CT transverse anatomy
|
|
|
- Imogene Horn
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
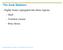
1 CT transverse anatomy
2
3
4 1. Aorta 2. Inferior Vena Cava 3. Ureter 4. Left Kidney 5. Small Bowel 6. Cecum 7. Descending Colon 8. Psoas Muscle 9. Erector Spinae Muscle 10. Rectus Abdominus Muscle 16. Vertebra (Spinous Process)
5 2.Inferior Vena Cava 3.ureter 5. Small Bowel 6.Cecum 7.Descending Colon 8.Psoas Muscle 9.Erector Spinae Muscle 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 11.External Oblique Muscle 12.Internal Oblique Muscle 13.Tranversus Abdominus Muscle 14. Quadratus Lumborum Muscle 16. Vertebra (Spinous Process
6 2.Inferior Vena Cava 3. Ureter 4.Left Kidney 5.Small Bowel 6.Cecum 7.Descending Colon 8. Psoas Muscle 9. Erector Spinae Muscle 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 11.External Oblique Muscle 12.Internal Oblique Muscle 13.Tranversus Abdominus Muscle 14.Quadratus Lumborum Muscle 15. Vertebra (Body) 16. Vertebra (Spinous Process 17. Common Iliac Arteries
7 2.Inferior Vena Cava 3. Ureter 4.Left Kidney 5.Small Bowel 6.Cecum 6a. Appendix 7.Descending Colon 8. Psoas Muscle 9. Erector Spinae Muscle 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 11.External Oblique Muscle 12.Internal Oblique Muscle 13.Tranversus Abdominus Muscle 14.Quadratus Lumborum Muscle 15. Vertebra (Body) 16. Vertebra (Spinous ProcessAorta 17. Common Iliac Arteries 17a. 17a. Common Iliac Veins 18. Iliac Wing
8 3. Ureter 5.Small Bowel 6.Cecum 7.Descending Colon 8. Psoas Muscle 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 11.External Oblique Muscle 12.Internal Oblique Muscle 13.Tranversus Abdominus Muscle 14.Quadratus Lumborum Muscle 15. Vertebra (Body) 16. Vertebra (Spinous Process 18. Iliac Wing
9 5.Small Bowel 8. Psoas Muscle 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 19. External Iliac Vessels 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle
10 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 19. External Iliac Vessels 23. Iliacus Muscle 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle 26. Gluteus Minimus Muscle 29. Sigmoid Colon 28. Bladder
11 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 19. External Iliac Vessels 23. Iliacus Muscle 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle 26. Gluteus Minimus Muscle 28. Bladder 29. Sigmoid Colon 3. Ureter 30. Rectum 34. Piriformis Muscle
12 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle 26. Gluteus Minimus Muscle 27. Sacrum 28. Bladder 30. Rectum
13 10.Rectus Abdominus Muscle 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle 26. Gluteus Minimus Muscle 27. Sacrum 28. Bladder 30. Rectum 46. Sartorius Muscle
14 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 25. Gluteus Medius Muscle 28. Bladder 30. Rectum 31. Seminal Vesicle 36. Femoral Head 38. Rectus Femoris Muscle 46. Sartorius Muscle
15 20. Common Femoral Artery and Vein 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 30. Rectum 32. Prostate Gland 35. Ischial Spine 36. Femoral Head 37. Greater Trochanter 38. Rectus Femoris Muscle 41. Ischiorectal Fossa 46. Sartorius Muscle 55. Pectineus Muscle
16 20. Common Femoral Artery and Vein 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 30. Rectum 32. Prostate Gland 35. Ischial Spine 36. Femoral Head 37. Greater Trochanter 38. Rectus Femoris Muscle 39. Internal Obturator Muscle 41. Ischiorectal Fossa 42. Symphysis Pubis 44. Ischial Tuberosity 46. Sartorius Muscle 50. Vastus Intermedius Muscle 54. Tensor Fascia Latae 55. Pectineus Muscle
17 20. Common Femoral Artery and Vein 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 38. Rectus Femoris Muscle 40. External Obturator Muscle 41. Ischiorectal Fossa 44. Ischial Tuberosity 49. Vastus Lateralis Muscle 50. Vastus Intermedius Muscle 54. Tensor Fascia Latae 55. Pectineus Muscle
18 20. Common Femoral Artery and Vein 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 33. Base of Penis 38. Rectus Femoris Muscle 40. External Obturator Muscle 41. Ischiorectal Fossa 44. Ischial Tuberosity 46. Sartorius Muscle 49. Vastus Lateralis Muscle 50. Vastus Intermedius Muscle 54. Tensor Fascia Latae 55. Pectineus Muscle
19 21. Superficial Femoral Artery 22. Deep Femoral Artery 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 46. Sartorius Muscle 47. Adductor Magnus Muscle 48. Adductor Longus Muscle 49. Vastus Lateralis Muscle 50. Vastus Intermedius Muscle 51. Vastus Medialis Muscle 54. Tensor Fascia Latae 55. Pectineus Muscle
20 21. Superficial Femoral Artery 22. Deep Femoral Artery 24. Gluteus Maximus Muscle 45. Gracilis Muscle 46. Sartorius Muscle 47. Adductor Magnus Muscle 48. Adductor Longus Muscle 49. Vastus Lateralis Muscle 50. Vastus Intermedius Muscle 51. Vastus Medialis Muscle 52. Semimembranousus and Semitendinosus Muscles 54. Tensor Fascia Latae 55. Pectineus Muscle
21 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 4. Gallbladder 5. Right Adrenal Gland 6. Left Adrenal Gland 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10. Superior Mesenteric Artery 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending colon 14. Stomach
22 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 4. Gallbladder 5. Right Adrenal Gland 6. Left Adrenal Gland 7. Inferior Vena Cava 9. Portal Vein 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon
23 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 4. Gallbladder 5. Right Adrenal Gland 6. Left Adrenal Gland 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 14. Stomach
24 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 4. Gallbladder 6. Left Adrenal Gland 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10. Superior Mesenteric Artery 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 14. Stomach 15. Distal Stomach
25 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 3+. Pancreas head 3*. Pancreas tail 4. Gallbladder 6. Left adrenal 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10*. Superior Mesenteric Vein 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney
26 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3. Pancreas 3-.pancreas uncinate process 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 10*. Superior Mesenteric Vein 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney
27 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3-.pancreas uncinate process 4. Gallbladder 5. Right Adrenal Gland 6. Left Adrenal Gland 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10. Superior Mesenteric Artery 10*. Superior Mesenteric Vein 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney 19. Duodenum, 2nd part 19*. Duodenum, 3rd part 20. Left Renal Vein
28 1.Liver. 2. Spleen 3-.pancreas uncinate process 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10. Superior Mesenteric Artery 10*. Superior Mesenteric Vein 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney 19. Duodenum, 2nd part 19*. Duodenum, 3rd part 20. Left Renal Vein 21..right renal vein
29 1.Liver. 3-. Pancreas uncinate process 4. Gallbladder 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 9. Portal Vein 10. Superior Mesenteric Artery 10*. Superior Mesenteric Vein 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney 21.Right renal vein
30 1.Liver. 7. Inferior Vena Cava 8. Aorta 11. Ascending Colon 12. Descending Colon Descending Colon 13. Transverse Colon 16.Right kideny 17. Left kidney 19. Duodenum, 2nd part
31 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 4*. Right Clavicle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 7. Supraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 9. Pectoralis Minor Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 13. Left Subclavian Artery 13a. Distal Subclavian Artery 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 15. Left Internal Jugular Vein 26. Left Subclavian Vein/Axillary Vein
32 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 4. Left Clavicle 4*. Right Clavicle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 7. Supraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 9. Pectoralis Minor Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 13. Left Subclavian Artery 13a. Distal Subclavian Artery 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 15. Left Internal Jugular Vein 17. First Rib 18. Manubrium of Sternum
33 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 7. Supraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 9. Pectoralis Minor Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 13. Left Subclavian Artery 13a. Distal Subclavian Artery 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 14*. Right Common Carotid Artery 18. Manubrium of Sternum 21. Right Brachiocephalic Vein
34 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 7. Supraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 9. Pectoralis Minor Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 18. Manubrium of Sternum 21. Right Brachiocephalic Vein 21*.left Brachiocephalic Vein 27. Brachiocephalic Artery
35 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 18*. Body of Sternum 21. Right Brachiocephalic Vein 21*.left Brachiocephalic Vein 24. Teres Major Muscle 27. Brachiocephalic Artery
36 3.Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 18*. Body of Sternum 21. Right Brachiocephalic Vein 21*.left Brachiocephalic Vein 24. Teres Major Muscle 27. Brachiocephalic Artery
37 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3.Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 14. Left Common Carotid Artery 18*. Body of Sternum 21. Right Brachiocephalic Vein 21*.left Brachiocephalic Vein 24. Teres Major Muscle 27. Brachiocephalic Artery
38 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 5. Subscapularis Infraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 19. Aortic Arch 19*. Ascending Aorta 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 25. Teres Minor Muscle
39 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 5. Subscapularis Infraspinatus Muscle 8. Pectoralis Major Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 18*. *. Body of Sternum 19. Aortic Arch 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 25. Teres Minor Muscle
40 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 12. Erector Spinae Muscles 18*. *. Body of Sternum 19. Aortic Arch 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 25. Teres Minor Muscle
41 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20*. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 25. Teres Minor Muscle
42 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 5. Subscapularis 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20*Arch of the Azygous 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle
43 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 29. Pulmonary Trunk 30*. Left Pulmonary Artery 30. Right Pulmonary Artery
44 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 29. Pulmonary Trunk 30*. Left Pulmonary Artery 30. Right Pulmonary Artery
45 1. Trachea 2. Esophagus 3. Trapezius muscle 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 29. Pulmonary Trunk 30*. Left Pulmonary Artery 30. Right Pulmonary Artery 32. Carina of Trachea
46 3.Trapezius muscle 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 16. Scapula 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 24. Teres Major Muscle 29. Pulmonary Trunk 30. Right Pulmonary Artery
47 3.Trapezius muscle 6. Infraspinatus Muscle 10. Serratus Anterior Muscle 11. Latissimus Dorsi Muscle 16. Scapula 18*. Body of Sternum 19*. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 22. Superior Vena Cava 30. Right Pulmonary Artery 34. Right Atrium
48 18*. Body of Sternum 19. Ascending Aorta 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 33. Right Ventricle 34. Right atrium 35. Left atrium 37. Right Pulmonary Vein
49 18*. Body of Sternum 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 33. Right Ventricle 34. Right atrium 35. Left atrium 36.Left ventricle 37. Right Pulmonary Vein 37*.l Pulmonary Vein
50 18*. Body of Sternum 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 33. Right Ventricle 34. Right atrium 35. Left atrium 36.Left ventricle 37. Right Pulmonary Vein 37*.l Pulmonary Vein 38. Septum 40. Tricuspid valve
51 18*. Body of Sternum 19+. Descending Aorta 20. Azygous Vein 33. Right Ventricle 34. Right atrium 35. Left atrium 36.Left ventricle 37. Right Pulmonary Vein 37*.l Pulmonary Vein 38. Septum 39. Coronary Sinus
52 49. Nasal Septum 54. Mastoid Air Cells 56. Maxillary Sinus 57. Cerebellar Tonsil 68. Nasopharynx 69. Masseter m. 70. Lateral Pterygoid muscle
53 49. Nasal Septum 44. Fourth Ventricle 45. Cerebellum 51. Clivus 52. Medulla 70. Lateral Pterygoid muscle
54 25. Vermis 34. Temporal Lobe 38. Lens 39. Internal Carotid A 43. Basilar A. 48. Pons 49. Nasal Septum 44. Fourth Ventricle 45. Cerebellum 50. Sphenoid Sinus 54. Mastoid Air Cells
55 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus 25. Vermis 29. Mamillary Bodies 30. Posterior Cerebral 32. Cerebral Peduncle 34. Temporal Lobe 35. Ethmoid Sinus 37. Cranial Nerve II 38. Lens 39. Internal Carotid A 52. Medulla
56 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus 3. Frontal Lobe 13. Lateral Ventricle 17. Middle Cerbral A. 20. Foramen of Monro 22. Third Ventricle 23. Frontal Sinus 25. Vermis
57 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus 13. Lateral Ventricle 14. Caudate Nucleus 15. Putamen 16. Genu/Splenium of Corpus Callosum 22. Third Ventricle 23. Frontal Sinus
58 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus 2. Falx Cerebri 7. Precentral Gyrus 13. Lateral Ventricle 11. Superior Frontal Gyrus 73. Amygdala
59 2.Falx Cerebri 3. Frontal Lobe 4. Parietal Lobe
60 2.Falx Cerebri 5. Central Sulcus 7. Precentral Gyrus 8. Postcentral Gyrus 11. Superior Frontal Gyrus 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus
61 2.Falx Cerebri 5. Central Sulcus 6. Superior Frontal Sulcus 7. Precentral Gyrus 8. Postcentral Gyrus 1. Superior Sagittal Sinus
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. IV. Hip
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines IV. Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human
 Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAT DISSECTION UNIT
 CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Glossary (continued)
 1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES
 HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES 0003 0008 0005 0008 0009 0019 0001 0000 0000 0001 0003 0005 0008 0009 0019 MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK*
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, [email protected] Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, [email protected] Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, [email protected] Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, [email protected] Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
Practice Anatomy Questions Semester 2
 1 - Which muscle layer does NOT wrap around the abdomen? a) external oblique b) internal oblique c) transversus abdominus d) rectus abdominus 2 - Which statement is correct? a) The fibres of the internal
1 - Which muscle layer does NOT wrap around the abdomen? a) external oblique b) internal oblique c) transversus abdominus d) rectus abdominus 2 - Which statement is correct? a) The fibres of the internal
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE
 RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb
 An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
An overview of the anatomy of the canine hindlimb Darren Kelly Artwork by Paddy Lennon Original photos courtesy of Mary Ferguson Students at University College Dublin, School of Veterinary Medicine. Video
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Name the muscle, A: (Action), O: (Origin), and I: (Insertion)
 FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
FRONTALIS - A: (Action) Elevates eyebrows in glancing upward and expressions of surprise or fright; draws scalp forward and wrinkles skin of forehead; O: (Origin) Galea aponeurotica; I: Subcutaneous tissue
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine. Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine. head neck greater trochanter intertrochanteric line lesser trochanter
 Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Ilium Bones The Skeleton Ischium Pubis Sacro-iliac Joint Iliac Crest Anterior Superior Superior Pubic Ramus Anterior Inferior Acetabulum Obturator Foramen Ischio-pubic ramus Ischial tuberosity Pubic Crest
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE
 ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis
 2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130)
 Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
Functional Human Morphology (2040) & Functional Anatomy of the Head, Neck and Trunk (2130) Gastrointestinal & Urogenital Systems Recommended Text: TEXTBOOK OF ANATOMY: ROGERS Published by Churchill Livingstone
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus
 LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
GROSS ANATOMY. Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs. Lecture Syllabus 2008
 GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
GROSS ANATOMY Lecture Syllabus 2008 Unit #4: Upper and Lower Limbs ANAT 6010 - Gross Anatomy Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy University of Utah School of Medicine G24- Upper Limb Overview, Shoulder,
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
Core Training for Improved Performance
 Core Training for Improved Performance Tracy Morgan Handzel, CSCS Core training has penetrated a variety of fitness and performance related fields. Health clubs offer core training group exercise classes.
Core Training for Improved Performance Tracy Morgan Handzel, CSCS Core training has penetrated a variety of fitness and performance related fields. Health clubs offer core training group exercise classes.
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength
 A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
A Woman s Guide to Muscle & Strength CORRESPONDENCE EDUCATION PROGRAM # 140. Check your receipt for course expiration date. After that date no credit will be awarded for this program. 2012 by Exercise
13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision
 Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Malawer Chapter 13 21/02/2001 15:36 Page 243 13 Adductor Muscle Group Excision Martin Malawer and Paul Sugarbaker OVERVIEW The adductor muscle group is the second most common site for high- and low-grade
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Administrative. Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality
 CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System
 Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
The Large Intestine. General Facts: (everything will be repeated in a more organized matter later on)
 The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
The Large Intestine Let's continue on our wild journey through the GI tract. We have just arrived at the junction between the ileum and cecum, crossing the border between the small and large intestine.
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Biology Dissection THE FROG
 Biology Dissection THE FROG Name Note: The organism you are cutting up today was once alive and vibrant, a living being. Dissection of a complex organism is not a right, but a privilege. Please be aware
Biology Dissection THE FROG Name Note: The organism you are cutting up today was once alive and vibrant, a living being. Dissection of a complex organism is not a right, but a privilege. Please be aware
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Surgical Approaches to Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Surgical Approaches to Total Hip Arthroplasty Daniel Kelmanovich, 1 Michael L. Parks, MD, 2 Raj Sinha, MD, PhD, 3 and William Macaulay, MD 4 Surgical exposure of the hip for trauma, infection, or reconstruction
Surgical Approaches to Total Hip Arthroplasty Daniel Kelmanovich, 1 Michael L. Parks, MD, 2 Raj Sinha, MD, PhD, 3 and William Macaulay, MD 4 Surgical exposure of the hip for trauma, infection, or reconstruction
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Lower limb nerve blocks
 Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
Lower limb nerve blocks Barry Nicholls is Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management at Musgrove Hospital, Taunton, UK. He qualified from Liverpool University and trained in Newcastle, UK, and Seattle,
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Rehabilitation with Pilates
 Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
Rehabilitation with Pilates Flat Feet Pes Planus Naiké Durel January 2016 Montreal, Canada Table of contents Title Table of contents Abstract Anatomy of the foot p.1 p.2 p.3 p.4-5- 6-7 Case of study BASI
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
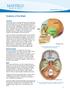 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
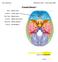 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
How Muscles are Named
 How Muscles are Named There are over 600 muscles in the human body. Identifying these six hundred muscles is a daunting task. Furthermore, the names of these muscles seem foreign to most of us. Most of
How Muscles are Named There are over 600 muscles in the human body. Identifying these six hundred muscles is a daunting task. Furthermore, the names of these muscles seem foreign to most of us. Most of
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SSE #47: ------------------------------------------------------------------------ GSSI
 SSE Roundtable #47: Core Strength Training ------------------------------------------------------------------------ GSSI Sports Science Exchange Roundtable 47 VOLUME 13 (2002) NUMBER 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------
SSE Roundtable #47: Core Strength Training ------------------------------------------------------------------------ GSSI Sports Science Exchange Roundtable 47 VOLUME 13 (2002) NUMBER 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book
 Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book Terms of Position and Direction 1. A section that separates the body in to right and left portions would be the A. Frontal section B. transverse
Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book Terms of Position and Direction 1. A section that separates the body in to right and left portions would be the A. Frontal section B. transverse
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
ESSENTIAL SURFACE & RELATED ANATOMY FOR CLINICAL PRACTICE
 ESSENTIAL SURFACE & RELATED ANATOMY FOR CLINICAL PRACTICE Compiled by Dr Robert Whitaker & Dr Jessica White (See also pages 210 234 in Instant Anatomy. Blackwell Publishing. 3 rd Edition by Whitaker &
ESSENTIAL SURFACE & RELATED ANATOMY FOR CLINICAL PRACTICE Compiled by Dr Robert Whitaker & Dr Jessica White (See also pages 210 234 in Instant Anatomy. Blackwell Publishing. 3 rd Edition by Whitaker &
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Hip relatively joint (acetabularfemoral) functions bony strong large stable due to The enhanced architecture
Gross Anatomy. Henryk Dancygier. Chapter Outline. Descriptive Anatomy
 Gross Anatomy Henryk Dancygier 2 Chapter Outline Descriptive Anatomy...11 Functional Anatomy...13 References...14 The present review of gross anatomy of the liver begins with a short discussion of the
Gross Anatomy Henryk Dancygier 2 Chapter Outline Descriptive Anatomy...11 Functional Anatomy...13 References...14 The present review of gross anatomy of the liver begins with a short discussion of the
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques
 SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often
SECTION II General Osteopathic Techniques Chapter Four The Lower Extremities 40 Ligamentous Articular Strain The lower extremities are among the most important structures of the body and yet are often
CHAPTER V SACROILIAC JOINT & PELVIS
 CHAPTER V SACROILIAC JOINT & PELVIS Chapter V: Sacroiliac Joint & Pelvis Note to Reader 151 Chapter Organization 152 Part I: Clinical Implications of Anatomy & Physiology 153 Anatomical Structures & Landmarks
CHAPTER V SACROILIAC JOINT & PELVIS Chapter V: Sacroiliac Joint & Pelvis Note to Reader 151 Chapter Organization 152 Part I: Clinical Implications of Anatomy & Physiology 153 Anatomical Structures & Landmarks
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
