Structure of Muscle Tissue and Associated Tissues
|
|
|
- Brendan Gray
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure of Muscle Tissue and Associated Tissues
2 Tissue Tissue combinations from muscle, fat and bone which are the gross components of carcasses, and their properties and proportions are responsible for quality and leanness of meat.
3 Muscle tissue Skeletal muscles constitute % of carcass weight of meat animals. Smooth muscle - blood vessels Cardiac muscle- is confined solely to the heart
4 Skeletal muscle Are organs of the muscular system There are more than 600 muscle in the animal body. Vary widely in shape, size and action. The structure of muscle will be showed in Figure
5
6
7
8
9 Muscle fiber Is the highly specialized cell. Constitute 75-92% of muscle volume Blood vessels, nerve fibers and extracellular fluid make up the other volume.
10 Skeletal muscle fiber Are long, unbranched, threadlike cells which taper slightly at both ends. Vary considerably in diameter. Ranged from 10um->100 um within the same species or the same muscle.(micrometer=one millionth of a meter)
11 Sarcolemma Surround the muscle fiber Is composed of protein and lipid material and it relatively elastic (adjust very well during contraction, relaxation and stretching). A network of tubules called transverse tubules T system or T tubules is circumferential on the surface.
12 Myofibrils Are long, thin, cylindrical rods, usually 1-2 um in diameter. A muscle fibers of meat animals with diameters of 50um have at least 1000 and could have as many as 2000 or more myofibrils.
13 Sarcomere In myofibrillar cross-section, a well ordered array of dots that have two distinct size. ( thin and thick filaments). Area of different density are visible within light and dark bands of myofibrils. The unit of the myofibril between two adjacent Z disks- a sarcomere
14 Sarcomere includes both an A band and the two half T bands located on either side of the A band. Is the repeating structural unit of the myofibril. Is also the basic unit in which events of the muscle s contraction-relaxation cycle occur.
15 myofilament Divided into thick and thin filaments. Thick filaments nm ( nanometer, one-billionth of a meter) in diameter and 1.5 um long, constitute the A band of the sarcomere ; referred as myosin filament. Some of which are located in the M line.
16 myofilament Thin filaments: are about 6-8 nm in diameter, 1.0 um long; on either side of the Z disk; they also constitute the I band and extend beyond the I band into the A band, referred as actin filaments
17 The orderly arrangement H zone : Only thick filaments (myosin) are present. A band : thin and thick filaments overlap, show six thin filaments surrounding each thick filament I band : only thin filaments (actin)are present.
18
19
20 Proteins of the myofilaments The protein actin and myosin :65% of the protein of the myofibril. The remaining fraction consists of regulatory (tropomyosin and troponin) and cyto-skeletal proteins ( c-proteinencircle the myosin filament, desminencircle the Z disks).
21 Actin or thin filament 20% of the myofibrillar protein A globular shaped molecule, 5.5 nm in diameter.referred to as G-actin F actin is linked by G-actin The actin filament : two strands of F- actin are spirally coiled around one another to form a super helix
22
23 Myosin or thick filament Is a fibrous protein. 45% of myofibrillar protein. Is an elongated rod shape, with a thickened portion at one end- referred to as the head region. Another is the long thin portion is called the rod or tail portion, between two is called the neck.
24
25 Sarcoplasmic Reticulum and T tubules Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)- is a membraneous system of tubules and cisternae (reservoirs for Ca+2). Longitudinal tubules and terminal cisternae Transverse tubules T system or T tubules is circumferential on the surface. Usually discussed together, are two separate and distinct membrane systems.
26
27 Connective tissue Connects and holds verious parts of the body together. Are distributed throughout the body. Such as blood vessel, tendon, nerve trunk. Or skin, hide Fat storage cells are located within a specialized type of connective tissue adipose tissue.
28 Connective tissue Ground substance containing soluble glycoprotein(carbohydrate +protein), such as proteoglycans or glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid can be found in joints and chondroitin sulfates- can be found in cartilage, tendons and adult bone)
29 Connective tissue Extracellular fibers: reticulin, collagen and elastin. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the animal body and significantly influences meat tenderness. Constitutes 20-25% of total body protein; is a glycoprotein.
30 Collagen Glycine is the most abundant amino acid in collagen and comprises about 1/3 of the total amino acids. Hydroxyproline, and proline account for another 1/3 of its amino acid content. Hydroxyproline is a relatively constant component of collagen (13-14 %).
31
32 Collagen In young animal, cross linkages are fewer in number and more easily broken. Collagen is more soluble in young animals and becomes less soluble as the animal ages.
33 Elastin Is a much less abundant connective tissue protein than collagen. Is a rather rubbery protein that is present throughout the body in ligaments and arterial walls Is highly resistant to digestive enzymes and no method of cookery has any appreciable solubilizing effect on it.
34 Reticulin Is composed of small fibers that form delicate networks around cells, blood vessels, neural structures which hold them in place. Are numerically overwhelmed by collagenous fibers.
35 Adipose tissue Accumulation of numerous adipocytes. Also know as fat. Contains two types of adipose tissue ; white and brown fat. White type is the most in meat animal. Brown type is present in all of them at birth, especially around the kidneys.
36 Muscle and Fiber type Muscle are usually classified as red, or white, based principally on their color intensity, which is attributable to the proportion of red and white fibers they contain. Few muscle are composed of all red or white fibers. Most are mixtures of red and white fibers For example, red muscle are those with higher proportion of red fibers than found in white muscle.
37 Muscle and Fiber type Such as leg muscle and breast muscle of chicken or turkey. Different color also can be showed in various parts in a meat animal. The structural, functional and metabolic characteristics of red, intermediate and white muscle fibers are different.
38
39
40
41 The chemical composition of meat Moisture :65-80% Protein:16-22% Lipid: % Carbohydrates: % Mineral: %
42 The end of this chapter
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory
 Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers
 Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers When a muscle cell contracts t it pulls on the collagen fibers creating tension
Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers When a muscle cell contracts t it pulls on the collagen fibers creating tension
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Muscles and Contraction
 Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Muscular System. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscular System Overview of Muscle Tissues Types of Muscle Tissue o Skeletal and smooth muscles which are elongated are called muscle fibers o Myo- and Mys- = muscle o Sarco = flesh refers to muscle; i.e.,
Muscular System Overview of Muscle Tissues Types of Muscle Tissue o Skeletal and smooth muscles which are elongated are called muscle fibers o Myo- and Mys- = muscle o Sarco = flesh refers to muscle; i.e.,
The Cell Interior and Function
 The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
Biological Sciences Initiative. Muscle Contraction
 BSI Activity Page 1 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Muscle Contraction SUMMARY In this activity, students will play the role of different proteins involved in muscle contraction and act out the process.
BSI Activity Page 1 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Muscle Contraction SUMMARY In this activity, students will play the role of different proteins involved in muscle contraction and act out the process.
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells
 Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
MUSCLE TISSUE. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 MUSCLE TISSUE Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Histologically identify and functionally characterize each of the 3 types of muscle tissues. Describe the organization of the sarcomere as seen
MUSCLE TISSUE Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Histologically identify and functionally characterize each of the 3 types of muscle tissues. Describe the organization of the sarcomere as seen
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE
 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid
 The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid The aqueous environment inside and outside a cell prevents membrane lipids from escaping from bilayer, but nothing stops these molecules from moving about and
The Lipid Bilayer Is a Two-Dimensional Fluid The aqueous environment inside and outside a cell prevents membrane lipids from escaping from bilayer, but nothing stops these molecules from moving about and
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Muscle Physiology and the. Pathology of Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscle Physiology and the Pathology of Muscular Dystrophy Angela Tompkins February 23, 2010 Everglades University Biology 1 Muscle Physiology and the Pathology of Muscular Dystrophy Humans are able to
Muscle Physiology and the Pathology of Muscular Dystrophy Angela Tompkins February 23, 2010 Everglades University Biology 1 Muscle Physiology and the Pathology of Muscular Dystrophy Humans are able to
Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training
 Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training Baechle Chapter 4, pp. 143-151, 151, Powers & Howley pp. 253-255 255 Lecture Overview Neural Adaptations Skeletal Muscle Adaptations Connective Tissue Anatomy Connective
Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training Baechle Chapter 4, pp. 143-151, 151, Powers & Howley pp. 253-255 255 Lecture Overview Neural Adaptations Skeletal Muscle Adaptations Connective Tissue Anatomy Connective
MUSCULAR SYSTEM. A. K. Sengupta 9/9/2010 1/12
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE
 BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE 18-1 Lecture Overview Muscles and motion Muscles Muscle structure Relevant properties Force-length properties Muscle states Force-velocity relationship Muscle fiber types Isometric
BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE 18-1 Lecture Overview Muscles and motion Muscles Muscle structure Relevant properties Force-length properties Muscle states Force-velocity relationship Muscle fiber types Isometric
tissues are made of cells that work together, organs are )
 Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Study Guide Cells Unit Test Matching. Write the letter of the correct response on the line. You may use the responses more than once. A. proteins B. simple carbohydrates C. complex carbohydrates D. lipids
Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function.
 Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of skeletal muscle 2. understand the function of a motor unit 3.
Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of skeletal muscle 2. understand the function of a motor unit 3.
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
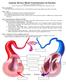 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Smooth Muscle. Smooth Muscle Structure
 Smooth Muscle Spindle-shaped Small (2-5 um wide, 50-300 um long) 1 centrally placed nucleus per cell Usually organized in small to moderate sized clusters of cells Lack sarcomeres No T-tubules or terminal
Smooth Muscle Spindle-shaped Small (2-5 um wide, 50-300 um long) 1 centrally placed nucleus per cell Usually organized in small to moderate sized clusters of cells Lack sarcomeres No T-tubules or terminal
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students
 Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
Quick Hit Activity Using UIL Science Contests For Formative and Summative Assessments of Pre-AP and AP Biology Students Activity Title: Quick Hit Goal of Activity: To perform formative and summative assessments
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Overview of Muscle Tissues (pp. 276 277) Types of Muscle Tissue (p. 276) Special Characteristics of Muscle Tissue (p. 276) Muscle Functions (pp. 276 277) Skeletal Muscle (pp. 277 305) Gross Anatomy of
Overview of Muscle Tissues (pp. 276 277) Types of Muscle Tissue (p. 276) Special Characteristics of Muscle Tissue (p. 276) Muscle Functions (pp. 276 277) Skeletal Muscle (pp. 277 305) Gross Anatomy of
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Cardiac Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Cardiac Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of cardiac muscle 2. understand the concept of the functional syncytium 3. give a basic
Cardiac Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of cardiac muscle 2. understand the concept of the functional syncytium 3. give a basic
Review of the Cell and Its Organelles
 Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Muscles and Muscle Tissue 9 Overview of Muscle Tissues (pp. 280=281) 1. Compare and contrast the basic types of muscle tissue. 2. List four important functions of muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle (pp. 281=309)
Muscles and Muscle Tissue 9 Overview of Muscle Tissues (pp. 280=281) 1. Compare and contrast the basic types of muscle tissue. 2. List four important functions of muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle (pp. 281=309)
11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions. Taft College Human Physiology
 11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Taft College Human Physiology Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Isotonic Contractions: Tension produced and overall shortening of the muscle as a load is
11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Taft College Human Physiology Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Isotonic Contractions: Tension produced and overall shortening of the muscle as a load is
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams
 The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Myosin motor proteins and cardiomyopathy contributions from synchrotron studies. Theresia Kraft Molecular and Cell Physiology
 Myosin motor proteins and cardiomyopathy contributions from synchrotron studies Theresia Kraft Molecular and Cell Physiology HASYLAB Users Meeting 28. 01. 2011 Overview: What is cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy
Myosin motor proteins and cardiomyopathy contributions from synchrotron studies Theresia Kraft Molecular and Cell Physiology HASYLAB Users Meeting 28. 01. 2011 Overview: What is cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy
Plant and Animal Cells
 Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. LIFE SCIENCES: Half-year exam
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES: Half-year exam MARKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours Section A Question 1 1.1.1 D 1.1.2 B 1.1.3 C 1.1.4 C 1.1.5 B (5 2) [10] 1.2.1 pericycle 1.2.2 Casparian band 1.2.3 ball-and-socket
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES: Half-year exam MARKS: 150 TIME: 2½ hours Section A Question 1 1.1.1 D 1.1.2 B 1.1.3 C 1.1.4 C 1.1.5 B (5 2) [10] 1.2.1 pericycle 1.2.2 Casparian band 1.2.3 ball-and-socket
The Functions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46341 1 The Functions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46341 1 The Functions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity)
 FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
FISH HEALTH/Activity Fish: One-of-a-kind Animals (30 minute activity) Objectives Materials Background I have known you in your streams and rivers where your fish flashed and danced in the sun, where the
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
CELLS: PLANT CELLS 20 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELLS: PLANT CELLS 20 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we will discuss the following: The Cell Theory Terminology Parts of Plant Cells: Organelles Difference between plant and animal cells
CELLS: PLANT CELLS 20 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we will discuss the following: The Cell Theory Terminology Parts of Plant Cells: Organelles Difference between plant and animal cells
Cell Structure & Function!
 Cell Structure & Function! Chapter 3! The most exciting phrase to hear in science, the one that heralds new discoveries, is not 'Eureka!' but 'That's funny.! -- Isaac Asimov Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell
Cell Structure & Function! Chapter 3! The most exciting phrase to hear in science, the one that heralds new discoveries, is not 'Eureka!' but 'That's funny.! -- Isaac Asimov Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment
 Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Comparing Plant And Animal Cells
 Comparing Plant And Animal Cells http://khanacademy.org/video?v=hmwvj9x4gny Plant Cells shape - most plant cells are squarish or rectangular in shape. amyloplast (starch storage organelle)- an organelle
Comparing Plant And Animal Cells http://khanacademy.org/video?v=hmwvj9x4gny Plant Cells shape - most plant cells are squarish or rectangular in shape. amyloplast (starch storage organelle)- an organelle
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
