Name: LAB: Patterns of Crustal Activity Adapted from Exploration in Earth Science, The Physical Setting, United Publishing Company, Inc.
|
|
|
- Joy Russell
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: LAB: Patterns of Crustal Activity Adapted from Exploration in Earth Science, The Physical Setting, United Publishing Company, Inc. INTRODUCTION: Studies of tectonics have shown that crustal activities are occurring worldwide. Earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain ranges do not occur randomly. Scientists discovered that when the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes were plotted on a world map, these locations occurred in a pattern. These patterns led scientists to believe that the Earth s crust is divided into different sections or plates. By plotting the locations of earthquakes, scientists have not only been able to locate plate boundaries, but have also been able to determine plate characteristics and predict the movement of the plates. The three types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent, and transform, describe how two plates move relative to one another. In this lab, you will look for the relationships between the locations of these crustal activities. OBJECTIVE: You will plot the areas in which earthquakes occur most frequently and identify other crustal activities that appear related to these zones. VOCABULARY: Mid-Ocean Ridges: Plate Tectonics: PROCEDURE: 1. On the blank world map provided, plot all the earthquakes from the Earthquakes Around the World Table. Use an x for each epicenter. 2. On December 26, 2004 the second most powerful earthquake ever recorded on a seismograph occurred undersea off the coast of Sumatra. This triggered a series of tsunamis that caused the deaths of over 200,000 people. This earthquake had an epicenter at 3.3ºN, 95.8ºE. Locate this earthquake on the chart and mark its position on your map with a dark blue T. 3. On March 11, 2011 the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan occurred off the and triggered a large tsunami that caused the deaths of over 15,000 people. This earthquake had an epicenter at 38ºN, 142ºE. Locate this earthquake on the chart and mark its position on your map with a dark blue T. 4. On the blank world map provided, plot all the volcanoes from the Active and Extinct Volcanoes Around the World Table. Use an for each volcano; label the following volcanoes when you plot them: Mauna Loa, Krakatau, Vesuvius, Mt. Ranier, Paricutin, Fuji, and Mt. St. Helens 5. Use a globe/world map (provided by your instructor) and the Tectonic Plates map from your Earth Science Reference Tables and plot on your map the location of the world s mountain ranges (including mid-ocean ridges). Shade in these areas on your map lightly using a brown colored pencil. 6. Use the World Seismicity map to lightly shade in the areas that earthquakes occur. Use a blue colored pencil. 7. Use the World Volcanoes map to lightly shade in the areas that volcanoes occur. Use a red colored pencil.
2 World Volcanoes
3
4
5 Discussion Questions: Answer using data from the lab and in complete thoughts. 1. What do you notice about the locations of earthquakes, mountains and volcanoes? 2. Compare the map of earthquakes and volcanoes with the map of mountains that you plotted. What similarities do you notice? 3. Which coast of North America has the greater amount of earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains? 4. Which ocean has the greater amount of earthquakes, volcanoes and mountains along its coasts? 5. According to the map what is the probability of either an earthquake or volcano occurring in your region? 6. Compare the world-wide crustal activity and the Tectonic Plates map on page 5 of the ESRT. How does the pattern of crustal activity compare to the location of the plate boundaries? 7. Why is the perimeter of around the Pacific Ocean referred to as the Ring of Fire? Part 2: Get to Know Tectonic Plates Directions: Use the attached tectonic map (which has been duplicated from the ESRT page 5) to answer the questions below. 1. Highlight the NAMES of each of the following: Trenches Hot Spots Ocean Ridges 2. Color each of the hot spot locations RED. 3. Fill in the names of the hot spots at each of the following locations: In the Continental United States On the Pacific Plate On the Nazca Plate On the Eurasian Plate On the African Plate
6 4. What do the arrows on the tectonic map indicate? 5. Look at the arrows along the trenches at any two adjacent plates. Which way are the plates moving? Toward or Away from each other? 6. What kind of boundary is located at a trench? 7. Look at the arrows along the ridges at any two adjacent plates. Which way are the plates moving? Toward or Away from each other? 8. What kind of boundary is located at a ridge? 9. Find the San Andreas Fault. What type of boundary is this? In which State is it located? 10. State the direction of movement of the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate at the San Andreas Fault. Pacific Plate North American Plate 11. Name the 2 plates located on either side of the following trenches: Aleutian Trench Tonga Trench 12. Name the two plates located on either side of each of the following ridges: Mid-Atlantic Ridge East Pacific Ridge Southeast Indian Ridge 13. Draw the symbols for each of the following boundaries in the space besides each: Convergent Plate Boundary Divergent Plate Boundary Transform Plate Boundary
7
8 Reading Comprehension Read the article on Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics below and answer the following questions based on the reading. Use complete sentences Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Abridged from Earthquake Information Bulletin, vol. 9, no. 6, November - December 1977, by Henry Spall, USGS, Reston, VA The world's earthquakes are not randomly distributed over the Earth's surface. They tend to be concentrated in narrow zones. Why is this? And why are volcanoes and mountain ranges also found in these zones, too? An explanation is to be found in plate tectonics, a concept which has revolutionized thinking in the Earth's sciences in the last 10 years. The theory of plate tectonics combines many of the ideas about continental drift (originally proposed in 1912 by Alfred Wegener in Germany) and sea-floor spreading (suggested originally by Harry Hess of Princeton University). Plate tectonics tells us that the Earth's rigid outer shell (lithosphere) is broken into a mosaic of oceanic and continental plates which can slide over the plastic aesthenosphere, which is the uppermost layer of the mantle. The plates are in constant motion. Where they interact, along their margins, important geological processes take place, such as the formation of mountain belts, earthquakes, and volcanoes. The lithosphere covers the whole Earth. Therefore, ocean plates are also involved, more particularly in the process of sea-floor spreading. This involves the midocean ridges which are a system of narrow submarine cracks that can be traced down the center of the major oceans. The ocean floor is being continuously pulled apart along these midocean ridges. Hot volcanic material rises from the Earth's mantle to fill the gap and continuously forms new oceanic crust. The midocean ridges themselves are broken by offsets know as transform faults. One of the keys to plate tectonics was the discovery that the Earth's magnetic field has reversed its polarity 170 times in the last 80 million years. As new basaltic material is squeezed up into the midocean cracks and solidifies, it is magnetized according to the polarity of the Earth's magnetic field. If the field reverses its polarity, the strip of new material is magnetized in an opposite sense. As the oceanic floor continues to spread, the new strips of rock are carried away on either side like a conveyer belt. Using these magnetic strips as evidence of movement, it became obvious that the Earth's surface consisted of a mosaic of crustal plates that were continually jostling one another. If the Earth was not to be blown up like a balloon by the continual influx of new volcanic material at the ocean ridges, then old crust must be destroyed at the same rate where plates collide. The required balanced occurs when plates collide, and one plate is forced under the other to be consumed deep in the mantle. We now know that there are seven major crustal plates, subdivided into a number of smaller plates. They are about 80 kilometers thick, all in constant motion relative to one another, at rates varying from 10 to 130 millimeters per year. Their pattern is neither symmetrical nor simple. As we learn more and more about the major plates, we find that many complicated and intricate maneuvers are taking place. We learn, too, that most of the geological action - mountains, rift valleys, volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting - is due to different types of interaction at plate boundaries. How are earthquakes connected with plate tectonics? In 1969, Muawia Barazangi and James Dorman published the locations of all earthquakes which occurred from 1961 to Most of the earthquakes are confined to narrow belts and these belts define the boundaries of the plates. The interiors of the plates themselves are largely free of large earthquakes, that is, they are aseismic. There are notable exceptions to this. An obvious one is the earthquakes at New Madrid, Missouri, and another is the 1886 earthquake at Charleston, South Carolina. As yet there is no satisfactory plate tectonic explanation for these isolated events; consequently, we will have to find alternative mechanisms.
9 Plate tectonics confirms that there are four types of seismic zones. The first follows the line of midocean ridges. Activity is low, and it occurs at very shallow depths. The point is that the lithosphere is very thin and weak at these boundaries, so the strain cannot build up enough to cause large earthquakes. Associated with this type of seismicity is the volcanic activity along the axis of the ridges (for example, Iceland, Azores, Tristan da Cunha). The second type of earthquake associated with plate tectonics is the shallow-focus event unaccompanied by volcanic activity. The San Andreas fault is a good example of this, so is the Anatolian fault in Northern Turkey. In these faults, two mature plates are scraping by one another. The friction between the plates can be so great that very large strains can build up before they are periodically relieved by large earthquakes. Nevertheless, activity does not always occur along the entire length of the fault during any one earthquake. For instance, the 1906 San Francisco event was caused by breakage only along the northern end of the San Andreas fault. The third type of earthquake is related to the collision of oceanic and continental plates. One plate is thrust or subducted under the other plate so that a deep ocean trench is produced. In the Philippines, ocean trenches are associated with curved volcanic island arcs on the landward plate, for example the Java trench. Along the Peru - Chile trench, the Nazca plate is being subducted under the South American plate which responds by crumpling to form the Andes. This type of earthquake can be shallow, intermediate, or deep, according to its location on the downgoing lithospheric slab. Such inclined planes of earthquakes are know as Benioff zones. The fourth type of seismic zone occurs along the boundaries of continental plates. Typical of this is the broad swath of seismicity from Burma to the Mediterranean, crossing the Himalayas, Iran, Turkey, to Gilbraltar. Within this zone, shallow earthquakes are associated with high mountain ranges where intense compression is taking place. Intermediate- and deep-focus earthquakes also occur and are known in the Himalayas and in the Caucasus. The interiors of continental plates are very complex, much more so than island arcs. For instance, we do not yet know the full relationship of the Alps or the East African rift system to the broad picture of plate tectonics. How can plate tectonics help in earthquake prediction? We have seen that earthquakes occur at the following three kinds of plate boundary: ocean ridges where the plates are pulled apart, margins where the plates scrape past one another, and margins where one plate is thrust under the other. Thus, we can predict the general regions on the Earth's surface where we can expect large earthquakes in the future. We know that each year about 140 earthquakes of magnitude 6 or greater will occur within this area which is 10 percent of the Earth's surface. But on a worldwide basis we cannot say with much accuracy when these events will occur. The reason is that the processes in plate tetonics have been going on for millions of years. Averaged over this interval, plate motions amount to a several millimeters per year. But at any instant in geologic time, for example, the year 1977, we do not know exactly where we are in the worldwide cycle of strain buildup and strain release. Only by monitoring the stress and strain in small areas, for instance, the San Andreas fault, in great detail can we hope to predict when renewed activity in that part of the place tectonics arena is likely to take place. In summary, plate tectonics is a blunt, but, nevertheless, strong tool in earthquake prediction. It tells us where 90 percent of the Earth's major earthquakes are likely to occur. It cannot tell us much about exactly when they will occur. For that, we must study in detail the plate boundaries themselves. Perhaps the most important role of plate tectonics is that it is a guide to the use of finer techniques for earthquake prediction.
10 1. In the third paragraph, the word mosaic is used. Mosaic means a picture or pattern produced by arranging together small pieces of hard material, such as stone, tile, or glass. How does the word mosaic relate to the concept of Plate Tectonics? 2. Using the paragraph that starts One of the keys to plate tectonics was, draw a picture to represent the reverse polarity conveyor belt that is described. 3. Why are earthquakes associated with faults such as the San Andreas Fault often very violent? 4. Why can we predict where earthquakes are going to occur, but not when they occur?
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates.
 Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into sections, called plates. These plates move around the mantle. Plates are composed of the crust and
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Does not include complete lecture notes. Continental drift: An idea before its time Alfred Wegener First proposed his continental drift hypothesis in 1915 Published The Origin
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
 4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67) Seafloor Spreading In the early 1960s, samples of basaltic ocean crust were dredged up from various locations across the ocean basins. The samples were then analyzed to
Chapter 2. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics: Learning Goals
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Plate Tectonics Chapter 2 Interactions at depend on the direction of relative plate motion and the type of crust. Which kind of plate boundary is associated with Earthquake activity? A. Divergent Boundary
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II
 Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 4: PLATE TECTONICS II 4. Which of the following statements about paleomagnetism at spreading ridges is FALSE? A. there is a clear pattern of paleomagnetic
Transform Boundaries
 Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Lecture 7 Plates and Mantle Plumes Transform Boundaries Transform boundaries occur where one segment of rigid lithosphere slides horizontally past another in response to stresses in the lithosphere. The
Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Plate Tectonics The unifying concept of the Earth sciences. The outer portion of the Earth is made up of about 20 distinct plates (~ 100 km thick), which move relative to each other This motion is what
Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter 8: Plate Tectonics -- Multi-format Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
DYNAMIC CRUST: Unit 4 Exam Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes NAME: BLOCK: DATE: 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas. Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics. The unifying concept of the Earth sciences.
 Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
Plate Tectonics: Big Ideas Our understanding of Earth is continuously refined. Earth s systems are dynamic; they continually react to changing influences from geological, hydrological, physical, chemical,
1. You are about to begin a unit on geology. Can anyone tell me what geology is? The study of the physical earth I.
 PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
PLATE TECTONICS ACTIVITY The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concept of plate tectonics and the formation of mountains. Students will discuss the properties of the earth s crust and plate tectonics.
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types
Plate Tectonics. Introduction. Boundaries between crustal plates
 Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics KEY WORDS: continental drift, seafloor spreading, plate tectonics, mid ocean ridge (MOR) system, spreading center, rise, divergent plate boundary, subduction zone, convergent plate boundary,
Plate Tectonics. Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2
 1 Plate Tectonics Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Continental Drift
1 Plate Tectonics Earth, 9 th edition Chapter 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Continental Drift
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
SIXTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SIXTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the structure of different types of volcanoes. LAB: Plotting
6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest
 Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Plate Tectonics Web-Quest Part I: Earth s Structure. Use the following link to find these answers: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html 1. Label the layers of Earth in the diagram
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones
 Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
Plate Tectonics: Ridges, Transform Faults and Subduction Zones Goals of this exercise: 1. review the major physiographic features of the ocean basins 2. investigate the creation of oceanic crust at mid-ocean
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
SECOND GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Investigating the parts of a volcano. LAB: Comparing the parts of a
Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
Earth Science Regents Questions: Plate Tectonics Name: Date: Period: August 2013 Due Date: 17 Compared to the oceanic crust, the continental crust is (1) less dense and more basaltic (3) more dense and
The Dynamic Crust 2) EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOVEMENT
 The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
The Dynamic Crust 1) Virtually everything you need to know about the interior of the earth can be found on page 10 of your reference tables. Take the time to become familiar with page 10 and everything
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science Grade 6. Unit Organizer: Geology: Inside the Earth (Approximate Time: 7 Weeks)
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Tectonic plates have different boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates move apart. BEFORE, you learned The continents join and break apart The sea floor provides evidence that tectonic plates move The theory of plate tectonics helps explain how the plates
KEY CONCEPT Plates move apart. BEFORE, you learned The continents join and break apart The sea floor provides evidence that tectonic plates move The theory of plate tectonics helps explain how the plates
11A Plate Tectonics. What is plate tectonics? Setting up. Materials
 11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
Puzzling Evidence What evidence suggests that continents move? In the late 1800s, Alfred Wegener proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. According to this hypothesis, the continents once formed a
Plate Tectonics. Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics. And I am Buddy Zed s mascot
 Plate Tectonics Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics And I am Buddy Zed s mascot Continental Drift Alfred Wegener proposed that continents were not always where
Plate Tectonics Hi, I am Zed and I am going to take you on a trip learning about Plate Tectonics And I am Buddy Zed s mascot Continental Drift Alfred Wegener proposed that continents were not always where
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007
 Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
Plate Tectonics Practice Questions and Answers Revised August 2007 1. Please fill in the missing labels. 2. Please fill in the missing labels. 3. How many large plates form the outer shell of the earth?
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers.
 1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers. Which statement about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have the curved shape shown? 1) Sediments were
Name Score /225. (Make sure you identify each key concept by identifying the section [1.1, 1.2, etc.].]
![Name Score /225. (Make sure you identify each key concept by identifying the section [1.1, 1.2, etc.].] Name Score /225. (Make sure you identify each key concept by identifying the section [1.1, 1.2, etc.].]](/thumbs/40/21046969.jpg) Name Score /225 Changing Earth Chapter 1 Worksheet Before reading Chapter 1 (pages 9 37). On a separate sheet of paper, make two columns. Title the first column Before I Read. Title the second column After
Name Score /225 Changing Earth Chapter 1 Worksheet Before reading Chapter 1 (pages 9 37). On a separate sheet of paper, make two columns. Title the first column Before I Read. Title the second column After
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
FIFTH GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Exploring the rocks produced by volcanoes. LAB: Comparing igneous rocks.
Plate Tectonics Lab. Continental Drift. The Birth of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Plate Tectonics Lab Continental Drift Take a look at a globe sometime and observe the remarkable fit between South America and Africa. Could they have, in fact, been connected? During the 19th and early
Name: Period: # Plate Tectonics. Journey to the center of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth Use pages 124 129 to answer the following questions. Exploring Inside Earth (p. 125-126) 1. What are the two main types of evidence that Geologist use
Rocks and Plate Tectonics
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
Continental Drift, Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics
 Page 1 of 13 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Continental Drift, Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics This page last updated on 26-Aug-2015 Plate Tectonics is a theory
Page 1 of 13 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Continental Drift, Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics This page last updated on 26-Aug-2015 Plate Tectonics is a theory
Step 2: Learn where the nearest divergent boundaries are located.
 What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
What happens when plates diverge? Plates spread apart, or diverge, from each other at divergent boundaries. At these boundaries new ocean crust is added to the Earth s surface and ocean basins are created.
FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST:
FIRST GRADE PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning the shapes of volcanoes. LAB: Experimenting with "lava." POST:
Continental Drift. Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on:
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Proposed that all of the continents were once part of a large supercontinent - Pangaea Based on: Similarities in shorelines
Plate Tectonics Visual Glossary and Atlas How to use this app in your classroom
 Plate Tectonics Visual Glossary and Atlas How to use this app in your classroom In addition to providing a comprehensive list of terms, definitions, illustrations, and animations related to plate tectonics,
Plate Tectonics Visual Glossary and Atlas How to use this app in your classroom In addition to providing a comprehensive list of terms, definitions, illustrations, and animations related to plate tectonics,
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics
 Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 laurel@princeton.edu Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Using Google Earth to Explore Plate Tectonics Laurel Goodell, Department of Geosciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 laurel@princeton.edu Inspired by, and borrows from, the GIS-based Exploring
Essential Question: How did the theory of Plate Tectonics evolve?
 Essential Question: How did the theory of Plate Tectonics evolve? 1. Look at a globe or a map of the Earth. Name the continents. (7 points) 2. How many continents are there? (3 points) 3. On a sheet of
Essential Question: How did the theory of Plate Tectonics evolve? 1. Look at a globe or a map of the Earth. Name the continents. (7 points) 2. How many continents are there? (3 points) 3. On a sheet of
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics
 Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013)
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines II. Earth Science (Geology) Section (9/18/2013) 1. Interior of the Earth Learning objectives: Understand the structure of the Earth s interior crust,
Plate Tectonics. Learning Guide. Pacific Plate. Pacific Ocean. Divergent boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Learning Guide North American Plate Eurasian Plate Arabian Plate Pacific Plate Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Cocos Plate Nazca Plate South American Plate African Plate Convergent boundary
Plate Tectonics Learning Guide North American Plate Eurasian Plate Arabian Plate Pacific Plate Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Cocos Plate Nazca Plate South American Plate African Plate Convergent boundary
Continents join together and split apart.
 KEY CONCEPT Continents change position over time. BEFORE, you learned Earth s main layers are the core, the mantle, and the crust The lithosphere and asthenosphere are the topmost layers of Earth The lithosphere
KEY CONCEPT Continents change position over time. BEFORE, you learned Earth s main layers are the core, the mantle, and the crust The lithosphere and asthenosphere are the topmost layers of Earth The lithosphere
[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics}
![[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} [Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics}](/thumbs/40/21755359.jpg) [Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} BACKGROUND Scientists and geologists have been able to do some drilling on Earth. They are also able
[Geology Layers of the Earth] [Basic: Grade 2-3] [Advanced: Grade 5: Introduction to Plate Tectonics} BACKGROUND Scientists and geologists have been able to do some drilling on Earth. They are also able
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Shaky Ground 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Earth Egg Model Teacher Notes
 Ancient Greeks tried to explain earthquakes and volcanic activity by saying that a massive bull lay underground and the land shook when it became angry. Modern theories rely on an understanding of what
Ancient Greeks tried to explain earthquakes and volcanic activity by saying that a massive bull lay underground and the land shook when it became angry. Modern theories rely on an understanding of what
Student Exploration: Plate Tectonics
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Plate Tectonics Vocabulary: collisional boundary, convergent boundary, crust, divergent boundary, earthquake, lithosphere, mantle, plate, plate tectonics, transform boundary,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Plate Tectonics Vocabulary: collisional boundary, convergent boundary, crust, divergent boundary, earthquake, lithosphere, mantle, plate, plate tectonics, transform boundary,
Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide?
 Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
Tectonics Investigation 6: Teacher Guide Investigation 6: What happens when plates collide? In this activity, students will use the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes in a Web GIS to learn about
Inside Earth Chapter 3
 Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Name Hour Due Date Inside Earth Chapter Page 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Page 2 Volcanic Activity Page - Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes Page 4 Mapping Earthquakes and Volcanoes table Page 5 - Mapping
Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics
 Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics Overview: In this assignment we will examine the ideas of continental drift and of sea-floor spreading that lead to the Theory of Plate Tectonics. This assignment is in two
Assignment #3: Plate Tectonics Overview: In this assignment we will examine the ideas of continental drift and of sea-floor spreading that lead to the Theory of Plate Tectonics. This assignment is in two
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
Study Guide Questions Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What evidence did Alfred Wegener present in 1912 to support the idea of continental drift? Why did most geologists at the time dismiss Wegener
1 Exploring Earth s Interior
 1 Exploring Earth s Interior Crust Mantle Outer Core Crust-to-Mantle Inner Core Cross Section From Surface to Center SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Earth Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2 Evidence for Continental
1 Exploring Earth s Interior Crust Mantle Outer Core Crust-to-Mantle Inner Core Cross Section From Surface to Center SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Earth Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2 Evidence for Continental
Plate Tectonics PuzzleMap User Guide
 About this Product: Plate tectonics is a key standards-based topic taught in earth science classrooms throughout the United States. The purpose of this map is to help educators (teachers, museum tour guides,
About this Product: Plate tectonics is a key standards-based topic taught in earth science classrooms throughout the United States. The purpose of this map is to help educators (teachers, museum tour guides,
Glossary. continental crust: the sections of crust, the outermost layer of the earth, that include the continents
 aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
aftershock: an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake or main shock and originates in or near the rupture zone of the larger earthquake. Generally, major earthquakes are followed by a number of aftershocks
Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Objectives: explain various ways the earth can be changed by natural forces define the term Geology define the terms Crust, Mantle, Outer Core and Inner Core classify
Layers of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Objectives: explain various ways the earth can be changed by natural forces define the term Geology define the terms Crust, Mantle, Outer Core and Inner Core classify
Chapter 16: Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 16: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary In the early 1900s Alfred Wegener set forth the continental drift hypothesis. One of its major tenets was that a supercontinent called Pangaea began breaking
Chapter 16: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary In the early 1900s Alfred Wegener set forth the continental drift hypothesis. One of its major tenets was that a supercontinent called Pangaea began breaking
Earthquake Hazards and Risks
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Page 1 of 7 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Earthquake Hazards and Risks This page last updated on 28-Aug-2013 Earthquake Risk Many seismologists have said that "earthquakes
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
 Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Chapter 6 Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes Day Activity Homework 1 Notes I, II Gondwanaland Take-Home Continental Drift* 2 Notes III- V B Edible Tectonics* 3 Notes V C- VI Article- One Boy s Experience
Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6 Created by: Debra McKey (Mountain Vista Middle School); Valerie Duncan (Upper Lake Middle School); and Lynn Chick (Coyote Valley
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Volcanoes Erupt Grade 6 Created by: Debra McKey (Mountain Vista Middle School); Valerie Duncan (Upper Lake Middle School); and Lynn Chick (Coyote Valley
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
LAB 2 SUPPLEMENT: THE JULES VERNE VOYAGER, JR.
 LAB 2 SUPPLEMENT: THE JULES VERNE VOYAGER, JR. For this section of the lab we will be using a very cool web-based map tool that provides access to an amazing suite of state-of-the-art scientific observations
LAB 2 SUPPLEMENT: THE JULES VERNE VOYAGER, JR. For this section of the lab we will be using a very cool web-based map tool that provides access to an amazing suite of state-of-the-art scientific observations
There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift There are numerous seams on the surface of the Earth Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence
The interior of the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties.
 Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes: Slide 1. Title Slide Slide 2. The interior of the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. The Earth has an outer silica-rich, solid crust,
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes: Slide 1. Title Slide Slide 2. The interior of the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. The Earth has an outer silica-rich, solid crust,
Introduction to Plate Tectonics via Google Earth
 Introduction to Plate Tectonics via Google Earth Plate tectonics is a unifying framework for understanding the dynamic geology of the Earth. The theory posits that the outermost layers of the Earth (the
Introduction to Plate Tectonics via Google Earth Plate tectonics is a unifying framework for understanding the dynamic geology of the Earth. The theory posits that the outermost layers of the Earth (the
Earth Science Chapter 14 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Continental Drift Key Concepts What is the hypothesis of continental drift? What evidence supported continental drift? Vocabulary continental drift Pangaea An Idea Before
Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Continental Drift Key Concepts What is the hypothesis of continental drift? What evidence supported continental drift? Vocabulary continental drift Pangaea An Idea Before
www.amnh.org Continental Drift is the movement of the Earth s continents in relation to one another.
 A Plate Tectonic Puzzle Introduction The Earth s crust is not a solid shell. It is made up of thick, interconnecting pieces called tectonic plates that fit together like a puzzle. They move atop the underlying
A Plate Tectonic Puzzle Introduction The Earth s crust is not a solid shell. It is made up of thick, interconnecting pieces called tectonic plates that fit together like a puzzle. They move atop the underlying
KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF KINDERGARTEN VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning that all mountains are not volcanoes. LAB: Investigating rocks
KINDERGARTEN PLATE TECTONICS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF KINDERGARTEN VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Learning that all mountains are not volcanoes. LAB: Investigating rocks
Ring of Fire. (15 minutes) Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other.
 Ring of Fire Lesson Concept Link Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other. Lesson 6.12 develops concepts about preparation for earthquakes in terms of home or school damage or lack
Ring of Fire Lesson Concept Link Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in relationship to each other. Lesson 6.12 develops concepts about preparation for earthquakes in terms of home or school damage or lack
Earth Science Grade 4 Minerals
 Earth Science Grade 4 Minerals Standards: Identifies the physical properties of minerals Teacher Background Minerals are pure substances and mix together to make rocks. Rocks have a cycle and different
Earth Science Grade 4 Minerals Standards: Identifies the physical properties of minerals Teacher Background Minerals are pure substances and mix together to make rocks. Rocks have a cycle and different
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise)
 PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
PLATE TECTONICS EXERCISE (Modified from North Seattle Community College online exercise) Introduction: As discussed in our textbook, the speed at which tectonic plates move has been calculated in several
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Chapter 5: Earthquakes
 Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Chapter 5: Earthquakes 1. Experiencing an Earthquake firsthand 2. The Science of Ghost Forests and Megaearthquakes 3. Faults, Earthquakes, and Plate Tectonics 4. Seismic Waves and Earthquake Detection
Exploring Plate Tectonics
 Unit 2 Exploring Plate Tectonics In this unit, you will Calculate the rate of spreading of the Atlantic Ocean. Investigate whether plate spreading rates change with time or vary across the globe. Predict
Unit 2 Exploring Plate Tectonics In this unit, you will Calculate the rate of spreading of the Atlantic Ocean. Investigate whether plate spreading rates change with time or vary across the globe. Predict
Exploring Plate Tectonics
 Unit 2 Exploring Plate Tectonics In this unit, you will Calculate the rate of spreading of the Atlantic Ocean. Investigate whether plate spreading rates change with time or vary across the globe. Predict
Unit 2 Exploring Plate Tectonics In this unit, you will Calculate the rate of spreading of the Atlantic Ocean. Investigate whether plate spreading rates change with time or vary across the globe. Predict
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Plate Tectonics Cylinder
 A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Plate Tectonics Cylinder Including: The Changing Earth by Gerald L. Mallon, Ed.D. v. 616-2008 by Science First /STARLAB, 86475 Gene Lasserre Blvd., Yulee, FL.
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Plate Tectonics Cylinder Including: The Changing Earth by Gerald L. Mallon, Ed.D. v. 616-2008 by Science First /STARLAB, 86475 Gene Lasserre Blvd., Yulee, FL.
Magnitude 7.2 GUERRERO, MEXICO
 A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
A powerful magnitude-7.2 earthquake shook central and southern Mexico on Friday. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 24 km (15 miles). Its epicenter was in the western state of Guerrero, near the seaside
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02
 Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
Unit Plan: Plate Tectonics Shannon B. Carpenter TE 804 1/25/02 This unit plan is intended to cover about seven weeks and would be appropriate for a middle school general science class or an introductory
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage
 Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
Chapter 7 Earthquake Hazards Practice Exam and Study Guide 1. Select from the following list, all of the factors that affect the intensity of ground shaking. a. The magnitude of the earthquake b. Rather
GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move?
 GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move? Background You know that the Earth s crustal plates are always moving, but how fast?
GENERAL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1110L Lab Experiment 9B: Tracking the Hawaiian Islands: How Fast Does the Pacific Plate Move? Background You know that the Earth s crustal plates are always moving, but how fast?
Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment
 Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment After reading the introduction to the Plate Tectonics exercises in the lab manual, complete the questions on a hard copy of this Lab Assignment. When finished, transfer your
Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment After reading the introduction to the Plate Tectonics exercises in the lab manual, complete the questions on a hard copy of this Lab Assignment. When finished, transfer your
Plate Tectonics. Plate Tectonics LEVELED READER Y. www.readinga-z.com. Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
 Plate Tectonics A Reading A Z Level Y Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,933 LEVELED READER Y Plate Tectonics Written by William Harryman Illustrated by Signe Nordin Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of
Plate Tectonics A Reading A Z Level Y Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,933 LEVELED READER Y Plate Tectonics Written by William Harryman Illustrated by Signe Nordin Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of
Magnitude 8.8 OFFSHORE MAULE, CHILE
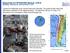 A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
A great 8.8-magnitude struck central Chile early Saturday. The quake hit 200 miles (325 kilometers) southwest of the capital Santiago. The epicenter was just 70 miles (115 kilometers) from Concepcion,
THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY
 Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Page 6 The Earth Scientist THE 2004 SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE AND INDIAN OCEAN TSUNAMI: WHAT HAPPENED AND WHY Seth Stein and Emile A. Okal Dept of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston Illinois
Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface
 PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
PART ONE Some Processes that Change the Earth s Surface Science standards To prepare students to understand the Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALRs) introduced at middle school, this series
EARTHQUAKES. Compressional Tensional Slip-strike
 Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Earthquakes-page 1 EARTHQUAKES Earthquakes occur along faults, planes of weakness in the crustal rocks. Although earthquakes can occur anywhere, they are most likely along crustal plate boundaries, such
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics. Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930.
 Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
Alfred Wegener s Theory of Continental Drift Became Modern Plate Tectonics Wegener in Greenland about 1912. He froze to death there in 1930. Science is self correcting. The Scientific Method The history
Presentations. Session 1. Slide 1. Earthquake Risk Reduction. 1- Concepts & Terminology
 Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Earthquake Risk Reduction Presentations Session 1 Slide 1 Earthquake Risk Reduction 1- Concepts & Terminology Welcome to the World Bank Institute s (WBI) Distance Learning (DL) course on Earthquake Risk
Geodynamics Lecture 2 Kinematics of plate tectonics
 Geodynamics Lecture 2 Kinematics of plate tectonics Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 4.9.2013 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Present the three types of plate
Geodynamics Lecture 2 Kinematics of plate tectonics Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi! 4.9.2013 Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Present the three types of plate
Students explore the mechanism behind plate motion as they investigate convection currents. KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS
 Convection Currents 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 46 L A B O R AT O R Y Students explore the mechanism behind plate motion as they investigate convection currents. KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS
Convection Currents 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW 46 L A B O R AT O R Y Students explore the mechanism behind plate motion as they investigate convection currents. KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS
Name Date Class. By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter.
 CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
CHAPTER 7 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET Earthquakes By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary In your
