EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
|
|
|
- Claud Chambers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such as the area called the Ring of Fire around the Pacific Rim. At plate boundaries the pressures can be compressional, tensional, or slip-strike faults where plates move past each other. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike For instance, the recent earthquake in the Los Angeles area was along a compressional thrust fault deep in the earth, a side effect of the main San Andreas slip-strike fault movements. The San Andreas Fault marks movement of the North American plate against the Pacific plate, which southern California and Baja California are attached to. These areas are essentially on their way to Alaska, while the rest of the U.S. is moving westerly. Earthquakes start at a focus, a point in the earth where the break starts. We calculate this point reflected on the earth s surface as the epicenter, by calculating the distance to the earthquake epicenter from three seismographs, the epicenter being where the distance circles cross each other. Earthquake waves (seismic waves) come as surface or body waves, that is they travel on the earth s surface or through the earth. Primary (P) waves, a body wave, arrive first, followed by the Secondary (S) wave, and then the surface waves on a seismograph. Damage from earthquake waves is caused by the effect at your location of the combination of the waves and the time the earthquake lasts. The longer the quake, the more damage. The closer to the epicenter usually implies more damage. The immediate damage is from shaking side to side, although tall buildings will have a vertical acceleration component also. The safest building is a single story frame house that does not have a tile roof.
2 Earthquakes-page 2 Other dangers from earthquakes are fires, ground failure, and the resultant landslides and tsunamis near the ocean. In fact, fire and the inability to put them out often causes the most loss of property from and earthquake. Earthquake power is measured by the Richter scale, which measures the size of the wave on a seismograph. On this scale, each whole number means a 10X greater amplitude and 30X greater release of energy. This is why a 5.0 is a minor shaking, and a 7.0 can cause major damage. (The 7.0 has a 100X greater amplitude and a 900X greater energy release than the 5.0.) We will now do a lab exercise to locate the epicenter of an earthquake and time of occurrence by working with seismographic records and a time travel graph.
3 Earthquakes-page 3 EARTHQUAKE RECORDS The earth is continually undergoing change due to stresses that exist within. At least a million times each year the earth suddenly fractures and the seismic waves of an earthquake radiate in all directions from the focus. Seismograph stations located throughout the world record these waves on seismograms. In this exercise we will examine how seismograms are used to determine the time of occurrence and location of an earthquake. Examining Seismograms The three basic types of waves produced by earthquakes are: P waves, S waves, and Surface waves. P waves travel most rapidly, therefore, they reach the seismograph station first. Examine Diagram 1, which is a typical seismogram. The dots on this seismogram mark time intervals of one minute. Answer the following two questions by referring to Diagram How many minutes elapsed between the arrival of the first p-wave and the arrival of the first S-wave? 2. How many minutes elapsed between the arrival of he first S-wave and the first surface wave? _
4 Earthquakes-page 4 Locating An Earthquake The difference in the velocities of the P and S waves provides a method for determining the distance to the location of the earthquake or epicenter. The principle used is analogous to a race between two autos, one faster than the other. The greater the distance of the race, the greater will be the difference in the arrival times at the finish line. 1. From the seismogram in Diagram 1, you should have determined that the arrival times of the first P and S waves differed by 4 minutes. Using the travel-time graph, determine the distance to the epicenter in this instance. This is done by finding the place on the graph where the vertical separation between the P and S lines is equal to 4 minutes (one square on the graph is one minute). Draw a vertical line at this location extending to the bottom of the graph. Label the line Bloomington. The distance to the earthquake in degrees can be read directly below your line. Answer = degrees (Have your answer checked before you continue.) 2. Using your answer from number 1 above, calculate how many kilometers to the earthquake epicenter. (One degree = 111 km or 69 Miles) km miles 3. The time travel graph can also be used to determine the time required for seismic waves to reach a seismograph station. Note on the time-travel graph that time is given on the vertical axis. Thus, for the example you did above, the first P-wave required 5 minutes and 15 seconds to reach the seismograph. This is determined by finding the place where the Bloomington line crossed the P-wave curve, and reading this value from the vertical axis. How many minutes were required for the first S-wave to reach the seismic station? _ minutes 4. In question #2 you determined the distance from an earthquake to a seismograph station. However, all we know is that the earthquake
5 Earthquakes-page 5 occurred somewhere along a circle, a given number of kilometers away. Records from three different seismograph stations are needed to more accurately locate an earthquake. In the following exercises you will interpret three seismograms in order to determine the location of an earthquake. a. On Diagram 3, label the arrival of the first P-wave and the first S- wave on each seismogram. b. In each case, how much time elapsed between the arrival of the first P-wave and the first S-wave? (Determine to the nearest ½ minute.) Nagpur Darwin Paris minutes minutes minutes c. Using the time-travel graph determine the distance to the epicenter from each seismograph station. Draw a line on the graph representing each situation and label each line with the city s name. Nagpur Darwin Paris DISTANCE degrees km miles degrees km miles degrees km miles d. Using the world map provided, determine the location of the earthquake epicenter. Do this by drawing three circles (one from each seismic station) using the distances from part c. Use the scale on the side of the map and a drawing compass to make your circles. In what country was the earthquake located? What is the approximate latitude and longitude of the earthquake epicenter?
6 Earthquakes-page 6 5. Next we will determine the time of origin of this earthquake. Each seismogram has a time designated on it. (9:43 GMT means 9 hours, 43 minutes, Greenwich Mean Time.) a. For Nagpur, India, note the time of the arrival of the first P-wave. b. Using the time-travel graph, determine the time required for the first P-wave to travel from the epicenter to the seismograph. c. Determine the time of the occurrence of the earthquake by taking the arrival time of the first P-wave minus the time required for the wave to reach the recording instrument. 6. Using the data for Darwin, determine the time of origin of the earthquake. a. For Darwin, note the time of arrival of the first P-wave. b. Using the time-travel graph, determine the time required for the first P-wave to travel from the epicenter to the seismograph. c. Determine the time of the occurrence of the earthquake by taking the arrival time of the first P-wave minus the time required fort he wave to reach the recording instrument.
7 Earthquakes-page 7 d. Does the time of the occurrence of the earthquake determined for Darwin agree with that determined for Nagpur? YES NO (circle one) Should they agree? YES NO (circle one) EXTRA CREDIT Determine the velocity of the wave from Darwin in feet per second and meters per second. We already have a value in miles per minute derived from how far the wave traveled and how long it took. Velocity of wave m/sec Velocity of wave ft/sec
8 Earthquakes-page 8
9 Earthquakes-page 9
10 Earthquakes-page 10
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level
 Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Earthquake Lab. A. Locate the Epicenter. Name: Lab Section:
 Earthquake Lab Name: Lab Section: The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand
Earthquake Lab Name: Lab Section: The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand
How do scientists measure earthquakes?
 Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Name: Source: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=4892 http://gizmodo.com/5833688/what-do-earthquake-magnitudes-mean http://www.kids-fun-science.com/moment-magnitude-scale.html http://tremor.nmt.edu/faq/how.html
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS
 Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS Student worksheet Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO master teacher; Andy Newman, Georgia Institute of Technology; Shelley Olds, UNAVCO; and revised by
Exploring plate motion and deformation in California with GPS Student worksheet Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO master teacher; Andy Newman, Georgia Institute of Technology; Shelley Olds, UNAVCO; and revised by
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Geology 112 Earthquakes. Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake?
 Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
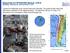 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008
 Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Tsunami Practice Questions and Answers Revised November 2008 1. What happened on 26 December 2004 off the west coast of Sumatra? 2. What is the final estimate of the magnitude of the Sumatra 26 December
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata
 Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Inside Earth Chapter 3
 Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics
 Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 [email protected] Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 [email protected] Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1
 Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
Magnitude calculator for the AS-1 Page 1 of 23 Earthquake Magnitude Calculator for the AS-1 Seismograph 1 Lawrence W. Braile and Saptarshi Dasgupta, Purdue University SKIP TO CALCULATORS Introduction:
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 04/30/2008 Today s
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 04/30/2008 Today s
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet
 Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
Seismographs. Lesson 7. Seismographs recording activity on Kilauea
 Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle
 EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle Grades 3 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness. The
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #1 Tsunami in a Bottle Grades 3 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness. The
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest
 Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A137270613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Thursday 23 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A137270613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
SPEED, VELOCITY, AND ACCELERATION
 reflect Look at the picture of people running across a field. What words come to mind? Maybe you think about the word speed to describe how fast the people are running. You might think of the word acceleration
reflect Look at the picture of people running across a field. What words come to mind? Maybe you think about the word speed to describe how fast the people are running. You might think of the word acceleration
Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located.
 What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
Curriculum Map Earth Science - High School
 September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
September Science is a format process to use Use instruments to measure Measurement labs - mass, volume, to observe, classify, and analyze the observable properties. density environment. Use lab equipment
Layers of the Earth s Interior
 Layers of the Earth s Interior 1 Focus Question How is the Earth like an ogre? 2 Objectives Explain how geologists have learned about the interior of the Earth. Describe the layers of the Earth s interior.
Layers of the Earth s Interior 1 Focus Question How is the Earth like an ogre? 2 Objectives Explain how geologists have learned about the interior of the Earth. Describe the layers of the Earth s interior.
Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra
 Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Topic Determination of source parameters from seismic spectra Authors Michael Baumbach, and Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany); E-mail: [email protected]
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Shaky Ground 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave?!does the object accelerate, or is the speed constant?!do two objects behave
Chapter 3 Falling Objects and Projectile Motion Gravity influences motion in a particular way. How does a dropped object behave?!does the object accelerate, or is the speed constant?!do two objects behave
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
FOR TEACHERS ONLY. The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/EARTH SCIENCE
 FOR TEACHERS ONLY PS ES The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/EARTH SCIENCE Tuesday, June 22, 2010 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING
FOR TEACHERS ONLY PS ES The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING/EARTH SCIENCE Tuesday, June 22, 2010 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only SCORING KEY AND RATING
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3
 Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Lines of Latitude and Longitude
 ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
ED 5661 Mathematics & Navigation Teacher Institute Keith Johnson Lesson Plan Lines of Latitude and Longitude Lesson Overview: This lesson plan will introduce students to latitude and longitude along with
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
Shake, Rattle, and Roll. Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
ABSG Consulting, Tokyo, Japan Email: [email protected] 2. Professor, Kogakuin University, Tokyo, Japan 3
 Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Application of Earthquake Early Warning System and Real-time Strong-motion Monitoring System to Earthquake Disaster Mitigation of a High-Rise Building in Tokyo, Japan Tomohiro Kubo 1, Yoshiaki Hisada 2,
Storms Assessment LESSON
 LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
Earthquakes. Was anyone hur t? 358 Chuck Nacke/TimeLife Pictures/Getty Images
 Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
SMIP2000 Seminar Proceedings COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER. Ralph Archuleta
 COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
COSMOS VIRTUAL STRONG MOTION DATA CENTER Ralph Archuleta Institute for Crustal Studies & Department of Geological Sciences University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT The COSMOS virtual data center
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
Earthquake Magnitude
 Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Which month has larger and smaller day time?
 ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
ACTIVITY-1 Which month has larger and smaller day time? Problem: Which month has larger and smaller day time? Aim: Finding out which month has larger and smaller duration of day in the Year 2006. Format
Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational field strength at the surface of the Earth is approximately 10 N kg 1.
 IB PHYSICS: Gravitational Forces Review 1. This question is about gravitation and ocean tides. (b) State Newton s law of universal gravitation. Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational
IB PHYSICS: Gravitational Forces Review 1. This question is about gravitation and ocean tides. (b) State Newton s law of universal gravitation. Use the following information to deduce that the gravitational
Plate Tectonics Lab. Continental Drift. The Birth of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Plotting Earthquakes LESSON
 13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers.
 1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
circular motion & gravitation physics 111N
 circular motion & gravitation physics 111N uniform circular motion an object moving around a circle at a constant rate must have an acceleration always perpendicular to the velocity (else the speed would
circular motion & gravitation physics 111N uniform circular motion an object moving around a circle at a constant rate must have an acceleration always perpendicular to the velocity (else the speed would
Ring of Fire. (15 minutes) Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other.
 Ring of Fire Lesson Concept Link Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other. Lesson 6.12 develops concepts about preparation for earthquakes in terms of home or school damage or lack
Ring of Fire Lesson Concept Link Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other. Lesson 6.12 develops concepts about preparation for earthquakes in terms of home or school damage or lack
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES
 DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales
 Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Activity 10 - Universal Time
 Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Activity 10 - Universal Time Teacher s Guide Scientists use the Universal Time reference to talk about data that is taken around the globe. Universal Time is the time kept in the time zone centered on
Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks
 Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
Vol. 1, 005 CSA Academic Perspective 0 Seismic Analysis and Design of Steel Liquid Storage Tanks Lisa Yunxia Wang California State Polytechnic University Pomona ABSTRACT Practicing engineers face many
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
Topic Area: Circles. Definitions. Formulas Distance Formula: D = ( x x ) + ( y ) Equation of a Circle: Activity 8 Algebra II with the Casio fx-9750gii
 Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones
 Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Latitude, Longitude, and Time Zones Typical Graph This is an example of a typical graph. It is made up of points that are connected by a line. Y axis Typical Graph Each point has two values: (4,7) An X
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS
 CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
CHAPTER 6 THE TERRESTRIAL PLANETS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages in the development of a terrestrial planet? 2. That Earth, evidence that Earth differentiated.
Friday 20 January 2012 Morning
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Friday 20 January 2012 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A131500112* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Friday 20 January 2012 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE PHYSICS A A181/02 Modules P1 P2 P3 (Higher Tier) *A131500112* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
Solar System. 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X?
 Solar System 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X? A) Earth B) Sun C) Moon D) Polaris 2. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered
Solar System 1. The diagram below represents a simple geocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X? A) Earth B) Sun C) Moon D) Polaris 2. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered
Tallahassee Community College PERIMETER
 Tallahassee Community College 47 PERIMETER The perimeter of a plane figure is the distance around it. Perimeter is measured in linear units because we are finding the total of the lengths of the sides
Tallahassee Community College 47 PERIMETER The perimeter of a plane figure is the distance around it. Perimeter is measured in linear units because we are finding the total of the lengths of the sides
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Brief Review of Global Earth Velocity Structures and Seismology
 Class 1: Introduction to Seismic Wave Propagation Wed, Sept 9, 2009 Today we are going to discuss about the following issues: Brief review of global Earth structures and seismology Near-surface geology
Class 1: Introduction to Seismic Wave Propagation Wed, Sept 9, 2009 Today we are going to discuss about the following issues: Brief review of global Earth structures and seismology Near-surface geology
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake
 Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Speed A B C. Time. Chapter 3: Falling Objects and Projectile Motion
 Chapter 3: Falling Objects and Projectile Motion 1. Neglecting friction, if a Cadillac and Volkswagen start rolling down a hill together, the heavier Cadillac will get to the bottom A. before the Volkswagen.
Chapter 3: Falling Objects and Projectile Motion 1. Neglecting friction, if a Cadillac and Volkswagen start rolling down a hill together, the heavier Cadillac will get to the bottom A. before the Volkswagen.
Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1)
 Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1) In discussing motion, there are three closely related concepts that you need to keep straight. These are: If x(t) represents the
Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1) In discussing motion, there are three closely related concepts that you need to keep straight. These are: If x(t) represents the
