THE CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PEPTIDES
|
|
|
- Marsha Cox
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TE EMIAL SYTESIS F PEPTIDES Peptides are the long molecular chains that make up proteins. Synthetic peptides are used either as drugs (as they are biologically active) or in the diagnosis of disease. Peptides are difficult to make as the synthetic chemist must ensure that the amino acids that make up the chain are added in the correct order and that they don't undergo any other reactions. This involves adding one amino acid, washing away any unreacted acid then adding the next and so on. As can be imagined, this is very time consuming and only gives very low yields. A technique that has been relatively recently developed involves attaching one end of the peptide to a solid polymer, meaning that the peptide cannot get washed away along with the excess acid. This is much quicker than classical synthesis, and leads to dramatically improved yields. The process consists of five steps carried out in a cyclic fashion. Step 1 - Attaching an amino acid to the polymer The amino acid is reacted with a molecule known as a "linkage agent" that enables it to attach to a solid polymer, and the other end of the linkage agent is reacted with the polymer support. Step 2 - Protection An amino acid is an acid with a basic group at one end and an acid group at the other. To prevent an amino acid from reacting with itself, one of these groups is reacted with something else to make it unreactive. Step 3 - oupling The protected amino acid is then reacted with the amino acid attached to the polymer to begin building the peptide chain. Step 4 - Deprotection The protection group is now removed from the acid at the end of the chain so it can react with the next acid to be added on. The new acid is then protected (Step 2) and the cycle continues until a chain of the required length has been synthesised. Step 5 - Polymer removal nce the desired peptide has been made the bond between the first amino acid and the linkage agent is broken to give the free peptide. Peptides synthesised at Massey University are widely used in medical research, as they can be synthesised quickly and accurately. When larger amounts of peptides are required they are synthesised in the same manner, although the equipment to produce peptides on this scale is not available in ew Zealand. XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-1
2 ITDUTI A peptide is a chain of special acids called amino acids linked together by bonds known as amide bonds. A protein consists of one peptide folded in a particular way, or several peptides folded together. Such peptides are synthesised very rapidly within living cells, but until recently could only be artificially synthesised in very long, slow processes that had poor yields and gave impure products. ecently a new technique known as solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) has been developed. SPPS results in high yields of pure products and works more quickly than classical synthesis, although still much more slowly in than living cells. This technique is discussed below. Uses of synthetic peptides Synthetic peptides have two main uses: as peptide drugs and as peptides for diagnostic purposes. Peptide drugs Peptide drugs are either naturally-occuring peptides or altered natural peptides. There are many naturally-occuring peptides that are biologically active. If a patient does not naturally produce a peptide that they need, this peptide can be synthesised and given to them. In addition, the amino acids in an active peptide can be altered to make analogues of the original peptide. If the analogue is more biochemically active than the original peptide it is known as an agonist and if it has the reverse effect is known as an antagonist. ontraceptives have been made by synthesising the antagonists of fertility peptides. Diagnostic peptides Peptides can be designed that change colour under certain conditions, and these can be used for diagnostic purposes. For example, a chromogenic peptide substrate can readily detect the presence, absence and varying blood levels of enzymes that control blood pressure and blood clotting ability. The SPPS laboratory at Massey University has supplied peptides for research purposes to universities, Is, research institutes and private industry since These peptides have been used for medical research into areas such as heart disease, leprosy and tuberculosis. The laboratory itself is involved in research into and development of synthetic methods and peptide production. Introduction to protein chemistry Peptides are polymers of amino acids made using anything from two to hundreds of amino acids. They are all based on the α-amino acid structure 2 There are twenty amino acids that commonly occur in nature (Table 1) and many others have been synthesised. XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-2
3 Table 1 - Side chains of the common naturally occurring amino acids ame Side chain Protection glycine (gly) alanine (ala) 3 valine (val) 3 3 leucine (leu) isoleucine (ile) lysine (lys) protection essential agent = tb arginine (arg) protection often useful agent = PM aspartic acid (asp) 2 asparagine (asn) 2 2 protection essential protection sometimes necessary glutamic acid (glu) 2 2 protection essential glutamine (gln) protection sometimes necessary agent = Trt threonine (thr) protection often useful 3 methionine (met) 2 2 S 3 protection sometimes necessary oxidise to S= XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-3
4 cysteine (cys) 2 S protection essential agent = Trt or tbu serine (ser) 2 protection often useful phenylalanine (phe) 2 tyrosine (tyr) 2 protection often useful histidine (his) 2 protection often useful agent = Trt tryptophan (trp) 2 protection sometimes necessary agent = tb proline (pro) 1 These peptides (or combinations of them) fold in characteristic ways to give proteins. In mammals all optically active 2 amino acids are in the L form, so one change that can be made to peptides is to substitute a D amino acid for one of the amino acids in the chain. 1 The full structure of proline (rather than just its side chain) is given because proline is cyclic and so doesn't have a side chain as such. 2 When a molecule is exposed to plane polarised light (i.e. light in which all the light waves are moving up and down in the same plane), some molecules rotate the light. Such molecules are spoken of as being optically active. Each optically active molecule has a mirror image which cannot be super-imposed on the orginal and which rotates light the same amount in the opposite direction. In glyceraldehyde (an optically active molecule) the form which rotates light to the left is called L-glyceraldehyde (from the Greek laevo, meaning left) and the other form is called D-glyceraldehyde (from the Latin dexter, meaning right). For amino acids, the form that looks like L- glyceraldehyde is the 'L' form of the amino acid and the form that looks like D-glyceraldehyde is known as the 'D' form, regardless of which way they rotate plane polarised light. All naturally occuring amino acids except glycine are optically active L-glyceraldehyde D-glyceraldehyde L-alanine D-alanine XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-4
5 The bonds between amino acids are called amide bonds. These are strong bonds but they can be hydrolysed by either strong acid or strong base, meaning that only neutral substances and weak acids and bases can be used in peptide synthesis. SLID PASE PEPTIDE SYTESIS Peptide synthesis is much more complicated than simply forming amide bonds by mixing the desired amino acids together in a test tube. With twenty natural amino acids and a number of unnatural ones as well the possible combinations formed with this technique are numerous. This complexity makes the synthesis of peptides both fascinating and challenging. If solutions containing two amino acids are mixed together, four different dipeptides (as well as other longer peptides) will be formed. (e.g. for a mixture of glycine and alanine the four dipeptides would be glygly, glyala, alagly, alaala. In this representation of peptides the free amino group or -terminus is on the lefthand amino acid and the free carboxylic acid group, the -terminus is at the righthand end.). To ensure that only the desired dipeptide is formed the basic group of one amino acid and the acidic group of the other must both be made unable to react. This 'deactivation' is known as the protection of reactive groups, and a group that is unable to react is spoken of as a protected group. In classical organic sythesis the acids are protected, allowed to react and deprotected, then one end of the dipeptide is protected and reacted with a new protected acid and so on. In SPPS the amino acid that will be at one end of the peptide is attached to a water-insoluble polymer and remains protected throughout the formation of the peptide, meaning both that fewer protection / deprotection steps are necessary and that the reagents can easily be rinsed away without losing any of the peptide. Step 1 - Attaching an amino acid to the polymer Peptide chains have two ends, known respectively as the -terminus and the -terminus 3, and which end is attached to the polymer depends on the polymer used. This article assumes that polyamide beads are used and hence that the the -terminus of the peptide is attached to the polymer. The attachment is done by reacting the amino acid with a linkage agent and then reacting the other end of the linkage agent with the polymer. This means that a peptidepolyamide link can be formed that will not be hydrolysed during the subsequent peptideforming reactions. ommon linkage agents are di- and tri-substituted benzenes such as those shown below: Me These then join the -terminus amino acid and resin together as follows: group. 3 The -terminus is the end that has a free 2 group and the -terminus is the end that has a free carboxyl XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-5
6 2 2 Me amino acid linkage agent resin Step 2 - Protection The next amino acid also needs to have its amino group protected to prevent the acids reacting with each other. This is done by protecting it with FM (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl). In addition, any amino acid side chains that are aromatic, acid, basic or highly polar are likely to be reactive (see Table 1). These must also be protected to prevent unwanted branched chains from forming. There are four main groups used in this way: tbu (a tertiary butyl group), Trt (a triphenylmethyl group), tb (a tertiary butyloxycarbonyl group) and PM (a 2,2,5,7,8-pentamethylchroman-6-sufonyl group). Examples of a carboxyl group protected with FM and examples of the different types of side chain protection are given below. 2 l FM 2 an amino acidprotected wuth FM serine serine protected with tbu 2 2 S 2 S 2 cysteine cysteine protected with Trt XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-6
7 2 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) lysine lysine protected with tb 2 2 arginine ( 2 ) 3 S arginine protected with PM Step 3 - oupling The FM protected amino acid is then reacted with the last amino acid attached to the polyamide. The reaction is catalysed by D (1,3 dicyclohexylcarbodiimide), which is itself reduced to DU (1,3-dicyclohexylurea). The reaction is shown in Figure 1 ( represents the FM protected acid and 2 represents the reactive end of the growing peptide chain). Step 4 - Deprotection Excess D is washed off the insoluble polymer with water, then the FM group removed with piperidine (a cyclic secondary amine). This is a trans amidification reaction. piperidine Steps 2 to 4 are repeated as each new amino acid is added onto the chain until the desired peptide has been formed. Step 5 - Polymer removal nce the peptide is complete it must be removed from the polyamide. This is done by cleaving the polyamide - peptide bond with a 95% solution of trifluoro acetic acid (TFA). The side-chain protecting groups are also removed at this stage. XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-7
8 F 3 2 ' - ' ' + Figure 1 - The amino acid coupling reaction PATIAL AD FIAIAL ADVATAGES F SPPS The primary advantage of SPPS is its high yield. As peptides consists of many amino acids, if the yield for each amino acid addition is much less than 100%, overall peptide yields are negligible. For example, if each amino acid addition has a 90% yield then the overall yield of a 50 amino acid peptide is only 0.5%. Modern SPPS instrumentation pushes coupling and deprotection yields to greater than 99.99%, giving an overall yield of greater than 99% for a 50 amino acid peptide. SPPS is also much quicker than conventional step-by-step solution synthesis. With SPPS, a 20 amino acid peptide can be synthesised in a 24 hour period and longer ones in less than a week. With the advent of automated synthesizers and sophisticated analytical and purification equipment the peptide chemist can now make peptides in the range of amino acids in length and in amounts from milligrams. This is often more than enough for biochemists and biologists to carry out extensive pilot studies, and as they often only look at a particular peptide once this speed is particularly useful. If very large amounts of peptide are required (e.g. for the industrial production of peptide drugs) then this speed is XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-8
9 sacrificed for purity. owever, production rates are still high, and hundreds of grams of peptide can be produced on kilograms of polymer every year. As often only milligrams of polymer is needed per dose, this represents hundreds of thousands of doses. UTILITIES The Massey facility has one 430A and one 431A Applied Biosystem fully automated peptide synthesizers. The latter is controlled by a Macintosh computer. For developmental work the Massey group also has a semi manual LKB 4174 Biolynz apparatus. In addition to purification equipment (PL and FPL facilities), the group has access to the Department of Biochemistry for amino acid analysis (AAA) and protein sequencing to aid in the analysis of the peptide products. EVIMETAL IMPLIATIS SPPS, like much of organic chemistry, makes use of organic solvents which are hazardous to the environment. The SPPS group at Massey University is currently researching ways of producing peptides in aqueous or partially aqueous (e.g. water/ethanol mixtures) solutions to avoid the use of organic solvents. Written by David arding (Massey University) and edited by eather Wansbrough with reference to: Beavis, onald.; Protecting groups used in peptide synthesis; [nline] 26 February 1997 Atherton, E. and Sheppard,..; Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis: a practical approach; xford University Press; 1989 Bodanszky, M.; Principles of Peptide Synthesis (2nd. ed.); Springer-Verlag; 1993 XII-Biotech-E-Peptide Synthesis-9
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
BOC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1. Calculating the charge of proteins
 BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
BC334 (Proteomics) Practical 1 Calculating the charge of proteins Aliphatic amino acids (VAGLIP) N H 2 H Glycine, Gly, G no charge Hydrophobicity = 0.67 MW 57Da pk a CH = 2.35 pk a NH 2 = 9.6 pi=5.97 CH
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw
 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute te of Biomedical Engineering ing E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ edu tw/pweb/users/splin/ Date: 10.13.2010
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Functions of proteins: Enzymes Transport and Storage Motion, muscle contraction Hormones Mechanical support Immune protection (Antibodies) Generate and transmit nerve impulses
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 26 Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl
Introduction to Chemical Biology
 Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
Professor Stuart Conway Introduction to Chemical Biology University of xford Introduction to Chemical Biology ecommended books: Professor Stuart Conway Department of Chemistry, Chemistry esearch Laboratory,
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM
 AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
AMINO ACIDS & PEPTIDE BONDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION & METABOLISM OBJECTIVES At the end of this session the student should be able to, recognize the structures of the protein amino acid and state their
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11 Enzyme Mechanisms II In the last class we studied the enzyme mechanisms of ribonuclease A
USP's Therapeutic Peptides Expert Panel discusses manufacturing processes and impurity control for synthetic peptide APIs.
 Control Strategies for Synthetic Therapeutic Peptide APIs Part III: Manufacturing Process Considerations By Brian Gregg,Aleksander Swietlow,Anita Y. Szajek,Harold Rode,Michael Verlander,Ivo Eggen USP's
Control Strategies for Synthetic Therapeutic Peptide APIs Part III: Manufacturing Process Considerations By Brian Gregg,Aleksander Swietlow,Anita Y. Szajek,Harold Rode,Michael Verlander,Ivo Eggen USP's
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 22 Proteins
 hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
hemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, ampbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, rganic and Biochemistry hapter 22 Proteins Step-growth polyamide (polypeptide) polymers or oligomers of L-α-aminoacids.
Structure and properties of proteins. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
Structure and properties of proteins Vladimíra Kvasnicová Chemical nature of proteins biopolymers of amino acids macromolecules (M r > 10 000) Classification of proteins 1) by localization in an organism
Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper
 Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper Writing an effective scientific paper is not easy. A good rule of thumb is to write as if your paper will be read by a person who knows about the field in general
Guidelines for Writing a Scientific Paper Writing an effective scientific paper is not easy. A good rule of thumb is to write as if your paper will be read by a person who knows about the field in general
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C)
CHAPTER 29 AMINO ACIDS, POLYPEPTIDES, AND PROTEINS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
APTER 29 AMI AIDS, PLYPEPTIDES, AD PRTEIS SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The designation, α, means that the amine group in common amino acids is connected to the carbon immediately adjacent to the carboxylic
The chemistry of insulin
 FREDERICK S ANGER The chemistry of insulin Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1958 It is great pleasure and privilege for me to give an account of my work on protein structure and I am deeply sensitive of the
FREDERICK S ANGER The chemistry of insulin Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1958 It is great pleasure and privilege for me to give an account of my work on protein structure and I am deeply sensitive of the
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
1) Technical informations. - a) How does it work? - b) Purification - c) Quality Control. 2) Standard synthesis
 1) Technical informations - a) How does it work? - b) Purification - c) Quality Control 2) Standard synthesis - a) Standard peptides - b) Modified peptides - c) Shipment and Delivery Time - d) How to order?
1) Technical informations - a) How does it work? - b) Purification - c) Quality Control 2) Standard synthesis - a) Standard peptides - b) Modified peptides - c) Shipment and Delivery Time - d) How to order?
Molecular Facts and Figures
 Nucleic Acids Molecular Facts and Figures DNA/RNA bases: DNA and RNA are composed of four bases each. In DNA the four are Adenine (A), Thymidine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). In RNA the four are
Nucleic Acids Molecular Facts and Figures DNA/RNA bases: DNA and RNA are composed of four bases each. In DNA the four are Adenine (A), Thymidine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). In RNA the four are
WORKING WITH PEPTIDES
 WORKING WITH PEPTIDES 1 Synthetic custom peptides offer an increasingly affordable approach for exploring protein-protein interactions and more complex phenomena such as immune responses directed against
WORKING WITH PEPTIDES 1 Synthetic custom peptides offer an increasingly affordable approach for exploring protein-protein interactions and more complex phenomena such as immune responses directed against
Chapter 27: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. monomer unit: α-amino acids
 Chapter 27: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. monomer unit: αamino acids 2 C 2! Amino Acid = sidechain Biopolymer: the monomeric amino acids are linked through an amide bond (the carboxylic acids of
Chapter 27: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. monomer unit: αamino acids 2 C 2! Amino Acid = sidechain Biopolymer: the monomeric amino acids are linked through an amide bond (the carboxylic acids of
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í
 I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
I V E S T I E D Z V J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á Í AMIAIDS PEPTIDES AMIAIDS = substitutional/functional derivatives of carboxylic acids = basic units of proteins (2-aminoacids) General formula of 2-aminoacids (α-aminoacids):
Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica
 PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica 1 Solution phase chemistry -Time consuming: isolation and purification at each step -Low yield: can t drive reaction
PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS Dr. Rita P.-Y. Chen Institute of Biological Chemistry Academia Sinica 1 Solution phase chemistry -Time consuming: isolation and purification at each step -Low yield: can t drive reaction
Protein Structure and Function
 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI Protein Structure and Function SETI I APTE 2 APTE 3 Protein Structure Protein Function 27 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI 2 Protein Structure
Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI Protein Structure and Function SETI I APTE 2 APTE 3 Protein Structure Protein Function 27 Jones & Bartlett Learning, LL. T F SALE DISTIBUTI 2 Protein Structure
Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthesis
 on-ibosomal Peptide Synthesis In contrast to proteins produced by ribosomal synthesis, many small peptide natural products contain not only the common 20 amino acids but also hundreds of different amino
on-ibosomal Peptide Synthesis In contrast to proteins produced by ribosomal synthesis, many small peptide natural products contain not only the common 20 amino acids but also hundreds of different amino
2. Couple the two protected amino acids.
 General Considerations The Strategy of Peptide Synthesis Making peptide bonds between amino acids is not difficult. The challenge is connecting amino acids in the correct sequence. andom peptide bond formation
General Considerations The Strategy of Peptide Synthesis Making peptide bonds between amino acids is not difficult. The challenge is connecting amino acids in the correct sequence. andom peptide bond formation
Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application. Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D.
 Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D. Presentation overview 1 2 3 4 Introduction Peptide Design Basics Advanced Design Strategy Strategy
Peptide Design Strategy: Basics, Optimization, and Application Presented by: Tiffany Gupton Campolongo, Ph.D. Presentation overview 1 2 3 4 Introduction Peptide Design Basics Advanced Design Strategy Strategy
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Short Peptide Synthesis
 Short Peptide Synthesis Keith ó Proinsias 8 th February 2010 Introduction Amide bond and basic amide synthesis Solution phase peptide synthesis Protecting groups required for peptide synthesis Coupling
Short Peptide Synthesis Keith ó Proinsias 8 th February 2010 Introduction Amide bond and basic amide synthesis Solution phase peptide synthesis Protecting groups required for peptide synthesis Coupling
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest
 Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
Peptides: Synthesis and Biological Interest Therapeutic Agents Therapeutic peptides approved by the FDA (2009-2011) 3 Proteins Biopolymers of α-amino acids. Amino acids are joined by peptide bond. They
PROTEIN SEQUENCING. First Sequence
 PROTEIN SEQUENCING First Sequence The first protein sequencing was achieved by Frederic Sanger in 1953. He determined the amino acid sequence of bovine insulin Sanger was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1958
PROTEIN SEQUENCING First Sequence The first protein sequencing was achieved by Frederic Sanger in 1953. He determined the amino acid sequence of bovine insulin Sanger was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1958
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
The three kinds of polymers that are prevalent in nature are
 23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins The three kinds of polymers that are prevalent in nature are polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are
23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins The three kinds of polymers that are prevalent in nature are polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are
Peptide Synthesis. Technical Document. www.altabioscience.com. Why use AltaBioscience?
 Peptide Synthesis Technical Document AltaBioscience offers a custom peptide synthesis service certified to ISO 9001:2008. With a strong focus on scientific excellence and 40 years of expertise we work
Peptide Synthesis Technical Document AltaBioscience offers a custom peptide synthesis service certified to ISO 9001:2008. With a strong focus on scientific excellence and 40 years of expertise we work
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Overview'of'Solid-Phase'Peptide'Synthesis'(SPPS)'and'Secondary'Structure'Determination'by'FTIR'
 verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
Dipeptide Synthesis. polarized light (Figure 2).
 Dipeptide Synthesis + Scheme 1: Peptide synthesis without carboxyl activation + 2 Throughout your organic chemistry tenure you have been taught the underlying principles necessary to construct simple organic
Dipeptide Synthesis + Scheme 1: Peptide synthesis without carboxyl activation + 2 Throughout your organic chemistry tenure you have been taught the underlying principles necessary to construct simple organic
Application Note. Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples. Summary. Introduction. Category Bio science, food Matrix
 Application Note Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples Category Bio science, food Matrix Baby food Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic amino acids, canonical amino acids,
Application Note Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in baby food samples Category Bio science, food Matrix Baby food Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic amino acids, canonical amino acids,
Rapid and Reproducible Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids for Clinical Research Using LC/MS/MS with the atraq Kit
 Rapid and Reproducible Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids for Clinical Research Using LC/MS/MS with the atraq Kit Fast, simple and cost effective analysis Many areas of biochemical research and
Rapid and Reproducible Amino Acid Analysis of Physiological Fluids for Clinical Research Using LC/MS/MS with the atraq Kit Fast, simple and cost effective analysis Many areas of biochemical research and
Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid.
 A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
A Acidic amino acids: Those whose side chains can carry a negative charge at certain ph values. Typically aspartic acid, glutamic acid. Active site: Usually applied to catalytic site of an enzyme or where
Concluding lesson. Student manual. What kind of protein are you? (Basic)
 Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
Concluding lesson Student manual What kind of protein are you? (Basic) Part 1 The hereditary material of an organism is stored in a coded way on the DNA. This code consists of four different nucleotides:
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Application Note. Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated OPA- Derivatization by the Autosampler. Summary. Fig. 1.
 Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS
 CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers:
 Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers: - Amino acids are weak acids - All have at least 2 titratable protons (shown below as fully protonated species) and therefore have 2 pka s o α-carboxyl (-COOH)
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes 1 Functions of Proteins Proteins in the body are polymers made from 20 different amino acids differ in characteristics and functions that depend on the order
Supporting Information. Minimum active structure of insulin-like. peptide 5 (INSL5)
 Supporting Information Minimum active structure of insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5) Alessia Belgi 1,2, Ross A.D. Bathgate *1,2,3, Martina Kocan *4, Nitin Patil 1,5, Suode Zhang 1, Geoffrey W. Tregear 1,2,
Supporting Information Minimum active structure of insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5) Alessia Belgi 1,2, Ross A.D. Bathgate *1,2,3, Martina Kocan *4, Nitin Patil 1,5, Suode Zhang 1, Geoffrey W. Tregear 1,2,
Chapter 2: Biochemistry Problems
 hapter 2: Biochemistry Problems Biochemistry Problems If you were a biochemist, you would study chemical substances and vital processes that occur in living organisms. You might study macromolecules such
hapter 2: Biochemistry Problems Biochemistry Problems If you were a biochemist, you would study chemical substances and vital processes that occur in living organisms. You might study macromolecules such
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Outline. Market & Technology Trends. LifeTein Technology Portfolio. LifeTein Services
 1 Outline Market & Technology Trends LifeTein Technology Portfolio LifeTein Services 2 Synthetic Therapeutic Peptides More than 60 synthetic therapeutic peptides under 50 amino acids in size have reached
1 Outline Market & Technology Trends LifeTein Technology Portfolio LifeTein Services 2 Synthetic Therapeutic Peptides More than 60 synthetic therapeutic peptides under 50 amino acids in size have reached
Patrick, An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 4e Chapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions. Pyrrole ring N H
 Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e hapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The pyrrole ring of DU 122290 serves to increase the rigidity
Patrick, An Introduction to dicinal hemistry 4e hapter 13 Drug design: optimizing target interactions Answers to end-of-chapter questions 1) The pyrrole ring of DU 122290 serves to increase the rigidity
How To Make A Drug From A Peptide
 MODERN PERSPECTIVES ON PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS INTRODUCTION WHITEPAPER www.almacgroup.com The complexity of synthetic peptide products, whether as reagents used in research or as therapeutic APIs, is increasing.
MODERN PERSPECTIVES ON PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS INTRODUCTION WHITEPAPER www.almacgroup.com The complexity of synthetic peptide products, whether as reagents used in research or as therapeutic APIs, is increasing.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(2): 372-380 ISSN No: 0975-7384 Determination of amino acid without derivatization by using
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2010, 2(2): 372-380 ISSN No: 0975-7384 Determination of amino acid without derivatization by using
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography
 Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
Combinatorial Chemistry and solid phase synthesis seminar and laboratory course
 Combinatorial Chemistry and solid phase synthesis seminar and laboratory course Topic 1: Principles of combinatorial chemistry 1. Introduction: Why Combinatorial Chemistry? Until recently, a common drug
Combinatorial Chemistry and solid phase synthesis seminar and laboratory course Topic 1: Principles of combinatorial chemistry 1. Introduction: Why Combinatorial Chemistry? Until recently, a common drug
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
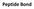 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS
 UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS 11.1 Types of Lipids Lipids are also biochemical compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But lipids, unlike carbohydrates, share no common
UNIT (11) MOLECULES OF LIFE: LIPIDS AND PROTEINS 11.1 Types of Lipids Lipids are also biochemical compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But lipids, unlike carbohydrates, share no common
2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award
 2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award 2010 Frost & Sullivan 1 We Accelerate Growth Frost & Sullivan s Global Research Platform Frost & Sullivan is entering its 50 th year in
2010 European Amino Acid Derivatives Product Line Strategy Award 2010 Frost & Sullivan 1 We Accelerate Growth Frost & Sullivan s Global Research Platform Frost & Sullivan is entering its 50 th year in
RNA and Protein Synthesis
 Name lass Date RN and Protein Synthesis Information and Heredity Q: How does information fl ow from DN to RN to direct the synthesis of proteins? 13.1 What is RN? WHT I KNOW SMPLE NSWER: RN is a nucleic
Name lass Date RN and Protein Synthesis Information and Heredity Q: How does information fl ow from DN to RN to direct the synthesis of proteins? 13.1 What is RN? WHT I KNOW SMPLE NSWER: RN is a nucleic
EMMI Intensive Programme "Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging Probes Torino, 19-30 September 2011
 EMMI Intensive rogramme "Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging robes Torino, 19-30 September 2011 Basic principles and procedures of solid phase peptide synthesis Lorenzo Tei, hd Dipartimento di
EMMI Intensive rogramme "Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging robes Torino, 19-30 September 2011 Basic principles and procedures of solid phase peptide synthesis Lorenzo Tei, hd Dipartimento di
PEPTIDES, AND PROTEINS
 A P T E AID, PEPTIDE, AD PTEI 24AMI Proteins are the most abundant organic molecules in animals, playing important roles in all aspects of cell structure and function. Proteins are biopolymers of acids,
A P T E AID, PEPTIDE, AD PTEI 24AMI Proteins are the most abundant organic molecules in animals, playing important roles in all aspects of cell structure and function. Proteins are biopolymers of acids,
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE. Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs,
 Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
Previously published in Biophysical Society On-line Textbook PROTEINS CHAPTER 1. PROTEIN STRUCTURE Section 1. Primary structure, secondary motifs, tertiary architecture, and quaternary organization Jannette
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 1 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam:.
1 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam:.
From Sequence to Structure
 1 From Sequence to Structure The genomics revolution is providing gene sequences in exponentially increasing numbers. onverting this sequence information into functional information for the gene products
1 From Sequence to Structure The genomics revolution is providing gene sequences in exponentially increasing numbers. onverting this sequence information into functional information for the gene products
A novel method for the synthesis of peptides
 A novel method for the synthesis of peptides in solution DioRaSSP (Diosynth Rapid Solution Synthesis of Peptides) offers substantial benefits for the large-scale synthesis of peptides meeting all the specifications
A novel method for the synthesis of peptides in solution DioRaSSP (Diosynth Rapid Solution Synthesis of Peptides) offers substantial benefits for the large-scale synthesis of peptides meeting all the specifications
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E.
 Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
Name Student # Ms. Campbell Protein Synthesis Practice Questions Regents L.E. 1. A sequence of three nitrogenous bases in a messenger-rna molecule is known as a 1) codon 2) gene 3) polypeptide 4) nucleotide
General Protein Metabolism
 General Protein Metabolism Protein Digestion Dietary proteins are very large complex molecules that cannot be absorbed from the intestine. To be absorbed, dietary proteins must be digested to small simple
General Protein Metabolism Protein Digestion Dietary proteins are very large complex molecules that cannot be absorbed from the intestine. To be absorbed, dietary proteins must be digested to small simple
AMINO ACIDS QUANTITATION IN BIOLOGICAL MEDIA. Monica Culea
 STUDIA UNIVERSITATIS BABEŞ BLYAI, PHYSICA, L, 4b, 25 AMIN ACIDS QUANTITATIN IN BILGICAL MEDIA Monica Culea Univ. Babes Bolyai, Biomedical Physics Dept., 1 Kogalniceanu str, 34 Cluj Napoca, Romania e mail:
STUDIA UNIVERSITATIS BABEŞ BLYAI, PHYSICA, L, 4b, 25 AMIN ACIDS QUANTITATIN IN BILGICAL MEDIA Monica Culea Univ. Babes Bolyai, Biomedical Physics Dept., 1 Kogalniceanu str, 34 Cluj Napoca, Romania e mail:
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin
 Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
Human Tubal Fluid (HTF) Media & Modifi ed Human Tubal Fluid (mhtf) Medium with Gentamicin HTF Media are intended for use in assisted reproductive procedures which include gamete and embryo manipulation
Peptide Library Synthesis
 Peptide Library Synthesis Jamie M. R. Moore Guy Laboratory UCSF I. verview.. page 2 II. Reagents and Apparatus. page 4 III. Flow Chart. page 6 IV. Protocol. page 7 IV. Tables A. List of Fmoc Amino. page
Peptide Library Synthesis Jamie M. R. Moore Guy Laboratory UCSF I. verview.. page 2 II. Reagents and Apparatus. page 4 III. Flow Chart. page 6 IV. Protocol. page 7 IV. Tables A. List of Fmoc Amino. page
Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy
 Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy Jonathan M. Collins, Michael J. Collins, Rebecca C. Steorts CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC 28106-0200, U.S.A. Presented at American
Novel Method for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Using Microwave Energy Jonathan M. Collins, Michael J. Collins, Rebecca C. Steorts CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC 28106-0200, U.S.A. Presented at American
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry for the Submission of Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls Information for Synthetic Peptide Substances Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Guidance for Industry for the Submission of Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls Information for Synthetic Peptide Substances Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation
Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian Office: Chemistry Bldn 2217
 Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217! http://web.chem.ucsb.edu/~zakariangroup/courses.html! 1 Amino acids: Resolution of Racemates 2 Peptides/Proteins: Peptide Bonds - - - - peptides:
Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217! http://web.chem.ucsb.edu/~zakariangroup/courses.html! 1 Amino acids: Resolution of Racemates 2 Peptides/Proteins: Peptide Bonds - - - - peptides:
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms
 In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
In addition to being shorter than a single bond, the double bonds in ethylene don t twist the way single bonds do. In other words, the other atoms attached to the carbons (hydrogens in this case) can no
Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following?
 MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
--not necessarily a protein! (all proteins are polypeptides, but the converse is not true)
 00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
00Note Set 5b 1 PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE: --chain containing only a few amino acids (see tetrapaptide, Fig 5.9) POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS: --many amino acids joined together --not necessarily
Syllabus. 1. Occurrence and Functions of Peptides in Nature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener,
 Syllabus 1. ccurrence and Functions of Peptides in ature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener, 2. Peptide Synthesis a) Aspartam: Properties of amino acids;
Syllabus 1. ccurrence and Functions of Peptides in ature and Every Day Life hormones, neurotransmitters, therapeutics, artificial sweetener, 2. Peptide Synthesis a) Aspartam: Properties of amino acids;
Previous lecture: Today:
 Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Previous lecture: The energy requiring step from substrate to transition state is an energy barrier called the free energy of activation G Transition state is the unstable (10-13 seconds) highest energy
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Methodology with Integrin α5 and Ligand Ac-RGDNP-NH2
 Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Methodology with Integrin α5 and Ligand Ac-RGDNP-NH2 Amy Ho The University of Texas at Dallas 2006 Abstract Peptides are short chains of amino acids that biologically function
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Methodology with Integrin α5 and Ligand Ac-RGDNP-NH2 Amy Ho The University of Texas at Dallas 2006 Abstract Peptides are short chains of amino acids that biologically function
PRACTICAL 3: DIGESTIVE ENZYMES, SPECIFICITY AND ph
 PRACTICAL 3: DIGESTIVE ENZYMES, SPECIFICITY AND ph 3.1 Introduction The aims of this practical are: to illustrate the different ph dependence of gastric and pancreatic digestive proteases to illustrate
PRACTICAL 3: DIGESTIVE ENZYMES, SPECIFICITY AND ph 3.1 Introduction The aims of this practical are: to illustrate the different ph dependence of gastric and pancreatic digestive proteases to illustrate
Course Content. Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins. Modules 06740 / 06741 / 06742
 Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Modules 06740 / 06741 / 06742 1 Course Content 1. Introduction to amino acids and peptides 2. Separation and purification of amino acids and proteins 3. Chemical and enzymatic
Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Modules 06740 / 06741 / 06742 1 Course Content 1. Introduction to amino acids and peptides 2. Separation and purification of amino acids and proteins 3. Chemical and enzymatic
Marmara Üniversitesi Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi Kimya Bölümü / Biyokimya Anabilim Dalı
 EXPERIMENT IX Marmara Üniversitesi DETERMINATION OF N-TERMINAL AMINO ACID RESIDUE OF PROTEINS BY THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Functions of the proteins depend upon its amino acid sequence. Because amino acid
EXPERIMENT IX Marmara Üniversitesi DETERMINATION OF N-TERMINAL AMINO ACID RESIDUE OF PROTEINS BY THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Functions of the proteins depend upon its amino acid sequence. Because amino acid
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 35
 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
