VHDL Implementation of Reversible Full Adder using PERES Gate
|
|
|
- Randall Daniels
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VHDL Implementation of Reversible Full Adder using PERES Gate Md. Riyaj 1, Anshul Gangwar 2, Gagan Goyal 3 M-tech ScholarSuresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur,India 1, M-tech ScholarSuresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur,India 2, M-tech Scholar Jaipur National University, Jaipur,India 3 Abstract In low power vlsi design and power optimization reversible logic method is being used more frequently. It is also the fundamental need for the emerging field of the quantum computing,digital signal processing and communications. The use of reversible logic in vlsi design has many advantages because it reduces number of gates and garbage outputs. When we use a logically irreversible gate we dissipate energy into the environment. The loss of energy equals to the information loss. One bit information lost dissipates KT ln2 of energy. By reversible logic we can reduce power dissipation. In reversible logic number of input equals to the number of outputs. i.e k*k. All the outputs are not used as input to other gate is called garbage output. This paper presents quantum implementation and combinational circuit of all basic reversible gates and its VHDL code. All reversible logic gates are verified andsimulatedbyxilinx8.2i. Keywords Reversible logic,not gate,feynman gate, PERES gate,,tr gate I. INTRODUCTION To increase the speed the clock frequency must be increased. In VLSI systems increase in number of transistors makes the system complex which[1] further increase the power consumed by the system. Moreover any Boolean function can be implemented by using logic of reversible logic gates as it has already been proved. When an input is applied to the reversible gate, a logical operation is performed and also there is los+s of some information which is dissipated as heat.so we can conclude that power dissipiation is the main concern for both producers and consumers. A reversible logic gate gives a unique output pattern for for each input pattern. It has k-inputs and k- outputs, hence denoted by k*k. In reversible logic gates we have one more aspect to focus on than that of number of gates,is the number of garbage outputs. Garbage and T is the absolute temperature at which the operation is performed. To reduce the power dissipation and to prevent the loss of information reversible logic is used it has application[3] in different field like as in field of low power computing quantum computing optical computing and other encoding computing technologies. In a reversible circuit the input vector can be reconstructed from the output vector. Not only outputs can be calculated from the input but also the inputs can be reconstructed the number of input and output are equal. It finds application in low power CMOS design, optical computing, DNA computing quantum computing, nano technology, bioinformatics and thermodynamic technology. in quantum circuits reversible logic gates are used. Fanout and feedback is not permitted in reversible logic gates. NOT gate is the simplest 1*1 reversible gate. An example of a 2*2 reversible gate is controlled gate(cnot).examples for 3*3 reversible gates are F,TG,PG and TR gate. The performance of the reversible gate is calculated by calculating the quantum cost by counting the number of V, V + and CNOT gates. Some properties of V and V + quantum gates are given below: V*V=NOT V* V + =V + * V= -1 V + * V = NOT II. BASIC REVERSIBLE GATE A. NOT Gate The reversible 1*1 gate[4] is NOT gate with zero quantum cost is as shown below. outputs are those outputs from a reversible ciruit that are not used as an output. In low power VLSI design another problem is the solution of Landaver s principle. It states that logical [2]computation of Fig 1 Quantum implementation of NOT gate irreversible gates generate KT*log2 Joules of heat energy on loss of every bit of information. K is the Bpltzman constant 622
2 Fig 2 1*1 NOT GATE architecture ckt of feynman is Y <=P xor Q; end ckt; C. PERES GATE The reversible 3*3 gate with quantum cost of four having mapping input (P,Q,R) to output(x,y,z) is as shown in figure. Fig 7 Quantum implementation of PERES gate Fig 3 Combinational circuit of NOT gate entity not is port(a : in std_logic; m :out std_logic); end not; B. FEYNMAN/CNOT GATE The reversible 2*2 gate with quantum cost of one having mapping [5]input (P,Q) to output(x,y) is as shown in figure. Fig 8 3*3 PERES gate Fig 4 Quantum implementation of FEYNMAN gate Fig 5 2*2 FEYNMAN gate Fig 9 Combinational circuit of PERES GATE Fig 6 Combinational circuit of FEYNMAN gate entity feynman is port(p,q : in std_logic; X,Y :out std_logic); end feynman; entity peres is port(p,q,r : in std_logic; X,Y,Z :out std_logic); end peres; architecture prs of peres is signal S1: std_logic 623
3 S1 <= P and Q; Y <= P xor Q; Z <= S1 xor R; end prs; 2.4 TR GATE III. PURPOSED PERES FULL ADDER Fig 13 PERES full adder Fig 10 Quantum implementation of TR gate Fig 11 3*3 TR gate Fig 12 Combinational circuit of TR gate entity trgate is aport(p,q,r : in std_logic; X,Y,Z :out std_logic); end trgate; architecture tr of trgate is signal Bbar,S1: std_logic; S1 <= P and Qbar; Y <= P xor Q; Z <= S1 xor R; end tr; Fig 14 Combinational crcuit of PERES full adder. Library ieee; USE ieee std_logic_1164 all; USE ieee numeric_std. all; Entity FA is Port (P: in std_logic; Q: in std_logic; Cin: in std_logic; Zero: in std_logic; X: out std_logic; Y: out std_logic; S: out std_logic; Cout: out std_logic; End FA ; Architecture behavioral of FA is Signal T1 :std_logic; Signal T2 :std_logic; Begin T1 <= P xor Q T2 <= (P xor Q) xor zero; Y <= T1; S <= T1 xor Cin; Cout <= (T1 and Cin) xor T2; End FA IV. RESULT The purposed PERES full adder as shown in figre 13&14 are implemented and resulted by using VHDL and simulated in Xilinx 8.2 i. The RTL schematic diagram and simulated results shown in figre 15 and figure 16 respectively. 624
4 Fig 15(A) RTL schematic diagram for PERES full adder Fig 16(A) Test Bench Waveform & simulation with results Fig 15(B) RTL schematic diagram for PERES full adder Fig 16(B) Test Bench Waveform & simulation with results V. CONCLUSION Reversible gate are used to implement arithmatic circuit using full adder. The main focus of this paper is the proposal of new reversible 4*4 PERES gate. The purposed PERES gate is used to design full adder. It is proved that the purposed PERES full adder is better than the existing counterparts in literature in terms of garbage outputs. By using purposed PERES full adder we can design large reversible systems. Here we can 625
5 calculate the power consumption and compare it with the irreversible full adder. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I wish to express my thanks to Mr. Rashid Hussain H.O.D electronics and communication Suresh Gyan Vihar university jaipur and my colleague. REFERENCES 1. T. Nagababu A low power adder using reversible logic gates IJERT Volume 1 issue 3 Nov Homework report reversible adder implementation in VHDL 3. Mr Devendra goyal VHDL implementation of reversible logic gates. 4. Rangaraju H.G. LOW POWER REVERSIBLE PARALLEL BINARY ADDER 5. V. Kanalakannan Design of adder /subtractor circuits based on based on reversible logic gate IJAREEIE vol 2 issue8 august Prashanth N.G. design and synthesis of fault tolerent full adder/subtractor using reversible logic gates IJERA vol 3 issue 4 july aug A. Kamraj design of 8-bit arithmatic processor unit based on reversible logic Global journals volume 13 issue Lakshmi viswanath Design and analysis of 16 bit reversible ALU IOSRJCE volume 1 Issue 1 june Md. Sajjad hussain design of control unit for low power ALU with a barrel shifter using reversible logic 10. Ravish Aradhya design of control unit for low power ALU with a barrel shifter using reversible logic IJSER volume 2 issue 9 september
A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder Circuits
 A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder s Himanshu Thapliyal Center for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology Hyderabad-500019,
A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder s Himanshu Thapliyal Center for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology Hyderabad-500019,
AN IMPROVED DESIGN OF REVERSIBLE BINARY TO BINARY CODED DECIMAL CONVERTER FOR BINARY CODED DECIMAL MULTIPLICATION
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (1): 69-73, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.69.73 Published Online 11 (1) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) AN IMPROVED
American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (1): 69-73, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.69.73 Published Online 11 (1) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) AN IMPROVED
A Beginning in the Reversible Logic Synthesis of Sequential Circuits
 A Beginning in the Reversible Logic Synthesis of Sequential s Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas Centre for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad,
A Beginning in the Reversible Logic Synthesis of Sequential s Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas Centre for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad,
NEW adder cells are useful for designing larger circuits despite increase in transistor count by four per cell.
 CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
Let s put together a Manual Processor
 Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates
 An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas ([email protected], [email protected]) Center
An Extension to DNA Based Fredkin Gate Circuits: Design of Reversible Sequential Circuits using Fredkin Gates Himanshu Thapliyal and M.B Srinivas ([email protected], [email protected]) Center
CSE140 Homework #7 - Solution
 CSE140 Spring2013 CSE140 Homework #7 - Solution You must SHOW ALL STEPS for obtaining the solution. Reporting the correct answer, without showing the work performed at each step will result in getting
CSE140 Spring2013 CSE140 Homework #7 - Solution You must SHOW ALL STEPS for obtaining the solution. Reporting the correct answer, without showing the work performed at each step will result in getting
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF 4-BIT AND 8-BIT REVERSIBLE BARREL SHIFTER DESIGNS USING REVKIT
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF 4-BIT AND 8-BIT REVERSIBLE BARREL SHIFTER DESIGNS USING REVKIT Hariprasad R. 1, Ganesh R. 1, Ravi S. 2, Marimuthu R. 1 and Balamurugan S. 1 1 School of Electrical Engineering, VIT
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF 4-BIT AND 8-BIT REVERSIBLE BARREL SHIFTER DESIGNS USING REVKIT Hariprasad R. 1, Ganesh R. 1, Ravi S. 2, Marimuthu R. 1 and Balamurugan S. 1 1 School of Electrical Engineering, VIT
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders
 Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path
 ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
ECE410 Design Project Spring 2008 Design and Characterization of a CMOS 8-bit Microprocessor Data Path Project Summary This project involves the schematic and layout design of an 8-bit microprocessor data
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research)
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) ISSN (Print): 2279-0020 ISSN (Online): 2279-0039 International
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) ISSN (Print): 2279-0020 ISSN (Online): 2279-0039 International
Understanding Logic Design
 Understanding Logic Design ppendix of your Textbook does not have the needed background information. This document supplements it. When you write add DD R0, R1, R2, you imagine something like this: R1
Understanding Logic Design ppendix of your Textbook does not have the needed background information. This document supplements it. When you write add DD R0, R1, R2, you imagine something like this: R1
Xilinx ISE. <Release Version: 10.1i> Tutorial. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York New Paltz
 Xilinx ISE Tutorial Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York New Paltz Fall 2010 Baback Izadi Starting the ISE Software Start ISE from the
Xilinx ISE Tutorial Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of New York New Paltz Fall 2010 Baback Izadi Starting the ISE Software Start ISE from the
Guru Ghasidas Vishwavidyalaya, Bilaspur (C.G.) Institute of Technology. Electronics & Communication Engineering. B.
 Guru Ghasidas Vishwavidyalaya, Bilaspur (C.G.) Institute of Technology Electronics & Communication Engineering B.Tech III Semester 1. Electronic Devices Laboratory 2. Digital Logic Circuit Laboratory 3.
Guru Ghasidas Vishwavidyalaya, Bilaspur (C.G.) Institute of Technology Electronics & Communication Engineering B.Tech III Semester 1. Electronic Devices Laboratory 2. Digital Logic Circuit Laboratory 3.
Fault Modeling. Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults. Transistor faults Summary
 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes of stuck-at
Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course
 Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course Prof. Swati Agrawal, BE, MS (SUNY, Buffalo, NY USA) 1 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Bhilai Institute
Verification & Design Techniques Used in a Graduate Level VHDL Course Prof. Swati Agrawal, BE, MS (SUNY, Buffalo, NY USA) 1 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Bhilai Institute
Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells
 Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells Sushil B. Bhaisare 1, Sonalee P. Suryawanshi 2, Sagar P. Soitkar 3 1 Lecturer in Electronics Department, Nagpur University, G.H.R.I.E.T.W. Nagpur,
Design of Low Power One-Bit Hybrid-CMOS Full Adder Cells Sushil B. Bhaisare 1, Sonalee P. Suryawanshi 2, Sagar P. Soitkar 3 1 Lecturer in Electronics Department, Nagpur University, G.H.R.I.E.T.W. Nagpur,
ONLINE TESTING IN TERNARY REVERSIBLE LOGIC
 ONLINE TESTING IN TERNARY REVERSIBLE LOGIC MD. RAQIBUR RAHMAN Bachelor of Science, University of Dhaka, 2004 Master of Science, University of Dhaka, 2005 A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies
ONLINE TESTING IN TERNARY REVERSIBLE LOGIC MD. RAQIBUR RAHMAN Bachelor of Science, University of Dhaka, 2004 Master of Science, University of Dhaka, 2005 A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies
VHDL Test Bench Tutorial
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory VHDL Test Bench Tutorial Purpose The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to automate
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory VHDL Test Bench Tutorial Purpose The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to automate
Implementation of Modified Booth Algorithm (Radix 4) and its Comparison with Booth Algorithm (Radix-2)
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT
 216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units
 Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY
 DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS
 COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!!
 ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
ECE 3401! Digital Systems Design! Lecture 1 - Introduction!! Course Basics Classes: Tu/Th 11-12:15, ITE 127 Instructor Mohammad Tehranipoor Office hours: T 1-2pm, or upon appointments @ ITE 441 Email:
Keywords Quantum logic gates, Quantum computing, Logic gate, Quantum computer
 Volume 3 Issue 10 October 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com An Introduction
Volume 3 Issue 10 October 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com An Introduction
earlier in the semester: The Full adder above adds two bits and the output is at the end. So if we do this eight times, we would have an 8-bit adder.
 The circuit created is an 8-bit adder. The 8-bit adder adds two 8-bit binary inputs and the result is produced in the output. In order to create a Full 8-bit adder, I could use eight Full -bit adders and
The circuit created is an 8-bit adder. The 8-bit adder adds two 8-bit binary inputs and the result is produced in the output. In order to create a Full 8-bit adder, I could use eight Full -bit adders and
9/14/2011 14.9.2011 8:38
 Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
Algorithms and Implementation Platforms for Wireless Communications TLT-9706/ TKT-9636 (Seminar Course) BASICS OF FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Waqar Hussain [email protected] Department of Computer
5 Combinatorial Components. 5.0 Full adder. Full subtractor
 5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
5 Combatorial Components Use for data transformation, manipulation, terconnection, and for control: arithmetic operations - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. logic operations - AND, OR,
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano
 Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes ([email protected]) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
ECE 3401 Lecture 7. Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
ECE 3401 Lecture 7 Concurrent Statements & Sequential Statements (Process) Concurrent Statements VHDL provides four different types of concurrent statements namely: Signal Assignment Statement Simple Assignment
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths
 An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC
 10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected] P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected]
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected] P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA [email protected]
How To Fix A 3 Bit Error In Data From A Data Point To A Bit Code (Data Point) With A Power Source (Data Source) And A Power Cell (Power Source)
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF 4D-PARITY BASED DATA CODING TECHNIQUE Vijay Tawar 1, Rajani Gupta 2 1 Student, KNPCST, Hoshangabad Road, Misrod, Bhopal, Pin no.462047 2 Head of Department (EC), KNPCST, Hoshangabad
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF 4D-PARITY BASED DATA CODING TECHNIQUE Vijay Tawar 1, Rajani Gupta 2 1 Student, KNPCST, Hoshangabad Road, Misrod, Bhopal, Pin no.462047 2 Head of Department (EC), KNPCST, Hoshangabad
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic
 CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 3.1 Introduction 121 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123 3.2.2 Boolean Identities 124 3.2.3 Simplification of Boolean Expressions 126 3.2.4
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL
 Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
Digital Design with Synthesizable VHDL Prof. Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 2012 Combinational Logic in a Dataflow Style Hierarchy: Instantiating Components (entities) Combinational Logic
University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54
 Fall 2005 Instructor Texts University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54 Lab: Section 1: OSS LL14 Tuesday
Fall 2005 Instructor Texts University of St. Thomas ENGR 230 ---- Digital Design 4 Credit Course Monday, Wednesday, Friday from 1:35 p.m. to 2:40 p.m. Lecture: Room OWS LL54 Lab: Section 1: OSS LL14 Tuesday
Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher
 International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
International Journal of Computer Science & Network Security VOL.10 No.8, 2010 Hardware Implementation of the Stone Metamorphic Cipher Rabie A. Mahmoud 1, Magdy Saeb 2 1. Department of Mathematics, Faculty
1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1.
 File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
File: chap04, Chapter 04 1. True or False? A voltage level in the range 0 to 2 volts is interpreted as a binary 1. 2. True or False? A gate is a device that accepts a single input signal and produces one
EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors
 EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors I. Introduction I.a. Objectives In this experiment, parallel adders, subtractors and complementors will be designed and investigated. In the
EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors I. Introduction I.a. Objectives In this experiment, parallel adders, subtractors and complementors will be designed and investigated. In the
CMOS Binary Full Adder
 CMOS Binary Full Adder A Survey of Possible Implementations Group : Eren Turgay Aaron Daniels Michael Bacelieri William Berry - - Table of Contents Key Terminology...- - Introduction...- 3 - Design Architectures...-
CMOS Binary Full Adder A Survey of Possible Implementations Group : Eren Turgay Aaron Daniels Michael Bacelieri William Berry - - Table of Contents Key Terminology...- - Introduction...- 3 - Design Architectures...-
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0
 Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
Optimization and Comparison of 4-Stage Inverter, 2-i/p NAND Gate, 2-i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort
 Optimization and Comparison of -Stage, -i/p NND Gate, -i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort Satyajit nand *, and P.K.Ghosh ** * Mody Institute of Technology & Science/ECE, Lakshmangarh,
Optimization and Comparison of -Stage, -i/p NND Gate, -i/p NOR Gate Driving Standard Load By Using Logical Effort Satyajit nand *, and P.K.Ghosh ** * Mody Institute of Technology & Science/ECE, Lakshmangarh,
Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ Jan. 25 ǁ PP.9-4 Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA Chandrasekhar
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ Jan. 25 ǁ PP.9-4 Implementation and Design of AES S-Box on FPGA Chandrasekhar
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users
 Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Quartus II Introduction for VHDL Users This tutorial presents an introduction to the Quartus II software. It gives a general overview of a typical CAD flow for designing circuits that are implemented by
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 9 - Register Transfer and Microoperations Microoperations Digital systems are modular in nature, with modules containing registers, decoders, arithmetic
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. For a complete data sheet, please also download:
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 14 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 50% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem
 A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design. Part 3: Verilog Tutorial. http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Part 3: Verilog Tutorial http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/ece232/ Basic Verilog module ();
DDS. 16-bit Direct Digital Synthesizer / Periodic waveform generator Rev. 1.4. Key Design Features. Block Diagram. Generic Parameters.
 Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core 16-bit signed output samples 32-bit phase accumulator (tuning word) 32-bit phase shift feature Phase resolution of 2π/2
Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core 16-bit signed output samples 32-bit phase accumulator (tuning word) 32-bit phase shift feature Phase resolution of 2π/2
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications
 Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Step : Create Dependency Graph for Data Path Step b: 8-way Addition? So, the data operations are: 8 multiplications one 8-way addition Balanced binary
 RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
RTL Design RTL Overview Gate-level design is now rare! design automation is necessary to manage the complexity of modern circuits only library designers use gates automated RTL synthesis is now almost
Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits
 Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Logical Effort of an Inverter
Module 4 : Propagation Delays in MOS Lecture 22 : Logical Effort Calculation of few Basic Logic Circuits Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Logical Effort of an Inverter
Gates. J. Robert Jump Department of Electrical And Computer Engineering Rice University Houston, TX 77251
 Gates J. Robert Jump Department of Electrical And Computer Engineering Rice University Houston, T 77251 1. The Evolution of Electronic Digital Devices...1 2. Logical Operations and the Behavior of Gates...2
Gates J. Robert Jump Department of Electrical And Computer Engineering Rice University Houston, T 77251 1. The Evolution of Electronic Digital Devices...1 2. Logical Operations and the Behavior of Gates...2
ASYNCHRONOUS COUNTERS
 LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
LB no.. SYNCHONOUS COUNTES. Introduction Counters are sequential logic circuits that counts the pulses applied at their clock input. They usually have 4 bits, delivering at the outputs the corresponding
Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design
 ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
ECE 561 Project 4-1 - Using Xilinx ISE for VHDL Based Design In this project you will learn to create a design module from VHDL code. With Xilinx ISE, you can easily create modules from VHDL code using
After opening the Programs> Xilinx ISE 8.1i > Project Navigator, you will come to this screen as start-up.
 After opening the Programs> Xilinx ISE 8.1i > Project Navigator, you will come to this screen as start-up. Start with a new project. Enter a project name and be sure to select Schematic as the Top-Level
After opening the Programs> Xilinx ISE 8.1i > Project Navigator, you will come to this screen as start-up. Start with a new project. Enter a project name and be sure to select Schematic as the Top-Level
IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR
 International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
International Journal of Engineering & Science Research IMPLEMENTATION OF BACKEND SYNTHESIS AND STATIC TIMING ANALYSIS OF PROCESSOR LOCAL BUS(PLB) PERFORMANCE MONITOR ABSTRACT Pathik Gandhi* 1, Milan Dalwadi
High Speed Gate Level Synchronous Full Adder Designs
 High Speed Gate Level Synchronous Full Adder Designs PADMANABHAN BALASUBRAMANIAN and NIKOS E. MASTORAKIS School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PL, UNITED
High Speed Gate Level Synchronous Full Adder Designs PADMANABHAN BALASUBRAMANIAN and NIKOS E. MASTORAKIS School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PL, UNITED
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition
 RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
RAPID PROTOTYPING OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS Second Edition A Tutorial Approach James O. Hamblen Georgia Institute of Technology Michael D. Furman Georgia Institute of Technology KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS Boston
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers
 High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers Mehta Shantanu Sheetal #1, Vigneswaran T. #2 # School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
High Speed and Efficient 4-Tap FIR Filter Design Using Modified ETA and Multipliers Mehta Shantanu Sheetal #1, Vigneswaran T. #2 # School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
Digital Logic Design. Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits. Pu-Jen Cheng
 Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Digital Logic Design Basics Combinational Circuits Sequential Circuits Pu-Jen Cheng Adapted from the slides prepared by S. Dandamudi for the book, Fundamentals of Computer Organization and Design. Introduction
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system
 Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
Design and analysis of flip flops for low power clocking system Gabariyala sabadini.c PG Scholar, VLSI design, Department of ECE,PSNA college of Engg and Tech, Dindigul,India. Jeya priyanka.p PG Scholar,
An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing
 2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
2009 International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC 2009) Proc.of CSIT vol.1 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore An Open Architecture through Nanocomputing Joby Joseph1and A.
Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor
 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number Page number 349 black chapter 7 Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and a Simple Processor 7. Ng f3, h7 h6 349 June 8, 22 5:56 vra235_ch7 Sheet number 2 Page number
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router
 Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Design and Verification of Nine port Network Router G. Sri Lakshmi 1, A Ganga Mani 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Pragathi Engineering College, Andhra
Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX
 White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
White Paper Testing Low Power Designs with Power-Aware Test Manage Manufacturing Test Power Issues with DFTMAX and TetraMAX April 2010 Cy Hay Product Manager, Synopsys Introduction The most important trend
Implementation Details
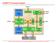 LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
LEON3-FT Processor System Scan-I/F FT FT Add-on Add-on 2 2 kbyte kbyte I- I- Cache Cache Scan Scan Test Test UART UART 0 0 UART UART 1 1 Serial 0 Serial 1 EJTAG LEON_3FT LEON_3FT Core Core 8 Reg. Windows
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z <= A; else Z <= B; end if; end process;
 if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
if-then else : 2-1 mux mux: process (A, B, Select) begin if (select= 1 ) then Z
Modeling Latches and Flip-flops
 Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Lab Workbook Introduction Sequential circuits are digital circuits in which the output depends not only on the present input (like combinatorial circuits), but also on the past sequence of inputs. In effect,
Aims and Objectives. E 3.05 Digital System Design. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus (1) Programmable Logic
 Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Aims and Objectives E 3.05 Digital System Design Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: [email protected] How to go
Multipliers. Introduction
 Multipliers Introduction Multipliers play an important role in today s digital signal processing and various other applications. With advances in technology, many researchers have tried and are trying
Multipliers Introduction Multipliers play an important role in today s digital signal processing and various other applications. With advances in technology, many researchers have tried and are trying
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS. IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE
 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic
 A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic Shawki Areibi Abstract Present industry practice has created a high demand for systems designers with knowledge and experience in using
A First Course in Digital Design Using VHDL and Programmable Logic Shawki Areibi Abstract Present industry practice has created a high demand for systems designers with knowledge and experience in using
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra
 Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Gates, Circuits, and Boolean Algebra Computers and Electricity A gate is a device that performs a basic operation on electrical signals Gates are combined into circuits to perform more complicated tasks
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology
 Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Conventional 6T SRAM Cell at 45nm Technology Nahid Rahman Department of electronics and communication FET-MITS (Deemed university), Lakshmangarh, India B. P. Singh Department
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: omputer Organization and Architecture Lecture 8: Registers and ounters Registers A register is a group of flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of data; n flip-flops are required to store
Systems I: omputer Organization and Architecture Lecture 8: Registers and ounters Registers A register is a group of flip-flops. Each flip-flop stores one bit of data; n flip-flops are required to store
System on Chip Design. Michael Nydegger
 Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
Short Questions, 26. February 2015 What is meant by the term n-well process? What does this mean for the n-type MOSFETs in your design? What is the meaning of the threshold voltage (practically)? What
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 13 / 40Gb/s COMMUNICATION ICS / PAPER 13.7 13.7 A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18µm CMOS Technology Jri Lee, Behzad Razavi University of California, Los Angeles, CA
Gray Code Generator and Decoder by Carsten Kristiansen Napier University. November 2004
 Gray Code Generator and Decoder by Carsten Kristiansen Napier University November 2004 Title page Author: Carsten Kristiansen. Napier No: 04007712. Assignment title: Design of a Gray Code Generator and
Gray Code Generator and Decoder by Carsten Kristiansen Napier University November 2004 Title page Author: Carsten Kristiansen. Napier No: 04007712. Assignment title: Design of a Gray Code Generator and
A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier using Dadda Algorithm
 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier using Dadda Algorithm Prakhi Agrawal 1, Prof. Shravan Sable 2, Dr. Rita Jain 3 M-Tech Research Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier using Dadda Algorithm Prakhi Agrawal 1, Prof. Shravan Sable 2, Dr. Rita Jain 3 M-Tech Research Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Implementation Of Clock Gating Logic By Matching Factored Forms A.kirankumari 1, P.P. Nagaraja Rao 2
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 7 July 2015, Page No. 13585-13600 Implementation Of Clock Gating Logic By Matching Factored Forms A.kirankumari
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 7 July 2015, Page No. 13585-13600 Implementation Of Clock Gating Logic By Matching Factored Forms A.kirankumari
CONTENTS PREFACE 1 INTRODUCTION 1 2 NUMBER SYSTEMS AND CODES 25. vii
 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is CONTENTS PREFACE xv 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 About Digital Design 1 1.2 Analog versus Digital 3 1.3 Digital Devices
2006 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is CONTENTS PREFACE xv 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 About Digital Design 1 1.2 Analog versus Digital 3 1.3 Digital Devices
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses.
 Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: [email protected]
Proceedings of the E2LP Workshop Warsaw, 2014, pp. 25 29 DOI: 10.15439/2014F672 ACSIS, Vol. 4 Design of Remote Laboratory dedicated to E2LP board for e-learning courses. Jan Piwiński Email: [email protected]
Combinational Logic Design
 Chapter 4 Combinational Logic Design The foundations for the design of digital logic circuits were established in the preceding chapters. The elements of Boolean algebra (two-element switching algebra
Chapter 4 Combinational Logic Design The foundations for the design of digital logic circuits were established in the preceding chapters. The elements of Boolean algebra (two-element switching algebra
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION
 Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Design and Synthesis INTRODUCTION The advances in digital design owe its progress to 3 factors. First the acceleration at which the CMOS technology has advanced in last few decades and the way
Digital Systems. Syllabus 8/18/2010 1
 Digital Systems Syllabus 1 Course Description: This course covers the design and implementation of digital systems. Topics include: combinational and sequential digital circuits, minimization methods,
Digital Systems Syllabus 1 Course Description: This course covers the design and implementation of digital systems. Topics include: combinational and sequential digital circuits, minimization methods,
Reconfigurable Low Area Complexity Filter Bank Architecture for Software Defined Radio
 Reconfigurable Low Area Complexity Filter Bank Architecture for Software Defined Radio 1 Anuradha S. Deshmukh, 2 Prof. M. N. Thakare, 3 Prof.G.D.Korde 1 M.Tech (VLSI) III rd sem Student, 2 Assistant Professor(Selection
Reconfigurable Low Area Complexity Filter Bank Architecture for Software Defined Radio 1 Anuradha S. Deshmukh, 2 Prof. M. N. Thakare, 3 Prof.G.D.Korde 1 M.Tech (VLSI) III rd sem Student, 2 Assistant Professor(Selection
AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores
 AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores Encryption/Decryption and Key Expansion Page 1 Revision History Date Version Description 24 February 2006 1.0 Initial draft. 15 March 2006 1.1 Block diagrams added. 26 March 2006
AES (Rijndael) IP-Cores Encryption/Decryption and Key Expansion Page 1 Revision History Date Version Description 24 February 2006 1.0 Initial draft. 15 March 2006 1.1 Block diagrams added. 26 March 2006
Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog
 Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and ystems Laboratory Lab 7 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To become familiar with continuous ments and procedural
Multiplexers Two Types + Verilog ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and ystems Laboratory Lab 7 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following: To become familiar with continuous ments and procedural
FAULT TOLERANCE FOR MULTIPROCESSOR SYSTEMS VIA TIME REDUNDANT TASK SCHEDULING
 FAULT TOLERANCE FOR MULTIPROCESSOR SYSTEMS VIA TIME REDUNDANT TASK SCHEDULING Hussain Al-Asaad and Alireza Sarvi Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California Davis, CA, U.S.A.
FAULT TOLERANCE FOR MULTIPROCESSOR SYSTEMS VIA TIME REDUNDANT TASK SCHEDULING Hussain Al-Asaad and Alireza Sarvi Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of California Davis, CA, U.S.A.
12. A B C A B C A B C 1 A B C A B C A B C JK-FF NETr
 2..,.,.. Flip-Flops :, Flip-Flops, Flip Flop. ( MOD)... -8 8, 7 ( ).. n Flip-Flops. n Flip-Flops : 2 n. 2 n, Modulo. (-5) -4 ( -), (-) - ( -).. / A A A 2 3 4 5 MOD-5 6 MOD-6 7 MOD-7 8 9 / A A A 2 3 4 5
2..,.,.. Flip-Flops :, Flip-Flops, Flip Flop. ( MOD)... -8 8, 7 ( ).. n Flip-Flops. n Flip-Flops : 2 n. 2 n, Modulo. (-5) -4 ( -), (-) - ( -).. / A A A 2 3 4 5 MOD-5 6 MOD-6 7 MOD-7 8 9 / A A A 2 3 4 5
