Lecture 2: Ray theory transmission in optical fibers
|
|
|
- Elwin Mason
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 2: Ray theory transmission in optical fibers Nature of light Ray optics Refractive indices Snell s Law Total internal reflection Acceptance angle Numerical Aperture Optical fiber structures Reading: Senior Keiser Part of the lecture materials were adopted from powerpoint slides of Gerd Keiser s book 2010, Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 1
2 A Brief Historical Note Beyond the middle ages: Newton ( ) and Huygens ( ) fight over nature of light 18 th 19 th centuries Fresnel, Young experimentally observe diffraction, defeat Newton s particle theory Maxwell formulates electro-magnetic equations, Hertz verifies antenna emission principle (1899) 20 th century Quantum theory explains wave-particle duality Invention of holography (1948) Invention of laser principle (1954) 1 st demonstration of laser (1960) Proposal of fiber optic communications (1966) 1 st demonstration of low-loss optical fibers (1970) Optical applications proliferate into the 21 st century: nonlinear optics, fiber optics, laser-based spectroscopy, computing, communications, fundamental science, medicine, biology, manufacturing, entertainment, (Let all flowers blossom!) 2
3 The nature of light 3
4 Light as waves, rays and photons Light is an electromagnetic wave. While light is a wave, it nevertheless travels along straight lines or rays, enabling us to analyze simple optical components (e.g. lenses and mirrors) and instruments in terms of geometrical optics. Light is also a stream of photons, discrete particles carrying packets of energy and momentum. (We will cover this after mid-term.) 4
5 Spherical waves and their associated rays e.g. a point source (like a stone dropped in water) Light is emitted in all directions as a spherical wave series of crests and troughs forming spherical wavefronts Distance between adjacent crests is the wavelength λ λ Rays lines perpendicular to wavefronts Wavefront - Surface of constant phase 5
6 Plane waves and their associated rays Spherical waves wavefronts are spherical (rays are perpendicular to the wavefronts and point radially outwards) Plane waves wavefronts are planes (rays are perpendicular to plane wavefronts in the direction of propagation) Spherical waves from a point source at a far distance from an observer appears as a plane wave Planes parallel to x-y plane Rays are collimated z 6
7 Ray Optics or Geometrical Optics ray λ Wavelength λ << size of the optical component wavefront In many applications of interest the wavelength λ of light is short compared with the relevant length scales of the optical components or system (e.g. mirrors, prisms, lenses). This branch of optics is referred to as Ray optics or Geometrical Optics, where energy of light is propagated along rays. The rays are perpendicular to the wavefronts. 7
8 Ray Optics: basic laws n i sin θ i = n t sin θ t 8
9 When a ray is incident on the interface between two dielectrics of different refractive indices (e.g. glass-air), reflection and refraction occur. normal low index n 2 (air) high index n 1 (glass) Snell s Law θ 2 θ 1 θ 1 refraction Plane of incidence plane that comprises the incident ray and the plane normal reflection The angle of incidence θ 1 and the angle of refraction θ 2 are related to each other, and to the refractive indices of the dielectrics by Snell s law of refraction: n 1 sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2 9
10 Refractive index In any dielectric medium, the speed of light becomes v = c/n The factor n is the index of refraction (or refractive index) of the medium. e.g. For air and gases, v ~ c, so that n ~ 1. At optic frequencies, the refractive index of water is e.g. Glass has many compositions, each with a slightly different n. An approximate refractive index of 1.5 is representative for the silica glasses used in fibers; more precise values for these glasses lie between ~1.45 and ~
11 Index of refraction for some materials Air 1.0 Water 1.33 Magnesium fluoride 1.38 Fused silica (SiO 2 ) 1.46 Sapphire (Al 2 O 3 ) 1.8 Lithium niobate (LiNbO 3 ) 2.25 Indium phosphide (InP) 3.21 Gallium arsenide (GaAs) 3.35 Silicon (Si) 3.48 Indium gallium arsenide phosphide (InGaAsP) 3.51 Aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) 3.6 Germanium (Ge) 4.0 *The index varies with a number of parameters, such as wavelength and temperature. 11
12 Critical angle For n 1 > n 2, the angle of refraction θ 2 is always greater than the angle of incidence θ 1. When the angle of refraction θ 2 is 90 o, the refracted ray emerges parallel to the interface between the media. This is the limiting case of refraction and the angle of incidence is known as the critical angle θ c. low index n 2 (air) θ 2 refraction sin θ c = n 2 / n 1 high index n 1 (glass) θ c θ c reflection 12
13 At angles of incidence θ > θ c, the light is totally reflected back into the incidence higher refractive index medium. This is known as total internal reflection. low index n 2 (air) Total internal reflection normal high index n 1 (glass) θ 1 > θ c TIR e.g. n 1 = 1.44, n 2 = 1, then θ c = sin -1 (1/1.44) = 44 o Total internal reflection: θ 1 > θ c 13
14 Light ray guiding condition Light ray that satisfies total internal reflection at the interface of the higher refractive index core and the lower refractive index cladding can be guided along an optical fiber. cladding n 2 core n 1 θ θ e.g. Under what condition will light be trapped inside the fiber core? n 1 = 1.46; n 2 = 1.44 θ > θ c θ c = sin -1 (n 2 /n 1 ) = sin -1 (1.44/1.46) = 80.5 o 14
15 Optical fiber structures A typical bare fiber consists of a core, a cladding and a polymer jacket (buffer coating). The polymer coating is the first line of mechanical protection. typically 250 µm including jacket for glass fibers The coating also reduces the internal reflection at the cladding, so light is only guided by the core. *In Lab1, we shall learn how to strip off the jacket to expose the cladding. This is necessary in order to cleave the fiber for a smooth 15 end face for light coupling.
16 Silica optical fibers Both the core and the cladding are made from a type of glass known as silica (SiO 2 ) which is almost transparent in the visible and near-ir. In the case that the refractive index changes in a step between the core and the cladding. This fiber structure is known as step-index fiber. The higher core refractive index (~ 0.3% higher) is typically obtained by doping the silica core with germanium dioxide (GeO 2 ). *In Lab 1, we should be able to see the step boundary between the core and the cladding, by end-illuminating the fiber and imaging the output-end cross-section using a microscope. 16
17 Numerical aperture An important characteristic of an optic system is its ability to collect light incident over a wide range of angles. f θ f The numerical aperture (NA) is defined as: NA = n o sin θ where n o is the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the image plane (e.g. a photodetector) and θ is the maximum acceptance angle. 17
18 The definition of numerical aperture applies to all light-collecting systems, including optical fibers. e.g. Light rays incident at angles outside the collection cone for a fiber will not propagate along the fiber (instead will attenuate rapidly). The numerical aperture is often measured in air, n o = 1 NA = sin θ A low NA indicates a small acceptance angle. Light coupling to a low-na optical system (e.g. fiber) is more difficult (alignment is more sensitive) and less efficient (some of the rays are outside the acceptance angle) than is coupling to a high-na optical system. 18
19 Acceptance angle Only rays with a sufficiently shallow grazing angle (i.e. with an angle to the normal greater than θ c ) at the core-cladding interface are transmitted by total internal reflection. A θ a n 1 n 2 n a α c θ c Ray A incident at the critical angle θ c at the core-cladding interface enters the fiber core at an angle θ a to the fiber axis, and is refracted at the air-core interface. 19
20 θ < θ a θ a n 1 n 2 n a α c θ c θ > θ a θ a n 1 n 2 n a α c θ c Any rays which are incident into the fiber core at an angle > θ a have an incident angle less than θ c at the core-cladding interface. These rays will NOT be totally internal reflected, thus eventually loss to radiation (at the cladding-jacket interface). 20
21 Light rays will be confined inside the fiber core if it is input-coupled at the fiber core end-face within the acceptance angle θ a. e.g. What is the fiber acceptance angle when n 1 = 1.46 and n 2 = 1.44? θ c = sin -1 (n 2 /n 1 ) = 80.5 o => α c = 90 o - θ c = 9.5 o using sin θ a = n 1 sin α c (taking n a = 1) θ a = sin -1 (n 1 sin α c ) = sin -1 (1.46 sin 9.5 o ) ~ 14 o => the acceptance angle θ a ~ 14 o 21
22 Fiber numerical aperture In fiber optics, we describe the fiber acceptance angle using Numerical Aperture (NA): NA = n a sin θ a = sin θ a = (n n 22 ) 1/2 θ a n 1 n 2 n a α c θ c We can relate the acceptance angle θ a and the refractive indices of the core n 1, cladding n 2 and air n a. 22
23 Assuming the end face at the fiber core is flat and normal to the fiber axis (when the fiber has a nice cleave), we consider the refraction at the air-core interface using Snell s law: At θ a : n a sin θ a = n 1 sin α c launching the light from air: (n a ~ 1) sin θ a = n 1 sin α c = n 1 cos θ c = n 1 (1 - sin 2 θ c ) 1/2 = n 1 (1 - n 22 /n 12 ) 1/2 = (n n 22 ) 1/2 23
24 Fiber NA therefore characterizes the fiber s ability to gather light from a source and guide the light. e.g. What is the fiber numerical aperture when n 1 = 1.46 and n 2 = 1.44? NA = sin θ a = ( ) 1/2 = 0.24 It is a common practice to define a relative refractive index Δ as: Δ = (n 1 - n 2 ) / n 1 (n 1 ~ n 2 ) => NA = n 1 (2Δ) 1/2 i.e. Fiber NA only depends on n 1 and Δ. 24
25 Lens coupling to fiber end faces Microscope objective lens collimated laser beam θ a few mm focal length θ a θ a focusing objective lens fiber under test collecting objective lens By measuring the output couple ray cone angle, we can measure the fiber acceptance angle. (This is like part of Lab 1 but without using lenses.) 25
26 Large-NA fibers? Developing ways for fiber to collect light efficiently was an important early step in developing practical fiber optic communications (particularly in the 1970s) It seems logical to have optical fibers with NA as large as possible with as large Δ as possible in order to couple maximum amount of light into the fiber. Soon, we will find out that such large-na fibers tend to be multimode and are unsuitable for high-speed communications because of a limitation known as modal dispersion. Relatively small-na fibers are therefore used for high-speed optical communication systems. 26
27 Typical fiber NA Silica fibers for long-haul transmission are designed to have numerical apertures from about 0.1 to 0.3. The low NA makes coupling efficiency tend to be poor, but turns out to improve the fiber s bandwidth! (details later) Plastic, rather than glass, fibers are available for short-haul communications (e.g. within an automobile). These fibers are restricted to short lengths because of the relatively high attenuation in plastic materials. Plastic optical fibers (POFs) are designed to have high numerical apertures (typically, ) to improve coupling efficiency, and so partially offset the high propagation losses and also enable alignment tolerance. 27
28 Limitation of ray optics For smaller fiber diameters that are only few times of the wavelength, geometrical optics approach becomes inadequate. This is because ray optics only describes the direction a plane wave component takes in the fiber, but does not take into account interference among such components. When interference phenomena are considered it is found that only rays with certain discrete characteristics propagate in the fiber core. Thus the fiber will only support a discrete number of guided modes. This becomes critical in small core diameter fibers which only support one (singlemode) or a few modes (multimode). Electromagnetic theory must be applied in this case. 28
29 Op#cal Fiber Type Comparisons Cladding 2a Core Cladding 2a Core n 1 n 1 n 2 Step-index fiber n 1 n 1 n 2 Graded-index fiber (a) Basic fiber types (b) Sample tailored profiles 29
30 Numerical Aperture Example 30
What are Fibre Optics?
 Fibre Optics Fibre Optics? Fibre optics (optical fibres) are the guiding channels through which light energy propagates. These are long, thin strands of very pure glass about the diameter of a human hair
Fibre Optics Fibre Optics? Fibre optics (optical fibres) are the guiding channels through which light energy propagates. These are long, thin strands of very pure glass about the diameter of a human hair
GLOBAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY: YSR DIST. Unit VII Fiber Optics Engineering Physics
 Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Introduction Fiber optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibers. Fiber optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics
 Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
Photonics Technical Note # 21 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric wave-guides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded
Lecture 3: Fibre Optics
 Lecture 3: Fibre Optics Lecture aims to explain: 1. Fibre applications in telecommunications 2. Principle of operation 3. Single- and multi-mode fibres 4. Light losses in fibres Fibre is a transparent
Lecture 3: Fibre Optics Lecture aims to explain: 1. Fibre applications in telecommunications 2. Principle of operation 3. Single- and multi-mode fibres 4. Light losses in fibres Fibre is a transparent
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES Vol. I -Optical Fibers - Atousa Vali Sichani and Hussein T. Mouftah
 OPTICAL FIBERS Atousa Vali Sichani and Hussein T. University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Keywords: attenuation, bandwidth, data transmission, dispersion, frequency, modulation, multiplexing. Contents 1.
OPTICAL FIBERS Atousa Vali Sichani and Hussein T. University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Keywords: attenuation, bandwidth, data transmission, dispersion, frequency, modulation, multiplexing. Contents 1.
Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber N.Ravi Teja, M.Aneesh Babu, T.R.S.Prasad, T.Ravi B.tech
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber N.Ravi Teja, M.Aneesh Babu, T.R.S.Prasad, T.Ravi B.tech
Optical Communications
 Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #2, May 2 2006 The Optical Communication System BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #2, May 2 2006 The Optical Communication System BLOCK DIAGRAM OF
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment
 Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to observe Fraunhofer, or far-field, diffraction through a single
Diffraction and Young s Single Slit Experiment Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to observe Fraunhofer, or far-field, diffraction through a single
AP Physics B Ch. 23 and Ch. 24 Geometric Optics and Wave Nature of Light
 AP Physics B Ch. 23 and Ch. 24 Geometric Optics and Wave Nature of Light Name: Period: Date: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Reflection,
AP Physics B Ch. 23 and Ch. 24 Geometric Optics and Wave Nature of Light Name: Period: Date: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Reflection,
Fiber optic communication
 Fiber optic communication Fiber optic communication Outline Introduction Properties of single- and multi-mode fiber Optical fiber manufacture Optical network concepts Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado
Fiber optic communication Fiber optic communication Outline Introduction Properties of single- and multi-mode fiber Optical fiber manufacture Optical network concepts Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado
Refractive Index Measurement Principle
 Refractive Index Measurement Principle Refractive index measurement principle Introduction Detection of liquid concentrations by optical means was already known in antiquity. The law of refraction was
Refractive Index Measurement Principle Refractive index measurement principle Introduction Detection of liquid concentrations by optical means was already known in antiquity. The law of refraction was
P R E A M B L E. Facilitated workshop problems for class discussion (1.5 hours)
 INSURANCE SCAM OPTICS - LABORATORY INVESTIGATION P R E A M B L E The original form of the problem is an Experimental Group Research Project, undertaken by students organised into small groups working as
INSURANCE SCAM OPTICS - LABORATORY INVESTIGATION P R E A M B L E The original form of the problem is an Experimental Group Research Project, undertaken by students organised into small groups working as
OPTICAL FIBERS INTRODUCTION
 OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
OPTICAL FIBERS References: J. Hecht: Understanding Fiber Optics, Ch. 1-3, Prentice Hall N.J. 1999 D. R. Goff: Fiber Optic Reference Guide (2 nd ed.) Focal Press 1999 Projects in Fiber Optics (Applications
4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet
 4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet Required: READ Hamper pp 115-134 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson, pp 473-477, 507-513 Tsokos, pp 216-242 REMEMBER TO. Work through all
4.4 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS 4.5 WAVE PROPERTIES HW/Study Packet Required: READ Hamper pp 115-134 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson, pp 473-477, 507-513 Tsokos, pp 216-242 REMEMBER TO. Work through all
Introduction to Optics
 Second Edition Introduction to Optics FRANK L. PEDROTTI, S.J. Marquette University Milwaukee, Wisconsin Vatican Radio, Rome LENO S. PEDROTTI Center for Occupational Research and Development Waco, Texas
Second Edition Introduction to Optics FRANK L. PEDROTTI, S.J. Marquette University Milwaukee, Wisconsin Vatican Radio, Rome LENO S. PEDROTTI Center for Occupational Research and Development Waco, Texas
EXPERIMENT O-6. Michelson Interferometer. Abstract. References. Pre-Lab
 EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
v = fλ PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to :
 PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
SINGLEMODE OR MULTIMODE FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS
 Features: SINGLEMODE OR MULTIMODE FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS Low insertion loss < 0.2 db Excellent repeatability FC/PC, SC, ST, LC, MU, E2000 termination available Custom ferrule termination available Designed
Features: SINGLEMODE OR MULTIMODE FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS Low insertion loss < 0.2 db Excellent repeatability FC/PC, SC, ST, LC, MU, E2000 termination available Custom ferrule termination available Designed
Reflection and Refraction
 Equipment Reflection and Refraction Acrylic block set, plane-concave-convex universal mirror, cork board, cork board stand, pins, flashlight, protractor, ruler, mirror worksheet, rectangular block worksheet,
Equipment Reflection and Refraction Acrylic block set, plane-concave-convex universal mirror, cork board, cork board stand, pins, flashlight, protractor, ruler, mirror worksheet, rectangular block worksheet,
Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect
 Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Modern Classical Optics
 Modern Classical Optics GEOFFREY BROOKER Department of Physics University of Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Electromagnetism and basic optics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Maxwell equations 1
Modern Classical Optics GEOFFREY BROOKER Department of Physics University of Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Electromagnetism and basic optics 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Maxwell equations 1
Diffraction of a Circular Aperture
 Diffraction of a Circular Aperture Diffraction can be understood by considering the wave nature of light. Huygen's principle, illustrated in the image below, states that each point on a propagating wavefront
Diffraction of a Circular Aperture Diffraction can be understood by considering the wave nature of light. Huygen's principle, illustrated in the image below, states that each point on a propagating wavefront
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB COMPUTATIONAL OPTICS RAYLEIGH-SOMMERFELD DIFFRACTION INTEGRAL OF THE FIRST KIND
 DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB COMPUTATIONAL OPTICS RAYLEIGH-SOMMERFELD DIFFRACTION INTEGRAL OF THE FIRST KIND THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE RADIANT FLUX DENSITY AT THE FOCUS OF A CONVERGENCE BEAM
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB COMPUTATIONAL OPTICS RAYLEIGH-SOMMERFELD DIFFRACTION INTEGRAL OF THE FIRST KIND THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE RADIANT FLUX DENSITY AT THE FOCUS OF A CONVERGENCE BEAM
Interference. Physics 102 Workshop #3. General Instructions
 Interference Physics 102 Workshop #3 Name: Lab Partner(s): Instructor: Time of Workshop: General Instructions Workshop exercises are to be carried out in groups of three. One report per group is due by
Interference Physics 102 Workshop #3 Name: Lab Partner(s): Instructor: Time of Workshop: General Instructions Workshop exercises are to be carried out in groups of three. One report per group is due by
and LP 11 are illustrated at right.
 Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric waveguides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded by a concentric cladding with slightly lower (by 1%)
Fiber Basics Optical fibers are circular dielectric waveguides that can transport optical energy and information. They have a central core surrounded by a concentric cladding with slightly lower (by 1%)
WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT - DIFFRACTION GRATING
 PURPOSE In this experiment we will use the diffraction grating and the spectrometer to measure wavelengths in the mercury spectrum. THEORY A diffraction grating is essentially a series of parallel equidistant
PURPOSE In this experiment we will use the diffraction grating and the spectrometer to measure wavelengths in the mercury spectrum. THEORY A diffraction grating is essentially a series of parallel equidistant
Procedure: Geometrical Optics. Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Equipment Needed
 Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Geometrical Optics Equipment Needed Light Source Ray Table and Base Three-surface Mirror Convex Lens Ruler Optics Bench Cylindrical Lens Concave Lens Rhombus
Theory Refer to your Lab Manual, pages 291 294. Geometrical Optics Equipment Needed Light Source Ray Table and Base Three-surface Mirror Convex Lens Ruler Optics Bench Cylindrical Lens Concave Lens Rhombus
INTRODUCTION FIGURE 1 1. Cosmic Rays. Gamma Rays. X-Rays. Ultraviolet Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red Infrared. Ultraviolet.
 INTRODUCTION Fibre optics behave quite different to metal cables. The concept of information transmission is the same though. We need to take a "carrier" signal, identify a signal parameter we can modulate,
INTRODUCTION Fibre optics behave quite different to metal cables. The concept of information transmission is the same though. We need to take a "carrier" signal, identify a signal parameter we can modulate,
Attenuation: Bending Loss
 Consequences of Stress Optical Communications Systems Stress Bending Loss and Reliability in Optical Fibres Increased Loss in the Fibre Increased Probability of Failure Bending Loss in Fibres At a bend
Consequences of Stress Optical Communications Systems Stress Bending Loss and Reliability in Optical Fibres Increased Loss in the Fibre Increased Probability of Failure Bending Loss in Fibres At a bend
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV
 Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Objective Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Physics Lab IV In this set of lab exercises, the basic properties geometric optics concerning converging lenses and mirrors will be explored. The
Study Guide for Exam on Light
 Name: Class: Date: Study Guide for Exam on Light Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is used
Name: Class: Date: Study Guide for Exam on Light Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is used
A NEW LOOK AT RISLEY PRISMS. By Craig Schwarze Senior Systems Engineer OPTRA Inc.
 As seen in Photonics Spectra June 2006: A NEW LOOK AT RISLEY PRISMS By Craig Schwarze Senior Systems Engineer OPTRA Inc. Introduction With laser beams finding more and more applications that require aiming
As seen in Photonics Spectra June 2006: A NEW LOOK AT RISLEY PRISMS By Craig Schwarze Senior Systems Engineer OPTRA Inc. Introduction With laser beams finding more and more applications that require aiming
Signal directionality Lower frequency signals are omnidirectional Higher frequency signals can be focused in a directional beam
 Transmission Media Transmission medium Physical path between transmitter and receiver May be guided (wired) or unguided (wireless) Communication achieved by using em waves Characteristics and quality of
Transmission Media Transmission medium Physical path between transmitter and receiver May be guided (wired) or unguided (wireless) Communication achieved by using em waves Characteristics and quality of
CHAPTER - 1. Chapter ONE: WAVES CHAPTER - 2. Chapter TWO: RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS. CHAPTER - 3 Chapter THREE: WAVE OPTICS PERIODS PERIODS
 BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION, A.P., HYDERABAD REVISION OF SYLLABUS Subject PHYSICS-II (w.e.f 2013-14) Chapter ONE: WAVES CHAPTER - 1 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 Transverse and longitudinal waves 1.3 Displacement
BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION, A.P., HYDERABAD REVISION OF SYLLABUS Subject PHYSICS-II (w.e.f 2013-14) Chapter ONE: WAVES CHAPTER - 1 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 Transverse and longitudinal waves 1.3 Displacement
Refraction of Light at a Plane Surface. Object: To study the refraction of light from water into air, at a plane surface.
 Refraction of Light at a Plane Surface Object: To study the refraction of light from water into air, at a plane surface. Apparatus: Refraction tank, 6.3 V power supply. Theory: The travel of light waves
Refraction of Light at a Plane Surface Object: To study the refraction of light from water into air, at a plane surface. Apparatus: Refraction tank, 6.3 V power supply. Theory: The travel of light waves
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems
 Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications
 Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515. Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another?
 12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515 Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another? Bending Light The light traveling from an object in water
12.1 What is Refraction pg. 515 Light travels in straight lines through air. What happens to light when it travels from one material into another? Bending Light The light traveling from an object in water
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors
 Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Volumes. Goal: Drive optical to high volumes and low costs
 First Electrically Pumped Hybrid Silicon Laser Sept 18 th 2006 The information in this presentation is under embargo until 9/18/06 10:00 AM PST 1 Agenda Dr. Mario Paniccia Director, Photonics Technology
First Electrically Pumped Hybrid Silicon Laser Sept 18 th 2006 The information in this presentation is under embargo until 9/18/06 10:00 AM PST 1 Agenda Dr. Mario Paniccia Director, Photonics Technology
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators
 A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
A Guide to Acousto-Optic Modulators D. J. McCarron December 7, 2007 1 Introduction Acousto-optic modulators (AOMs) are useful devices which allow the frequency, intensity and direction of a laser beam
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope
 Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
Physics 441/2: Transmission Electron Microscope Introduction In this experiment we will explore the use of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to take us into the world of ultrasmall structures. This
CREOL, College of Optics & Photonics, University of Central Florida
 OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
OSE6650 - Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Optical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Fall 2013 Class 3 slide 1 Challenge: excite and detect the near field Thus far: Nanostructured materials
PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER. Last Revision: August 21, 2007
 PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER Last Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How can an efficient atomic transition laser be constructed and characterized? INTRODUCTION: This lab exercise will allow
PUMPED Nd:YAG LASER Last Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: How can an efficient atomic transition laser be constructed and characterized? INTRODUCTION: This lab exercise will allow
HIGH POWER FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS
 HIGH POWER FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS USA PATENT #: 7431513 Features: Unique connector design minimizes thermal damage Patented connector designs for precise fiber to fiber coupling Able to withstand temperatures
HIGH POWER FIBER OPTIC PATCHCORDS USA PATENT #: 7431513 Features: Unique connector design minimizes thermal damage Patented connector designs for precise fiber to fiber coupling Able to withstand temperatures
WHITE PAPER. 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber
 WHITE PAPER 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber www.ixiacom.com 915-6919-01 Rev. A, July 2014 2 Table of Contents What are 50μm fiber and 62.5μm fiber?... 4 Why two standards?... 4 Which technology should
WHITE PAPER 50 versus 62.5 micron multimode fiber www.ixiacom.com 915-6919-01 Rev. A, July 2014 2 Table of Contents What are 50μm fiber and 62.5μm fiber?... 4 Why two standards?... 4 Which technology should
GRID AND PRISM SPECTROMETERS
 FYSA230/2 GRID AND PRISM SPECTROMETERS 1. Introduction Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. visible light) experiences reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction phenomena when entering and passing
FYSA230/2 GRID AND PRISM SPECTROMETERS 1. Introduction Electromagnetic radiation (e.g. visible light) experiences reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction phenomena when entering and passing
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
 Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Helium-Neon Laser. Figure 1: Diagram of optical and electrical components used in the HeNe laser experiment.
 Helium-Neon Laser Experiment objectives: assemble and align a 3-mW HeNe laser from readily available optical components, record photographically the transverse mode structure of the laser output beam,
Helium-Neon Laser Experiment objectives: assemble and align a 3-mW HeNe laser from readily available optical components, record photographically the transverse mode structure of the laser output beam,
Fiber Optics: Fiber Preparation and Fiber Connectors
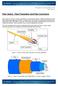 Photonics Technical Note # 20 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Preparation and Fiber Connectors Fiber optics are used for a variety of applications in the photonics industry. Different applications require
Photonics Technical Note # 20 Fiber Optics Fiber Optics: Fiber Preparation and Fiber Connectors Fiber optics are used for a variety of applications in the photonics industry. Different applications require
Crystal Optics of Visible Light
 Crystal Optics of Visible Light This can be a very helpful aspect of minerals in understanding the petrographic history of a rock. The manner by which light is transferred through a mineral is a means
Crystal Optics of Visible Light This can be a very helpful aspect of minerals in understanding the petrographic history of a rock. The manner by which light is transferred through a mineral is a means
Near-field scanning optical microscopy (SNOM)
 Adviser: dr. Maja Remškar Institut Jožef Stefan January 2010 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fluorescence Raman and surface enhanced Raman 7 Conventional optical microscopy-limited resolution Two broad classes of techniques
Adviser: dr. Maja Remškar Institut Jožef Stefan January 2010 1 2 3 4 5 6 Fluorescence Raman and surface enhanced Raman 7 Conventional optical microscopy-limited resolution Two broad classes of techniques
Science In Action 8 Unit C - Light and Optical Systems. 1.1 The Challenge of light
 1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
1.1 The Challenge of light 1. Pythagoras' thoughts about light were proven wrong because it was impossible to see A. the light beams B. dark objects C. in the dark D. shiny objects 2. Sir Isaac Newton
1. Basics of LASER Physics
 1. Basics of LASER Physics Dr. Sebastian Domsch (Dipl.-Phys.) Computer Assisted Clinical Medicine Medical Faculty Mannheim Heidelberg University Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer 1-3 D-68167 Mannheim, Germany sebastian.domsch@medma.uni-heidelberg.de
1. Basics of LASER Physics Dr. Sebastian Domsch (Dipl.-Phys.) Computer Assisted Clinical Medicine Medical Faculty Mannheim Heidelberg University Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer 1-3 D-68167 Mannheim, Germany sebastian.domsch@medma.uni-heidelberg.de
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba +
 A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
A More Efficient Way to De-shelve 137 Ba + Abstract: Andrea Katz Trinity University UW REU 2010 In order to increase the efficiency and reliability of de-shelving barium ions, an infrared laser beam was
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014
 Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Laboratory #3 Guide: Optical and Electrical Properties of Transparent Conductors -- September 23, 2014 Introduction Following our previous lab exercises, you now have the skills and understanding to control
Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs)
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 2, 2009 Bandwidth analysis of multimode fiber passive optical networks (PONs) GRZEGORZ STEPNIAK *, LUKASZ MAKSYMIUK, JERZY SIUZDAK Institute of Telecommunications, Warsaw
Physics 10. Lecture 29A. "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton
 Physics 10 Lecture 29A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Converging Lenses What if we wanted to use refraction to converge parallel
Physics 10 Lecture 29A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Converging Lenses What if we wanted to use refraction to converge parallel
Plastic Optical Fiber for In-Home communication systems
 Plastic Optical Fiber for In-Home communication systems Davide Visani 29 October 2010 Bologna E-mail: davide.visani3@unibo.it Summary Reason for Fiber in the Home (FITH) FITH scenario Comparison of CAT5
Plastic Optical Fiber for In-Home communication systems Davide Visani 29 October 2010 Bologna E-mail: davide.visani3@unibo.it Summary Reason for Fiber in the Home (FITH) FITH scenario Comparison of CAT5
Overview. What is EMR? Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing
 LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Dr. Ragab Khalil Department of Landscape Architecture Faculty of Environmental Design King AbdulAziz University Room 103 Overview What
LA502 Special Studies Remote Sensing Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Dr. Ragab Khalil Department of Landscape Architecture Faculty of Environmental Design King AbdulAziz University Room 103 Overview What
LASER TO FIBER SOURCE COUPLERS APPLICATION NOTES
 LASER TO FIBER SOURCE COUPLERS APPLICATION NOTES Laser To Fiber Coupler With Adjustable Focus Laser To Fiber Coupler With A Beam Splitter Laser To Fiber Coupler With A Shutter Application Notes OZ Optics
LASER TO FIBER SOURCE COUPLERS APPLICATION NOTES Laser To Fiber Coupler With Adjustable Focus Laser To Fiber Coupler With A Beam Splitter Laser To Fiber Coupler With A Shutter Application Notes OZ Optics
OPTICAL FIBER CABLES
 OPTICAL FIBER CABLES CONTENTS INTRODUCTION QUALITY ASSURANCE RECOMMENDED ORDERING PARAMETERS GENERALITIES :. Advantage. General Description.. Construction.. Principle TYPICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF OPTICAL
OPTICAL FIBER CABLES CONTENTS INTRODUCTION QUALITY ASSURANCE RECOMMENDED ORDERING PARAMETERS GENERALITIES :. Advantage. General Description.. Construction.. Principle TYPICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF OPTICAL
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
ELECTRICAL POWER OVER FIBER OPTICS
 International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization on TPE (IOTPE) ISSN 077-358 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com December
International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization on TPE (IOTPE) ISSN 077-358 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com December
Basic Geometrical Optics
 F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.3 Basic Geometrical Optics Leno S. Pedrotti CORD Waco, Texas Optics is the cornerstone of photonics systems and applications. In this module, you will learn about one
F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.3 Basic Geometrical Optics Leno S. Pedrotti CORD Waco, Texas Optics is the cornerstone of photonics systems and applications. In this module, you will learn about one
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02
 104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
104 Practice Exam 2-3/21/02 1. Two electrons are located in a region of space where the magnetic field is zero. Electron A is at rest; and electron B is moving westward with a constant velocity. A non-zero
Physics 25 Exam 3 November 3, 2009
 1. A long, straight wire carries a current I. If the magnetic field at a distance d from the wire has magnitude B, what would be the the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance d/3 from the wire,
1. A long, straight wire carries a current I. If the magnetic field at a distance d from the wire has magnitude B, what would be the the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance d/3 from the wire,
Teacher s Resource. 2. The student will see the images reversed left to right.
 Answer Booklet Reflection of Light With a Plane (Flat) Mirror Trace a Star Page 16 1. The individual students will complete the activity with varying degrees of difficulty. 2. The student will see the
Answer Booklet Reflection of Light With a Plane (Flat) Mirror Trace a Star Page 16 1. The individual students will complete the activity with varying degrees of difficulty. 2. The student will see the
Hard Clad Silica (Standard OH) Radius
 guide Industries DESCRIPTION With numerical aperture (N.A.) of 0.39 and a hard polymer cladding that allows a high core-to-clad ratio, the is the low cost fiber of choice. The pure fused silica (SiO 2
guide Industries DESCRIPTION With numerical aperture (N.A.) of 0.39 and a hard polymer cladding that allows a high core-to-clad ratio, the is the low cost fiber of choice. The pure fused silica (SiO 2
Convex Mirrors. Ray Diagram for Convex Mirror
 Convex Mirrors Center of curvature and focal point both located behind mirror The image for a convex mirror is always virtual and upright compared to the object A convex mirror will reflect a set of parallel
Convex Mirrors Center of curvature and focal point both located behind mirror The image for a convex mirror is always virtual and upright compared to the object A convex mirror will reflect a set of parallel
Revision problem. Chapter 18 problem 37 page 612. Suppose you point a pinhole camera at a 15m tall tree that is 75m away.
 Revision problem Chapter 18 problem 37 page 612 Suppose you point a pinhole camera at a 15m tall tree that is 75m away. 1 Optical Instruments Thin lens equation Refractive power Cameras The human eye Combining
Revision problem Chapter 18 problem 37 page 612 Suppose you point a pinhole camera at a 15m tall tree that is 75m away. 1 Optical Instruments Thin lens equation Refractive power Cameras The human eye Combining
Raman spectroscopy Lecture
 Raman spectroscopy Lecture Licentiate course in measurement science and technology Spring 2008 10.04.2008 Antti Kivioja Contents - Introduction - What is Raman spectroscopy? - The theory of Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy Lecture Licentiate course in measurement science and technology Spring 2008 10.04.2008 Antti Kivioja Contents - Introduction - What is Raman spectroscopy? - The theory of Raman spectroscopy
waves rays Consider rays of light from an object being reflected by a plane mirror (the rays are diverging): mirror object
 PHYS1000 Optics 1 Optics Light and its interaction with lenses and mirrors. We assume that we can ignore the wave properties of light. waves rays We represent the light as rays, and ignore diffraction.
PHYS1000 Optics 1 Optics Light and its interaction with lenses and mirrors. We assume that we can ignore the wave properties of light. waves rays We represent the light as rays, and ignore diffraction.
FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY
 FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES SCIENCE AND MATH OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing results
FIFTH GRADE TECHNOLOGY 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES SCIENCE AND MATH OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing results
Waves Sound and Light
 Waves Sound and Light r2 c:\files\courses\1710\spr12\wavetrans.doc Ron Robertson The Nature of Waves Waves are a type of energy transmission that results from a periodic disturbance (vibration). They are
Waves Sound and Light r2 c:\files\courses\1710\spr12\wavetrans.doc Ron Robertson The Nature of Waves Waves are a type of energy transmission that results from a periodic disturbance (vibration). They are
Light and its effects
 Light and its effects Light and the speed of light Shadows Shadow films Pinhole camera (1) Pinhole camera (2) Reflection of light Image in a plane mirror An image in a plane mirror is: (i) the same size
Light and its effects Light and the speed of light Shadows Shadow films Pinhole camera (1) Pinhole camera (2) Reflection of light Image in a plane mirror An image in a plane mirror is: (i) the same size
Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications
 Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. 2149 E. Pratt Boulevard Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 USA Phone: (847)
Advancements in High Frequency, High Resolution Acoustic Micro Imaging for Thin Silicon Applications Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. 2149 E. Pratt Boulevard Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 USA Phone: (847)
With the advent of Gigabit Ethernet
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NETWORK MANAGEMENT Int. J. Network Mgmt 2001; 11:139 146 (DOI: 10.1002/nem.396) The importance of modal bandwidth in Gigabit Ethernet systems By David N. Koon Ł This article deals
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NETWORK MANAGEMENT Int. J. Network Mgmt 2001; 11:139 146 (DOI: 10.1002/nem.396) The importance of modal bandwidth in Gigabit Ethernet systems By David N. Koon Ł This article deals
Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions
 Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions Sergiusz Patela, Dr Sc Room I/48, Th. 13:00-16:20, Fri. 9:20-10:50 sergiusz.patela@pwr.wroc.pl eportal.pwr.wroc.pl Copying and processing permitted for noncommercial
Limiting factors in fiber optic transmissions Sergiusz Patela, Dr Sc Room I/48, Th. 13:00-16:20, Fri. 9:20-10:50 sergiusz.patela@pwr.wroc.pl eportal.pwr.wroc.pl Copying and processing permitted for noncommercial
C) D) As object AB is moved from its present position toward the left, the size of the image produced A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same
 1. For a plane mirror, compared to the object distance, the image distance is always A) less B) greater C) the same 2. Which graph best represents the relationship between image distance (di) and object
1. For a plane mirror, compared to the object distance, the image distance is always A) less B) greater C) the same 2. Which graph best represents the relationship between image distance (di) and object
LINOS distributors: Refer to Service Worldwide at the end of this catalog
 page 203 Optics Coupler Introduction 204 Coupler Ordering Information 205 Functional Principle of s 206 Configuration 208 Ordering Information 210 Collimators 212 Collimator Ordering Information 213 Coupler
page 203 Optics Coupler Introduction 204 Coupler Ordering Information 205 Functional Principle of s 206 Configuration 208 Ordering Information 210 Collimators 212 Collimator Ordering Information 213 Coupler
INTERFERENCE OBJECTIVES PRE-LECTURE. Aims
 53 L4 INTERFERENCE Aims OBJECTIVES When you have finished this chapter you should understand how the wave model of light can be used to explain the phenomenon of interference. You should be able to describe
53 L4 INTERFERENCE Aims OBJECTIVES When you have finished this chapter you should understand how the wave model of light can be used to explain the phenomenon of interference. You should be able to describe
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson
 Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
A down-under undergraduate optics and photonics laboratory
 A down-under undergraduate optics and photonics laboratory Barry Perczuk and Michael Gal School of Physics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia ABSTRACT Our senior undergraduate
A down-under undergraduate optics and photonics laboratory Barry Perczuk and Michael Gal School of Physics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia ABSTRACT Our senior undergraduate
Integrated Photonic. Electronic. Optics. Optoelettronics. Integrated Photonic - G. Breglio L1. Quantum Mechanics Materials Science Nano/Bio-photonic
 Integrated Photonic Quantum Mechanics Materials Science Nano/Bio-photonic Optoelettronics Optics Electronic Applications of Optoelectronic Systems Solar cells OLED display LED Laser diodes Flexible OLED
Integrated Photonic Quantum Mechanics Materials Science Nano/Bio-photonic Optoelettronics Optics Electronic Applications of Optoelectronic Systems Solar cells OLED display LED Laser diodes Flexible OLED
DIRECTIONAL FIBER OPTIC POWER MONITORS (TAPS/PHOTODIODES)
 Features: DIRECTIONAL FIBER OPTIC POWER MONITORS (TAPS/PHOTODIODES) PATENT NUMBERS: CANADA 2,494,133, USA 7095931, 7295731 AND CHINA 1672073 Telcordia GR-468 qualified Available in versions for any wavelength
Features: DIRECTIONAL FIBER OPTIC POWER MONITORS (TAPS/PHOTODIODES) PATENT NUMBERS: CANADA 2,494,133, USA 7095931, 7295731 AND CHINA 1672073 Telcordia GR-468 qualified Available in versions for any wavelength
Acousto-optic modulator
 1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
Code number given on the right hand side of the question paper should be written on the title page of the answerbook by the candidate.
 Series ONS SET-1 Roll No. Candiates must write code on the title page of the answer book Please check that this question paper contains 16 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the
Series ONS SET-1 Roll No. Candiates must write code on the title page of the answer book Please check that this question paper contains 16 printed pages. Code number given on the right hand side of the
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
ME 472 Engineering Metrology
 ME 472 Engineering Metrology and Quality Control Chp 6 - Advanced Measurement Systems Mechanical Engineering University of Gaziantep Dr. A. Tolga Bozdana Assistant Professor Coordinate Measuring Machines
ME 472 Engineering Metrology and Quality Control Chp 6 - Advanced Measurement Systems Mechanical Engineering University of Gaziantep Dr. A. Tolga Bozdana Assistant Professor Coordinate Measuring Machines
First let us consider microscopes. Human eyes are sensitive to radiation having wavelengths between
 Optical Differences Between Telescopes and Microscopes Robert R. Pavlis, Girard, Kansas USA icroscopes and telescopes are optical instruments that are designed to permit observation of objects and details
Optical Differences Between Telescopes and Microscopes Robert R. Pavlis, Girard, Kansas USA icroscopes and telescopes are optical instruments that are designed to permit observation of objects and details
Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology
 Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology theremino System - Theremino Spectrometer Technology - August 15, 2014 - Page 1 Operation principles By placing a digital camera with a diffraction grating
Theremino System Theremino Spectrometer Technology theremino System - Theremino Spectrometer Technology - August 15, 2014 - Page 1 Operation principles By placing a digital camera with a diffraction grating
Simulation of Gaussian Pulses Propagation Through Single Mode Optical Fiber Using MATLAB . MATLAB
 Iraqi Journal of Science, 213, Vol.4, No.3, pp.61-66 Simulation of Gaussian Pulses Propagation Through Single Mode Optical Fiber Using MATLAB Salah Al Deen Adnan Taha *, Mehdi M. Shellal, and Ahmed Chyad
Iraqi Journal of Science, 213, Vol.4, No.3, pp.61-66 Simulation of Gaussian Pulses Propagation Through Single Mode Optical Fiber Using MATLAB Salah Al Deen Adnan Taha *, Mehdi M. Shellal, and Ahmed Chyad
Implementation of Short Reach (SR) and Very Short Reach (VSR) data links using POET DOES (Digital Opto- electronic Switch)
 Implementation of Short Reach (SR) and Very Short Reach (VSR) data links using POET DOES (Digital Opto- electronic Switch) Summary POET s implementation of monolithic opto- electronic devices enables the
Implementation of Short Reach (SR) and Very Short Reach (VSR) data links using POET DOES (Digital Opto- electronic Switch) Summary POET s implementation of monolithic opto- electronic devices enables the
PHYS 222 Spring 2012 Final Exam. Closed books, notes, etc. No electronic device except a calculator.
 PHYS 222 Spring 2012 Final Exam Closed books, notes, etc. No electronic device except a calculator. NAME: (all questions with equal weight) 1. If the distance between two point charges is tripled, the
PHYS 222 Spring 2012 Final Exam Closed books, notes, etc. No electronic device except a calculator. NAME: (all questions with equal weight) 1. If the distance between two point charges is tripled, the
The following terms are defined within the context of the fiber optic industry
 The following terms are defined within the context of the fiber optic industry Adapter A mechanical media termination device designed to align and join fiber optic connectors. Often referred to as coupling,
The following terms are defined within the context of the fiber optic industry Adapter A mechanical media termination device designed to align and join fiber optic connectors. Often referred to as coupling,
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT AND DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATIONS
 PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT AND DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATIONS 1. Photons 2. Photoelectric Effect 3. Experimental Set-up to study Photoelectric Effect 4. Effect of Intensity, Frequency, Potential on P.E.
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT AND DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATIONS 1. Photons 2. Photoelectric Effect 3. Experimental Set-up to study Photoelectric Effect 4. Effect of Intensity, Frequency, Potential on P.E.
