ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
|
|
|
- Scarlett Hodges
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION 3.1 CHAPTER 1 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS STUDENT NOTE Please note that most answers are not exact, and that equivalent answers are usually acceptable. CHAPTER 1: Short-term physiological preparation Text between pages 12 to 25, answers to questions on page 25 of the text book. 1) a) From a physiological standpoint, explain why warm-up is important within an exercise regime. 8 marks Warm-up: Raises body temperature. Increases metabolic rate. Raises energy release. Reduces response times. This increase in temperature reduces blood viscosity. And therefore increases blood flow to working muscles. Slightly increasing demand for oxygen will increase heart rate and breathing volumes. Which makes more oxygen available to working tissue. Blood supply is redistributed to working tissue (vascular shunt). A warm-up prepares the body for skill demands of the activity - reducing the risk of injury. b) Stretching is a key element in any warm-up. Using an example, identify two other elements of a warm-up and explain how they help to prepare an athlete. 4 marks Jogging: Gradually elevates heart rate and ventilation rates. Increases core temperature. Sport specific skill practice: This works the neuromuscular systems related to the chosen activity. c) Describe three different methods of stretching and state a sport that would benefit most from each type. 6 marks Passive stretching: This happens when the stretch is assisted by a partner or object to stretch the muscle beyond its normal range. Suitable for activities where movement range is important example gymnastics. Could be developed into PNF. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF): PNF involves stretching. Followed by an isometric contraction. Followed by further stretching (PNF). Suitable for activities where range of movement is important, for example gymnastics. Static stretching: This is a form of stretching when the muscle is stretched to a point of tension. And then held for a time period. Very relevant to activities where static balance is important, for example gymnastics balance. Active stretching: Occurs when the stretch is done slowly to extend the joint. And stretch the muscle to an unassisted range of movement. Suitable for all sports. Ballistic stretching: Occurs when body movements are used in a swinging/bouncing fashion to extend joint range. Suitable for explosive events such as sprinting. 2
2 SHORT-TERM PREPARATION 2) Define energy, and briefly describe how energy is released from food in the body? 5 marks 1 mark for definition: Energy is the capacity or ability to perform work. 4 marks for energy is released from food in the body: Fuel foods are fuel stored in the body, the first is carbohydrate (CHO - digested to glucose). The second type of fuel food consists of fats (digested to fatty acids & glycerol). These are used to create chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is an endothermic reaction (it takes in energy from the food and creates the ATP). This process is both aerobic and anaerobic, within all living tissue. ATP is an immediate usable form of chemical energy for all body processes. Including that used by skeletal muscle to perform mechanical work. The usage of ATP to create energy is an exothermic reaction. 3) a) Prescribe a prudent recommendation for approximate percentages of protein, lipid and carbohydrate intake for a general all-round athletic performer. 3 marks CHO 50% - 60%. Lipid 25% - 35%. Protein 10% - 15%. b) Suggest some general dietary guidelines you would give to a gymnast who is preparing for a major competition. 3 marks Regular weighing. Limit fat intake. Increase liquid intake (rehydration). Maintain a balanced diet that stresses high CHO content. Use of food supplements such as creatine, glutamine, iron tablets and vitamin C. 4) Discuss the value of using protein supplementation to enhance performance in power and endurance events. 4 marks It was generally believed that protein supplementation was essential for athletes who train hard in power and endurance events. The role of protein differs for power-based and endurance-based athletes. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) is and grams per kilogram of body mass respectively. This is because the rate of protein breakdown and resynthesis is greater due to muscle hypertrophy. Providing the RDA of protein is included in the athlete s balanced diet there should be no reason for protein supplementation. However, recent studies have shown that supplementing protein immediately following heavy bouts of training seems to have a beneficial effect. Since elevation of plasma amino acids during recovery stimulates protein synthesis. This protein supplementation is mixed with glucose and electrolytes and is readily available from a variety of Sports drinks. It is also thought that athletes, who are starting on a new rigorous training programme, may benefit from protein supplementation. 5) What is creatine and how does creatine supplementation improve anaerobic power? 4 marks Creatine is a natural substance found in skeletal muscle, stored as phosphocreatine (PC). Creatine supplementation, together with a large amount of carbohydrate, is found to increase muscle uptake of creatine. Thus increasing PC levels to enhance the ATP-PC system. Increasing peak power production. And enabling the performer to train at higher intensities. By delaying the alactic/lactic threshold. Chapter 1 3
3 SECTION 3.1 CHAPTER 1 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 6) Briefly describe the process of carbohydrate degradation to re-create energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 12 marks Essay-style answer or equivalent diagram (figure Q1.1): 2 marks for: CHO is digested (broken down) to form glucose, and is transported to muscle cells for tissue respiration. The process of CHO degradation to re-create energy involves three stages within the muscle cell: 3 marks for three of: Stage one Glycolysis: Energy release takes place within the muscle cell sarcoplasm. Involving a process called glycolysis or the incomplete breakdown of glucose. Using glycolytic enzymes such as phosphofructokinase (PFK). Without oxygen being present. protein One molecule of glucose releases 2 molecules of ATP. And pyruvic acid. fats 3 marks for three of: Stage two - Kreb s cycle or the citric acid cycle: Occurs in the presence of oxygen. In the muscle cell mitochondria within the inner fluid filled matrix. Pyruvic combines oxaloacetic acid and acetyl CoA combine to form citric acid. To enter Kreb s cycle where pairs of hydrogen atoms are released. CO 2 is formed. 2ATPs are produced. 4 marks for four of: Stage three electron transport chain: Coenzymes transport hydrogen atoms (ions and electrons) into the electron transport chain. Within the inner part (cristae) of the muscle cell mitochondria. Hydrogen ions and electrons are charged with potential energy. Which is released in a step-by-step manner. As O 2 is delivered to react with the hydrogen ions and electrons. To create a large energy yield per mole of glucose (32/34 ATP molecules) and water. 1 molecule of glucose glycolysis pyruvic acid acetyl coa citric acid figure Q1.1 the aerobic system 7) Discuss the influence of dietary carbohydrates (CHO) and fats on muscle glycogen stores. 5 marks Carbohydrate and fats are the main fuel foods to provide the body s energy needs. Muscle glycogen depletion has been shown to be a major cause of fatigue. Studies have demonstrated that athletes who ate a high-cho diet for three days stored nearly twice their normal amounts of glycogen. And when they were asked to exercise to exhaustion. Their exercise performance significantly increased. But when a low-cho diet was consumed, muscle glycogen rapidly depleted. Reducing the exercise time to exhaustion. Showing that the secondary fuel food fat is unable to supplement reduced muscle and liver glycogen levels to the same level as carbohydrates. O 2 2ATP Kreb's cycle H+ ions and electrons H O 2 oxaloacetic acid lactic acid electron transpor t chain 2ATP CO 2 up to 32 ATP 4
4 SHORT-TERM PREPARATION 8) a) Discuss how a balanced diet could be manipulated to increase an athlete s glucose reserves prior to a marathon race. 6 marks Carboloading (or glycogen loading) before the event (modern method). This consists of tapering of training, whilst eating 50% CHO diet. Partially depletes glycogen stores. Therefore energy levels are not compromised. And glycogen synthase activity is increased. Then, gradually increase CHO intake to 70% of diet. With light training. Day of rest and 70% CHO diet. Repletes glycogen stores above normal level on day of marathon. Referred to as glycogen supercompensation. Taking in isotonic fluids during the event will top up blood glucose levels during the event. b) Carbohydrates are used as an energy source during both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. It is therefore beneficial that an elite athlete s stores of carbohydrate are at a maximum before competition day. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of glycogen loading. 4 marks Advantages: Enhanced glycogen stores in muscle and liver. Overall effect is for overall times in aerobic activities beyond 90 minutes to improve significantly. Disadvantages: Increased body mass due to increased water retention. Needed for enhanced glycogen storage. During CHO depletion phase decreased energy levels. And increased fatigue (if using classic 10 day method of carboloading). c) How can an athlete s diet aid the recovery process? 2 marks Quick ingestion of carbohydrates and proteins (2 hour window of opportunity) will speed up recovery. Could be taken as a drinks supplement immediately following exercise or as a meal as soon as possible. Water needed to rehydrate the body. Electrolyte replenishment needed to aid metabolic process. Protein needed to aid tissue damage, repair and growth. 9) Describe how an athlete is able to control his or her body temperature during a marathon race. 4 marks Replace body fluids to prevent dehydration and over heating. Wear suitable clothing such as mesh running vest. That allows air to circulate. Hence body is cooled by evaporation of sweat, convection and radiation. Use sponge stations to cool down body parts. 10) What are the major avenues for loss of body heat energy? Which of these four pathways is important for controlling body temperature at rest, and during exercise? 4 marks for the major avenues: Radiation. Conduction. Convection. Evaporation. 1 mark for which of these four pathways is most important: Radiation is the primary method for discharging the resting body s excess heat. 1 mark for during exercise: Evaporation is the primary method for heat dissipation during exercise. 6 marks Chapter 1 5
5 SECTION 3.1 CHAPTER 1 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 11) Why is humidity an important factor when an athlete is performing in high temperatures? Why are wind and cloud cover important? 4 marks 2 marks for humidity: Water vapour in the air plays a major role in evaporative heat loss. Hence high humidity limits sweat evaporation and heat loss. 2 marks for wind and cloud cover: Wind increases heat loss by convection. Known as the windchill factor. Cloud cover reduces heat gain by solar radiation. 12) What is meant by heat acclimatisation? Outline the main physiological adaptations which occur to allow an athlete to acclimatise to training and competition in high temperatures? 8 marks 2 marks for heat acclimatisation: Refers to the physiological adaptive responses that improve heat tolerance. Repeated exercise in the heat causes a relatively fast physiological adjustment that enables an athlete to perform better in hot conditions: 6 marks for major physiological adaptations: Improves cutaneous blood flow: Transports metabolic heat from deep tissues to the body s shell. Lowers threshold for start of sweating: Hence evaporative cooling in the form sweating, particularly on exposed body parts such as arms and legs. Increased sweat output maximises evaporative cooling. Lowers sweat s salt concentration: Dilute sweat preserves electrolytes in extra cellular fluid. Cardiovascular functioning: Short-term physiological adjustments to cardiovascular functioning result in increased plasma volume. Thus supporting stroke volume. And allowing the body to maintain cardiac output. Giving greater stability in blood pressure during training and competition. Acclimatisation to hot, humid conditions: Results in increased sweating. Because high humidity contributes little to evaporative cooling. Combined effect of improved sweating and cardiovascular adaptations is to reduce core temperature and heart rate response. Therefore more training can be done before the onset of fatigue. And no adverse heat effects during a competition. 13) Describe the conditions at altitude that could limit performance. 3 marks Altitude causes hypobaric conditions or a reduction in barometric pressure. Resulting in decreased partial pressure of oxygen (po 2 ) throughout the body. Reducing the oxygenation of haemoglobin. Air temperature decreases as altitude increases. Solar radiation is more intense. Thus limiting human activity when compared with sea level performance. 6
6 SHORT-TERM PREPARATION 14) Describe the major physiological responses and adaptations that accompany acclimatisation to altitude over a period of three weeks. 10 marks 4 marks for four of immediate physiological responses: Pulmonary: Hyperventilation occurs immediately. As body fluids become more alkaline. Due to reduced CO 2 (H 2 CO 3 ) with hyperventilation. Corrected by the kidneys, which excretes a more alkaline urine solution. Cardiovascular: Increased submaximal heart rate. Increased submaximal cardiac output. Stroke volume remains the same or lowers slightly. Maximum cardiac output remains the same or lowers slightly. 6 marks for six of longer term physiological adaptations following 3 weeks of altitude training: Cardiovascular: Stroke volume lowers. Maximum cardiac output lowers. Decreased plasma volume. Increased haematocrit (the percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells). Increased haemoglobin concentration. Increased total number of red blood cells. Possible increased capillarisation of skeletal muscle. Cellular changes: Increased mitochondria. Increased oxidative enzymes such as pyruvic dehydrogenase. Net effect is to improve the aerobic working capacity of muscles to compensate for the reduced po 2. And to improve the capacity of the oxygen transport system. To purge the oxygen debt. 15) What is meant by the concept living high and training low? Identify two advantages of using this acclimatisation method. 6 marks 4 marks for four of: Living high and training low is an at-home acclimatisation method achieved at sea level. The athlete rests and sleeps in a hypobaric or hypoxic chamber. Created by a hypoxic generator that continually feeds altitude-stimulating hypoxic air into the tent. The hypoxic chamber provides an environment in which the athlete will gain the beneficial physiological adaptations expected from being exposed to hypobaric conditions. This is called living high. Training low refers to the athlete maintaining a sea level training environment. 2 marks for two of advantages: Less costly. Less disruptive to lifestyle, such as family relations. Maintains relationships and support systems such as quality training facilities, the personal coach, training group and medical team. Chapter 1 7
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
Work and Energy in Muscles
 Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
The correct answer is d C. Answer c is incorrect. Reliance on the energy produced by others is a characteristic of heterotrophs.
 1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
1. Enzymes. Biochemical Reactions. Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism. 1. Enzymes. 2. ATP Production. 3. Autotrophic Processes
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance
 Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
Learning aim B Know about the different energy systems used during sports performance Assessment criteria 2B.P5 2B.M5 2B.D2 Describe the function of the three energy systems in the production and release
Understanding energy systems
 Understanding energy systems Key terms & definitions: Anaerobic: A process that does not require oxygen. Aerobic: A process that requires oxygen. ATP Yield: The total amount of ATP produced by an energy
Understanding energy systems Key terms & definitions: Anaerobic: A process that does not require oxygen. Aerobic: A process that requires oxygen. ATP Yield: The total amount of ATP produced by an energy
1. Explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration.
 : Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
: Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Twenty Three 1
 23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS
 CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.
![- Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells. - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood brings oxygen to the cells.](/thumbs/40/21014327.jpg) Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy - Oxygen is needed for cellular respiration [OVERHEAD, fig. 6.2, p. 90 / 4th: 6.1] - ATP - this is provided by the lungs - lungs provide oxygen to blood, blood
Interval Training. Interval Training
 Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Cellular Respiration An Overview
 Why? Cellular Respiration An Overview What are the phases of cellular respiration? All cells need energy all the time, and their primary source of energy is ATP. The methods cells use to make ATP vary
Why? Cellular Respiration An Overview What are the phases of cellular respiration? All cells need energy all the time, and their primary source of energy is ATP. The methods cells use to make ATP vary
Exercise Metabolism II
 Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
What affects an enzyme s activity? General environmental factors, such as temperature and ph. Chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme.
 CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
CH s 8-9 Respiration & Metabolism Metabolism A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. An enzyme is a catalytic protein. Hydrolysis of sucrose by
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Electrons carried in NADH Mitochondrion Glucose Glycolysis Pyruvic acid Krebs Cycle Electrons carried in NADH and FADH 2 Electron Transport Chain Cytoplasm Mitochondrion
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Electrons carried in NADH Mitochondrion Glucose Glycolysis Pyruvic acid Krebs Cycle Electrons carried in NADH and FADH 2 Electron Transport Chain Cytoplasm Mitochondrion
008 Chapter 8. Student:
 008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase
 Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase Pyruvic Acid Dehydrogenase Complex Pyruvate to ACETYL coa CC CoA + CO 2 Mitochondria 3 carbon Pyruvate to 2 carbon ACETYL Coenzyme A Pyruvate Acetyl CoA + CO 2 + NADH + H + CO2
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase Pyruvic Acid Dehydrogenase Complex Pyruvate to ACETYL coa CC CoA + CO 2 Mitochondria 3 carbon Pyruvate to 2 carbon ACETYL Coenzyme A Pyruvate Acetyl CoA + CO 2 + NADH + H + CO2
Photosynthesis (CO 2 + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 )
 The vital role of A This is the energy-rich compound that is the source of energy for all living things. It is a nucleotide, comprising a 5C sugar (ribose); an organic base (adenosine); and 3 phosphate
The vital role of A This is the energy-rich compound that is the source of energy for all living things. It is a nucleotide, comprising a 5C sugar (ribose); an organic base (adenosine); and 3 phosphate
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Altitude. Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments. The Stress of Altitude. Reduced PO 2. O 2 Transport Cascade. Oxygen loading at altitude:
 Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes. What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it?
 Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Rowing Physiology. Intermediate. Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR)
 2 Intermediate Rowing Physiology Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR) Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 34 1.0 INTRODUCTION The FISA CDP booklet titled BASIC ROWING PHYSIOLOGY provided information
2 Intermediate Rowing Physiology Author: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR) Editors: Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 34 1.0 INTRODUCTION The FISA CDP booklet titled BASIC ROWING PHYSIOLOGY provided information
BCOR 011 Exam 2, 2004
 BCOR 011 Exam 2, 2004 Name: Section: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to the first law of thermodynamics, A. the universe
BCOR 011 Exam 2, 2004 Name: Section: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. According to the first law of thermodynamics, A. the universe
Todays Outline. Metabolism. Why do cells need energy? How do cells acquire energy? Metabolism. Concepts & Processes. The cells capacity to:
 and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
and Work Metabolic Pathways Enzymes Features Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Membrane Transport Diffusion Osmosis Passive Transport Active Transport Bulk Transport Todays Outline -Releasing Pathways
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Cellular Respiration
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Cellular Respiration Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways Photoautotrophs make ATP during photosynthesis and use it to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Cellular Respiration Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways Photoautotrophs make ATP during photosynthesis and use it to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates
The diagram below summarizes the effects of the compounds that cells use to regulate their own metabolism.
 Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program
 Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
 Phases of aerobic cellular respiration 1. Glycolysis 2. Transition or Acetyl-CoA reaction 3. Krebs cycle 4. Electron transport system Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration These phases are nothing more than metabolic
Phases of aerobic cellular respiration 1. Glycolysis 2. Transition or Acetyl-CoA reaction 3. Krebs cycle 4. Electron transport system Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration These phases are nothing more than metabolic
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Text, Diagrams, Assessments, and Link to Standards Focus Questions 1) What is cellular respiration? 2) How is cellular respiration connected to breathing? 3) If
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview
 GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, M Med Part I
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, M Med Part I
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Insulin s Effects on Testosterone, Growth Hormone and IGF I Following Resistance Training
 Insulin s Effects on Testosterone, Growth Hormone and IGF I Following Resistance Training By: Jason Dudley Summary Nutrition supplements with a combination of carbohydrate and protein (with a ratio of
Insulin s Effects on Testosterone, Growth Hormone and IGF I Following Resistance Training By: Jason Dudley Summary Nutrition supplements with a combination of carbohydrate and protein (with a ratio of
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
 Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic compounds (carbohydrates,
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic compounds (carbohydrates,
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration. Chapter 8
 Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Overview of Glucose Breakdown The overall equation for the complete breakdown of glucose is: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP The
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Overview of Glucose Breakdown The overall equation for the complete breakdown of glucose is: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP The
Is Chocolate Milk the answer?
 Is Chocolate Milk the answer? Is Chocolate Milk the answer? Karp, J.R. et al. Chocolate Milks as a Post-Exercise Recovery Aid, Int. J of Sports Ntr. 16:78-91, 2006. PROS Study focused on trained athletes
Is Chocolate Milk the answer? Is Chocolate Milk the answer? Karp, J.R. et al. Chocolate Milks as a Post-Exercise Recovery Aid, Int. J of Sports Ntr. 16:78-91, 2006. PROS Study focused on trained athletes
Is ATP worth the investment?
 Is ATP worth the investment? ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) can be thought of as the currency of the cell. Most cellular metabolic processes cost a certain amount of ATP in order to happen. Furthermore,
Is ATP worth the investment? ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) can be thought of as the currency of the cell. Most cellular metabolic processes cost a certain amount of ATP in order to happen. Furthermore,
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Integration of Metabolism
 I. Central Themes of Metabolism 1. ATP is the universal energy carrier. Integration of Metabolism Bryant Miles 2. ATP is generated by the oxidation of metabolic fuels Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 3.
I. Central Themes of Metabolism 1. ATP is the universal energy carrier. Integration of Metabolism Bryant Miles 2. ATP is generated by the oxidation of metabolic fuels Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 3.
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Summary of Metabolism. Mechanism of Enzyme Action
 Summary of Metabolism Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1. The substrate contacts the active site 2. The enzyme-substrate complex is formed. 3. The substrate molecule is altered (atoms are rearranged, or the
Summary of Metabolism Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1. The substrate contacts the active site 2. The enzyme-substrate complex is formed. 3. The substrate molecule is altered (atoms are rearranged, or the
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
 Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? A) Biotin participates in the decarboxylation.
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? A) Biotin participates in the decarboxylation.
Chapter 12. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation. Heat Balance. An Overview of Heat Balance. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Anabolic and Catabolic Reactions are Linked by ATP in Living Organisms
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes.
 This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
advanced military training in hot weather such as ABN / Ranger School or ROTC camp.
 Individual Guidance for Heat Acclimatization This heat acclimatization guidance is for those soldiers who will be attending strenuous advanced military training in hot weather such as ABN / Ranger School
Individual Guidance for Heat Acclimatization This heat acclimatization guidance is for those soldiers who will be attending strenuous advanced military training in hot weather such as ABN / Ranger School
Training our energy systems
 Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
ATP accounting so far ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN & CHEMIOSMOSIS. The Essence of ETC: The Electron Transport Chain O 2
 accounting so far The final stage of cellular respiration: ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN & CHEMIOSMOSIS Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4! There
accounting so far The final stage of cellular respiration: ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN & CHEMIOSMOSIS Glycolysis 2 Kreb s cycle 2 Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4! There
Photosynthesis takes place in three stages:
 Photosynthesis takes place in three stages: Light-dependent reactions Light-independent reactions The Calvin cycle 1. Capturing energy from sunlight 2. Using energy to make ATP and NADPH 3. Using ATP and
Photosynthesis takes place in three stages: Light-dependent reactions Light-independent reactions The Calvin cycle 1. Capturing energy from sunlight 2. Using energy to make ATP and NADPH 3. Using ATP and
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1
 Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
Cellular Respiration: Practice Questions #1 1. Which statement best describes one of the events taking place in the chemical reaction? A. Energy is being stored as a result of aerobic respiration. B. Fermentation
American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand: Exercise and Fluid Replacement Summary
 American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand: Exercise and Fluid Replacement Summary American College of Sports Medicine. Position Stand on Exercise and Fluid Replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc.,
American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand: Exercise and Fluid Replacement Summary American College of Sports Medicine. Position Stand on Exercise and Fluid Replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc.,
TRAINING. chapter. how does. affect performance? Energy
 chapter 5 how does TRAINING affect performance? When individuals begin to train they are trying to improve the way their bodies function. They may wish to improve a particular way their bodies deliver
chapter 5 how does TRAINING affect performance? When individuals begin to train they are trying to improve the way their bodies function. They may wish to improve a particular way their bodies deliver
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Biology for Science Majors
 Biology for Science Majors Lab 10 AP BIOLOGY Concepts covered Respirometers Metabolism Glycolysis Respiration Anaerobic vs. aerobic respiration Fermentation Lab 5: Cellular Respiration ATP is the energy
Biology for Science Majors Lab 10 AP BIOLOGY Concepts covered Respirometers Metabolism Glycolysis Respiration Anaerobic vs. aerobic respiration Fermentation Lab 5: Cellular Respiration ATP is the energy
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration
 AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The sum of all of the biochemical processes going on within the human body at any
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The sum of all of the biochemical processes going on within the human body at any
-Loss of energy -Loss of hydrogen from carbons. -Gain of energy -Gain of hydrogen to carbons
 Cellular Respiration- Equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 +6H20 and energy -The energy is released from the chemical bonds in the complex organic molecules -The catabolic process of releasing energy from food
Cellular Respiration- Equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 +6H20 and energy -The energy is released from the chemical bonds in the complex organic molecules -The catabolic process of releasing energy from food
Biology I. Chapter 8/9
 Biology I Chapter 8/9 NOTEBOOK #1 Interest Grabber Suppose you earned extra money by having a part-time job. At first, you might be tempted to spend all of the money, but then you decide to open a bank
Biology I Chapter 8/9 NOTEBOOK #1 Interest Grabber Suppose you earned extra money by having a part-time job. At first, you might be tempted to spend all of the money, but then you decide to open a bank
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball
 Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball Salma Mehter Smith College 1/31/2011 Introduction A wise person once said, Practice doesn't make perfect; perfect practice makes perfect. This is clear when
Energy System Demands of Fastpitch Softball Salma Mehter Smith College 1/31/2011 Introduction A wise person once said, Practice doesn't make perfect; perfect practice makes perfect. This is clear when
Management of Fibromyalgia: Rationale for the use of Magnesium and Malic Acid. Journal of Nutritional Medicine
 Management of Fibromyalgia: Rationale for the use of Magnesium and Malic Acid 1 Journal of Nutritional Medicine Guy E. Abraham MD and Jorge D. Flechas MD, MPH FROM ABSTRACT: Primary Fibromyalgia (FM) is
Management of Fibromyalgia: Rationale for the use of Magnesium and Malic Acid 1 Journal of Nutritional Medicine Guy E. Abraham MD and Jorge D. Flechas MD, MPH FROM ABSTRACT: Primary Fibromyalgia (FM) is
FAT 411: Why you can t live without it
 FAT 411: Why you can t live without it In the many nutrition talks I have done in the past, I have received numerous questions surrounding the somewhat misunderstood macronutrient of fat. Question range
FAT 411: Why you can t live without it In the many nutrition talks I have done in the past, I have received numerous questions surrounding the somewhat misunderstood macronutrient of fat. Question range
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels*
 Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1. 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain.
 Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain. 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular
Cellular Respiration Worksheet 1 1. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain. 2. Where in the cell does the glycolysis part of cellular
Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration
 1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
1 of 5 11/9/2011 8:11 PM Name: Hour: Chapter 9 Review Worksheet Cellular Respiration Energy in General 1. Differentiate an autotroph from a hetertroph as it relates to obtaining energy and the processes
Citric Acid Cycle Review Activity
 Citric Acid Cycle Review Activity Goals Students will be able to appreciate the details of steps within the Kreb s Cycle. Students will be able to understand the steps of the Kreb s Cycle at functional
Citric Acid Cycle Review Activity Goals Students will be able to appreciate the details of steps within the Kreb s Cycle. Students will be able to understand the steps of the Kreb s Cycle at functional
How To Train For Flexibility
 FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
Respiration Worksheet. Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food. Types of Respiration. Aerobic Respiration
 Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
Respiration Worksheet Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food The food involved in respiration is usually Internal respiration is controlled by which allow energy to be released in The
Cellular Respiration & Metabolism. Metabolism. Coupled Reactions: Bioenergetics. Cellular Respiration: ATP is the cell s rechargable battery
 Cellular Respiration & Metabolism Metabolic Pathways: a summary Metabolism Bioenergetics Flow of energy in living systems obeys: 1 st law of thermodynamics: Energy can be transformed, but it cannot be
Cellular Respiration & Metabolism Metabolic Pathways: a summary Metabolism Bioenergetics Flow of energy in living systems obeys: 1 st law of thermodynamics: Energy can be transformed, but it cannot be
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas
 Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES. Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator
 HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
Topic 3: Nutrition, Photosynthesis, and Respiration
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
1. Base your answer to the following question on the chemical reaction represented below and on your knowledge of biology. If this reaction takes place in an organism that requires sunlight to produce
Metabolism Poster Questions
 Metabolism Poster Questions Answer the following questions concerning respiration. 1. Consider the mitochondrial electron transport chain. a. How many hydrogen ions can be pumped for every NADH? b. How
Metabolism Poster Questions Answer the following questions concerning respiration. 1. Consider the mitochondrial electron transport chain. a. How many hydrogen ions can be pumped for every NADH? b. How
Water It s Crucial Role in Health. By: James L. Holly, MD
 Water It s Crucial Role in Health By: James L. Holly, MD After a two week hiatus, we return to our series entitled, Aging Well. It is often the case that in health we become so infatuated with the exotic,
Water It s Crucial Role in Health By: James L. Holly, MD After a two week hiatus, we return to our series entitled, Aging Well. It is often the case that in health we become so infatuated with the exotic,
Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps):
 Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps): 1) How many ATP molecules are produced for each glucose molecule used in fermentation?
Biology 20 Cellular Respiration Review NG Know the process of Cellular Respiration (use this picture if it helps): 1) How many ATP molecules are produced for each glucose molecule used in fermentation?
Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain
 Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain 2006-2007 Cellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP ATP accounting so far Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes
Cellular Respiration Stage 4: Electron Transport Chain 2006-2007 Cellular respiration What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP ATP accounting so far Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes
1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain.
 Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Which of the following can be determined based on this model? The atmosphere is the only reservoir on Earth that can store carbon in any form. A.
 Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Avoiding the Wall : Why women do not need to carbohydrate load. Jamie Justice. Audience: Women s marathon running groups and charity marathon coaches
 1 Avoiding the Wall : Why women do not need to carbohydrate load Jamie Justice Audience: Women s marathon running groups and charity marathon coaches The marathon s dreaded mile 18 wall is enough to give
1 Avoiding the Wall : Why women do not need to carbohydrate load Jamie Justice Audience: Women s marathon running groups and charity marathon coaches The marathon s dreaded mile 18 wall is enough to give
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
CELL/ PHOTOSYNTHESIS/ CELLULAR RESPIRATION Test 2011 ANSWER 250 POINTS ANY WAY IN WHICH YOU WANT
 CELL/ PHOTOSYNTHESIS/ CELLULAR RESPIRATION Test 2011 ANSWER 250 POINTS ANY WAY IN WHICH YOU WANT Completion: complete each statement. (1 point each) 1. All cells arise from. 2. The basic unit of structure
CELL/ PHOTOSYNTHESIS/ CELLULAR RESPIRATION Test 2011 ANSWER 250 POINTS ANY WAY IN WHICH YOU WANT Completion: complete each statement. (1 point each) 1. All cells arise from. 2. The basic unit of structure
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
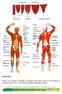 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul
 rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
rt and Exercise Sciences uncorrected first proofs issued by marketing 9/7/2013. This material is Hodder Education 2013 and shoul Contents Acknowledgements Introduction ix xi Mandatory units 1 Anatomy for
Photo Cell Resp Practice. A. ATP B. oxygen C. DNA D. water. The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants.
 Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
Name: ate: 1. Which molecule supplies the energy for cellular functions?. TP. oxygen. N. water 2. Photosynthesis The following equation represents the process of photosynthesis in green plants. What happens
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Does Lactic Acid Cause Muscular Fatigue?
 Does Lactic Acid Cause Muscular Fatigue? Ernest W. Maglischo, Ph.D. 1970 Lazy Meadow Lane Prescott, AZ 86303 USA ewmaglischo@cox.net Abstract. Until recently, lactic acid accumulation and the acidosis
Does Lactic Acid Cause Muscular Fatigue? Ernest W. Maglischo, Ph.D. 1970 Lazy Meadow Lane Prescott, AZ 86303 USA ewmaglischo@cox.net Abstract. Until recently, lactic acid accumulation and the acidosis
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Heart Monitor Training for the Compleat Idiot By John L. Parker, Jr.
 Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
