Medical Biology. Epithelial tissue
|
|
|
- Phoebe King
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lec: five Dr:Fadia Al-kahyat Medical Biology Epithelial tissue The human body consists of many interacting systems. Each system contributes to the maintenance of homeostasis, of itself, other systems, and the entire body. A system consists of two or more organs, which are functional collections of tissue. Each tissue composed from cells, extracellular substances. Although all cells of the body share common structures such as nuclei, centrosomes, Golgi apparatus...etc., they differ in size, shape and function. The human body has approximately 5x10 cells. Histology: The science which deals with form, structure and function of tissues. Histology bridges the gap between cytology and gross anatomy and provides the bases for understanding system physiology. Tissue: A group of closely associated cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related function. Primary tissues: four basic tissues interweave to form the "fabric" of the body. These are: Epithelial tissues. Connective tissues. Muscular tissues. Nervous tissues. Epithelial tissue or epithelium is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a body cavity or form glands. Location of Epithelia: Epithelia are found in form of sheets or membranes lining or covering surfaces and also present as masses in many glands Epithelia perform the following functions: protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion and sensation Characteristics of Epithelia: Epithelial tissues have the following characteristics that distinguish them from other tissue types 1-Cellularity: Epithelial tissue is composed of closely packed cells with a tiny amount of extracellular material lies in the narrow spaces between cells. 2-Specialized contacts: Epithelial cells fit close together at many points to form a continuous sheet. Adjacent cells are bound together at many points by lateral contacts such as tight junctions, desmosomes...etc. 1 13
2 3-Polarity: All epithelia have a free surface (apical surface) "-and an attached surface (basal surface). All epithelia exhibit polarity, meaning that cells near the apical surface differ from those at the basal surface. Although some apical surfaces are smooth and slick, most have microvilli (fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane which increase the exposed area). In epithelia that absorb or secret substances (lining the intestine or kidney tubules), the microvilli are often so dense that the cell apices have a fuzzy appearance called a brush border. Some epithelia, such as those lining the trachea, have motile cilia that propel substances along their free surfaces. 4-Innervated but avascular: Although epithelium is innervated (supplied by nerve fibers), it is avascular (contains no blood vessels). Epithelial cells are nourished by substances diffusing from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue. 5-Rest on a basal lamina: A thin supporting sheet called the basal separates the epithelium from the connective tissue deep to it. Basal lamina is noncellular adhesive sheet consisting largely of glycoproteins secreted by the epithelial cells. Directly deep to the basal lamina, is the reticular lamina which is a similar layer of extracellular material containing a fine network of collagen protein fibers. The two lamina (basal lamina and reticular lamina) form the basement membrane. The basal lamina acts as a selective barrier between connective tissue and other cells, contains information necessary for cell-cell interaction and orients the epithelial cell location of movement. 6-Regeneration: Epithelium has a high regenerative capacity. Some epithelia are exposed to friction and their surface cells are removed by abrasion. Others are damaged by hostile substances in the external environment (bacteria, acids, smoke... etc.). As long as epithelial cells receive adequate nutrition, they can replace lost cells rapidly by mitosis. Classification of Epithelia: Epithelial tissues are classified according to the number of their layers into: simple, stratified and pseudostratified. Simple tissues are composed of only one layer of cells. Stratified tissues are composed of two or more layers of cells. Pseudostratified tissues present a superficial stratification appearance. Epithelial tissues are also classified according to the shape of the cells (in simple tissue) and shape of apical cells (in stratified tissues) as: squamous (flattened and scale like), cuboidal (approximately as tall as they are wide) and columnar (tall and column shaped). By mixing the above criteria of classification, epithelial tissues are classified into the following groups: 1-Simple E.P ( squamous, cuboidal and columnar) 2-Pseudostratified (ciliated, plain) 3-Stratifid E.P (squamous, cuboidal, columnar and transitional) 2
3 Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue The cells are very thin, flat and irregular in outline, with rounded, central nuclei and wavy edges. In longitudinal section, cells are spindle in shape with oval central nuclei Located in air sacks of the lungs, Bowman's capsule (kidney glomeruli), endothelium that lines blood vessels and lymphatic vessels and mesothelium that lines the peritoneal cavity (serosa). Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosa. Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue The cells are block like in cross section and hexagonal from a surface view with spherical central nuclei Found in many glands such as thyroid gland, salivary gland, pancreas, ovary surface, collecting tubes of the kidney and capsule surrounding the eye lens. Functions as secretion and absorption. 3
4 Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue Cells are elongated between their apical and basal surfaces with oval basal nuclei. When the free surfaces are observed, the cells have a prolonged configuration. Some secretory cells (goblet cells) may be present. They produce mucus (a protective glycoprotein). The cells of this tissue may have cilia on their free surfaces and hence they are known as ciliated. In other cases,-free surfaces have no cilia and hence they are known as plain or non-ciliated. Another modification of the free surface of the columnar cells is the presence of microvilli. These structures are seen as brush border when observed with light microscope under oil immersion. Columnar cells that line the small intestine and make up the wall of kidney collecting tubules exhibit distinct brush border. Function: Absorption, secretion of mucus enzymes and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by cilia action. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue Cells are varied in height. All cells rest on the basal lamina, but only the tallest reach the apical surface of the epithelium. Cell nuclei are located at different levels above the basal lamina, giving the false(pseudo) impression that several cell layers are present also Goblet cells are found. Two types are present: Plain type is found in parts of the male urethra and parotid gland. The ciliated type is more common and found in trachea, bronchi, auditory tube and part of middle ear. Function: secretion, particularly of mucus 4
5 Stratified epithelia Stratified epithelia consist of two (or more) cell layers: basal layer, (intermediate layer or layers) and superficial or apical layer. The basal cells divide by mitosis and push apically to replace the older apical cells. The nomination of stratified epithelia depends on shape of the cells in the apical layer. The following tissues are known: - Stratified squamous epithelial tissues (non-keratinized and keratinized) Stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue Stratified columnar epithelial tissue Transitional epithelial tissue The following is a brief account on description, function and location of the different stratified epithelia. Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissues These include non-keratinized and keratinized types. a) Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue composed of several layers: Basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active, intermediate cells are polyhedral and the apical cells are flattened (squamous). Location: Forms the moist linings of the mouth, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, vagina and cornea. Function: Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion. b) Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue The keratinized epithelium is a dry membrane represented by the epidermis of the skin, which is keratinized (its surface cells contain keratin, a tough protective protein). The epidermis consists of an outer region (many layers of scaly remains of dead epithelial cells known as stratum corneum), thin translucent layer (stratum lucidum), a darkly stained layer (stratum granulosum) and a mulitlayerd stratum spinosum. All these four layers of epidermis originate from the deepest layer of cells of the stratum spinosum. which is known as stratum basale or stratum germinativum. Function: Protects underlying tissue in area subjected to abrasion. 5
6 Non-keratinized S.S.E Keratinized S.S.E the epithelial cells lack protein keratin serves as a wet lining capable of withstanding moderate abrasive stresses. the epithelial cells contain keratin serves as a dry covering capable of withstanding severe abrasive stresses. epithelium is bathed by mucus the surface is free of mucus and dry 6
7 Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue This consists of two layers of cuboidal cells. Location: Large ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands and Salivary glands. Function: Protection Cuboidal layers nucleus lumen Stratified Columnar Epithelial Tissue This consists of several cell layers. The basal layer is usually cuboidal while the superficial columnar cells are variable in height. Location: Rare in the body; small amount in male urethra and large ducts of some glands. Function: Protection and secretion 7
8 Transitional Epithelial Tissue This tissue contains many layers of cells; the basal layer consists of cuboidal or columnar. The apical cells vary in appearance, depending on the degree of distension of the organ. When the organ is not stretched, the membrane is many layered and the superficial cells are rounded and dome like.when the organ is distended with urine, the epithelium thins (undergoes a transition) from about six cell layers to three, and it's apical cells flatten and become squamous like. The ability of transitional cells to change their shape allows a greater volume of urine to flow through a tube like organ. Location: Lines the ureter, urinary bladder and part of the urethra. Function: Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine. Glandular epithelium A gland consists of one or more cells that make and secrete a particular product. This product, called a secretion, is an water-based fluid that usually contains proteins. The term secretion can refer to the gland's product and the process of making and releasing that product. Through the embryonic development, glands develop by an invagination of the epithelial cells into connective tissue underlying an epithelial membrane. In exocrine glands (glands that secret their products through a duct), the site of the original invagination persists as the duct system, while in endocrine (ductless) glands; connection with the epithelial membrane is lost, so the secretion passes into a vascular system. Classification of Glands Glands can be classified according to the following criteria: 1- According to the number of their cells: - 8
9 A-Unicellular glands: Glands composed of one cell such as the goblet cells that scattered between simple epithelial cells or pseudostratified cells. Goblet cell is a cupshaped with flattened basal nucleus. It also has abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum and large Golgi apparatus.goblet cells produce mucin (a complex glycoprotein). Upon dissolving in water after its secretion, mucin forms mucus which is a slimy coating that protects and lubricates surfaces. B-Multicellular glands: Glands which are composed of many cells as in the majority of glands in human body. 2- According to the route of their product: Glands are either endocrine or exocrine. Endocrine glands: Also known as ductless glands. As these glands lose their ducts, they produce hormones directly into the blood or lymph. These include thyroid, adrenal...etc. Exocrine glands: These glands are composed of epithelial-derived duct and a secretory unit consisting of secretory cells. They secrete their products through their ducts onto body surface or into body cavity. These include sweat glands, sebaceous gland, salivary glands... etc. 3-According to structure of their ducts: compound. Exocrine glands are either simple or - Simple glands: Glands with single unbranched ducts as in sweat and sebaceous glands. - Compound glands: Glands with branched duct as in salivary and mammary glands 4-According to the structure of their secretory parts: The secretory-cells form one of the following structures :- 1-Tubular: The secretory cells form a tube. 2-Alveolar (acinar): The secretory cells form small, flask-like sac. 3-Tubuloalveolar: The glands contain both tubular and alveolar secretory units. 5- According to the structure of their ducts and secretory parts: The terms denoting duct and secretory part structure are combined to describe the whole gland in the following way Simple tubular Simple coiled tubular Simple branched tubular Simple alveolar Simple branched alveolar Compound tubular Compound alveolar Compound Tubuloalveolar 9
10 6- According to their mode of secretion: Glands are either: - A-Merocrine glands: Glands which secrete their products by exocytosis as they are produced. The secretory cells are not altered. These include pancreas, most sweat glands and salivary glands. B- Holocrine glands: Glands accumulate their products within them until they rupture. These cells are replaced by the division of the underlying cells as in the sebaceous glands. C- Apocrine glands: Glands of this type also accumulate their products, but in this case accumulation occurs only just beneath the free surface. Eventually, the apex of the cell pinches off and secretion is released. The cell repairs its damage and repeats the process again and again, as in the mammary glands. According to the nature of their secretion: Glands fall in three different types in this respect. 11
11 Serous cell glands: Serous alveoli are composed of serous cells which are pyramidal cells arranged around a small visible lumen. These cells have a small, round nucleus located in the basal zone of deeply basophilic cytoplasm and a lighter apical cytoplasm. Secretory granules (zymogen) are seen in the apical area. Their secretion is watery filled with zymogen. Their numbers vary with the state of cell activity. Myoepithelial (basket) cells lie between the basement lamina and the epithelial cells; usually the nucleus of basket cell is visible. Mucous cell glands: Mucous alveoli are larger than serous alveoli and more variable in size and shape. They are composed of often more columnar form of mucous cells,.with pale (almost colorless staining reaction), oval or flattened nuclei at the bases of the cells and somewhat larger, more apparent lumen. Sero-mucous cell glands (Mixed glands): Mixed alveoli are typically mucous alveoli surrounded by one or more groups of serous cells known as serous demilune or serous crescent. Basket cells are present, especially around the serous cells. In addition to the glandular epithelia, two other types of epithelial cells are known: - Myoepithelial cells: Branched cells that contain myosin and large number of actin microfilaments. They are specialized for contraction, mainly of the alveoli of mammary, sweat and salivary glands. Neuroepithelial cells: Cells of epithelial origin with specialized sensory function due to the presence of nerve endings in these cells as in the case of taste buds in the tongue. 11
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 CHAPTER4 I Tissue: The Living Fabric Chapter Outline and Student Objectives Preview of Selected Key Terms Epithelial Tissue (pp. 101-112) 1. List several characteristics that typify epithelial tissue.
CHAPTER4 I Tissue: The Living Fabric Chapter Outline and Student Objectives Preview of Selected Key Terms Epithelial Tissue (pp. 101-112) 1. List several characteristics that typify epithelial tissue.
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Laboratory 3 Histology
 Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Tissue: The Living Fabric Muscle Tissue (pp. 136 138)
 Preparing Human Tissue for Microscopy (pp. 11 115) Epithelial Tissue (pp. 115 12) Special Characteristics of Epithelium (pp. 115 116) Classification of Epithelia (pp. 116 121) Glandular Epithelia (pp.
Preparing Human Tissue for Microscopy (pp. 11 115) Epithelial Tissue (pp. 115 12) Special Characteristics of Epithelium (pp. 115 116) Classification of Epithelia (pp. 116 121) Glandular Epithelia (pp.
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The cells of the human body do not operate independently of
 4 Tissues I. Epithelial Tissue 65 Special Characteristics of Epithelia 66 Classification of Epithelia 66 Glands 72 Epithelial Surface Features 74 II. Connective Tissue 77 Special Characteristics of Connective
4 Tissues I. Epithelial Tissue 65 Special Characteristics of Epithelia 66 Classification of Epithelia 66 Glands 72 Epithelial Surface Features 74 II. Connective Tissue 77 Special Characteristics of Connective
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Small & Large Intestines
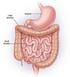 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams
 The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
Location: air sacs of lungs; nephrons of kidney; lining of circulatory system, lymphatic vessels, & ventral body cavity
 Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System Digestive Tract
 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Review of the Cell and Its Organelles
 Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Epithelial and Connective Tissues. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells
 Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Outline Digestive System
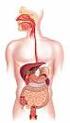 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
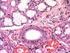 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
h. Large intestine 3
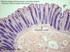 (1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
(1) General features (a) Large intestine is last organ of digestive tract proper divided into 3 or 4 regions cecum appendix in humans colon rectum 1 b) No villi lumenal epithelium has microvilli This brush
Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope
 Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope Robert Hooke = first to observe small compartments in dead
Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope Robert Hooke = first to observe small compartments in dead
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Date: Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George. Score: 1) A cell with 1% solute concentration is placed in a beaker with a 5% solute concentration.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
PCB 4023 Cell Biology. Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs
 PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin
 Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages. The Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipids. I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II.
 BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
