Physics 107 Problem 11.1 O. A. Pringle State the number of neutrons and protons in each of the following: 3. Li 6, 10
|
|
|
- Harold Gardner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 07 Problem. O. A. Pringle State the number of neutrons and protons in each of the following: Li 6, 0 Ne 22, 40 Zr 94, 72 Hf 80. Note that I haven't figured out how to makemathcad write both a superscript and a subscript immediately in front of a symbol, so I will use the old fashioned notation and write the atomic number (the subscript) first, the element abbreviation second, and the atomic mass (the superscript) last. The modern convention is to write both the subscript and superscript immediately in front of the symbol. Li6 has Z=, A=6, and N=A-Z=. Therefore Li 6 has protons and electrons, plus neutrons. 0 Ne22 has Z=0, A=22, and N=A-Z=2. Therefore it has 0 protons and 0 electrons, plus 2 neutrons. 40 Zr94 has Z=40, A=94, and N=A-Z=54. Therefore it has 40 protons and 40 electrons, plus 54 neutrons. 72 Hf80 has Z=72, A=80, and N=A-Z=08. Therefore it has 72 protons and 72 electrons, plus 08 neutrons. Physics 07 Problem.2 O. A. Pringle Ordinary boron is a mixture of the 5 B 0 and 5 B isotopes and has a composite atomic mass of 0.82 u. What percentage of each isotope is present in ordinary boron? Let α be the fraction of ordinary boron which is 5 B 0. Then -α is the fraction of ordinary boron which is 5 B. Ordinary boron is composed of α parts 5 B 0 and -α parts of 5 B. Therefore α. 0 ( α ) α.( 0 ) 0.82 α α = B0 makes up 8% of boron α = B makes up 82% of boron There are two ways to double-check the answer: α ( α ) = total boron had better be 00% α.( 0) ( α ). = 0.82 the composite mass had better be 0.82 You could get more accurate, and put in more decimal places for the masses of boron-0 and boron-. The answer would change by percent at most. It doesn't make sense to go to more than the.0 place on masses anyway, because 0.82 is only given to the.0 place. Physics 07 Problem. O. A. Pringle Electrons of what energy have wavelengths comparable with the radius of a 79 Au 97 nucleus? Use a relativistic calculation. This problem has two steps. Step is to calculate the radius of the 79 Au 97 nucleus. Step 2 is to calculate the energy of an electron having this wavelength. Gold has A=97. The radius of gold, in meters, is given by equation.. A 97
2 R.2. A. 0 5 R = meters Step 2 is to use this electron wavelength to calculate the electron momentum, use the momentum to calculate the total energy, and use relativity to calculate the kinetic energy. h λ R c. 0 8 m e p h p = Electron momentum. λ The electron energy is given by 2 E m. 4 e c p 2. c 2 Remember, we use the non-relativistic mass here. The kinetic energy is then K E m. e c 2 K = Joules K Or, in ev, K ev K ev = or K=77 MeV That's a lot of energy, but it represents a lower bound on the energy you would need to probe a gold nucleus with an electron. Just for kicks, let's calculate the electron velocity. E m. c 2 E m. e c 2 v 2 c 2 v 2 c 2 m. e c 2 E v 2 c 2 m. e c 2 E 2 m. e c 2 v c. v = E v = a very fast electron c Physics 07 Problem.4 O. A. Pringle The greater the atomic number of an atom, the larger its nucleus and the closer its inner electrons are to the nucleus. Compare the radius of the 92 U28 nucleus with the radius of its innermost Bohr orbit. The equation for orbital radii are given by equation 4. n 2. h 2. ε 0 r n π. m. e e 2 This is valid for hydrogen, Z=. To modify it for uranium, we realize that the nuclear charge is +Z instead of +, so that one of the e's in the denominator is replaced by Ze. ε h m e e
3 Z h 2. ε 0 r π. m. e Z. e 2 r = meters The radius of the uranium nucleus is given by equation. A 28 R A R = meters Let's compare the two radii: r = The Bohr radius is about 77 times the nuclear radius. R If you load HYDROGEN.MCD and calculate the probability of finding a hydrogen s electron at a distance less than a.0/77 of the nucleus, you get a probability of about %. That's not big, but it is finite, and suggests the uranium s electron might close enough to the nucleus to get captured. Physics 07 Problem.5 O. A. Pringle It is believed on the basis of the shell model that the nuclide of Z=0 and A=294 may be exceptionally long-lived. Estimate its nuclear radius. A 294 R R R. 0 A R = meters or R 7.979fm Physics 07 Problem.6 O. A. Pringle Show that the nuclear density of H is over 0 4 times greater than its atomic density. (Assume the atom to have the radius of the first Bohr orbit). The mass of H is m H kg The hydrogen atom radius is R m Note the error on the inside front cover of Beiser; he gives the wrong radius.
4 The atomic density of hydrogen is m H ρ H 4. π. R ρ H = kg/m It sounds like a lot, but we don't normally find these atoms packed very close together. The nuclear mass of H is m nucleus m H The nuclear radius is R nuc The nuclear density of hydrogen is ρ nuc m nucleus ρ nuc = π. R nuc The ratio of densities is ρ nuc = ρ H A simpler solution is to realize the masses are approximately the same, so the ratio of the densities is approximately that of the cube of the ratio of the radii ratio R R nuc ratio = Physics 07 Problem.2 O. A. Pringle What happens to the atomic number and mass number of a nucleus when it: a) emits an alpha particle? An alpha particle has Z=2 and A=4. When a nucleus emits an alpha particle, the atomic number Z decreases by two and the mass number A decreases by 4. b) emits an electron? For a nucleus to emit an electron, a neutron must change into a proton and an electron. Therefore, the nucleus has gained + in Z but has not gained in mass number. Therefore the atomic number Z increases by and the mass number A is unchanged. c) emits a positron? A positron is a positive electron. A proton must have decayed into a neutron and the electron. Therefore, the nucleus has lost in Z and has not changed in mass number. Therefore, the atomic number Z decreases by and the mass number A is unchanged. d) captures an electron? For a neutron to capture an electron, a proton and an electron must combine to form a neutron. The effect is the loss of a proton and the gain of a neutron. Therefore, as in c), the atomic number Z decreases by and the mass number A is unchanged. 4
5 Physics 07 Problem. O. A. Pringle Which nucleus would you expect to be more stable, Li 7 or Li 8 ; 6 C or 6 C 5? Even-even nuclei are most stable, odd-odd are least, and mixed are in between. Li 8 has Z= N=5 and Li7 has Z= N=4, so Li 7 ought to be more stable. The appendix on page 507 confirms this prediction. 6 C has Z=6 N=7 and 6 C 5 has Z=6 N=9. Based on this argument, we can't tell which would be more stable. However, 6 C 5 has two more neutrons in high energy levels than does 6 C, so we would expect 6 C5 to be less stable. Once again, the appendix on page 507 confirms our prediction. Nuclides with few nucleons (neutrons plus protons) tend to be most stable when they have about the same number of neutrons as protons. The neutrons are important because they provide binding energy to hold the nucleus together. On the other hand, every time you add two neutrons (two, because of the neutron spin) you have to populate a higher nuclear energy level. Thus, there is a tradeoff between more binding energy (reduced total energy) due to more neutrons, and less binding energy (increased total energy) due to putting neutrons in higher energy levels. If you look at Appendix V, you find that the most stable or the most abundant nuclides of the low-z elements are H, 2 He 4, Li 7, 4 Be 9, 5 B, 6 C 2, 7 N 4, 8 O 6, 9 F 9, 0 Ne 20, Na 2, 2 Mg 24, Al 27, 4 Si 2 8, 5 P 0, 6 S 2, 7 Cl5, 8 Ar 40, 9 K 9, 20 Ca 40, 2 Sc 45, 2 V 5, 24 Cr 52, etc. Notice the trends. H is an exception; it needs no neutrons because it has only one proton. Elements with even Z up to Argon have the same number of neutrons and protons (He, C, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S) with the exception of beryllium. Elements with odd Z up to potassium (Li, B, N, F, Na, Al, P, Cl, K) have one more neutron than protons, or else the same number of neutrons as protons. Thus, given a multiple choice problem, the BEST answer would be to look for either N=Z or N=Z+. Physics 07 Problem.4 O. A. Pringle Both 8 O 4 and 8 O 9 undergo beta decay. Which would you expect to emit a positron and which an electron? Why? 8 O4 has 8 protons and 6 neutrons. It has an excess of protons compared to neutrons. We should expect it to undergo positron emission, where a proton changes into a neutron and an electron. 8 O9 has 8 protons and neutrons. It has an excess of neutrons compared to protons. We should expect it to undergo beta decay, where a neutron changes into a proton and an electron. Physics 07 Problem.5 O. A. Pringle Find the binding energy per nucleon in 0 Ne 20 and 26 Fe 56. Binding energy per nucleon problems are solved by finding the mass of Z hydrogen atoms plus A-Z neutrons and subtracting the atomic mass of the nuclide in question. This mass difference is converted to energy and is said to the the total binding energy of the nuclide. This energy is then divided by A, the number of nucleons to find the binding energy per nucleon. Atomic mass of neutron: m n u Atomic mass of hydrogen: m h u 5
6 Binding energy of nuclide of mass M, atomic mass A, and atomic number Z: E b ( M, A, Z) M Z. m h ( A Z). m. n 9.5 The 9.5 converts amu to MeV. Binding energy per nucleon: E b ( MA,, Z) E per_n ( MA,, Z) A Binding energy per nucleon for 20 Ne 0, of mass u E per_n ( , 79, 5) = Binding energy per nucleon for 26 Fe 56, of mass u E per_n ( , 56, 26) = 8.79 The numbers above show the reduction in energy upon creation of the nucleus. Don't forget that the binding energy is expressed as a positive energy, so that the binding energies per nucleon are 8.0 MeV for Ne and 8.79 MeV for iron. Physics 07 Problem.6 O. A. Pringle Find the binding energy per nucleon in 5 Br 79 and 79 Au 97. Binding energy per nucleon problems are solved by finding the mass of Z hydrogen atoms plus A-Z neutrons and subtracting the atomic mass of the nuclide in question. This mass difference is converted to energy and is said to the the total binding energy of the nuclide. This energy is then divided by A, the number of nucleons to find the binding energy per nucleon. Atomic mass of neutron: m n u Atomic mass of hydrogen: m h u Binding energy of nuclide of mass M, atomic mass A, and atomic number Z: E b ( M, A, Z) M Z. m h ( A Z). m n. 9.5 Binding energy per nucleon: E per_n ( MA,, Z) E b ( MA,, Z) A Binding energy per nucleon for 5 Br 79, of mass u E per_n ( , 79, 5) = Binding energy per nucleon for 79 Au 97, of mass u E per_n ( , 97, 79) = 7.96 The numbers above show the reduction in energy upon creation of the nucleus. Don't forget that the binding energy is expressed as a positive energy, so that the binding energies per nucleon are 8.69 MeV for Br and 7.92 MeV for gold. 6
7 Physics 07 Problem.7 O. A. Pringle Find the energies needed to remove a neutron from 2 He 4, then to remove a proton, and finally to separate the remaining neutron and proton. Compare the total with the binding energy of 2 He 4. Atomic mass of neutron: m n u Atomic mass of hydrogen: m h u Atomic mass of 2 He 4 : m 2He Atomic mass of 2 He : m 2He Atomic mass of H 2 : m H The energy needed to remove a neutron from 2 He 4 is: E m 2He m n m. 2He4 9.5 E = The energy needed to remove a proton from 2 He is: The energy needed to separate the remaining neutron and proton is: E 2 m H2 m h m. 2He 9.5 E 2 = E m n m h m. H2 9.5 E = The total energy is: E t E E 2 E E t = The binding energy of 2 He 4 is : E b ( M, A, Z) Z. m h ( A Z). m n M. 9.5 E b ( , 4, 2) = This formula gives the positive number which is the BE/nucleon. Physics 07 Problem.8 O. A. Pringle The binding energy of 2 Mg 24 is MeV. Find its atomic mass. This is just a binding energy per nucleon (except we are given the total binding energy) but in reverse. BE I'm going to do this step-by-step. First step: calculate from the binding energy how much mass is missing from the nucleus (how much mass was converted to binding energy). mass_difference mass_difference = 0.2 mass units, u 7
8 Second step: if I take this mass difference and subtract it from the mass of 2 hydrogens plus 2 neutrons (which we have in 2 Mg 24 ), I'll get the actual mass of 2 Mg 24 m H u m n u M 2Mg24 2. m H 2. m n mass_difference M 2Mg24 = This is the mass given on page 508, to decimal places. I can't give more decimal places because Beiser only gave the binding energy to digits. 8
Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics comprises the study of:
 Nuclear Physics Nuclear Physics comprises the study of: The general properties of nuclei The particles contained in the nucleus The interaction between these particles Radioactivity and nuclear reactions
Nuclear Physics Nuclear Physics comprises the study of: The general properties of nuclei The particles contained in the nucleus The interaction between these particles Radioactivity and nuclear reactions
Objectives 404 CHAPTER 9 RADIATION
 Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Main properties of atoms and nucleus
 Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
( + and - ) ( - and - ) ( + and + ) Atoms are mostly empty space. = the # of protons in the nucleus. = the # of protons in the nucleus
 Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
Basic Nuclear Concepts
 Section 7: In this section, we present a basic description of atomic nuclei, the stored energy contained within them, their occurrence and stability Basic Nuclear Concepts EARLY DISCOVERIES [see also Section
Section 7: In this section, we present a basic description of atomic nuclei, the stored energy contained within them, their occurrence and stability Basic Nuclear Concepts EARLY DISCOVERIES [see also Section
CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers
 1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
Masses in Atomic Units
 Nuclear Composition - the forces binding protons and neutrons in the nucleus are much stronger (binding energy of MeV) than the forces binding electrons to the atom (binding energy of ev) - the constituents
Nuclear Composition - the forces binding protons and neutrons in the nucleus are much stronger (binding energy of MeV) than the forces binding electrons to the atom (binding energy of ev) - the constituents
Chapter NP-1. Nuclear Physics. Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES
 Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Chapter NP-1 Nuclear Physics Atomic Nature of Matter TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 PROPERTIES OF SUBSTANCES 1.1 CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 2.0 COMPOSITION OF ATOMS 2.1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
 2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
............... [2] At the time of purchase of a Strontium-90 source, the activity is 3.7 10 6 Bq.
![............... [2] At the time of purchase of a Strontium-90 source, the activity is 3.7 10 6 Bq. ............... [2] At the time of purchase of a Strontium-90 source, the activity is 3.7 10 6 Bq.](/thumbs/40/21837699.jpg) 1 Strontium-90 decays with the emission of a β-particle to form Yttrium-90. The reaction is represented by the equation 90 38 The decay constant is 0.025 year 1. 90 39 0 1 Sr Y + e + 0.55 MeV. (a) Suggest,
1 Strontium-90 decays with the emission of a β-particle to form Yttrium-90. The reaction is represented by the equation 90 38 The decay constant is 0.025 year 1. 90 39 0 1 Sr Y + e + 0.55 MeV. (a) Suggest,
Physics 1104 Midterm 2 Review: Solutions
 Physics 114 Midterm 2 Review: Solutions These review sheets cover only selected topics from the chemical and nuclear energy chapters and are not meant to be a comprehensive review. Topics covered in these
Physics 114 Midterm 2 Review: Solutions These review sheets cover only selected topics from the chemical and nuclear energy chapters and are not meant to be a comprehensive review. Topics covered in these
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes
 Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Chapter 7. Electron Structure of the Atom. Chapter 7 Topics
 Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:)
 Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
PHYA5/1. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2011. Unit 5 Nuclear and Thermal Physics Section A
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 1. The number of electrons in an atom of atomic number Z and mass number A is 1) A 2) Z 3) A+Z 4) A-Z 2. The repulsive force between the positively charged protons does
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 1. The number of electrons in an atom of atomic number Z and mass number A is 1) A 2) Z 3) A+Z 4) A-Z 2. The repulsive force between the positively charged protons does
Atomic Calculations. 2.1 Composition of the Atom. number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number
 2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25. 4 Atoms and Elements
 47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
3 Atomic Structure 15
 3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
3 Atomic Structure 15 3.1 Atoms You need to be familiar with the terms in italics The diameter of the nucleus is approximately 10-15 m and an atom 10-10 m. All matter consists of atoms. An atom can be
Lecture 09 Nuclear Physics Part 1
 Lecture 09 Nuclear Physics Part 1 Structure and Size of the Nucleus Νuclear Masses Binding Energy The Strong Nuclear Force Structure of the Nucleus Discovered by Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden in 1909
Lecture 09 Nuclear Physics Part 1 Structure and Size of the Nucleus Νuclear Masses Binding Energy The Strong Nuclear Force Structure of the Nucleus Discovered by Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden in 1909
2 The Structure of Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission
 Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY
 MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY The separate laws of Conservation of Mass and Conservation of Energy are not applied strictly on the nuclear level. It is possible to convert between mass and energy. Instead
MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY The separate laws of Conservation of Mass and Conservation of Energy are not applied strictly on the nuclear level. It is possible to convert between mass and energy. Instead
13- What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the subshell 3d? a) 1 b) 3 c) 5 d) 2
 Assignment 06 A 1- What is the energy in joules of an electron undergoing a transition from n = 3 to n = 5 in a Bohr hydrogen atom? a) -3.48 x 10-17 J b) 2.18 x 10-19 J c) 1.55 x 10-19 J d) -2.56 x 10-19
Assignment 06 A 1- What is the energy in joules of an electron undergoing a transition from n = 3 to n = 5 in a Bohr hydrogen atom? a) -3.48 x 10-17 J b) 2.18 x 10-19 J c) 1.55 x 10-19 J d) -2.56 x 10-19
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure
 Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
9/13/2013. However, Dalton thought that an atom was just a tiny sphere with no internal parts. This is sometimes referred to as the cannonball model.
 John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
Chapter NP-5. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 NUCLEAR REACTIONS 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS
 Chapter NP-5 Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS 2.1 ELASTIC SCATTERING 2.2 INELASTIC SCATTERING 2.3 RADIATIVE CAPTURE 2.4 PARTICLE
Chapter NP-5 Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 1.0 2.0 NEUTRON INTERACTIONS 2.1 ELASTIC SCATTERING 2.2 INELASTIC SCATTERING 2.3 RADIATIVE CAPTURE 2.4 PARTICLE
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements
 EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
ANSWER KEY : BUILD AN ATOM PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom )
 ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
PHYA5/1. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012. Unit 5 Nuclear and Thermal Physics Section A
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examinerʼs Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examinerʼs Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 Question 1 2 Mark Physics
2014 Spring CHEM101 Ch1-2 Review Worksheet Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai,
 Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Chapter 13 & 14 Assignment & Problem Set
 Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters. 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle?
 1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
1. In the general symbol cleus, which of the three letters Z A X for a nu represents the atomic number? 2. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? 3. What is the mass number of a beta particle? 4.
Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table
 Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Basic Concepts in Nuclear Physics
 Basic Concepts in Nuclear Physics Paolo Finelli Corso di Teoria delle Forze Nucleari 2011 Literature/Bibliography Some useful texts are available at the Library: Wong, Nuclear Physics Krane, Introductory
Basic Concepts in Nuclear Physics Paolo Finelli Corso di Teoria delle Forze Nucleari 2011 Literature/Bibliography Some useful texts are available at the Library: Wong, Nuclear Physics Krane, Introductory
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39)
 ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom
 NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
Nuclear ZPE Tapping. Horace Heffner May 2007
 ENERGY FROM UNCERTAINTY The uncertainty of momentum for a particle constrained by distance Δx is given, according to Heisenberg, by: Δmv = h/(2 π Δx) but since KE = (1/2) m v 2 = (1/(2 m) ) (Δmv) 2 ΔKE
ENERGY FROM UNCERTAINTY The uncertainty of momentum for a particle constrained by distance Δx is given, according to Heisenberg, by: Δmv = h/(2 π Δx) but since KE = (1/2) m v 2 = (1/(2 m) ) (Δmv) 2 ΔKE
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table
 Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Introduction to Nuclear Physics
 Introduction to Nuclear Physics 1. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table According to the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom, also called the solar system model, the atom consists of a central nucleus
Introduction to Nuclear Physics 1. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table According to the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom, also called the solar system model, the atom consists of a central nucleus
2. John Dalton did his research work in which of the following countries? a. France b. Greece c. Russia d. England
 CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126.
 Chapter 5 Nuclear Shell Model 5.1 Magic Numbers The binding energies predicted by the Liquid Drop Model underestimate the actual binding energies of magic nuclei for which either the number of neutrons
Chapter 5 Nuclear Shell Model 5.1 Magic Numbers The binding energies predicted by the Liquid Drop Model underestimate the actual binding energies of magic nuclei for which either the number of neutrons
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems
 Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
Lesson 43: Alpha, Beta, & Gamma Decay
 Lesson 43: Alpha, Beta, & Gamma Decay The late 18s and early 19s were a period of intense research into the new nuclear realm of physics. In 1896 Henri Becquerel found that a sample of uranium he was doing
Lesson 43: Alpha, Beta, & Gamma Decay The late 18s and early 19s were a period of intense research into the new nuclear realm of physics. In 1896 Henri Becquerel found that a sample of uranium he was doing
PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes.
 1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry. Part I Multiple Choice Questions Part II Free Response Questions Selected Questions from1970 to 2010
 The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Part I Multiple Choice Questions Part II Free Response Questions Selected Questions from1970 to 2010 Atomic Theory and Periodicity Part I 1984 1. Which of
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Part I Multiple Choice Questions Part II Free Response Questions Selected Questions from1970 to 2010 Atomic Theory and Periodicity Part I 1984 1. Which of
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems
 Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life.
 PHY 192 Half Life 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity as a function
PHY 192 Half Life 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity as a function
Atoms and Elements. Atoms: Learning Goals. Chapter 3. Atoms and Elements; Isotopes and Ions; Minerals and Rocks. Clicker 1. Chemistry Background?
 Chapter 3 Atoms Atoms and Elements; Isotopes and Ions; Minerals and Rocks A Review of Chemistry: What geochemistry tells us Clicker 1 Chemistry Background? A. No HS or College Chemistry B. High School
Chapter 3 Atoms Atoms and Elements; Isotopes and Ions; Minerals and Rocks A Review of Chemistry: What geochemistry tells us Clicker 1 Chemistry Background? A. No HS or College Chemistry B. High School
The Structure of the Atom
 The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary
 Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems
 Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE
 CHAPTER 5 EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Elements are composed of indivisable particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same properties; atoms of different
CHAPTER 5 EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Elements are composed of indivisable particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same properties; atoms of different
About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY. Recommended literature: Chemistry: science of the matter. Responsible for the course: Dr.
 About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY University of Pécs Medical School Academic year 2009-2010. Responsible for the course: Dr. Attila AGÓCS Optional course for 2 credit points. To have grade at the and
About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY University of Pécs Medical School Academic year 2009-2010. Responsible for the course: Dr. Attila AGÓCS Optional course for 2 credit points. To have grade at the and
Structure and Properties of Atoms
 PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
F321 THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS. ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... in the nucleus of an atom
 Atomic Structure F32 TE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Atomic Structure F32 TE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Unit 1 Practice Test. Matching
 Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table
 Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry
 Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry Why? Chemists are concerned with mass relationships in chemical reactions, usually run on a macroscopic scale (grams, kilograms, etc.). To deal with
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Moles & Stoichiometry Why? Chemists are concerned with mass relationships in chemical reactions, usually run on a macroscopic scale (grams, kilograms, etc.). To deal with
CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS (END OF CHAPTER 7 TOO)
 CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS (END OF CHAPTER 7 TOO) Information that most likely will be on the front cover of your exam: h i Z 2 ΔE = @ 2.18 x 10 @ 18 f Z 2 f J j @ k n f 2 n i 2 1. Which of the
CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS (END OF CHAPTER 7 TOO) Information that most likely will be on the front cover of your exam: h i Z 2 ΔE = @ 2.18 x 10 @ 18 f Z 2 f J j @ k n f 2 n i 2 1. Which of the
1. Degenerate Pressure
 . Degenerate Pressure We next consider a Fermion gas in quite a different context: the interior of a white dwarf star. Like other stars, white dwarfs have fully ionized plasma interiors. The positively
. Degenerate Pressure We next consider a Fermion gas in quite a different context: the interior of a white dwarf star. Like other stars, white dwarfs have fully ionized plasma interiors. The positively
Elements, Atoms & Ions
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
(b) find the force of repulsion between a proton at the surface of a 12. 6 C nucleus and the remaining five protons.
 Chapter 13 Nuclear Structure. Home Work s 13.1 Problem 13.10 (a) find the radius of the 12 6 C nucleus. (b) find the force of repulsion between a proton at the surface of a 12 6 C nucleus and the remaining
Chapter 13 Nuclear Structure. Home Work s 13.1 Problem 13.10 (a) find the radius of the 12 6 C nucleus. (b) find the force of repulsion between a proton at the surface of a 12 6 C nucleus and the remaining
B) atomic number C) both the solid and the liquid phase D) Au C) Sn, Si, C A) metal C) O, S, Se C) In D) tin D) methane D) bismuth B) Group 2 metal
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
3. What would you predict for the intensity and binding energy for the 3p orbital for that of sulfur?
 PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table. Ron Robertson
 Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table Ron Robertson History of Chemistry Before 16 th Century Alchemy Attempts (scientific or otherwise) to change cheap metals into gold no real
Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table Ron Robertson History of Chemistry Before 16 th Century Alchemy Attempts (scientific or otherwise) to change cheap metals into gold no real
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 3650, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 31, 2005 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 3650, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 31, 2005 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 3650, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 31, 2005 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
Solar Energy Production
 Solar Energy Production We re now ready to address the very important question: What makes the Sun shine? Why is this such an important topic in astronomy? As humans, we see in the visible part of the
Solar Energy Production We re now ready to address the very important question: What makes the Sun shine? Why is this such an important topic in astronomy? As humans, we see in the visible part of the
neutrons are present?
 AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
KE A = PE MAX 1/2M v 2 = k q1 q2 /R
 CHAPTER 13 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE NUCLEAR FORCE The nucleus is help firmly together by the nuclear or strong force, We can estimate the nuclear force by observing that protons residing about 1fm = 10-15m apart
CHAPTER 13 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE NUCLEAR FORCE The nucleus is help firmly together by the nuclear or strong force, We can estimate the nuclear force by observing that protons residing about 1fm = 10-15m apart
Matter. Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole
 Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating
 Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating K-Ar Dating In 10,000 K atoms: 9326 39 K 673 41 K 1 40 K Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Argon About 1% of atmosphere is argon Three stable isotopes of argon
Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) Dating K-Ar Dating In 10,000 K atoms: 9326 39 K 673 41 K 1 40 K Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Potassium Decay Argon About 1% of atmosphere is argon Three stable isotopes of argon
Element of same atomic number, but different atomic mass o Example: Hydrogen
 Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
Atomic mass: p + = protons; e - = electrons; n 0 = neutrons p + + n 0 = atomic mass o For carbon-12, 6p + + 6n 0 = atomic mass of 12.0 o For chlorine-35, 17p + + 18n 0 = atomic mass of 35.0 atomic mass
Level 3 Achievement Scale
 Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
Atomic Structure Chapter 5 Assignment & Problem Set
 Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Introduction to Chemistry
 1 Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use. Introduction to Chemistry In Chemistry the word weight is commonly used in place of the more proper term mass. 1.1 Atoms, Ions, and
1 Copyright ç 1996 Richard Hochstim. All rights reserved. Terms of use. Introduction to Chemistry In Chemistry the word weight is commonly used in place of the more proper term mass. 1.1 Atoms, Ions, and
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom
 Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
Atoms and Elements. Outline Atoms Orbitals and Energy Levels Periodic Properties Homework
 Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Materials Molecules Atoms Atoms = protons (p) + neutrons (n) + electrons (e) Protons and neutrons are made of quarks Quantitative measurements need units:
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Materials Molecules Atoms Atoms = protons (p) + neutrons (n) + electrons (e) Protons and neutrons are made of quarks Quantitative measurements need units:
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION (SHORT FORM) # of electrons in the subshell. valence electrons Valence electrons have the largest value for "n"!
 179 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION (SHORT FORM) - We can represent the electron configuration without drawing a diagram or writing down pages of quantum numbers every time. We write the "electron configuration".
179 ELECTRON CONFIGURATION (SHORT FORM) - We can represent the electron configuration without drawing a diagram or writing down pages of quantum numbers every time. We write the "electron configuration".
Untitled Document. 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? 4. Which statement best describes the density of an atom s nucleus?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Brief remarks. m 2hyp,i + p2π,i + 2π + p 2π,i = m 2 hyp,i + p2 π,i + E π,i (2) m K + m A =
 1 Brief remarks In FINUDA the strangeness-exchange reaction is used to produce Λ- hypernuclei with stopped K s: K stop + Z A Z Λ A + π (1) Thanks to the energy conservation, we can write for each bound
1 Brief remarks In FINUDA the strangeness-exchange reaction is used to produce Λ- hypernuclei with stopped K s: K stop + Z A Z Λ A + π (1) Thanks to the energy conservation, we can write for each bound
WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
 WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION All waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency and speed. Wavelength (lambda, ): the distance between any 2 successive crests or troughs. Frequency (nu,):
WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION All waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency and speed. Wavelength (lambda, ): the distance between any 2 successive crests or troughs. Frequency (nu,):
Photons. ConcepTest 27.1. 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy. Which has more energy, a photon of:
 ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which has more energy, a photon of: 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which
ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which has more energy, a photon of: 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which
6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties
 324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
Atomic Theory Part 1
 Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Lesson 6: Earth and the Moon
 Lesson 6: Earth and the Moon Reading Assignment Chapter 7.1: Overall Structure of Planet Earth Chapter 7.3: Earth s Interior More Precisely 7-2: Radioactive Dating Chapter 7.5: Earth s Magnetosphere Chapter
Lesson 6: Earth and the Moon Reading Assignment Chapter 7.1: Overall Structure of Planet Earth Chapter 7.3: Earth s Interior More Precisely 7-2: Radioactive Dating Chapter 7.5: Earth s Magnetosphere Chapter
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 2: Nuclear reactions and radiation. Marc R. Roussel
 Chemistry 1000 Lecture 2: Nuclear reactions and radiation Marc R. Roussel Nuclear reactions Ordinary chemical reactions do not involve the nuclei, so we can balance these reactions by making sure that
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 2: Nuclear reactions and radiation Marc R. Roussel Nuclear reactions Ordinary chemical reactions do not involve the nuclei, so we can balance these reactions by making sure that
THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27)
 THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27) THE PERIODIC TABLE In 1872, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table arranged
THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27) THE PERIODIC TABLE In 1872, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table arranged
Bohr s Model of the Atom
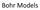 Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Periodic Table Questions
 Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
Multi-electron atoms
 Multi-electron atoms Today: Using hydrogen as a model. The Periodic Table HWK 13 available online. Please fill out the online participation survey. Worth 10points on HWK 13. Final Exam is Monday, Dec.
Multi-electron atoms Today: Using hydrogen as a model. The Periodic Table HWK 13 available online. Please fill out the online participation survey. Worth 10points on HWK 13. Final Exam is Monday, Dec.
