Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology
|
|
|
- Dorothy Henry
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding Feed Analysis Terminology One of the most important steps in developing a ration suitable for dairy animals is feed testing. It is essential to have a starting point in order to formulate a ration to the recommended level for high producing cows. Forages are the most variable of all the feedstuffs tested and because of the large inclusion rate in the rations require the most attention. The test results are only useful if the recipient can interpret the report. The following is designed to give some explanation and insight into the various terminologies. AS FED AND DRY MATTER BASIS As fed refers to the actual amount of a feed or nutrient fed to livestock and includes the moisture present in the feed, whereas dry matter basis refers to the quantity of feed after the water is removed. All nutrients in forages are contained in its dry matter and animals consume feeds to meet their dry matter requirements. High moisture content in feeds means the animal has to consume more feed to receive the same amount of dry matter as it would from a drier feed. For instance, when an animal consumes 10 kg hay at 90% DM, it consumes 9 kg DM. But if the animal consumes haylage at 40%, it would have to consume 22.5 kg to get the same amount of DM (9 kg/0.4 = 22.5kg). PROTEIN FRACTIONS Proteins are made up of complex combinations of various aminoacids and are required on a daily basis for maintenance, especially for muscle development and milk production. CRUDE PROTEIN (CP) is the total nitrogen content of the feed (true protein and non-protein nitrogen) multiplied by This is based on the assumption that true protein contains 16% nitrogen. Grains generally have a CP content of 8 to 14 percent, with corn often being at the 7 to 9 percent range and wheat and oats in the 10 to 14 percent range. The CP is used by rumen bacteria for digesting forage and concentrates in the diet. In addition to the rumen microbes (source of protein for the cow), high-performing animals, especially milking dairy cows, need larger amounts of protein to be absorbed from the intestines (by pass protein or UIP). ACID DETERGENT INSOLUBLE PROTEIN OR BOUND PROTEIN (ADF-CP or ADP) is the portion of CP that is bound to the ADF fraction of the cell wall. This value represents heat damaged protein because excessive heating has occurred and is unavailable to both microbes and the cow. The Maillard reaction causes heat damage by covalently linking nitrogen from amino acids to sugar residues of the plant cell wall. Moisture and heat are needed to promote this reaction. This protein is often subtracted from the feed s total crude protein to estimate available crude protein. Values higher than 12% (as % CP) in silages indicate that some overheating of the silage has occurred. An adjusted CP value will be included in the report if the bound protein becomes too high (>12% of CP). If an adjusted CP value is included, this value should be used in ration formulation.
2 Heat treated soybeans, distillers and brewers grains, corn gluten feed and meal among other products should be tested for ADP if their color ranges from light to dark brown. Silages are also of concern with bound protein and all silage analyses should have ADP determined. NEUTRAL DETERGENT INSOLUBLE PROTEIN OR BOUND PROTEIN (NDF-CP or NDP) is a measure similar to ADP, except the procedure to determine nitrogen content is completed on the NDF fraction of a feed. Nitrogen found in NDF includes that in ADP in addition to other feed proteins less soluble in neutral detergent or associated with cell wall fiber. These proteins are not all indigestible, similar to ADP, but are considered more slowly degraded in the rumen. This protein fraction is used by rumen computer models (CNCPS, CPM) to estimate rumen undegraded protein fraction. DIGESTIBLE PROTEIN measures of rumen availability of feed nitrogen. Because of the feeding rate and the retention time in the rumen, not all of the protein present has time to be digested. Rumen degradable protein includes all soluble protein and those rumen insoluble proteins that can be degraded in the rumen providing their residence time is sufficient (e.g., most affected by rate of passage issues). SOLUBLE PROTEIN (SP) is the portion of the available protein that is potentially soluble in rumen fluid. It can be expressed as percent of CP. In the new ration evaluation models, SP is measured as protein soluble in a borate-phosphate buffer (ph=6.9). SP is rapidly degraded by rumen microbes. It is present in large amounts in alfalfa silage. Haylages are generally in the range of 40-60% soluble protein, hay 20%, dry corn 12%, high moisture corn 40%, corn silage 55%, soybean meal 20%, and roasted beans 15%. UIP BYPASS PROTEIN (% of CP) is the protein that has a slow rate of degradability and escape digestion in the rumen because it is not used by the rumen microbes. UIP is also known as escape or bypass protein and it may either be absorbed in the small intestine or part of it may not be used at all by the cow and will end up in the manure. AMMONIA NITROGEN as a percent of total nitrogen measures the NPN component of the soluble protein fraction. This analysis is most often used as part of a fermentation profile to assess the amount of proteolytic activity within the silage. One goal of silage is to minimize proteolytic activity from plant respiratory enzymes or microbes, primarily Clostridium spp. High proteolytic activity will buffer and increase silage ph making it less stable. In addition, some toxic NPN compounds such as amines can reduce feed intake. The goal is to have ammonia nitrogen less than 8% and 10-12% of total nitrogen for corn silage and hay-crop silage, respectively. In wet, Clostridial fermentation silages this value may exceed 20% or even higher. Higher ammonia nitrogen in silage increases the rapidly degraded rumen nitrogen and can contribute to high blood and milk urea nitrogen concentrations. CARBOHYDRATE FRACTIONS FIBRE Fibre is the portion of the plant that provides the plant s structural strength and form. Generally, the vegetative parts, especially the stem, have the highest fibre content. Seed hulls and/or coats also often contain fibre. Fibre is composed of several different types of compounds and is the major constituent of plant cell walls. The components of fibre that provide the fibre value are hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin. Fibre values in plants are a function of the growing
3 conditions and maturity. As plants mature, the fibre levels increase. Fibre is important for maintaining normal rumen function, however, excessive fibre in a ration will limit nutrient intake and ration utilization. NEUTRAL DETERGENT FIBRE (NDF) estimates the total fibre content of a forage (cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin). NDF results are reported as andf as the procedure includes sodium sulphite and α-amylase. NDF is partially digestible depending on forage crop and maturity stage. NDF levels are used to predict feed intake. High NDF levels in a forage not only decrease intake, but also limit forage value, for example, in high milk production. NDF DIGESTIBILITY (NDFD) is the portion of NDF that is digestible in the rumen after 24 or 48 hr. Research has shown that cows eat more and produce more milk when forages with higher NDFD levels are fed. Therefore, the use of NDFD values will result in more accurately balanced rations and more predictable production. Factors such as forage species, maturity, genetics and environment influence NDFD levels. NDFD values can vary significantly among forages with similar NDFs as well as among various forage species. Although legumes tend to have lower %NDF levels than grasses, the NDFD of legumes tends to be lower than that of grass NDF. Legumes have a greater degree of lignification compared to grasses. This may explain why we often see cows producing more milk on grass forages than we would expect, based on the available feed analysis. The range of NDFD in grasses is greater than that found in legumes or corn silage because of the extreme range in conditions under which grasses are often harvested. Corn silage, which is generally harvested within a narrow range of maturity, has a narrower range of NDFDs. ACID DETERGENT FIBRE (ADF) measures cellulose and lignin contents of a plant and is related to the digestibility of a forage. ADF is also partially digestible. When ADF levels increase, forage digestibility usually decreases, so that low levels of ADF are desirable. Some factors that increase ADF in a forage are maturity, weathering, rain damage, high temperatures and weeds. LIGNIN is a non-carbohydrate constituent that is the main factor which influences the digestibility of plant cell wall material. It is a fibre compound with no energy value for animals but it can affect the digestibility of other fibre components. Low levels are desirable. When lignin increases, digestibility, intake and performance usually decrease. It is more abundant in legume forages than in grasses or corn silage. NON FIBRE CARBOHYDRATES (NFC) Non fibre carbohydrates estimate readily available CHO (organic acids, sugars, starches, soluble fibre). They represent the components of the plant that provide energy to the animal and are stored within the cell. In ruminants, NFC are broken down by the microbial population in the rumen and used as an energy source. Starch is a polysaccharide made up of units of glucose bounded together and found primarily in the grain or seed and/or root portions of plants. Depending on the starch source and processing, the glucose units may be very tightly bonded and compacted together or they may be weakly linked together. For this reason, different starches may be either rapidly or slowly fermented in the rumen. Most of the NFC fraction is made up of starch (28-32% of the total ration DM). Starch is a good source of energy.
4 Sugars are fermented in the rumen to the stronger acids, propionic acid and lactic acid. Sugars are not present in large amounts (4-6% of the ration DM) in traditional dairy cattle diets. Starch and sugars are used as an energy source for the rumen microbes. The microbes convert the starch and sugars into volatile fatty acids, primarily propionic acid, which is absorbed across the rumen wall. The volatile fatty acids are used for energy or for glucose production by the cow. MINERALS Minerals are the inorganic component of animals and plants and are determined by burning off the organic matter and weighing the residue. The total mineral content of a forage is called Ash and represents 3-12% of DM. Values above 10% for grasses or 14% for legumes usually indicate soil contamination of forage. MACRO MINERALS are those required in relatively large amounts by livestock and include: Calcium (Ca), Phosphorous (P), Potassium (K), Magnesium (Mg) and Sulphur (S). MICRO MINERALS are those required in relatively small amounts by livestock and include: Manganese (Mn), Iron, (Fe), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn) and Molybdenum (Mo). ENERGY Energy is the nutrient required in the greatest amount. For livestock, energy requirements are determined for maintenance, growth or gain, lactation, reproduction and activity level. It is predicted based on the amounts of nutrients, such as protein, fibre, non-structural carbohydrates, and fat. Accurately predicting the digestible energy of forages for ration formulation and animal performance is important. There are different measures to describe the energy value of a feed. The most popular ones are: net energy (NE), total digestible nutrients (TDN) and relative feed values (RFV) that can be calculated from core analyses. TDN represents the digestible portion of a feed and it can also be used to estimate the energy content of a forage. TDN is the sum of the digestible fiber, protein, lipid, and carbohydrate components of a feedstuff or diet. TDN is directly related to digestible energy and is often calculated based on ADF. TDN is useful for beef cow rations that are primarily forage. When moderate to high concentrations of concentrate are fed, net energy (NE) should be used to formulate diets and predict animal performance. TDN values tend to underpredict the feeding value of concentrate relative to forage. SGS AgriFood Labs provides two different approaches to predict total digestible nutrients (TDN) and net energy for lactation (NEl). a) Summative equations based on contributions of protein, fibre, non-structural carbohydrates and fat and; b) Equations based on a single fibre fraction (ADF). NET ENERGY (NE) is the energy used for maintenance and for productive purposes (growth, gestation, and lactation). NE is derived from animal studies by measuring the gross energy minus fecal energy, minus energy lost in urine and minus combustible gases and heat loss. NET ENERGY FOR LACTATION (NEl) represents the amount of digestible nutrients in a feed or forage fed to a milking cow whose energy needs are 3 times what they would be if she were just
5 in a maintenance state. It also represents the nutrients that are used for non-productive purposes (such as heat) and the efficiency with which the cow uses energy for milk production, pregnancy and maintenance. For a lactating dairy cow, NEl is the only energy estimate needed for ration balancing. NET ENERGY FOR GAIN (NEg) reports the energy value of a feed used for body weight gain above that required for maintenance. NET ENERGY FOR MAINTENANCE (NEm) reports the energy value of a feed used to keep an animal at a stable weight. RELATIVE FEED VALUE is a factor that evaluates forage quality based on ADF and NDF as compared to full bloom alfalfa with assigned value of 100. RFV is an index that accounts for an animal s potential forage intake and its energy or digestibility. It is useful for comparing forages of the same type although nutritionists are more interested in the amount of CP, ADF, NDF and minerals in a forage. Higher RFV indicate higher quality forage. RELATIVE FEED QUALITY (RFQ) is a factor that combines predicted intake (NDF) and digestibility (ADF). However, RFQ differs from RFV because it is based on estimates of forage intake and digestibility determined by incubating the feedstuff with rumen microorganisms in a simulated digestion. Therefore, it is a more accurate predictor of forage value than RFV. Neither RFV nor RFQ are used in ration formulation.
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources. Introduction
 Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
Forage Crises? Extending Forages and Use of Non-forage Fiber Sources Mike Allen and Jennifer Voelker Michigan State University Dept. of Animal Science Introduction Forage availability is sometimes limited
FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION
 Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Department of Animal Science FEEDING THE DAIRY COW DURING LACTATION Dairy Cattle Production 342-450A Page 1 of 8 Feeding the Dairy Cow during Lactation There are main stages in the lactation cycle of the
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets
 Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Understanding CNCPS and CPM: Biology, Modeling, and Best Cost Applications for Balancing the Nutrient Requirements in Dairy Diets T. R. Overton, M. E. Van Amburgh, and L. E. Chase Department of Animal
Opportunities Inputting Lab Values in Ration Software
 Opportunities Inputting Lab Values in Ration Software NIRSC/NFTA/FeedAC Joint Annual Meeting Feb 13, 2008 Indianapolis, IN Dr. Tim Snyder Nutrition Manager Nutritional and management consulting serving
Opportunities Inputting Lab Values in Ration Software NIRSC/NFTA/FeedAC Joint Annual Meeting Feb 13, 2008 Indianapolis, IN Dr. Tim Snyder Nutrition Manager Nutritional and management consulting serving
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION
 EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
EXTENSION CIRCULAR 422 FROM FEED TO MILK: UNDERSTANDING RUMEN FUNCTION CONTENTS Part I: Background in Basic Nutrition of Dairy Cattle... 1 Rumen physiology...1 Rumination and saliva production... 3 Function
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS
 CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada Inc. CORN BY-PRODUCTS IN DAIRY COW RATIONS Dennis Lunn, Ruminant Nutritionist Shur-Gain, Nutreco Canada
Energy in the New Dairy NRC. Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University
 Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Energy in the New Dairy NRC Maurice L. Eastridge 1 Department of Animal Sciences The Ohio State University Introduction Energy is vital to the function of all cells, and thus physiologically, it is vital
Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices
 87 Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices Joanne Knapp J.D. Heiskell & Co. Abstract Due to unprecedented changes in grain prices during the past year, the dairy industry is reexamining how
87 Strategies for Diet Formulation with High Corn Prices Joanne Knapp J.D. Heiskell & Co. Abstract Due to unprecedented changes in grain prices during the past year, the dairy industry is reexamining how
6/29/2009 6.8 5.3 TDN
 Common Sense Meat Goat-Nutrition Brian Freking OSU LeFlore Co. Extension Nutrition Feeding goats is the single largest expense behind the purchase cost of the animals. Can be as high as 60% of the total
Common Sense Meat Goat-Nutrition Brian Freking OSU LeFlore Co. Extension Nutrition Feeding goats is the single largest expense behind the purchase cost of the animals. Can be as high as 60% of the total
Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows
 Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
Feed Management A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Effective Fiber for Dairy Cows R. D. Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College
BEC Feed Solutions. Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions
 BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
BEC Feed Solutions Presenter: Steve Blake BEC Feed Solutions Nutritional Role of Phosphorus Phosphorus (P) is present in all cells in the body Essential for many digestive and metabolic processes, including
Heat of combustion (gross energy)
 J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
J.D. Pagan 71 MEASURING THE DIGESTIBLE ENERGY CONTENT OF HORSE FEEDS JOE D. PAGAN Kentucky Equine Research, Inc., Versailles, Kentucky, USA One of the most important measures of a horse feed s value is
NUTRIENT SPECIFICATIONS OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL
 UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
UTILIZATION OF TURKEY WASTE MATERIAL IN BEEF CATTLE DIETS Dale R. ZoBell, PhD, Beef Cattle Specialist Gary Anderson, Sanpete County Agent Clell Bagley, DVM, Extension Veterinarian July 1999 AG504 INTRODUCTION
Understanding the. Soil Test Report. Client and Sample Identification
 Understanding the Soil Test Report Page 1 of 7 Crops absorb the nutrients required from soil in order to grow, so ensuring that your soil is meeting the crops needs is critical. Having the proper level
Understanding the Soil Test Report Page 1 of 7 Crops absorb the nutrients required from soil in order to grow, so ensuring that your soil is meeting the crops needs is critical. Having the proper level
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT. No. 12 April, 2001. Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey
 BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
BURNETT CENTER INTERNET PROGRESS REPORT No. 12 April, 2001 Summary of the 2000 Texas Tech University Consulting Nutritionist Survey M. L. Galyean and J. F. Gleghorn Department of Animal Science and Food
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands
 Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Protein and Energy Supplementation to Beef Cows Grazing New Mexico Rangelands Cooperative Extension Service Circular 564 College of Agriculture and Home Economics CONTENTS General ruminant nutrition...
Land O Lakes Feed DDGS. Nutrients Concentrate: United States Ethanol Outlook. A Growing Opportunity
 DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
DDGS A Growing Opportunity Dr. Harold Tilstra Region Manager Land O Lakes Feed hdtilstra@landolakes.com 4/9/2004 Land O' Lakes Feed; Tilstra 2 Land O Lakes Feed Vision: To To be the leading animal nutrition
Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle
 Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle Terry Klopfenstein Distillers byproducts are excellent feed resources for feedlot cattle. Distillers byproducts are normally available for use in feedlot finishing diets
Distillers Grains for Beef Cattle Terry Klopfenstein Distillers byproducts are excellent feed resources for feedlot cattle. Distillers byproducts are normally available for use in feedlot finishing diets
Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis
 Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis Dan Undersander 1 University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Introduction Dairymen use feed and forage testing to reduce feed costs and maximize production. As such, accuracy
Uses and Abuses of NIR for Feed Analysis Dan Undersander 1 University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Introduction Dairymen use feed and forage testing to reduce feed costs and maximize production. As such, accuracy
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs
 61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
61 Grouping to Increase Milk Yield and Decrease Feed Costs Michael S. Allen 1 Department of Animal Science Michigan State University Abstract There are many advantages of grouping cows to optimize their
NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED
 NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED Dan B. Faulkner and Mike F. Hutjens University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Drought conditions often result in poor pastures and reduced forage yields. Often producers wish
NITRATES IN LIVESTOCK FEED Dan B. Faulkner and Mike F. Hutjens University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Drought conditions often result in poor pastures and reduced forage yields. Often producers wish
Corn Stalks and Drought-Damaged Corn Hay as Emergency Feeds for Beef Cattle
 Contacts: Matt Poore, Science, 919.515.7798 Jim Turner, Science, 828.246.4466 North Carolina Cooperative Extension College of Agriculture and Life Sciences North Carolina State University or contact your
Contacts: Matt Poore, Science, 919.515.7798 Jim Turner, Science, 828.246.4466 North Carolina Cooperative Extension College of Agriculture and Life Sciences North Carolina State University or contact your
Summary. Keywords: methanol, glycerin, intake, beef cattle. Introduction
 Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
Effect of Methanol Infusion on Intake and Digestion of a Grain-based Diet by Beef Cattle K.N. Winsco, N.M. Kenney, R.O. Dittmar, III, J.A. Coverdale, J.E. Sawyer, and T.A. Wickersham Texas A & M University,
Carbon-organic Compounds
 Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS?
 WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS? Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories Inc. Kearney, NE Commercial fertilizer is a source of plant nutrients that can be applied to soil to nourish crops when the
WHAT IS IN FERTILIZER OTHER THAN NUTRIENTS? Raymond C. Ward Ward Laboratories Inc. Kearney, NE Commercial fertilizer is a source of plant nutrients that can be applied to soil to nourish crops when the
Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle
 DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Agriculture and Natural Resources Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle FSA3047 Shane Gadberry Associate Professor - Animal Science
DIVISION OF AGRICULTURE RESEARCH & EXTENSION University of Arkansas System Agriculture and Natural Resources Alternative Feeds for Beef Cattle FSA3047 Shane Gadberry Associate Professor - Animal Science
Pasture Forage Quality in West Virginia
 Pasture Forage Quality in West Virginia WVU Pasture Quality Program Team 1 December 2003 Cattle and sheep need to obtain most of their nutrients from forage, particularly pasture, if they are to be fed
Pasture Forage Quality in West Virginia WVU Pasture Quality Program Team 1 December 2003 Cattle and sheep need to obtain most of their nutrients from forage, particularly pasture, if they are to be fed
World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition
 World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition INTRODUCTION Most kids are taught to eat their fruits and vegetables. Why? Because they are good for you, and provide several essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy,
World of Dairy Cattle Nutrition INTRODUCTION Most kids are taught to eat their fruits and vegetables. Why? Because they are good for you, and provide several essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy,
Beef Cattle Handbook
 Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5610 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Nitrates in Livestock Feed Dan B. Faulkner, Extension Beef Specialist, University of Illinois Mike F. Hutjens, Extension
Beef Cattle Handbook BCH-5610 Product of Extension Beef Cattle Resource Committee Nitrates in Livestock Feed Dan B. Faulkner, Extension Beef Specialist, University of Illinois Mike F. Hutjens, Extension
Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle
 Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle T.C. Gilbery, G.P. Lardy, D.S. Hagberg and M.L. Bauer NDSU
Effect of Flaxseed Inclusion on Ruminal Fermentation, Digestion and Microbial Protein Synthesis in Growing and Finishing Diets for Beef Cattle T.C. Gilbery, G.P. Lardy, D.S. Hagberg and M.L. Bauer NDSU
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock
 Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
Feeding Flood-Damaged or Sprouted Crops to Livestock High moisture conditions often lead to crop damage and losses. Some losses are from grain sprouting in the head before harvest. These sprouted grains
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition
 Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Practical Beef Cattle Nutrition About HCC Hybu Cig Cymru/Meat Promotion Wales (HCC) is the strategic body for the promotion and development of red meat in Wales and the development of the Welsh red meat
Sheep Nutrition. Sheep Nutrition. Nutrient Needs. Sheep Nutrition Water. Products Produced. Use of Pasture\Range and Forages.
 Products Produced Muscle (Meat) Milk Fiber (wool, mohair, cashmere) Use of Pasture\Range and Forages Able to produce acceptable product on forage Nutrient Needs Water Energy (TDN, ME, or NE) Protein (CP
Products Produced Muscle (Meat) Milk Fiber (wool, mohair, cashmere) Use of Pasture\Range and Forages Able to produce acceptable product on forage Nutrient Needs Water Energy (TDN, ME, or NE) Protein (CP
OPTIMIZING DIFFERENT HAY TYPES FOR HORSES: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNED? Anne Rodiek 1 ABSTRACT
 OPTIMIZING DIFFERENT HAY TYPES FOR HORSES: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNED? Anne Rodiek 1 ABSTRACT Good quality hay is the cornerstone of all horse feeding programs. Healthy adult horses can do well on diets composed
OPTIMIZING DIFFERENT HAY TYPES FOR HORSES: WHAT HAVE WE LEARNED? Anne Rodiek 1 ABSTRACT Good quality hay is the cornerstone of all horse feeding programs. Healthy adult horses can do well on diets composed
Feed Management Plan Template (06. 21. 10) Address: Address: Town, State, Zip: Homer City. Farm Name: Phone: Fax: e-mail:
 Feed Management Plan Template (06. 21. 10) Producer's Name: Address: LG Address: Town, State, Zip: Homer City Farm Name: Phone: Fax: e-mail: Consultant's Name: Cargill Animal Nutrition Address: Address:
Feed Management Plan Template (06. 21. 10) Producer's Name: Address: LG Address: Town, State, Zip: Homer City Farm Name: Phone: Fax: e-mail: Consultant's Name: Cargill Animal Nutrition Address: Address:
PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING
 PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING AND FINISHING CATTLE D.R. ZoBell and W. C. Burrell October 2002 AG 514 INTRODUCTION Roughage is the principal component of most cattle diets and as such can greatly influence
PRODUCING WHEY SILAGE FOR GROWING AND FINISHING CATTLE D.R. ZoBell and W. C. Burrell October 2002 AG 514 INTRODUCTION Roughage is the principal component of most cattle diets and as such can greatly influence
Mammalian digestive tracts
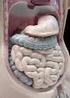 Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Mammalian digestive tracts Mouth: mastication, some digestive enzymes Esophagus: simple transport tube Stomach: most initial digestion, some physical processing Small intestine: digestion continues, some
Ruminant Digestive System
 Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Ruminant Digestive System Complex structure with four compartments Source: Animal Feeding and Nutrition (Jurgens) Ruminant Characteristics Primarily herbivores Cattle, sheep, goats, deer, elk Camelids
Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure
 Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA4017 Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure Jodie A. Pennington Professor - Dairy and Goats Karl VanDevender Professor - Waste Management John A. Jennings Professor
Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA4017 Nutrient and Fertilizer Value of Dairy Manure Jodie A. Pennington Professor - Dairy and Goats Karl VanDevender Professor - Waste Management John A. Jennings Professor
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates
 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
Sugars, Starches, and Fibers Are All Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? Today's food advertisements call them carbs, but they are not all the same. They are a group of compounds that have some similarities
ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS
 ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS D. S. Secrist 1, F. N. Owens 2, W. J. Hill 1 and S. D. Welty 3 Story in Brief The differences between rolled (2 particle sizes)
ROLLED VERSUS WHOLE CORN: EFFECTS ON RUMINAL FERMENTATION OF FEEDLOT STEERS D. S. Secrist 1, F. N. Owens 2, W. J. Hill 1 and S. D. Welty 3 Story in Brief The differences between rolled (2 particle sizes)
2014 Virginia State Feed Association & Nutritional Management "Cow" College 2/20/2014. Patton Nittany Dairy Nutrition, Inc.
 The Practical Application of Balancing Lactating Cow Rations for Amino Acids Robert A. Patton Nittany Dairy Nutrition, Inc Mifflinburg, PA Background Nature has made the protein and AA nutrition of the
The Practical Application of Balancing Lactating Cow Rations for Amino Acids Robert A. Patton Nittany Dairy Nutrition, Inc Mifflinburg, PA Background Nature has made the protein and AA nutrition of the
How Do I Select Quality Hay?
 How Do I Select Quality Hay? Hay is an important part of the diet for horses and livestock so it only makes sense to choose a high quality hay to feed to your animals. There are two methods of hay evaluation:
How Do I Select Quality Hay? Hay is an important part of the diet for horses and livestock so it only makes sense to choose a high quality hay to feed to your animals. There are two methods of hay evaluation:
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART
 UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
Minerals. by Dr. Rick Machen Associate Professor & Extension Livestock Specialist Texas Agric ultural Exte nsio n Service, Uvalde
 Minerals Small Ruminant Series by Dr. Rick Machen Associate Professor & Extension Livestock Specialist Texas Agric ultural Exte nsio n Service, Uvalde As mentioned in previous articles, the nutrient requirements
Minerals Small Ruminant Series by Dr. Rick Machen Associate Professor & Extension Livestock Specialist Texas Agric ultural Exte nsio n Service, Uvalde As mentioned in previous articles, the nutrient requirements
Feeding Corn to Beef Cows
 ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
ExEx 2048 September 2005 Animal & Range Sciences COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES / SOUTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY / USDA Feeding Corn to Beef Cows Cody Wright, Extension beef specialist In
ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS
 Fact Sheet 93-23 ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS John Balliette, Eureka County Extension Educator Ron Torell, Northeast Area Livestock Specialist Introduction Protein and energy supplements do not necessarily need
Fact Sheet 93-23 ALFALFA FOR BEEF COWS John Balliette, Eureka County Extension Educator Ron Torell, Northeast Area Livestock Specialist Introduction Protein and energy supplements do not necessarily need
Dr Erhard Briendenhann
 Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Dr Erhard Briendenhann Protein Research Foundation Soya processing nutritional and financial benefits Sponsored by: Protein Research Foundation SOYBEAN PROCESSING Nutritional and financial benefits Dr
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Grass Legume Mixtures:
 Mid Atlantic Dairy Grazing Conference Grass Legume Mixtures: Dairy grazing is high value grazing. Persistence (seedbank or root system), Quality (digestibility) Productivity per acre and per animal Perennials
Mid Atlantic Dairy Grazing Conference Grass Legume Mixtures: Dairy grazing is high value grazing. Persistence (seedbank or root system), Quality (digestibility) Productivity per acre and per animal Perennials
Feeding Dairy Cows. Cooperative Extension Service Kansas State University Manhattan
 Feeding Dairy Cows Cooperative Extension Service Kansas State University Manhattan The dairy feeding program affects productivity and profitability more than any other single factor. The effects of good
Feeding Dairy Cows Cooperative Extension Service Kansas State University Manhattan The dairy feeding program affects productivity and profitability more than any other single factor. The effects of good
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Corn Silage Gary Bates, Associate Professor, Plant and Soil Science
 Agricultural Extension Service The University of Tennessee SP434-D Corn Silage Gary Bates, Associate Professor, Plant and Soil Science CCorn silage is a high-quality forage crop that is used on many dairy
Agricultural Extension Service The University of Tennessee SP434-D Corn Silage Gary Bates, Associate Professor, Plant and Soil Science CCorn silage is a high-quality forage crop that is used on many dairy
High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D.
 High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D. Just about everybody has heard the hype about low-starch or high-fiber diets for horses, but what is the rationale behind
High-Fiber Low-Starch Diets: The New Nutritional Wisdom Kathleen Crandell, Ph.D. Just about everybody has heard the hype about low-starch or high-fiber diets for horses, but what is the rationale behind
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf
 3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
3 Digestion of feeds in the milk-fed calf This chapter describes the various processes of digestion in the milk-fed calf. The main points in this chapter The adult animal requires a fully functioning rumen
Feedlot Lamb Nutrition
 Feedlot Lamb Nutrition Joseph S. Rook, D.V.M. MSU Extension & Ag Experiment Station College of Veterinary Medicine Due to the relatively small number of sizable lamb feeder operations in MI, practitioners
Feedlot Lamb Nutrition Joseph S. Rook, D.V.M. MSU Extension & Ag Experiment Station College of Veterinary Medicine Due to the relatively small number of sizable lamb feeder operations in MI, practitioners
What a re r Lipids? What a re r Fatty y Ac A ids?
 2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
2010 - Beef Cattle In-Service Training Inclusion of Lipids into Beef Cattle Diets Reinaldo F. Cooke, Ph. D. Oregon State University EOARC, Burns What are Lipids? Organic compounds Plant and animal compounds
Feeding Dairy Cows. A manual for use in the Target 10 Nutrition Program. Edited by Joe Jacobs with Ann Hargreaves. Third Edition
 Feeding Dairy Cows A manual for use in the Target 10 Nutrition Program Edited by Joe Jacobs with Ann Hargreaves Third Edition Dairy Research and Development Corporation Department of Natural Resources
Feeding Dairy Cows A manual for use in the Target 10 Nutrition Program Edited by Joe Jacobs with Ann Hargreaves Third Edition Dairy Research and Development Corporation Department of Natural Resources
Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations
 Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations Dan N. Waldner Extension Dairy Specialist Oklahoma State University Introduction A variety of software programs are available in the marketplace
Comparison of Software Applications for Formulating Dairy Rations Dan N. Waldner Extension Dairy Specialist Oklahoma State University Introduction A variety of software programs are available in the marketplace
SOIL FERTILITY MANAGEMENT BASICS. Organic Soil Amendments and Fertilizers
 SOIL FERTILITY MANAGEMENT BASICS Organic Soil Amendments and Fertilizers What are Your Objectives for Soil and Crops? Increase soil organic matter Improve soil tilth Enhance nitrogen availability Increase
SOIL FERTILITY MANAGEMENT BASICS Organic Soil Amendments and Fertilizers What are Your Objectives for Soil and Crops? Increase soil organic matter Improve soil tilth Enhance nitrogen availability Increase
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488
 Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Forage Sorghum Production Guide
 Forage Sorghum Production Guide Dr. Twain Butler, Extension Agronomist Stephenville Dr. Brent Bean, Extension Agronomist - Amarillo Introduction The use of Sorghum has increased in recent years due to
Forage Sorghum Production Guide Dr. Twain Butler, Extension Agronomist Stephenville Dr. Brent Bean, Extension Agronomist - Amarillo Introduction The use of Sorghum has increased in recent years due to
How To Feed Cows In The Winter
 A l a s k a L i v e s t o c k S e r i e s Winter Feeding Programs For Beef Cattle and Calves LPM-00741 Before making management and feeding decisions about beef cattle and calves, consider the following
A l a s k a L i v e s t o c k S e r i e s Winter Feeding Programs For Beef Cattle and Calves LPM-00741 Before making management and feeding decisions about beef cattle and calves, consider the following
Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef
 Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef WDGS can be added to corn-based rations for finishing cattle at levels ranging from 10 to 40% of total ration dry matter. When added at levels
Summary of Distillers Grains Feeding Recommendations for Beef WDGS can be added to corn-based rations for finishing cattle at levels ranging from 10 to 40% of total ration dry matter. When added at levels
MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE
 MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE K. W. Cotanch and R. J. Grant W. H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute Chazy, NY INTRODUCTION This paper is a follow-up to our 2005
MEASURING PHYSICALLY EFFECTIVE FIBER ON-FARM TO PREDICT COW RESPONSE K. W. Cotanch and R. J. Grant W. H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute Chazy, NY INTRODUCTION This paper is a follow-up to our 2005
Beef cattle nutrition
 Nutrition Grazing Land Management Selling Managing the Breeder Herd Marketing Beef cattle nutrition An introduction to the essentials Published by Meat & Livestock Australia Limited Revised March 2015
Nutrition Grazing Land Management Selling Managing the Breeder Herd Marketing Beef cattle nutrition An introduction to the essentials Published by Meat & Livestock Australia Limited Revised March 2015
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State
 Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
Spawning and Casing Supplements David M. Beyer, Penn State Spawning and Casing Supplements What is our current understanding of mushroom nutrition? What is the purpose of supplementation? How many years
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant
 Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in Agriculture Now a Real Option Guy Webb B.Sc. REM Agricultural Consultant The Pursuit of Protein and Profit All agricultural enterprises, in essence, are based on the pursuit
As grain prices fluctuate
 MICHIGAN STATE U N I V E R S I T Y EXTENSION Extension Bulletin E-3074 New December 2009 Incorporating Distiller s Grain in Beef Cattle Diets As grain prices fluctuate over time, beef cattle producers
MICHIGAN STATE U N I V E R S I T Y EXTENSION Extension Bulletin E-3074 New December 2009 Incorporating Distiller s Grain in Beef Cattle Diets As grain prices fluctuate over time, beef cattle producers
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
POTASSIUM. Functions of Potassium in Plants. Potassium Deficiency Symptoms
 POTASSIUM Potassium is the last of what might be called the big three soil nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These three primary nutrients are, by far, the nutrients most commonly limiting
POTASSIUM Potassium is the last of what might be called the big three soil nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These three primary nutrients are, by far, the nutrients most commonly limiting
Forage Management Guide
 Forage Management Guide Helping farmers to preserve quality forage Farmers Introduction The key objective for any livestock farmer when preserving forage is to make a stable and nutritious feedstuff, with
Forage Management Guide Helping farmers to preserve quality forage Farmers Introduction The key objective for any livestock farmer when preserving forage is to make a stable and nutritious feedstuff, with
Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs
 Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs Michael F. Hutjens Department of Animal Sciences, University of Illinois, 232 ASL, 1207 W. Gregory Drive, Urbana, Illinois 61801 Email: hutjensm@uiuc.edu
Accelerated Replacement Heifer Feeding Programs Michael F. Hutjens Department of Animal Sciences, University of Illinois, 232 ASL, 1207 W. Gregory Drive, Urbana, Illinois 61801 Email: hutjensm@uiuc.edu
Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management
 Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Agriculture and Natural Resources FSA3038 Digestive System of the Horse and Feeding Management Steven M. Jones Associate Professor Animal Science Animals have different types of digestive systems based
Elliot Block, Ph.D. Senior Manager, Animal Research and Technical Services ARM & HAMMER Animal Nutrition Church & Dwight Co., Inc.
 Rumen Microbial Protein Production: Are We Missing an Opportunity to Improve Dietary and Economic Efficiencies in Protein Nutrition of the High Producing Dairy Cow? Elliot Block, Ph.D. Senior Manager,
Rumen Microbial Protein Production: Are We Missing an Opportunity to Improve Dietary and Economic Efficiencies in Protein Nutrition of the High Producing Dairy Cow? Elliot Block, Ph.D. Senior Manager,
Commodity Exchange Endorsement for Livestock Gross Margin for Dairy Cattle
 Commodity Exchange Endorsement for Livestock Gross Margin for Dairy Cattle This endorsement contains the exchange prices that are used to set expected and actual prices for LGM for Dairy Cattle. To find
Commodity Exchange Endorsement for Livestock Gross Margin for Dairy Cattle This endorsement contains the exchange prices that are used to set expected and actual prices for LGM for Dairy Cattle. To find
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Effect of corn silage kernel processing score on dairy cow starch digestibility
 Effect of corn silage kernel processing score on dairy cow starch digestibility William L. Braman, PhD, PAS John E. Kurtz Chr. Hansen, Inc. Milwaukee, Wisconsin (USA) Introduction In the USA, dairy producers
Effect of corn silage kernel processing score on dairy cow starch digestibility William L. Braman, PhD, PAS John E. Kurtz Chr. Hansen, Inc. Milwaukee, Wisconsin (USA) Introduction In the USA, dairy producers
pathway that involves taking in heat from the environment at each step. C.
 Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
Study Island Cell Energy Keystone Review 1. Cells obtain energy by either capturing light energy through photosynthesis or by breaking down carbohydrates through cellular respiration. In both photosynthesis
FEEDING AND MANAGING DRY COWS
 Extension Circular 372 FEEDING AND MANAGING DRY COWS College of Agricultural Sciences Cooperative Extension CONTENTS The dry period 3 Feeding the dry cow 4 Forages 4 Grain 5 Management 7 Dry-off day and
Extension Circular 372 FEEDING AND MANAGING DRY COWS College of Agricultural Sciences Cooperative Extension CONTENTS The dry period 3 Feeding the dry cow 4 Forages 4 Grain 5 Management 7 Dry-off day and
How To Get Healthy
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Utilization of Corn Co-Products in the Dairy Industry 1st Edition February 2008
 Utilization of Corn Co-Products in the Dairy Industry 1st Edition February 2008 A joint project of the Nebraska Corn Board and the University of Nebraska Lincoln Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources
Utilization of Corn Co-Products in the Dairy Industry 1st Edition February 2008 A joint project of the Nebraska Corn Board and the University of Nebraska Lincoln Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Which of the following can be determined based on this model? The atmosphere is the only reservoir on Earth that can store carbon in any form. A.
 Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Earth s Cycles 1. Models are often used to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results. A model of the carbon cycle is shown below. Which of the following can be determined based on this model?
Optimal livestock diet formulation with farm environmental compliance consequences. Joleen Hadrich, Christopher Wolf. and.
 Optimal livestock diet formulation with farm environmental compliance consequences Joleen Hadrich, Christopher Wolf and Stephen Harsh Michigan State University Selected Paper prepared for presentation
Optimal livestock diet formulation with farm environmental compliance consequences Joleen Hadrich, Christopher Wolf and Stephen Harsh Michigan State University Selected Paper prepared for presentation
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist
 What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist Many beef producers are familiar with high nitrates in forages and their toxic effects in cattle. Probably
What is Nitrite Toxicity? Georgia Cattleman, June 2002 John Andrae, Forage Extension Specialist Many beef producers are familiar with high nitrates in forages and their toxic effects in cattle. Probably
2011 Evaluation of Cool Season Grass Haylage Fermented with Small Grains
 2011 Evaluation of Cool Season Grass Haylage Fermente with Small Grains Dr. Heather Darby Chantel Cline, Erica Cummings, Rosalie Maen, an Hannah Harwoo January 2012, University of Vermont Extension Visit
2011 Evaluation of Cool Season Grass Haylage Fermente with Small Grains Dr. Heather Darby Chantel Cline, Erica Cummings, Rosalie Maen, an Hannah Harwoo January 2012, University of Vermont Extension Visit
The effects of partial replacement of corn silage on biochemical blood parameters in lactating primiparous dairy cows
 The effects of partial replacement of corn silage on biochemical blood parameters in lactating primiparous dairy cows U. Polat, H. Gencoglu, I.I. Turkmen Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Uludag,
The effects of partial replacement of corn silage on biochemical blood parameters in lactating primiparous dairy cows U. Polat, H. Gencoglu, I.I. Turkmen Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Uludag,
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Corn Silage Evaluation: MILK2000 Challenges and Opportunities with MILK2006. Randy Shaver
 Corn Silage Evaluation: Challenges and Opportunities with Randy Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College of Agricultural and Life Sciences University of Wisconsin
Corn Silage Evaluation: Challenges and Opportunities with Randy Shaver Professor and Extension Dairy Nutritionist Department of Dairy Science College of Agricultural and Life Sciences University of Wisconsin
Cellular Energy. 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following?
 Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
2. Which type of macromolecule contains high-energy bonds and is used for long-term energy storage?
 Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Energy Transport Study Island 1. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use energy from the Sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. These products are, in turn, used by the
Overview of Fat Digestion and Metabolism in Dairy Cows
 Overview of Fat Digestion and Metabolism in Dairy Cows James K. Drackley Professor of Animal Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana email: drackley@uiuc.edu Introduction Over the last 25 years, the use
Overview of Fat Digestion and Metabolism in Dairy Cows James K. Drackley Professor of Animal Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana email: drackley@uiuc.edu Introduction Over the last 25 years, the use
Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply
 Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply Cycle meeting 26. may - 2014 Hallgeir Sterten Felleskjøpet Fôrutvikling AS Outline Global trends feed and food Situation
Challenges in animal feed production - focus on sustainable raw material supply Cycle meeting 26. may - 2014 Hallgeir Sterten Felleskjøpet Fôrutvikling AS Outline Global trends feed and food Situation
CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats
 CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats A. Ahmadi 1, P.H. Robinson 1 1 Animal Science, University of California, Davis, California, USA, phrobinson@ucdavis.edu Abstract
CAPRICORN: A Windows Program for Formulating and Evaluating Rations for Goats A. Ahmadi 1, P.H. Robinson 1 1 Animal Science, University of California, Davis, California, USA, phrobinson@ucdavis.edu Abstract
Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle
 Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle Introduction: A preliminary investigation at Harper Adams University
Animal Science Research Centre - Beef Unit Trial Results 2005 (a) Evaluation of head-cut whole crop wheat and barley for beef cattle Introduction: A preliminary investigation at Harper Adams University
