The Abdomen and Pelvis
|
|
|
- Eleanore Reynolds
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Abdomen and Pelvis
2 Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Abdomen and Pelvis Table of Contents Abdomen and Pelvis 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Lumbar Vertebrae...3 2: Bony Pelvis...4 3: Sacrum and Coccyx...7 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC):...9 Abdomen and Pelvis 2- The Muscular System : Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Muscles : Posterior Abdominal Wall Muscles : Pelvic Floor...13 Abdomen and Pelvis 3- The Cardiovascular System : Paired Branches of the Abdominal Aorta : Unpaired Branches of the Abdominal Aorta : Pelvic Arteries : Venous Caval System : Venous Portal System...23 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC):...25 Abdomen and Pelvis 3- The Digestive System : Stomach : Small Intestine : Large Intestine : Accessory Digestive Organs and Spleen...32 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC):...34 Abdomen and Pelvis 4- The Urinary and Female Reproductive System : Urinary System : Female Reproductive System...36 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC):...38 Appendix...39
3 Abdomen and Pelvis 1- The Skeletal System 1: Lumbar Vertebrae Describe the primary and secondary curvatures of the vertebral column Describe the dominant movements allowed within each of the various vertebral regions Describe the variation between the various vertebral levels for typical vertebrae Inferior articular process Lamina Median sacral crest Superior articular process T12, L1-L5 Spinous process Transverse process 1. a. Lumbar Vertebrae (Posterior) L3 Spinous process L3 Vertebral body Lamina Pedicle Transverse process Vertebral foramen 1. b. Vertebral Arch (Superior)
4 Inferior vertebral notch Intervertebral disc L3/L4 Intervertebral foramen L3 Spinous process L3 Vertebral body L4 Vertebral body Pedicle Superior vertebral notch Transverse process 1. c. Intervertebral Foramen (Lateral) Coccyx Intervertebral disc L4/L5 Intervertebral disc L5/S1 L4-L5 Vertebral body Point of lumbosacral angle Sacral body Sacral canal Sacral promontory Vertebral canal 1. d. Lumbosacral Angle (X-ray Lateral) 2: Bony Pelvis Describe the bony components of the pelvic girdle Describe the boundaries of the pelvic inlet and outlet and the difference between the true and false pelvis
5 Coccyx Ilium Ischium Pubic symphysis Pubis Sacroiliac joint Sacrum 2. a. Bony Pelvis (Anterior) Ilium Median sacral crest Sacral ala Sacral body Sacral canal Sacroiliac joint 2. b. SacroIliac Joint (Axial-cut Superior) Ala of sacrum Arcuate line Ilium Pelvic brim (Inlet) Pubic symphysis Sacral promontory Superior pubic ramus 2. c. Pelvic Inlet (Superior)
6 Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) Iliac crest Iliac fossa Ilium Pelvic brim (inlet) Sacral promontory 2. d. False Pelvis (Anterior) Coccyx Inferior pubic ramus Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity Obturator foramen Pelvic brim (inlet) Pubic symphysis Sacral body Superior pubic ramus 2. e. True Pelvis (Posterior) Ilium Ischial tuberosity Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen Pubic symphysis Pubis Senior pubic ramus 2. f. Obturator Foramen (Anterolateral)
7 3: Sacrum and Coccyx Describe the difference between the orientation of the sacral foramina as compared to the intervertebral foramen Ala of sacrum Anterior sacral foramen Cocyx L5, S1-S5 Vertebral body Sacral promontory 3. a. Anterior Sacral Foramina (Anterior) Coccyx L5 Spinous process Median sacral crest Posterior sacral foramen S4/S5 Vertebral body 3. b. Posterior Sacral Foramina (Posterior)
8 Coccyx Medial sacral crest Pubic symphysis S1-S5 Vertebral body Sacral canal Sacral hiatus Vertebral canal 3. c. Sacral Canal (Sagittal Cut - Lateral) Coccyx Median sacral crest Posteiror sacral foramen Sacral hiatus 3. d. Sacral Hiatus and Coccyx (Posterior)
9 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC): Cholelithiasis without Cholecystitis Marked Scoliosis with Thoracolumbosacral Fusion Case 0319 Spina Bifida Comminuted Burst Fracture of Right Acetabulum Case 0297 Fx Pelvis
10 Abdomen and Pelvis 2- The Muscular System 1: Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Muscles Identify the surface features and major muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall Describe the formation of the rectus sheath and the attachments of each muscle Costal cartilagescostal margin Linea alba Pubic symphysis Pubic tubercle Rectus abdominis Rectus abdominis Tendinous intersections Umbilicus Xiphoid process 1. a. Rectus Abdominis (Anterior) 5th-10th Rib ASIS Costal margin External oblique Iliac crest Linea alba Pubic tubercle Rectus abdominis Semilunar line 1.b. External Abdominal Oblique (Anterolateral)
11 External oblique Internal oblique Linea alba Lumbar vertebral body Semilunar line Skin Spinous process Transverse process Transversus abdominis Transversus abdomnis 1.c. Obliques (Axial Cut- Inferior) External oblique Internal oblique Transverse abdominis 1. d. Anterolateral Abdominal Wall (Coronal-cut Anterior) 2: Posterior Abdominal Wall Muscles Name the movements of the trunk and describe the muscles associated with each movement Identify the core muscles or the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
12 Iliacus Psoas major T12, L1-L4 Vertebral body 2. a. Psoas Major and Iliacus (Coronal-cut Anterior) Iliac crest L. Kidney Liver Quadratus lumborum R. Kidney Spleeen Transverse process 2.b. Quadratus Lumborum (Coronal-cut Anterior) Erector spinae L. Kidney Psoas major Quadratus lumborum R. kidney Spinous process Transverse process 2.c. Posterior Abdominal Wall (Axial Cut- Superior)
13 3: Pelvic Floor Describe the component parts of the pelvic floor and describe the orientation of the levator ani Anus Ilium Ischioanal fossa Ischium Levator ani Levator ani Obturator internus 3. a. Levator Ani (Coronal-cut Anterior) Ilium Ischium Obturator externus Obturator foramen Urinary bladder Uterus 3.b. Obturator Internus (Coronal-cut Anterior)
14 Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Ilium Piriformis Sacrum 3.c. Piriformis (Coronal-cut Anterior) Anus Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Ilium Ischioanal fossa Levator ani Obturator internus Piriformis Sacrum 3.d. Ishioanal Fossa (Coronal-cut Posterior)
15 Abdomen and Pelvis 3- The Cardiovascular System 1: Paired Branches of the Abdominal Aorta Identify the paired branches off the abdominal aorta Identify the vertebral level associated with the common iliac arteries External iliac a. Internal iliac a. Common iliac a. Abdominal aorta 1. a. Common Iliac aa. Abdominal aorta Common iliac a. L. Renal a. R. Renal a. Thoracic aorta 1. b. Renal aa.
16 Common iliac a. L. 1st-4th lumbar a. R. 1st- 4th lumbar a. L. Renal a. R. Renal a. Abdominal aorta 1. c. Lumbar aa. Deep circumflex iliac a. External iliac a. Inferior epigastric a. 1. d. Inferior Epigastric aa. 2: Unpaired Branches of the Abdominal Aorta Identify the unpaired branches off the abdominal aorta Identify the branches and organs supplied by the celiac trunk, and the superior and inferior mesenteric vessels
17 Abdominal aorta Celiac trunk Common hepatic a. Left gastric a. Splenic a. 2. a. Celiac Trunk Abdominal aorta Celiac trunk Common hepatic a. Cystic a. Gastroduodenal a. Hepatic artery proper L. Hepatic a. R. Hepatic a. 2. b. Common Hepatic a. Anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. Gastroduodenal a. L. Gastric a. R. Gastroomental a. Superior pancreaticoduodenal a. 2. c. Gastroduodenal Artery
18 Celiac trunk Segmental splenic a. Spleen Splenic a. 2. d. Splenic a. Abdominal aorta Ileocolic a. Intestinal a. Middle colic a. Superior mesenteric a. 2. e. Superior Mesenteric a. Abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric a. L. Colic a. Sigmoidal a. Superior rectal a. 2. f. Inferior Mesenteric a.
19 3: Pelvic Arteries Describe and identify the arteries found within the true and false pelvis Abdominal aorta Common iliac a. External iliac a. Internal iliac a. 3. a. Pelvic Vasculature (Anterior) Abdominal aorta Anterior division of internal iliac a. Common iliac a. External iliac a. Internal iliac a. Posterior division of internal iliac a. 3. b. Internal Iliac Artery (Sagittal-cut Medial)
20 Internal iliac a. Iliolumbar a. Lateral sacral a. Superior gluteal a. 3. c. Posterior Division of the Internal Iliac a. Inferior gluteal a. Internal iliac a. Internal pudendal a. Obturator a. Visceral branch 3. d. Anterior Division of the Internal Iliac a. Anterior division of internal iliac a. Internal iliac a. Inferior gluteal a. Posterior division of internal iliac a. Superior gluteal a. 3. e. Gluteal Arteries
21 4: Venous Caval System Review the pattern of venous drainage for the caval system and identify the organs that would have venous return to the heart through the IVC Abdominal aorta Common iliac a. Inferior vena cava L. Common iliac v. R. Common iliac v. 4. a. Inferior Vena Cava External iliac v. Inferior vena cava Internal iliac v. L. Common iliac v. R. Common iliac v. 4. b. Common Iliac Veins
22 Ascending lumbar v. Inferior vena cava L. Common iliac v. R. Common iliac v. 4. c. Ascending Lumbar Veins (Low-visibility) External iliac v. Internal iliac v. L. Common iliac v. 4. d. Internal Iliac Vein (Sagittal-cut Medial) L. Renal v. L. Ovarian v. R. Renal v. Inferior vena cava 4. e. Renal Veins
23 5: Venous Portal System Review the pattern of venous drainage for the portal system and identify the organs that would have venous return to the heart through the hepatic portal v. Abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric v. Inferior vena cava Portal v. Splenic v. Superior mesetneric v. 5. a. Portal v. Inferior vena cava Left hepatic v. Liver Middle hepatic v. Portal v. Right lung 5. b. Hepatic vv.
24 Abdominal aorta Inferior mesenteric v. Inferior mesetenteric a. Portal v. Splenic v. 5. c. Inferior Mesenteric v. Ileocolic v. Jejunal and ilial vv. Middle colic v. Right colic v. Superior mesenteric a. Superior mesenteric v. 5. d. Superior Mesenteric v. Inferior mesenteric v. Portal v. Spleen Splenic v. 5. e. Splenic v. (Axial-cut Superior)
25 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC): Angio-infrarenal Aortic Aneurysm Large Descending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Occluded Left Renal Artery Case 0206 Infrarenal Aortic Aneurysm Bilateral Popliteal Aneurysm Slight Wall Thickening and Focal Irregularity of Abdominal Aorta with Fusiform Dilatation Small Pericardial Effusion Case 0167 Bilateral Aneurysm
26 Abdomen and Pelvis 3- The Digestive System 1: Stomach Describe the orientation, parts, and external features of the stomach Identify the associated viscera in contact with the stomach Aorta Azygos v. Body of stomach Cardia of stomach Fundus of stomach Greater curvature of stomach Hemiazygos v. Left dome of diaphragm Lesser curvature of stomach Liver Spleen 1. a. Stomach Curvatures (Axial-cut Low-visibility) Aorta Body of stomach Cardia of stomach Esophagus Fundus of stomach Left dome of diaphragm Left kidney Pylorus Spleen 1. b. Body of Stomach (Sagittal-cut Lateral)
27 Body of stomach Duodenum Greater curvature of stomach Lesser curvature of stomach Liver Pyloric sphincter Pylorus 1. c. Pyloric Sphincter (Coronal-cut Anterior) 2: Small Intestine Identify the three portions of the small intestine and review the typcial orientation and length of each portion Describe the four segments of the duodenum and the respective vertebral level for each Review the arterial branches supplying the various portions of the small intestine 1st (Superior ) part of the duodenum Ampulla of duodenum Body of gallbladder Liver Pyloric canal of stomach Pyloric sphincter 2. a. 1st part of Duodenum (Coronal-cut Anterior)
28 2nd (descending) part of duodenum 3rd (horizontal) part of duodenum 4th (ascending) part of duodenum Proximal jejunum Superior mesenteric a. Superior mesenteric v. 2. b. 2nd-4th parts of Duodenum (Low-visibility) Duodenum Ileum Jejunum 2. c. Small Intestine (Coronal-cut Anterior) Ascending colon Cecum Ileocecal junction Ileocolic a. and v. Ileum 2. d. Ileocecal Junction (Low-visbility)
29 3: Large Intestine Identify the portions and respective locations of the portions of the large intestine Describe which portions of the large intestine are retroperitoneal Review the arterial supply and venous drainage for the portions of the large intestine Ascending colon Cecum Ileum 3. a. Cecum and Ascending Colon (Low-visbility) 1st (superior) part of the duodenum Hepatic flexure Liver Pyloric sphincter Splenic flexure Stomach Transverse colon 3. b. Transverse Colon (Sagittal-cut Lateral)
30 Body of gallbladder Hepatic flexure Liver Transverse colon 3. c. Hepatic Flexure (Axial-cut Low-visbility) Aorta Spleen Splenic a. Splenic flexure Stomach 3. d. Splenic Flexure (Axial-cut Low-visbility) Ascending colon Descending colon Left kidney Right kidney Small intestine 3. e. Ascending and Descending Colon (Axial-cut)
31 Bladder Descending colon Sigmoid colon 3. f. Sigmoid Colon (Low-visbility) Anal canal Bladder Coccyx Pubic symphysis Sacral body Uterus Vaginal canal 3. g. Anal Canal (Sagittal-cut Low-visbility) Ascending colon Cecum Descending colon Hepatic flexure Sigmoid colon Splenic flexure Transverse colon 3. h. Large Intestine (Low-visbility)
32 Ascending colon Cecum Descending colon Hepatic flexure Sigmoid colon Splenic flexure Transverse colon 3. i. Large Intestine (X-ray) 4: Accessory Digestive Organs and Spleen Identify the parts and features of the accessory digestive organs Describe the location, vasculature, and role of the spleen Describe the course of the superior mesenteric arteries for the accessory digestive organs Describe the normal position and external features of the liver including its lobes Aorta Body of pancreas Head of pancreas Neck of pancreas Spleen Splenic a. Splenic v. Superior mesenteric a. Tail of pancreas 4. a. Pancreas (Axial-cut Low-visibility)
33 Body of pancreas Colic impression Diaphragmatic surface Gastric impression Hilum Left kidney Lower pole Spleen Splenic a. Splenic v. Upper pole 4. b. Spleen (Anterior) Hepatic portal v. I-VIII segments of liver Left lobe of liver Right lobe of liver 4. c. Liver Lobes and Segments (Coronal-cut Anterior) Body of gallbladder Liver 4. d. Gallbladder (Low-visbility)
34 Body of gallbladder Cystic duct Fundus of gallbladder Liver Neck of gallbladder 4. e. Biliary System (Axial-cut Inferior Low-visibility) Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC): Chronic Pancreatitis Status Post Liver Transplant Status Post Right Partial Nephrectomy Case 0276 Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Bone and Liver Metastases Whipple's Resection Case 0295 Pancreas and Liver Cancer
35 Abdomen and Pelvis 4- The Urinary and Female Reproductive System 1: Urinary System Describe the external and internal features of the kidney Discuss the possible points of constricture for the ureters Describe the location of the bladder and discuss the differences between the male and female urethra Abdominal aorta Anterior surface Inferior pole Lateral margin Left kidney Medial margin Renal hilum Right kidney Superior pole 1. a. Kidneys (Anterior) Abdominal aorta Left kidney Left renal a. Renal hilum Right kidney Right renal a. 1. b. Renal Hilum (Axial-cut Inferior)
36 Left kidney Pubic bone Pubic symphysis Renal hilum Right kidney Urinary bladder 1. c. Urinary Bladder (Coronal-cut Low-visibility) Apex of bladder Fundus of bladder Inferior surface of bladder Labia Neck of bladder Pubic symphysis Superior surface of bladder Urethra Uretuers Urinary bladder Vaginal canal 1. d. Urethra (Sagittal-cut Low-visibility) 2: Female Reproductive System Describe the structure of the external and internal features of the female reproductive system
37 Ampulla Fundus of uterus Labia Pubic symphysis Uterine tube Vaginal canal 2. a. Uterus (Anterolateral) Body of uterus Cervix Fundus of uterus Pubic symphysis Urinary bladder Uterine cavity Vaginal canal 2. b. Vaginal Canal (Sagittal-cut Low-visibility) Labia majora Mons pubis 2. c. Female External Genitalia (Low-visibility)
38 Suggested Clinical Correlates (CC): Hyperemic and Enlarged Uterus Large Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy with Fetus in Right Abdomen Case 0178 Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy Large Right Sided Pelvic and Retroperitoneal Mass Right-Sided Hydronephrosis with Ureter Stent Several Enlarged Inguinal Lymph Nodes Case 0336 Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
39 Appendix Abdomen and Pelvis 1- The Skeletal System Library Case: 0318 Goal(s): Identify, describe structures, and discuss clinical correlates of the (1) vertebral column and (2) bony pelvis. Annotated Anatomy: 1: Lumbar Vertebrae Inferior articular process, Lamina, Transverse process, Superior articular process, T12, L1-L5 Spinous process, Median sacral crest, Pedicle, L3, L4 Vertebral body, Vertebral foramen, Intervertebral disc L3/L4, L4/L5, L5/S1,Superior vertebral notch, Inferior vertebral notch, Intervertebral foramen, Point of lumbosacral angle, Sacral promontory, Sacral body, Coccyx, Sacral canal, Vertebral canal 2: Bony Pelvis Ischium, Coccyx, Ilium, Sacroiliac joint, Sacrum, Obturator foramen, Pubis, Pubic symphysis, Sacral body, Sacral canal, Median sacral crest, Sacral ala, Pelvic brim (inlet), Superior pubic ramus, Arcuate line, Ala of sacrum, Sacral promontory, Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), Iliac fossa, Iliac crest, Ischial spine, Ischial tuberosity, Ischial tubrosity, Obturator foramen, Inferior pubic ramus, Superior pubic ramus, Ischiopubic ramus 3: Sacrum and Coccyx L5, S1-S5 Vertebral body, Coccyx, Anterior sacral foramen, Sacral promontory, Ala of sacrum, L5 Spinous process, Median sacral crest, Posterior sacral foramen, Pubic symphysis, Coccyx, Sacral hiatus, Median sacral crest, Sacral canal, Vertebral canal, Sacral hiatus
40 Abdomen and Pelvis 2-The Muscular System Library Case: 0318 Goal(s): Identify, describe structures, attachments, functions and discuss clinical correlates of the (1) anterolateral abdominal wall muscles, (2) posterior abdominal wall muscles, (3) pelvic floor, and (4) trunk movements. Annotated Anatomy: 1: Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Muscles Pubic symphysis, Pubic tubercle, Linea alba, Umbilicus, Rectus abdominis, Costal cartilage, Costal margin, Xiphoid process, Tendinous intersection, Semilunar line, 5th- 10th Rib, External oblique, Iliac crest, ASIS, Pubic tubercle, Internal oblique, Transversus abdominis, Skin, Umbilicus, Lumbar vertebral body, Spinous process, Transverse process 2: Posterior Abdominal Wall Muscles Iliacus, Psoas major, T12, L1-L4 Vertebral body, Iliac crest, Quadratus lumborum, Transvese process, Left kidney, Spleen, Liver, Right kidney, Erector spinae 3: Pelvic Floor Ilium, Ischium, Obturator internus, Ischioanal fossa, Levator ani, Anus, Uterus, Urinary bladder, Obturator foramen, Obturator externus, Piriformis, Gluteus medius, Gluteus maximus, Sacrum Abdomen and Pelvis 3- The Cardiovascular System Library Case: 0198 (Topic 1-3), 0318 (Topic 4-5) Goal(s): Identify, describe structures, and discuss clinical correlates of the (1) abdominal aorta, (2) common iliac artery and its branches, (3) superior mesenteric artery and its branches, (4) venous caval system, and (5) venous portal system. Annotated Anatomy: 1: Paired Branches of the Abdominal aorta, Common iliac a., Internal iliac a., External iliac a., Thoracic aorta, Left renal a., Right
41 Abdominal Aorta renal a., Left 1st-4th lumbar a., Right 1st-4th lumbar a., Deep circumflex iliac a., Inferior epigastric a. 2: Unpaired Branches of the Abdominal Aorta Celiac trunk, Splenic a., Left gastric a., Common hepatic a., Abdominal aorta, Gastroduodendal a., Hepatic artery proper, Cystic a., Right hepatic a., Left hepatic a., Right gastroomental a., Anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a., Superior pancreaticoduodenal a., Segmental splenic a., Spleen, Ileocolic a., Middle colic a., Superior mesenteric a., Intestinal a., Inferior mesenteric a., Left colic a., Sigmoidal a., Superior rectal a. 3: Pelvic Artery Abdominal aorta, Common iliac a., External iliac a., Internal iliac a., Anterior division of internal iliac a., Posterior division of internal iliac a., Iliolumbar a., Lateral sacral a., Superior gluteal a., Inferior gluteal a., Visceral branch, Internal pudendal a., Obturator a., 4: Venous Caval System Abdominal aorta, Common iliac a., Left common iliac v., Right common iliac v., Inferior vena cava, Internal iliac v., External iliac v., Ascending lumbar v., Left renal v., Left ovarian v., Right renal v., Inferior mesenteric v. 5: Venous Portal System Superior mesenteric v., Inferior mesenteric v., Inferior vena cava, Abdominal aorta, Portal v., Splenic v., Middle hepatic v., Left hepatic v., Liver, Right lung, Inferior mesenteric a., Jejunal and ileal vv., Superior mesenteric a., Middle colic v., Right colic v., Ileocolic v., Spleen Abdomen and Pelvis 4- The Digestive System Library Case: 0296 Goal(s): Identify, describe structures, and discuss clinical correlates of the (1) stomach, (2) small and large intestine, (3) liver, (4) spleen, and (5) other accessory digestive organs. Annotated Anatomy: 1: Stomach Greater curvature of stomach, Body of stomach, Lesser curvature of stomach, cardia of stomach,
42 Liver,Azygos v., Aorta, Hemiazygos v., Left dome of diaphragm, Fundus of stomach, Spleen, Left kidney, Esophagus, Pylorus, Pyloric sphincter, Duodenum, 2: Small Intestine Ampulla of duodenum, 1st (Superior) part of duodenum, Body of gallbladder, Pyloric canal of stomach, Ampulla of duodenum, Liver, 2nd (descending) part of duodenum, 3rd (horizontal) part of duodenum, 4th (ascending) part of duodenum, Proximal jejunum, Superior mesenteric a., Superior mesenteric v., Jejunum, Ileum, Duodenum, Ileocolic a., and v., Ileum, Ileocecal junction, Ascending colon, Cecum 3: Large Intestine Ileum, Cecum, Ascending colon, Stomach, Splenic flexure, Transverse colon, Pyloric sphincter, 1st (superior) part of the duodenum, Liver, Hepatic flexure, Body of gallbladder, Aorta, Small intestine, Descending colon, Left kidney, Right kidney, Sigmoid colon, Bladder, Uterus, Pubic symphysis, Vaginal canal, Anal canal, Coccyx, Sacral body 4: Accessory Digestive Organ and Spleen Spleen, Splenic a., Splenic v., Aorta, Tail of pancreas, Body of pancreas, Neck of pancreas, Superior mesenteric a., Head of pancreas, Diaphragmatic surface, Gastric impression, Upper pole, Lower pole, Colic impression, Hilum, Left kidney, Left lobe of liver, Right lobe of liver, IIVIII segments of liver, Hepatic portal v., Liver, Body of gallbladder, Neck of gallbladder, Fundus of gallbladder, Cystic duct Abdomen and Pelvis 5- The Urinary and Female Reproductive System Library Case: 0296 Goal(s): Identify, describe structures, and discuss clinical correlates of the (1) urinary system and (2) female reproductive system Annotated Anatomy: 1: Urinary System Left kidney, Lateral margin, Anterior surface, Inferior pole, Medial margin, Abdominal aorta,
43 Renal hilum, Superior pole, Right kidney, Renal hilum, Left renal a., Right renal a., Urinary bladder, Pubic bone, Pubic symphysis, Apex of bladder, Inferior surface of bladder, Superior surface of bladder, Uterus, Fundus of bladder, Vaginal canal, Urethra, Neck of bladder, Labia 2: Female Reproductive System Uterine tube, Fundus of uterus, Ampulla, Uterine tube, Vaginal canal, Pubic symphysis, Labia, Urinary bladder, Cervix, Body of uterus, Uterine cavity, Mons pubis, Labia majora
Practice Anatomy Questions Semester 2
 1 - Which muscle layer does NOT wrap around the abdomen? a) external oblique b) internal oblique c) transversus abdominus d) rectus abdominus 2 - Which statement is correct? a) The fibres of the internal
1 - Which muscle layer does NOT wrap around the abdomen? a) external oblique b) internal oblique c) transversus abdominus d) rectus abdominus 2 - Which statement is correct? a) The fibres of the internal
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130)
 Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis
 2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Pelvic Anatomy. Robert E. Gutman, MD
 Pelvic Anatomy Robert E. Gutman, MD Objectives Understand pelvic anatomy Organs and structures of the female pelvis Vascular Supply Neurologic supply Pelvic and retroperitoneal contents and spaces Bony
Pelvic Anatomy Robert E. Gutman, MD Objectives Understand pelvic anatomy Organs and structures of the female pelvis Vascular Supply Neurologic supply Pelvic and retroperitoneal contents and spaces Bony
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
The Large Intestine. General Facts: (everything will be repeated in a more organized matter later on)
 The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations
 Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 24 January 2012 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 24 January 2012 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM
 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM 1 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM Reading Gray s Anatomy for Students (GAFS), Chapters 4-5 Gray s Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy (GDGHA), Labs 10-17 Unit
UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM 1 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM Reading Gray s Anatomy for Students (GAFS), Chapters 4-5 Gray s Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy (GDGHA), Labs 10-17 Unit
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual
 Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual Arash Bedayat, MD; Hemang Kotecha, DO; Matthew L. Hoimes, MD; Byron Y. Chen, MD; Hao S. Lo, MD; Adib R. Karam, MD Objectives Review the radiologic anatomy and
Abdominal Wall Hernias: Classic and Unusual Arash Bedayat, MD; Hemang Kotecha, DO; Matthew L. Hoimes, MD; Byron Y. Chen, MD; Hao S. Lo, MD; Adib R. Karam, MD Objectives Review the radiologic anatomy and
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
The Anterior Abdominal Wall, Inguinal Region and Hernias Anatomy of the Abdomen & Pelvis 1 Mr Barry Paraskeva ([email protected].
 The Anterior Abdominal Wall, Inguinal Region and Hernias Anatomy of the Abdomen & Pelvis 1 Mr Barry Paraskeva ([email protected]) 1. Demonstrate in the living subject, and on a skeleton where
The Anterior Abdominal Wall, Inguinal Region and Hernias Anatomy of the Abdomen & Pelvis 1 Mr Barry Paraskeva ([email protected]) 1. Demonstrate in the living subject, and on a skeleton where
BIOLOGY 453 - COMPARATIVE VERT. ANATOMY WEEK 9, Abdominal Circulation (Cats) & Urinary Systems of Mammals
 BIOLOGY 453 - COMPARATIVE VERT. ANATOMY WEEK 9, Abdominal Circulation (Cats) & Urinary Systems of Mammals Assignments Readings Kardong & Zalisko Chapter 8:164-166, 168-171 & Chapter 9: 179, 181-183 Presentation
BIOLOGY 453 - COMPARATIVE VERT. ANATOMY WEEK 9, Abdominal Circulation (Cats) & Urinary Systems of Mammals Assignments Readings Kardong & Zalisko Chapter 8:164-166, 168-171 & Chapter 9: 179, 181-183 Presentation
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias. Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK
 The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
An Overview of Cancer Staging and AJCC Guidelines for the Staging of
 An Overview of Cancer Staging and AJCC Guidelines for the Staging of Gastrointestinal Cancers Pooja Rohatgi From Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas For information, contact Pooja Rohatgi, Baylor
An Overview of Cancer Staging and AJCC Guidelines for the Staging of Gastrointestinal Cancers Pooja Rohatgi From Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas For information, contact Pooja Rohatgi, Baylor
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Administrative. Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality
 CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
MD 2016. Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy. A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI)
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of a tubular system and its accessory organs and is referred to as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract (GI) I. A tube traveling through the body
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Pylorus-Preserving Whipple Procedure)
 Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Pylorus-Preserving Whipple Procedure) Operative Indications: Pancreaticoduodenectomy, or the Whipple procedure, may be indicated for a variety of benign and malignant diseases.
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Pylorus-Preserving Whipple Procedure) Operative Indications: Pancreaticoduodenectomy, or the Whipple procedure, may be indicated for a variety of benign and malignant diseases.
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
PELVIS. 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins S59 BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61)
 PELVIS BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61) Types: A. Lesion sparing (or with no displacement of) posterior arch (61-A) B. Incomplete disruption of posterior arch, partially stable (61-B) C. Complete
PELVIS BONE: PELVIS (6) Location: Pelvic ring (61) Types: A. Lesion sparing (or with no displacement of) posterior arch (61-A) B. Incomplete disruption of posterior arch, partially stable (61-B) C. Complete
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus
 LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen
 The Abdomen NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen Abdominal Cavity The body systems in the abdomen Gastrointestinal Urinary Reproductive Vascular The Gastrointestional System Alimentary canal Mouth Pharynx Tongue
The Abdomen NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen Abdominal Cavity The body systems in the abdomen Gastrointestinal Urinary Reproductive Vascular The Gastrointestional System Alimentary canal Mouth Pharynx Tongue
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
ANTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION (ALIF) Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Anterior Lumbar Spine
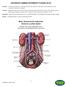 (ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
(ALIF) Anterior In human anatomy, referring to the front surface of the body or the position of one structure relative to another Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems
 PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
Anatomicalintroduction
 3rd INTERVENTIONAL HANDS-ON PAIN RELIEF & NEUROMODULATION CADAVER WORKSHOP Anatomicalintroduction Gdansk-Poland Programmeofthelecture Shortintroductionto theanatomyof: 1.Vertebralcolumn 2.Intervertebraldiscs
3rd INTERVENTIONAL HANDS-ON PAIN RELIEF & NEUROMODULATION CADAVER WORKSHOP Anatomicalintroduction Gdansk-Poland Programmeofthelecture Shortintroductionto theanatomyof: 1.Vertebralcolumn 2.Intervertebraldiscs
Glossary (continued)
 1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum. S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD.
 The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
The Vertebral Column, The Ribs and The Sternum S. LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD. PhD. The Vertebral Column (Spine) The Vertebral Column-The spine (Columna vertebralis) forms the skeleton of the back is part of the
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column
 Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision
 Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES
 HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol
 Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol Sandra Hagen-Ansert, M.S., RDMS, RDCS Ultrasound Education Specialist and Clinical Consultant Charleston, South Carolina Table of Contents 1. Objectives
Basic Abdominal Sonographic Anatomy and Protocol Sandra Hagen-Ansert, M.S., RDMS, RDCS Ultrasound Education Specialist and Clinical Consultant Charleston, South Carolina Table of Contents 1. Objectives
Cancer Surgery Volume Study: ICD-9 and CPT Codes
 This paper contains the ICD-9 diagnostic and procedure codes and the CPT procedure codes used by researchers for a project of the California HealthCare Foundation (CHCF) and the California Office of Statewide
This paper contains the ICD-9 diagnostic and procedure codes and the CPT procedure codes used by researchers for a project of the California HealthCare Foundation (CHCF) and the California Office of Statewide
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
National Program of Cancer Registries Education and Training Series. How to Collect High Quality Cancer Surveillance Data
 National Program of Cancer Registries Education and Training Series How to Collect High Quality Cancer Surveillance Data 1 NAACCR Administers NPCR-Education Contract for the Centers for Disease Control
National Program of Cancer Registries Education and Training Series How to Collect High Quality Cancer Surveillance Data 1 NAACCR Administers NPCR-Education Contract for the Centers for Disease Control
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC
 Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction
 Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction, with Indirect,Direct and HVLA Techniques (Counterstrain and Muscle Energy) F. P Wedel, D.O.
Evaluation and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction Diagnosis and Treatment of Sacral Somatic Dysfunction, with Indirect,Direct and HVLA Techniques (Counterstrain and Muscle Energy) F. P Wedel, D.O.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAT DISSECTION UNIT
 CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE
 CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 23 DIGESTIVE nutrition requires : getting nutrients digesting nutrients transporting nutrients Digestive System musculo-skeletal digestive circulatory Digestive System alimentary canal ~ gastrointestinal
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
TSI Summit 2008: Session #606 The Mechanics of Low Back Pain and Corrective Solutions
 TSI Summit 2008: Session #606 The Mechanics of Low Back Pain and Corrective Solutions Eric Beard Senior Master Instructor National Academy of Sports Medicine [email protected] www.nasm.org Description
TSI Summit 2008: Session #606 The Mechanics of Low Back Pain and Corrective Solutions Eric Beard Senior Master Instructor National Academy of Sports Medicine [email protected] www.nasm.org Description
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Vivian Gonzalez Gillian Lieberman, MD. January 2002. Lumbar Spine Trauma. Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
LUMBAR LAMINECTOMY AND DISCECTOMY. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Posterior View Lumbar Spine
 Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
BODY BODY PEDICLE PEDICLE TRANSVERSE TRANSVERSE PROCESS PROCESS
 Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Learning Objective Radiology Anatomy of the Spine and Upper Extremity Identify anatomic structures of the spine and upper extremities on standard radiographic and cross-sectional images Timothy J. Mosher,
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
