Basic Chemistry and the Periodic Table (1) -
|
|
|
- Kristopher Jefferson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basic Chemistry and the Periodic Table (1) - Elements Periodic Table Atomic Number Mass number SUMMARY: Chemistry deals with the properties of substances as well as the process of chemical substances making contact with each other, reacting with each other with the formation of new substances. Substances reacting with each other during a chemical reaction are described as reactants. During a chemical reaction the reactants are converted into products. Composition of the Atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Electron structure Aufbau diagram Lewis structure Substances reacting with each other (reactants) during a chemical reaction as well as substances produced (products) during a chemical reaction are described as matter as these substances have mass and occupy space. Matter is composed of atoms and atoms consist of protons, neutrons and electrons. Elements are important components of chemistry and are described as substances that could not be resolved into simpler substances. Properties of elements are reflected on the Periodic Table. Atoms are composed of a central section known as the nucleus of the atom with electric positive charged particles known as protons located inside the nucleus. Answers Available: D: Answer Basic Chemistry and the Periodic Table (1) Neutrons are electric neutral particles located in the nucleus of the atom. Around the nucleus are electrons that are negatively charged particles. 1
2 1. Complete: a.) The universe is composed of matter. Describe the meaning of matter. b.) Name the three phases in which matter can exist. c.) Describe the meaning of elements. 2. Name three elements as well as their symbols: a.) b.) c.) 3. Name the three sub-atomic particles: 4. a.) All the known elements that exist in nature as well as a few laboratory synthesized elements are summarized in a table known as the. b.) The Periodic Table is composed of Columns, which provide information from (left to right / top to bottom) (i) and Rows, which reflect information from (left to right / top to bottom) (ii) about the various elements that exist in nature. c.) The columns are also known as (series / groups / sections) (i) and there are (5 / 7 / 8) (ii) main groups and a few sub-groups on the table and these sub-groups are known as (metals / transition elements / non-metals) (iii). 5. Write the common names for each of the following groups on the Periodic Table: a.) Main group 1 elements: b.) Main group 2 elements: c.) Main group 7 elements: d.) Main group 8 elements: 6. ELEMENTS are described as 7.a.) Elements on the left side of the Periodic Table are known as (metals / non-metals) (i) with elements on the right side described as (metals / non-metals) (ii). b.) The Periodic Table is composed of columns, which provide information from (left to right / top to bottom) (i) and rows, which reflect information from (left to right / top to bottom) (ii) about the various elements that exist in nature. c.) The columns are also known as (series / groups / sections) (i) and there are (5 / 7 / 8) (ii) main groups and a few sub-groups on the table and these sub-groups are known as (metals / transition elements / non-metals) (iii). 8. a.) Write the names of three metals, their symbols, group number and row number: i.) ii.) iii.) b.) Write the names of three non-metals, their symbols, group number and row number: i.) _ ii.) iii.) 2
3 9. a.) Elements on the left side of the periodic table are known as (metals / non-metals / transition elements) (i) while elements on the right side of the table are described as (metals / non-metals / transition elements) (ii). 11.) Complete the following. a.) Name: (i) with a (positive / negative / neutral) (ii) electric charge. A number of elements separate these two groups of elements and these elements are known as (metals / non-metals / transition elements) (iii). b.) Elements exist in the following phases: (i) solids - for example the (metals / non-metals) (d) e - + o o + e - b.) Name: (i) with a (positive / negative / neutral) (ii) electric charge. (ii) gases - for example the (metals / non-metals) Two elements, namely (iii) and (iv), exist as liquids. c.) Name: (i) with a (positive / negative / neutral) (ii) electric charge. c.) The Periodic Table reflects information regarding all the elements that exists in nature and each element is represented by a (number / symbol) (i). Associated with the symbol are two values of which the smallest represents the (atomic / mass) (ii) number while the other figure indicates the (atomic / mass) (iii) number of the element. 10. Complete the following: 2 He 4 a.) (Atomic / Mass) number; b.) What is indicated by this number: c.) What is indicated by the symbol? d.) (Atomic / Mass) number; 12. a.) A single Helium atom contains (1/2/3) (i) protons and, as a result, (1/2/3) (ii) positive electric charges. This atom contains (1/2/3) (iii) negative charges. The resultant electric charge of a single He-atom is (iv) because the number of positive charges equals the number of negative charges. b.) Protons and neutrons in an atom are located (in / around) (i) the nucleus and these two sub-atomic particles (smaller than the atom) provide (mass / volume) (ii) to the atom. Electrons are found (in / around ) (iii) the nucleus and provide (mass / volume) (iv) to the atom. Protons and neutrons are equal in magnitude and are (v) times the size of electrons. e.) What is indicated by this number: 3
4 c.) The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by 15. Name: Oxygen subtracting the (mass / atomic) (i) number from the (mass / a.) Symbol: b.) Number of protons: atomic) (ii) number. c.) Number of electrons: d.) Number of neutrons: e.) Number of positive charges: 13. Name: Sodium f.) Number of negative charges: a.) Symbol: b.) Number of protons: g.) Resultant electric charge: c.) Number of electrons: d.) Number of neutrons: h.) Why is the resultant electric charge of a sodium atom equal to zero? e.) Number of positive charges: Explain: f.) Number of negative charges: g.) Resultant electric charge: i.) Metal or Non-metal: h.) Why is the resultant electric charge of a sodium atom equal to zero? 16. Name: Calcium Explain: a.) Symbol: b.) Number of protons: c.) Number of electrons: d.) Number of neutrons: i.) Metal or Non-metal: e.) Number of positive charges: 14. Symbol: Mg f.) Number of negative charges: a.) Name: b.) Number of protons: g.) Resultant electric charge: c.) Number of electrons: d.) Number of neutrons: h.) Why is the resultant electric charge of a calcium atom equal to zero? e.) Number of positive charges: Explain: f.) Number of negative charges: g.) Resultant electric charge of a Mg-atom: i.) Metal or Non-metal: h.) Why is the resultant electric charge of a magnesium atom equal to 17. Name: Neon zero? Explain: : a.) Symbol: b.) Number of protons: c.) Number of electrons: d.) Number of neutrons: i.) Metal or Non-metal: e.) Number of positive charges: f.) Number of negative charges: g.) Resultant electric charge: h.) Why is the resultant electric charge of a neon atom equal to zero? Explain: i.) Metal or Non-metal: 4
5 18. The collective name for protons and neutrons is. 21. The mass number indicates the following of an element: a.) the number of protons only b.) the number of electrons only c.) the number of neutrons only 19. True / False: d.) the number of protons and electrons a.). Sodium is a group I element and this group is known as alkalinemetals. e.) the number of protons and neutrons. b.) Neon is a noble gas and is more reactive than Chlorine. c.) A row on the periodic table is from left to right. 22. The following are true about protons: d.) Metals are on the left-side of the Periodic Table. a.) inside the nucleus and positively charged e.) The Periodic Table reflects information on all elements in nature. b.) outside the nucleus and positively charged c.) inside the nucleus and negatively charged f.) The atomic number is an indication of the number of protons in an d.) outside the nucleus and negatively charged atom. e.) inside the nucleus with a neutral electric charged. g.) The atomic number can be used to determine the number of electrons in an atom. 23. The following are true about electrons: h.) The mass number is the total of electrons and neutrons in one atom. a.) inside the nucleus and positively charged b.) outside the nucleus and positively charged i.) The symbol of an element represents the name of an element. c.) inside the nucleus and negatively charged d.) outside the nucleus and negatively charged e.) inside the nucleus with a neutral electric charged. 20. The atomic number indicates the following of an element: a.) the number of protons only 24. The following are true about neutrons: b.) the number of electrons only a.) inside the nucleus and positively charged c.) the number of neutrons only b.) outside the nucleus and positively charged d.) the number of protons and electrons c.) inside the nucleus and negatively charged e.) the number of protons and neutrons. d.) ouside the nucleus and negatively charged e.) inside the nucleus with a neutral electric charged. 5
6 25. The following are true about a calcium atom: a.) atomic number of 40, mass number of 20 and in group 1, positive atom b.) atomic number of 20, mass number of 40 and in group 1, negative atom c.) atomic number of 20, mass number of 40 and in group 2, neutral atom d.) atomic number of 20, mass number of 40 and in group 2, positive atom e.) atomic number of 20, mass number of 40 and in group 2, negative atom. 26. The following are true about an oxygen atom: a.) atomic number of 8, mass number of 16 and in group 18, positive atom b.) atomic number of 16, mass number of 8 and in group 17, negative atom c.) atomic number of 8, mass number of 16 and in group 17, neutral atom d.) atomic number of 8, mass number of 16 and in group 2, positive atom e.) atomic number of 8, mass number of 16 and in group 16, neutral atom. 27. The following are true about the periodic table : a.) group 1 are known as alkaline-earth metals, group 17 the halogens and metals are on the left side of the table b.) group 2 are known as alkaline-earth metals, group 17 the halogens and metals are on the left side of the table c.) group 2 are known as alkaline-earth metals, group 17 the halogens and metals are on the right side of the table d.) group 2 are known as alkaline metals, group 17 the halogens and metals are on the right side of the table e.) group 2 are known as alkaline metals, group 7 the halogens and metals are on the left side of the table. 28. a.) Describe the meaning for each of the following: (i) element: (ii) symbol: (iii) atomic number: (iv) mass number: 29. How many main groups are on the Periodic Table? 30. a.) Write the common names for each of the following groups on the Periodic Table. (i) Main group 1: (ii) Main group 2: (iii) Main group 7: (iv) Main group 8: b.) Write the name and symbol for two elements that are classified as: (i) metal: (ii) non-metal: (iii) transition element: 31. Name the three sub-atomic particles in an atom. 6
7 32. Give the function, electric charge and location for each of the following sub-atomic particles. (i) proton: (ii) neutron: (iii) electron: 33. Write the collective name for protons and neutrons. 34. Which sub-atomic particle is the smallest? 35. How many electrons can be accommodated in each of the following energy levels surrounding the nucleus of an atom? (i) 1 st Energy level: (ii) 2 nd Energy level: (iii) 3 rd Energy level: 36. Which sub-atomic particle can be removed from or added to the atom? Give two reasons. 37. From which energy level will the first electron be removed from an atom. 38. What is the process of removing electrons called? 39. An electron is added to an atom. Which energy level will accept the electron? 40. What is the process of accepting electrons called? 41. Argon is a noble gas. a.) How many electrons are in one argon atom? b.) Complete the following electron structures for each element. Name each energy level. Ar c.) How many electrons are in the outer energy level of argon? d.) How many electrons more can be accommodated in this energy level? e.) Is it possible to remove electrons from this energy level? Explain. f.) Noble gases are (reactive / stabile) g.) Which phenomenon is responsible for your answer in (f)? h.) What are the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom called? i.) How many valence electrons are in one Ar-atom? 7
8 42. a.) Sodium is in group (1,2,3) (i) on the periodic table with an atomic number of (ii). b.) One sodium atom has how many protons? c.) What is the resulting electric charge of a sodium atom? d.) What is the resulting electric charge of a sodium cation? e.) How many energy levels of a sodium atom can be fully occupied by electrons? f.) Name these energy levels. g.) Complete the electron structure of a sodium atom. 43. Sodium undergoes a process called oxidation. a.) How many electrons are left after oxidation? b.) How many protons are left after oxidation? c.) What is the resultant electric charge of sodium after oxidation? d.) What is the sodium atom called after oxidation? e.) Write the formula of the sodium atom after it has donated one electron. 44. Complete the electron structure of a chlorine atom. Na Cl 45. Chlorine undergoes a process called reduction. h.) How many electrons are in the outer energy level of a sodium atom? a.) How many electrons are left after reduction? b.) How many protons are left after reduction? i.) What would be the easiest for a sodium atom to obtain an electron c.) What is the resultant electric charge of chlorine after reduction? structure with the outer energy level completely occupied with electrons? d.) What is the chlorine atom called after reduction? e.) Write the formula of the chlorine atom after it has accepted one j.) What is this process called? electron. k.) Which Nobel gas electron structure will a sodium atom exhibit when it reaches a condition with its outer energy level fully occupied with electrons? 8
9 46. Explain the following : a.) Atomic number: b.) Mass number: c.) Orbital: d.) Energy level: e.) Valence electron(s): f.) Lewis structure: g.) The number of valence electrons can be derived from the (row / group) number of oxygen on the Periodic Table. 49. Complete the following: a.) Hydrogen: i.) Atomic number: ii.) Mass number: iii.) Number of protons: iv.) Number of electrons: v.) Number of neutrons: vi.) Molecular formula: vii.) Molecular mass: viii.) Symbol: ix.) Group number: x.) Number of valence electrons: xi.) Lewis structure: xii.) Afbau diagram: h.) All the elements would like to obtain the electron structure of a noble gas and to achieve this status the metals (donate / accept) (i) electrons during a process called (oxidation / reduction) (ii). In an attempt to achieve a noble gas structure the atoms from non-metals (accept / donate) (iii) electrons and this process is described as (oxidation / reduction) (iv). i.) Describe the difference in the outer energy level of noble gases and non-noble gases. j.) Explain the meaning of the term isotope: k.) Example of isotope. : Names of orbitals: xiii.) Complete the electron structure: xiv.) Electron configuration; xv.) Phase at room temperature: 9 H
10 50. Complete the following: a.) Helium: i.) Atomic number: ii.) Mass number: iii.) Number of protons: iv.) Number of electrons: v.) Number of neutrons: vi.) Molecular formula: vii.) Molecular mass: viii.) Symbol: ix.) Group number: x.) Number of valence electrons: xi.) Lewis structure: xii.) Afbau diagram: 51. Complete the following: a.) Lithium: i.) Atomic number: ii.) Mass number: iii.) Number of protons: iv.) Number of electrons: v.) Number of neutrons: vi.) Atomic formula: vii.) Atomic mass: viii.) Symbol: ix.) Group number: x.) Number of valence electrons: xi.) Lewis structure: xii.) Afbau diagram: Names of orbitals: Names of orbitals: xiii.) Complete the electron structure: He xiii.) Complete the electron structure: Li xiv.) Electron configuration; xiv.) Electron configuration; xv.) Phase at room temperature: xv.) Phase at room temperature: 10
Untitled Document. 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? 4. Which statement best describes the density of an atom s nucleus?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
******* KEY ******* Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide
 Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name
 Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
7.4. Using the Bohr Theory KNOW? Using the Bohr Theory to Describe Atoms and Ions
 7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary
 Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels
 Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels As you already know, all atoms are made of subatomic particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Positive protons and neutral neutrons are found
Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels As you already know, all atoms are made of subatomic particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Positive protons and neutral neutrons are found
The Periodic Table: Periodic trends
 Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table
 Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Periodic Table Questions
 Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
SCPS Chemistry Worksheet Periodicity A. Periodic table 1. Which are metals? Circle your answers: C, Na, F, Cs, Ba, Ni
 SCPS Chemistry Worksheet Periodicity A. Periodic table 1. Which are metals? Circle your answers: C, Na, F, Cs, Ba, Ni Which metal in the list above has the most metallic character? Explain. Cesium as the
SCPS Chemistry Worksheet Periodicity A. Periodic table 1. Which are metals? Circle your answers: C, Na, F, Cs, Ba, Ni Which metal in the list above has the most metallic character? Explain. Cesium as the
Lewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions
 Why? The chemical properties of an element are based on the number of electrons in the outer shell of its atoms. We use Lewis dot structures to map these valence electrons in order to identify stable electron
Why? The chemical properties of an element are based on the number of electrons in the outer shell of its atoms. We use Lewis dot structures to map these valence electrons in order to identify stable electron
Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck. atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element
 Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element are the building blocks of matter consists of protons and
Name Block Date Ch 17 Atomic Nature of Matter Notes Mrs. Peck atoms- the smallest particle of an element that can be identified with that element are the building blocks of matter consists of protons and
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39)
 ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
Periodic Table. 1. In the modern Periodic Table, the elements are arranged in order of increasing. A. atomic number B. mass number
 Name: ate: 1. In the modern, the elements are arranged in order of increasing. atomic number. mass number. oxidation number. valence number 5. s the elements in Group I are considered in order of increasing
Name: ate: 1. In the modern, the elements are arranged in order of increasing. atomic number. mass number. oxidation number. valence number 5. s the elements in Group I are considered in order of increasing
PROTONS AND ELECTRONS
 reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
19.1 Bonding and Molecules
 Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
ANSWER KEY : BUILD AN ATOM PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom )
 ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes.
 1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
 Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements 1. Elements in the modern version of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing. (a). oxidation number (b). atomic mass (c). average atomic mass
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements 1. Elements in the modern version of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing. (a). oxidation number (b). atomic mass (c). average atomic mass
Chemistry. The student will be able to identify and apply basic safety procedures and identify basic equipment.
 Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
2014 Spring CHEM101 Ch1-2 Review Worksheet Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai,
 Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE
 ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
B) atomic number C) both the solid and the liquid phase D) Au C) Sn, Si, C A) metal C) O, S, Se C) In D) tin D) methane D) bismuth B) Group 2 metal
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) molar mass D) oxidation number 2. Which list of elements consists of a metal, a metalloid, and
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements
 EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
Elements, Atoms & Ions
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Chemistry: The Periodic Table and Periodicity
 Chemistry: The Periodic Table and Periodicity Name: per: Date:. 1. By what property did Mendeleev arrange the elements? 2. By what property did Moseley suggest that the periodic table be arranged? 3. What
Chemistry: The Periodic Table and Periodicity Name: per: Date:. 1. By what property did Mendeleev arrange the elements? 2. By what property did Moseley suggest that the periodic table be arranged? 3. What
Atoms and Molecules. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4
 Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
2. John Dalton did his research work in which of the following countries? a. France b. Greece c. Russia d. England
 CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems
 Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet Practice problems 1. What are the SI units for a. Wavelength of light b. frequency of light c. speed of light Meter hertz (s -1 ) m s -1 (m/s) 2. T/F (correct
9/13/2013. However, Dalton thought that an atom was just a tiny sphere with no internal parts. This is sometimes referred to as the cannonball model.
 John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
PERIODIC TABLE. reflect
 reflect Suppose you wanted to organize your locker at school. How could you separate and arrange everything in an organized way? You could place the books, notebooks, and folders on a shelf that is separate
reflect Suppose you wanted to organize your locker at school. How could you separate and arrange everything in an organized way? You could place the books, notebooks, and folders on a shelf that is separate
Chapter 3, Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 1. Which two scientists in 1869 arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic masses to form a precursor of the modern periodic table of elements? Ans. Mendeleev and Meyer 2. Who stated that the
1. Which two scientists in 1869 arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic masses to form a precursor of the modern periodic table of elements? Ans. Mendeleev and Meyer 2. Who stated that the
5.4 Trends in the Periodic Table
 5.4 Trends in the Periodic Table Think about all the things that change over time or in a predictable way. For example, the size of the computer has continually decreased over time. You may become more
5.4 Trends in the Periodic Table Think about all the things that change over time or in a predictable way. For example, the size of the computer has continually decreased over time. You may become more
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2)
 Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2) Atomic Structure 1. Historical View - Dalton's Atomic Theory Based on empirical observations, formulated as Laws of: Conservation of Mass Definite Proportions
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2) Atomic Structure 1. Historical View - Dalton's Atomic Theory Based on empirical observations, formulated as Laws of: Conservation of Mass Definite Proportions
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Chapter 13 & 14 Assignment & Problem Set
 Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Name: Worksheet: Electron Configurations. I Heart Chemistry!
 1. Which electron configuration represents an atom in an excited state? 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3p 1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 Worksheet: Electron Configurations Name:
1. Which electron configuration represents an atom in an excited state? 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3p 1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 2 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 Worksheet: Electron Configurations Name:
Atomic Structure Chapter 5 Assignment & Problem Set
 Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table
 Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions
 Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Chemistry Diagnostic Questions Answer these 40 multiple choice questions and then check your answers, located at the end of this document. If you correctly answered less than 25 questions, you need to
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Ionic and Metallic Bonding BNDING AND INTERACTINS 71 Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 1, 3 5, 7 12, 14, 15, 18 20 Essential Understanding Ions form when atoms gain or lose
Ionic and Metallic Bonding BNDING AND INTERACTINS 71 Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 1, 3 5, 7 12, 14, 15, 18 20 Essential Understanding Ions form when atoms gain or lose
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25. 4 Atoms and Elements
 47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
3. What would you predict for the intensity and binding energy for the 3p orbital for that of sulfur?
 PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
PSI AP Chemistry Periodic Trends MC Review Name Periodic Law and the Quantum Model Use the PES spectrum of Phosphorus below to answer questions 1-3. 1. Which peak corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1.06
Electron Arrangements
 Section 3.4 Electron Arrangements Objectives Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms using electron configurations and Lewis valence electron dot structures New Vocabulary Heisenberg uncertainty
Section 3.4 Electron Arrangements Objectives Express the arrangement of electrons in atoms using electron configurations and Lewis valence electron dot structures New Vocabulary Heisenberg uncertainty
Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions. Chemistry 11
 Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11 Note: Of the 3 subatomic particles, the electron plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties
Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11 Note: Of the 3 subatomic particles, the electron plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties
TRENDS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE
 Noble gases Period alogens Alkaline earth metals Alkali metals TRENDS IN TE PERIDI TABLE Usual charge +1 + +3-3 - -1 Number of Valence e - s 1 3 4 5 6 7 Electron dot diagram X X X X X X X X X 8 Group 1
Noble gases Period alogens Alkaline earth metals Alkali metals TRENDS IN TE PERIDI TABLE Usual charge +1 + +3-3 - -1 Number of Valence e - s 1 3 4 5 6 7 Electron dot diagram X X X X X X X X X 8 Group 1
Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D
 Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D Electrons in Atoms (std.1d) What are Bohr Models? planetary model in which the negatively-charged electrons orbit a small, positively-charged
Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D Electrons in Atoms (std.1d) What are Bohr Models? planetary model in which the negatively-charged electrons orbit a small, positively-charged
Structure and Properties of Atoms
 PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
TOPIC 7. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights.
 TOPIC 7. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually
TOPIC 7. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually
Look at a periodic table to answer the following questions:
 Look at a periodic table to answer the following questions: 1. What is the name of group 1? 2. What is the name of group 2? 3. What is the name of group 17? 4. What is the name of group 18? 5. What is
Look at a periodic table to answer the following questions: 1. What is the name of group 1? 2. What is the name of group 2? 3. What is the name of group 17? 4. What is the name of group 18? 5. What is
Noble Gases. Outline Nobel Gas Elements Radon and Health Chemistry Homework
 Radon and Other Noble Gases The elements in the last column of the periodic table are all very stable, mono-atomic gases. Until 1962, they were called inert gases because they did not react with other
Radon and Other Noble Gases The elements in the last column of the periodic table are all very stable, mono-atomic gases. Until 1962, they were called inert gases because they did not react with other
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
Bohr s Model of the Atom
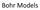 Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Bonding Practice Problems
 NAME 1. When compared to H 2 S, H 2 O has a higher 8. Given the Lewis electron-dot diagram: boiling point because H 2 O contains stronger metallic bonds covalent bonds ionic bonds hydrogen bonds 2. Which
NAME 1. When compared to H 2 S, H 2 O has a higher 8. Given the Lewis electron-dot diagram: boiling point because H 2 O contains stronger metallic bonds covalent bonds ionic bonds hydrogen bonds 2. Which
Science 20. Unit A: Chemical Change. Assignment Booklet A1
 Science 20 Unit A: Chemical Change Assignment Booklet A FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter Assignment Total Possible Marks 79 Your Mark Science 20 Unit A: Chemical Change Assignment
Science 20 Unit A: Chemical Change Assignment Booklet A FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter Assignment Total Possible Marks 79 Your Mark Science 20 Unit A: Chemical Change Assignment
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes
 Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table
 Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Chapter Test. Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a 13. c 14. d 15. c 16. b 17. d 18. a 19. d 20. c 21. d 22. a
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a 13. c 14. d 15. c 16. b 17. d 18. a 19. d 20. c 21. d 22. a
Trends of the Periodic Table Basics
 Trends of the Periodic Table Basics Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Trends of the Periodic Table Basics Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS
 IONISATION ENERGY IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS What is Ionisation Energy? Definition of t Ionisation Energy What affects Ionisation Energy? General variation across periods Variation down groups Variation
IONISATION ENERGY IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS What is Ionisation Energy? Definition of t Ionisation Energy What affects Ionisation Energy? General variation across periods Variation down groups Variation
neutrons are present?
 AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties
 324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1. A chemical equation. (C-4.4)
 Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112
 Study Guide Chapter 5 Periodic Table Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112 DISCOVERING A PATTERN 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the elements? a. by increasing density b. by increasing melting point
Study Guide Chapter 5 Periodic Table Section 1: Arranging the Elements Pages 106-112 DISCOVERING A PATTERN 1. How did Mendeleev arrange the elements? a. by increasing density b. by increasing melting point
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:)
 Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
Find a pair of elements in the periodic table with atomic numbers less than 20 that are an exception to the original periodic law.
 Example Exercise 6.1 Periodic Law Find the two elements in the fifth row of the periodic table that violate the original periodic law proposed by Mendeleev. Mendeleev proposed that elements be arranged
Example Exercise 6.1 Periodic Law Find the two elements in the fifth row of the periodic table that violate the original periodic law proposed by Mendeleev. Mendeleev proposed that elements be arranged
Chapter 7. Electron Structure of the Atom. Chapter 7 Topics
 Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
 APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
Getting the most from this book...4 About this book...5
 Contents Getting the most from this book...4 About this book....5 Content Guidance Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table...8 Topic 2 Bonding and structure...14 Topic 2A Bonding....14 Topic 2B
Contents Getting the most from this book...4 About this book....5 Content Guidance Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table...8 Topic 2 Bonding and structure...14 Topic 2A Bonding....14 Topic 2B
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY. Recommended literature: Chemistry: science of the matter. Responsible for the course: Dr.
 About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY University of Pécs Medical School Academic year 2009-2010. Responsible for the course: Dr. Attila AGÓCS Optional course for 2 credit points. To have grade at the and
About the course GENERAL CHEMISTRY University of Pécs Medical School Academic year 2009-2010. Responsible for the course: Dr. Attila AGÓCS Optional course for 2 credit points. To have grade at the and
2 The Structure of Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding 1. There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for a phosphorus atom. (a). 4, 2 (b). 2, 4 (c). 4, 3 (d). 2, 3 Explanation: Read the question
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of the Chemical Bonding 1. There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for a phosphorus atom. (a). 4, 2 (b). 2, 4 (c). 4, 3 (d). 2, 3 Explanation: Read the question
Chapter 5 Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table.
 Chapter 5 Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table. How did he organize the elements? According to similarities in their chemical and physical
Chapter 5 Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Russian Chemist credited with the discovery of the periodic table. How did he organize the elements? According to similarities in their chemical and physical
Section 11.3 Atomic Orbitals Objectives
 Objectives 1. To learn about the shapes of the s, p and d orbitals 2. To review the energy levels and orbitals of the wave mechanical model of the atom 3. To learn about electron spin A. Electron Location
Objectives 1. To learn about the shapes of the s, p and d orbitals 2. To review the energy levels and orbitals of the wave mechanical model of the atom 3. To learn about electron spin A. Electron Location
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
 Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3 The Periodic Table Skim Section 3 and write three questions based on your brief preview. 1. Accept all reasonable answers. How are the elements organized
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3 The Periodic Table Skim Section 3 and write three questions based on your brief preview. 1. Accept all reasonable answers. How are the elements organized
Copyrighted by Gabriel Tang B.Ed., B.Sc.
 Chapter 8: The Periodic Table 8.1: Development of the Periodic Table Johann Dobereiner: - first to discover a pattern of a group of elements like Cl, Br, and I (called triads). John Newland: - suggested
Chapter 8: The Periodic Table 8.1: Development of the Periodic Table Johann Dobereiner: - first to discover a pattern of a group of elements like Cl, Br, and I (called triads). John Newland: - suggested
7-5.5. Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including:
 7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234
 Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
Physical Science 1 Progression
 Physical Science 1 Progression This progression is the about the structure and properties of matter. Matter is composed of material that is too small to be seen, but is understood in terms of the types
Physical Science 1 Progression This progression is the about the structure and properties of matter. Matter is composed of material that is too small to be seen, but is understood in terms of the types
Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s)
 BONDING MIDTERM REVIEW 7546-1 - Page 1 1) Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s) 2) The bond between hydrogen and oxygen in
BONDING MIDTERM REVIEW 7546-1 - Page 1 1) Which substance contains positive ions immersed in a sea of mobile electrons? A) O2(s) B) Cu(s) C) CuO(s) D) SiO2(s) 2) The bond between hydrogen and oxygen in
P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST
 P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A line spectrum is produced when an electron moves from one energy
P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A line spectrum is produced when an electron moves from one energy
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Periodic Table, Valency and Formula
 Periodic Table, Valency and Formula Origins of the Periodic Table Mendelѐѐv in 1869 proposed that a relationship existed between the chemical properties of elements and their atomic masses. He noticed
Periodic Table, Valency and Formula Origins of the Periodic Table Mendelѐѐv in 1869 proposed that a relationship existed between the chemical properties of elements and their atomic masses. He noticed
Ions & Their Charges Worksheet
 Ions & Their Charges Worksheet Name Date Teacher Diagram of charges based on groups on the periodic table including transition metals and noble gases: IA IIA Transition IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA metals
Ions & Their Charges Worksheet Name Date Teacher Diagram of charges based on groups on the periodic table including transition metals and noble gases: IA IIA Transition IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA metals
Chem term # 1 review sheet C. 12 A. 1
 hem term # 1 review sheet Name: ate: 1. n isotope of which element has an atomic number of 6 and a mass number of 14?. carbon. magnesium. nitrogen. silicon 6. Which atoms represent different isotopes of
hem term # 1 review sheet Name: ate: 1. n isotope of which element has an atomic number of 6 and a mass number of 14?. carbon. magnesium. nitrogen. silicon 6. Which atoms represent different isotopes of
Atoms and Elements. Outline Atoms Orbitals and Energy Levels Periodic Properties Homework
 Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Atoms and the Periodic Table The very hot early universe was a plasma with cationic nuclei separated from negatively charged electrons. Plasmas exist today where the energy of the particles is very high,
Chem101: General Chemistry Lecture 9 Acids and Bases
 : General Chemistry Lecture 9 Acids and Bases I. Introduction A. In chemistry, and particularly biochemistry, water is the most common solvent 1. In studying acids and bases we are going to see that water
: General Chemistry Lecture 9 Acids and Bases I. Introduction A. In chemistry, and particularly biochemistry, water is the most common solvent 1. In studying acids and bases we are going to see that water
Class Notes Standards Addressed: 8.3.11
 Name: Period #: Class Notes Standards Addressed: 8.3.11 History of the Periodic Table: Demitri Mendeleev = Russian chemist who discovered a pattern to the in 1869. o How did he discovery a pattern to the
Name: Period #: Class Notes Standards Addressed: 8.3.11 History of the Periodic Table: Demitri Mendeleev = Russian chemist who discovered a pattern to the in 1869. o How did he discovery a pattern to the
Composition of the Atmosphere. Outline Atmospheric Composition Nitrogen and Oxygen Lightning Homework
 Molecules of the Atmosphere The present atmosphere consists mainly of molecular nitrogen (N2) and molecular oxygen (O2) but it has dramatically changed in composition from the beginning of the solar system.
Molecules of the Atmosphere The present atmosphere consists mainly of molecular nitrogen (N2) and molecular oxygen (O2) but it has dramatically changed in composition from the beginning of the solar system.
CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers
 1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
