Earth Science Chapter 8 Section 2 Review
|
|
|
- Chrystal Roberta Williams
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 8 Section 2 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which seismic waves travel most rapidly? a. P waves c. surface waves b. S waves d. tsunamis 2. Which one of the following statements is true about P waves? a. They travel only through solids. b. They travel faster than S waves. c. They are the most destructive type of seismic wave. d. They cannot be recorded on a seismograph. 3. Which seismic waves compress and expand rocks in the direction the waves travel? a. P waves c. surface waves b. S waves d. transverse waves 4. What is the minimum number of seismic stations that is needed to determine the location of an earthquake s epicenter? a. two c. four b. one d. three 5. A travel-time graph can be used to find the. a. focus of an earthquake b. strength of an earthquake c. damage caused by an earthquake d. distance to the epicenter of an earthquake 6. An earthquake s magnitude is a measure of the. a. size of seismic waves it produces b. amount of shaking it produces c. number of surface waves it produces d. damage it causes 7. The scale most widely used by scientists for measuring earthquakes is the. a. seismic scale c. moment magnitude scale b. Richter scale d. epicenter magnitude scale 8. What instrument records earthquake waves? a. seismogram c. Richter scale b. seismograph d. barometer 9. The amount of shaking produced by an earthquake at a given location is called the. a. intensity c. epicenter b. magnitude d. Richter magnitude 1
2 Name: 10. The trace that records an earthquake from seismic instruments is called a. a. seismograph c. richtergram b. seismogram d. magnitude Completion Complete each statement. 11. The seismic waves that travel through Earth s interior are waves. Short Answer: ON THE TEST, you will have to complete TWO SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS from ALL of the short answer questions that appear in the chapter. 12. What are the three types of seismic waves? 13. If you know the distance of an earthquake epicenter from three seismic stations, how can you find the exact location of the epicenter of the earthquake? 14. Describe the two types of measurements scientists use to describe earthquakes. 2
3 Name: Essay: ON THE TEST, you will have to complete ONE ESSAY QUESTION from ALL of the essay questions that appear in the chapter. 15. Describe how the three different types of seismic waves move and affect the movement of the material they pass over or through. 3
4 Earth Science Chapter 8 Section 2 Review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: 8.6 COMPLETION 11. ANS: body PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: 8.4 SHORT ANSWER 12. ANS: surface waves, P waves, and S waves PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: On a map, draw a circle around each seismic station, making sure that the radius of each circle represents the distance of the epicenter from each station; the epicenter is the point where the three circles intersect. PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: ANS: Intensity is the amount of damage an earthquake causes at a particular location, and magnitude is a measure of the size of seismic waves or the amount of energy released at the source of the earthquake. PTS: 1 DIF: L1 OBJ: 8.6 1
5 ESSAY 15. ANS: Surface waves travel along Earth s surface and move the ground from side to side, and in an up-and-down motion. P waves travel through Earth s interior. P waves compress and expand material through which they pass in the direction the waves travel, producing a temporary volume change in the material as the waves pass. P waves create a back-and-forth motion along the surface that makes the ground buckle and crack. P waves can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. S waves also travel through Earth s interior and shake material at right angles to their direction of motion, temporarily changing the shape of the material they pass through and making the ground shake up-and-down and sideways. S waves can only travel through solids. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 8.4 2
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Topic Area: Circles. Definitions. Formulas Distance Formula: D = ( x x ) + ( y ) Equation of a Circle: Activity 8 Algebra II with the Casio fx-9750gii
 Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
Seismographs. Lesson 7. Seismographs recording activity on Kilauea
 Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level
 Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
How do scientists measure earthquakes?
 Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata
 Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Geology 112 Earthquakes. Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake?
 Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Earthquake Magnitude
 Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1
 Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Earthquake Lab. A. Locate the Epicenter. Name: Lab Section:
 Earthquake Lab Name: Lab Section: The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand
Earthquake Lab Name: Lab Section: The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
Review 1. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei a. the nuclei die. c. particles collide. b. energy
Review 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei a. the nuclei die. c. particles collide. b. energy
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
Shake, Rattle, and Roll. Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
Name: Period: # Plate Tectonics. Journey to the center of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior
 Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earthquakes. Was anyone hur t? 358 Chuck Nacke/TimeLife Pictures/Getty Images
 Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 04/30/2008 Today s
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 04/30/2008 Today s
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Curriculum Map Earth Science - High School
 September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Shaky Ground 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake
 Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface
 PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. I - Earthquake Parameters Including Strong Earthquakes- S.L.Yunga EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES
 EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Layers of the Earth s Interior
 Layers of the Earth s Interior 1 Focus Question How is the Earth like an ogre? 2 Objectives Explain how geologists have learned about the interior of the Earth. Describe the layers of the Earth s interior.
Layers of the Earth s Interior 1 Focus Question How is the Earth like an ogre? 2 Objectives Explain how geologists have learned about the interior of the Earth. Describe the layers of the Earth s interior.
A G U / F E M A 142 S E I S M I C S L E U T H S
 U N I T T H R E E 3 I N T R O D U C T I O N In the first lesson, students will learn about the movement of earthquake waves in our Earth and on its surface. It was the study of this movement, by Mohorovicic,
U N I T T H R E E 3 I N T R O D U C T I O N In the first lesson, students will learn about the movement of earthquake waves in our Earth and on its surface. It was the study of this movement, by Mohorovicic,
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Test 2 f14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Carbon cycles through the Earth system. During photosynthesis, carbon is a. released from wood
Test 2 f14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Carbon cycles through the Earth system. During photosynthesis, carbon is a. released from wood
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES
 DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
Name: Class: Date: 10. Some substances, when exposed to visible light, absorb more energy as heat than other substances absorb.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A PS Chapter 13 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. In all cooling
Name: Class: Date: ID: A PS Chapter 13 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. In all cooling
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet
 Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02
 Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA
 B SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA The Working Group on Magnitudes (Magnitude WG) of the International Association of Seismology
B SUMMARY OF MAGNITUDE WORKING GROUP RECOMMENDATIONS ON DETERMINING EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDES FROM DIGITAL DATA The Working Group on Magnitudes (Magnitude WG) of the International Association of Seismology
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Balanced & Unbalanced Forces
 3 rd Grade Force in Motion An object's motion changes because of force. Pushing and Pulling are Kinds of Forces Motion is movement that changes an object's position. Pushing or pulling forces can be used
3 rd Grade Force in Motion An object's motion changes because of force. Pushing and Pulling are Kinds of Forces Motion is movement that changes an object's position. Pushing or pulling forces can be used
Earth Science Chapter 14 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
COSMOS 2012: Earthquakes in Action COSMOS 2012
 COSMOS 2012 What is SFSI and why is it important? Soil issues in Earthquakes Structures where SFSI important Retaining structures (lateral earth pressure) Foundations (spread and pile footings, bearing
COSMOS 2012 What is SFSI and why is it important? Soil issues in Earthquakes Structures where SFSI important Retaining structures (lateral earth pressure) Foundations (spread and pile footings, bearing
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies
 Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Project Report. Structural Investigations Hotel del Sol Yuma, Arizona
 Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues
 Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
After a wave passes through a medium, how does the position of that medium compare to its original position?
 Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK
 SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
SESSION III HAZARD MAPPING, RISK ASSESSMENT, AND INSURANCE COVERAGE OF NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISK Mr. Sumarjono Insurance Bureau of The Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Geological Position
Exponent Law Review 3 + 3 0. 12 13 b. 1 d. 0. x 5 d. x 11. a 5 b. b 8 a 8. b 2 a 2 d. 81u 8 v 10 81. u 8 v 20 81. Name: Class: Date:
 Name: Class: Date: Eponent Law Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question The epression + 0 is equal to 0 Simplify 6 6 8 6 6 6 0 Simplify ( ) (
Name: Class: Date: Eponent Law Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question The epression + 0 is equal to 0 Simplify 6 6 8 6 6 6 0 Simplify ( ) (
Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6 Created by: Debra McKey (Mountain Vista Middle School); Valerie Duncan (Upper Lake Middle School); and Lynn Chick (Coyote Valley
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6 Created by: Debra McKey (Mountain Vista Middle School); Valerie Duncan (Upper Lake Middle School); and Lynn Chick (Coyote Valley
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: [email protected] 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity
 Name: Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity Materials: Tape Measure, Stopwatch, & Calculator. In this activity, we will explore wave properties using the Giant Slinky. Let s start by describing the
Name: Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity Materials: Tape Measure, Stopwatch, & Calculator. In this activity, we will explore wave properties using the Giant Slinky. Let s start by describing the
Monday 11 June 2012 Afternoon
 Monday 11 June 2012 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) G495 Field and Particle Pictures *G412090612* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
Monday 11 June 2012 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICS B (ADVANCING PHYSICS) G495 Field and Particle Pictures *G412090612* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
Name Date Class STATES OF MATTER. SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 385 389)
 13 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 385 389) This section introduces the kinetic theory and describes how it applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature
13 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 385 389) This section introduces the kinetic theory and describes how it applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Multiple Choice For questions 1-10, circle only one answer.
 Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics}
![[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} [Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics}](/thumbs/40/21755359.jpg) [Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} BACKGROUND Scientists and geologists have been able to do some drilling on Earth. They are also able
[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} BACKGROUND Scientists and geologists have been able to do some drilling on Earth. They are also able
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
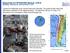 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS
 CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales
 Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
GEOMETRY B: CIRCLE TEST PRACTICE
 Class: Date: GEOMETRY B: CIRCLE TEST PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measures of the indicated angles. Which statement
Class: Date: GEOMETRY B: CIRCLE TEST PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measures of the indicated angles. Which statement
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3
 Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Earth Science Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion Reading Comprehension. Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion
 Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid.
 Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
Fluid Statics When the fluid velocity is zero, called the hydrostatic condition, the pressure variation is due only to the weight of the fluid. Consider a small wedge of fluid at rest of size Δx, Δz, Δs
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science Grade 6. Unit Organizer: UNIVERSE AND SOLAR SYSTEM (Approximate Time 3 Weeks)
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8
 Science and Technology Chapter 1. What Is Science? 1. Science and the Natural World 2.Thinking Like a Scientist 3. Scientific Inquiry Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8 Chapter 2. Science,
Science and Technology Chapter 1. What Is Science? 1. Science and the Natural World 2.Thinking Like a Scientist 3. Scientific Inquiry Scope and Sequence Interactive Science grades 6-8 Chapter 2. Science,
Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect
 Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant:
 12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
12.1: Tangent Lines Congruent Circles: circles that have the same radius length Diagram of Examples Center of Circle: Circle Name: Radius: Diameter: Chord: Secant: Tangent to A Circle: a line in the plane
v = fλ PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to :
 PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
1. The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of atoms and molecules that are in a constant state of constant random motion
 Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
