Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Francis
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General characteristics of epithelium Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Is avascular tissue (without blood supply cells receive nourishment by diffusion from a highly vascular area of loose connective tissue just below the basement membrane called the lamina propria ) is highly cellular tissue cells are arranged to form cohesive sheet or groups with no or little extracellular matrix displays a free surface usualy luminal surface (turned to the lumen) opposite (basal) surface adheres to extracellular basement membrane or lamina basalis epithelial cells display polarity apical (luminal), lateral and basal surfaces with structural specialization epithelial cells are specialised for absorption, secretion or to act as barrier lateral surfaces display junctional complexes for intercellular cohesion and communication One type of epithelium may change into another type metaplasia (examples: pseudostratified ep. of respiratory passages transforms into stratified squamous ep. on the surface of epiglottis and soft palate) Membrane specializations of epithelia Lateral surface Specialised structures are present in epithelia which link individual cells together. Two main adhesion types are distinguished: 1. Cell membrane proteins acting as specialised cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) 2. Specialised areas of the cell membrane incorporated into cell junctions. Three types are recognized: occluding junctions, anchoring or adherence junctions and communicating junctions. o o o Occluding junctions bind cell together to form an impermeable barrier Zonula occludens or tight junction Anchoring junctions link the cytoskeleton of cells to each other and two underlying tissues Zonula adherens provides mechanical strength Macula adherens or desmosomes provides mechanical strength in tissues where there are tensile or shearing stresses, eg skin Communications junctions allow direct cell-cell communication Gap junction or nexus allow rapid communication for coordinated action
2 Luminal (free, apical) surface Microvilli short finger-like projection of the cell membrane to increased surface area (regularly arranged microvilli in intestines striated border, in kidney tubules brush border) striated border brush border Cilia hair-like surface projections of cells involved in transport Glycocalyx thin extracellular layer consisting of protein glycoprotein and sugar residues; stains PAS positive; can act as enzyme, CAM or for cell recognition Basal surface Basal invaginations or folds greatly enhance surface area; folded membrane with ions pumps + mitochondria form basal labyrinth in kidney tubules.
3 Note the striation of basal parts of the cells = basal labyrinth Epithelial tissues are physically separated from underlying connective tissues by a basement membrane or basal lamina. The portion of an epithelial cell attached to the basement membrane is called its basal surface. The opposite side - facing the external environment, or lumen of a body cavity, is its apical surface. Basement membranes are composed of a special type of collagen and a substance called laminin (see below). The basement membrane helps epithelial cells orient themselves in relation to other tissues. After epithelial injury (e.g., an abrasion), the basement membrane serves as a scaffolding upon which new cells attach themselves during healing.
4 Cassification of epithelia I. surface epithelium is 1 or more layers of cells arranged into sheet; According to number of layers SURFACE EPITHELIUM simple layerd squamous cuboid columnar stratified According to shape of cells in the outermost layer pseudostratified columnar squamous non-cornified (non-keratinized) squamous cornified (keratinized) columnar transitional
5 SIMPLE EPITHELIA only 1 (single) layer on basement membrane Squamous single layer of flattened thin cells with little cytoplasm and prominent nucleus. (In the smallest tubules and ducts of different organs, Henle s loop or Bowman s capsule in kidney) Endothelium squamous epithelium in cardiovascular system. Mesothelium - squamous epithelium of mesodermal origin lining serous membranes and cavities. Cuboidal - cell height, width and depth are the same, round centrally placed nucleus. (In renal tubules and small glanular ducts) Columnar - cell height greater than width, nucleus elliptical or cigar shaped. (In the intestines, in the oviduct) Pseudostratified single layer but nuclei situated at different levels in the cell. All cells are in contact with the basement membrane, but not all cells reach the apical surface. Both conditions create the illusion of several cell layers. (In the respiratory passages nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi)
6 STRATIFIED EPITHELIUM consists of basal layer on basement membrane, several layers of polyhedral cells and surface layer. According to the shape of cells in this layer the epithelium is named (squamous, columnar, transitional) Stratified squamous resiting to mechanical influences (press) non-keratinised (mouth cavity, vocal cords, vagina, anus) keratinised (epidermis of the skin) the cells are released continously from the surface Is not described in human organism Stratified columnar 2 or more layers of cells, columnar cells form the upper layer (twolayered in ductus epididymis and ductus deferens, more-layered male urethra, conjunctive) Transitional - stratified, top layer dome or umbrella shaped. (only in some urinary passages renal pelvis, ureter and urinary bladder). Epithelium change the shape of cells and number of layers according to wall conditions of urinary passages distansion or contraction. Epithelia with special functions: resorptive, sensory, respiratory, myoepithelial cells
7 II. glandular epithelium multicellular epithelial structures that specialize in synthesizing and secreting complex molecules. Glandular cell rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus secretory granules nucleus with nucleoli CLASSIFICATION OF GLANDS GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM unicellular Single cells in coverinrg epithelium (Paneth cells, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells, Leydig cells) multicellular Accordin to mechanism of secretion endocrine exocrine merocrine, apokrine,holocrine According to loclalization intraepithelial extraepithelial According to arrangement of ducts simple branched compound According to type of secretory portions tubular alveolar (acinar) tuboalveolar According to product properties mucous serous mixed
8 According of mechanism of secretion endocrine glands withou ducts, product is released into the blood through the wall of capilareis exocrine secretory cells of exocrine glands release their products into ducts in three different ways: merocrine apocrine holocrine - membrane-bound secretory granules are moved to the apical surface where they coalesce with the membrane on to release the product. - the apical portions of cells are pinched off and lost during the secretory process. - secretory cell degenerates and as it breaks apart, the contents of the cell become the secretory product.
9 According to type of secretory units tubular are usually mucous alveolar are usually (acinar) serous tuboalveolar mixed to product properties simple branched compound Secretory units Serous acinus (alveolus) Mucous tubule Serous demilune (Giannuzzi)
10 Functions of epithelia: Barrier: Epithelial tissue commonly functions as a covering or lining for organs and other tissues (e.g., skin, mucous membranes, pleural cavity, etc.). Epithelial cells serve as selective barriers between the environment and the internal structures of the body. They protect underlying tissues from drying, and from mechanical and chemical injury. Tight junctions between individual cells play an important role in the barrier function of epithelium. Some barrier epithelial cells have motile cilia that propel fluid or particulate matter over tissue surfaces (e.g., cells lining the bronchi). Absorption: Epithelial cells are found in those organs (e.g., intestine) which are involved in absorption of substances important for life. These cells often microvilli which increase cell surface area in order to facilitate absorption. Secretion: The secretory cells of endocrine and exocrine glands are epithelia. Sensory: Many of the more complex sensory receptors of the nervous system are derived from specialized epithelia called neuroepithelia (e.g., the rods and cones of the retina, olfactory receptors of the nose, taste
11 receptors on the tongue, etc.). Sensory receptors function by converting mechanical, chemical, or electromagnetic signals from the environment into nerve impulses which can be processed by the nervous system. Contractility: Some very specialized epithelial cells (myoepithelia) contain the contractile proteins myosin and actin similar to muscle. Myoepithelia are associated with the ducts of sweat, salivary, lacrimal, amd mammary glands and assist in the secretory process. Origin: Epithelial tissues are derived from all three primary germ cell layers. Ectoderm: The epithelial cells of the skin and oral cavity (epidermis) are derived from ectoderm. Epithelial cells covering the cornea and lens, as well as sensory receptors of the eyes, ears, and nose, are also ectodermal in origin. Mesoderm: The epithelial lining of blood vessels (endothelium) is derived from mesoderm. The epithelial lining of the pleural and peritoneal cavities (mesothelium) also originate from mesodermal cells. Endoderm: The epithelial lining of the respiratory system and digestive tracts - as well as the functional cells (parenchyma) of the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, thyroid, and parathyroid, are derived from endoderm.
12 Protocol Simple squamous Simple cuboidal
13 Simple columnar Pseudostratified columnar with cilia
14 Stratified squamous Transitional
15 Serous acinus Mucous tubule
16 Appendix: atlas Parotid gland: serous acini Parotid gland: SU serous acinus D - striated duct SG secretory granules N nucleus of serous cell
17 Submandibular gland: SA serous acini MA mucous tubuli D striated duct Submandibular gland: serous demilunes
18
19
20
21
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
CHAPTER 5: TISSUES. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term tissue. 2. Name the four primary adult tissue types, and give a brief description of each. 3. Describe the functions and types of extracellular fluid (ECF). 4. Compare and
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The four main types of tissues include A) epithelium. B) muscle. C) nerve.
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 CHAPTER4 I Tissue: The Living Fabric Chapter Outline and Student Objectives Preview of Selected Key Terms Epithelial Tissue (pp. 101-112) 1. List several characteristics that typify epithelial tissue.
CHAPTER4 I Tissue: The Living Fabric Chapter Outline and Student Objectives Preview of Selected Key Terms Epithelial Tissue (pp. 101-112) 1. List several characteristics that typify epithelial tissue.
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Laboratory 3 Histology
 Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Laboratory 3 Histology Goals: For epithelial tissues: o discuss the major features; o classify based on simple/stratified and squamous/cubodial/columnar; o identify each type by microscopy; o identify
Epithelial and Connective Tissues. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
Epithelial and Connective Tissues Danil Hammoudi.MD Figure 4.1 4 types of human tissues Epithelium Connective tissue Muscle tissue Skeletal Cardiac Smooth muscles Nerve tissue Tissue derivation Ectoderm
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Small & Large Intestines
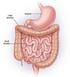 Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Small & Large Intestines Small Intestine: principal site for digestion of food and absorption of the products of digestion Large Intestine: reabsorption of water and elimination of undigested food and
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
The cells of the human body do not operate independently of
 4 Tissues I. Epithelial Tissue 65 Special Characteristics of Epithelia 66 Classification of Epithelia 66 Glands 72 Epithelial Surface Features 74 II. Connective Tissue 77 Special Characteristics of Connective
4 Tissues I. Epithelial Tissue 65 Special Characteristics of Epithelia 66 Classification of Epithelia 66 Glands 72 Epithelial Surface Features 74 II. Connective Tissue 77 Special Characteristics of Connective
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Tissue: The Living Fabric Muscle Tissue (pp. 136 138)
 Preparing Human Tissue for Microscopy (pp. 11 115) Epithelial Tissue (pp. 115 12) Special Characteristics of Epithelium (pp. 115 116) Classification of Epithelia (pp. 116 121) Glandular Epithelia (pp.
Preparing Human Tissue for Microscopy (pp. 11 115) Epithelial Tissue (pp. 115 12) Special Characteristics of Epithelium (pp. 115 116) Classification of Epithelia (pp. 116 121) Glandular Epithelia (pp.
Digestive System Digestive Tract
 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Location: air sacs of lungs; nephrons of kidney; lining of circulatory system, lymphatic vessels, & ventral body cavity
 Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Bio. 2304 - Human Anatomy HISTOLOGY (STUDY OF TISSUES) - Lab & Lecture Objectives Important: For each slide know 1.) specific tissue type 2.) any specialized structures or cells in the tissue (& know their
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Liver, pancreas, esophagus, stomach fundus, small intestine, large intestine, appendix; preparations B9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, (19) Institute of Histology and Embryology RNDr. Lucie
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
The Respiratory System Introduction and Overview During a 24-hour period, more than 9000 liters of air enter the interior of the body to participate in gas exchange. This air must be warmed, cleansed,
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles
 Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles Structure of Animal Cells The Phospholipid Structure Phospholipid structure Encases all living cells Its basic structure is represented by the fluidmosaic model Phospholipid
Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles Structure of Animal Cells The Phospholipid Structure Phospholipid structure Encases all living cells Its basic structure is represented by the fluidmosaic model Phospholipid
Cell Structure and Function. Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron
 Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells: Blood Cells Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells: Bacteria Cell Structure and Function All living
Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells: Blood Cells Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells: Bacteria Cell Structure and Function All living
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
Date: Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George. Score: 1) A cell with 1% solute concentration is placed in a beaker with a 5% solute concentration.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz Homeostasis and Transport - (BIO.A.4.1.1 ) Plasma Membrane, (BIO.A.4.1.2 ) Transport Mechanisms, (BIO.A.4.1.3 ) Transport Facilitation Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages. The Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. Phospholipids. I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II.
 BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
The Cell Interior and Function
 The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Epithelium. HistoNotes LEARNING OBJECTIVES OUTLINE
 Epithelium 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES OUTLINE I. FEATURES & FUNCTIONS A. Composition 1. Cells 2. ECM (limited) B. Classification of epithelia 1. Surface epithelia 2. Glandular epithelia 3. Special epithelia
Epithelium 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES OUTLINE I. FEATURES & FUNCTIONS A. Composition 1. Cells 2. ECM (limited) B. Classification of epithelia 1. Surface epithelia 2. Glandular epithelia 3. Special epithelia
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
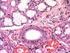 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Microscopes. Eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells are characterized by having: DNA in a nucleus that is bounded by a membranous nuclear envelope
 CH 6 The Cell Microscopy Scientists use microscopes to visualize cells too small to see with the naked eye. In a light microscope (LM), visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass
CH 6 The Cell Microscopy Scientists use microscopes to visualize cells too small to see with the naked eye. In a light microscope (LM), visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Review of the Cell and Its Organelles
 Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
PCB 4023 Cell Biology. Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs
 PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
PCB 4023 Cell Biology Lab 8: Organology II Digestive tract and accessory organs Name: Name: SSN: SSN: N.B. Since this document is in pdf format, the URLs (web addresses) cannot be linked. To use them,
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell. 1. Cell Basics. Limits to Cell Size. 1. Cell Basics. 2. Prokaryotic Cells. 3. Eukaryotic Cells
 Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell 1. Cell Basics 2. Prokaryotic Cells 3. Eukaryotic Cells 1. Cell Basics Limits to Cell Size There are 2 main reasons why cells are so small: If cells get too large: 1) there
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell 1. Cell Basics 2. Prokaryotic Cells 3. Eukaryotic Cells 1. Cell Basics Limits to Cell Size There are 2 main reasons why cells are so small: If cells get too large: 1) there
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
MUSCLE TISSUE. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 MUSCLE TISSUE Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Histologically identify and functionally characterize each of the 3 types of muscle tissues. Describe the organization of the sarcomere as seen
MUSCLE TISSUE Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Histologically identify and functionally characterize each of the 3 types of muscle tissues. Describe the organization of the sarcomere as seen
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams
 The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
