Physical Design Implementation of 32 bit DDR SDRAM Controller
|
|
|
- Edgar Welch
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology Volume 2, Issue 6, September 2014, PP ISSN (Print) & ISSN (Online) Physical Design Implementation of 32 bit DDR SDRAM Controller Anuraag Marepally PG Scholar, Department of ECE, Aurora s technological and Research Institute, JNTU Hyderabad, Telangana, India [email protected] V.V.N.S. Sudha Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Aurora s Technological and Research Institute, JNTU Hyderabad, Telangana, India [email protected] Abstract: Present day SOC s and other high-end applications that don t contain a microprocessor require a dedicated memory controller. Synchronous DRAM is the major off-chip memory module being used presently. A memory controller is required to meet the high speed and high performance requirement of any design. This paper discusses the functional design of a 32-bit DDR SDRAM controller and implementation of the design through the synthesis and physical design flow which form a part of ASIC Design Flow. This block level, semicustom implementation is done using Synopsys Design Compiler and IC Compiler at 90nm technology node. Keywords: DDR SDRAM, Synopsys Design Compiler, IC Compiler, Physical Design, SOC, semi-custom. 1. INTRODUCTION Modern day SOC s and high end systems all demand for memory devices that provide high speed and high performance. The need for controllers comes in when there are many modules that share the memory resource simultaneously and to maintain high throughput and speed. To attain such high speeds the memory controllers should be designed to work at clock rates which lie in megahertz increasing the complexity of the controller. The speed of the design would also depend on the speed of the off-chip memory module. Synchronous DRAM's provide such facility of high data transfer rate and the Double Data Rate (DDR) SDRAM is one such memory module in the family. In this paper the functional design of DDR SDRAM controller is demonstrated and implementation of the design through the synthesis and physical design phase are done. The controller would act as an interface between the bus master and the memory module simplifying the command signals like refresh, read and write operation and initialization of the DDR SDRAM. This would minimize the effort of the bus master to communicate with the memory. Figure 1 demonstrates the block diagram of the DDR SDRAM memory controller that is located between the bus master and the memory. SDRAM s are classified based on their data transfer rates as Single Data Rate(SDR) SDRAM, in which the data transfer takes place on a single clock edge and Double Data Rate(DDR) SDRAM where the transfer takes place on both the clock edges (positive and negative). This property of DDR SDRAM s provides for higher data transfer rate without much increase in clock frequency and bus width [1]. IJEERT 56
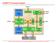
2 Anuraag Marepally & V.V.N.S. Sudha Fig 1. DDR SDRAM controller system [1] 2. IMPLEMENTATION METHODOLOGY The DDR SDRAM Controller architecture is designed using Verilog HDL. The basic steps that an ASIC design must go through are specifications, architectural and behavioural description, simulation, logic synthesis of the RTL code, physical design flow, GDS-II [4]. The implementation of the controller design forms a part of the ASIC Design flow concentrating on Logic Synthesis and Physical Design phases. 3. ARCHITECTURAL DESCRIPTION DDR SDRAM Controller module receives addresses and control signals from the BUS Master. The Controller generates command signals, based on these signals the data is either read or write to a particular memory location. The DDR SDRAM Controller architecture is shown in Figure 2. It consists of three modules: 1) Main control module 2) signal generation module 3) data path module. The main control module has two state machines and a refresh counter. The two state machines are for initialization of the SDRAM and for generating the commands to the SDRAM. The data paths modules can performs the read and write operations between the bus master and DDR [2]. The main control module consists of three sub modules: 1) Initialization FSM module (INIT_FSM). 2) Command FSM module. 3) Counter module. Fig 2. Architecture of the controller [2] International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 57
3 Physical Design Implementation of 32 bit DDR SDRAM Controller The finite state machines that are associated with the design are shown in Figure 3 and Figure IMPLEMENTATION OF THE DESIGN Fig 3. The DDR SDRAM Initialization fsm (INIT_FSM) [2] The implementation of the design is carried out in two phases: A) Logic Synthesis, B) Physical Design flow also known as Place and Route. A) Logic Synthesis: Fig4.The DDR SDRAM Command FSM (CMD_FSM)[2] International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 58
4 Anuraag Marepally & V.V.N.S. Sudha Logic Synthesis is a process in which the verified RTL is converted in to an optimized, technology mapped Gate-Level Netlist. The CAD tool used for Synthesis is Design Compiler from Synopsys. Synthesis is the phase in which the design would be translated and mapped into actual hardware in the form of logic gates interconnected through nets. The mapping of the RTL is done taking the technology libraries as reference. The technology libraries used here are at 90nm node. The libraries along with the verified RTL and a set of constraints would constitute the necessary files required by the Design Compiler to synthesize the design. The tool would generate the Gate-level Netlist, timing and area reports, delay files(.sdf) and constraints(.sdc) files [5]. The top-level schematic of the design after logic synthesis is shown in figure 5. B) Physical Design Flow (Place and Route): The Physical Design Flow also called the Place and Route is a process in which the Gate-Level Netlist generated in the Synthesis phase would be converted into the physical layout of the design. In this phase the standard cells present in the physical libraries would be placed and routing is done accordingly. The CAD tool used for Place and Route is IC Compiler from Synopsys. A typical Place and Route phase would undergo the following hierarchical sequence: i) Floor planning. ii) Placement. iii) Clock Tree Synthesis. iv) Routing. After passing through above sequence of steps, one would have completely routed layout of the design along with the delay information. The tool accepts the Gate-Level Netlist, physical libraries, TLU+ files which contain the electrical characteristics of the interconnect wires and the required constraints file generated from synthesis. Before proceeding to the Floor Plan phase, the Milky-Way library should be setup which serves as the design environment. The physical libraries, technology files, TLU+ files are also defined [6]. i) Floor Planning: Floor panning is the first step in the hierarchy. In this phase the basic skeleton of our block would be established. Floor planning is the process of identifying structures and it should be placed close together. It allocating space for them in such a manner as to meet the sometimes conflicting goals of available space (cost of the chip), required performance, and the desire to have everything close to everything else. Floor planning also decides the IO structure, aspect ratio of the design, utilization of the core area, power and ground rails would be laid and the necessary power straps are laid over running right through the core area. A bad floor plan will lead to wastage of die area and routing congestion. Figure 6 illustrates the Floor planning result of the controller. ii) Placement: Placement is the predominant phase in physical design which would decide the efficiency of the routing process that follows. Both placement and routing go hand-in-hand iteratively. The standard cells required would be placed initially and coarse routing is done. The In-Placement optimization would perform iterations of set-up fixing, incremental timing and congestion driven placement. To fix setup, hold and max transition time Post-placement Optimization (PPO) is done before and after CTS. PPO before CTS would take ideal clocks into consideration whereas PPO after CTS would consider the propagated clock preserving useful skew if presents [3]. Sufficient care would be taken such that cell overlap is avoided and also the empty spaces that result after placement would be filled using filler cells which protect the block during the fabrication process. The placement is carried out using the place_opt command. Figure 7 shows the controller design post placement. International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 59
5 Physical Design Implementation of 32 bit DDR SDRAM Controller Fig 5. Top level schematic of the Controller iii) Clock Tree Synthesis (CTS): Fig 6. Post Floorplan schematic of the controller Until now in the design the clocks that were used were ideal clock sources defined during the synthesis phase. CTS is the phase during which the clock would be actually propagated through the design. The main reason to perform CTS is to reduce clock skew and insertion delays. As the name suggests the clock would be synthesized as a H-tree and is fed to all the sequential elements present in the design. This tree is synthesized using buffer cells called clock buffers and placed at appropriate positions to reduce the skew and insertion delay. Hold slack if any is improved after CTS. clock_opt is the command that would perform CTS. Figure 8 shows the controller design post CTS. iv) Routing: Fig 7. Post placement schematic of the controller Routing is the final phase in the place and route of the controller design. All the placed standard cells would receive actual physical interconnections between them depending on the netlist. Routing is done in two steps which are Global routing and detailed routing. Global routing would provide International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 60
6 Anuraag Marepally & V.V.N.S. Sudha routing resources that provide the connections. Specific metal layers and routing tracks within the global routing resources for detailed routing assigns routes. Cross talk reduction is also process during this. The routing is done using the route_opt command. Figure 9 shows a sample routed area of the controller design. 5. RESULTS Fig 8. Post CTS structure of the controller The design is simulated using Synopsys VCS to verify the functionality. Logic synthesis of the verified RTL was performed using Synopsys Design Compiler and the Place and Route was performed using Synopsys IC Compiler. Figures 10 and 11 shows the internal schematic of the DDR SDRAM controller showing all the modules after synthesis and the completely routed controller post routing. The reports related to synthesis and the physical design phase are generated and tabulated in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively. Fig 9. Sample routed area of the DDR SDRAM controller Fig 10. Internal schematic of the DDR SDRAM controller International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 61
7 Physical Design Implementation of 32 bit DDR SDRAM Controller Table 1. Synthesis results of the controller Design Area (nm 2 ) Cell count 356 Dynamic power (µw) Leakage power (µw) Clock period (ns) 1.20 Table 2. Physical design results of the DDR SDRAM memory Controller Design Area (nm 2 ) Dynamic power (mw) Leakage power (µw) Net Length(nm) CONCLUSION Fig 11. Completely routed DDR SDRAM Memory Controller Logic Synthesis and Physical Design Implementation of 32-bit DDR SDRAM Memory Controller is done which forms a part of the ASIC Design Flow at 90 nm technology node. The CAD tools used for Synthesis were Synopsys Design Compiler and Synopsys IC Compiler for Physical Design Flow. Future work may include performing the same for a smaller technology node. REFERENCES [1] DDR SDRAM Controller white paper, Lattice Semiconductor Corporation, Reference Design: RD1020, April [2] Amit Bakshi, SudhanshuShekhar Pandey, Tribikram Pradhan Ratnadip Dey, ASIC Implementation of DDR SDRAM Memory Controller,2013 IEEE International Conference on Emerging Trends in Computing, Communication and Nanotechnology (ICECCN 2013). [3] International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 62
8 Anuraag Marepally & V.V.N.S. Sudha [4] al.pdf. [5] Synopsys Design Compiler User Guide Version D SP2, June [6] Synopsys IC Compiler User Guide Version B , International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology 63
University of Texas at Dallas. Department of Electrical Engineering. EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design
 University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
University of Texas at Dallas Department of Electrical Engineering EEDG 6306 - Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design Synopsys Tools Tutorial By Zhaori Bi Minghua Li Fall 2014 Table of Contents
How To Design A Chip Layout
 Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
Spezielle Anwendungen des VLSI Entwurfs Applied VLSI design (IEF170) Course and contest Intermediate meeting 3 Prof. Dirk Timmermann, Claas Cornelius, Hagen Sämrow, Andreas Tockhorn, Philipp Gorski, Martin
IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR
 International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
IL2225 Physical Design
 IL2225 Physical Design Nasim Farahini [email protected] Outline Physical Implementation Styles ASIC physical design Flow Floor and Power planning Placement Clock Tree Synthesis Routing Timing Analysis Verification
IL2225 Physical Design Nasim Farahini [email protected] Outline Physical Implementation Styles ASIC physical design Flow Floor and Power planning Placement Clock Tree Synthesis Routing Timing Analysis Verification
Design Compiler Graphical Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation
 Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Datasheet Create a Better Starting Point for Faster Physical Implementation Overview Continuing the trend of delivering innovative synthesis technology, Design Compiler Graphical delivers superior quality
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN
 TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
TRUE SINGLE PHASE CLOCKING BASED FLIP-FLOP DESIGN USING DIFFERENT FOUNDRIES Priyanka Sharma 1 and Rajesh Mehra 2 1 ME student, Department of E.C.E, NITTTR, Chandigarh, India 2 Associate Professor, Department
Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip
 Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip Ms Lavanya Thunuguntla 1, Saritha Sapa 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, HITAM, Telangana
Design and Implementation of an On-Chip timing based Permutation Network for Multiprocessor system on Chip Ms Lavanya Thunuguntla 1, Saritha Sapa 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, HITAM, Telangana
Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow
 Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow Bradley R. Quinton Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia [email protected]
Asynchronous IC Interconnect Network Design and Implementation Using a Standard ASIC Flow Bradley R. Quinton Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia [email protected]
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design
 White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
White Paper Engineering Change Order (ECO) Support in Programmable Logic Design A major benefit of programmable logic is that it accommodates changes to the system specification late in the design cycle.
Implementation Details
 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield
 DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
DDR subsystem: Enhancing System Reliability and Yield Agenda Evolution of DDR SDRAM standards What is the variation problem? How DRAM standards tackle system variability What problems have been adequately
Introduction to Digital System Design
 Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Introduction to Digital System Design Chapter 1 1 Outline 1. Why Digital? 2. Device Technologies 3. System Representation 4. Abstraction 5. Development Tasks 6. Development Flow Chapter 1 2 1. Why Digital
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Digital IC Design Flow
 Collège Militaire Royal du Canada (Cadence University Alliance Program Member) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Départment de Génie Electrique et Informatique RMC Microelectronics Lab
Collège Militaire Royal du Canada (Cadence University Alliance Program Member) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Départment de Génie Electrique et Informatique RMC Microelectronics Lab
Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA. Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Quartus II 1
 (DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
(DSF) Quartus II Stand: Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] Quartus II 1 Quartus II Software Design Series : Foundation 2007 Altera
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog
 A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
A New Paradigm for Synchronous State Machine Design in Verilog Randy Nuss Copyright 1999 Idea Consulting Introduction Synchronous State Machines are one of the most common building blocks in modern digital
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy
 1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
1. Memory technology & Hierarchy RAM types Advances in Computer Architecture Andy D. Pimentel Memory wall Memory wall = divergence between CPU and RAM speed We can increase bandwidth by introducing concurrency
State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop
 Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop Michael Holmes Manager, Mixed Signal ASIC/SoC
Photos placed in horizontal position with even amount of white space between photos and header State-of-Art (SoA) System-on-Chip (SoC) Design HPC SoC Workshop Michael Holmes Manager, Mixed Signal ASIC/SoC
Hardware Implementation of Improved Adaptive NoC Router with Flit Flow History based Load Balancing Selection Strategy
 Hardware Implementation of Improved Adaptive NoC Rer with Flit Flow History based Load Balancing Selection Strategy Parag Parandkar 1, Sumant Katiyal 2, Geetesh Kwatra 3 1,3 Research Scholar, School of
Hardware Implementation of Improved Adaptive NoC Rer with Flit Flow History based Load Balancing Selection Strategy Parag Parandkar 1, Sumant Katiyal 2, Geetesh Kwatra 3 1,3 Research Scholar, School of
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected]. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: [email protected] 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Hunting Asynchronous CDC Violations in the Wild
 Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
Hunting Asynchronous Violations in the Wild Chris Kwok Principal Engineer May 4, 2015 is the #2 Verification Problem Why is a Big Problem: 10 or More Clock Domains are Common Even FPGA Users Are Suffering
A Verilog HDL Test Bench Primer Application Note
 A Verilog HDL Test Bench Primer Application Note Table of Contents Introduction...1 Overview...1 The Device Under Test (D.U.T.)...1 The Test Bench...1 Instantiations...2 Figure 1- DUT Instantiation...2
A Verilog HDL Test Bench Primer Application Note Table of Contents Introduction...1 Overview...1 The Device Under Test (D.U.T.)...1 The Test Bench...1 Instantiations...2 Figure 1- DUT Instantiation...2
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic
 Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Example-driven Interconnect Synthesis for Heterogeneous Coarse-Grain Reconfigurable Logic Clifford Wolf, Johann Glaser, Florian Schupfer, Jan Haase, Christoph Grimm Computer Technology /99 Overview Ultra-Low-Power
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines. Memory elements. Memory element terminology. Clock terminology
 Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
Topics of Chapter 5 Sequential Machines Memory elements Memory elements. Basics of sequential machines. Clocking issues. Two-phase clocking. Testing of combinational (Chapter 4) and sequential (Chapter
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
Fault Modeling. Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults. Transistor faults Summary
 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Getting the Most Out of Synthesis
 Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
Outline Getting the Most Out of Synthesis Dr. Paul D. Franzon 1. Timing Optimization Approaches 2. Area Optimization Approaches 3. Design Partitioning References 1. Smith and Franzon, Chapter 11 2. D.Smith,
Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed VLSI
 International Journal of Advances in Engineering Science and Technology 225 www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaest/ and www.ijaestonline.com ISSN: 2319-1120 Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed
International Journal of Advances in Engineering Science and Technology 225 www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaest/ and www.ijaestonline.com ISSN: 2319-1120 Two-Phase Clocking Scheme for Low-Power and High- Speed
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques
 Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
Finite State Machine Design and VHDL Coding Techniques Iuliana CHIUCHISAN, Alin Dan POTORAC, Adrian GRAUR "Stefan cel Mare" University of Suceava str.universitatii nr.13, RO-720229 Suceava [email protected],
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Clock Network. Clock Power
 Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Power Reduction Techniques in the SoC Network Low Power Design for SoCs ASIC Tutorial SoC.1 Power Why clock power is important/large» Generally the signal with the highest frequency» Typically drives a
Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin
 BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
BUS ARCHITECTURES Lizy Kurian John Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas as Austin Keywords: Bus standards, PCI bus, ISA bus, Bus protocols, Serial Buses, USB, IEEE 1394
Figure 1 FPGA Growth and Usage Trends
 White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
White Paper Avoiding PCB Design Mistakes in FPGA-Based Systems System design using FPGAs is significantly different from the regular ASIC and processor based system design. In this white paper, we will
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops
 CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
CHAPTER 11: Flip Flops In this chapter, you will be building the part of the circuit that controls the command sequencing. The required circuit must operate the counter and the memory chip. When the teach
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Route Power 10 Connect Powerpin 10.1 Route Special Route 10.2 Net(s): VSS VDD
 SOCE Lab (2/2): Clock Tree Synthesis and Routing Lab materials are available at ~cvsd/cur/soce/powerplan.tar.gz Please untar the file in the folder SOCE_Lab before lab 1 Open SOC Encounter 1.1 % source
SOCE Lab (2/2): Clock Tree Synthesis and Routing Lab materials are available at ~cvsd/cur/soce/powerplan.tar.gz Please untar the file in the folder SOCE_Lab before lab 1 Open SOC Encounter 1.1 % source
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC)
 Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
Testing of Digital System-on- Chip (SoC) 1 Outline of the Talk Introduction to system-on-chip (SoC) design Approaches to SoC design SoC test requirements and challenges Core test wrapper P1500 core test
LatticeECP3 High-Speed I/O Interface
 April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1180 LatticeECP3 devices support high-speed I/O interfaces, including Double Data Rate (DDR) and Single Data Rate (SDR) interfaces, using the logic built into the
April 2013 Introduction Technical Note TN1180 LatticeECP3 devices support high-speed I/O interfaces, including Double Data Rate (DDR) and Single Data Rate (SDR) interfaces, using the logic built into the
The implementation and performance/cost/power analysis of the network security accelerator on SoC applications
 The implementation and performance/cost/power analysis of the network security accelerator on SoC applications Ruei-Ting Gu [email protected] Kuo-Huang Chung [email protected]
The implementation and performance/cost/power analysis of the network security accelerator on SoC applications Ruei-Ting Gu [email protected] Kuo-Huang Chung [email protected]
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors
 Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Low Power AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Processors Hot Chips 2004 Presenter: Marius Evers Block Diagram of AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron Based on AMD s 8 th generation architecture AMD Athlon 64 and AMD
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users
 Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler
 ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore Multicore Processor Hierarchical Implementation with IC Compiler DAC 2008 Philip Watson Philip Watson Implementation Environment Program Manager ARM Ltd Background - Who Are We? Processor
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design
 Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems 路 論 Chapter 15 System-Level Physical Design Dept. of Electronic Engineering National Chin-Yi University of Technology Fall 2007 Outline Clocked Flip-flops CMOS
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745. Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation
 Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
Testing & Verification of Digital Circuits ECE/CS 5745/6745 Hardware Verification using Symbolic Computation Instructor: Priyank Kalla ([email protected]) 3 Credits Mon, Wed, 1:25-2:45pm, WEB L105 Office
VLSI Design Verification and Testing
 VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
VLSI Design Verification and Testing Instructor Chintan Patel (Contact using email: [email protected]). Text Michael L. Bushnell and Vishwani D. Agrawal, Essentials of Electronic Testing, for Digital,
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter
 Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Serial port interface for microcontroller embedded into integrated power meter Mr. Borisav Jovanović, Prof. dr. Predrag Petković, Prof. dr. Milunka Damnjanović, Faculty of Electronic Engineering Nis, Serbia
Experiment # 9. Clock generator circuits & Counters. Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa
 Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
Experiment # 9 Clock generator circuits & Counters Eng. Waleed Y. Mousa 1. Objectives: 1. Understanding the principles and construction of Clock generator. 2. To be familiar with clock pulse generation
CONSTRAINT RANDOM VERIFICATION OF NETWORK ROUTER FOR SYSTEM ON CHIP APPLICATION
 CONSTRAINT RANDOM VERIFICATION OF NETWORK ROUTER FOR SYSTEM ON CHIP APPLICATION T.S Ghouse Basha 1, P. Santhamma 2, S. Santhi 3 1 Associate Professor & Head, Department Electronic & Communication Engineering,
CONSTRAINT RANDOM VERIFICATION OF NETWORK ROUTER FOR SYSTEM ON CHIP APPLICATION T.S Ghouse Basha 1, P. Santhamma 2, S. Santhi 3 1 Associate Professor & Head, Department Electronic & Communication Engineering,
Case Study: Improving FPGA Design Speed with Floorplanning
 Case Study: Improving FPGA Design Speed with Floorplanning - An introduction to Xilinx PlanAhead 10.1 by Consultant Kent Salomonsen ([email protected]) Picture this: the RTL is simulating
Case Study: Improving FPGA Design Speed with Floorplanning - An introduction to Xilinx PlanAhead 10.1 by Consultant Kent Salomonsen ([email protected]) Picture this: the RTL is simulating
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine
 The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
The 104 Duke_ACC Machine The goal of the next two lessons is to design and simulate a simple accumulator-based processor. The specifications for this processor and some of the QuartusII design components
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL
 FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS
 SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
SOLVING HIGH-SPEED MEMORY INTERFACE CHALLENGES WITH LOW-COST FPGAS A Lattice Semiconductor White Paper May 2005 Lattice Semiconductor 5555 Northeast Moore Ct. Hillsboro, Oregon 97124 USA Telephone: (503)
Memory unit. 2 k words. n bits per word
 9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
9- k address lines Read n data input lines Memory unit 2 k words n bits per word n data output lines 24 Pearson Education, Inc M Morris Mano & Charles R Kime 9-2 Memory address Binary Decimal Memory contents
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications
 Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
EXPERIMENT 8. Flip-Flops and Sequential Circuits I. Introduction I.a. Objectives The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the basic operational principles of flip-flops and counters.
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices. John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division
 Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Introduction to Programmable Logic Devices John Coughlan RAL Technology Department Detector & Electronics Division PPD Lectures Programmable Logic is Key Underlying Technology. First-Level and High-Level
Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO Faculty of Engineering E&CE 438: Digital Integrated Circuits Sequential 4-bit Adder Design Report Prepared by: Ian Hung (ixxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Annette Lo (axxxxxx), 99XXXXXX Pamela
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices. Chapter 10 Counters. Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies
 ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
ETEC 2301 Programmable Logic Devices Chapter 10 Counters Shawnee State University Department of Industrial and Engineering Technologies Copyright 2007 by Janna B. Gallaher Asynchronous Counter Operation
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
Lecture 7: Clocking of VLSI Systems MAH, AEN EE271 Lecture 7 1 Overview Reading Wolf 5.3 Two-Phase Clocking (good description) W&E 5.5.1, 5.5.2, 5.5.3, 5.5.4, 5.5.9, 5.5.10 - Clocking Note: The analysis
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Computer Architecture Random Access Memory Technologies 2015. április 2. Budapest Gábor Horváth associate professor BUTE Dept. Of Networked Systems and Services [email protected] 2 Storing data Possible
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL
 2011 2nd International Conference on Networking and Information Technology IPCSIT vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL Muhammad Ali
2011 2nd International Conference on Networking and Information Technology IPCSIT vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Design and Implementation of Vending Machine using Verilog HDL Muhammad Ali
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Space product assurance
 ECSS-Q-ST-60-02C Space product assurance ASIC and FPGA development ECSS Secretariat ESA-ESTEC Requirements & Standards Division Noordwijk, The Netherlands Foreword This Standard is one of the series of
ECSS-Q-ST-60-02C Space product assurance ASIC and FPGA development ECSS Secretariat ESA-ESTEC Requirements & Standards Division Noordwijk, The Netherlands Foreword This Standard is one of the series of
Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC
 Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, Lukas Perktold DLL design review meeting, 16 03 2011 Outline Introduction Purpose and objectives Reminder Challenges of
Status of the design of the TDC for the GTK TDCpix ASIC Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, Lukas Perktold DLL design review meeting, 16 03 2011 Outline Introduction Purpose and objectives Reminder Challenges of
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 11 Memory Management Computer Architecture Part 11 page 1 of 44 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte, M.Sc. Benjamin
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 8: Clocking of VLSI Systems David Harris Harvey Mudd College [email protected] Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH
TIMING DIAGRAM O 8085
 5 TIMING DIAGRAM O 8085 5.1 INTRODUCTION Timing diagram is the display of initiation of read/write and transfer of data operations under the control of 3-status signals IO / M, S 1, and S 0. As the heartbeat
5 TIMING DIAGRAM O 8085 5.1 INTRODUCTION Timing diagram is the display of initiation of read/write and transfer of data operations under the control of 3-status signals IO / M, S 1, and S 0. As the heartbeat
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
2003 IC/CAD Contest Problem 5: Clock Tree Optimization for Useful Skew
 2003 IC/CAD Contest Problem 5: Clock Tree Optimization for Useful Skew Source: Global UniChip Corp. February 11, 2003, revised on March 21, 2003 & April 22, 2003 1. Introduction There are two approaches
2003 IC/CAD Contest Problem 5: Clock Tree Optimization for Useful Skew Source: Global UniChip Corp. February 11, 2003, revised on March 21, 2003 & April 22, 2003 1. Introduction There are two approaches
Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow
 Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
Design Verification and Test of Digital VLSI Circuits NPTEL Video Course Module-I Lecture-I Introduction to Digital VLSI Design Flow Introduction The functionality of electronics equipments and gadgets
MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE
 in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
Life Cycle of a Memory Request. Ring Example: 2 requests for lock 17
 Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
Life Cycle of a Memory Request (1) Use AQR or AQW to place address in AQ (2) If A[31]==0, check for hit in DCache Ring (3) Read Hit: place cache word in RQ; Write Hit: replace cache word with WQ RDDest/RDreturn
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8
 GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
GETTING STARTED WITH PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES, THE 16V8 AND 20V8 Robert G. Brown All Rights Reserved August 25, 2000 Alta Engineering 58 Cedar Lane New Hartford, CT 06057-2905 (860) 489-8003 www.alta-engineering.com
Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms
 Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms Brian Sibilsky and Fredrik Brosser April 2016 Page 1 of 17 Contents Introduction... 3 Gating... 4 RAM Implementation... 7 esign Partitioning...
Prototyping ARM Cortex -A Processors using FPGA platforms Brian Sibilsky and Fredrik Brosser April 2016 Page 1 of 17 Contents Introduction... 3 Gating... 4 RAM Implementation... 7 esign Partitioning...
OpenSoC Fabric: On-Chip Network Generator
 OpenSoC Fabric: On-Chip Network Generator Using Chisel to Generate a Parameterizable On-Chip Interconnect Fabric Farzad Fatollahi-Fard, David Donofrio, George Michelogiannakis, John Shalf MODSIM 2014 Presentation
OpenSoC Fabric: On-Chip Network Generator Using Chisel to Generate a Parameterizable On-Chip Interconnect Fabric Farzad Fatollahi-Fard, David Donofrio, George Michelogiannakis, John Shalf MODSIM 2014 Presentation
DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL
 IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: [email protected]
IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 15-20 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF LSR OF THE MPLS NETWORK USING VHDL Suvarna A. Jadhav 1 and U.L. Bombale 2 1,2 Department of Technology Shivaji university, Kolhapur, 1 E-mail: [email protected]
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING - Microprocessor Systems - Mitchell Aaron Thornton
 MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS Mitchell Aaron Thornton, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Mississippi State University, PO Box 9571, Mississippi State, MS, 39762-9571, United States. Keywords:
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEMS Mitchell Aaron Thornton, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Mississippi State University, PO Box 9571, Mississippi State, MS, 39762-9571, United States. Keywords:
PCB Project (*.PrjPcb)
 Project Essentials Summary The basis of every design captured in Altium Designer is the project. This application note outlines the different kinds of projects, techniques for working on projects and how
Project Essentials Summary The basis of every design captured in Altium Designer is the project. This application note outlines the different kinds of projects, techniques for working on projects and how
OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1
 IBM POWER 6 MICROPROCESSOR OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1 WHAT S IBM POWER 6 MICROPOCESSOR The IBM POWER6 microprocessor powers the new IBM i-series* and p-series* systems. It s based on IBM POWER5
IBM POWER 6 MICROPROCESSOR OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1 WHAT S IBM POWER 6 MICROPOCESSOR The IBM POWER6 microprocessor powers the new IBM i-series* and p-series* systems. It s based on IBM POWER5
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Asynchronous & Synchronous Reset Design Techniques - Part Deux
 Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
Clifford E. Cummings Don Mills Steve Golson Sunburst Design, Inc. LCDM Engineering Trilobyte Systems [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] ABSTRACT This paper will investigate
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI. Digital Systems Design. Digital Circuits Advanced Topics
 PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
PROGETTO DI SISTEMI ELETTRONICI DIGITALI Digital Systems Design Digital Circuits Advanced Topics 1 Sequential circuit and metastability 2 Sequential circuit - FSM A Sequential circuit contains: Storage
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs
 Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
Rapid System Prototyping with FPGAs By R.C. Coferand Benjamin F. Harding AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Newnes is an imprint of
