Erythro and Threo. Terms used for diastereomers with two adjacent chiral Carbons, without symmetric ends. For symmetric molecules, use meso or d,l.
|
|
|
- Emory Baker
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Erythro and Threo Terms used for diastereomers with two adjacent chiral Carbons, without symmetric ends. For symmetric molecules, use meso or d,l.
2 Aldotetroses This also works for non O (Use regular rules) O O O O O O O O O O O O C 2 O O C 2 O O D-(-)-Erythrose D-(-)-Threose zig-zag Fischer erythro same side (syn) opposite sides (anti) threo opposite sides (anti) same side (syn)
3 Epimers Sugars that differ only in their stereochemistry at a single carbon.
4 Cyclic Structure for Glucose Glucose cyclic hemiacetal formed by reaction of -CO with -O on C5. D-glucopyranose
5 Anomers
6 Reactions of monosaccharides Normal chemical reactions related to the presence of C=O in aldehyde and ketone groups O groups Special reactions due to the large number of very closely spaced functional groups in the molecule
7 Reactions of carbohydrates Epimerization Enediol Rearrangement emiacetal Formation Reduction Oxidation Osazone Formation Chain Shortening Chain Lengthening
8 Epimerization In base, on C2 may be removed to form enolate ion. Reprotonation may change the stereochemistry of C2.
9 Enediol Rearrangement In base, the position of the C=O can shift. Chemists use acidic or neutral solutionsof sugars to preserve their identity.
10 Formation of Glycosides React the sugar with alcohol in acid. Since the open chain sugar is in equilibrium with its - and -hemiacetal, both anomers of the acetal are formed. Aglycone is the term used for the group bonded to the anomeric carbon.
11 Ether Formation Conversion of all -O groups to -OR, Modified Williamson synthesis After converting sugar to acetal, stable in base. elps to purify by recrystallization from water.
12 Ester Formation Acetic anhydride with pyridine catalyst converts all the free oxygens to acetate esters.
13 Reduction to Alditols The carbonyl group of a monosaccharide can be reduced to a hydroxyl group by a variety of reducing agents, including NaB 4 and 2 /M O CO O O + O C 2 O 2 Ni O C 2 O O O O C 2 O D-Glucose D-Glucitol (D-Sorbitol)
14 Reduction of Simple Sugars C=O of aldoses or ketoses can be reduced to C-O by NaB 4 or 2 /Ni. Name the sugar alcohol by adding -itol to the root name of the sugar. Reduction of D-glucose produces D-glucitol, commonly called D-sorbitol. Reduction of D-fructose produces a mixture of D-glucitol and D-mannitol.
15 Sorbitol About 60% as sweet as sucrose Sugar substitute for diabetics Used in manufactured of sweets Sugar-free really means sucrose-free Moisturing creams ( Sorbolene )
16 Pentanepentols
17 Nonreducing Sugars Glycosides are acetals, stable in base, so they do not react with Tollens reagent. Disaccharides and polysaccharides are also acetals, nonreducing sugars.
18 Oxidation by Tollens Reagent Tollens reagent reacts with aldehyde, but the base promotes enediol rearrangements, ketoses react too. Sugars that give a silver mirror with Tollens are called reducing sugars.
19 Oxidation by Bromine Bromine water oxidizes aldehyde, but not ketone or alcohol; forms aldonic acid.
20 Oxidation to Aldonic Acids Oxidation of the Aldehyde group of an aldose to a carboxyl group can be carried out using Tollens, Benedict s, or Fehling s solutions O RC + A g( N 3 ) 2 + Tollens' solution N 3, 2 O O RCO - + N 4 + Ag Precipitates as a silver mirror O RC + citrate or tartrate buffer Cu 2 + RCO - + Cu 2 O Precipitates as a red solid O
21 Oxidation to Aldonic Acids 2-Ketoses are also oxidized by these reagents because, under the conditions of the oxidation, 2-ketoses equilibrate with isomeric aldoses C 2 O C=O CO C-O CO CO (C O) n (C O) n (C O) n C 2 O C 2 O C 2 O A 2-ketose An enediol An aldose
22 Oxidation by Nitric Acid Nitric acid oxidizes the aldehyde and the terminal alcohol; forms aldaric acid.
23 Stereochemistry L D L Rotate 180 D 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid meso achiral diastereomer, (optically inactive overall) (+)-tartaric acid: [ ] D = +12 m.p. 170 C (-)-tartaric acid: [ ] D = -12 m.p. 170 C meso-tartaric acid: [ ] D = 0 m.p. 140 C
24 Aldaric Acids
25 Question #1 Which of the following aldaric acids are optically active? C and D A B C D E No stereocenter meso R, R S, S meso
26 Question #2 Draw a hexose that would give the same aldaric acid product as D-Glucose O CO O CO O O O + O O O C 2 O C 2 O d-(+)- glucose D diastereomers L- (+)- gulose Core of alcohols - mild oxidation or strong oxidation X O O O O X Same product No Symmetry
27 Question #2 Draw a hexose that would give the same aldaric acid product as D-Glucose O CO O CO O O O + O O O C 2 O C 2 O d-(+)- glucose D diastereomers L- (+)- gulose Core of alcohols - mild oxidation or strong oxidation X O O O O X Same product No Symmetry
28 Question #3 There are four D-aldopentoses. Draw Fischer projections of each of them. Then draw Fischer projections of the aldaric acids they would yield. Which of those aldaric acids would be optically inactive? O O O O C 2 O D-Ribose O O O O C 2 O D-Arabinose O O O O O O C 2 O D-Xylose O O C 2 O D-Lyxose (2R, 3R, 4R) (2S, 3R, 4R) (2R, 3S, 4R) (2S, 3S, 4R)
29 Question #3 There are four D-aldopentoses. Draw Fischer projections of each of them. Then draw Fischer projections of the aldaric acids they would yield. Which of those aldaric acids would be optically O O inactive? D-Ribose O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O D-Arabinose D-Xylose D-Lyxose MESO (S,S) MESO (S,S)
30 Osazone Formation Both C1 and C2 react with phenylhydrazine.
31 Osazone Sugars that differ in configuration only at the -carbon Give the same product.
32 Question #4 Select the compounds that would produce the same osazone. A and D, B and C
3) How many monosaccharides are connected to each other in a disaccharide? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 2e (Frost) HOMEWORK Chapter 6 Carbohydrates Life s Sweet Molecules 6.1 Multiple-Choice 1) Which of the following is a polysaccharide? Glucose Sucrose C) Starch D) Maltose
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
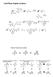 Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Fischer Projections revisited C C C Remember that group rotations are always allowed C C 80 rotations of entire molecule are allowed C 80 C 90 rotations of entire molecule
CHEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) Page 1
 CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
CEM 121. Chapter 18. Name: Date: 1. Which of the following compounds is both an aldose and a hexose? A) B) C) D) Page 1 2. Which of the following structures is that of an L-monosaccharide? A) B) C) D)
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates
 The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
The Chemistry of Carbohydrates Experiment #5 Objective: To determine the carbohydrate class of an unknown by carrying out a series of chemical reactions with the unknown and known compounds in each class
Catalysis by Enzymes. Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction.
 Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
Catalysis by Enzymes Enzyme A protein that acts as a catalyst for a biochemical reaction. Enzymatic Reaction Specificity Enzyme Cofactors Many enzymes are conjugated proteins that require nonprotein portions
Isomers Have same molecular formula, but different structures
 Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Isomers ave same molecular formula, but different structures Constitutional Isomers Differ in the order of attachment of atoms (different bond connectivity) Stereoisomers Atoms are connected in the same
Molecule Projections
 Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
Key Definitions ü Stereochemistry refers to the chemistry in 3 dimensions (greek stereos = solid). This science was created by Pasteur (1860), van Hoff et LeBel (1874). ü Stereisomers are isomeric molecules
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2
 Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
Organic Molecules of Life - Exercise 2 Objectives -Know the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar. -Distinguish Monosaccharides from Disaccharides and Polysaccharides -Understand
Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
 Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur 1 Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) that replaces a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached
Qualitative Testing for Carbohydrates
 R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
R E A 446 modular laboratory program in chemistry program editor:. A. Neidig Qualitative Testing for arbohydrates prepared by James. Schreck, University of Northern olorado, and William M. Loffredo, East
Q.1 Carbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols;
 arbonyl compounds 814 1 ARBYL MPUDS - Aldehydes and Ketones Q.1 arbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols; a) Which type of alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde? b) Which type of alcohol is oxidised
arbonyl compounds 814 1 ARBYL MPUDS - Aldehydes and Ketones Q.1 arbonyl compounds are formed by oxidation of alcohols; a) Which type of alcohol is oxidised to an aldehyde? b) Which type of alcohol is oxidised
SUMMARY OF ALKENE REACTIONS
 SUMMARY F ALKENE REACTINS Alkenes are primarily prepared by elimination reactions of molecules that contain good leaving groups attached to sp 3 carbons. Examples of such reactions are dehydrohalogenations
SUMMARY F ALKENE REACTINS Alkenes are primarily prepared by elimination reactions of molecules that contain good leaving groups attached to sp 3 carbons. Examples of such reactions are dehydrohalogenations
Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells
 Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
Bio 100 Molecules of cells 1 Chapter 3 Molecules of Cells Compounds containing carbon are called organic compounds Molecules such as methane that are only composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT
 EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
EXPERIMENT 5: DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Pre-Lab Questions: None. 64 I. Background Information DIPEPTIDE RESEARCH PROJECT Methods developed by organic chemists for the synthesis of biopolymers have had
Double Bonds. Hydration Rxns. Hydrogenation Rxns. Halogenation. Formation of epoxides. Syn addition of 2 OH. Ozonolysis
 Double Bonds What do we do with double bonds? We do addition reactions. In an addition reaction, something is added to both carbons involved in a double bond (or not involved in the double bond, in the
Double Bonds What do we do with double bonds? We do addition reactions. In an addition reaction, something is added to both carbons involved in a double bond (or not involved in the double bond, in the
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins
 Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Recognizing Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Oct 15 8:05 PM What is an Organic Molecule? An Organic Molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Carbon is found
Aldehydes can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals. 340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C=O with loss of carbonyl oxygen
 340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C= with loss of carbonyl oxygen Ph In Chapter 13 we saw this way of making a reaction go faster by raising the energy of the starting material. We also saw that the
340 14. Nucleophilic substitution at C= with loss of carbonyl oxygen Ph In Chapter 13 we saw this way of making a reaction go faster by raising the energy of the starting material. We also saw that the
CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. Carbohydrates. Organic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R.
 hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
hapter 7 Notes EM 2353 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry hapter 7 arbohydrates rganic and Biochemistry for Today (4 th ed.) Spencer L. Seager / Michael R. Slabaugh Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux Angelo State University
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
LABORATORY 5 DETECTION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
 LABATY 5 DETETIN F FUNTINAL GUPS IN GANI MPUNDS I. haracteristic reactions differentiating saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons from unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons 1. The test of bromine addition. Unsaturated
LABATY 5 DETETIN F FUNTINAL GUPS IN GANI MPUNDS I. haracteristic reactions differentiating saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons from unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons 1. The test of bromine addition. Unsaturated
I. Chapter 5 Summary. II. Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. III. Lipids
 I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
I. Chapter 5 Summary A. Simple Sugars (CH 2 O) n : 1. One C contains a carbonyl (C=O) rest contain - 2. Classification by functional group: aldoses & ketoses 3. Classification by number of C's: trioses,
IR Applied to Isomer Analysis
 DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
DiscovIR-LC TM Application Note 025 April 2008 Deposition and Detection System IR Applied to Isomer Analysis Infrared spectra provide valuable information about local configurations of atoms in molecules.
Lab 2 Biochemistry. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Lipid Structure and Role in Food. The lab has the following learning objectives.
 1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
1 Lab 2 Biochemistry Learning Objectives The lab has the following learning objectives. Investigate the role of double bonding in fatty acids, through models. Developing a calibration curve for a Benedict
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1
 CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
CHEMISTRY AND BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE BODY-1 Chiral centers: Asymmetric carbons, i.e carbon atom with four different substituents Enantiomers : Mirror images Stereoisomers MONOSACCHARIDE
3Reactions of Sugars. Introduction. Mutarotation
 3eactions of Sugars Introduction 35 Mutarotation 35 xidation of Sugars 39 Glycoside Formation 40 Acid atalyzed Sugar eactions 42 Alkaline-atalyzed Sugar eactions 43 Summary 45 Vocabulary 47 eferences 47
3eactions of Sugars Introduction 35 Mutarotation 35 xidation of Sugars 39 Glycoside Formation 40 Acid atalyzed Sugar eactions 42 Alkaline-atalyzed Sugar eactions 43 Summary 45 Vocabulary 47 eferences 47
Final Examination, Organic Chemistry 1 (CHEM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* A. B. C. D.
 Final Examination, rganic hemistry 1 (EM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* 1. What are the hybridization of, and the geometrical shape around, the nitrogen atom in the following molecule? N 3 3 A. sp, linear
Final Examination, rganic hemistry 1 (EM 2210) December 2000 Version *A* 1. What are the hybridization of, and the geometrical shape around, the nitrogen atom in the following molecule? N 3 3 A. sp, linear
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein
 Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
Conduct A Qualitative Test For Starch, Fat, A Reducing Sugar, A Protein Biology Leaving Cert Experiments Materials/Equipment Starch solution (1%) Iodine Solution Glucose Solution (1%) 100 C) Benedict s
Alcohols. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH 1-propanol OH
 Chapter 12 rganic Compounds with xygen and Sulfur 12.1 Alcohols, Thiols, and Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( ) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( )
Chapter 12 rganic Compounds with xygen and Sulfur 12.1 Alcohols, Thiols, and Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( ) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( )
Suggested solutions for Chapter 3
 s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
s for Chapter PRBLEM Assuming that the molecular ion is the base peak (00% abundance) what peaks would appear in the mass spectrum of each of these molecules: (a) C5Br (b) C60 (c) C64Br In cases (a) and
II. Chemistry of Sugars
 II. Chemistry of Sugars Sugars-or saccharides- are the most abundant bio-molecule on the planet. They are important in a number of biological roles. Most obviously you will know them as a major component
II. Chemistry of Sugars Sugars-or saccharides- are the most abundant bio-molecule on the planet. They are important in a number of biological roles. Most obviously you will know them as a major component
EXPERIMENT 6 (Organic Chemistry II) Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes
 EXPERIMENT 6 (rganic hemistry II) Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes Pahlavan/herif hemicals 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine(DNP) 0.10 M AgN 3 2-propanol Benzaldehyde 10% Na 2-butanol Methyl ethyl Ketone
EXPERIMENT 6 (rganic hemistry II) Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes Pahlavan/herif hemicals 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine(DNP) 0.10 M AgN 3 2-propanol Benzaldehyde 10% Na 2-butanol Methyl ethyl Ketone
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and itriles Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: There are really only four things to worry about under this heading; acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides. We ll start with
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and itriles Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: There are really only four things to worry about under this heading; acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides. We ll start with
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS
 IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS Alcohols are organic compounds that which considered as derivatives of water. One of the hydrogen atoms of water molecule (H-O-H) has been replaced by an alkyl or substituted
IDENTIFICATION OF ALCOHOLS Alcohols are organic compounds that which considered as derivatives of water. One of the hydrogen atoms of water molecule (H-O-H) has been replaced by an alkyl or substituted
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information
 Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information Basic rganic Chemistry rganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. rganic compounds are compounds
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry Terms and Background Information Basic rganic Chemistry rganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. rganic compounds are compounds
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Structure Deduction using lassification Tests 1 Determination of Structure Determining the structure of an unknown organic compound is an exercise in deductive reasoning.
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Structure Deduction using lassification Tests 1 Determination of Structure Determining the structure of an unknown organic compound is an exercise in deductive reasoning.
IB Chemistry 1 Mole. One atom of C-12 has a mass of 12 amu. One mole of C-12 has a mass of 12 g. Grams we can use more easily.
 The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
The Mole Atomic mass units and atoms are not convenient units to work with. The concept of the mole was invented. This was the number of atoms of carbon-12 that were needed to make 12 g of carbon. 1 mole
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil
 Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
Syllabus for General Organic Chemistry M07A- Fall 2013 Prof. Robert Keil Textbook and Materials What you must buy: Organic Chemistry 4 th Ed. Janice G. Smith, McGraw Hill. (Older edition is fine) Chem
EXPERIMENT 9 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan - Cherif Synthesis of Aspirin - Esterification
 EXPERIMENT 9 (rganic hemistry II) Pahlavan - herif Materials Hot plate 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask Melting point capillaries Melting point apparatus Büchner funnel 400-mL beaker Stirring rod hemicals Salicylic
EXPERIMENT 9 (rganic hemistry II) Pahlavan - herif Materials Hot plate 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask Melting point capillaries Melting point apparatus Büchner funnel 400-mL beaker Stirring rod hemicals Salicylic
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses
 Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
Chem 1100 Chapter Three Study Guide Answers Outline I. Molar Mass and Moles A. Calculations of Molar Masses B. Calculations of moles C. Calculations of number of atoms from moles/molar masses 1. Avagadro
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry 13-1. Carbon Bonds 13-2. Alkanes 13-3. Petroleum Products 13-4. Structural Formulas 13-5. Isomers 13-6. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13-7. Benzene 13-8. Hydrocarbon Groups 13-9.
Carbon-organic Compounds
 Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ
 CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Module Title: Topics in Organic Chemistry Module Code: CHEO 7003 School : Science Programme Title: Bachelor of Science in Analytical & Pharmaceutical
CORK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHORCAÍ Module Title: Topics in Organic Chemistry Module Code: CHEO 7003 School : Science Programme Title: Bachelor of Science in Analytical & Pharmaceutical
Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below:
 CHEM 3311 Exam #1 Name Dr. Minger June 8, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received
CHEM 3311 Exam #1 Name Dr. Minger June 8, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor received
1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule?
 Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2210, rganic Chem I 1. What is the hybridization of the indicated atom in the following molecule? A. sp 3 B. sp 2 C. sp D. not hybridized 2. Name the functional groups in
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Name. Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem 322 - Organic Chemistry II Examination #2 - March 14, 2005 ANSWERS
 Name INSTRUTINS --- Department of hemistry and Biochemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #2 - March 14, 2005 ANSWERS This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice
Name INSTRUTINS --- Department of hemistry and Biochemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #2 - March 14, 2005 ANSWERS This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids & Phospholipids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Prerequisites: Course Description: Textbook: CHM 212 Organic
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIVISION OF MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES STUDENT COURSE OUTLINE Course Title: Prerequisites: Course Description: Textbook: CHM 212 Organic
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
PROPERTIES OF GLYCERINE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
 PROPERTIES OF GLYCERINE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 1) Molecular weight = 92.09 2) Melting point =18.17ºC 3) Boiling point(760mm Hg) = 290ºC 4) Density (20ºC) =1.261 g/cm 3 5) Vapor pressure = 0.0025 mm Hg at
PROPERTIES OF GLYCERINE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 1) Molecular weight = 92.09 2) Melting point =18.17ºC 3) Boiling point(760mm Hg) = 290ºC 4) Density (20ºC) =1.261 g/cm 3 5) Vapor pressure = 0.0025 mm Hg at
These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A.
 Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
Lesson Element Keyword activities Instructions for teachers These instructions are for a classroom activity which supports OCR A Level Chemistry A. Just a minute! To run this activity you will need a set
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
Name: Hour: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami. Tel: (618)545-3361. Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu. Web: www.kc.cc.il.
 CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
CHEM 208(Organic Chemistry I) Instructor: Dr. Niranjan Goswami Tel: (618)545-3361 Email: Ngoswami@kaskaskia.edu Web: www.kc.cc.il.us/ngoswami CHEM 208 COURSE SYLLABUS KASKASKIA COLLEGE NAME TERM YEAR TEXT:
methyl RX example primary RX example secondary RX example secondary RX example tertiary RX example
 ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols
 Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
Introduction Experiment #8 properties of Alcohols and Phenols As has been mentioned before, over 20 million organic compounds have been identified. If each substance had to be studied as an entity completely
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Avg. 16.4 / 25 Stnd. Dev. 8.2
 QUIZ TREE Avg. 16.4 / 25 Stnd. Dev. 8.2 xidation of Alcohols with Chromium (VI): Jones xidation 2 Alcohols are oxidized by a solution of chromium trioxide in aqueous acetone (2), in the presence of an
QUIZ TREE Avg. 16.4 / 25 Stnd. Dev. 8.2 xidation of Alcohols with Chromium (VI): Jones xidation 2 Alcohols are oxidized by a solution of chromium trioxide in aqueous acetone (2), in the presence of an
Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds
 Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds Introduction The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often
Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds Introduction The identification and characterization of the structures of unknown substances are an important part of organic chemistry. Although it is often
Water. Definition: A mole (or mol ) Water can IONIZE transiently. NONpolar covalent molecules do not dissolve in water + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
 Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
Today s Topics Polar Covalent Bonds ydrogen bonding Properties of water p Water C bonds are Nonpolar Will these molecules dissolve in water? Start Macromolecules Carbohydrates & Lipids Sept 4, 05 Why are
How To Calculate Mass In Chemical Reactions
 We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
We have used the mole concept to calculate mass relationships in chemical formulas Molar mass of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH)? Molar mass = 2 x 12.011 + 6 x 1.008 + 1 x15.999 = 46.069 g/mol Mass percentage of
Chapter 14 Glycolysis. Glucose. 2 Pyruvate 2 Lactate (sent to liver to be converted back to glucose) TCA Cycle
 Chapter 14 Glycolysis Requires mitochondria and O 2 Glucose glycolysis anaerobic respiration 2 Pyruvate 2 Lactate (sent to liver to be converted back to glucose) pyruvate dehydrogenase acetyl-coa TCA Cycle
Chapter 14 Glycolysis Requires mitochondria and O 2 Glucose glycolysis anaerobic respiration 2 Pyruvate 2 Lactate (sent to liver to be converted back to glucose) pyruvate dehydrogenase acetyl-coa TCA Cycle
Worksheet 13.1. Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary
 Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Worksheet 13.1 Chapter 13: Human biochemistry glossary α-helix Refers to a secondary structure of a protein where the chain is twisted to form a regular helix, held by hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Fourteen 1
 An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
An alcohol has an OH bonded to an alkyl group; a phenol has an OH bonded directly to an aromatic ring; and an ether has an O bonded to two organic groups. Chapter Fourteen 1 Ethyl alcohol, dimethyl ether,
ALCOHOLS: Properties & Preparation
 ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
ALLS: Properties & Preparation General formula: R-, where R is alkyl or substitued alkyl. Ar-: phenol - different properties. Nomenclature 1. ommon names: Name of alkyl group, followed by word alcohol.
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to a benzene ring.
 Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
Chapter : rganic Compounds with xygen Alcohols, Ethers Alcohols An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a carbon chain. A phenol contains a hydroxyl group ( H) attached to a benzene ring.
for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency of the vibration
 ! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
! = 1 2"c k (m + M) m M wavenumbers! =!/c = 1/" wavelength frequency! units: cm 1 for excitation to occur, there must be an exact match between the frequency of the applied radiation and the frequency
Laboratory 22: Properties of Alcohols
 Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids
 Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids Outline Fats and Oils Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Biodiesel Homework We hear quite a lot about the place of fats and oils in human nutrition. Foods high in fat are at the
Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids Outline Fats and Oils Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Biodiesel Homework We hear quite a lot about the place of fats and oils in human nutrition. Foods high in fat are at the
Elements in Biological Molecules
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Question Bank Electrolysis
 Question Bank Electrolysis 1. (a) What do you understand by the terms (i) electrolytes (ii) non-electrolytes? (b) Arrange electrolytes and non-electrolytes from the following substances (i) sugar solution
Question Bank Electrolysis 1. (a) What do you understand by the terms (i) electrolytes (ii) non-electrolytes? (b) Arrange electrolytes and non-electrolytes from the following substances (i) sugar solution
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1021 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
How To Understand The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules
 CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
CHAPTER 3 THE CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 3.1 Organic Molecules The chemistry of carbon accounts for the diversity of organic molecules found in living things. Carbon has six electrons, four of which
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Date: Per: Table # Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Name Period Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7. Alcohols, Ethers and More
 Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Organic Functional Groups Chapter 7 Alcohols, Ethers and More 1 What do you do when you are in Pain? What do you do when you are in a lot of pain? 2 Functional Groups A functional group is an atom, groups
Georgia Perimeter College - Dunwoody Campus Chemistry 1152-200 Fall 2011 Course Syllabus(revised)
 Georgia Perimeter College - Dunwoody Campus Chemistry 1152-200 Fall 2011 Course Syllabus(revised) Course Title: Survey of Chemistry II, TR 1000 1115 Room NE-1260 Instructor: Dr. Jerry L. Poteat, Associate
Georgia Perimeter College - Dunwoody Campus Chemistry 1152-200 Fall 2011 Course Syllabus(revised) Course Title: Survey of Chemistry II, TR 1000 1115 Room NE-1260 Instructor: Dr. Jerry L. Poteat, Associate
MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
 MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
MCAT rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? Question #01 (A) Serine (B) Proline (C)
T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride
 Technology StrengthS T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride The coupling agent of the future Coupling and water removal are synthesis tools that stand at the cutting edge of purity and cost effective manufacture
Technology StrengthS T3P Propane Phosphonic Acid Anhydride The coupling agent of the future Coupling and water removal are synthesis tools that stand at the cutting edge of purity and cost effective manufacture
experiment5 Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Learning how to perform a vacuum filtration.
 81 experiment5 LECTURE AND LAB SKILLS EMPHASIZED Synthesizing an organic substance. Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Determining percent yield. Learning how to perform a vacuum
81 experiment5 LECTURE AND LAB SKILLS EMPHASIZED Synthesizing an organic substance. Understanding and applying the concept of limiting reagents. Determining percent yield. Learning how to perform a vacuum
Experiment 6 Qualitative Tests for Alcohols, Alcohol Unknown, IR of Unknown
 Experiment 6 Qualitative Tests for Alcohols, Alcohol Unknown, I of Unknown In this experiment you are going to do a series of tests in order to determine whether or not an alcohol is a primary (1 ), secondary
Experiment 6 Qualitative Tests for Alcohols, Alcohol Unknown, I of Unknown In this experiment you are going to do a series of tests in order to determine whether or not an alcohol is a primary (1 ), secondary
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
 IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
IUPAC System of Nomenclature The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is composed of chemists representing the national chemical societies of several countries. ne committee of the
a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler units
 Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Chemical Bonds 1. Which of the following is NOT a true compound? a. pure substance b. composed of combinations of atoms c. held together by chemical bonds d. substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
reflect Wind turbines shown in the photo on the right are large structures with blades that move in response to air movement. When the wind blows, the blades rotate. This motion generates energy that is
Electrophilic Addition Reactions
 Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Electrophilic Addition Reactions Electrophilic addition reactions are an important class of reactions that allow the interconversion of C=C and C C into a range of important functional groups. Conceptually,
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemistry 1110 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
 hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
hemistry 1110 rganic hemistry IUPA Nomenclature 1 f the approximately 32 million unique chemical compounds presently known, over 95% of them can be classified as organic; i.e., containing carbon. The IUPA
17.5 ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC OXIDATION
 17.5 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI XIDATIN 803 Nuc d d Nuc d 2 3 2 overlap of 2p orbitals X d no p-orbital overlap X d (a) (b) Figure 17.2 Transition states for N 2 reactions at (a) an allylic carbon and (b) a nonallylic
17.5 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI XIDATIN 803 Nuc d d Nuc d 2 3 2 overlap of 2p orbitals X d no p-orbital overlap X d (a) (b) Figure 17.2 Transition states for N 2 reactions at (a) an allylic carbon and (b) a nonallylic
[1] [Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Davis, CA 95616]
![[1] [Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Davis, CA 95616] [1] [Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Davis, CA 95616]](/thumbs/26/8946803.jpg) Supplementary Information for Multi-generation gas-phase oxidation, equilibrium partitioning, and the formation and evolution of secondary organic aerosol Christopher D. Cappa 1, Kevin R. Wilson [1] [Department
Supplementary Information for Multi-generation gas-phase oxidation, equilibrium partitioning, and the formation and evolution of secondary organic aerosol Christopher D. Cappa 1, Kevin R. Wilson [1] [Department
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
Chapter 3: Biological Molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids Elements in Biological Molecules Biological macromolecules are made almost entirely of just 6 elements: Carbon (C)
