How do scientists measure earthquakes?
|
|
|
- Briana Dennis
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Source: How do scientists measure earthquakes? An earthquake, one of the most dreaded natural disasters, occurs as a result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth s crust creating seismic waves. We all are aware of the fact that high-intensity earthquakes can result in a massive destruction of life and property. 1. Predict: How are earthquakes detected and measured? Earthquakes are detected using a seismometer. A seismometer, also known as a seismograph, is an instrument that records movements of the ground. It is used to detect seismic waves generated by earthquakes. A seismoscope can also be used for the detection of underground movements. It indicates that motion has occurred, but does not give a continuous record of the ground movements. Think of a seismograph as a kind of sensitive pendulum that records the shaking of the Earth. The output of a seismograph is known as a seismogram. In the early days, seismograms were produced using ink pens on paper or beams of light on photographic paper, but now it's most often done digitally using computers. 2. Sketch a pendulum instrument that could record the movement of the Earth s surface.
2 There are two ways in which scientists quantify the size of earthquakes: magnitude and intensity. Magnitude is a measure of the amount of energy released during an earthquake, and you've probably heard news reports about earthquake magnitudes measured using a scale. Something like, "A magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck Japan today. Details at ten." Did you ever wonder why, if it's that important, they just don't tell you right away? 3. Why is there a delay in the information? The Richter scale was invented, in the 1930s by Dr. Charles Richter, a seismologist at the California Institute of Technology. It is a measure of the largest seismic wave recorded on a particular kind of seismograph located 100 kilometers (about 62 miles) from the epicenter of the earthquake and was a way for scientists to compare earthquakes of different sizes. 4. What is the root word, prefixes/suffixes in seismologist, that help us determine the meaning of the word? The reason the Richter scale was so popular was that the earthquake's magnitude could be determined by looking at the largest wave recorded on a seismogram right after the earthquake. News stories about the size of the earthquake could then be quickly given to the public on the radio and television stations.
3 Richter scale's faults So what's wrong with the good old Richter scale? Nothing, really. It was a great tool for its time. But like last year's computer, it's been nudged aside by new technology. It isn't straightforward, like a ruler, but logarithmic. In theory, for each increase of one full point on the Richter scale, the ground shakes 10 times harder, and 32 times as much energy is released. The Richter magnitude is based on the size of the largest waves arriving at a particular type of instrument, the Wood Anderson seismograph. It's known as a local magnitude scale because it considers only waves arriving within 370 miles of the epicenter -- the spot on the ground directly above where the earthquake started. If there are no instruments within this distance, the size is estimated from readings taken closer and farther away. However, each earthquake is a rich blend of seismic waves. If you imagine the ground as the surface of a sea, these waves range from ripples to choppy whitecaps to long, slow swells.the Richter scale measures only the chop -- high-frequency waves that travel through the body of the rock, rather than at the surface. These are the ones most damaging to small structures, from homes to buildings a few stories tall. But the bigger the earthquake, the more long, slow waves it produces. In fact, this turns out to be a key difference between major earthquakes and the more moderate kind. The big ones don't necessarily shake the ground 10 times harder; but they do shake it longer, and they put out more long, slow swells of the type that can resonate with -- and damage -- big structures like high-rises and bridges. When it came to measuring these big earthquakes, the Richter scale fell short. So more than a decade ago, scientists started to use the moment magnitude scale. It's based on the full range of waves coming from an earthquake, including those that take up to 100 seconds to pass a given spot. This type of analysis has made possible for new seismic instruments that capture everything instead of only part of the energy released. 5. Why is the Richter scale no longer used? Explain your answer using evidence from the text. (Hint: There should be 3 reasons)
4 Moment Magnitude Scale Measures Great Earthquakes The moment magnitude scale (MMS) was devised by scientists after the 1960 Chilean earthquake and the 1964 Alaskan earthquake that were so large that the Richter scale did not adequately show the magnitude and size of what happened during these great earthquakes of the last century. The moment magnitude scale includes the area of the fault's rupture and slippage along the fault. It also includes the size of the seismic waves recorded on the seismograms. Today the MMS is used to estimate the magnitudes for all moderate to large earthquakes. Other scales are used for earthquakes less than 3.5 magnitude, which is the majority of earthquakes felt worldwide. 6. What incident led scientists to develop a new scale? Why? The MMS measures movement in three directions: north/south, east/west and, and vertical (up/down). Like the Richter scale, it's logarithmic, which, in English means that a small numeric bump equates to a serious increase in the violence with which the Earth shakes. It works in orders of magnitude where a 5.0 earthquake is not 20% stronger than a 4.0 quake; it is 10 times as strong One-thousand percent. There is a massive difference between a 6.0 and a 7.0 quake. 7. Explain the difference between a 4.0 and 5.0 earthquake.
5 The MMS measures the total energy of an earthquake, called the seismic moment. The seismic moment of an earthquake is determined based on three factors. The first factor is the distance that rock slides along a fault surface after it breaks, called the fault slip. The second factor is the area of the fault surface that is actually broken by the earthquake. And the third factor is the measurement of how rigid the rocks are near the broken fault. A strong rock, such as granite, cannot be broken easily. That makes it a highly rigid rock. 8. Make a list and sketch each of the three factors that determines the seismic moment. The most powerful seismic moment ever measured registered a 9.5 on the MMS it happened when an earthquake struck just off the coast of Chile on May 22, Here is an approximate and basic description of what happens when earthquakes of different strengths strike. You ll notice that the higher the number gets, the worse the damage becomes. 9.0 and above Causes complete devastation and large-scale loss of life. 8.0 Very few buildings stay up. Bridges fall down. Underground pipes burst. Railroad rails bend. Large rocks move. Smaller objects are tossed into the air. Some objects are swallowed up by the earth. 7.0 It is hard to keep your balance. The ground cracks. Roads shake. Weak buildings fall down. Other buildings are badly damaged. 6.0 Pictures can fall off walls. Furniture moves. In some buildings, walls may crack. 5.0 If you are in a car, it may rock. Glasses and dishes may rattle. Windows may break. 4.0 Buildings shake a little. It feels like a truck is passing by your house. 3.0 You may notice this quake if you are sitting still, or upstairs in a house. A hanging object, like a model airplane, may swing. 2.0 Trees sway. Small ponds ripple. Doors swing slowly. But you can't tell that an earthquake is to blame. 1.0 Earthquakes this small happen below ground. You can't feel them.
6 9. At what number would expect some casualties? Explain your answer. What if the earthquake was in Indonesia instead of in the United States, would there be the same number of casualties? Why or Why not? Reassessing quakes For instance, the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska both had surface-wave magnitudes of 8.3. Yet the Alaskan quake involved a much bigger fault and released 100 times as much energy, so when the more accurate moment magnitude scale came along, San Francisco was downgraded to 7.8, and the Alaskan quake was boosted to 9.2. The 1989 Loma Prieta quake was demoted, too. Its official surface-wave magnitude is 7.1, but on the moment scale it's only a 6.9. After the 1960 Chile earthquake the Richter scale registered the earthquake size at 8.5 magnitude. Scientists using the MMS revised the earthquakes size up to a 9.5, the highest ever recorded since seismographs were invented. 10. Why are some earthquakes being reduced while others are increased on the scale?
7 This is a comparison between the two scales for four other large earthquakes that occurred in the past. New Madrid, MO Richter scale MMS 8.1 San Francisco, CA Richter scale MMS 7.7 Prince William, AK Richter scale MMS 9.2 Northridge, CA Richter scale MMS 6.7 Five earthquakes of magnitude 9 or above have been recorded during the past 45 years, which averages out to one every decade. It turns out that earthquake occurrences seem to follow what is called a power-law distribution, meaning that if there is on average on magnitude 9 earthquake every ten years somewhere in the world, then on average there should be one magnitude 8 earthquake every year, 10 magnitude 7 earthquakes every year, and 100 magnitude 6 earthquakes every year. So, if someone "predicts" that a magnitude 6 earthquake will occur somewhere in the world during the next week, don't be too impressed if it happens because random probability tells us that there should be a magnitude 6 earthquake somewhere in the world every 365/100 = 3.65 days! In reality, things are a little more complicated. But, you get the picture. 11. What is your opinion of this data? Give details to support this data or argue it.
Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet
 Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Example Answers Name: Date: Class: Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes Worksheet Objective: To use seismic data and an interactive simulation to triangulate the location and measure the magnitude
Unit 4 Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
Shake, Rattle, and Roll What happens during an earthquake? As plates of the lithosphere move, the stress on rocks at or near the edges of the plates increases. This stress causes faults to form. A fault
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey
 The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
The Severity of an Earthquake - ---- U.S. Department of the Interior/Geological Survey ----~ Earthquakes can be measured in terms of either the effect of the earthquake (intensity) or of the energy released
Earthquakes. Earthquakes: Big Ideas. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
Earthquakes Earthquakes: Big Ideas Humans cannot eliminate natural hazards but can engage in activities that reduce their impacts by identifying high-risk locations, improving construction methods, and
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
The earthquake source
 Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
Global seismology: The earthquake source Reading: Fowler p111-140 and Bolt Appendix G Earthquake location Earthquake focus: Latitude, longitude, depth Earthquake epicenter: Latitude, longitude Earthquakes
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Locating the Epicenter and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake
 Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Locating the and Determining the Magnitude of an Earthquake Locating the Measuring the S-P time interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues
 Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
Earthquakes: Risk & Insurance Issues An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock beneath the earth s surface. This shaking can sometimes trigger
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE
 EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE Earliest measure of earthquake size Dimensionless number measured various ways, including M L local magnitude m b body wave magnitude M s surface wave magnitude M w moment magnitude
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude
 Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude Locating Earthquakes Last time, we learned that we could obtain a rough estimate of the distance in miles to an earthquake epicenter by multiplying the S - P time interval
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level
 Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
Activity #1-HS What is a Seismometer? High School Level Objective Students will learn that a seismometer detects 3 components of motion and that a seismogram is the record of an earthquake. Background
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake
 Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Evaluating an Illinois Earthquake Grade Level: 7-8 Adapted from an activity by Robert A. Bauer, GeoActivity HAZD-1, ISGS GeoActivities Series, Activities and Other Resources for Teaching Geology, Illinois
Seismographs. Lesson 7. Seismographs recording activity on Kilauea
 Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Seismographs Lesson 7 E arthquakes generate seismic waves that travel all around the world and can be detected by sensitive instruments called seismographs. The earliest instrument to detect earthquakes
Seismic Waves Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows models of two types of earthquake waves. Model A best represents the motion of earthquake waves called 1) P-waves (compressional
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
Plotting Earthquakes LESSON
 13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
13 LESSON Plotting Earthquakes INTRODUCTION On September 19, 1985, a strong earthquake occurred in Mexico City. The quake killed more than 9000 people and destroyed thousands of buildings. Two months later,
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
89.325 Geology for Engineers Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk
 Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
Earthquakes www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. There are around 100 earthquakes each year of a size that could cause serious damage. They strike
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale
 EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale All Grades 4 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness.
EARTH SCIENCE ACTIVITY #5 The Mercalli Scale All Grades 4 and Up This activity is one of several in a basic curriculum designed to increase student knowledge about earthquake science and preparedness.
Earthquakes. www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk. Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey
 Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
Seismograph stations operated by the British Geological Survey Earthquakes Photograph supplied by Andy Thompson, Arup Advanced Technology, EEFIT Mission www.earthquakes.bgs.ac.uk Introduction Earthquakes
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies
 Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Earthquake Preparedness Tips & Strategies What to Do BEFORE an Earthquake What to Do DURING an Earthquake BE PREPARED! For more information, log onto: www.gema.ga.gov www.ready.ga.gov www.geophysics.eas.gatech.edu
Earthquake Magnitude
 Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude Earthquake magnitude scales: Logarithmic measure of earthquake size amplitude of biggest wave: Magnitude 6 quake 10 * Magnitude 5 energy: Magnitude 6 quake is about 32 * Magnitude
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them
 Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
Five reasons buildings fail in an earthquake and how to avoid them by Jeff White, AIA Published in Healthcare Design magazine There s a saying among seismologists: Earthquakes don t kill people. Buildings
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
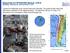 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION
 Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Lecture 15 Earthquake Prediction EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION To successfully predict an earthquake we would like to know:- PLACE TIME MAGNITUDE (rather like a weather forecast) 1 Evidence must be integrated
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Mitigation Works. 0 Earthquakes move mountains. But so do imagination and ingenuity when matched with implementation.
 0 Earthquakes move mountains. But so do imagination and ingenuity when matched with implementation. 0 Earthquakes have long been feared as one of nature s most damaging hazards. Earthquakes continue to
0 Earthquakes move mountains. But so do imagination and ingenuity when matched with implementation. 0 Earthquakes have long been feared as one of nature s most damaging hazards. Earthquakes continue to
EARTHQUAKE. Definition of Hazard. History of Hazard as it Affects the City of Kent. Hazard Identification
 EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
EARTHQUAKE Definition of Hazard Earthquakes are defined as the sudden release of energy occurring from the collision or shifting of crustal plates on the earth s surface or from the fracture of stressed
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet
 Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
Reading GPS Time Series Plots Worksheet By: Roger Groom and Cate Fox-Lent, UNAVCO Master Teachers in-residence, Shelley Olds, UNAVCO The Global Positioning System, GPS, is used to study the Earth, how
1 Branches of Earth Science
 CHAPTER 1 1 Branches of Earth Science SECTION The World of Earth Science BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four major branches of Earth
CHAPTER 1 1 Branches of Earth Science SECTION The World of Earth Science BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the four major branches of Earth
Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues
 Page 1 of 8 HOT TOPICS & INSURANCE ISSUES Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues THE TOPIC JULY 2003 An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock
Page 1 of 8 HOT TOPICS & INSURANCE ISSUES Earthquakes: Risk and Insurance Issues THE TOPIC JULY 2003 An earthquake is a sudden and rapid shaking of the earth caused by the breaking and shifting of rock
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy
 February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
February 28 Earthquake: We got off easy State Geologist John Beaulieu Lucky may not be the first word that comes to mind after an earthquake that injured more than 200 and caused more than $1 billion damage,
NATURAL DISASTERS Vol. I - Earthquake Parameters Including Strong Earthquakes- S.L.Yunga EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES
 EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
EARTHQUAKE PARAMETERS INCLUDING STRONG EARTHQUAKES S.L.Yunga United Institute of physics of the Earth, Russian academy of sciences. B. Gruzinskaya,10, Moscow, 123810, Russia Keywords earthquake, epicenter,
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales
 Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
Earthquakes, faulting, beach-balls, magnitude scales Faulting Geometry Faulting is a complex process and the variety of faults that exists is large. We will consider a simplified but general fault classification
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Suggested Activities Processes that Shape the Earth: Earth s Structure and Plate Tectonics From Harcourt Science Teacher Ed. Source (Grade Level) Title Pages Concept Harcourt Science (4) The Layers of
Geology 112 Earthquakes. Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake?
 Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Geology 112 Earthquakes Name Activity 1 Worksheet Introduction to the Course. What is a Fault? What is an Earthquake? Activity 1 Objectives: Introduce student to the topics, requirements and format of
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery
 Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
Plotting Earthquake Epicenters an activity for seismic discovery Tammy K Bravo Anne M Ortiz Plotting Activity adapted from: Larry Braile and Sheryl Braile Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Purdue
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES
 DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
DISASTER RESISTANCE EARTHQUAKES AND STRUCTURES EARTHQUAKES Origin of earthquakes The earth was a single land about two hundred million years ago. This land split progressively over a long period of time
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
PUSD High Frequency Word List
 PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
PUSD High Frequency Word List For Reading and Spelling Grades K-5 High Frequency or instant words are important because: 1. You can t read a sentence or a paragraph without knowing at least the most common.
Shake, Rattle, and Roll. Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz
 Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
Shake, Rattle, and Roll Tina Moore, Denise Robinette, & Matt Utz Shake, Rattle, and Roll - Earthquakes Lesson Plan - Day One I. Objective: A. Student will be able to read and label a two axis graph. B.
Earthquake detection systems can sound the alarm in the moments before a big tremor strikes time enough to save lives
 SEISMOLOGY Earthquake detection systems can sound the alarm in the moments before a big tremor strikes time enough to save lives By Richard Allen in brief Earthquake early-warning networks detect the earliest
SEISMOLOGY Earthquake detection systems can sound the alarm in the moments before a big tremor strikes time enough to save lives By Richard Allen in brief Earthquake early-warning networks detect the earliest
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Freely Falling Objects
 Freely Falling Objects Physics 1425 Lecture 3 Michael Fowler, UVa. Today s Topics In the previous lecture, we analyzed onedimensional motion, defining displacement, velocity, and acceleration and finding
Freely Falling Objects Physics 1425 Lecture 3 Michael Fowler, UVa. Today s Topics In the previous lecture, we analyzed onedimensional motion, defining displacement, velocity, and acceleration and finding
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q.
 Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Earthquakes: Interesting Facts and F.A.Q. Earthquakes kill approximately 8,000 people each year and have caused an estimated 13 million deaths in the past 4,000 years. The moment magnitude scale (MMS)
Can earthquakes be predicted? Karen Felzer U.S. Geological Survey
 Can earthquakes be predicted? Karen Felzer U.S. Geological Survey Earthquake predictions that most seismologists agree with Long term earthquake probabilities These kinds of predictions are important for
Can earthquakes be predicted? Karen Felzer U.S. Geological Survey Earthquake predictions that most seismologists agree with Long term earthquake probabilities These kinds of predictions are important for
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system
 Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Lessons learned from the tsunami disaster caused by the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and improvements in JMA's tsunami warning system October 2013 Japan Meteorological Agency Lessons learned from the
Fry Phrases Set 1. TeacherHelpForParents.com help for all areas of your child s education
 Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Set 1 The people Write it down By the water Who will make it? You and I What will they do? He called me. We had their dog. What did they say? When would you go? No way A number of people One or two How
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Storms Assessment LESSON
 LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
LESSON 8 Storms Assessment What will happen to the helix above a hot lamp? TERRY G. McCREA/SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION INTRODUCTION You have now completed Storms, the first part of Catastrophic Events. After
Topic Area: Circles. Definitions. Formulas Distance Formula: D = ( x x ) + ( y ) Equation of a Circle: Activity 8 Algebra II with the Casio fx-9750gii
 Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
Where Did That Come From? Teacher Notes Topic Area: Circles NCTM Standards: Use symbolic algebra to represent and explain mathematical relationships. Use geometric models to gain insights into, and answer
EARTHQUAKES AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES
 EARTHQUAKES AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES by K. C. Makropoulos Human rights in Disasters: Search and Rescue Operations in disasters especially for vulnerable people Hotel Electra, 5-6 November 2009 INSTRUMENTS
EARTHQUAKES AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES by K. C. Makropoulos Human rights in Disasters: Search and Rescue Operations in disasters especially for vulnerable people Hotel Electra, 5-6 November 2009 INSTRUMENTS
Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior
 Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
Melissa Duran, Hoover Middle School, San Jose, CA 1/9/03 Bay Area Science Museum Collaboratory Project Unit: Restless Earth Lesson: Earth s Interior Introduction Standards: 1.b, 7.e Objectives Students
Earthquakes in Hawaii:
 Earthquakes in Hawaii: What you need to know U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Prepared by: Janet L. Babb Hawaiian Volcano Observatory Hawaii Standard Time The State of Hawaii experiences
Earthquakes in Hawaii: What you need to know U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Prepared by: Janet L. Babb Hawaiian Volcano Observatory Hawaii Standard Time The State of Hawaii experiences
After a wave passes through a medium, how does the position of that medium compare to its original position?
 Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
Light Waves Test Question Bank Standard/Advanced Name: Question 1 (1 point) The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequencies are called A. radio waves. B. gamma rays. C. X-rays. D. visible light.
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata
 Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Geological Maps 3: Faulted Strata Brittle deformation in rocks is characterized by fractures, joints and faults. Fractures and joints can be of any size, orientation or pattern. Some joints form regular
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS
 EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS STEP 1. IDENTIFY POTENTIAL HAZARDS IN YOUR HOME AND BEGIN TO FIX THEM. Earthquake safety is more than minimizing damage to buildings. We must also secure the contents of our buildings
EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS STEP 1. IDENTIFY POTENTIAL HAZARDS IN YOUR HOME AND BEGIN TO FIX THEM. Earthquake safety is more than minimizing damage to buildings. We must also secure the contents of our buildings
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Shaky Ground 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
Earth Science Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion Reading Comprehension. Landforms, Weathering, and Erosion
 Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
Reading Comprehension Name 1 How many people have been to the Rocky Mountains or the Grand Canyon? When people go to visit these natural wonders, they may not realize that it took millions of years for
Earthquakes Natural and Induced. Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University
 Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Earthquakes Natural and Induced Rick Aster Professor of Geophysics and Department Head Geosciences Department Colorado State University Overview What causes earthquakes? How do we detect, locate, and measure
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3
 Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Questions & Answers Proposed for Exam #3 GE50 Introduction to Physical Geology (Geology for Engineers) Missouri University of Science and Technology Fall Semester 2007, Leslie Gertsch ([email protected])
Understanding the altimeter
 Understanding the altimeter What you see isn't always what you have by Jack Willams Flying is an adventure for most pilots--sometimes more adventure than they really want. A pilot's report to Canada's
Understanding the altimeter What you see isn't always what you have by Jack Willams Flying is an adventure for most pilots--sometimes more adventure than they really want. A pilot's report to Canada's
KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF KINDERGARTEN VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning that all mountains are not volcanoes. LAB: Investigating rocks
KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF KINDERGARTEN VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning that all mountains are not volcanoes. LAB: Investigating rocks
RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE
 RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE By: William G. Byers, P.E. Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway 4515 Kansas Avenue Kansas City, Kansas 66106 Phone (913) 551-4070 Fax
RAILROAD DAMAGE FROM THE OCTOBER 16, 1999 HECTOR MINE EARTHQUAKE By: William G. Byers, P.E. Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway 4515 Kansas Avenue Kansas City, Kansas 66106 Phone (913) 551-4070 Fax
EARTHQUAKE PROBLEM: Do's and Don'ts for Protection
 EARTHQUAKE PROBLEM: Do's and Don'ts for Protection Sponsored by Rajiv Gandhi Foundation, New Delhi and Prepared by Department of Earthquake Engineering, University of Roorkee, Roorkee PREFACE A large number
EARTHQUAKE PROBLEM: Do's and Don'ts for Protection Sponsored by Rajiv Gandhi Foundation, New Delhi and Prepared by Department of Earthquake Engineering, University of Roorkee, Roorkee PREFACE A large number
CHAPTER 11 STRATEGY FOR SURVIVAL
 CHAPTER 11 STRATEGY FOR SURVIVAL Copyright 2008 Tom T. Moore If you re reading this several months in advance, there are a number of things that you can do to prepare for these coming earthquakes. I realize
CHAPTER 11 STRATEGY FOR SURVIVAL Copyright 2008 Tom T. Moore If you re reading this several months in advance, there are a number of things that you can do to prepare for these coming earthquakes. I realize
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation The greatest moments in science are when two phenomena that were considered completely separate suddenly are seen as just two different versions of the same thing.
Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation The greatest moments in science are when two phenomena that were considered completely separate suddenly are seen as just two different versions of the same thing.
Name: Period: # Plate Tectonics. Journey to the center of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Beginning of the Universe Classwork 6 th Grade PSI Science
 Beginning of the Universe Classwork Name: 6 th Grade PSI Science 1 4 2 5 6 3 7 Down: 1. Edwin discovered that galaxies are spreading apart. 2. This theory explains how the Universe was flattened. 3. All
Beginning of the Universe Classwork Name: 6 th Grade PSI Science 1 4 2 5 6 3 7 Down: 1. Edwin discovered that galaxies are spreading apart. 2. This theory explains how the Universe was flattened. 3. All
Earthquakes. Was anyone hur t? 358 Chuck Nacke/TimeLife Pictures/Getty Images
 Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
Academic Standard 3: Students collect and organize data to identify relationships between physical objects, events, and processes. They use logical reasoning to question their own ideas as new information
PRODUCTION. 1The Surplus
 1The Surplus 2 The US economy produces an amazing number of different products: thousands of different foods, countless movies, dozens of different type cars, hundreds of entertainment products, dozens
1The Surplus 2 The US economy produces an amazing number of different products: thousands of different foods, countless movies, dozens of different type cars, hundreds of entertainment products, dozens
LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES
 55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
55 Name Date Partners LAB 6: GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly Bodies by the attraction
Allison Gallahan s Early Childhood Lesson Plan
 Allison Gallahan s Early Childhood Lesson Plan Lesson: Big Book: Reading Maps Length: 20-30 minutes Age or Grade Level Intended: 2 nd Grade Academic Standard(s): Social Studies 2.3.2: The World in Spatial
Allison Gallahan s Early Childhood Lesson Plan Lesson: Big Book: Reading Maps Length: 20-30 minutes Age or Grade Level Intended: 2 nd Grade Academic Standard(s): Social Studies 2.3.2: The World in Spatial
Multiple Choice For questions 1-10, circle only one answer.
 Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Interaction at a Distance
 Interaction at a Distance Lesson Overview: Students come in contact with and use magnets every day. They often don t consider that there are different types of magnets and that they are made for different
Interaction at a Distance Lesson Overview: Students come in contact with and use magnets every day. They often don t consider that there are different types of magnets and that they are made for different
Eye of the Storm: Chasing Storms with Warren Faidley
 Eye of the Storm: Chasing Storms with Warren Faidley BUILD BACKGROUND Theme 1, Grade 5 California State Standards Reading Vocabulary and Concept Development 1.2 Use word origins to determine the meaning
Eye of the Storm: Chasing Storms with Warren Faidley BUILD BACKGROUND Theme 1, Grade 5 California State Standards Reading Vocabulary and Concept Development 1.2 Use word origins to determine the meaning
Project Report. Structural Investigations Hotel del Sol Yuma, Arizona
 Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
Project Report Structural Investigations Yuma, Arizona Prepared by: 2619 Spruce Street Boulder, CO 80302 303-444-3620 Prepared for: Principle Engineering Group, Inc. 833 East Plaza Circle, Suite 100 Yuma,
FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST:
FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST:
