LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
- Ira Parrish
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis 4. Yellow marrow 9. Distal epiphysis 5. Compact bone FIG Spongy bone 6. Perforating canal 2. Compact bone 7. Blood vessels 3. Osteon 8. Nerve 4. Perisoteum 9. Canaliculus 5. Central canal 10. Osteocyte Critical Thinking Application Answers The closest blood supply to an osteocyte is located in the central canal of an osteon unit. Nutrients and wastes can move from one cell to another via small cellular processes located in minute tubes in the matrix called canaliculi. In this way, all of the osteocytes of one osteon are tied together to a blood source. 1. Flat 8. Hyaline cartilage covers the articular ends of a long bone. 2. Short 9. Dense irregular connective tissue comprises the periosteum that 3. Long encloses the bone except for its articular ends 4. Irregular 10. Periosteum composed of irregular dense connective tissue forms 5. Sesamoid or round the outer covering of a bone, whereas endosteum composed 6. Flat of reticular connective tissue lines its hollow, internal chambers. 7. Epiphysis refers to the expanded end of a long bone; diaphysis refers to the shaft between the ends of such a bone. PART B 1. Compact bone has osteons closely packed together, 3. The marrow of the medullary cavity of an adult is yellow, but and spongy bone has large spaces between thin marrow in the spaces of spongy bone is red. bony plates called trabeculae. 2. Compact bone provides strength in the shaft and along the borders of the bone. Spongy bone reduces the weight of the bone and provides spaces occupied by red marrow. PART C (FIG a-b) 1. Epiphysis (distal) 4. Medullary cavity 2. Diaphysis 5. Compact bone 3. Epiphysis (proximal) 6. Spongy bone 13
2 LABORATORY EXERCISE 13 ORGANIZATION OF THE SKELETON FIG. 3.1a 1. Cranial bones (cranium) 5. Sternum 8. Hip bone 12. Patella 2. Facial bones (face) 6. Rib 9. Carpals 13. Tarsals 3. Skull 7. Vertebral column 10. Metacarpal 14. Matatarsal 4. Clavicle (vertebra) 11. Phalanx 15. Phalanx FIG. 13.1b 16. Scapula 19. Radius 22. Fibula 24. Sacrum 17. Humerus 20. Femur 23. Vertebral column 25. Coccyx 18. Ulna 21. Tibia (vertebra) Critical Thinking Application Answers The largest foramen in the skull is the foramen magnum in the occipital bone. The largest foramen in the human body is the obturator foramen in the hip bones. 1. Sutural bones (wormian bones) 6. Sternum 11. Sacrum 2. Axial 7. Twelve 12. Pelvis 3. Skull 8. Pectoral girdle 13. Patella 4. Hyoid 9. Ulna 14. Tarsals 5. Coccyx 10. Carpals 15. Phalanges PART B 1. c 3. a 5. g 7. d 2. f 4. e 6. b PART C 1. c 3. g 5. b 7. f 2. a 4. e 6. d PART D (FIG. 13.2) 1. Hip bone 5. Ulna 9. Humerus 13. Rib 2. Sternum 6. Scapula 10. Patella 3. Sacrum 7. Radius 11. Femur 4. Fibula 8. Clavicle 12. Tibia 14
3 LABORATORY EXERCISE 14 SKULL Instructional Suggestion You might want to have the students use colored pencils to color the bones in figures 14.1 and They should use a different color for each of the individual bones in the series. This activity should cause the students to observe the figures more carefully and help them to locate the various bones that are shown from different views in the figures. The students can check their work by referring to the corresponding full-color figures in the textbook. FIG Parietal bone 9. Supraorbital foramen 2. Frontal bone 10. Nasal bone 3. Coronal suture 11. Sphenoid bone 4. Temporal bone 12. Zygomatic bone 5. Perpendicular plate (of ethmoid bone) 13. Middle nasal concha (of ethmoid bone) 6. Infraorbital foramen 14. Inferior nasal concha 7. Vomer bone 15. Maxilla 8. Mandible 16. Mental foramen FIG Parietal bone 11. Zygomatic process (of temporal bone) 2. Squamous suture 12. Coronal suture 3. Lambdoid suture 13. Frontal bone 4. Temporal bone 14. Sphenoid bone 5. Occipital bone 15. Lacrimal bone 6. Temporal process (of zygomatic bone) 16. Nasal bone 7. External acoustic meatus 17. Zygomatic bone 8. Mastoid process 18. Maxilla 9. Styloid process 19. Mandible 10. Mandibular condyle 20. Coronoid process FIG Maxilla 8. Occipital condyle 2. Zygomatic bone 9. Temporal bone 3. Sphenoid bone 10. Palatine process (of maxilla) 4. Vomer bone 11. Palatine bone 5. Zygomatic arch 12. Foramen magnum 6. Styloid process 13. Lambdoid suture 7. Mastoid process 14. Occipital bone FIG Ethmoid bone 6. Sphenoid bone 2. Foramen magnum 7. Temporal bone 3. Crista galli 8. Sella turcica 4. Cribriform plate (olfactory foramina) 9. Parietal bone 5. Frontal bone 10. Occiptal bone FIG Coronal suture 9. Squamous suture 2. Frontal bone 10. Lambdoid suture 3. Sphenoid bone 11. Occipital bone 4. Frontal sinus 12. Sella turcica 5. Nasal bone 13. Styloid process 6. Maxilla 14. Sphenoidal sinus 7. Parietal bone 15. Vomer bone 8. Temporal bone 16. Mandible 15
4 Critical Thinking Application Answers The cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone with numerous olfactory foramina is a weak location of the cranium. Excessive pressure on the cribiform plate could result in a skull fracture. 1. d 4. f 7. f 10. e 2. a 5. c 8. a 11. f 3. a 6. f 9. c 12. b PART B 1. Coronal 4. Squamous 2. Sagittal 5. Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid 3. Lambdoid 6. Maxillary bone PART C 1. e 4. h 7. h 10. c 2. c 5. d 8. a 11. f 3. c 6. g 9. d 12. b PART D 1. c 3. g 5. d 7. e 2. a 4. f 6. b PART E (FIG ) FIG Frontal bone 6. Mandible 2. Nasal bone 7. Middle nasal concha (of ethmoid bone) 3. Zygomatic bone 8. Inferior nasal concha 4. Infraorbital foramen 9. Mental foramen 5. Maxilla FIG Parietal bone 8. Mandibular condyle 2. Squamous suture 9. Coronal suture 3. Temporal bone 10. Frontal bone 4. Lambdoid suture 11. Zygomatic process (of temporal bone) 5. Occipital bone 12. Zygomatic bone 6. External acoustic meatus 13. Maxilla 7. Mastoid process 14. Mandible FIG Maxilla 7. Palatine process of maxilla 2. Zygomatic bone 8. Palatine bone 3. Sphenoid bone 9. Vomer bone 4. Temporal bone 10. Occipital condyle 5. Occipital bone 11. Foramen magnum 6. Incisive foramen FIG Frontal bone 5. Ethmoid bone 2. Temporal bone 6. Sphenoid bone 3. Parietal bone 7. Sella turcica 4. Occiptal bone 8. Foramen magnum FIG Parietal bone 5. Maxilla 2. Sphenoid bone 6. Frontal bone 3. Temporal bone 7. Mandible 4. Zygomatic bone 16
5 LABORATORY EXERCISE 15 VERTEBRAL COLUMN AND THORACIC CAGE FIG Cervical vertebrae 5. Coccyx 2. Thoracic vertebrae 6. Intervertebral foramina 3. Lumbar vertebrae 7. Intervertebral discs 4. Sacrum FIG a-b FIG a-c FIG Superior articular process 5. Superior articular process 2. Anterior sacral foramen 6. Tubercles of median sacral crest 3. Coccyx 7. Posterior sacral foramen 4. Sacral canal 8. Sacral hiatus Critical Thinking Application Answers The four curvatures allow more resiliency and flexibility, which will enable the vertebal column to function more like a spring instead of a rigid rod. FIG True ribs 6. Xiphoid process 2. False ribs 7. Sternum 3. Thoracic vertebra 8. Costal cartilage 4. Manubrium 9. Floating ribs 5. Body 1. Spinal cord 8. Atlas Axis 3. Bodies 10. Dens 4. Intervertebral discs 11. Lumbar 5. Spinous process 12. Five 6. Spinal nerves 13. Sacral promontory 7. Vertebral arteries 14. Sacral hiatus 17
6 PART B Vertebra Number Size Body Spinous Process Transsverse Foramina Cervical 7 Smallest Smallest C2 through C5 are Present forked Thoracic 12 Intermediate Intermediate Pointed and angled Absent downward Lumbar 5 Largest Largest Short, blunt, and nearly horizontal Absent PART C Clavicles 2. Floating 6. a. Supports shoulder girdle and upper limbs 3. Seven b. Protects visceral organs 4. Hyaline cartilage c. Functions in breathing PART D (FIG. 15.6) 1. Spinous process 4. Transverse process 2. Atlas 5. Intervertebral disc 3. Axis 6. Body (of sixth cervical vertebra) 18
7 LABORATORY EXERCISE 16 PECTORAL GIRDLE AND UPPER LIMB FIG Clavicle 7. Ulna 2. Rib 8. Radius 3. Sternum 9. Acromion process 4. Costal cartilage 10. Head of humerus 5. Scapula 11. Coracoid process 6. Humerus FIG Acromion process 6. Glenoid cavity 2. Coracoid process 7. Acromion process 3. Spine 8. Coracoid process 4. Supraspinous fossa 9. Glenoid cavity 5. Infraspinous fossa Critical Thinking Application Answers The clavicles brace the freely movable scapulae, helping to hold the shoulders in place. If an excessive lengthwise force occurs on this structurally weak bone, as when a person breaks a fall with an outstretched rigid upper limb, it is likely to fracture. FIG. 16.3a-b 1. Head 6. Capitulum 2. Lesser tubercle 7. Trochlea 3. Deltoid tuberosity 8. Greater tubercle 4. Coronoid fossa 9. Medial epicondyle 5. Lateral epicondyle 10. Olecranon fossa FIG Head of radius 5. Trochlear notch 2. Radial tuberosity 6. Coronoid process 3. Styloid process of radius 7. Head of ulna 4. Olecranon process FIG Olecranon process 4. Head of radius 2. Humerus 5. Radius 3. Olecranon fossa 6. Ulna FIG Scaphoid 7. Phalanges 2. Capitate 8. Lunate 3. Trapezoid 9. Proximal phalanx 4. Trapezium 10. Middle phalanx 5. Carpals (carpus) 11. Distal phalanx 6. Metacarpals (metacarpus) 1. Scapulae 5. Spine 2. Manubrium (clavicular notch) 6. Acromion process 3. Acromion processes 7. Coracoid process 4. Clavicle 8. Head 19
8 PART B 1. a 4. b 7. b 10. e 2. b 5. c 8. a 11. a 3. b 6. d 9. b 12. f PART C (FIGS. 16.7, 16.8, and 16.9) FIG FIG FIG Humerus 1. Acromion process 1. Phalanges 2. Olecranon process 2. Head of humerus 2. Metacarpals 3. Head of radius 3. Humerus 3. Carpals 4. Radius 4. Clavicle 4. Distal phalanx 5. Ulna 5. Scapula 5. Proximal phalanx 6. Rib PART D (FIG )
9 LABORATORY EXERCISE 17 PELVIC GIRDLE AND LOWER LIMB FIG Hip bone (coxa; pelvic bone; innominate) 3. Coccyx 2. Sacrum FIG. 17.2a 1. Ilium 6. Anterior superior iliac spine 2. Greater sciatic notch 7. Acetabulum 3. Ischial spine 8. Pubis 4. Ischium 9. Obturator foramen 5. Iliac crest FIG. 17.2b 10. Anterior superior iliac spine 13. Iliac crest 11. Ilium 14. Ischial spine 12. Pubis 15. Ischium Critical Thinking Application Answers All of the features examined are wider in the female pelvis which will result in a larger pelvic cavity and must also serve as a birth canal for a vaginal delivery. FIG. 17.3a-b 1. Head 5. Lateral epicondyle 2. Fovea capitis 6. Lesser trochanter 3. Greater trochanter 7. Lateral condyle 4. Neck 8. Medial condyle FIG Head of fibula 5. Tibial tuberosity 2. Fibula 6. Tibia 3. Lateral malleolus 7. Medial malleolus 4. Medial condyle FIG Medial condyle 4. Fibula 2. Femur 5. Tibia 3. Lateral condyle FIG Calcaneus 8. Proximal phalanx 2. Talus 9. Middle phalanx 3. Cuboid 10. Distal phalanx 4. Navicular 11. Tarsals (tarsus) 5. Lateral cuneiform 12. Metatarsals (metatarsus) 6. Intermediate cuneiform 13. Phalanges 7. Medial cuneiform 1. Hip bones 4. Ischial spines 7. Tuberosity 10. Sacroiliac 2. Acetabulum 5. Symphysis pubis 8. Pubic arch 3. Ilium 6. Iliac crest 9. Obturator foramen 21
10 PART B 1. e 4. a 7. g 10. b 2. a 5. f 8. f 11. d 3. g 6. f 9. a 12. c PART C (FIGS. 17.7, 17.8, and 17.9) FIG FIG FIG Obturator foramen 1. Lateral epicondyle 1. Metatarsal 2. Symphysis pubis 2. Lateral condyle 2. Proximal phalanx 3. Ilium 3. Head of fibula 3. Distal phalanx 4. Sacrum 4. Fibula 4. Tibia 5. Head of femur 5. Femur 5. Talus 6. Pubis 6. Tibia 6. Calcaneus PART D (FIG ) 1. Distal phalanges 7. Navicular 2. Proximal phalanges 8. Talus 3. Metatarsals 9. Middle phalanges 4. Medial cuneiform 10. Cuboid 5. Intermediate cuneiform 11. Calcaneus 6. Lateral cuneiform 22
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
relating to head, neck, and trunk 206 bones organized into structural framework Skeleton relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis
 Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
Axial relating to head, neck, and trunk Skeleton 206 bones organized into structural framework Appendicular relating to limbs and their attachments to the axis Function of Skeletal System 1. Movement 2.
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
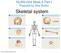 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM. 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200)
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 7.1 Bone Shape and Structure UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 7: SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Classify bones according to their shapes, and name an example from each group. (p. 200) 2. Describe the macroscopic
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 6 The Skeletal System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Functions of the skeletal system include A) support. B) storage. C) protection. D) blood
The human skeleton anterior view
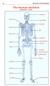 45 The human skeleton anterior view cranium clavicle mandible scapula sternum rib humerus vertebra radius innominate sacrum ulna carpals metacarpals phalanges femur patella tibia fibula tarsals metatarsals
45 The human skeleton anterior view cranium clavicle mandible scapula sternum rib humerus vertebra radius innominate sacrum ulna carpals metacarpals phalanges femur patella tibia fibula tarsals metatarsals
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
The Axial Skeleton. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
The Human Skeleton. Bone and Bone Growth
 The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
Anatomy of Bones and Joints
 C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals
 Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals 6 Bones and skeletal system Contents Bones Introduction Classification of Bones Bone Structure Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Chemical Composition
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
BONE BINGO. Blood Production Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, a substance found inside the larger bones of the body.
 BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Skeletal System. Skeletal Anatomy. bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework
 Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week daily Calcium requirement: 1200mg/day Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week daily Calcium requirement: 1200mg/day Functions of Skeletal
The Skeleton. The word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up THE AXIAL SKELETON THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
1 )~ ~V? 1) I, \ Chapter One: Introduction. b. g._----- h. 1. _ )...lii('---:-----':----;-~.k.-- h... I l«=~.. \! a. _. a. _. e. _
 Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Chapter One: Introduction ANATOMICAL POSITION AND TERMS OF DIRECTION When studying the human body it is important to place the body in anatomical position. Anatomical position is described as the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3)
 Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Skeletal System. Skeletal Anatomy. bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework
 Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week Functions of Skeletal System: 1. Support strong and relatively
Skeletal System bones, cartilage and ligaments are tightly joined to form a strong, flexible framework bone is active tissue:!5-7% bone mass/week Functions of Skeletal System: 1. Support strong and relatively
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which
 To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
To access the Podiatry tools; open a Patient Study, left click on 2020 logo at the top left which is the Main Menu, then click on PODIATRY and select the tool you wish to plot. After plotting all of your
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues
 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues Cartilage Location and basic structure Found throughout adult body Ear and epiglottis Articular cartilages and costal cartilage Larynx, trachea, and nose Intervertebral discs,
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education. Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh
 Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science
 Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum. S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD.
 The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Brunswick School Department: Grades 11-12. Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Internal Anatomy. Figure 2. The bones of the avian skull (a) lateral view (b) posterior view (c) sclerotic ring.
 Internal Anatomy Skeletal System The skeletal system (Figure 1) is highly modified to meet the structural and energetic demands of flight. Throughout the skeleton are examples of three types of adaptive
Internal Anatomy Skeletal System The skeletal system (Figure 1) is highly modified to meet the structural and energetic demands of flight. Throughout the skeleton are examples of three types of adaptive
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 ANATOMY FOR X-RAY SPECIALISTS SUBCOURSE MD0956 EDITION 200
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 ANATOMY FOR X-RAY SPECIALISTS SUBCOURSE MD0956 EDITION 200 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 ANATOMY FOR X-RAY SPECIALISTS SUBCOURSE MD0956 EDITION 200 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER5 INTRODUCTION COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The submicroscopic particles that make up all substances
Human Anatomy and Physiology CHAPTER5 INTRODUCTION COMPLETION: In the space(s) provided, write the word(s) that correctly complete(s) each statement. 1. The submicroscopic particles that make up all substances
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
DIGITAL X-RAY AUNTMINNIE.COM X-RAY PATIENT POSITIONING MANUAL HTTP://XRAY.AUNTMINNIE.COM. Proper positioning for the pelvis and proximal femur
 A R T I C L E S Proper positioning for the pelvis and proximal femur The lowdown on lumbar spine positioning Radiographic positioning techniques for the cervical spine Boning up on humerus, clavicle, and
A R T I C L E S Proper positioning for the pelvis and proximal femur The lowdown on lumbar spine positioning Radiographic positioning techniques for the cervical spine Boning up on humerus, clavicle, and
MSK MRI PROTOCOL OVERVIEW
 TABLE OF CONTENTS UNSUPERVISED PROTOCOLS SHOULDER (ROUTINE)...2 SHOULDER + PROXIMAL BICEPS...6 ELBOW (ROUTINE)...10 ELBOW + DISTAL BICEPS TENDON...13 ELBOW + DISTAL TRICEPS TENDON...17 WRIST (ROUTINE)...20
TABLE OF CONTENTS UNSUPERVISED PROTOCOLS SHOULDER (ROUTINE)...2 SHOULDER + PROXIMAL BICEPS...6 ELBOW (ROUTINE)...10 ELBOW + DISTAL BICEPS TENDON...13 ELBOW + DISTAL TRICEPS TENDON...17 WRIST (ROUTINE)...20
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging
 The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Musculoskeletal System Editors Harald Ostensen M.D. Holger Pettersson M.D. Authors A. Mark Davies M.D. Holger Pettersson
The WHO manual of diagnostic imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of the Musculoskeletal System Editors Harald Ostensen M.D. Holger Pettersson M.D. Authors A. Mark Davies M.D. Holger Pettersson
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Your Practice. Your Preference. Your Productivity Solution. USER MANUAL
 Your Practice. Your Preference. Your Productivity Solution. USER MANUAL 1 2 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 4 Basic Keyboard Functionality 4 Image View Orientation 4 Annotation Customization. 5 2 General
Your Practice. Your Preference. Your Productivity Solution. USER MANUAL 1 2 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 4 Basic Keyboard Functionality 4 Image View Orientation 4 Annotation Customization. 5 2 General
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 203 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Figure 6.1 Child Looking at Bones Bone is a living tissue. Unlike the bones of a fossil made inert by a process of
CHAPTER 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 203 6 BONE TISSUE AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Figure 6.1 Child Looking at Bones Bone is a living tissue. Unlike the bones of a fossil made inert by a process of
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term.
 This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
This is your Anatomy and Physiology Mid-term. 1 Run for your lives!!! (Just Kidding) Matching - Anatomy or Physiology? A 1. Study of structure A. Anatomy 2. muscle actions B. Physiology 3. Brain Function
Sri Jayendra Saraswathy Maha Vidyalaya College of Arts and Science Coimbatore 641 005. 2 Associate Professor, Dept. of Computer Science
 A brief study on human bone anatomy and bone fractures 1 N.Umadevi, 2 Dr.S.N.Geethalakshmi 1 Head, Dept. of Computer Science and IT Sri Jayendra Saraswathy Maha Vidyalaya College of Arts and Science Coimbatore
A brief study on human bone anatomy and bone fractures 1 N.Umadevi, 2 Dr.S.N.Geethalakshmi 1 Head, Dept. of Computer Science and IT Sri Jayendra Saraswathy Maha Vidyalaya College of Arts and Science Coimbatore
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND
 SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
