IL2225 Physical Design
|
|
|
- Eric Pope
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IL2225 Physical Design Nasim Farahini
2 Outline Physical Implementation Styles ASIC physical design Flow Floor and Power planning Placement Clock Tree Synthesis Routing Timing Analysis Verification and Energy Calculation 1 December 2013 Slide 2
3 Overview: Digital Design Flow System Specification X=(AB*CD)+(A+D)+(A(B+C)) Y=(A(B+C))+AC+D+A(BC+D)) Architectural Design Logic Synthesis Physical Synthesis Physical Verification / Sign-off Fabrication Packaging and Testing 3
4 Physical Design Physical design converts a circuit description into a geometric description. This description is used to manufacture a chip. Design Objectives Power (dynamic/static) Performance (frequency) Area (cost) Yield (cost) Gate Level Netlist Physical Layout 1 December 2013 Slide 4
5 Physical Design challenges 1- Design complexity Number of transistors on the chip is increasing 2- Scaling More design rules Manufacturability Variability 3- Productivity Time-to-market Engineering efficiency 1 December 2013 Slide 5
6 Physical Design Styles Full-custom design Manual placement of the transistors and wiring. Advantages: Less area, Better performance, Less power Disadvantages: High engineering effort, Long time-to-market, High development cost Semi-custom design (standard-cell based) Pre-physically designed commonly used logic cells which are characterized and stored in standard cell libraries. Used in Electronic Design Automation Routing of inter-cell connections Programmable Logic Devices Array of logic cells connected via routing channels Like FPGAs, Gate Arrays 6
7 Standard-Cell Based Physical Design Standard cells: layouts of library cells including logic elements like gates, flip-flops, and ALU functions The height of the cells are constant. 7
8 Physical Design Flow Gate Level Netlist Floor and Power gate-level Planning circuit Placement A very brief tour of physical design floorplanning placement Clock Tree Synthesis Timing analysis floorplanning placement Routing repeater insertion Post Route Analysis clock tree synthesis Post Route Verification P/G network / routing Metal Fill Insertion metal fill insertion Mask Generation/OPC Sign off mask generation / OPC reticles GDSII Parasitic Static extraction Timing Analysis Power Parasitic analysis extraction Power Analysis Signal Integrity Signal Integrity Clock Tree mask Metal Wires mask after OPC Slide 8
9 Cadence SoC Encounter Design Flow Input Files: Generated and verified files from logic synthesis Gate Level Netlist (.v file) SDC file: Standard Delay Constraints, Generated by logic synthesis tool Technology Files: LEF file: Standard-cell layout information, Contains layer, via and macro definition Lib file (.TLF) Output Files: Standard-cell timing information, e.g. delay and capacitance GDSII: database file format which is the industry standard for data exchange of IC layout design information. DEF file: Design exchange format to output the design so it is readable by other modules. 1 December 2013 Slide 9
10 Design Import Designà Import Design Veriglog Netlist File Toplevel of the design.lib.tlf Files.LEF File.SDC File 1 December 2013 Slide 10
11 Design Import Advance à Power 1 December 2013 IL2200, ASIC Design Slide 11
12 Flattening the Netlist: Logic Hierarchy and Physical Hierarchy Flattening the Netlist: Logic Hierarchy & Physical Hierarchy The Layout is Flat The netlist is not Netlist - hierarchical Top Layout view FLAT! A2 Top C1 C3 RAM A4 A3 C2 A B A1 A1 A2 A3 A4 C RAM Netlist - Expanded Top C1 C2 C3 = leaf cell (std or macro cell) A1 A2 A3 A4 C1 C2 C3 RAM 1 December 2013 Slide 12 Columbia University
13 Floor Planning The floorplanning problem is to plan the positions and shapes of the modules at the beginning of the design PS Step 2: Floorplan cycle to optimize the circuit performance: chip area total wirelength delay of critical path Routability Setting X/Y_BOUNDS Of CLUSTER or CELL Setting XY location of CELL Creation of core area for rough placement Creation of SITEs for detailed placement RAM Update of port s XY coordinates Creation of routing OBSTRUCTION 1 December 2013 Slide 13 Columbia Unive
14 Automatic Floor Planning Automatic Floor Planning: Analyzes the data flow between design blocks based on their connectivity and their location Relative Floor Planning: Capture and define the placement relationship of floorplan objects independently from the actual coordinates in a floorplan flexible way to place objects, such as modules, blocks, groups, blockages, pin guides, pre-routed wires, and power domains I/O pins can be used as reference objects but they cannot be relative objects 1 December 2013 Slide 14
15 Relative Floor Planning Pre-route example: S1 and S2 are relative to the object I2 and the Core_Boundary 1 December 2013 Slide 15
16 Floorplanning example Manually Floor Planed DRRA Fabric 1 December 2013 Slide 16
17 Floor Planning Aspect Ratio Height/Width Core Utilization Area of Stand. Cell/Area of Core Core to IO Boundary Distance from IO Boundary Core to Die Boundary Distance from Die Boundary 1 December 2013 Slide 17
18 Partitioning Part of Floor Planning Standard Cells are in Floating States before placement. Have not been assigned a fixed location in Core Time to define clusters and regions To keep time critical component close Soft Regions Boundary can change during standard cell placement Hard Regions Prevent Standard cell crossing boundaries 1 December 2013 Slide 18
19 Power Planning Deal with Power Distribution Network Power nets are considered as special nets. Need to consider current density (IR drop). Three levels of Power Distribution Rings Carries VDD and VSS around the chip Stripes Rails Carries VDD and VSS from Rings across the chip Connect VDD and VSS to the standard cell VDD and VSS 1 December 2013 Slide 19
20 Power Planning Rings Stripes (vertical or horizontal) VDD VSS Rails Special Route Power Distribution Network 1 December 2013 Slide 20
21 Power Planning 21
22 Power Distribution network Example Power Distribution Network in DRRA 1 December 2013 Slide 22
23 Placement Global placement (rough location) Detailed placement (legalization) Two associated cost functions Reduce total wiring or routing length Distribute standard cell instances homogeneously in ASIC Core such that optimal equilibrium among vertical and horizontal routing is achieved 1 December 2013 Slide 23
24 Placement Problem Formulation Input: Blocks (standard cells and macros) B 1,..., B n Shapes and Pin Positions for each block B i Output: Nets N 1,..., N m Coordinates (x i, y i ) for block B i. No overlaps between blocks The total wire length is minimized The area of the resulting block is minimized or given a fixed die Other consideration: timing, routability, clock, buffering
25 Global Placement Example bad placement good placement
26 Detailed Placement After global placement To Refine placement based on congestion, timing and power Congestion Driven Placement To distance standard cell instances from each other such that more routing tracks are created between them Timing Driven Placement To optimize large sets of path delays Net Based Try to control the delay on signal path by imposing an upper bound delay or weight to net 1 December 2013 Slide 26
27 Floor planned Hard Block Placement
28 Unconstrained Placement
29 Clock Tree Synthesis Clock Tree: General Concept Automatic insertion of buffers along the clock path to balance the clock delay to all Flip Flops. CLK CLK Main concerns for clock design? Skew For increased clock frequency, skew may contribute over 10% of the system cycle time Skew Delay Area Minimize the propagation delay Number of buffers and total wire length Power It switches at every clock cycle, a major power consumer! Slew rate is important (sharp transition) Noise May need shielding, Clock is often a very strong aggressor Unbuffered clock tree Buffered/balanced clock tree Area Power Slew rates Co
30 Clock Distribution: How? 1 December 2013 Slide 30
31 Advanced clock tree synthesis methods 0-skew clock tree synthesis Clock tree synthesis considering process variations 1 December 2013 Slide 31
32 Clock Distribution 1 December 2013 Slide 32
33 Clock tree generation based on structure and load balance (H-tree) Clock Distribution Clock tree generation based on structure and load balance (Fish-bone) Taping point Structure balance H-Tree: Structure Balancing Minimize skew by making Interconnections to subunits equal in length Structure and load balance Fish-Bone: Clock Tree Generation based on structure and load balance 1 December 2013 Slide 33
34 CTS considering process variations P-variations cause unpredictable delay variations in transistors and wires -> uncontrollable skew The delay variations in common part of clock tree between launch and capture flops do not cause skew Goal is to minimize non-common part of clock tree between Launch and capture clock nodes clk D Q Combinational Logic D Q Without On-Chip Variation Awareness clk D Q Combinational Logic D Q With On-Chip Variation Awareness 2 December 2013 Slide 34
35 Clock Tree Synthesis in SoC Encounter Fish Bone Routing Style 1 December 2013 Slide 35
36 Clock Tree Synthesis in SoC Encounter The color Difference tells us about clock skew 1 December 2013 Slide 36
37 Routing Fundamentals Goal is to realize the metal/copper connections between the pins of standard cells and macros Input : placed design fixed number of metal/copper layers Goal: routed design that is DRC clean and meets setup/hold timing Consists of two phases 1. Global route: To estimate the routing congestion 2. Detail route: To assign the nets to the routing tracks Standard cell pin Vertical routing tracks Horizontal routing tracks 37
38 Interconnect Organization In 65 nm technology, up to 12 metal layers for routing Higher metal layers: Wider, less resistance Proper for assigning global wires and clock nets Less delay, less power consumption Power nets are always assigned to the top level metal layer Less IR drop 1 December 2013 Slide 38
39 Routing Issues for 90nm Technology and Beyond 1. Timing driven routing 2. Signal integrity aware 3. DRC 4. OPC
40 1- Timing-Driven Routing At 90nm net delay becomes significant Quality of route can effect timing Optimize critical paths Route some nets first (Net weights) Order of routing (priorities : eg. Default : Clocks 50, others 2) Most routing freedom at start Use shortest paths possible If you have a congested design you may need to set the timing driven effort to low
41 2- What is Signal Integrity or SI? Signal delay caused by crosstalk noise Possible in 2 directions : push-out pull-down net 1 Aggressor net 2 Victim Speed Up Delay
42 What is SI? Glitch caused by crosstalk noise Aggressor Extra clock cycle! à Functional Failure Vdd Victim ^ D Q Clk
43 Crosstalk Prevention : Routing Routing solution Limit length of parallel nets Wire spreading (skip track - clocks) Shield special nets Coupling free routing 43
44 3- DRC (Design Rule Check) Design rules: Guidelines about the geometry constraints for constructing process masks Information like: Routing layers: width, spacing, pitches General Rules: a) enclosure, b) space, c) overlap d) width, e) extension Specific rules Antenna rules, metal density rules, minimum area A compromise between performance and yield More conservative rules increase probability of correct circuit function (yield) More aggressive rules increase circuit performance ( area, power, delay) 44 d a b c e
45 DRC Challenges 45 Count of Design rules in the runset The number of design rules in the DRC runsets for different technology processes nm Reasons: - More metal layers - Diff spacing rules depending on width - Recommended rules è general rules 45
46 4- Optical Proximity Correction (OPC) 2 December 2013 Slide 46
47 OPC-Aware Routing More OPC friendly 2 December 2013 Slide 47
48 Mask Layout Data ->Physical Mask layout data physical mask? mask layout data Basic lithographic system Resolution Enhancement Techniques fracture mask writer physical masks (ALTA 4700 mask writer) [source: Schellenberg/IEEE Spectrum] Basic Lithography system 2 December 2013 Slide 48 5
49 RC Extraction RC extraction is the calculation of all the routed net capacitances and resistances Used for Delay calculation Static Timing Analysis Circuit Simulation Signal Integrity Analysis 2 December 2013 Slide 49
50 Electromigration Electromigration is the movement of the lattice ions of the interconnect material as the result of the momentum transfer form electrons. High current density or irregular shapes for the interconnects may cause the electromigration to happen in a short time. LSI Design, IL
51 Power Analysis Power analysis Reduces risk of IR voltage drops in power nets Reduces Electromigration effects due to high current density Resistance of power and ground net extracted Average current of each transistor connected to power net is calculated Average currents are distributed throughout the power net Calculate node voltages and branch currents 2 December 2013 Slide 51
52 Power Analysis Average power is sufficient when "time constants" of effects are large Battery Life Thermal Analysis VCD is needed to simulate instantaneous power (current) Necessary for estimation of Simultaneous Switching Noise (SSN) Important for Power Grid signal integrity analysis 2 December 2013 IL2200, ASIC Design Slide 52
53 Energy Calculation Save your design as a Verilog Netlist Simulate the Design in NCSim/ModelSim Create a VCD File Restore the Design in Encounter Read the VCD Activity file Report Power to get the average power Energy= P ave * T period * No of Cycles 1 December 2013 Slide 53
54 VCD File Script run -timepoint 0 ns -absolute database -open /media/disk-1/mdpu/add2/mac_0.vcd - vcd -default -timescale us probe -create :mtile -vcd -all -depth all run -timepoint 100 us -absolute database -close /media/disk-1/mdpu/add2/mac_0.vcd 1 December 2013 Slide 54
55 Power Calculation in Encounter restoredesign /home/ali/physicaldesign/icad2/mdpu/ Tile_final.enc.dat Tile extractrc -outfile file.cap read_activity_file -format VCD -vcd_scope Tile_tb/mTile /media/ disk-1/mdpu/add2/mac_0.vcd reportpower -norailanalysis -outfile /media/disk-1/mdpu/add2/ reports/powenc_0.rep exit 2 December 2013 Slide 55
56 Verification The complete placed and routed design is verified before fabrication Functional Verification Verification is performed against behavioral RTL pre-layout and post-layout structural description (netlist) for the design validation. Rule Based Assertion based verification Assertions macros are expressions that, if false, indicate and error Instantiated in RTL Code 2 December 2013 Slide 56
57 LVS(Layout vs. Schematic) Top level labels needed for VDD,VSS, inputs and outputs vdd LVS IN OUT vss Extract the designed devices (nmos, pmos,n-well tap, ) Extract the connectivity between Build a netlist Compare both netlist 57
University of Texas at Dallas. Department of Electrical Engineering. EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design
 University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
How To Design A Chip Layout
 Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution
 Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
Alpha CPU and Clock Design Evolution This lecture uses two papers that discuss the evolution of the Alpha CPU and clocking strategy over three CPU generations Gronowski, Paul E., et.al., High Performance
Route Power 10 Connect Powerpin 10.1 Route Special Route 10.2 Net(s): VSS VDD
 SOCE Lab (2/2): Clock Tree Synthesis and Routing Lab materials are available at ~cvsd/cur/soce/powerplan.tar.gz Please untar the file in the folder SOCE_Lab before lab 1 Open SOC Encounter 1.1 % source
SOCE Lab (2/2): Clock Tree Synthesis and Routing Lab materials are available at ~cvsd/cur/soce/powerplan.tar.gz Please untar the file in the folder SOCE_Lab before lab 1 Open SOC Encounter 1.1 % source
Impact of Signal Integrity on System-On-Chip Design Methodologies
 EDP 2004 Impact of Signal Integrity on System-On-Chip Methodologies Juan-Antonio Carballo [email protected] VSIA IMP co-chair Raminderpal Singh IBM Systems and Technology [email protected] VSIA IMP
EDP 2004 Impact of Signal Integrity on System-On-Chip Methodologies Juan-Antonio Carballo [email protected] VSIA IMP co-chair Raminderpal Singh IBM Systems and Technology [email protected] VSIA IMP
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Clocking. Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 Clocks 1
 ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
ing Figure by MIT OCW. 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05 L06 s 1 Why s and Storage Elements? Inputs Combinational Logic Outputs Want to reuse combinational logic from cycle to cycle 6.884 - Spring 2005 2/18/05
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
StarRC Custom: Next-Generation Modeling and Extraction Solution for Custom IC Designs
 White Paper StarRC Custom: Next-Generation Modeling and Extraction Solution for Custom IC Designs May 2010 Krishnakumar Sundaresan Principal Engineer and CAE Manager, Synopsys Inc Executive Summary IC
White Paper StarRC Custom: Next-Generation Modeling and Extraction Solution for Custom IC Designs May 2010 Krishnakumar Sundaresan Principal Engineer and CAE Manager, Synopsys Inc Executive Summary IC
TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING
 TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING BARIS TASKIN, JOHN WOOD, IVAN S. KOURTEV February 28, 2005 Research Objective Objective: Electronic design automation
TIMING-DRIVEN PHYSICAL DESIGN FOR DIGITAL SYNCHRONOUS VLSI CIRCUITS USING RESONANT CLOCKING BARIS TASKIN, JOHN WOOD, IVAN S. KOURTEV February 28, 2005 Research Objective Objective: Electronic design automation
Design Compiler Graphical Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation
 Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Implementation Details
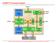 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
CADENCE LAYOUT TUTORIAL
 CADENCE LAYOUT TUTORIAL Creating Layout of an inverter from a Schematic: Open the existing Schematic Page 1 From the schematic editor window Tools >Design Synthesis >Layout XL A window for startup Options
CADENCE LAYOUT TUTORIAL Creating Layout of an inverter from a Schematic: Open the existing Schematic Page 1 From the schematic editor window Tools >Design Synthesis >Layout XL A window for startup Options
Digital IC Design Flow
 Collège Militaire Royal du Canada (Cadence University Alliance Program Member) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Départment de Génie Electrique et Informatique RMC Microelectronics Lab
Collège Militaire Royal du Canada (Cadence University Alliance Program Member) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Départment de Génie Electrique et Informatique RMC Microelectronics Lab
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
Layout and Cross-section of an inverter. Lecture 5. Layout Design. Electric Handles Objects. Layout & Fabrication. A V i
 Layout and Cross-section of an inverter Lecture 5 A Layout Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London V DD Q p A V i V o URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/
Layout and Cross-section of an inverter Lecture 5 A Layout Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London V DD Q p A V i V o URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow
 Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow Bradley R. Quinton Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia [email protected]
Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow Bradley R. Quinton Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia [email protected]
CAD TOOLS FOR VLSI. FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING
 FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING Floorplanning: taking layout information into account at early stages of the design process. BEHAVIORAL D. STRUCTURAL D. Systems Algorithms Processors Register transfers
FLOORPLANNING Page 1 FLOORPLANNING Floorplanning: taking layout information into account at early stages of the design process. BEHAVIORAL D. STRUCTURAL D. Systems Algorithms Processors Register transfers
Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
Signal Integrity: Tips and Tricks
 White Paper: Virtex-II, Virtex-4, Virtex-5, and Spartan-3 FPGAs R WP323 (v1.0) March 28, 2008 Signal Integrity: Tips and Tricks By: Austin Lesea Signal integrity (SI) engineering has become a necessary
White Paper: Virtex-II, Virtex-4, Virtex-5, and Spartan-3 FPGAs R WP323 (v1.0) March 28, 2008 Signal Integrity: Tips and Tricks By: Austin Lesea Signal integrity (SI) engineering has become a necessary
Total Hot Spot Management from Design Rule Definition to Silicon Fabrication
 Total Management from Rule Definition to Silicon Fabrication Soichi Inoue, Toshiya Kotani, Shigeki Nojima, Satoshi Tanaka, Kohji Hashimoto, and Ichiro Mori & Manufacturing Engineering Center, Toshiba Corporation,
Total Management from Rule Definition to Silicon Fabrication Soichi Inoue, Toshiya Kotani, Shigeki Nojima, Satoshi Tanaka, Kohji Hashimoto, and Ichiro Mori & Manufacturing Engineering Center, Toshiba Corporation,
Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization. TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu
 Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu 1 Outline Introduction Engineering Change Order (ECO) Voltage drop (IR-DROP) New design
Reconfigurable ECO Cells for Timing Closure and IR Drop Minimization TingTing Hwang Tsing Hua University, Hsin-Chu 1 Outline Introduction Engineering Change Order (ECO) Voltage drop (IR-DROP) New design
Hunting Asynchronous CDC Violations in the Wild
 Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop
 Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop Michael Holmes Manager, Mixed Signal ASIC/SoC
Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop Michael Holmes Manager, Mixed Signal ASIC/SoC
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Chapter 13: Verification
 Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
Chapter 13: Verification Prof. Ming-Bo Lin Department of Electronic Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology Digital System Designs and Practices Using Verilog HDL and FPGAs @ 2008-2010,
System-on. on-chip Design Flow. Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems. jouni.tomberg@tut.
 System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
System-on on-chip Design Flow Prof. Jouni Tomberg Tampere University of Technology Institute of Digital and Computer Systems [email protected] 26.03.2003 Jouni Tomberg / TUT 1 SoC - How and with whom?
Fault Modeling. Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults. Transistor faults Summary
 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
IBIS for SSO Analysis
 IBIS for SSO Analysis Asian IBIS Summit, November 15, 2010 (Presented previously at Asian IBIS Summits, Nov. 9 & 12, 2010) Haisan Wang Joshua Luo Jack Lin Zhangmin Zhong Contents Traditional I/O SSO Analysis
IBIS for SSO Analysis Asian IBIS Summit, November 15, 2010 (Presented previously at Asian IBIS Summits, Nov. 9 & 12, 2010) Haisan Wang Joshua Luo Jack Lin Zhangmin Zhong Contents Traditional I/O SSO Analysis
Latch Timing Parameters. Flip-flop Timing Parameters. Typical Clock System. Clocking Overhead
 Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
Clock - key to synchronous systems Topic 7 Clocking Strategies in VLSI Systems Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Clocks help the design of FSM where
Training Course of SOC Encounter
 Training Course of SOC Encounter REF: CIC Training Manual Cell-Based IC Physical Design and Verification with SOC Encounter, July, 2006 CIC Training Manual Mixed-Signal IC Design Concepts, July, 2007 Speaker:
Training Course of SOC Encounter REF: CIC Training Manual Cell-Based IC Physical Design and Verification with SOC Encounter, July, 2006 CIC Training Manual Mixed-Signal IC Design Concepts, July, 2007 Speaker:
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN
 TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic
 Infineon Page 1 CHES 2006 - Yokohama Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic L. Giancane, R. Luzzi, A. Trifiletti {marco.bucci, raimondo.luzzi}@infineon.com {giancane, trifiletti}@die.mail.uniroma1.it Summary
Infineon Page 1 CHES 2006 - Yokohama Three-Phase Dual-Rail Pre-Charge Logic L. Giancane, R. Luzzi, A. Trifiletti {marco.bucci, raimondo.luzzi}@infineon.com {giancane, trifiletti}@die.mail.uniroma1.it Summary
Design Methodology for Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) in a Flat Physical Standard Cells Based Design Environment
 Diploma Thesis Design Methodology for Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) in a Flat Physical Standard Cells Based Design Environment submitted by Anton Klotz Standard-Cells Based Design Flow (1) Picture of
Diploma Thesis Design Methodology for Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) in a Flat Physical Standard Cells Based Design Environment submitted by Anton Klotz Standard-Cells Based Design Flow (1) Picture of
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Sentinel-SSO: Full DDR-Bank Power and Signal Integrity. Design Automation Conference 2014
 Sentinel-SSO: Full DDR-Bank Power and Signal Integrity Design Automation Conference 2014 1 Requirements for I/O DDR SSO Analysis Modeling Package and board I/O circuit and layout PI + SI feedback Tool
Sentinel-SSO: Full DDR-Bank Power and Signal Integrity Design Automation Conference 2014 1 Requirements for I/O DDR SSO Analysis Modeling Package and board I/O circuit and layout PI + SI feedback Tool
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
EEC 119B Spring 2014 Final Project: System-On-Chip Module
 EEC 119B Spring 2014 Final Project: System-On-Chip Module Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: March 14, 2014 Subject to Revision Final Report Due: June
EEC 119B Spring 2014 Final Project: System-On-Chip Module Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: March 14, 2014 Subject to Revision Final Report Due: June
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Slides adapted from: N. Weste,. Harris, CMOS VLSI esign, Addison-Wesley, 3/e, 24 Introduction Integrated Circuits: many transistors on one chip Very Large Scale Integration
Introduction to CMOS VLSI esign Slides adapted from: N. Weste,. Harris, CMOS VLSI esign, Addison-Wesley, 3/e, 24 Introduction Integrated Circuits: many transistors on one chip Very Large Scale Integration
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Core Power Delivery Network Analysis of Core and Coreless Substrates in a Multilayer Organic Buildup Package
 Core Power Delivery Network Analysis of Core and Coreless Substrates in a Multilayer Organic Buildup Package Ozgur Misman, Mike DeVita, Nozad Karim, Amkor Technology, AZ, USA 1900 S. Price Rd, Chandler,
Core Power Delivery Network Analysis of Core and Coreless Substrates in a Multilayer Organic Buildup Package Ozgur Misman, Mike DeVita, Nozad Karim, Amkor Technology, AZ, USA 1900 S. Price Rd, Chandler,
ESP-CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation
 Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Datasheet -CV Custom Design Formal Equivalence Checking Based on Symbolic Simulation Overview -CV is an equivalence checker for full custom designs. It enables efficient comparison of a reference design
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops. Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 24 p. 1/20 EE 42/100 Lecture 24: Latches and Flip Flops ELECTRONICS Rev B 4/21/2010 (2:04 PM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California,
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI. Digital Systems Design. Digital Circuits Advanced Topics
 PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
Design-Kits, Libraries & IPs
 Design-Kits, Libraries & IPs Supported CAD tools Design-kits overview Digital, Analog, and RF Libraries IPs Supported CAD tools Design-kits overview ST 65nm Tanner PDK Standard cell Libraries IPs austriamicrosystems
Design-Kits, Libraries & IPs Supported CAD tools Design-kits overview Digital, Analog, and RF Libraries IPs Supported CAD tools Design-kits overview ST 65nm Tanner PDK Standard cell Libraries IPs austriamicrosystems
Lab 3 Layout Using Virtuoso Layout XL (VXL)
 Lab 3 Layout Using Virtuoso Layout XL (VXL) This Lab will go over: 1. Creating layout with Virtuoso layout XL (VXL). 2. Transistor Chaining. 3. Creating Standard cell. 4. Manual Routing 5. Providing Substrate
Lab 3 Layout Using Virtuoso Layout XL (VXL) This Lab will go over: 1. Creating layout with Virtuoso layout XL (VXL). 2. Transistor Chaining. 3. Creating Standard cell. 4. Manual Routing 5. Providing Substrate
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
On-Chip Interconnect: The Past, Present, and Future
 On-Chip Interconnect: The Past, Present, and Future Professor Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester URL: http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~friedman Future
On-Chip Interconnect: The Past, Present, and Future Professor Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester URL: http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~friedman Future
Clock Distribution Networks in Synchronous Digital Integrated Circuits
 Clock Distribution Networks in Synchronous Digital Integrated Circuits EBY G. FRIEDMAN Invited Paper Clock distribution networks synchronize the flow of data signals among synchronous data paths. The design
Clock Distribution Networks in Synchronous Digital Integrated Circuits EBY G. FRIEDMAN Invited Paper Clock distribution networks synchronize the flow of data signals among synchronous data paths. The design
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
A Utility for Leakage Power Recovery within PrimeTime 1 SI
 within PrimeTime 1 SI Bruce Zahn LSI Corporation [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper describes a utility which is run within the PrimeTime SI signoff environment that recovers leakage power and achieves
within PrimeTime 1 SI Bruce Zahn LSI Corporation [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper describes a utility which is run within the PrimeTime SI signoff environment that recovers leakage power and achieves
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler
 ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
1.Introduction. Introduction. Most of slides come from Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by Michael Quirk and Julian Serda.
 .Introduction If the automobile had followed the same development cycle as the computer, a Rolls- Royce would today cost $00, get one million miles to the gallon and explode once a year Most of slides
.Introduction If the automobile had followed the same development cycle as the computer, a Rolls- Royce would today cost $00, get one million miles to the gallon and explode once a year Most of slides
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS
 VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
VHDL GUIDELINES FOR SYNTHESIS Claudio Talarico For internal use only 1/19 BASICS VHDL VHDL (Very high speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that allows
E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design. Alarm Clock
 E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design Alarm Clock Sarah Yi & Samuel (Tae) Lee 4/19/2010 Introduction The Alarm Clock chip includes the basic functions of an alarm clock such as a running clock time and alarm
E158 Intro to CMOS VLSI Design Alarm Clock Sarah Yi & Samuel (Tae) Lee 4/19/2010 Introduction The Alarm Clock chip includes the basic functions of an alarm clock such as a running clock time and alarm
Royal Military College of Canada
 Microelectronics Lab Cadence Tutorials Layout Design and Simulation (Using Virtuoso / Diva / Analog Artist) Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Royal Military College of Canada Cadence University
Microelectronics Lab Cadence Tutorials Layout Design and Simulation (Using Virtuoso / Diva / Analog Artist) Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Royal Military College of Canada Cadence University
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures
 McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
McPAT: An Integrated Power, Area, and Timing Modeling Framework for Multicore and Manycore Architectures Sheng Li, Junh Ho Ahn, Richard Strong, Jay B. Brockman, Dean M Tullsen, Norman Jouppi MICRO 2009
Place & Route Tutorial #1
 Place & Route Tutorial #1 In this tutorial you will use Cadence Encounter to place, route, and analyze the timing and wire-length of two simple designs. This tutorial assumes that you have worked through
Place & Route Tutorial #1 In this tutorial you will use Cadence Encounter to place, route, and analyze the timing and wire-length of two simple designs. This tutorial assumes that you have worked through
Class 11: Transmission Gates, Latches
 Topics: 1. Intro 2. Transmission Gate Logic Design 3. X-Gate 2-to-1 MUX 4. X-Gate XOR 5. X-Gate 8-to-1 MUX 6. X-Gate Logic Latch 7. Voltage Drop of n-ch X-Gates 8. n-ch Pass Transistors vs. CMOS X-Gates
Topics: 1. Intro 2. Transmission Gate Logic Design 3. X-Gate 2-to-1 MUX 4. X-Gate XOR 5. X-Gate 8-to-1 MUX 6. X-Gate Logic Latch 7. Voltage Drop of n-ch X-Gates 8. n-ch Pass Transistors vs. CMOS X-Gates
Quality. Stages. Alun D. Jones
 Quality - by Design Quality Design Review Stages Alun D. Jones Design Review Stages Design Review 0 (DR0) Pre-order & quotation stage Design Review 1 (DR1) Initial kick-off and preliminary specification
Quality - by Design Quality Design Review Stages Alun D. Jones Design Review Stages Design Review 0 (DR0) Pre-order & quotation stage Design Review 1 (DR1) Initial kick-off and preliminary specification
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
An Advanced Behavioral Buffer Model With Over-Clocking Solution. Yingxin Sun, Joy Li, Joshua Luo IBIS Summit Santa Clara, CA Jan.
 An Advanced Behavioral Buffer Model With Over-Clocking Solution Yingxin Sun, Joy Li, Joshua Luo IBIS Summit Santa Clara, CA Jan. 31, 2014 Agenda 1. SPICE Model and Behavioral Buffer Model 2. Over-Clocking
An Advanced Behavioral Buffer Model With Over-Clocking Solution Yingxin Sun, Joy Li, Joshua Luo IBIS Summit Santa Clara, CA Jan. 31, 2014 Agenda 1. SPICE Model and Behavioral Buffer Model 2. Over-Clocking
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
ICS379. Quad PLL with VCXO Quick Turn Clock. Description. Features. Block Diagram
 Quad PLL with VCXO Quick Turn Clock Description The ICS379 QTClock TM generates up to 9 high quality, high frequency clock outputs including a reference from a low frequency pullable crystal. It is designed
Quad PLL with VCXO Quick Turn Clock Description The ICS379 QTClock TM generates up to 9 high quality, high frequency clock outputs including a reference from a low frequency pullable crystal. It is designed
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs
 High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
High-Level Synthesis for FPGA Designs BRINGING BRINGING YOU YOU THE THE NEXT NEXT LEVEL LEVEL IN IN EMBEDDED EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT DEVELOPMENT Frank de Bont Trainer consultant Cereslaan 10b 5384 VT Heesch
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system
 Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
ANN Based Modeling of High Speed IC Interconnects. Q.J. Zhang, Carleton University
 ANN Based Modeling of High Speed IC Interconnects Needs for Repeated Simulation Signal integrity optimization Iterative design and re-optimization Monte-Carlo analysis Yield optimization Iterative design
ANN Based Modeling of High Speed IC Interconnects Needs for Repeated Simulation Signal integrity optimization Iterative design and re-optimization Monte-Carlo analysis Yield optimization Iterative design
CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS
 TECHNICAL PAPER CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview...........................................................................1
TECHNICAL PAPER CLOCK DOMAIN CROSSING CLOSING THE LOOP ON CLOCK DOMAIN FUNCTIONAL IMPLEMENTATION PROBLEMS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview...........................................................................1
Advanced VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology
 Isolation of transistors, i.e., their source and drains, from other transistors is needed to reduce electrical interactions between them. For technologies
Isolation of transistors, i.e., their source and drains, from other transistors is needed to reduce electrical interactions between them. For technologies
Module 22: Signal Integrity
 Module 22: Signal Integrity Module 22: Signal Integrity 22.1 Signal Integrity... 22-1 22.2 Checking Signal Integrity on an FPGA design... 22-3 22.2.1 Setting Up...22-3 22.2.2 Importing IBIS Models...22-3
Module 22: Signal Integrity Module 22: Signal Integrity 22.1 Signal Integrity... 22-1 22.2 Checking Signal Integrity on an FPGA design... 22-3 22.2.1 Setting Up...22-3 22.2.2 Importing IBIS Models...22-3
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
An ASCII data format, used to describe a standard cell library
 Advanced VLSI Design Standard Cell Library/ CMPE 641 An ASCII data format, used to describe a standard cell library Includes the design rules for routing and the Abstract of the cells, no information about
Advanced VLSI Design Standard Cell Library/ CMPE 641 An ASCII data format, used to describe a standard cell library Includes the design rules for routing and the Abstract of the cells, no information about
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
On-Chip Interconnection Networks Low-Power Interconnect
 On-Chip Interconnection Networks Low-Power Interconnect William J. Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University ISLPED August 27, 2007 ISLPED: 1 Aug 27, 2007 Outline Demand for On-Chip Networks
On-Chip Interconnection Networks Low-Power Interconnect William J. Dally Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University ISLPED August 27, 2007 ISLPED: 1 Aug 27, 2007 Outline Demand for On-Chip Networks
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
PL-277x Series SuperSpeed USB 3.0 SATA Bridge Controllers PCB Layout Guide
 Application Note PL-277x Series SuperSpeed USB 3.0 SATA Bridge Controllers PCB Layout Guide Introduction This document explains how to design a PCB with Prolific PL-277x SuperSpeed USB 3.0 SATA Bridge
Application Note PL-277x Series SuperSpeed USB 3.0 SATA Bridge Controllers PCB Layout Guide Introduction This document explains how to design a PCB with Prolific PL-277x SuperSpeed USB 3.0 SATA Bridge
Rapid Software Development with OpenAccess. Dean Marvin Exec Director, Product Development
 Rapid Software Development with OpenAccess Dean Marvin Exec Director, Product Development Presentation Overview Conditions for rapid OA development Discussion of development styles C++ object oriented
Rapid Software Development with OpenAccess Dean Marvin Exec Director, Product Development Presentation Overview Conditions for rapid OA development Discussion of development styles C++ object oriented
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course. Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-VII Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Testing VLSI Design, Verification and Test Flow Customer's Requirements Specifications
Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC
 Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, Lukas Perktold DLL design review meeting, 16 03 2011 Outline Introduction Purpose and objectives Reminder Challenges of
Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, Lukas Perktold DLL design review meeting, 16 03 2011 Outline Introduction Purpose and objectives Reminder Challenges of
3D NAND Technology Implications to Enterprise Storage Applications
 3D NAND Technology Implications to Enterprise Storage Applications Jung H. Yoon Memory Technology IBM Systems Supply Chain Outline Memory Technology Scaling - Driving Forces Density trends & outlook Bit
3D NAND Technology Implications to Enterprise Storage Applications Jung H. Yoon Memory Technology IBM Systems Supply Chain Outline Memory Technology Scaling - Driving Forces Density trends & outlook Bit
ZL40221 Precision 2:6 LVDS Fanout Buffer with Glitchfree Input Reference Switching and On-Chip Input Termination Data Sheet
 Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts two differential or single-ended inputs LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Glitch-free switching of references On-chip input termination and biasing for AC coupled inputs Six
Features Inputs/Outputs Accepts two differential or single-ended inputs LVPECL, LVDS, CML, HCSL, LVCMOS Glitch-free switching of references On-chip input termination and biasing for AC coupled inputs Six
Distributed Elastic Switch Architecture for efficient Networks-on-FPGAs
 Distributed Elastic Switch Architecture for efficient Networks-on-FPGAs Antoni Roca, Jose Flich Parallel Architectures Group Universitat Politechnica de Valencia (UPV) Valencia, Spain Giorgos Dimitrakopoulos
Distributed Elastic Switch Architecture for efficient Networks-on-FPGAs Antoni Roca, Jose Flich Parallel Architectures Group Universitat Politechnica de Valencia (UPV) Valencia, Spain Giorgos Dimitrakopoulos
S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India
 Power reduction on clock-tree using Energy recovery and clock gating technique S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India Abstract Power consumption of
Power reduction on clock-tree using Energy recovery and clock gating technique S. Venkatesh, Mrs. T. Gowri, Department of ECE, GIT, GITAM University, Vishakhapatnam, India Abstract Power consumption of
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
Document Contents Introduction Layout Extraction with Parasitic Capacitances Timing Analysis DC Analysis
 Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group rev S06 (convert to spectre simulator) Document Contents Introduction
Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group rev S06 (convert to spectre simulator) Document Contents Introduction
Interconnection Network of OTA-based FPAA
 Chapter S Interconnection Network of OTA-based FPAA 5.1 Introduction Aside from CAB components, a number of different interconnect structures have been proposed for FPAAs. The choice of an intercmmcclion
Chapter S Interconnection Network of OTA-based FPAA 5.1 Introduction Aside from CAB components, a number of different interconnect structures have been proposed for FPAAs. The choice of an intercmmcclion
