The dermatophytes Fungi that stalk you and your loved ones as their petri plate
|
|
|
- Corey Reeves
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The dermatophytes Fungi that stalk you and your loved ones as their petri plate Dr. Richard Summerbell Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto Geraldine Kaminski Medical Mycology Library Bacteria Purple bacteria Cyanobacteria Gram positives Clostridium Mycoplasma Archaebacteria Methanobacterium Methanococcus Pyrococcus Archaeglobus Eukarya Animals Slime moulds Fungi Plants Pyrobaculum Borrelia Thermologa Deinococcus Green nonsulfur bacteria Aquifex Flagellates Trichomonads Microsporidia Image courtesy of the late Dr. Julius Kane Source: Oak Ridge National Laboratory 1
2 Chytridiomycota (water moulds) Zygomycota (sweet rots) Basidiomycota (mushrooms, rusts, smuts) Ascomycota (sac fungi, true moulds, yeasts) 300 MYA 600 MYA after Purves et al, 1998 Talaromyces = Penicillium sexual stage called: teleomorph asexual stage called: anamorph 2
3 Character evolution and speciation in dermatophytes Mating Dikaryotization Meiosis Mitosis Onygena cervina Jan Zavrel ˆ 3
4 Soil association characters Morphology conidial abundance and variety formation of perforating organs in dissociated i dhair arthropod antipredation or dispersal features conidial ornamentation rigid peridial "wireframe" peridial spirals, hooks and spines Physiology osmotolerance vitamin and amino acid autotrophy constitutive protease and urease activity Genetics intact heterothallic mating system conspicuous teleomorph Dikaryotization Mitosis Mitosis Mating Meiosis Mitosis Characters associated with non-soil associated animals Morphology attenutated conidiation, trend to monomorphic to aconidial strains l f h i f i loss of hair perforating organs loss of arthropod antipredation or dispersal features smooth conidia loss of teleomorph structures including peridial appendages, coils, etc. Physiology osmosensitive vitamin and amino acid auxotrophy i d d t ti it ( t b lit i ) induced protease activity (catabolite repression) attenuated urease activity Genetics heterothallic mating system dismantled loss of teleomorph and related structures 4
5 What are the dermatophytes? anamorph (asexual genera) Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton both Trichophyton and Microsporum also contain some nonpathogenic species (not defined as dermatophytes = skin plants, ergo called dermatophytoids = look like dermatophytes. ) teleomorphs, formed only in some species, all in genus Arthroderma Tinea (dermatophytosis) dermatophytosis different tinea disease types for scalp, beard area, glabrous skin (face, trunk, leg, arm), groin, foot skin, nails (finger or toe). Main categories scalp dermatophytes mostly affecting children, but often converting some adults to cryptic carriers, e.g., Trichophyton tonsurans glabrous skin dermatophytes acquired from animals, e.g., Microsporum canis from cats human-associated dermatophytes mainly of feet, hands and groin, e.g., Trichophyton rubrum Ecological categories host/substrate Anthropophilic typically growing on humans Zoophilic have animal population hosts, but occasional human infections occur Geophilic associated with keratinous habitats in soil, e.g., decomposing hair and feathers 5
6 Dermatophyte eco-morphological types Soil-associated dermatophytes (and dermatophytoids = nonpathogenic members of Trichophyton and Microsporum) ) full slate of soil association characters listed in previous slide geophiles, zoophiles of burrowing and denning animals Non-soil-associated dermatophytes genetic drift for unselected characters allows fixation of mutations leading to loss of soil-association characters; usually at least two of the items listed are altered, e.g., in typical Trichophyton rubrum, urease and hair perforation lost, sexuality lost along with one mating type, growth rate moderate not fast, osmotolerance lost, macroconidia very sparsely formed if at all. anthropophiles, zoophiles of ungulates (cows, sheep) and horses Mating type determination Mat genes now amplified in dermatophytes Mating type can often be identified in classical genetics by crossing members of most species with testers of Arthroderma simii. Partial mating reaction with formation of non-maturing ascomata seen in pairings of opposite mating type Dermatophytosis: body site specificities here tinea barbae, infection of beard area from Emedicine website Tinea capitis mainly in children adult carriers, usually an older woman in the family may cause y school and other outbreaks 6
7 Tinea corporis (T. verrucosum on finger) Tinea manuum usually caused by zoophilic species usually caused by T. rubrum T. rubrum may also cause it, esp. the afroasiatic form Tinea pedis (severe) Foot dermatophytosis (severe) anthropophilic species involved: mostly T. rubrum, T. interdigitale 7
8 Tinea pedis (moccasin foot) Nail dermatophytosis (tinea unguium, a subcategory of onychomycosis) mostly same species as cause tinea pedis T. rubrum attacks nails from below (moist); T. interdigitale from above (dry) fungus typically grows in tinea pedis for 20+ years, then gradually moves in to colonize nails Dermatophytosis: hair invasion in vivo for species causing t. capitis Ectothrix: M. canis coating hair surface with substrate-arthroconidia endothrix: Trichophyton tonsurans, T. violaceum, T. soudanense ectothrix: M. canis, M. audouinii, M. ferrugineum ( small-spored ), T. verrucosum, T. megninii ( large-spored ) favic: air channels and large hyphae in hair, seen only in T. schoenleinii infection 8
9 Endothrix: T. tonsurans filling hair shaft with substrate-arthroconidia Favic hair invasion: T. schoenleinii Zoophilic infections: Dog with severe M. canis infection Microsporum canis on cat 9
10 Microsporum canis on cat: fluorescence Population host vs. occasional host M. canis populations maintain themselves perpetually petua on cats, Trichophyton (mentagrophytes complex) state of Arthroderma benhamiae on rabbits and cavies, T. (m. complex) state of A. vanbreuseghemii on rats and squirrels, etc Such species can all cause occasional infections in atypical hosts, e.g., in humans, deer, horses, seals, dogs, etc. They are not chronically carried in populations of these occasional hosts and there is minimal effect of this host cross-over on the population genetics of the fungal species. Taxonomy problems I species now mainly based on phylogenetic study traditional taxonomy distinguished species distinguished by profound changes occurring in switch from soil-associated to non-soil-associated niches: strong morphological change (slower growth, few conidia, etc.) often also physiological change (e.g., gain of a vitamin requirement, loss of hair perforation ability) population-host jump (to human, cow, sheep, camel or horse) loss of sexuality and generally also of one mating type many of these transformed niche-jumpers are now found to be very phylogenetically close to the soil-associated ancestral species, leading to controversy about whether they should retain their separate names or not, e.g., chicken dermatophyte Microsporum gallinae, derived from geophilic Arthroderma grubyi/microsporum vanbreuseghemii Taxonomy problems II Some traditional species were long known to be species-complexes p composed of organisms distinguishable only by mating, e.g., T. mentagrophytes complex (A. benhamiae, A. vanbreuseghemii) and M. gypseum complex (A. gypseum, A. incurvatum, A. fulvum). There is now a trend to name these species individually (e.g, T. interdigitale for anamorphs related to A. vanbreuseghemii) even though they can only be reliably identified using molecular techniques (still too expensive for routine diagnostic work) 10
11 Dendrogram Identification: traditional characters Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids macroconidia alone, smooth-walled (Epidermophyton) h t with microconidia, rough-walled (Microsporum) with microconidia, smooth walled (Trichophyton) problem is that macroconidia are often not seen at all. Also, microconidia may be absent, and are essentially always absent in some species. Identification: BCP (bromcresyl purple) milk solids glucose agar The BCP indicator detects: acid production by many bacteria and nondermatophytic fungi (and then turns yellow) alkaline ammonium ion production by dermatophytes (and some nonpathogens) utilizing amino acids from protein as a sole carbon source The milk solids show: peptonization (clearing) showing the presence of proteases cleaving proteins into short segments Some other common physiological identification techniques Christensen urea broth or agar indicates urease enzyme Vitamin and other growth factor requirement tests series of 7 Trichophyton agars, but usually only 3 4 are regularly used hair perforation in vitro Sabouraud + 3% or 5% salt 11
12 BCP MSG reactions of common fast-growing dermatophytes T. rubrum vs. T. mentagrophytes complex on BCP MSG + reactions T. rubrum ( ) common Microsporum spp.: ( ) reactions Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex on BCP MSG and urea broth Trichophyton rubrum on BCP MSG, Christensen urea broth at 7 d 12
13 Bacterially contaminated Trichophyton rubrum on BCP MSG, Christensen urea broth at 7 d Hair perforation antibiotic-polyresistant bacteria carried over into urease test may cause false + reactions. The BCP MSG medium is used antibiotic-free so that it, in various ways, will reveal this cryptic bacterial contamination Here the bacteria are evidenced by the atypical yellowish colour of the T. rubrum colony Trichophyton violaceum (pale form), vitamin test Dendrogram Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids 13
14 Microsporum canis, the cat ringworm fungus (also infects humans, especially children, who handle cats) from Univ. of Alberta dermatophytes website teleomorph A. otae Image courtesy of Dr. Joe Kowalski Microsporum canis colony Image courtesy of Dr. E. Pierard 14
15 Microsporum canis colony reverse Sabouraud Microsporum audouinii colony on Sabouraud anthropophile, infects mostly scalp of patients < 19 yr old now mainly restricted to central and west Africa, but may arrive on travellers, immigrants Microsporum audouinii beaked macroconidium Microsporum audouinii microconidia 15
16 Microsporum audouinii on diagnostic media Microsporum audouinii on rice Microsporum ferrugineum An anthropophilic fungus causing epidemic juvenile tinea capitis in humans. The clinical features are similar to those of infections caused by M. audouinii. Invaded hairs show an ectothrix infection and fluoresce a greenish-yellow under Wood's ultra-violet light. Distribution: Central Asia, central Africa, possibly still rarely present in Korea and Romania (historical endemic strongholds). Key Features: Culture characteristics and distinctive "bamboo" hyphae
17 Microsporum gallinae colony considered a synonym of M. vanbreuseghemii by Gräser et al. Microsporum gallinae asexual species, typically on glabrous skin of fowl 17
18 Microsporum vanbreuseghemii macroconidia anamorph of A. grubyi, geophilic Microsporum gypseum colony geo- philic, but may infect humans and animals infections often selflimiting but inflammatory Microsporum gypseum macroconidia Microsporum cookei colony teleomorph A. cajetani nonpathogen, subject of a few very weak case reports, probably all in error 18
19 Microsporum cookei colony reverse Microsporum cookei conidia Microsporum persicolor colony Microsporum persicolor macroconidium teleomorph A. persicolor may be a zoophile associated with voles and bats (pipistrelle) or possibly a geophile may infect people, e.g., gardeners; also not uncommon from dogs noses hard to distinguish from T. mentagrophytes complex, thus under-reported in many areas 19
20 Microsporum persicolor microconidia Microsporum persicolor microconidia and spiral appendages Microsporum nanum colony Microsporum nanum colony reverse teleomorph A. obtusum zoophile with swine population host 20
21
22 Epidermophyton floccosum colonies on Sabouraud and Sab - 3% salt Epidermophyton floccosum conidia anthropophile mainly associated with tinea cruris, but some t. corporis, t. pedis and t. unguium now becoming very uncommon in developed world 22
23 Epidermophyton floccosum conidia T. mentagrophytes complex zoophilic Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii and very closely related anthropophilic Trichophyton interdigitale. The former is mainly from rats and causes inflammatory tinea corporis in humans, while the latter is the most common fungus in this complex in human infection and mainly causes tinea pedis and t. unguium zoophilic Arthroderma benhamiae, mainly from rabbits and cavies; some typical humanassociated strains in North America and eastern Europe also mate with this species T. mentagrophytes sensu stricto, zoophilic, associated with mice, causing inflammatory tinea corporis, a single mating type mating with A. benhamiae T. erinacei, the hedgehog dermatophyte, a single mating type mating with A. benhamiae Dendrogram again / T. equinum Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids University of Iowa, Dept of Dermatology 23
24 Foot dermatophytosis (severe) Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex vs. yellow T. rubrum on BCP MSG Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex on BCP MSG and urea broth Anamorph of Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii (genetically Trichophyton interdigitale) 24
25 Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex (T. interdigitale?) velvety form Trichophyton interdigitale (cottony) Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex: spiral appendage Trichophyton mentagrophytes complex: macroconidia 25
26 Arthoderma simii mating cross Trichophyton simii conidia and Arthoderma simii ascospores Trichophyton verrucosum colony zoophile with cattle population host mainly infects handlers of animals or their fomites inflammatory tinea corporis, capitis, barbae 26
27 Geraldine Kaminski Medical Mycology Library Image courtesy of the late Dr. Libero Ajello Trichophyton verrucosum primary outgrowth Trichophyton verrucosum vitamins: inos + thiam (#3), thiam alone (#4), vit-free (#1) 27
28 Trichophyton verrucosum chlamydospores Trichophyton verrucosum chlamydospores Trichophyton verrucosum macroconidia Trichophyton concentricum causal agent of tinea imbricata endemic to Pacific Islands and to southeast Asian indigenous hill tribe peoples, as well as a few groups of South American indigenous people susceptibility inherited as a recessive allele often a chronic lifelong infection affecting much of the body surface 28
29
30 198 T. mentagrophytes ss. str. / T. schoenleinii / T. sarkisovii complex T. mentagrophytes, after molecular study, was strictly redefined with a taxonomic Neotype to include only the mouse dermatophyte, the former T. m. var. quinckeanum, and isolate types that could not be separated from it genetically (most notably the Bactrian camel dermatophyte, T. sarkisovii). very closely related is the anthropophilic T. schoenleinii, agent of favus. Dendrogram / T. equinum Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. quinckeanum Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids A zoophilic form of T. mentagrophytes and the cause of "mouse favus" seen on mice as thick saucer-shapedshaped yellow crusted lesions called scutula. Infections in humans are usually inflammatory and sometimes produce scutula. Invaded hairs are rarely seen but they may show either ectothrix or endothrix infection. Infected human hairs do not fluoresce under Wood's ultra-violet light, but very occasional hairs from experimental lesions in guinea pigs may show a pale yellow fluorescence. Distribution: Difficult to establish but probably world-wide. Often associated with mice plagues in the Australian Wheat Belt. Key Features: Culture characteristics, microscopic morphology, contact with mice, odour and rapid urease test. 30
31
32
33 249 Trichophyton schoenleinii primary outgrowth anthropophile, causal agent of favus and severe scarring alopecia now extirpated except in central Africa, central Asia Trichophyton schoenleinii colony 33
34 Dendrogram / T. equinum Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids 34
35 Trichophyton tonsurans colony (striate morphology) anthropophile, main agent of endothrix childhood tinea capitis in most of the world increasingly predominant, especially in urban areas with minority communities living in relative poverty most common dermatophyte in some parts of USA Trichophyton tonsurans Trichophyton tonsurans mahogany red form, reverse 35
36 Trichophyton tonsurans sulfureum form, reverse Trichophyton tonsurans thiamine stimulation Trichophyton tonsurans conidia Trichophyton tonsurans caterpillar forms 36
37 Trichophyton equinum colony zoophile with horse population host Triochophyton equinum colony reverse closely related to anthropophile T. tonsurans is + mating type while T. tonsurans is Triochophyton equinum vitamin test (nicotinic acid required)
38
39 208 Trichophyton erinacei European type long known: yellow colony reverse, urease negative, population host is European hedgehog Erinaceus europaeus Trichophyton erinacei African type often urease positive; forms teleomorph newly described d by Japanese researchers, occurs on African hedgehog Atelerix albiventris Trichophyton erinacei European type: yellow colony reverse, urease negative 39
40 Trichophyton rubrum vs. T. mentagrophytes complex on BCP MSG Trichophyton rubrum: emerging as the most common dermatophyte in most parts of the world anthropophilic, mostly causing tinea pedis, t. unguium, t. cruris, t. manuum and t. corporis microsatellite typing shows two types, the afro-asiatic type (synonymous name T. raubitschekii still used informally), mainly involved in inflammatory, chronic tinea corporis and t. cruris in south Asia and central Africa, is type A, while the typical T. rubrum, predominantly from non-inflammatory tinea pedis and t. unguium (also other sites) is type B Dendrogram T. rubrum /T. violaceum complex / T. equinum / T. yaoundei / T. soudanense / T. gourvilii / T. megninii Trichophyton dermatophytes, M. canis complex and E. floccosum main Microsporum group mostly nonpathogenic Trichophyton dermatophytoids Image courtesy of the late Dr. Julius Kane 40
41 Nail dermatophytosis (onychomycosis) Trichophyton rubrum colony Trichophyton rubrum colony reverse Trichophyton rubrum microconidia 41
42 Trichophyton rubrum on BCP MSG, PDA, CEA, SAB at 7 d Trichophyton rubrum melanoid form Trichophyton rubrum melanoid form Trichophyton rubrum rodhainii form 42
43 Trichophyton rubrum yellow form Trichophyton rubrum yellow form on SAB and plain casamino acids agar (reverse) Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) colonies Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) colony reverse 43
44 Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) conidia Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) colonies Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) conidia Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) on BCP and Christensen urea broth 44
45 Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) distribution Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite genotype A ( T. raubitschekii ) Trichophyton megninii colony reverse Trichophyton megninii colony similar but not identical to T. rubrum in ITS sequence, considered a synonym by some authors causes tinea corporis, t. capitis and dt. barbae b mainly in Portugal mating type + whereas T. rubrum is 45
46 Trichophyton rubrum vs. T. megninii on BCP MSG Trichophyton violaceum colony T. megninii requires exogenous L-histidine histidine, and thus grows on test medium Trichophyton agar # 7 but not the histidine-free # 6. urease positive, but may be slow and is better seen in an indole-urea broth test. anthropophile mainly causing tinea capitis (endothrix) in children endemic to middle east and north and east Africa Trichophyton violaceum on three media Trichophyton violaceum asymmetrical chlamydospores 46
47 Trichophyton violaceum microconidia (from pleomorphic colony) Trichophyton violaceum (pale form) on BCP MSG Trichophyton soudanense on BCP MSG anthrophophile: endothrix tinea capitis agent endemic to sub-saharan Africa recently proposed as synonymous with T. rubrum, which does not cause endothrix tinea capitis and is strongly morphologically different, but is only consistently different in common sequence types at a relatively low level nonetheless, clinically and in the diagnostic lab, can only be handled as a distinct entity Trichophyton soudanense Sabouraud and BCP MSG 47
48 Trichophyton soudanense on Sabouraud Trichophyton soudanense microconidia Trichophyton soudanense red variant Trichophyton soudanense red variant with yellow colour restored on SAB-3% salt 48
49 Trichophyton soudanense red variant Trichophyton soudanense reflexive branch Trichophyton soudanense reflexive branch Trichophyton soudanense reflexive branch 49
50 Further development T1 Microsatellites in T. rubrum lineage Microsatellite types in T. rubrum lineage members (Ohst et al. taxonomy) T. violaceum (violaceum) C T. violaceum (yaoundei) D T. rubrum T. violaceum T. rubrum (soudanense!) T. rubrum (raubitschekii) A A T. rubrum (megninii) A T. rubrum (common rubrum) B Ohst T et al J Clin Microbiol 42: T1 microsatellite patterns Ohst et al. (2004) JCM 42: Trichophyton rubrum microsatellite studies Traditional species name T1 type T. violaceum C T. yaoundei D T. gourvilii A T. soudanense A T. megninii A T. rubrum granular / T. raubitschekii tropical torso/groin dermatophyte T. rubrum cottony cosmopolitan foot and hand dermatophyte, sometimes infecting torso/groin A B Asterisks indicate isolates with reflexive branching 50
51 Trichophyton ajelloi colonies Trichophyton ajelloi conidia non- pathogenic geophile subject of some dubious case reports teleomorph A. uncinatum Trichophyton terrestre complex: colony species complex of nonpathogenic geophiles no growth at 37 degrees in vitro regular object of false case reports due to common isolation as a contaminant from T. rubrum etc. lesions Trichophyton terrestre complex: conidia distinguishing morphological feature: range of conidial sizes intergrading from micro- to macro- 51
52 Trichophyton terrestre complex: colony Arthoderma quadrifidum ascoma most common teleomorph in T. terrestre complex Arthroderma quadrifidum appendages 52
A twenty-year survey of dermatophytoses in Braga, Portugal
 Oxford, IJD International 1365-4632 Blackwell 45 UK Publishing, Journal Ltd, of Ltd. Dermatology 2005 Tropical medicine rounds Dermatophytes Valdigem MISCELLANEOUS et al. in Portugal A twenty-year survey
Oxford, IJD International 1365-4632 Blackwell 45 UK Publishing, Journal Ltd, of Ltd. Dermatology 2005 Tropical medicine rounds Dermatophytes Valdigem MISCELLANEOUS et al. in Portugal A twenty-year survey
IMAGE ASSISTANT: DERMATOMYCOSES
 IMAGE ASSISTANT: DERMATOMYCOSES Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
IMAGE ASSISTANT: DERMATOMYCOSES Summary: The Image Assistant has been developed to provide medical doctors with a software tool to search, display, edit and use medical illustrations of their own specialty,
Challenges in prevention and case management of tinea capitis.
 & Challenges in prevention and case management of tinea capitis. An example from a primary school outbreak in 2013. Amber Litzroth, Scientific Institute of Public Health, detached to Agency for Care and
& Challenges in prevention and case management of tinea capitis. An example from a primary school outbreak in 2013. Amber Litzroth, Scientific Institute of Public Health, detached to Agency for Care and
In vitro activity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil against dermatophytes and other filamentous fungi
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2002) 50, 195 199 DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkf112 In vitro activity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil against dermatophytes and other filamentous fungi K. A. Hammer
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2002) 50, 195 199 DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkf112 In vitro activity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil against dermatophytes and other filamentous fungi K. A. Hammer
Museum Victoria http://museumvictoria.com.au/ CRC National Plant Biosecurity http://www.crcplantbiosecurity.com.au/
 1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (E.F. Sm.) W.C. Snyder & H.N. Hansen Anamorphic fungi (Ascomycetes) Common Name Panama disease of banana Live link: http://www.padil.gov.au:80/pests-and-diseases/pest/main/136609
1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (E.F. Sm.) W.C. Snyder & H.N. Hansen Anamorphic fungi (Ascomycetes) Common Name Panama disease of banana Live link: http://www.padil.gov.au:80/pests-and-diseases/pest/main/136609
FOX 1064 - Laser Therapy ONYCHOMYKOSIS FUNGAL NAIL INFECTION (ONYCHOMYCOSIS) FOX 1064 nm LASER INNOVATION MA DE IN GERMA NY
 US? G N U F L I A N N A IL S FOX: CLEAR DICATION WITHOUT ME FOX 1064 - Laser Therapy ONYCHOMYKOSIS FUNGAL NAIL INFECTION (ONYCHOMYCOSIS) FOX 1064 LASER INNOVATION MA DE IN GERMA NY FOX Laser offers an
US? G N U F L I A N N A IL S FOX: CLEAR DICATION WITHOUT ME FOX 1064 - Laser Therapy ONYCHOMYKOSIS FUNGAL NAIL INFECTION (ONYCHOMYCOSIS) FOX 1064 LASER INNOVATION MA DE IN GERMA NY FOX Laser offers an
Use of Single-enzyme PCR-restriction Digestion Barcode Targeting the Internal Transcribed Spacers (ITS rdna) to Identify Dermatophyte Species
 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 41, No.3, 2012, pp.82-94 Original Article Use of Single-enzyme PCR-restriction Digestion Barcode Targeting the Internal Transcribed Spacers (ITS rdna) to Identify Dermatophyte
Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 41, No.3, 2012, pp.82-94 Original Article Use of Single-enzyme PCR-restriction Digestion Barcode Targeting the Internal Transcribed Spacers (ITS rdna) to Identify Dermatophyte
Bovine Mastitis. 062612tr
 Bovine Mastitis 062612tr Hardy Diagnostics has everything for your laboratory! Mastitis Microbiology Made Easy! Our products are designed to aid in the rapid identification of bovine mastitis organisms
Bovine Mastitis 062612tr Hardy Diagnostics has everything for your laboratory! Mastitis Microbiology Made Easy! Our products are designed to aid in the rapid identification of bovine mastitis organisms
FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE NAILS
 FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE NAILS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about fungal infections of the nails. It tells you what they are, what causes
FUNGAL INFECTIONS OF THE NAILS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about fungal infections of the nails. It tells you what they are, what causes
Enteric Unknowns Miramar College Biology 205 Microbiology
 Enteric Unknowns Miramar College Biology 205 Microbiology Enteric (Greek enteron = intestine) bacteria are comprised of several different genera, but all reside in the digestive tract of mammals. Because
Enteric Unknowns Miramar College Biology 205 Microbiology Enteric (Greek enteron = intestine) bacteria are comprised of several different genera, but all reside in the digestive tract of mammals. Because
Additional details >>> HERE <<<
 Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Additional details >>> HERE http://dbvir.com/ringworm12/pdx/comw23/ Tags:
Cells are tiny building blocks that make up all living things. Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them.
 FC01 CELLS s are tiny building blocks that make up all living things. s are so small that you need a microscope to see them. ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL This is the control centre of the cell. It contains chromosomes
FC01 CELLS s are tiny building blocks that make up all living things. s are so small that you need a microscope to see them. ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL This is the control centre of the cell. It contains chromosomes
A and B are not absolutely linked. They could be far enough apart on the chromosome that they assort independently.
 Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
Lecture 10 Friday, March 20, 2009
 Lecture 10 Friday, March 20, 2009 Reproductive isolating mechanisms Prezygotic barriers: Anything that prevents mating and fertilization is a prezygotic mechanism. Habitat isolation, behavioral isolation,
Lecture 10 Friday, March 20, 2009 Reproductive isolating mechanisms Prezygotic barriers: Anything that prevents mating and fertilization is a prezygotic mechanism. Habitat isolation, behavioral isolation,
Introduction. Contamination sources
 Introduction Tim Sandle www.pharmamicro.com Cleanrooms and environmental monitoring Contamination sources Contamination control The human microbiome and the microbial ecology of people Case study: Microorganisms
Introduction Tim Sandle www.pharmamicro.com Cleanrooms and environmental monitoring Contamination sources Contamination control The human microbiome and the microbial ecology of people Case study: Microorganisms
Summary. 16 1 Genes and Variation. 16 2 Evolution as Genetic Change. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1
 Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1 The arrangement of genes and other DNA markers is compared between species in Comparative genome mapping. As early as 1915, the geneticist J.B.S Haldane reported that
Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1 The arrangement of genes and other DNA markers is compared between species in Comparative genome mapping. As early as 1915, the geneticist J.B.S Haldane reported that
Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005
 Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION
 NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION NIZORAL (ketoconazole) 2% Shampoo is a red-orange liquid for topical application, containing the broad spectrum synthetic antifungal agent ketoconazole in
NIZORAL (KETOCONAZOLE) 2% SHAMPOO DESCRIPTION NIZORAL (ketoconazole) 2% Shampoo is a red-orange liquid for topical application, containing the broad spectrum synthetic antifungal agent ketoconazole in
Protists and Fungi. What color are the cells in the living culture?
 Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
HASPI Medical Life Science Summary; Revised June 2015 1
 HASPI Medical Life Science Core Labs Summary As funding is available, many of the supplies needed to implement the following labs will available for purchase through HASPI. Visit www.haspi.org for updates,
HASPI Medical Life Science Core Labs Summary As funding is available, many of the supplies needed to implement the following labs will available for purchase through HASPI. Visit www.haspi.org for updates,
A guide to diagnosing skin infections in practice
 A guide to diagnosing skin infections in practice Special Thanks Pfi zer Animal Health would like to thank the following people for kindly supplying the images for this booklet and without whose support
A guide to diagnosing skin infections in practice Special Thanks Pfi zer Animal Health would like to thank the following people for kindly supplying the images for this booklet and without whose support
Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
Genetics Test Biology I
 Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
Genetics Test Biology I Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Avery s experiments showed that bacteria are transformed by a. RNA. c. proteins.
CCpp X ccpp. CcPp X CcPp. CP Cp cp cp. Purple. White. Purple CcPp. Purple Ccpp White. White. Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white
 P F 1 CCpp X ccpp Cp Cp CcPp X CcPp F 2 CP Cp cp cp CP Cp cp cp CCPP CCPp CcPP CcPp CCPp CCpp CcPp Ccpp CcPP CcPp ccpp ccpp Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white CcPp Ccpp ccpp ccpp AABB X aabb P AB ab Gametes
P F 1 CCpp X ccpp Cp Cp CcPp X CcPp F 2 CP Cp cp cp CP Cp cp cp CCPP CCPp CcPP CcPp CCPp CCpp CcPp Ccpp CcPP CcPp ccpp ccpp Summary: 9/16 purple, 7/16 white CcPp Ccpp ccpp ccpp AABB X aabb P AB ab Gametes
COMMON SKIN DISEASES. Robin Marks Anne Plunkett Kate Merlin Nicole Jenner. Department of Dermatology St Vincent s Hospital, Melbourne
 A T L A S O F COMMON SKIN DISEASES I N A U S T R A L I A A U T H O R S Robin Marks Anne Plunkett Kate Merlin Nicole Jenner Department of Dermatology St Vincent s Hospital, Melbourne Published by the Department
A T L A S O F COMMON SKIN DISEASES I N A U S T R A L I A A U T H O R S Robin Marks Anne Plunkett Kate Merlin Nicole Jenner Department of Dermatology St Vincent s Hospital, Melbourne Published by the Department
Biological Sciences Initiative. Human Genome
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
 Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Pathology, Infection, and Disease Disease: An abnormal state in which the body is not functioning normally Pathology: The study of disease Etiology: The study of
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Pathology, Infection, and Disease Disease: An abnormal state in which the body is not functioning normally Pathology: The study of disease Etiology: The study of
Fast and reliable PCR/sequencing/RFLP assay for identification of fungi in onychomycoses
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2006), 55, 1211 1216 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46723-0 Fast and reliable PCR/sequencing/RFLP assay for identification of fungi in onychomycoses Michel Monod, Olympia Bontems, Christophe
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2006), 55, 1211 1216 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.46723-0 Fast and reliable PCR/sequencing/RFLP assay for identification of fungi in onychomycoses Michel Monod, Olympia Bontems, Christophe
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant
 Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
BJD British Journal of Dermatology. 1.0 Purpose and scope. 2.0 Stakeholder involvement and peer review. 3.0 Methodology GUIDELINES
 GUIDELINES BJD British Journal of Dermatology British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of tinea capitis 2014 L.C. Fuller, 1 R.C. Barton, 2 M.F. Mohd Mustapa, 3 L.E. Proudfoot,
GUIDELINES BJD British Journal of Dermatology British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of tinea capitis 2014 L.C. Fuller, 1 R.C. Barton, 2 M.F. Mohd Mustapa, 3 L.E. Proudfoot,
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KETODERM
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KETODERM Cream 2% (Ketoconazole, USP) Topical Antifungal Agent TaroPharma A Division of Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc. 130 East Drive Brampton, Ontario L6T 1C1 Preparation Date: Control #
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH KETODERM Cream 2% (Ketoconazole, USP) Topical Antifungal Agent TaroPharma A Division of Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc. 130 East Drive Brampton, Ontario L6T 1C1 Preparation Date: Control #
CHEM 107. Hair handout. Basic Structure of Hair. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05
 CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
Ecology 1 Star. 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the
 Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
Name: ate: 1. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the 5. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.. biotic factors and decomposers.
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research
 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
BioBoot Camp Genetics
 BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
BioBoot Camp Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information DNA Replication is the process of DNA being copied before
Carcinogens from Fungi Pathogenic for Man1
 (CANCER RESEARCH 28, 2276-2281, November 1968] Carcinogens from Fungi Pathogenic for Man1 F. Blank, O. Chin, G. Just, D. R. Meranze, M. B. Shimkin, and R. Wieder Skin and Cancer Hospital and Fels Research
(CANCER RESEARCH 28, 2276-2281, November 1968] Carcinogens from Fungi Pathogenic for Man1 F. Blank, O. Chin, G. Just, D. R. Meranze, M. B. Shimkin, and R. Wieder Skin and Cancer Hospital and Fels Research
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 10 BACTERIAL GROWTH Eye of Science / Science Photo Library WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Increase in numbers is one of the requirements for infection. This increase is dependent upon bacterial growth.
CHAPTER 10 BACTERIAL GROWTH Eye of Science / Science Photo Library WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Increase in numbers is one of the requirements for infection. This increase is dependent upon bacterial growth.
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Helen Geeson BSc PGCE. Background
 The Genetics of Dachshund Coats and Colours Helen Geeson Sc PGCE ackground Dogs have 39 pairs of Chromosomes (one from each parent). Chromosomes are long chains of genes which are the coded instructions
The Genetics of Dachshund Coats and Colours Helen Geeson Sc PGCE ackground Dogs have 39 pairs of Chromosomes (one from each parent). Chromosomes are long chains of genes which are the coded instructions
Medical Microbiology Culture Media :
 Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
Bacterial Transformation Post lab Questions:
 Bacterial Transformation Post lab Questions: 1. This graph represents typical bacteria growth and death on any culture plate. This trend occurs in both Luria Broth/ agarose and Luria broth/ Agarose/ Ampicillin/Arabinose
Bacterial Transformation Post lab Questions: 1. This graph represents typical bacteria growth and death on any culture plate. This trend occurs in both Luria Broth/ agarose and Luria broth/ Agarose/ Ampicillin/Arabinose
Worksheet: The theory of natural selection
 Worksheet: The theory of natural selection Senior Phase Grade 7-9 Learning area: Natural Science Strand: Life and living Theme: Biodiversity, change and continuity Specific Aim 1: Acquiring knowledge of
Worksheet: The theory of natural selection Senior Phase Grade 7-9 Learning area: Natural Science Strand: Life and living Theme: Biodiversity, change and continuity Specific Aim 1: Acquiring knowledge of
HUMAN PROTEINS FROM GENETIC ENGINEERING OF ORGANISMS
 HUMAN PROTEINS FROM GM BACTERIA Injecting insulin is an everyday event for many people with diabetes. GENETIC ENGINEERING OF ORGANISMS involves transferring genes from one species into another. Genetic
HUMAN PROTEINS FROM GM BACTERIA Injecting insulin is an everyday event for many people with diabetes. GENETIC ENGINEERING OF ORGANISMS involves transferring genes from one species into another. Genetic
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2
 Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
XII. Biology, Grade 10
 XII. Biology, Grade 10 Grade 10 Biology Pilot Test The spring 2004 Grade 10 MCAS Biology Test was based on learning standards in the Biology content strand of the Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering
XII. Biology, Grade 10 Grade 10 Biology Pilot Test The spring 2004 Grade 10 MCAS Biology Test was based on learning standards in the Biology content strand of the Massachusetts Science and Technology/Engineering
The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps
 The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps Prof. Kristien Van Reeth Laboratory of Virology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Belgium H1N1, H3N2 and
The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps Prof. Kristien Van Reeth Laboratory of Virology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Belgium H1N1, H3N2 and
Terms: The following terms are presented in this lesson (shown in bold italics and on PowerPoint Slides 2 and 3):
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Principles of Evolution - Origin of Species
 Theories of Organic Evolution X Multiple Centers of Creation (de Buffon) developed the concept of "centers of creation throughout the world organisms had arisen, which other species had evolved from X
Theories of Organic Evolution X Multiple Centers of Creation (de Buffon) developed the concept of "centers of creation throughout the world organisms had arisen, which other species had evolved from X
GENE CLONING AND RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY
 GENE CLONING AND RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY What is recombinant DNA? DNA from 2 different sources (often from 2 different species) are combined together in vitro. Recombinant DNA forms the basis of cloning.
GENE CLONING AND RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY What is recombinant DNA? DNA from 2 different sources (often from 2 different species) are combined together in vitro. Recombinant DNA forms the basis of cloning.
CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 9 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Genetic engineering is possible
Culture media ISO 6579
 Culture media ISO 6579 Buffered Peptone Water Urea Indol TSI Agar Cat. 1172 β Galactosidase Lisine Decarboxilase Broth Cat. 1176 Voges-Proskauer Salmonella Buffered Peptone Water BUFFERED PEPTONE WATER
Culture media ISO 6579 Buffered Peptone Water Urea Indol TSI Agar Cat. 1172 β Galactosidase Lisine Decarboxilase Broth Cat. 1176 Voges-Proskauer Salmonella Buffered Peptone Water BUFFERED PEPTONE WATER
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
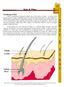 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions
 AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
Molecular and Cell Biology Laboratory (BIOL-UA 223) Instructor: Ignatius Tan Phone: 212-998-8295 Office: 764 Brown Email: ignatius.tan@nyu.
 Molecular and Cell Biology Laboratory (BIOL-UA 223) Instructor: Ignatius Tan Phone: 212-998-8295 Office: 764 Brown Email: ignatius.tan@nyu.edu Course Hours: Section 1: Mon: 12:30-3:15 Section 2: Wed: 12:30-3:15
Molecular and Cell Biology Laboratory (BIOL-UA 223) Instructor: Ignatius Tan Phone: 212-998-8295 Office: 764 Brown Email: ignatius.tan@nyu.edu Course Hours: Section 1: Mon: 12:30-3:15 Section 2: Wed: 12:30-3:15
A Correlation of Pearson Miller & Levine Biology 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Biology Grades 9-12
 A Correlation of Pearson To the Utah Core State Standards Resource Title: Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): SE: 9780133242003
A Correlation of Pearson To the Utah Core State Standards Resource Title: Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): SE: 9780133242003
19th Swiss TB Symposium Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010
 19 th SWISS TUBERCULOSIS SYMPOSIUM Update on culture and identification Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010 Dr. Thomas Bodmer, M.D. Institute for Infectious Diseases Culture of mycobacteria Cultivation of MTB in
19 th SWISS TUBERCULOSIS SYMPOSIUM Update on culture and identification Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010 Dr. Thomas Bodmer, M.D. Institute for Infectious Diseases Culture of mycobacteria Cultivation of MTB in
Veterinary Testing. Classes of Test
 Veterinary Testing Classes of Test July 2014 Copyright National Association of Testing Authorities, Australia 2014 This publication is protected by copyright under the Commonwealth of Australia Copyright
Veterinary Testing Classes of Test July 2014 Copyright National Association of Testing Authorities, Australia 2014 This publication is protected by copyright under the Commonwealth of Australia Copyright
Propico UK Ltd 100% Natural Products
 Propico UK Ltd 100% Natural Products NEW APPROACH IN COSMETOLOGY ADVANCED DIAGNOSTIC TECHNOLOGY BACKED UP WITH SCIENTIFICALLY PROVED TREATMENT FOR ALL FORMS OF HAIR LOSS INCLUDING: ANDROGENIC ALOPECIA
Propico UK Ltd 100% Natural Products NEW APPROACH IN COSMETOLOGY ADVANCED DIAGNOSTIC TECHNOLOGY BACKED UP WITH SCIENTIFICALLY PROVED TREATMENT FOR ALL FORMS OF HAIR LOSS INCLUDING: ANDROGENIC ALOPECIA
GUIDELINES FOR THE REGISTRATION OF BIOLOGICAL PEST CONTROL AGENTS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE REGISTRATION OF BIOLOGICAL PEST CONTROL AGENTS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS -ii- GUIDELINES ON THE REGISTRATION OF BIOLOGICAL PEST CONTROL AGENTS FOOD AND
GUIDELINES FOR THE REGISTRATION OF BIOLOGICAL PEST CONTROL AGENTS FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS -ii- GUIDELINES ON THE REGISTRATION OF BIOLOGICAL PEST CONTROL AGENTS FOOD AND
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Can receive blood from: * I A I A and I A i o Type A Yes No A or AB A or O I B I B and I B i o Type B No Yes B or AB B or O
 Genetics of the ABO Blood Groups written by J. D. Hendrix Learning Objectives Upon completing the exercise, each student should be able: to explain the concept of blood group antigens; to list the genotypes
Genetics of the ABO Blood Groups written by J. D. Hendrix Learning Objectives Upon completing the exercise, each student should be able: to explain the concept of blood group antigens; to list the genotypes
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers:
 Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
AUS DEM SCHWEIZERISCHEN TROPENINSTITUT BASEL UND DER UNIVERSITÄTS-HAUTKLINIK
 AUS DEM SCHWEIZERISCHEN TROPENINSTITUT BASEL UND DER UNIVERSITÄTS-HAUTKLINIK DER ALBERT-LUDWIGS-UNIVERSITÄT FREIBURG I.BR. EFFICACY OF TRICLOSAN SOAP AGAINST SUPERFICIAL DERMATOMYCOSES AND SCABIES - A
AUS DEM SCHWEIZERISCHEN TROPENINSTITUT BASEL UND DER UNIVERSITÄTS-HAUTKLINIK DER ALBERT-LUDWIGS-UNIVERSITÄT FREIBURG I.BR. EFFICACY OF TRICLOSAN SOAP AGAINST SUPERFICIAL DERMATOMYCOSES AND SCABIES - A
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology
 Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
AP Biology 2013 Free-Response Questions
 AP Biology 2013 Free-Response Questions About the College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900,
AP Biology 2013 Free-Response Questions About the College Board The College Board is a mission-driven not-for-profit organization that connects students to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900,
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Discover Entomology. Discover Entomology. A Science, a Career, a Lifetime. A Science, a Career, a Lifetime
 Discover Entomology A Science, a Career, a Lifetime Discover Entomology A Science, a Career, a Lifetime What is Entomology? Entomology is the study of insects. Entomologists study bees, ants, beetles,
Discover Entomology A Science, a Career, a Lifetime Discover Entomology A Science, a Career, a Lifetime What is Entomology? Entomology is the study of insects. Entomologists study bees, ants, beetles,
Heredity. Sarah crosses a homozygous white flower and a homozygous purple flower. The cross results in all purple flowers.
 Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
240Tutoring Life Science Study Material
 240Tutoring Life Science Study Material This information is a sample of the instructional content and practice questions found on the 240Tutoring GACE Early Childhood Education. This information is meant
240Tutoring Life Science Study Material This information is a sample of the instructional content and practice questions found on the 240Tutoring GACE Early Childhood Education. This information is meant
General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets. Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs
 General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs Flea Tick Mite Louse Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs What types of skin
General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs Flea Tick Mite Louse Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs What types of skin
Sampling of the surface contamination using sterile cotton swabs from toys obtained from
 RESULTS Sampling of the surface contamination using sterile cotton swabs from toys obtained from the Nursery at Queen Mary, University of London showed diverse microorganism growth. A variety of species
RESULTS Sampling of the surface contamination using sterile cotton swabs from toys obtained from the Nursery at Queen Mary, University of London showed diverse microorganism growth. A variety of species
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15
 Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
MDM. Metabolic Drift Mutations - Attenuation Technology
 MDM Metabolic Drift Mutations - Attenuation Technology Seite 2 Origin of MDM attenuation technology Prof. Dr. Klaus Linde Pioneer in R&D of human and animal vaccines University of Leipzig Germany Origin
MDM Metabolic Drift Mutations - Attenuation Technology Seite 2 Origin of MDM attenuation technology Prof. Dr. Klaus Linde Pioneer in R&D of human and animal vaccines University of Leipzig Germany Origin
Koch s s Postulates. Lesson plan submitted for EDG6905 Communicating Science: Topics in Emerging Pathogens. Sue Latshaw and Asha Brunings
 Koch s s Postulates Lesson plan submitted for EDG6905 Communicating Science: Topics in Emerging Pathogens Sue Latshaw and Asha Brunings (Heinrich Hermann) Robert Koch 1843-1910 1910 German physician Isolated
Koch s s Postulates Lesson plan submitted for EDG6905 Communicating Science: Topics in Emerging Pathogens Sue Latshaw and Asha Brunings (Heinrich Hermann) Robert Koch 1843-1910 1910 German physician Isolated
IDENTIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
 reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE. BIOL 101 Introduction to Biology
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 101 Introduction to Biology Prepared By: W. David Barnes SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH & PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 101 Introduction to Biology Prepared By: W. David Barnes SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH & PROFESSIONAL STUDIES SCIENCE
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
Immunisation and Health Information for Health Care Workers and Others in At Risk Occupations
 Chapter 4 Occupations 04 Information for Health Care Workers and Others in At Risk Occupations Introduction Workers in a variety of occupations may be exposed to infectious agents during their employment.
Chapter 4 Occupations 04 Information for Health Care Workers and Others in At Risk Occupations Introduction Workers in a variety of occupations may be exposed to infectious agents during their employment.
Successful Treatment of Trichophytonrubrum Onychomycosis and Warts (Verruca Plantae) with BioCool
 Successful Treatment of Trichophytonrubrum Onychomycosis and Warts (Verruca Plantae) with BioCool Gunnar Sandström 1, J-O Eriksson 2 and Amir Saeed 1 1 Karolinska Institute, Department of Laboratory Medicine,
Successful Treatment of Trichophytonrubrum Onychomycosis and Warts (Verruca Plantae) with BioCool Gunnar Sandström 1, J-O Eriksson 2 and Amir Saeed 1 1 Karolinska Institute, Department of Laboratory Medicine,
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 17 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The correct order for the levels of Linnaeus's classification system,
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 17 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The correct order for the levels of Linnaeus's classification system,
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity
 12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
12.1 The Role of DNA in Heredity Only in the last 50 years have scientists understood the role of DNA in heredity. That understanding began with the discovery of DNA s structure. In 1952, Rosalind Franklin
Prestige EnviroMicrobiology, Inc.
 Fungal spores in the Air: How to use the results of spore count? Chin S. Yang, Ph.D. & Dewei Li, Ph.D. Introduction Sampling and testing for airborne fungal spores is a practice that has been very popular
Fungal spores in the Air: How to use the results of spore count? Chin S. Yang, Ph.D. & Dewei Li, Ph.D. Introduction Sampling and testing for airborne fungal spores is a practice that has been very popular
Extinction; Lecture-8
 I. introduction Definition Current extinction Genetic drift Extinction; Lecture-8 II. 3 types of extinction 1. background 2. mass 3. stochastic III. 5 periods of mass IV. human caused 1. on land and in
I. introduction Definition Current extinction Genetic drift Extinction; Lecture-8 II. 3 types of extinction 1. background 2. mass 3. stochastic III. 5 periods of mass IV. human caused 1. on land and in
Transformation of the bacterium E. coli. using a gene for Green Fluorescent Protein
 Transformation of the bacterium E. coli using a gene for Green Fluorescent Protein Background In molecular biology, transformation refers to a form of genetic exchange in which the genetic material carried
Transformation of the bacterium E. coli using a gene for Green Fluorescent Protein Background In molecular biology, transformation refers to a form of genetic exchange in which the genetic material carried
DNA Fingerprinting. Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA
 DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
DNA Fingerprinting Unless they are identical twins, individuals have unique DNA DNA fingerprinting The name used for the unambiguous identifying technique that takes advantage of differences in DNA sequence
Cell and Membrane Practice. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: ate: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains N?. chromosome. gene. mitochondrion. vacuole 2. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which
Name: ate: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains N?. chromosome. gene. mitochondrion. vacuole 2. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which
Gene Switches Teacher Information
 STO-143 Gene Switches Teacher Information Summary Kit contains How do bacteria turn on and turn off genes? Students model the action of the lac operon that regulates the expression of genes essential for
STO-143 Gene Switches Teacher Information Summary Kit contains How do bacteria turn on and turn off genes? Students model the action of the lac operon that regulates the expression of genes essential for
