Unit A451: Computer systems and programming. Section 2: Computing Hardware 1/5: Central Processing Unit
|
|
|
- Lorraine Crawford
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit A451: Computer systems and programming Section 2: Computing Hardware 1/5: Central Processing Unit
2 Section Objectives Candidates should be able to: (a) State the purpose of the CPU (b) Understand the fetch execute cycle (c) Explain how common characteristics of CPUs such as clock speed, cache size and number of cores affect their performance.
3 Introduction The central processing unit (CPU) is a microprocessor - a silicon chip - composed of tiny electrical switches called 'transistors'. The speed at which the it carries out operations is measured in megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz). The higher the number of MHz the faster the computer can process information. (a) state the purpose of the CPU
4 (a) state the purpose of the CPU The Purpose of a CPU The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is the hardware that executes instructions from programs and manages hardware. Think of the CPU as the brain of the computer. It has parts that remember things, parts that think and parts that make the rest of computer (the body) operate.
5 The Purpose of a CPU (a) state the purpose of the CPU
6 Computer Motherboard (a) state the purpose of the CPU
7 Installing CPU (a) state the purpose of the CPU
8 CPU / Inside CPU (a) state the purpose of the CPU
9 (a) state the purpose of the CPU The purpose of the CPU is to process instructions from memory. Instructions from software programs and hardware) It performs mathematical and logical calculations on data the data, but can only process one instruction at a time.
10 Fetch-execute cycle The main purpose of the CPU is to process instructions. To do this it loads the data and the program associated with that data in RAM memory. To run the program the processor fetches an instruction, decodes it and then executes it. The processor executes one instruction at a time. This is called the fetch-execute cycle. (b) describe the function of the CPU as fetching and executing instructions stored in memory
11 In real terms The CPU gets an input from the user. The CPU then fetches this instruction. The CPU then decodes the instruction. The instruction is then executed by the system (b) describe the function of the CPU as fetching and executing instructions stored in memory
12 Clock Speed The clock speed is the rate at which the CPU processes data at. A high clock speed will process more instructions per second and will therefore have a higher performance than the equivalent CPU with a lower clock speed. The CPU clock speed is measured in cycles per second. 1 cycle per second is also known as 1 Hertz. (millions of instructions per second.) This is how a computer allows you to type in word, whilst listening to music and downloading something all at the same time. It only actually processes one thing at a time, but can do them so fast, it gives the impression they are running simultaneously. Some people practice over-clocking their PC (setting the CPU to run at a faster rate, but this creates more heat and therefore fan use / noise) (c) explain how clock speed, cache size and number of cores affect a CPU s performance.
13 Cache Size Cache memory is a small chunk of fast memory that is built into the CPU. It greatly increases the speed of a computer by storing data that is most often accessed. As the CPU processes data, it looks first in the cache memory and if it finds the data there. This saves it time in having to read data from larger RAM memory (attached separately on the motherboard) A CPU with a larger cache memory and more levels of cache memory will have a higher performance than one without cache memory. (c) explain how clock speed, cache size and number of cores affect a CPU s performance.
14 Number of Cores Early processors originally had only one core so could only process one instruction at a time. A dual-core processor contains two cores and a quad-core processor contains four cores. Each core can process instructions independently of the other cores. Multi-core processors work best with operating systems and software that has been specifically designed to run on multiple cores. (c) explain how clock speed, cache size and number of cores affect a CPU s performance.
15 Your Task State the purpose of a CPU (2 marks) Explain the factors that affect the performance of a CPU (6 marks) (b) describe the function of the CPU as fetching and executing instructions stored in memory
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Chapter 6. Inside the System Unit. What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future. What You Will Learn... Describing Hardware Performance
 What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
What You Will Learn... Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Understand how computers represent data Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and data storage capacity List the components
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT)
 Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
Basic Concepts of Information Technology (IT) Objectives Define Computer and Identify the Four Basic Computing Functions Identify the Different Types of Computers Describe Hardware Devices and Their Uses
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX
 CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
CHAPTER 2: HARDWARE BASICS: INSIDE THE BOX Multiple Choice: 1. Processing information involves: A. accepting information from the outside world. B. communication with another computer. C. performing arithmetic
Discovering Computers 2011. Living in a Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
Discovering Computers 2011 Living in a Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips,
TYPES OF COMPUTERS AND THEIR PARTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
Block diagram of typical laptop/desktop
 What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett
 Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
Technical Product Specifications Dell Dimension 2400 Created by: Scott Puckett Page 1 of 11 Table of Contents Technical Product Specifications Model 3 PC Technical Diagrams Front Exterior Specifications
Generations of the computer. processors.
 . Piotr Gwizdała 1 Contents 1 st Generation 2 nd Generation 3 rd Generation 4 th Generation 5 th Generation 6 th Generation 7 th Generation 8 th Generation Dual Core generation Improves and actualizations
. Piotr Gwizdała 1 Contents 1 st Generation 2 nd Generation 3 rd Generation 4 th Generation 5 th Generation 6 th Generation 7 th Generation 8 th Generation Dual Core generation Improves and actualizations
New Mexico Broadband Program. Basic Computer Skills. Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software
 New Mexico Broadband Program Basic Computer Skills Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software Basic Computer Skills Learning Objectives Acquire introductory familiarity with basic
New Mexico Broadband Program Basic Computer Skills Module 1 Types of Personal Computers Computer Hardware and Software Basic Computer Skills Learning Objectives Acquire introductory familiarity with basic
Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports. [email protected] http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en
 BMTS 242: Computer and Systems Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports Yousef Alharbi Email Website [email protected] http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en The System Unit McGraw-Hill Copyright 2011
BMTS 242: Computer and Systems Lecture 2: Computer Hardware and Ports Yousef Alharbi Email Website [email protected] http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/y.alharbi/en The System Unit McGraw-Hill Copyright 2011
Overview. CPU Manufacturers. Current Intel and AMD Offerings
 Central Processor Units (CPUs) Overview... 1 CPU Manufacturers... 1 Current Intel and AMD Offerings... 1 Evolution of Intel Processors... 3 S-Spec Code... 5 Basic Components of a CPU... 6 The CPU Die and
Central Processor Units (CPUs) Overview... 1 CPU Manufacturers... 1 Current Intel and AMD Offerings... 1 Evolution of Intel Processors... 3 S-Spec Code... 5 Basic Components of a CPU... 6 The CPU Die and
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications. Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global
 CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
CSCA0102 IT & Business Applications Foundation in Business Information Technology School of Engineering & Computing Sciences FTMS College Global Chapter 2 Data Storage Concepts System Unit The system unit
Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging
 Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging In some markets and scenarios where competitive advantage is all about speed, speed is measured in micro- and even nano-seconds.
Achieving Nanosecond Latency Between Applications with IPC Shared Memory Messaging In some markets and scenarios where competitive advantage is all about speed, speed is measured in micro- and even nano-seconds.
Understanding Digital Components
 Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices and Output Devices Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 2-2 Understanding Your Computer Objectives 1. What exactly is a computer
INTEL HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONSUMER DESKTOP MICROPROCESSOR TIMELINE
 INTEL HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONSUMER DESKTOP MICROPROCESSOR TIMELINE 1971: 4004 Microprocessor The 4004 was Intel's first microprocessor. This breakthrough invention powered the Busicom* calculator and paved
INTEL HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONSUMER DESKTOP MICROPROCESSOR TIMELINE 1971: 4004 Microprocessor The 4004 was Intel's first microprocessor. This breakthrough invention powered the Busicom* calculator and paved
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
CPU Benchmarks Over 600,000 CPUs Benchmarked
 Shopping cart Search Home Software Hardware Benchmarks Services Store Support Forums About Us Home» CPU Benchmarks» Multiple CPU Systems CPU Benchmarks Video Card Benchmarks Hard Drive Benchmarks RAM PC
Shopping cart Search Home Software Hardware Benchmarks Services Store Support Forums About Us Home» CPU Benchmarks» Multiple CPU Systems CPU Benchmarks Video Card Benchmarks Hard Drive Benchmarks RAM PC
Application Performance Analysis of the Cortex-A9 MPCore
 This project in ARM is in part funded by ICT-eMuCo, a European project supported under the Seventh Framework Programme (7FP) for research and technological development Application Performance Analysis
This project in ARM is in part funded by ICT-eMuCo, a European project supported under the Seventh Framework Programme (7FP) for research and technological development Application Performance Analysis
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU is the heart and brain It interprets and executes machine level instructions Controls data transfer from/to Main Memory (MM) and CPU Detects any errors In the following
Central Processing Unit (CPU) CPU is the heart and brain It interprets and executes machine level instructions Controls data transfer from/to Main Memory (MM) and CPU Detects any errors In the following
What's in a computer?
 What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
What's in a computer? logical or functional organization: "architecture" what the pieces are, what they do, how they work how they are connected, how they work together what their properties are physical
CPU. Motherboard RAM. Power Supply. Storage. Optical Drives
 CPU Motherboard RAM Power Supply Storage Optical Drives GPU 2 The CPU is the brain of a computer CPU receives instructions from software programs stored in memory Instructions are read and the tasks performed
CPU Motherboard RAM Power Supply Storage Optical Drives GPU 2 The CPU is the brain of a computer CPU receives instructions from software programs stored in memory Instructions are read and the tasks performed
Legal Notices and Important Information
 Legal Notices and Important Information Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different processor families.
Legal Notices and Important Information Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different processor families.
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware. Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA
 Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
Introduction to Information System Layers and Hardware Introduction to Information System Components Chapter 1 Part 1 of 4 CA M S Mehta, FCA 1 Information System Layers Learning Objectives Task Statements
The Motherboard Chapter #5
 The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
The Motherboard Chapter #5 Amy Hissom Key Terms Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) A type of L2 cache contained within the Pentium processor housing that is embedded on the same core processor die as the CPU
Enabling Technologies for Distributed and Cloud Computing
 Enabling Technologies for Distributed and Cloud Computing Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. 2010-14 FIS Distinguished Professor of Computer Science School of Computing, UNF Multi-core CPUs and Multithreading
Enabling Technologies for Distributed and Cloud Computing Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. 2010-14 FIS Distinguished Professor of Computer Science School of Computing, UNF Multi-core CPUs and Multithreading
Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5
 Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5 This paper is based on my experience purchasing a new laptop in January, 2010. I ll lead you through my selection criteria and point you to some on-line
Choosing a Computer for Running SLX, P3D, and P5 This paper is based on my experience purchasing a new laptop in January, 2010. I ll lead you through my selection criteria and point you to some on-line
Chapter 4 System Unit Components. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Chapter 4 System Unit Components Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook
Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth
 White Paper Joshua Ruggiero Computer Systems Engineer Intel Corporation Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth For use with Intel Architecture December 2008 1 321074 Executive Summary
White Paper Joshua Ruggiero Computer Systems Engineer Intel Corporation Measuring Cache and Memory Latency and CPU to Memory Bandwidth For use with Intel Architecture December 2008 1 321074 Executive Summary
IT@Intel. Comparing Multi-Core Processors for Server Virtualization
 White Paper Intel Information Technology Computer Manufacturing Server Virtualization Comparing Multi-Core Processors for Server Virtualization Intel IT tested servers based on select Intel multi-core
White Paper Intel Information Technology Computer Manufacturing Server Virtualization Comparing Multi-Core Processors for Server Virtualization Intel IT tested servers based on select Intel multi-core
Industry First X86-based Single Board Computer JaguarBoard Released
 Industry First X86-based Single Board Computer JaguarBoard Released HongKong, China (May 12th, 2015) Jaguar Electronic HK Co., Ltd officially launched the first X86-based single board computer called JaguarBoard.
Industry First X86-based Single Board Computer JaguarBoard Released HongKong, China (May 12th, 2015) Jaguar Electronic HK Co., Ltd officially launched the first X86-based single board computer called JaguarBoard.
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Legal Notices... 2. Introduction... 3
 HP Asset Manager Asset Manager 5.10 Sizing Guide Using the Oracle Database Server, or IBM DB2 Database Server, or Microsoft SQL Server Legal Notices... 2 Introduction... 3 Asset Manager Architecture...
HP Asset Manager Asset Manager 5.10 Sizing Guide Using the Oracle Database Server, or IBM DB2 Database Server, or Microsoft SQL Server Legal Notices... 2 Introduction... 3 Asset Manager Architecture...
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7
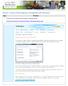 How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
How do I Check if My Computer is Compatible with Windows 7 Enterprise Computing & Service Management 1 Follow this link to download the Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor http://www.microsoft.com/windows/windows-7/get/upgrade-advisor.aspx
PassMark - CPU Mark Multiple CPU Systems - Updated 17th of July 2012
 1 z 5 2012-07-17 08:26 Shopping cart Search Home Software Hardware Benchmarks Services Store Support Forums About Us Home» CPU Benchmarks ť Multiple CPU Systems CPU Benchmarks Video Card Benchmarks Hard
1 z 5 2012-07-17 08:26 Shopping cart Search Home Software Hardware Benchmarks Services Store Support Forums About Us Home» CPU Benchmarks ť Multiple CPU Systems CPU Benchmarks Video Card Benchmarks Hard
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Vocera Voice 4.3 and 4.4 Server Sizing Matrix
 Vocera Voice 4.3 and 4.4 Server Sizing Matrix Vocera Server Recommended Configuration Guidelines Maximum Simultaneous Users 450 5,000 Sites Single Site or Multiple Sites Requires Multiple Sites Entities
Vocera Voice 4.3 and 4.4 Server Sizing Matrix Vocera Server Recommended Configuration Guidelines Maximum Simultaneous Users 450 5,000 Sites Single Site or Multiple Sites Requires Multiple Sites Entities
Learning Outcomes. Simple CPU Operation and Buses. Composition of a CPU. A simple CPU design
 Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards [email protected] At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
Learning Outcomes Simple CPU Operation and Buses Dr Eddie Edwards [email protected] At the end of this lecture you will Understand how a CPU might be put together Be able to name the basic components
Arrow ECS sp. z o.o. Oracle Partner Academy training environment with Oracle Virtualization. Oracle Partner HUB
 Oracle Partner Academy training environment with Oracle Virtualization Technology Oracle Partner HUB Overview Description of technology The idea of creating new training centre was to attain light and
Oracle Partner Academy training environment with Oracle Virtualization Technology Oracle Partner HUB Overview Description of technology The idea of creating new training centre was to attain light and
Central Processing Unit
 Computer Components c 2015 by David W. Gerbing School of Business Administration Portland State University Computer Components Central Processing Unit CPU Characteristics Other Components of a Computer
Computer Components c 2015 by David W. Gerbing School of Business Administration Portland State University Computer Components Central Processing Unit CPU Characteristics Other Components of a Computer
FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins
 FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins Robert J. Halstead, Ildar Absalyamov, Walid A. Najjar, Vassilis J. Tsotras University of California, Riverside Outline Background What are FPGAs Multithreaded
FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins Robert J. Halstead, Ildar Absalyamov, Walid A. Najjar, Vassilis J. Tsotras University of California, Riverside Outline Background What are FPGAs Multithreaded
Packet Sniffer using Multicore programming. By B.A.Khivsara Assistant Professor Computer Department SNJB s KBJ COE,Chandwad
 Packet Sniffer using Multicore programming By B.A.Khivsara Assistant Professor Computer Department SNJB s KBJ COE,Chandwad Outline Packet Sniffer Multicore Command for CPU info Program in Python Packet
Packet Sniffer using Multicore programming By B.A.Khivsara Assistant Professor Computer Department SNJB s KBJ COE,Chandwad Outline Packet Sniffer Multicore Command for CPU info Program in Python Packet
Introduction to Microprocessors
 Introduction to Microprocessors Yuri Baida [email protected] [email protected] October 2, 2010 Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology Agenda Background and History What is a microprocessor?
Introduction to Microprocessors Yuri Baida [email protected] [email protected] October 2, 2010 Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology Agenda Background and History What is a microprocessor?
GPUs for Scientific Computing
 GPUs for Scientific Computing p. 1/16 GPUs for Scientific Computing Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research
GPUs for Scientific Computing p. 1/16 GPUs for Scientific Computing Mike Giles [email protected] Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Enabling Technologies for Distributed Computing
 Enabling Technologies for Distributed Computing Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF Multi-core CPUs and Multithreading Technologies
Enabling Technologies for Distributed Computing Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF Multi-core CPUs and Multithreading Technologies
PROBLEMS. which was discussed in Section 1.6.3.
 22 CHAPTER 1 BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTERS (Corrisponde al cap. 1 - Introduzione al calcolatore) PROBLEMS 1.1 List the steps needed to execute the machine instruction LOCA,R0 in terms of transfers between
22 CHAPTER 1 BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTERS (Corrisponde al cap. 1 - Introduzione al calcolatore) PROBLEMS 1.1 List the steps needed to execute the machine instruction LOCA,R0 in terms of transfers between
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Slide Set 8. for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
Slide Set 8 for ENCM 369 Winter 2015 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2015 ENCM 369 W15 Section
PC Build and Manual Part 1
 PC Build and Manual Part 1 Applying IT best practices in working with computer systems: Section 1: Workspace Preparation completing IT-related tasks: Sections 1-5 of the manual Section 2: Installing Motherboard
PC Build and Manual Part 1 Applying IT best practices in working with computer systems: Section 1: Workspace Preparation completing IT-related tasks: Sections 1-5 of the manual Section 2: Installing Motherboard
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Computer System: User s View. Computer System Components: High Level View. Input. Output. Computer. Computer System: Motherboard Level
 System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module
 Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
Desktop Publishing 5N0785 Learning Outcome 2 Monaghan Institute Level 5 Module Contents Learners will be able to describe the characteristics of key components of DTP systems including those used for input,
W o r k s h e e t : P r o c e s s o r s
 Time: 1 Hour Revision Date: 6/26/10 Overview This activity is designed to ensure that you understand the topics covered in your courseware. You are required to know the names, purposes and characteristics
Time: 1 Hour Revision Date: 6/26/10 Overview This activity is designed to ensure that you understand the topics covered in your courseware. You are required to know the names, purposes and characteristics
AMD PhenomII. Architecture for Multimedia System -2010. Prof. Cristina Silvano. Group Member: Nazanin Vahabi 750234 Kosar Tayebani 734923
 AMD PhenomII Architecture for Multimedia System -2010 Prof. Cristina Silvano Group Member: Nazanin Vahabi 750234 Kosar Tayebani 734923 Outline Introduction Features Key architectures References AMD Phenom
AMD PhenomII Architecture for Multimedia System -2010 Prof. Cristina Silvano Group Member: Nazanin Vahabi 750234 Kosar Tayebani 734923 Outline Introduction Features Key architectures References AMD Phenom
Introduction to Computer Architecture Concepts
 to Computer Architecture Concepts 1. We will start at the very beginning, first with the fundamental concepts behind the modern digital computer, and then some details of their implementation. Many people,
to Computer Architecture Concepts 1. We will start at the very beginning, first with the fundamental concepts behind the modern digital computer, and then some details of their implementation. Many people,
Parallel Programming Survey
 Christian Terboven 02.09.2014 / Aachen, Germany Stand: 26.08.2014 Version 2.3 IT Center der RWTH Aachen University Agenda Overview: Processor Microarchitecture Shared-Memory
Christian Terboven 02.09.2014 / Aachen, Germany Stand: 26.08.2014 Version 2.3 IT Center der RWTH Aachen University Agenda Overview: Processor Microarchitecture Shared-Memory
An Introduction to High-Frequency Circuits and Signal Integrity
 An Introduction to High-Frequency Circuits and Signal Integrity 1 Outline The electromagnetic spectrum Review of market and technology trends Semiconductors industry Computers industry Communication industry
An Introduction to High-Frequency Circuits and Signal Integrity 1 Outline The electromagnetic spectrum Review of market and technology trends Semiconductors industry Computers industry Communication industry
Introduction to Cloud Computing
 Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
OBJECTIVE ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER MATCH FLASH. TO THE PROCESSOR Why Multithreading Requires Parallelized Flash ATCHING
 OBJECTIVE ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER MATCH ATCHING FLASH TO THE PROCESSOR Why Multithreading Requires Parallelized Flash T he computing community is at an important juncture: flash memory is now generally accepted
OBJECTIVE ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER MATCH ATCHING FLASH TO THE PROCESSOR Why Multithreading Requires Parallelized Flash T he computing community is at an important juncture: flash memory is now generally accepted
Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices. A PC in Every Home. Assembling a Computer System
 C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
C H A P T E R 3 Hardware: Input, Processing, and Output Devices A PC in Every Home February 3, 2000 Ford will make available to all 330,000 employees hourly and salaried an HP Pavilion PC, an HP DeskJet
EMBEDDED X86 PROCESSOR PERFORMANCE RATING SYSTEM
 EMBEDDED X86 PROCESSOR PERFORMANCE RATING SYSTEM The Problem Clock speed has become a standard marketing tool for computer vendors and microprocessor companies seeking to gain mindshare with system designers.
EMBEDDED X86 PROCESSOR PERFORMANCE RATING SYSTEM The Problem Clock speed has become a standard marketing tool for computer vendors and microprocessor companies seeking to gain mindshare with system designers.
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software in a computing system. To learn what computer
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software in a computing system. To learn what computer
Lecture 3: Modern GPUs A Hardware Perspective Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com
 CSCI-GA.3033-012 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): Architecture and Programming Lecture 3: Modern GPUs A Hardware Perspective Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com Modern GPU
CSCI-GA.3033-012 Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): Architecture and Programming Lecture 3: Modern GPUs A Hardware Perspective Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) [email protected] http://www.mzahran.com Modern GPU
Determining Your Computer Resources
 Determining Your Computer Resources There are a number of computer components that must meet certain requirements in order for your computer to perform effectively. This document explains how to check
Determining Your Computer Resources There are a number of computer components that must meet certain requirements in order for your computer to perform effectively. This document explains how to check
Communicating with devices
 Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
Introduction to I/O Where does the data for our CPU and memory come from or go to? Computers communicate with the outside world via I/O devices. Input devices supply computers with data to operate on.
This Unit: Putting It All Together. CIS 501 Computer Architecture. Sources. What is Computer Architecture?
 This Unit: Putting It All Together CIS 501 Computer Architecture Unit 11: Putting It All Together: Anatomy of the XBox 360 Game Console Slides originally developed by Amir Roth with contributions by Milo
This Unit: Putting It All Together CIS 501 Computer Architecture Unit 11: Putting It All Together: Anatomy of the XBox 360 Game Console Slides originally developed by Amir Roth with contributions by Milo
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications
 Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Glitch Free Frequency Shifting Simplifies Timing Design in Consumer Applications System designers face significant design challenges in developing solutions to meet increasingly stringent performance and
Computer Organization. and Instruction Execution. August 22
 Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
Computer Organization and Instruction Execution August 22 CSC201 Section 002 Fall, 2000 The Main Parts of a Computer CSC201 Section Copyright 2000, Douglas Reeves 2 I/O and Storage Devices (lots of devices,
Chapter 2 Parallel Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Parallel Computer Architecture The possibility for a parallel execution of computations strongly depends on the architecture of the execution platform. This chapter gives an overview of the general
Chapter 2 Parallel Computer Architecture The possibility for a parallel execution of computations strongly depends on the architecture of the execution platform. This chapter gives an overview of the general
Why Computers Are Getting Slower (and what we can do about it) Rik van Riel Sr. Software Engineer, Red Hat
 Why Computers Are Getting Slower (and what we can do about it) Rik van Riel Sr. Software Engineer, Red Hat Why Computers Are Getting Slower The traditional approach better performance Why computers are
Why Computers Are Getting Slower (and what we can do about it) Rik van Riel Sr. Software Engineer, Red Hat Why Computers Are Getting Slower The traditional approach better performance Why computers are
Processor Architectures
 ECPE 170 Jeff Shafer University of the Pacific Processor Architectures 2 Schedule Exam 3 Tuesday, December 6 th Caches Virtual Memory Input / Output OperaKng Systems Compilers & Assemblers Processor Architecture
ECPE 170 Jeff Shafer University of the Pacific Processor Architectures 2 Schedule Exam 3 Tuesday, December 6 th Caches Virtual Memory Input / Output OperaKng Systems Compilers & Assemblers Processor Architecture
Figure 1. Front and Back of a Computer Case
 Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
Introduction Almost everyone uses a computer daily, but many don't know how a computer works or all the different individual pieces that make it up. In fact, many people erroneously look at a computer
LSN 2 Computer Processors
 LSN 2 Computer Processors Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Computer Processors Microprocessors Design Instruction set Processor organization Processor performance Bandwidth Clock speed LSN 2
LSN 2 Computer Processors Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Computer Processors Microprocessors Design Instruction set Processor organization Processor performance Bandwidth Clock speed LSN 2
Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin
 BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
Thread level parallelism
 Thread level parallelism ILP is used in straight line code or loops Cache miss (off-chip cache and main memory) is unlikely to be hidden using ILP. Thread level parallelism is used instead. Thread: process
Thread level parallelism ILP is used in straight line code or loops Cache miss (off-chip cache and main memory) is unlikely to be hidden using ILP. Thread level parallelism is used instead. Thread: process
Unit 4: Performance & Benchmarking. Performance Metrics. This Unit. CIS 501: Computer Architecture. Performance: Latency vs.
 This Unit CIS 501: Computer Architecture Unit 4: Performance & Benchmarking Metrics Latency and throughput Speedup Averaging CPU Performance Performance Pitfalls Slides'developed'by'Milo'Mar0n'&'Amir'Roth'at'the'University'of'Pennsylvania'
This Unit CIS 501: Computer Architecture Unit 4: Performance & Benchmarking Metrics Latency and throughput Speedup Averaging CPU Performance Performance Pitfalls Slides'developed'by'Milo'Mar0n'&'Amir'Roth'at'the'University'of'Pennsylvania'
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
Four Keys to Successful Multicore Optimization for Machine Vision. White Paper
 Four Keys to Successful Multicore Optimization for Machine Vision White Paper Optimizing a machine vision application for multicore PCs can be a complex process with unpredictable results. Developers need
Four Keys to Successful Multicore Optimization for Machine Vision White Paper Optimizing a machine vision application for multicore PCs can be a complex process with unpredictable results. Developers need
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
COMSC 101 Virtual Dream Computer Project
 COMSC 101 Virtual Dream Computer Project This assignment requires you to build a virtual dream computer from the motherboard up. Price is no object. You can go to several computer stores that have individual
COMSC 101 Virtual Dream Computer Project This assignment requires you to build a virtual dream computer from the motherboard up. Price is no object. You can go to several computer stores that have individual
10.2 Requirements for ShoreTel Enterprise Systems
 10.2 Requirements for ShoreTel Enterprise Systems The ShoreTel Enterprise Edition system is scalable. For economy, ShoreTel Enterprise customers provide their own server hardware, allowing them to build
10.2 Requirements for ShoreTel Enterprise Systems The ShoreTel Enterprise Edition system is scalable. For economy, ShoreTel Enterprise customers provide their own server hardware, allowing them to build
QLIKVIEW SERVER MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND CPU UTILIZATION
 QLIKVIEW SERVER MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND CPU UTILIZATION QlikView Scalability Center Technical Brief Series September 2012 qlikview.com Introduction This technical brief provides a discussion at a fundamental
QLIKVIEW SERVER MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND CPU UTILIZATION QlikView Scalability Center Technical Brief Series September 2012 qlikview.com Introduction This technical brief provides a discussion at a fundamental
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Accelerating Data Compression with Intel Multi-Core Processors
 Case Study Predictive Enterprise Intel Xeon processors Intel Server Board Embedded technology Accelerating Data Compression with Intel Multi-Core Processors Data Domain incorporates Multi-Core Intel Xeon
Case Study Predictive Enterprise Intel Xeon processors Intel Server Board Embedded technology Accelerating Data Compression with Intel Multi-Core Processors Data Domain incorporates Multi-Core Intel Xeon
Lecture 11: Multi-Core and GPU. Multithreading. Integration of multiple processor cores on a single chip.
 Lecture 11: Multi-Core and GPU Multi-core computers Multithreading GPUs General Purpose GPUs Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH 1 Multi-Core System Integration of multiple processor cores on a single chip. To provide
Lecture 11: Multi-Core and GPU Multi-core computers Multithreading GPUs General Purpose GPUs Zebo Peng, IDA, LiTH 1 Multi-Core System Integration of multiple processor cores on a single chip. To provide
Programming Logic controllers
 Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
