphics Computer graphics deals with all aspects of creating images with a computer Hardware Software Applications Computer graphics is using computers to generate and display images based on
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions)
 www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
www.eazynotes.com Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1 COMPUTER GRAPHICS (Short Answer type Questions) Q 1. Can you give some basic features of computer graphics? Ans. The salient feature of computer graphics
2: Introducing image synthesis. Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system architecture Overview of OpenGL / GLU / GLUT
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Important Question with Answer
 Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
Important Question with Answer Q1. What do you mean by computer graphics? Ans. The branch of science and technology concerned with methods and techniques for converting data to or from visual presentation
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203.
 VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
VALLIAMMAI ENGNIEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Year & Semester : III Year, V Semester Section : CSE - 1 & 2 Subject Code : CS6504 Subject
Image Processing and Computer Graphics. Rendering Pipeline. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1
 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Overview. Raster Graphics and Color. Overview. Display Hardware. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
 Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Raster Graphics and Color Greg Humphreys CS445: Intro Graphics University of Virginia, Fall 2004 Color models Color models Display Hardware Video display devices Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display
Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
 LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
LECTURE SCHEDULE 1 Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no longer solvable without
Computer Graphics. Anders Hast
 Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Sample Exam Questions 2007
 Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Course Overview. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1. Administrative Issues Modeling Animation Rendering OpenGL Programming [Angel Ch.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
Introduction Week 1, Lecture 1
 CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I Introduction Week 1, Lecture 1 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel University
CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I Introduction Week 1, Lecture 1 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel University
Displays. Cathode Ray Tube. Semiconductor Elements. Basic applications. Oscilloscope TV Old monitors. 2009, Associate Professor PhD. T.
 Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
Displays Semiconductor Elements 1 Cathode Ray Tube Basic applications Oscilloscope TV Old monitors 2 1 Idea of Electrostatic Deflection 3 Inside an Electrostatic Deflection Cathode Ray Tube Gun creates
1. Application of Computer Graphics
 1. Application of Computer Graphics Computer-Aided Design for engineering and architectural systems etc. Objects maybe displayed in a wireframe outline form. Multi-window environment is also favored for
1. Application of Computer Graphics Computer-Aided Design for engineering and architectural systems etc. Objects maybe displayed in a wireframe outline form. Multi-window environment is also favored for
CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems. Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010
 CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010 Overview Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Comparing CRT and LCD The future of computer displays Overview
CRT and LCD monitors properties and problems Maarten Demeyer October 27 2010 Overview Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Comparing CRT and LCD The future of computer displays Overview
COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics involves display, manipulation and storage of pictures and experimental data for proper visualization using a computer. Typical graphics system comprises of a host computer
COMPUTER GRAPHICS Computer Graphics involves display, manipulation and storage of pictures and experimental data for proper visualization using a computer. Typical graphics system comprises of a host computer
How To Teach Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2
 1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
COMPUTER GRAPHICS IMPORTANT QUESTION AND ANSWERS. Computer graphics
 Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Computer graphics 1. Define Computer graphics. Computer graphics remains one of the most existing and rapidly growing computer fields. Computer graphics may be defined as a pictorial representation or
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics
 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics INTRODUCTION! Sergio Benini! Department of Information Engineering Faculty of Engineering University of Brescia Via Branze, 38 25231 Brescia - ITALY 1 Overview Here you
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics INTRODUCTION! Sergio Benini! Department of Information Engineering Faculty of Engineering University of Brescia Via Branze, 38 25231 Brescia - ITALY 1 Overview Here you
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Version 1.1, January 2016 David J. Eck Hobart and William Smith Colleges This is a PDF version of a free, on-line book that is available at http://math.hws.edu/graphicsbook/.
Introduction to Computer Graphics Version 1.1, January 2016 David J. Eck Hobart and William Smith Colleges This is a PDF version of a free, on-line book that is available at http://math.hws.edu/graphicsbook/.
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal
 Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
Prof. Dr. M. H. Assal AS 26/10/2014 Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system Computer hardware can be classified as following: o Input devices o Output devices
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING. Chapter 4 Output Devices
 CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
CSCA0201 FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTING Chapter 4 Output Devices 1 Topics: Output Devices Examples of Output Device Printer Monitor Speakers Projector 2 Output Devices Any peripheral that receives or displays
MMGD0203 Multimedia Design MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN. Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations
 MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations 1 Topics: Definition of Graphics Why use Graphics? Graphics Categories Graphics Qualities File Formats Types of Graphics Graphic File Size Introduction
MMGD0203 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN Chapter 3 Graphics and Animations 1 Topics: Definition of Graphics Why use Graphics? Graphics Categories Graphics Qualities File Formats Types of Graphics Graphic File Size Introduction
Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware. Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005
 Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005 Overview XBOX360 GPU : Xenos Rendering performance GPU architecture Unified shader Memory Export Texture/Vertex
Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005 Overview XBOX360 GPU : Xenos Rendering performance GPU architecture Unified shader Memory Export Texture/Vertex
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1.
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1. What is Computer Graphics? Synthesis of images User Computer Image Applications 2D Display Text User Interfaces (GUI) - web - draw/paint
Introduction to Computer Graphics Reading: Angel ch.1 or Hill Ch1. What is Computer Graphics? Synthesis of images User Computer Image Applications 2D Display Text User Interfaces (GUI) - web - draw/paint
Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform
 Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform Contents Introduction... 1 Graphics Processing Units... 1 RapidMind Development Platform... 2 Writing RapidMind Enabled Applications...
Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform Contents Introduction... 1 Graphics Processing Units... 1 RapidMind Development Platform... 2 Writing RapidMind Enabled Applications...
Instructor. Goals. Image Synthesis Examples. Applications. Computer Graphics. Why Study 3D Computer Graphics?
 Computer Graphics Motivation: Why do we study 3D Graphics? http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Instructor http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir PhD Stanford, 2002. PhD thesis developed Spherical Harmonic Lighting widely
Computer Graphics Motivation: Why do we study 3D Graphics? http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Instructor http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir PhD Stanford, 2002. PhD thesis developed Spherical Harmonic Lighting widely
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT IMAGING
 AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
AIIM: Association for Information and Image Management. Trade association and professional society for the micrographics, optical disk and electronic image management markets. Algorithm: Prescribed set
Visualization of 2D Domains
 Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series. By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith
 GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith Overview History of GPU s GPU Definition Classical Graphics Pipeline Geforce 6 Series Architecture Vertex
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith Overview History of GPU s GPU Definition Classical Graphics Pipeline Geforce 6 Series Architecture Vertex
Touchstone -A Fresh Approach to Multimedia for the PC
 Touchstone -A Fresh Approach to Multimedia for the PC Emmett Kilgariff Martin Randall Silicon Engineering, Inc Presentation Outline Touchstone Background Chipset Overview Sprite Chip Tiler Chip Compressed
Touchstone -A Fresh Approach to Multimedia for the PC Emmett Kilgariff Martin Randall Silicon Engineering, Inc Presentation Outline Touchstone Background Chipset Overview Sprite Chip Tiler Chip Compressed
CSE 564: Visualization. GPU Programming (First Steps) GPU Generations. Klaus Mueller. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
CS130 - Intro to computer graphics. Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz. Objectives
 CS130 - Intro to computer graphics Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz Objectives Explore basics of computer graphics Survey application areas Today, brief introduction to graphics
CS130 - Intro to computer graphics Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz Objectives Explore basics of computer graphics Survey application areas Today, brief introduction to graphics
ICS : 435. Computer Graphics Applications. Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh
 ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
ICS : 435 Computer Graphics Applications Instructor : Da'ad Albalawneh Course Outline Applications CAD/CAM, Art, Entertainment, Education, Training, Visualization, GUI, Image Processing. Overview of Computer
Primary Memory. Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit)
 Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Basic Concepts of Computer Hardware Primary Memory Input Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Output Units This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neuman compute Programs and
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Computer Peripherals Reading: Chapter 10 (except 10.6) Peripherals Devices that are separate from the basic computer Not the CPU, memory, or power supply Classified as input, output, and storage Connect
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices
 Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
Chapter 9 Input/Output Devices Contents: I. Introduction II. Input Devices a. Keyboard,mouse,joystick,scanners,digital camera, bar code reader, touch Sreeen,Speech input device (microphone) III. Output
CS 4810 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 CS 4810 Introduction to Computer Graphics Connelly Barnes University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David Dobkin
CS 4810 Introduction to Computer Graphics Connelly Barnes University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David Dobkin
Computer Applications in Textile Engineering. Computer Applications in Textile Engineering
 3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
L20: GPU Architecture and Models
 L20: GPU Architecture and Models scribe(s): Abdul Khalifa 20.1 Overview GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are large parallel structure of processing cores capable of rendering graphics efficiently on displays.
L20: GPU Architecture and Models scribe(s): Abdul Khalifa 20.1 Overview GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are large parallel structure of processing cores capable of rendering graphics efficiently on displays.
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 12 (Part 1) Curves. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
GUI GRAPHICS AND USER INTERFACES. Welcome to GUI! Mechanics. Mihail Gaianu 26/02/2014 1
 Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
OpenGL & Delphi. Max Kleiner. http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22
 OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
CAD and Creativity. Contents
 CAD and Creativity K C Hui Department of Automation and Computer- Aided Engineering Contents Various aspects of CAD CAD training in the university and the industry Conveying fundamental concepts in CAD
CAD and Creativity K C Hui Department of Automation and Computer- Aided Engineering Contents Various aspects of CAD CAD training in the university and the industry Conveying fundamental concepts in CAD
Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling
 Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling Prof. B.Brüderlin Brüderlin,, M Heyer 3Dinteractive GmbH & TU-Ilmenau, Germany SGI VizDays 2005, Rüsselsheim Demands in Engineering & Styling Engineering: :
Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling Prof. B.Brüderlin Brüderlin,, M Heyer 3Dinteractive GmbH & TU-Ilmenau, Germany SGI VizDays 2005, Rüsselsheim Demands in Engineering & Styling Engineering: :
The Evolution of Computer Graphics. SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA
 The Evolution of Computer Graphics Tony Tamasi SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA Graphics Make great images intricate shapes complex optical effects seamless motion Make them fast invent clever techniques
The Evolution of Computer Graphics Tony Tamasi SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA Graphics Make great images intricate shapes complex optical effects seamless motion Make them fast invent clever techniques
Computer Peripherals
 Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
Computer Peripherals School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological University Singapore These notes are part of a 3rd year undergraduate course called "Computer Peripherals", taught at Nanyang Technological
Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course :
 Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course : Computer Graphics (CSI-425) Course Coordinator : Mr. ISSA ALSMADI
Institution : Majmaah University. Academic Department : College of Science at AzZulfi. Programme : Computer Science and Information Course : Computer Graphics (CSI-425) Course Coordinator : Mr. ISSA ALSMADI
Agilent Television Power Consumption Testing. Application Note
 Agilent Television Power Consumption Testing Application Note Introduction Today, there are many types of televisions (TVs) on the market: the cathode ray tube (CRT) TV, liquid crystal display (LCD) TV,
Agilent Television Power Consumption Testing Application Note Introduction Today, there are many types of televisions (TVs) on the market: the cathode ray tube (CRT) TV, liquid crystal display (LCD) TV,
Real-Time Graphics Architecture
 Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Display and Framebuffer Displays Key properties Bandwidth Framebuffers Definitions and key
Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Display and Framebuffer Displays Key properties Bandwidth Framebuffers Definitions and key
CPIT-285 Computer Graphics
 Department of Information Technology B.S.Information Technology ABET Course Binder CPIT-85 Computer Graphics Prepared by Prof. Alhasanain Muhammad Albarhamtoushi Page of Sunday December 4 0 : PM Cover
Department of Information Technology B.S.Information Technology ABET Course Binder CPIT-85 Computer Graphics Prepared by Prof. Alhasanain Muhammad Albarhamtoushi Page of Sunday December 4 0 : PM Cover
Dynamic Digital Depth (DDD) and Real-time 2D to 3D conversion on the ARM processor
 Dynamic Digital Depth (DDD) and Real-time 2D to 3D conversion on the ARM processor November 2005 Abstract The use of mobile devices for entertainment consumption is a rapidly growing, global industry.
Dynamic Digital Depth (DDD) and Real-time 2D to 3D conversion on the ARM processor November 2005 Abstract The use of mobile devices for entertainment consumption is a rapidly growing, global industry.
Introduction to GPGPU. Tiziano Diamanti [email protected]
 [email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
[email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O
 Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware Components: CPU, Memory, and I/O What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? The Computer Continuum 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did
Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 OBJECTIVES
 Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
Cork Education and Training Board. Programme Module for. 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics. Leading to. Level 5 FETAC
 Cork Education and Training Board Programme Module for 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics Leading to Level 5 FETAC 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics 5N5029 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics 5N5029 1 Version 3
Cork Education and Training Board Programme Module for 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics Leading to Level 5 FETAC 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics 5N5029 3 Dimensional Computer Graphics 5N5029 1 Version 3
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER
 DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
Data Storage 3.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 3 Data Storage 3.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List five different data types used in a computer. Describe how
3 Data Storage 3.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List five different data types used in a computer. Describe how
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 01 / 25 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Review the syllabus Review course policies Color CIE system chromaticity diagram color gamut, complementary colors, dominant
CS 325 Computer Graphics 01 / 25 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Review the syllabus Review course policies Color CIE system chromaticity diagram color gamut, complementary colors, dominant
COMPUTER HARDWARE. Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems
 COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays
 Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays Introduction Backlights are used for compact, portable, electronic devices with flat panel Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) that require illumination from behind.
Optical Design Tools for Backlight Displays Introduction Backlights are used for compact, portable, electronic devices with flat panel Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) that require illumination from behind.
Computer Graphics AACHEN AACHEN AACHEN AACHEN. Public Perception of CG. Computer Graphics Research. Methodological Approaches - - - - - - - - - -
 Public Perception of CG Games Computer Graphics Movies Computer Graphics Research algorithms & data structures fundamental continuous & discrete mathematics optimization schemes 3D reconstruction global
Public Perception of CG Games Computer Graphics Movies Computer Graphics Research algorithms & data structures fundamental continuous & discrete mathematics optimization schemes 3D reconstruction global
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010
 COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, [email protected] Course
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, [email protected] Course
Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing
 Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing Helen H. Hu Westminster College, Salt Lake City, UT [email protected] Figure 1. Examples of student work. For fun, enthusiastic students
Teaching Introductory Computer Graphics Via Ray Tracing Helen H. Hu Westminster College, Salt Lake City, UT [email protected] Figure 1. Examples of student work. For fun, enthusiastic students
QuickSpecs. NVIDIA Quadro K5200 8GB Graphics INTRODUCTION. NVIDIA Quadro K5200 8GB Graphics. Technical Specifications
 J3G90AA INTRODUCTION The NVIDIA Quadro K5200 gives you amazing application performance and capability, making it faster and easier to accelerate 3D models, render complex scenes, and simulate large datasets.
J3G90AA INTRODUCTION The NVIDIA Quadro K5200 gives you amazing application performance and capability, making it faster and easier to accelerate 3D models, render complex scenes, and simulate large datasets.
Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL
 Step-by-Step Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL This Step-by-Step Card covers the basics of using the animation features of Cinema 4D XL. Note: Before you start this Step-by-Step Card, you need to have
Step-by-Step Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL This Step-by-Step Card covers the basics of using the animation features of Cinema 4D XL. Note: Before you start this Step-by-Step Card, you need to have
CAD/CAM. Hardware and software. CAD/CAM/CAE System. Shahrood University. Display Processing Unit
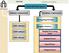 CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
CAD/CAM/CAE System Software requirement Hardware requirement Computing Machine CAD software CAM software CAE software Graphics Devices Display Processing Unit Display Device Input Device Output Device
Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE. M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science. Friday 18 th January 2008.
 COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
Graphics Cards and Graphics Processing Units. Ben Johnstone Russ Martin November 15, 2011
 Graphics Cards and Graphics Processing Units Ben Johnstone Russ Martin November 15, 2011 Contents Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) Graphics Pipeline Architectures 8800-GTX200 Fermi Cayman Performance Analysis
Graphics Cards and Graphics Processing Units Ben Johnstone Russ Martin November 15, 2011 Contents Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) Graphics Pipeline Architectures 8800-GTX200 Fermi Cayman Performance Analysis
B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN
 COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
COURSE GUIDE B.A IN GRAPHIC DESIGN GRD 126 COMPUTER GENERATED GRAPHIC DESIGN I UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION, WINNEBA DEPARTMENT OF GRAPHIC DESIGN Copyright Acknowledgements The facilitating agent of the course
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics Computer Animation Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Outline Principles of Animation Keyframe Animation Additional challenges in animation 2 Classic animation Luxo
CS 4204 Computer Graphics Computer Animation Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Outline Principles of Animation Keyframe Animation Additional challenges in animation 2 Classic animation Luxo
Hardware design for ray tracing
 Hardware design for ray tracing Jae-sung Yoon Introduction Realtime ray tracing performance has recently been achieved even on single CPU. [Wald et al. 2001, 2002, 2004] However, higher resolutions, complex
Hardware design for ray tracing Jae-sung Yoon Introduction Realtime ray tracing performance has recently been achieved even on single CPU. [Wald et al. 2001, 2002, 2004] However, higher resolutions, complex
Degree Reduction of Interval SB Curves
 International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:13 No:04 1 Degree Reduction of Interval SB Curves O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Ball basis was introduced
International Journal of Video&Image Processing and Network Security IJVIPNS-IJENS Vol:13 No:04 1 Degree Reduction of Interval SB Curves O. Ismail, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Ball basis was introduced
We can display an object on a monitor screen in three different computer-model forms: Wireframe model Surface Model Solid model
 CHAPTER 4 CURVES 4.1 Introduction In order to understand the significance of curves, we should look into the types of model representations that are used in geometric modeling. Curves play a very significant
CHAPTER 4 CURVES 4.1 Introduction In order to understand the significance of curves, we should look into the types of model representations that are used in geometric modeling. Curves play a very significant
Computer Graphics. Introduction. Computer graphics. What is computer graphics? Yung-Yu Chuang
 Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Chapter 2. Point transformation. Look up Table (LUT) Fundamentals of Image processing
 Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Image processing Point transformation Look up Table (LUT) 1 Introduction (1/2) 3 Types of operations in Image Processing - m: rows index - n: column index Point to point transformation
Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Image processing Point transformation Look up Table (LUT) 1 Introduction (1/2) 3 Types of operations in Image Processing - m: rows index - n: column index Point to point transformation
CS 378: Computer Game Technology
 CS 378: Computer Game Technology http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~fussell/courses/cs378/ Spring 2013 University of Texas at Austin CS 378 Game Technology Don Fussell Instructor and TAs! Instructor: Don Fussell!
CS 378: Computer Game Technology http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~fussell/courses/cs378/ Spring 2013 University of Texas at Austin CS 378 Game Technology Don Fussell Instructor and TAs! Instructor: Don Fussell!
WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING
 What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
What You should Know About Scanning WHAT You SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SCANNING If you re thinking about purchasing a scanner, you may already know some of the ways they can add visual interest and variety to
Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II)
 Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II) Informatica Multimediale Docente: Umberto Castellani *I lucidi sono tratti da una lezione di Maura Melotti ([email protected]) RENDERING Rendering What is rendering? Rendering
Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II) Informatica Multimediale Docente: Umberto Castellani *I lucidi sono tratti da una lezione di Maura Melotti ([email protected]) RENDERING Rendering What is rendering? Rendering
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
What Is Hardware? Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware is the physical components of a computer system e.g., a monitor, keyboard, mouse and the computer
Visualisatie BMT. Introduction, visualization, visualization pipeline. Arjan Kok Huub van de Wetering ([email protected])
 Visualisatie BMT Introduction, visualization, visualization pipeline Arjan Kok Huub van de Wetering ([email protected]) 1 Lecture overview Goal Summary Study material What is visualization Examples
Visualisatie BMT Introduction, visualization, visualization pipeline Arjan Kok Huub van de Wetering ([email protected]) 1 Lecture overview Goal Summary Study material What is visualization Examples
CS 3530 Operating Systems. L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson
 CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
GPU Architecture. Michael Doggett ATI
 GPU Architecture Michael Doggett ATI GPU Architecture RADEON X1800/X1900 Microsoft s XBOX360 Xenos GPU GPU research areas ATI - Driving the Visual Experience Everywhere Products from cell phones to super
GPU Architecture Michael Doggett ATI GPU Architecture RADEON X1800/X1900 Microsoft s XBOX360 Xenos GPU GPU research areas ATI - Driving the Visual Experience Everywhere Products from cell phones to super
QuickSpecs. NVIDIA Quadro K5200 8GB Graphics INTRODUCTION. NVIDIA Quadro K5200 8GB Graphics. Overview. NVIDIA Quadro K5200 8GB Graphics J3G90AA
 Overview J3G90AA INTRODUCTION The NVIDIA Quadro K5200 gives you amazing application performance and capability, making it faster and easier to accelerate 3D models, render complex scenes, and simulate
Overview J3G90AA INTRODUCTION The NVIDIA Quadro K5200 gives you amazing application performance and capability, making it faster and easier to accelerate 3D models, render complex scenes, and simulate
ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide
 Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
Adobe Training Services Exam Guide ACE: Illustrator CC Exam Guide Adobe Training Services provides this exam guide to help prepare partners, customers, and consultants who are actively seeking accreditation
