LIGAMENTS AND TENDONS OF THE HUMAN BODY
|
|
|
- Nigel Horace Davis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APP14 ligaments.qxd 8/13/05 1:31 PM Page APP 67 Shoulder/Upper Arm Lm. acromioclaviculare acromioclavicular l. Connects acromion to clavicle; strengthens articular capsule Lm. anulare radii anular l. of radius Connects head of radius in radial notch Lm. collaterale ulnare collateral ulnar l. Connects medial epicondyle to humerus and coronoid process of ulna and olecranon Lm. conoideum conoid l. Connects coracoid process of scapula to clavicle Lm. coracoacromiale coracoacromial l. Connects coracoid process to acromion Lm. coracoclaviculare coracoclavicular l. Connects coracoid process of scapula to clavicle Lm. coracohumerale coracohumeral l. Connects coracoid process of scapula to humerus Lm. costoclaviculare costoclavicular l. Connects 1st costal cartilage to clavicle Lm. glenohumeralia glenohumeral ligs. Connects articular capsule of humerus to glenoid cavity and anatomic neck of humerus Lm. interclaviculare interclavicular l. Connects clavicle to opposite clavicle Lm. orbiculare radii annular l. of radius Encircles and holds the head of the radius in the radial notch of the ulna Lm. sternoclaviculare anterius anterior sternoclavicular l. Fibrous band that reinforces the sternoclavicular joint anteriorly Lm. sternoclavicular posterius posterior sternoclavicular l. Fibrous band that reinforces the sternoclavicular joint posteriorly Lm. suspensorium axillae suspensory l. Connects between the clavipectoral fascia downward to the axillary fascia Lm. transversum humeri transverse humeral l. Connects obliquely from the greater to the lesser tuberosity of the humerus Lm. transversum scapulae inferius inferior transverse l. Connects scapula to glenoid cavity; creates foramen of scapula for vessels/nerves Lm. transversum scapulae superius superior transverse l. Connects coracoid process to scapular notch of scapula Lm. trapezoideum trapezoid l. Connects coracoid process to clavicle Hand/Forearm Lm. anulare radii anular l. of radius Connects radius to ulna Lm. carpi radiatum radiate l. of wrist Multiple fibrous bands on palmar surface of metacarpal joint Lm. carpi transversum transverse carpal l. Continuous with antebrachial fascia Lm. carpi volare transverse carpal l. Reinforcing fibers in antebrachial fascia, palmar surface of wrist La. carpometacarpalia dorsalia dorsal carpometacarpal ligs. Join carpal bones to bases of metacarpals La. carpometacarpalia palmaria palmar carpometacarpal metacarpals Join carpal bones to metacarpals ligs. La. collateralia articulationum collateral ligs. of interphalangeal Fibrous bands on each side of interphalangeal joints of fingers interphalangealium manus La. collateralia articulationum collateral ligs. of metacarpophalangeal Fibrous bands on sides of each meta-carpophalangeal joint metacarpophalangealium Lm. collaterale carpi radiale radial carpal collateral l. Connects styloid process of radius to scaphoid Lm. collaterale carpi ulnare ulnar carpal collateral l. Connects styloid process of ulna to triquetral and pisiform bones Lm. collaterale radiale collateral radial l. Connects lateral epicondyle of humerus to anular l. of radius Lm. intercarpalia dorsalia interossea dorsal intercarpal ligs. Connect carpal bones Lm. intercarpalia interossea interosseous intercarpal ligs. Connect various carpal bones Lm. intercarpalia palmaria palmar intercarpal ligs. Connect various carpal bones La. metacarpalia dorsalia dorsal metacarpal ligs. Interconnects bases of metacarpal bones La. metacarpalia interossea interosseous metacarpal ligs. Interconnects bases of metacarpal bones La. metacarpalia palmaria palmar metacarpal ligs. Interconnects bases of metacarpals La. metacarpeum transversum deep transverse metacarpal l. Interconnects heads of metacarpals Lm. metacarpale transversum superficial transverse metacarpal l. Between longitudinal bands of palmar aponeurosis Lm. natatorium superficial transverse metacarpal l. Thickening of the deep fascia in most distal part of the base of the triangular palmar APP 67
2 APP14 ligaments.qxd 8/13/05 1:31 PM Page APP 68 APP 68 Lm. palmaria palmar l. Connects anterior aspect of each metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joint of the hand La. palmaria articulationis palmar ligs. of interphalangeal Interphalangeal of hand between collateral interphalangeae manus joints of the hand La. palmaria articulationis palmar ligs. of metacarpal joints Connects metacarpophalangeal joints to the collateral ligs. metacarpophalangeae Lm. pisohamatum pisohamate l. Connects pisiform bone to hook of hamate bone Lm. pisometacarpeum pisometacarpal l. Connects pisiform bone to bases of metacarpals Lm. quadratum quadrate l. Connects radial notch of ulna to neck of radius Lm. radiocarpale dorsale dorsal radiocarpal l. Connects radius to carpal bones Lm. radiocarpale palmare palmar radiocarpal l. Connects radius to lunate, triquetral, capitate, and hamate bones Lm. ulnocarpale palmare palmar ulnocarpal l. Connects styloid process of ulna to carpal bones Spine La. alaria alar l. Connects axis to occiput; limits rotation of head Lm. apicis dentis axis apical dental l. Connects axis to occiput La. atlantooccipitale laterale lateral atlantooccipital l. Connects occiput to atlas Lm. capitis costae intraarticulare interarticular l. of head of rib Connects crest of rib to intervertebral disk Lm. capitis costae radiatum radiate l. of head of rib Connects head of rib to adjacent vertebrae/disks Lm. caudale integumenti communis caudal retinaculum Forms coccygeal foveola Lm. costotransversarium costotransverse l. Connects neck of rib to transverse process of corresponding vertebra Lm. costotransversarium laterale lateral costotransverse l. Connects transverse process of vertebra to corresponding rib Lm. costotransversarium superius superior costotransverse l. Connects neck of rib to transverse process of vertebra above Lm. cruciforme atlantis cruciform l. of atlas Connects transverse l. of atlas to longitudinal fascicles La. flava yellow ligs. Joins laminae of two adjacent vertebrae Lm. iliofemorale iliofemoral l. Connects anterior/inferior iliac spine and intertrochanteric femur Lm. iliolumbale iliolumbar l. Connects L4-L5 to iliac crest Lm. interspinale interspinous l. Interconnect spinous processes Lm. intertransversarium intertransverse l. Interconnect vertebral transverse processes Lm. longitudinale anterius anterior longitudinal l. Extends from occiput/atlas to sacrum Lm. longitudinale posterius posterior longitudinal l. Extends from occiput to coccyx Lm. lumbocostale lumbocostal l. Connects 12th rib to transverse processes of L1-L2 Lm. nuchae radiate l. Connects head of each rib to bodies of the two vertebrae with which it articulates Lm. sacrococcygeum anterius anterior sacrococcygeal l. Connects sacrum to coccyx Lm. sacrococcygeum laterale lateral sacrococcygeal l. Connects 1st coccygeal vertebra to sacrum; completes foramen of S5 Lm. sacrococcygeum posterius deep posterior sacrococcygeal l. Terminal portion of posterior longitudinal l.; unites S5 and coccyx Lm. sacrococcygeum posterius superficial posterior sacrococcygeal l. Connects sacral hiatus to coccyx La. sacroiliaca anteriora anterior sacroiliac ligs. Connects sacrum to ilium La. sacroiliaca interossea interosseous sacroiliac ligs. Numerous bundles connecting tuberosities of sacrum to those of ilium La. sacroiliaca posteriora posterior sacroiliac ligs. Connects ilium and iliac spines to sacrum Lm. sacrospinale sacrospinous l. Connects ischium to lateral margins of sacrum Lm. sacrotuberale sacrotuberous l. Connects ischial tuberosity to sacrum and coccyx and iliac spine Lm. supraspinale supraspinous l. Interconnects tips of spinous processes of vertebrae Lm. transversum atlantis transverse l. of atlas Horizontal portion of cruciform l. of atlas
3 APP14 ligaments.qxd 8/13/05 1:31 PM Page APP 69 APP 69 Abdominal/Pelvic Lm. arcuatum laterale lateral arcuate l. Connects first lumbar vertebrae and 12th rib to diaphragm Lm. arcuatum mediale medial arcuate l. Connects body of first lumbar vertebra to transverse process Lm. arcuatum pubis inferior pubic l. Arches across pubic symphysis Lm. falciforme falciform process of sacrotuberous l. Passes from ischial tuberosity to ilium, sacrum, and coccyx Lm. laterale vesicae lateral bladder l. Passes from one side of the bladder to blend with the pelvic fascia Lm. pectineale pectineal l. A strong fibrous band that passes laterally from the lacunar l. along the pectineal line of the pubis Lm. pubicum inferius inferior pubic l. Arches across the inferior aspect of the pubic symphysis Lm. pubicum superius superior pubic l. Passes transversely above the pubic symphysis Lm. pubofemorale pubofemoral l. Connects from the superior ramus of the pubis to the intertrochanteric femur Lm. sacrodurale sacrodural l. Connects between the midline of the inferior part of the dorsal sac to the posterior longitudinal l. of the sacrum. Lm. sacroiliacum posterius posterior sacroiliac ligs. Connects from the ilium to the sacrum posterior to the sacroiliac joint Lm. sacrospinale sacrospinal l. Connects between the ischial spine and the sacrum and coccyx Hip/Thigh Lm. capitis femoris l. of head of femur Connects femur, acetabular notch, and transverse l. of acetabulum Lm. inguinale inguinal l. Connects ilium to pubis Lm. ischiofemorale ischiofemoral l. Connects ischium to femur Lm. transversum acetabuli transverse acetabular l. Connects acetabular lip of hip joint to acetabular notch Knee/Calf Lm. capitis fibulae anterius anterior l. of fibular head Connects head of fibula to lateral condyle of tibia Lm. capitis fibulae posterius posterior l. of fibular head Connects head of fibula to lateral condyle of tibia Lm. collaterale fibulare collateral fibular l. Connects lateral epicondyle of femur to head of fibula Lm. collateral tibiale tibial collateral l. Connects medial epicondyle of femur to medial meniscus and tibia Lm. cruciatum anterius genus anterior cruciate l. of knee Connects lateral condyle of femur to condylar eminence of tibia La. cruciata genus cruciate ligs. of knee Bundles in knee joint between condyles of femur Lm. cruciatum posterius genus posterior cruciate l. of knee Connects medial condyle of femur to intercondylar area of tibia Lm. menisci lateralis posterior meniscofemoral l. Connects between the medial condyle of the femur to the posterior crus of the lateral meniscus Lm. meniscofemorale anterius anterior meniscofemoral l. Connects lateral meniscus to posterior cruciate l. Lm. meniscofemorale posterius posterior meniscofemoral l. Connects lateral meniscus to medial condyle of femur Lm. patellae patellar l. Connects patella to tibial tuberosity Lm. popliteum arcuatum arcuate popliteal l. Connects fibula to articular capsule Lm. popliteum obliquum oblique popliteal l. Connects medial condyle of tibia to lateral epicondyle of femur Lm. teres femoris head of femur l. Connects from the fovea in the head of the femur to the borders of the acetabular notch Lm. tibiofibulare anterius anterior tibiofibular l. Connects tibia to fibula Lm. tibiofibulare posterius posterior tibiofibular l. Connects tibia to distal fibula Lm. tibionaviculare tibionavicular part of medial l. of Connects from medial malleolus of the ankle joint tibia downward to the tarsal bones Lm. transversum genus transverse l. of knee Connects lateral meniscus to medial meniscus
4 APP14 ligaments.qxd 8/13/05 1:31 PM Page APP 70 APP 70 Foot and Ankle m. bifurcatum bifurcate l. Dorsum of foot; comprises calcaneonavicular and calcaneocuboid ligs. Lm. calcaneocuboideum calcaneocuboid l. Connects calcaneus to cuboid Lm. calcaneocuboideum plantare plantar calcaneocuboid l., short Connects calcaneus to cuboid plantar l. Lm. calcaneofibulare calcaneofibular l. Connects fibula to calcaneus Lm. calcaneonaviculare calcaneonavicular l. Connects calcaneus to navicular bone Lm. calcaneonaviculare dorsale dorsal calcaneonavicular l. Connects calcaneus to navicular bone Lm. calcaneonaviculare plantare plantar calcaneonavicular l. Connects sustentaculum tali to navicular; supports talus Lm. calcaneotibiale calcaneotibial l. Connect medial malleolus to sustentaculum tali of calcaneus Lm. collateralia articulationum collateral ligs. of metatarsophalangeal Fibrous bands on sides of each metatarsophalangeal joint Lm. cruciatum cruris inferior extensor of foot Joins malleolus to dorsum of foot Lm. cuboideonaviculare dorsale dorsal cuboideonavicular l. Connects cuboid and navicular bones Lm. cuboideonaviculare plantare plantar cuboideonavicular l. Connects cuboid and navicular bones Lm. cuneocuboideum dorsale dorsal cuneocuboid l. Connects cuboid and lateral cuneiform bones Lm. cuneocuboideum interosseum interosseus cuneocuboid l. Connects cuboid and lateral cuneiform bones Lm. cuneocuboideum plantare plantar cuneocuboid l. Connects cuboid and lateral cuneiform bones La. cuneometatarsalia interossea interosseous cuneometatarsal ligs. Connects cuneiform and metatarsal bones La. cuneonavicularia dorsalia dorsal cuneonavicular ligs. Connects navicular and cuneiform bones La. cuneonavicularia plantaria plantar cuneonavicular ligs. Connects navicular to cuneiform bones La. intercuneiformia dorsalia dorsal intercuneiform ligs. Connects dorsal surfaces of cuneiform bones La. intercuneiformia interossea interosseous intercuneiform ligs. Connects adjacent cuneiform bones La. intercuneiformia plantaria plantar intercuneiform ligs. Joins plantar surfaces of cuneiform bones Lm. laterale articulationis talocruralis lateral l. of ankle joint Lateral side of ankle joint Lm. mediale articulationis medial l. of ankle Connects medial malleolus of tibia to tarsal bones talocruralis La. meniscofemoralia meniscofemoral ligs. Connects from posterior part of lateral meniscus to the lateral surface of the medial meniscus Lm. metatarsale transversum deep transverse metatarsal l. Joins heads of metatarsals Lm. metatarsale transversum superficial transverse metatarsal l. Lies on sole of foot beneath heads of metatarsals La. metatarsalia dorsalia dorsal metatarsal ligs. Interconnects bases of metatarsal bones La. metatarsalia interossea interosseous metatarsal ligs. Interconnects bases of metatarsal bones La. metatarsalia plantaria plantar metatarsal ligs. Plantar surface of metatarsal bones La. plantaria articulationum plantar ligs. of interphalangeal Interphalangeal of foot between collateral ligs. interphalangealium pedis La. plantaria articulationum plantar ligs. of metatarsophalangeal Plantar surface of metatarsophalangeal between metatarsophalangeae collateral ligs. Lm. plantare longum long plantar l. Connects calcaneus to bases of metatarsal bones Lm. talocalcaneum talocalcaneal l. Connects talus to calcaneus Lm. talocalcaneum laterale lateral talocalcaneal l. Connects talus to calcaneus Lm. talocalcaneum mediale medial talocalcaneal l. Connects tubercle of talus to sustentaculum tali of calcaneus La. talocalcaneum interosseum talocalcaneal interosseous l. Connects calcaneus to talus Lm. talofibulare anterius anterior talofibular l. Connects lateral malleolus of fibula to posterior process of talus Lm. talonaviculare talonavicular l. Connects neck of talus to navicular bone Lm. talotibiale medial tibiotalar l. Connects downward from the medial malleolus of the tibia of the tarsal bones La. tarsi tarsal ligs. Connects bones of tarsus La. tarsi dorsalia dorsal ligs. of tarsus Collectively, bifurcate, dorsal cuboideonavicular, cuneocuboid, cuneonavicular, intercuneiform, and talonavicular ligs. La. tarsi interossea interosseous ligs. of tarsus Collectively, interosseous, cuneocuboid, intercuneiform, and talocalcaneal ligs. La. tarsi plantaria plantar ligs. of tarsus Inferior ligs. of foot (long plantar, plantar calcaneocuboid, calcaneonavicular, cuneonavicular, cuboideonavicular, intercuneiform, cuneocuboid)
5 APP14 ligaments.qxd 8/13/05 1:31 PM Page APP 71 APP 71 La. tarsometatarsalia dorsalia dorsal tarsometatarsal ligs. Connects bases of metatarsals to dorsal cuboid and cuneiform bones La. tarsometatarsalia plantaria plantar tarsometatarsal ligs. Connects metatarsal bones to cuboid and cuneiform bones Lm. transversum cruris superior extensor retinaculum ligs. of Connects tibia to fibula; holds extensor tendons in place foot Tendo calcaneus achilles tendon, calcaneal tendon Connects triceps surae muscle to tuberosity of calcaneus
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
relating to head, neck, and trunk 206 bones organized into structural framework Skeleton relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
 Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Acceptable CPT Codes for the ABOS Sports Subspecialty Case List
 20520 Removal of foreign body in muscle or tendon sheath; simple 20525 Removal of foreign body in muscle or tendon sheath; deep or complicated 20670 Removal of implant; superficial, (eg, buried wire, pin
20520 Removal of foreign body in muscle or tendon sheath; simple 20525 Removal of foreign body in muscle or tendon sheath; deep or complicated 20670 Removal of implant; superficial, (eg, buried wire, pin
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
MSK MRI PROTOCOL OVERVIEW
 TABLE OF CONTENTS UNSUPERVISED PROTOCOLS SHOULDER (ROUTINE)...2 SHOULDER + PROXIMAL BICEPS...6 ELBOW (ROUTINE)...10 ELBOW + DISTAL BICEPS TENDON...13 ELBOW + DISTAL TRICEPS TENDON...17 WRIST (ROUTINE)...20
TABLE OF CONTENTS UNSUPERVISED PROTOCOLS SHOULDER (ROUTINE)...2 SHOULDER + PROXIMAL BICEPS...6 ELBOW (ROUTINE)...10 ELBOW + DISTAL BICEPS TENDON...13 ELBOW + DISTAL TRICEPS TENDON...17 WRIST (ROUTINE)...20
The human skeleton anterior view
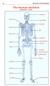 45 The human skeleton anterior view cranium clavicle mandible scapula sternum rib humerus vertebra radius innominate sacrum ulna carpals metacarpals phalanges femur patella tibia fibula tarsals metatarsals
45 The human skeleton anterior view cranium clavicle mandible scapula sternum rib humerus vertebra radius innominate sacrum ulna carpals metacarpals phalanges femur patella tibia fibula tarsals metatarsals
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
GROSS ANATOMY. Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs. Lecture Syllabus 2008
 GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY. Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery. Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch
 CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which
 To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques
 SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often
The Muscular System. Appendicular Musculature
 11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
11 The Muscular System Appendicular Musculature CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the functions of the appendicular musculature. 2. Identify and locate the principal appendicular muscles of the body, together
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Thank You for Your Support!
 Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed on the Internet with the goal of providing quality learning material at a low price to cover web operating expenses. This document is shareware,
Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed on the Internet with the goal of providing quality learning material at a low price to cover web operating expenses. This document is shareware,
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education. Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh
 Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives
 Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives 1. Describe the current best evidence for manual therapy in the management of a variety of disorders. 2. Recognize subgroups
Manual Therapy for the Upper and Lower Quadrant: What Do I Need to Know? Objectives 1. Describe the current best evidence for manual therapy in the management of a variety of disorders. 2. Recognize subgroups
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Principles of Functional Exercise
 Principles of Functional Exercise FOR PROFESSIONAL FITNESS TRAINERS FIRST EDITION Charles DeFrancesco, NASM, NFPT Dr. Robert Inesta, DC, CCSp, CSCS For more information vist us online at: www.nfpt.com
Principles of Functional Exercise FOR PROFESSIONAL FITNESS TRAINERS FIRST EDITION Charles DeFrancesco, NASM, NFPT Dr. Robert Inesta, DC, CCSp, CSCS For more information vist us online at: www.nfpt.com
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES
 Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES CCMH Halifax CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education Courses ONLINE* allowing therapists across the country to avoid the cost of travel and accommodation,
Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES CCMH Halifax CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education Courses ONLINE* allowing therapists across the country to avoid the cost of travel and accommodation,
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum. S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD.
 The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
PELVIS. 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins S59 BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61)
 PELVIS BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61) Types: A. Lesion sparing (or with no displacement of) posterior arch (61-A) B. Incomplete disruption of posterior arch, partially stable (61-B) C. Complete
PELVIS BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61) Types: A. Lesion sparing (or with no displacement of) posterior arch (61-A) B. Incomplete disruption of posterior arch, partially stable (61-B) C. Complete
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
MB, ChB Phase II Theory Modules. Musculoskeletal System
 MB, ChB Phase II Theory Modules Musculoskeletal System 52302 371 2015 MB, ChB Phase II Theory Modules 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 52302 371 MODULE SUPERVISOR: Dr ICM Robertson MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
MB, ChB Phase II Theory Modules Musculoskeletal System 52302 371 2015 MB, ChB Phase II Theory Modules 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 52302 371 MODULE SUPERVISOR: Dr ICM Robertson MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
Upper Extremity Special Tests. Cervical Tests. TMJ Dysfunction
 Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
Upper Extremity Special Tests Cervical Tests Vertebral Artery Test: used to test for vertebral artery occlusion or insufficiency. The subject lies supine on the plinth with the examiner seated behind with
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging
 The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Musculoskeletal System Editors Harald Ostensen M.D. Holger Pettersson M.D. Authors A. Mark Davies M.D. Holger Pettersson
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Musculoskeletal System Editors Harald Ostensen M.D. Holger Pettersson M.D. Authors A. Mark Davies M.D. Holger Pettersson
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. I. Shoulder
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines I. Shoulder Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Lower limb nerve blocks
 Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3)
 Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Injuries in Orthopedics
 Injuries in Orthopedics Jaci Johnson CPC CPCH CPMA CEMC CPCI President Elect AAPC National Advisory Board 2013-2015 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
Injuries in Orthopedics Jaci Johnson CPC CPCH CPMA CEMC CPCI President Elect AAPC National Advisory Board 2013-2015 No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
Basic Radiographic Procedures
 Basic Radiographic Procedures The GPT Method G. Patrick Thomas, Jr., DC, DACBR Copyright 2002 G. Patrick Thomas, Jr., DC, DACBR PO Box 1000 Blue Springs, MO 64013-1000 gptdacbr@juno.com Table of Contents
Basic Radiographic Procedures The GPT Method G. Patrick Thomas, Jr., DC, DACBR Copyright 2002 G. Patrick Thomas, Jr., DC, DACBR PO Box 1000 Blue Springs, MO 64013-1000 gptdacbr@juno.com Table of Contents
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb
 An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
Certification Exam Study Guide
 Certification Exam Study Guide Neuromechanical Innovations 101 South Roosevelt Avenue Chandler, AZ 85226 U.S.A. Tel. 480-785-8448 Fax. 480-785-3916 www.impulseseminars.com 1 Table of Contents General Certification
Certification Exam Study Guide Neuromechanical Innovations 101 South Roosevelt Avenue Chandler, AZ 85226 U.S.A. Tel. 480-785-8448 Fax. 480-785-3916 www.impulseseminars.com 1 Table of Contents General Certification
Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology
 Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology 2 chapter CHAPTER OUTLINE Areas of Competence Anatomical Position Planes of Motion Cavities of the Body Body Movements Types of Contractions Muscle
Detailed Knowledge of Anatomy, Physiology, and Kinesiology 2 chapter CHAPTER OUTLINE Areas of Competence Anatomical Position Planes of Motion Cavities of the Body Body Movements Types of Contractions Muscle
Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction
 Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction, with Indirect,Direct and HVLA Techniques (Counterstrain and Muscle Energy) F. P Wedel, D.O.
Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction, with Indirect,Direct and HVLA Techniques (Counterstrain and Muscle Energy) F. P Wedel, D.O.
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Chart for Massage Therapists code description ICD9 / 10 250 Diabetes 9 E08 Diabetes Mellitus 10 307.81 Headaches, tension
 ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Chart for Massage Therapists code description ICD9 / 10 250 Diabetes 9 E08 Diabetes Mellitus 10 307.81 Headaches, tension 9 G44.209 Tension-type headache, unspecified, not intractable
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion Chart for Massage Therapists code description ICD9 / 10 250 Diabetes 9 E08 Diabetes Mellitus 10 307.81 Headaches, tension 9 G44.209 Tension-type headache, unspecified, not intractable
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. IV. Hip
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
I have been provided with information to answer your request by Ms Lyn McDonald, Site Director, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh.
 Lothian NHS Board = Waverley Gate 2-4 Waterloo Place Edinburgh EH1 3EG = Telephone: 0131 536 9000 www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk Date: 15/06/2015 Our Ref: 5229 Enquiries to : Bryony Pillath Extension: 35676
Lothian NHS Board = Waverley Gate 2-4 Waterloo Place Edinburgh EH1 3EG = Telephone: 0131 536 9000 www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk Date: 15/06/2015 Our Ref: 5229 Enquiries to : Bryony Pillath Extension: 35676
Imaging of Sports Injuries
 Imaging of Sports Injuries Capable of tremendous mobility Paradox Must be loose enough to function but stable enough to prevent symptoms Shoulder injuries occur when the balance between stability & mobility
Imaging of Sports Injuries Capable of tremendous mobility Paradox Must be loose enough to function but stable enough to prevent symptoms Shoulder injuries occur when the balance between stability & mobility
Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes
 Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes STANDARD 8 Students will explore specific sports injuries. Objective 1: Recognize common injuries to the head and neck to include: concussion, cervical spine
Unit 8 SPECIFIC SPORTS INJURIES Lecture Notes STANDARD 8 Students will explore specific sports injuries. Objective 1: Recognize common injuries to the head and neck to include: concussion, cervical spine
Volume 1 September, 2003. Disability Duration Guidelines and Expected Healing Times
 Volume 1 September, 2003 Disability Duration Guidelines and Expected Healing Times Disability Duration Guidelines Acknowledgement The Workers Compensation Board of Prince Edward Island (WCB PEI) acknowledges
Volume 1 September, 2003 Disability Duration Guidelines and Expected Healing Times Disability Duration Guidelines Acknowledgement The Workers Compensation Board of Prince Edward Island (WCB PEI) acknowledges
Joints. The graceful movements of ballet dancers and the rough-and-tumble. Classification of Joints
 Classification of Joints (pp. 24 249) Fibrous Joints (pp. 249 250) Sutures (p. 249) Syndesmoses (pp. 249 250) Gomphoses (p. 250) Cartilaginous Joints (pp. 250 251) Synchondroses (pp. 250 251) Symphyses
Classification of Joints (pp. 24 249) Fibrous Joints (pp. 249 250) Sutures (p. 249) Syndesmoses (pp. 249 250) Gomphoses (p. 250) Cartilaginous Joints (pp. 250 251) Synchondroses (pp. 250 251) Symphyses
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants.
 Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers. Current Procedural Terminology 2013 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved.
 Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers Rotator Cuff Repair 23420 February 2002 page 11 Code 23420 describes a repair of a complete shoulder (rotator) cuff avulsion, referring to the repair of
Coding for Difficult Tendon Repairs and Transfers Rotator Cuff Repair 23420 February 2002 page 11 Code 23420 describes a repair of a complete shoulder (rotator) cuff avulsion, referring to the repair of
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. V. Knee
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines V. Knee Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines V. Knee Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM. 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200)
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
