Role of Enzymes in Poultry Nutrition
|
|
|
- Kerry Miles
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Role of Enzymes in Poultry Nutrition
2 Role of Enzymes in Poultry Nutrition Introduction At the most basic level, feedstuffs consist of protein, starch, fat and fiber. In monogastric animals the fiber component has been considered to be wasted and in some instances, compounds called Non-starch polysaccharides (NSP) can exert anti-nutritive activity on the animal. The NSP of barley, wheat and rye has been the most intensively investigated. Beta glucan in concentrations ranging from g/kg dry matter has been shown to depress production in broilers and cause sticky droppings (pasted vents). Wheat and rye contain relatively high levels of arabinoxylans or pentosans (50-80 g/kg dry matter for wheat; 100 g/kg dry matter for rye) which can also have a negative effect on broiler performance. Ingestion of NSP by monogastrics results in increased viscosity of the digesta. This increased viscosity reduces the passage rate of the feed leading to overall reductions in consumption and decreased performance, sticky droppings and dirty eggs. The addition of enzymes to the diet to address NSP viscosity can improve feed efficiency, improve manure quality and increase the use of lower cost feed ingredients. Characteristics of Enzymes Effectiveness of an enzyme include: 1. Specific degradation site in the molecule 2. PH value 3. Temperature 4. Water content 5. Presence of aerators / Inhibitors 6. Substrate concentrations Animal nutrition requires the enzymes, which are active at 40 C and also withstand at C (Pelleting temperature). Pre-requisite of Enzyme used in Animal Nutrition: Must act under acidic ph condition of stomach Resist low ph Resist pepsin s proteolytic action It should act other parts of digestive tract - Plant enzymes Microbial enzymes Narrow spectrum hydrolyzing enzymes. Synthetic broad-spectrum hydrolytic enzymes. Less stable in extreme reaction More stable enzymes on extreme conditions. reaction conditions. Standardization not done. Better standardized. Lower yield. Higher yield. Not economical. Economical.
3 Advantage of Microbial Enzymes Production Microbes are capable of producing a variety of enzymes. Due to high production capacity, there is unlimited supply of enzymes. Production capacity can be expanded by strain improvement. They can be manipulated easily in the laboratory. Large number of enzymes can be obtained economically from microorganism. Only well-designed, & intensive search among microbial strains can usually find an appropriate organism to produce any enzyme. It is possible to introduce genetic changes in them rather easily, due to simplicity of their genome. Their growth requirements are simple & can be precisely defined, which is of immense importance in industrial production to maintain consistency of product quality. Specific enzyme conversion is required. The only disadvantage is the presence of contaminating enzymes, which can cause undesirable reaction. These contaminated enzymes can be removed by enzyme purification techniques. For production of enzymes 1. Select suitable strain 2. Composition of nutritive media Enzyme producing micro-organisms Fungi: Largest group among enzyme producing micro organism Aspergillus spp. (A. niger) Penicillium spp. Humicola spp. (H. insolens) Trichoderma spp. These fungi produce enzymes for degradation of various substances. But they all have one thing in common i.e. the production of enzymes for the breakdown of plant cell wall components in the form of high polymer carbohydrates. Bacteria: Bacillus spp. (α-amylase, proteases) B. licheniformis and B. subtilis
4 Microbes used in commercial enzyme production: ENZYME SOURCE ACTION α-amylase Bacillus subtilis Bacillus licheniformis Aspergillus oryzae β-glucanase Pectinase Bacillus subtilis Aspergillus niger Penicillium emersonii Aspergillus oryzae Aspergillus niger Rhizopus oryzae Endo-hydrolysis of α-1, 4-glucosidic linkages Degrades β-glucan by cleaving β- 1,3(4) glucosidic linkages Degrades pectin α-1,4-linked anhydrogalacuronic acid Pullulanase Klebsiella aerogenes Splits the α-1,6-glycosidic linkages Substances other than NSP (Non-starch Polysaccharides) Indigestible oligosaccharides (present mainly in vegetable protein carriers) α- Galactosides Raffinose Stachyose Verbascose Phytic acid (Ester of hexa-phosphoric acid of inositol) Tannins Phytates Lactins Vicins Trypsin inhibitors Classification of Polysaccharides Homopolysaccharides Heteropolysaccharides Glucans Fructans Hemicellulose pectin Mucilage Gum Starch Dextrins Cellulose Levan Inulin Effects of NSP compounds and phytate in animals 1. Influence on energy density (Dilution effect) Poorly digestible Dilute the metabolizable energy Dilute the nutrient content of feed 2. Entrapping of nutrients (Cage effect) Entrapping other nutrients mainly starch, fat and protein This is applied to the insoluble parts of the NSP which are present in the various cell wall structures.
5 3. Increasing the viscosity of digesta Viscosity increasing polysaccharides Increased intestinal viscosity Reduced passage rate of digesta Reduced feed intake Increased growth of intestinal flora Nutrient competition between host and microflora Reduced nutrient intake Increased intestinal viscosity Reduced nutrient availability Detoriation of growth performance and feed conversion 4. Reduction of nutrient absorption In this, multiple factors take part Viscosity Altered composition of intestinal flora Increased absorption of bile Influence on the intestinal mucosa Reduced nutrient absorption Higher than normal excretion of digestive enzymes Endogenous loss of protein According to the purpose of application, feed enzymes can be fundamentally divided in to: a. Enzymes which are to quantitatively supplement endogenous digestive enzymes of mono gastric animals Eg. Proteases, lipases, Amylases b. Enzymes which are not produced by mono gastric animals Eg. β-glucanases Pentosanases Phytases.
6 Role of enzymes in poultry nutrition General: Poultry do not produce enzyme for the hydrolyses of these nonstarch polysaccharide (NSP) present in the cell wall of the grains Addition of enzymes specific for a given feed formulation will enhance the bioavailability of above feed components. The exogenous enzyme in feed additive, can complement to endogenous enzymes in the digestive system during adverse climatic condition and at an early age, to give an increase role of digestion. The production of endogenous enzymes may be a limiting factor due to various reasons depending on the age, health, type of feed, environment etc. Enzyme Stability In animals: For optimum activity an enzyme should be capable of surviving low ph of 2 in stomach and high ph of 6.5 in the intestine. The temperature inside the animal digestive system is significantly lower than that which causes enzyme in activation. In feed: Enzymes are stable at C for 1-2 min as required for pelleting and ph of 5.5 to 6.5 in feed. Mode of Action Addition of enzymes to feed functions in various ways in birds body thus improving its nutrients utilization and overall performance. 1. By reducing the gut viscosity: Cereals contain high proportions of their energy in the form of non-starch polylsaccharides Cereals contain soluble indigestible polysaccharides like arabinoxylan (wheat), mixed linked β-glucans (in barley and rye), lignin, limit dextrin, antinutritional factors like phytic acid and cellulose fibre These NSP are able to bind large amount of water - increasing viscosity in the gut - affects rate of passage of digesta - rate of mixing of bile, pancreatic and intestinal secretions with digesta -rate of absorption of digesta - increases the amount of sticky droppings.
7 Addition of suitable multienzyme preparation improves animal performance in following ways. a. Increasing the effectiveness of host (endogenous) enzymes: Breaking down the gel form characteristic of soluble fibres allows the birds digestive enzyme to function more efficiently. This improves starch, protein, fat, amino acids and energy digestibility. b. Alteration in feed passage rate: The enzymes reduce the water holding capacity of the gut contents thus increasing the dry matter content stimulating feed intake. c. Effect on Excreta characteristics: Addition of enzymes also reduces the dry matter outside the body thus has marked impact on excreta volume and composition. Due to protein digestibility lowering of excreta output is observed. d. Effect on litter problems: Reduced viscosity improves nutrient digestion, lower water intake and help to reduce litter problems. 2. Release of Nutrients: Enzymatic depolymerization renders the NSP free releasing nutrients in the gut and it available to the animal. Starch masked by cell structure is released leading to increase in metabolisable energy. Proteins are also released by action of proteases. This release leads to maximum absorption of minerals and results in improvement in nutrient utilization. 3. Availability of phosphorus: Cereals and oilseeds contain 1-2% of phytate, and 60-90% of total phosphorus present in the seeds in this phytate phosphorus. Phytase hydrolyses phytic acid to myoinositol and phosphoric acid in step wise manner forming myoinositol phosphatic intermediates (IP 5, IP 4, IP 3, IP 2, IP 1 ). Benefits of enzymes A. To Poultry a. In Digestibility 1. Enhances the feed intake and efficiency, growth rate and productivity.
8 2. Increases the energy value of cereal feed stuffs. More nutrients are made available by hydrolysing fibrous material. 3. Better digestibility of feed ingredients by better feed conversion. 4. Enzymes act as supplement to the normal digestive enzymes especially during stress condition. 5. Reduces antinutritional products like tannins, saponin and goitrogen. 6. Promotes weight gain and overall improved performance. 7. Release minerals for assimilation - eg: Ca, Mg, Zn, P etc. 8. Stabilization of microbial flora by making these nutrients readily available to them. 9. Checks chelating of minerals such as Zn, Mn, Fe, Ca, K with phytic acid, less chelation means more mineral availability. 10. Prevents precipitation of pentacalcium phosphate and there by improves absorption of calcium and phosphorus. b. In Animal Health 1. Improvement in animal hygiene and health. 2. Corrects digestive disorders especially when birds are crowded. 3. Fattening performance is increased. 4. Prevents damages to chicken anaemia agent. 5. Prevents damages to chicken anaemia agent. 6. Checks cellular damages caused by toxins. 7. Promotes growth to bones. 8. Prevents diarrhoea due to poor fibre digetion. 9. Minimizes excreta, water droppings and of ammonia. 10. Reduces viscosity and ammonia level in intestine. c. In Poultry Product 1. Increases egg production and hatchability in layers. 2. Egg quality is also maintained. More cleanly eggs and with thick shell is maintained. 3. Improves flock uniformity leading to more consistent sized birds. 4. Improved slaughter results, high carcass weights and better grading. 5. Genetic Potential of birds can be explored enabling them to consume more quality of feed to achieve maximum growth and production. B. To feed 1. Greater flexibility in feed formulation. 2. Readily available material can be advantageously utilized. 3. Use of newly harvested grains. 4. Use of cheaper raw materials as choice of raw material is increased. Barley can be easily used in place of wheat. 5. Feed additives hold promise to lower the overall production cost. Better profits as inexpensive feed stuffs can be taken.
9 6. Cereal replacement due to use of enzymes. High M.E. cereals can be fully replaced by low M.E. cereals without compromising growth performance. 7. Elimination of anti-nutritional factors from feed and feed ingredients eg: galactoside and pectins etc. C. To environment 1. Reduction in manure volume. 2. Reduced nitrogen and Phosphorus exertion. 3. Less environmental waste and therefore less pollution. 4. Reduced environmental stress resulting from reduced litter volume. Use of Enzymes in Feed To enhance the feed intake and efficiency growth rate & productivity, by overcoming many nutritional problems and correcting digestive disorders especially when birds are crowded To increase the energy value of cereal feedstuffs. More nutrients are made available by hydrolysing fibrous material To minimise excreta, waterly dropping and ammonia To reduce anti-nutritional products like tannins, saponins and goitrogens To provide choice of raw materials. For eg. Barley, which was not earlier used, is now successfully used with enzymes. To promote faster growth by increasing feed efficiency and promoting weight gain To increase egg production and hatchability in layers To reduce early mortality due to the problems associated with harmful moulds and aflatoxin in poultry feeds. Advantages Enzyme-added feed provide additional option where certain feedstuffs are in short supply Readily available materials can be advatageously utilised Price advantage over more traditional and inexpensive feedstuffs can be taken As growth promoters, feed enzyme additives hold promise to lower the overall production costs while improving the performance of birds The genetic potential of birds can be explored, enabling them to consume more quality of feed to achieve maximum growth and production.
10 The Hidden Benefits Of Enzymes Reduction in manure out put: Wet excreta leads to dirty eggs and they are not suitable for sale as second grade eggs. Wet droppings may also cause increased gas production (i.e. ammonia) and fly and rodent population in the shed. Wet dropping can also affect the health of the staff working in the shed. Improved well being of birds: Coccidiosis control, change in gut microflora and elimination of certain diseases. An increase in digeta passage rate and reduction in excreta moisture are often noted when glycanases are added to poultry diets, which may be detrimental to the life cycle of the organism. It is often noted that addition of antibiotics to high soluble-nsp poultry diets markedly improves bird performance (Misir and Marquardt, 1978). Enzyme supplementation largely eliminated the fermentation in the small intestine and improved nutrient digestibility and the well-being of the birds. Increased precision and flexibility in least cost feed formulation: An increased precision in least cost feed formulation, hence a more uniform performance of the birds. Enzymes also allow a wide range of ingredients to be used in a diet with a desired outcome. This gives the producer a great deal of flexibility to formulate a nutritionally balanced least-cost diet. Conclusions It is now well recognised that ingredients such as maize, soybean and, particularly, grain byproducts contain relatively high levels of dietary fibre and that this fibre has negative impacts on feed digestibility and performance. This allows for the option of using the enzyme to improve growth and feed:gain or, alternatively, to use it in diets with lowered levels of energy and protein/amino acids, with higher by-product levels, to maintain performance with lower net feed costs. For Further information please refer to our Product details of: SynerZyme-FS SynerZyme-P-FS
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology
 Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate
Dr Erhard Briendenhann
 Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Working With Enzymes. a world of learning. Introduction. How Enzymes Work. Types and Sources of Enzymes
 Working With Enzymes a world of learning Presented by Peter J Ball, Southern Biological. For further information, please contact the author by phone (03) 9877-4597 or by email peterjball@southernbiological.com.
Working With Enzymes a world of learning Presented by Peter J Ball, Southern Biological. For further information, please contact the author by phone (03) 9877-4597 or by email peterjball@southernbiological.com.
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources. Introduction
 Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Broiler Nutrition Supplement
 Broiler Nutrition Supplement 2009 2 Contents Introduction... 4 Supply of Nutrients... 4 Protein and Amino Acids... 5 Macro Minerals... 6 Non-Nutritive Feed Additives... 7 Broiler Diet Specifications...
Broiler Nutrition Supplement 2009 2 Contents Introduction... 4 Supply of Nutrients... 4 Protein and Amino Acids... 5 Macro Minerals... 6 Non-Nutritive Feed Additives... 7 Broiler Diet Specifications...
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates
 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
NUTRIENT SPECIFICATIONS OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL
 UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Mammalian digestive tracts
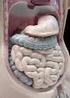 Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Optimizing Broiler Feed Conversion Ratio
 Optimizing Broiler Feed Conversion Ratio July 2011 This article has been written specifically for poultry producers in Latin America. However, the recommendations given are expected to be useful and informative
Optimizing Broiler Feed Conversion Ratio July 2011 This article has been written specifically for poultry producers in Latin America. However, the recommendations given are expected to be useful and informative
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION
 EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
Analysis of Dietary Fibre
 Analysis of Dietary Fibre 1 HK Regulation Dietary fibre means any fibre analyzed by means of any official methods adopted by AOAC International. 2 AOAC Official Methods AOAC 985.29 Total Dietary Fibre
Analysis of Dietary Fibre 1 HK Regulation Dietary fibre means any fibre analyzed by means of any official methods adopted by AOAC International. 2 AOAC Official Methods AOAC 985.29 Total Dietary Fibre
BEC Feed Solutions. Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions
 BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Enzymes. Chapter 3. 3.1 Enzymes and catalysts. Vital mistake. What is an enzyme?
 Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
Chapter 3 Enzymes Vital mistake We may not be able to see them, but enzymes are absolutely crucial to the lives of ourselves and all other living organisms. The Quarter Horse (Figure 3.1) is a breed of
FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION
 Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Caecotrophy in Rabbits
 Caecotrophy In Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Caecotrophy in Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
Caecotrophy In Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Caecotrophy in Rabbits Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Most limiting amino acid concept...
 Review... Proteins are composed of amino acids Amino acids are the essential nutrients The dietary provision of amino acids in correct amount and provisions determines the adequacy of the protein in the
Review... Proteins are composed of amino acids Amino acids are the essential nutrients The dietary provision of amino acids in correct amount and provisions determines the adequacy of the protein in the
Nutrition Guide For Bobwhite Quail Production
 Nutrition Guide For Bobwhite Quail Production Cooperative Extension Service The University of Georgia College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences Table of Contents Nutrients...3 Diet Formulation...4
Nutrition Guide For Bobwhite Quail Production Cooperative Extension Service The University of Georgia College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences Table of Contents Nutrients...3 Diet Formulation...4
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS. (derived from Pancreatin USP) Sodium tauroglycocholate BPC 65mg (with sugar coating containing essential carminative oils)
 ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
ENZAR FORTE TABLETS COMPOSITION Each enteric-coated tablet contains: Amylase activity -15,000 USP units Lipase activity -4,000 USP units Protease activity -15,000 USP units of (derived from Pancreatin
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules
 A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules June 2013 Primefact 1292 1 st edition Jayce Morgan, Livestock Officer Pigs, Tamworth NSW Introduction When a pig is fed a proper diet there are benefits to the pig
A diet fit for a pig: seven basic rules June 2013 Primefact 1292 1 st edition Jayce Morgan, Livestock Officer Pigs, Tamworth NSW Introduction When a pig is fed a proper diet there are benefits to the pig
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
The Use of Enzymes in Dietary Supplements USP Enzyme Workshop July 8, 2009
 The Use of Enzymes in Dietary Supplements USP Enzyme Workshop July 8, 2009 Nena Dockery Introduction and History of Use Commercial production of enzymes for use as digestive aids has an extensive history
The Use of Enzymes in Dietary Supplements USP Enzyme Workshop July 8, 2009 Nena Dockery Introduction and History of Use Commercial production of enzymes for use as digestive aids has an extensive history
Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants
 Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants Agriculture production is a very intensive business and is related to better quality and better yield leading to better profitability Every farmer s dreams to achieve this
Effect Of Amino Acids On Plants Agriculture production is a very intensive business and is related to better quality and better yield leading to better profitability Every farmer s dreams to achieve this
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART
 UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
Welcome To: Ultra Bio-Logics Inc.
 Welcome To: Ultra Bio-Logics Inc. Feed Manufacturers Ingredients - Enzyme Division Enzymes & Microflora Information Web Site: www.ublcorp.com Email: http://www.biologicssecure.com/message.html International
Welcome To: Ultra Bio-Logics Inc. Feed Manufacturers Ingredients - Enzyme Division Enzymes & Microflora Information Web Site: www.ublcorp.com Email: http://www.biologicssecure.com/message.html International
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State
 Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
FEEDING MANUAL Feed manual TOPIGS Finishers
 FEEDING MANUAL Feed manual TOPIGS Finishers TOPIGS Support & Development Updated: 13 August 2012 Copyright TOPIGS Feeding advice Tempo progeny Target Group: Nutritionists and Farm managers Explanation:
FEEDING MANUAL Feed manual TOPIGS Finishers TOPIGS Support & Development Updated: 13 August 2012 Copyright TOPIGS Feeding advice Tempo progeny Target Group: Nutritionists and Farm managers Explanation:
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf
 3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
Heat of combustion (gross energy)
 J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS
 CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
Land O Lakes Feed DDGS. Nutrients Concentrate: United States Ethanol Outlook. A Growing Opportunity
 DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
FARMING FOR THE FUTURE How mineral fertilizers can feed the world and maintain its resources in an Integrated Farming System
 How mineral fertilizers can feed the world and maintain its resources in an Integrated Farming System european fertilizer manufacturers association Global trends in population growth (Population 1000 million),
How mineral fertilizers can feed the world and maintain its resources in an Integrated Farming System european fertilizer manufacturers association Global trends in population growth (Population 1000 million),
DOCTORAL (PhD) DISSERTATION
 1 DOCTORAL (PhD) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF KAPOSVÁR FACULTY OF ANIMAL SCIENCE Department of Animal Nutrition Kaposvár, Hungary Supervisor: PROF. LÁSZLÓ BABINSZKY PhD Author: LÁSZLÓ DÉGEN DIETARY INFLUENCE
1 DOCTORAL (PhD) DISSERTATION UNIVERSITY OF KAPOSVÁR FACULTY OF ANIMAL SCIENCE Department of Animal Nutrition Kaposvár, Hungary Supervisor: PROF. LÁSZLÓ BABINSZKY PhD Author: LÁSZLÓ DÉGEN DIETARY INFLUENCE
Managing Heat Stress in Poultry
 Managing Heat Stress in Poultry Amy E. Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Heat stress has several serious and economical effects on poultry. In broilers and turkeys, it can
Managing Heat Stress in Poultry Amy E. Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. Heat stress has several serious and economical effects on poultry. In broilers and turkeys, it can
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology The Master Degree in Food Science and Technology / Department of Nutrition and Food Technology,
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology The Master Degree in Food Science and Technology / Department of Nutrition and Food Technology,
Water Quality For Poultry
 Water Quality For Poultry Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Water Quality For Poultry Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco
Water Quality For Poultry Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. January 2008 Water Quality For Poultry Amy E. Halls, M.Sc. Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol. Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
What Is Humic Acid? Where Does It Come From?
 What Is Humic Acid? Humic and Fulvic acids are the final break-down constituents of the natural decay of plant and animal materials. These organic acids are found in pre-historic deposits. Humic matter
What Is Humic Acid? Humic and Fulvic acids are the final break-down constituents of the natural decay of plant and animal materials. These organic acids are found in pre-historic deposits. Humic matter
Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems
 Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems by John B. Marler and Jeanne R. Wallin The alarming fact is that foods fruits, vegetables and grains now being raised
Human Health, the Nutritional Quality of Harvested Food and Sustainable Farming Systems by John B. Marler and Jeanne R. Wallin The alarming fact is that foods fruits, vegetables and grains now being raised
Getting Enough Fiber In Your Diet Does Not Have To Be Like This!
 Getting Enough Fiber In Your Diet Does Not Have To Be Like This! What is Fiber? Fiber is indigestible carbohydrate found in plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and grain products. Your body cannot
Getting Enough Fiber In Your Diet Does Not Have To Be Like This! What is Fiber? Fiber is indigestible carbohydrate found in plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and grain products. Your body cannot
Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs
 61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
How To Get Healthy
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Farm-fresh products, such as eggs and chickens,
 A l a b a m a A & M a n d A u b u r n U n i v e r s i t i e s Nutrition for Backyard Chicken Flocks ANR-1317 Farm-fresh products, such as eggs and chickens, have always had a special appeal. A small backyard
A l a b a m a A & M a n d A u b u r n U n i v e r s i t i e s Nutrition for Backyard Chicken Flocks ANR-1317 Farm-fresh products, such as eggs and chickens, have always had a special appeal. A small backyard
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS?
 WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS? Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories Inc. Kearney, NE Commercial fertilizer is a source of plant nutrients that can be applied to soil to nourish crops when the
WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS? Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories Inc. Kearney, NE Commercial fertilizer is a source of plant nutrients that can be applied to soil to nourish crops when the
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets
 Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
General Properties Protein Nature of Enzymes Folded Shape of Enzymes H-bonds complementary
 Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
Proteins that function as biological catalysts are called enzymes. Enzymes speed up specific metabolic reactions. Low contamination, low temperature and fast metabolism are only possible with enzymes.
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
DOE Office of Biological & Environmental Research: Biofuels Strategic Plan
 DOE Office of Biological & Environmental Research: Biofuels Strategic Plan I. Current Situation The vast majority of liquid transportation fuel used in the United States is derived from fossil fuels. In
DOE Office of Biological & Environmental Research: Biofuels Strategic Plan I. Current Situation The vast majority of liquid transportation fuel used in the United States is derived from fossil fuels. In
Detailed Course Descriptions for the Human Nutrition Program
 1 Detailed Course Descriptions for the Human Nutrition Program Major Required Courses NUTR221 Principles of Food Science and Nutrition Credit (Contact) Hours 2 CH(2 Theory) Prerequisites Course Description
1 Detailed Course Descriptions for the Human Nutrition Program Major Required Courses NUTR221 Principles of Food Science and Nutrition Credit (Contact) Hours 2 CH(2 Theory) Prerequisites Course Description
O 2. What is anaerobic digestion?
 What is anaerobic digestion? Microbial degradation of organic material under anaerobic conditions Ubiquitous, naturally-occurring process Occurs in swamps, hydric soils, landfills, digestive tracks of
What is anaerobic digestion? Microbial degradation of organic material under anaerobic conditions Ubiquitous, naturally-occurring process Occurs in swamps, hydric soils, landfills, digestive tracks of
WHITE PAPER BROILER STARTER FEEDS
 WHITE PAPER BROILER STARTER FEEDS HAMLET PROTEIN White Paper / Broiler Starter Feeds / 2 Reaching the growth potential of newly hatched broilers relies on several factors such as feed, feeding strategy,
WHITE PAPER BROILER STARTER FEEDS HAMLET PROTEIN White Paper / Broiler Starter Feeds / 2 Reaching the growth potential of newly hatched broilers relies on several factors such as feed, feeding strategy,
New Dextrins. Supplementing Fiber with Innovation DATA AND REVIEW
 New Dextrins Supplementing Fiber with Innovation Ashish A. Joshi and Sergio Neves Formulations containing a novel soluble dextrin fiber have been shown to exhibit several advantages in processibility and
New Dextrins Supplementing Fiber with Innovation Ashish A. Joshi and Sergio Neves Formulations containing a novel soluble dextrin fiber have been shown to exhibit several advantages in processibility and
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 5 The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols I The THREE types of LIPIDS A. Triglycerides (fats & oils)- the MAJOR type of lipid in food and humans. 1. 2 parts of triglyceridesa)
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees II; scientific co-operation and networks Revision of the
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees II; scientific co-operation and networks Revision of the
CODEX STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN 156-1987. This standard applies to the composition and labelling of follow-up formula.
 CODEX STAN 156-1987 Page 1 of 9 CODEX STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN 156-1987 1. SCOPE This standard applies to the composition and labelling of follow-up formula. It does not apply to foods
CODEX STAN 156-1987 Page 1 of 9 CODEX STANDARD FOR FOLLOW-UP FORMULA CODEX STAN 156-1987 1. SCOPE This standard applies to the composition and labelling of follow-up formula. It does not apply to foods
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
UBIC MARKETING ASPECTS OF FIBER INGREDIENTS. Marketing Development Strategy Consulting Partnership searches Informations systems C O N S U L T I N G
 Science Market Regulation UBIC C O N S U L T I N G 2014 Marketing Development Strategy Consulting Partnership searches Informations systems Technical & Competitive Scanning Regulations Manufacturers This
Science Market Regulation UBIC C O N S U L T I N G 2014 Marketing Development Strategy Consulting Partnership searches Informations systems Technical & Competitive Scanning Regulations Manufacturers This
Dietary fibre: What is it and how to measure it correctly
 Dietary fibre: What is it and how to measure it correctly Introduction It is generally recognized that dietary fibre is an essential part of the human food. In our western world the daily intake of dietary
Dietary fibre: What is it and how to measure it correctly Introduction It is generally recognized that dietary fibre is an essential part of the human food. In our western world the daily intake of dietary
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
Feeding Corn to Beef Cows
 ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
Controlling intestinal microflora with BioHealth, MicroHealth and LactoHealth. Below illustration shows clearly the effects of unbalanced microflora
 Controlling intestinal microflora with BioHealth, MicroHealth and LactoHealth Probiotics are products aimed at delivering living bacterial cells to the guts ecosystem of humans and other animals, whereas
Controlling intestinal microflora with BioHealth, MicroHealth and LactoHealth Probiotics are products aimed at delivering living bacterial cells to the guts ecosystem of humans and other animals, whereas
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
B12 & Cobalamin. Learning objectives
 Learning objectives B12 & Cobalamin Define vitamins Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and biological active coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources
Learning objectives B12 & Cobalamin Define vitamins Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and biological active coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates
 Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
Diet formulation: making use of non-linear functions
 Diet formulation: making use of non-linear functions Rick Kleyn, Nutrition Consultant, SPESFEED (Pty) Ltd. Introduction Traditionally, feed formulation is achieved through the use of linear programming
Diet formulation: making use of non-linear functions Rick Kleyn, Nutrition Consultant, SPESFEED (Pty) Ltd. Introduction Traditionally, feed formulation is achieved through the use of linear programming
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition
 Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide monomers covalently linked by a glycosidic bond. They function in sugar transport.
 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1.
Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies
 Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies Diana Sammataro, Ph.D. USDA-ARS Carl Hayden Bee Research Center Tucson, AZ Our Website: http://gears.tucson.ars.ag.gov Lactobacillus spp. Bifidobacterium spp.
Beneficial Microflora in Honey Bee Colonies Diana Sammataro, Ph.D. USDA-ARS Carl Hayden Bee Research Center Tucson, AZ Our Website: http://gears.tucson.ars.ag.gov Lactobacillus spp. Bifidobacterium spp.
Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply
 Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply Cycle meeting 26. may - 2014 Hallgeir Sterten Felleskjøpet Fôrutvikling AS Outline Global trends feed and food Situation
Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply Cycle meeting 26. may - 2014 Hallgeir Sterten Felleskjøpet Fôrutvikling AS Outline Global trends feed and food Situation
The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates
 The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates David D. Maenz Chief Scientific Officer MCN BioProducts Inc. Conventional Canola Processing Whole seed Solvent extraction or double press
The Production and Use of High-Valued Canola Protein Concentrates David D. Maenz Chief Scientific Officer MCN BioProducts Inc. Conventional Canola Processing Whole seed Solvent extraction or double press
DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES
 Page 1 DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES Drugs to know are: Actrapid HM Humulin R, L, U Penmix SUNALI MEHTA The three principal hormones produced by the pancreas are: Insulin: nutrient metabolism:
Page 1 DRUGS FOR GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT AND DIABETES Drugs to know are: Actrapid HM Humulin R, L, U Penmix SUNALI MEHTA The three principal hormones produced by the pancreas are: Insulin: nutrient metabolism:
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT. No. 12 April, 2001. Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey
 BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I. Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU
 Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU Objectives At the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Define key terms. Identify the basic
Microbial Nutrition And bacterial Classification Microbiology Unit-I Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMU Objectives At the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Define key terms. Identify the basic
EGG FORMATION AND EGGSHELL QUALITY IN LAYERS
 EGG FORMATION AND EGGSHELL QUALITY IN LAYERS Amy Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. 01/05 1 EGG FORMATION AND EGGSHELL QUALITY IN LAYERS Amy Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist
EGG FORMATION AND EGGSHELL QUALITY IN LAYERS Amy Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. 01/05 1 EGG FORMATION AND EGGSHELL QUALITY IN LAYERS Amy Halls, Monogastric Nutritionist
High Available Phosphorus Corn and Phytase in Layer Diets 1
 High Available Phosphorus Corn and Phytase in Layer Diets 1 N. Ceylan, 3 S. E. Scheideler, 2 and H. L. Stilborn 4 Department of Animal Sciences, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, Nebraska 68583-0908 ABSTRACT
High Available Phosphorus Corn and Phytase in Layer Diets 1 N. Ceylan, 3 S. E. Scheideler, 2 and H. L. Stilborn 4 Department of Animal Sciences, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, Nebraska 68583-0908 ABSTRACT
