Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
|
|
|
- Moses Freeman
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Describe similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscles tissue, and indicate where they are found in the body. 2. Define muscular system. 3. Define and explain the role of the following: endomysium, perimysium, epimysium, tendon, and aponeurosis. 4. Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle and explain the role of actin- and myosin- containing myofilaments. 5. Describe how an action potential is initiated in a muscle cell. 6. Describe the events of muscle cell contraction. 7. Define graded response, tetanus, isotonic and isometric contractions, and muscle tone as these terms apply to a skeletal muscle. 8. Define oxygen deficit and muscle fatigue, and list possible causes of muscle fatigue. 9. Define origin, insertion, prime mover, antagonist, synergist, and fixator as they relate to muscles. 10. Demonstrate or identify the different types of body movements. 11. List some criteria used in naming muscles. 12. Name and locate the major muscles of the human body (do not have to write this one out) 13. Explain the importance of a nerve supply and exercise in keeping muscles healthy. 14. Describe the changes that occur in aging muscles. Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet. Notes Outline I. Muscular system II. Characteristics of muscles III. Comparison of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles IV. Microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscles V. Types of muscles contractions VI. Muscle tone VII. Effect of exercise on muscles VIII. Muscles and body movement IX. Types of muscles X. Naming skeletal muscles XI. Head and neck muscles
2 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6: The Muscular System Name: 1. Nine characteristics of muscle tissue are listed below. Identify the type of muscle by myofilament, myofibril, perimysium, sarcolemma, sarcomere, sarcoplasm, tendon checking the appropriate box(s). Description Smooth Cardiac Skeletal 1. Connective tissue surrounding a Involuntary fascicle Banded 2. Connective tissue ensheathing the appearance entire muscle Longitudinally 3. Contractile unit of muscle and circularly arranged 4. A muscle cell layers 5. Thin connective tissue investing each Dense connective muscle cell tissue 6. Plasma membrane of the muscle cell packaging Figure-8 7. A long, filamentous organelle found packaging within muscle cells that has a banded Coordinated activity to act as a pump appearance 8. Actin- or myosin-containing structure Moves bones 9. Cordlike extension of connective and facial skin tissue beyond muscle, serving to Referred to as attach it to the bone muscular system 10. A discrete bundle of muscle cells Voluntary _ 2. Regarding functions of muscle tissue, circle the term in each of the groupings that does not belong with the other terms. A. Urine, Food stuffs, Bones, Smooth muscle B. Heart, Cardiac muscle, Blood pump, Promotes labor during birth C. Excitability, Response to a stimulus, Contractility, Action potential D. Ability to shorten, Contractility, Pulls on bones, Stretchability E. Maintains posture, Movement, Promotes growth, Generates heat 4. Color each of the following: Endomysium, Epimysium, Fiber, Myofibril, Perimysium, and tendon 3. Identify structures by matching the descriptions. Use the following words: endomysium, epimysium, fascicle, fiber,
3 5. Below is a small portion of a relaxed muscle cell. First, select different colors for the structures listed below. Label an A band, an I band, and a sarcomere.. o Myosin o Actin filaments o Z disc 7. Complete the following statements relating to the neuromuscular junction. A motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscle cells it stimulates is called a. The axon of each motor neuron has numerous endings called. The actual gap between an axonal ending and the muscle cell is called a. Within the axonal endings are many small vesicles containing a neurotransmitter substance called. When the reaches the ends of the axon, the neurotransmitter is released, and it diffuses to the muscle cell membrane to combine with receptors there. Binding of the neurotransmitters with muscle membrane receptors causes the membrane to become permeable to sodium, resulting in the influx of sodium ions and of the membrane. Then contraction of the muscle cell occurs. Draw a contracted sarcomere and label same structures, as well as light and dark bands. 8. Number the following statements in their proper sequence to describe the contraction mechanism in a skeletal muscle cell. Step 1 has already been identified. 6. Looking at your diagram of a contracted sarcomere from a slightly different angle, which region of the sarcomere shortens during contraction- the dark band, the light band or both? 1. Acetyolcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction by the axonal terminal The action potential, carried deep into cell, causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca ions The muscle cell relaxes and lengthens Acetylcholine diffuses across the neuromuscular junction and binds to receptors on the sarcolemma The Ca ion concentration at the myofilaments increases; the myofilaments slide past one another, and the cell shortens Depolarization occurs, and action potential is generated As Ca is actively reabsorbed into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, its concentration at the myofilaments decreases
4 9. The following statements refer to a muscle cell in the resting state just before polarization. Complete each statement below using the table. A Activation of the Na-K pump which moves K into the cell and Na out of the cell B Na diffuses out of the cell C Inside the cell D Outside the cell E Relative ionic concentrations on the two sides of the membrane during rest F Electrical conditions G K diffuses out of the cell H Na diffuses into cell There is a greater concentration of Na, and there is a greater concentration of K. When the stimulus is delivered, the permeability of the membrane is changed, and, initiating the depolarization of the membrane. Almost as soon as the depolarization wave begins, a repolarization wave follows it across the membrane. This occurs as a. Repolarization restores the of the resting cell membrane. The is (are) reestablished by 10. Complete the following statements by choosing the correct response from the key choices. Fatigue Muscle cell Muscle tone Isotonic Isometric Whole muscle contraction contraction Tetanus Few motor units Many motor units Repolarization Depolarization 1. Is a continuous contraction that shows no evidence of relaxation 2. A(n) is a contraction in which the muscle shortens and work is done 3. To accomplish a strong contraction, are stimulated at a rapid rate 4. When a weak but smooth muscle contraction is desired, are stimulated at a rapid rate. 5. When a muscle is being stimulated but is not able to respond because of oxygen debt the condition is called 6. A(n) is a contraction in which the muscle does not shorten, but tension in the muscle keeps increasing. 11. Using the following terms select one of the three ways that muscle cells replenish their ATP supplies A. Coupled reaction of creatine phosphate and ADP B. Anaerobic glycolysis C. Aerobic respiration 1. Accompanied by lactic acid formation 2. Supplies the highest ATP yield per glucose molecule 3. Involves the simple transfer of a phosphate group 4. Requires no oxygen 5. The slowest ATP regeneration process 6. Produces carbon dioxide and water 7. The energy mechanism used in the second hour of running in a marathon 8. Used when the oxygen supply is inadequate over time 9. Good for a sprint 12. Briefly describe how you can tell when you are repaying the oxygen deficit.
5 13. Which of the following occur within a muscle cell during oxygen debt? Place an X in correct choices Decreased ATP Increased lactic acid Increased oxygen Increased CO2 Increased ATP Decreased oxygen Decreased CO2 Increased glucose 14. Complete the following statements. Insert your answer in the blanks. Standing on your toes as in ballet is of the foot. Walking on your heels is. Winding up for a pitch in baseball is. To keep your seat when riding a horse, the tendency is to your thighs. In running, the action at the hip joint is in reference to the leg moving forward and in reference to the leg in the posterior position. When kicking a football, the action at the knee is. In climbing stairs, the hip and knee of the forward leg are both. You have just touched your chin to your chest; this is of the neck. Using a screwdriver with a straight arm requires of the arm. Consider all movements of which the arm is capable. One often used for strengthening all the upper arm and shoulder muscles is. Moving the head to signify no is. Action that moves the distal end of the radius across the ulna is. Raising the arms laterally away from the body is called of the arms. 15. Use the terms provided below to describe the manner in which muscles interact with other muscles. Antagonist, Fixator, Prime mover, Synergist 1. Agonist 2. Postural muscles for most part 3. Stabilizes a joint so that the prime mover can act at more distal joints 4. Performs the same movement as the prime mover 5. Reverses and/or opposes the action of a prime mover 6. Immobilizes the origin of a prime mover 16. Several criteria are applied to naming of muscles. Match the criteria that pertain to each muscle. Some may have more than one answer Gluteus maximus Adductor magnus Biceps femoris Transversus abdominis Extensor carpi ulnaris Trapezius Rectus femoris External oblique A. Action of muscle B. Shape of muscle C. Location of muscle s origin and or insertion D. Number of origins E. Location of muscle relative to a bone or body region F. Direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line G. Relative size of the muscle
6 17. Identify major muscles described below: Buccinator, frontalis, Masseter, Orbicularis oculi, Orbicularis oris, sternocleidomastoid, Temporalis, Trapezius, Zygomaticus 1. Used in smiling 2. Used to suck in your cheeks 3. Used in winking 4. Used to form the horizontal frown crease on forehead 5. The kissing muscle 6. Prime mover for jaw closer 7. Synergist muscle for jaw closure 8. Prime mover of head flexion; a twoheaded muscle 18. Color code and label each muscle: Buccinator, Frontalis, Masseter, Orbicularis oculi, Orbicularis oris, Sternocleidomastoid, Temporalis, Trapezius, Zygomaticus Zygomatic bone 19. Identify major muscles described below; Deltoid, Diaphragm, external incercostal, external oblique, Internal intercostal, Internal oblique, Latissimus dorsi, Pectoralis major, Rectus abdominis, Sternocleidomastoid, Transcersus abdominis 1. The name means straight muscle of the abdomen 2. Prime mover for shoulder flexion and adduction 3. Prime mover for shoulder abduction 4. Part of the abdominal girdle; forms the external lateral walls of the abdomen 5. Acting alone, each muscle of this pair turns the head toward the opposite shoulder 6. Besides the two abdominal muscles (pairs) two muscle pairs that help form the natural pelvic girdle, and 7. Deep muscles of the thorax that promote the inspiratory phase of breathing 8. An unpaired muscle that acts with the muscles name immediately above to accomplish inspiration 20. Color code and label each of the following, on the picture below; sternocleidomastoid, Deltoid, Pectoralis major, rectus abdominis, external oblique
7 6. Fleshy muscle forming part of the posterior abdominal wall that helps maintain upright posture Clavicle Sternum 22. Use the follwing terms to color code and label the picture below; trapezius, deltoid, latissimus dorsi, quadratus lumborum 21. Identify the following using the words below; Deltoid, Erector spinae, External oblique, Gluteus maximus, Latissimus dorsi, Quadratus lumborum, Trapezius 1. Muscle that allows you to shrug your shoulders or extend your head 2. Muscle that adducts the shoulder and causes extension of the shoulder joint 3. Shoulder muscle that is the antagonist of the muscle just described 4. Prime mover of back extension; a deep composite muscle consisting of three columns 5. Large paired superficial muscle of the lower back
8 23. Identify the follwing below using the key words; adductors, biceps femoris, fibularis muscles, gastrocnemius, fluteus maximus, gluteus medius, hamstrings, iliopsoas, quadriceps, rectus femoris, sartorius, semimembranousus, semitendinosus, soleus, tibialis anterior, bastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis 1. Hip flexor, deep in pelvis; a composite of 2 muscles 2. Used to extend the hip when climbing stairs 3. Toe dancer s muscle; a two-bellied muscle of the calf 4. Inverts and dorsiflexes the foot 5. Muscle group that allows you to draw your legs to the midline of your body, as when standing at attention 6. Muscle group that extends the knee 7. Muscle group that extends the thight and flexes the knee 8. Smaller hip muscle commonly used as an injection site 9. Muscle group of the lateral leg; plantar flex and evert the foot _ 10. Straplike muscle that is a weak thigh flexor; the tailors muscle 11. Like the two-bellied muscle that lies over it, this muscle is a plantar flexor _ 24. Using the following pictures label where the leader lines indicate, color code them as well.
9 25. Identify the muscles described below; Biceps brachii, deltoid, extensor carpi radialis, extensor digitorum, Flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum superficialis, triceps brachii 1. Wrist flexor that follows the ulna 2. Muscle that extends the fingers 3. Muscle the flexes the fingers 4. Muscle that allows you to bend (flex) the elbow ) 5. Muscle that extends your elbow 6. Powerful shoulder abductor, used to raise the arm overhead 26. Color and label the following picture below using these terms; deltoid, biceps brachii, triceps brachii, extensor digitorum, flexor carpi ulnaris 27. During an overambitious workout, a high school athelete pulled some muscles by forcing his knee into extension when his hip is already fully flexed. What muscles did he pull? 28. In an emergency appendectomy, the incision was made at the lateral edge of the right iliac abdominopelvic region. Was the rectus abdominis cut? 29. Gregor, who works at a pestide factory, comes to the clinic complaining of muscle spasms that interfere with his ovemevement and breathing. A blood test shows that he has abeen contaminated with organophosphate pesticide, which is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. How would you explain to Gregor what this means?
10 Define Chapter 6 Vocabulary 1. Muscle fibers 2. Skeletal muscle 3. Endomysium 4. Perimysium 5. Fasicle 6. Epimysium 7. Aponeuroses 8. Smooth muscle 9. Cardiac muscle 10. Sarcolemma 11. Myofibrils 12. Light (I) band 13. Dark (A) band 14. Sarcomeres 15. Myofilaments 16. Thick filaments 17. Mysoin 18. Cross bridges 19. Thin filaments 20. Actin 21. Sarcoplasmic reticulum 22. Motor unit 23. Axon 24. Axon terminals 25. Nuromuscular junctions 26. Neurotransmitter 27. Acetylcholine 28. Synatptic cleft 29. Action potential 30. Graded response 31. Creatine phosphate 32. Aerobic respriation
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Practice Chapter 6. Figure 6.3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Practice Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Voluntary muscle tissue is; a. smooth muscle b. skeletal muscle c. dense regular d.
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Figure 6.1. 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B.
 Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Chapter 8 - Muscular System 8.1 Introduction (p. 178 ) A. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. B. This chapter focuses on skeletal muscle. 8.2 Structure of a
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
The Muscular System General & Anatomy
 The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
The Muscular System General & Anatomy General Functions: 1. movement voluntary skeletal muscles 2. internal movement of substances through various tubes and passageways eg blood, food, urine heart pumps
Deltoid Trapezius. Identify the muscle pair(s) that work together to produce the movements listed above.
 Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Shoulder- the major muscles in this group are the infraspinatus, subscapularis, terems major, teres minor deltoid, and trapezius. These muscles work together to move the shoulder area, allowing you, for
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
UNIT 5 - MUSCULAR SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 5.0I MUSCLE TISSUE FUNCTIONS A. Motion by moving the skeletal levers of the body B. Posture - stabilizing body positions C. Regulation of organ volume D. Thermogenesis
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
CHAPTER 9: THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare and contrast the types of muscle tissues in terms of structure, control, location, and type of contraction, and function. 2. Describe three similarities among the three muscle tissues.
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 9.1 Introduction UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 9: MUSCULAR SYSTEM 1. List various outcomes of muscle actions. 9.2 Structure of a Skeletal Muscle 2. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. 3.
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscle Organization and Function. Chapter 10: The Muscular System. Parallel (Fusiform) Muscles. Organization of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
 Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Muscle Organization and Function Chapter 10: The Muscular System Muscle organization affects power, range, and speed of muscle movement Muscle cells (fibers) are organized in bundles (fascicles) Fibers
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Biology 105 Human Biology PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM 1. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 7 The Muscular System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) a function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B)
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
Chapter 9: Muscular System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 9: Muscular System Chapter 9: Muscular System I. Structure of a Skeletal Muscle A. Introduction 1. A skeletal muscle is
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 11-1 Describe the arrangement of
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory
 Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of 4-20 myofibrils Myofibrils are
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson
 Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
Flexibility Assessment and Improvement Compiled and Adapted by Josh Thompson Muscles must have a full and normal range of motion in order for joints and skeletal structure to function properly. Flexibility
TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES
 Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Referring to Chapters 12-14 TOTAL BODY: POWER/EXPLOSIVE EXERCISES Power Snatch hip extension Muscle group/ gluteals gluteus maximis hamstrings semimembranosus semitendinosus biceps femoris knee extension
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE. Striations Present or Absent?
 BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
BIO 2401 MUSCLE TISSUE page 1 Types of Muscle MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE Type of Muscle Skeletal Location of Muscle attaches to and covers bony skeleton Striations Present or Absent? present Control of
Muscular System Teacher s lecture notes, curriculum and guides 2012
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
MUSCULAR SYSTEM INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move a. Movement caused by ability of muscle cells (called fibers) to shorten or contract b. Muscle cells shorten by converting
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
Chapter 10: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Describe the three key functions of muscle. 2. Describe the four special properties of muscle tissue. SKELETAL MUSCLE
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM
 EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM EXERCISE MANUAL PERSONALITY GYM legs. 1 calves raise Stand with the wide part of one foot on the seated row foot support. Start in a position with your calves stretched.
Muscles and Contraction
 Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Muscles and Contraction Muscle tissue forms the organs called muscle. Three types of muscle tissue are (1) skeletal, (2) cardiac, and (3) smooth. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
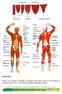 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Sternocleidomastoid (anterior neck) Origin Insertion Action
 Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Muscular movements of the head (at the cervical spine/neck) and of the torso (thoracic and lumbar spine/upper, middle, and lower back): flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Muscles of the Neck
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
MUSCULAR SYSTEM. A. K. Sengupta 9/9/2010 1/12
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
MUSCULAR SYSTEM Introduction Functions and basic types of muscle cells Skeletal muscle cells and connective tissues The nervous system Mechanism of muscle contraction Motor unit Action potential basis
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
CHAPTER XV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Types of Muscle Tissue Classified by location, appearance, and by the type of nervous system control or innervation. Skeletal
Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb
 2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
2 Stretching the Major Muscle Groups of the Lower Limb In this chapter, we present appropriate stretching exercises for the major muscle groups of the lower limb. All four methods (3S, yoga, slow/static,
Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or
 Chapter The Muscular System 5 Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or contracting. This unique ability is what makes body movements possible. Without muscle the powerful movements required
Chapter The Muscular System 5 Muscle is the only human tissue capable of shortening, or contracting. This unique ability is what makes body movements possible. Without muscle the powerful movements required
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE
 MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUE The muscular system provides for movement of the body and its parts (as muscles shorten), maintains posture, generates heat and stabilizes joints. The various types of muscles
Muscular System. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscular System Overview of Muscle Tissues Types of Muscle Tissue o Skeletal and smooth muscles which are elongated are called muscle fibers o Myo- and Mys- = muscle o Sarco = flesh refers to muscle; i.e.,
Muscular System Overview of Muscle Tissues Types of Muscle Tissue o Skeletal and smooth muscles which are elongated are called muscle fibers o Myo- and Mys- = muscle o Sarco = flesh refers to muscle; i.e.,
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST
 Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Ken Ross BSc ST, Nat Dip ST Trunk Most people will suffer from back pain at some point in their lives. Good spinal posture places minimal strain on the muscles which maintain the natural curve of the spine
Muscles of Mastication
 Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscles of Mastication Masseter Zygomatic Arch Mandibular angle Elevates mandible Mandibular ramus Temporalis Temporal fossa of the temporal bone Coronoid process of the mandible Elevates mandible Retracts
Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Muscular System: Muscle Tissue (Chapter 10) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers
 Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers When a muscle cell contracts t it pulls on the collagen fibers creating tension
Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues are specialized to contract. Muscle cells are connected together, primarily by collagen fibers When a muscle cell contracts t it pulls on the collagen fibers creating tension
Don t. Hamstrings. Calf Muscles. both legs 2-3 times. stretch is felt in the back of the calf. Repeat with both legs 2-3 times.
 Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols
 NeuroTrac Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols 1 Contents Contents Page Introduction 4 Muscle profile 4 Classification of the various
NeuroTrac Electrode Placement Manual Visit our website: www.veritymedical.co.uk for detailed application protocols 1 Contents Contents Page Introduction 4 Muscle profile 4 Classification of the various
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, muma@ithaca.edu Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, mbamberger@ithaca.edu Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
DSM Spine+Sport - Mobility
 To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
To set yourself up for success, practice keeping a neutral spine throughout all of these movements. This will ensure the tissue mobilization is being applied to the correct area, and make the techniques
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights
 Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
Chair Exercises and Lifting Weights Why are chair exercises and lifting weights important? Physical activity is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your diabetes control as well as
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Get Moving! All About Muscles
 Get Moving! All About Muscles A Reading A Z Level U Quick Reader Word Count: 2,002 Q U I C K R E A D E R U Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Get Moving! All About Muscles A Reading A Z Level U Quick Reader Word Count: 2,002 Q U I C K R E A D E R U Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function.
 Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of skeletal muscle 2. understand the function of a motor unit 3.
Skeletal Muscle Structure & Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of skeletal muscle 2. understand the function of a motor unit 3.
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Oatis_CH04_045-068.qxd 4/18/07 2:21 PM Page 45 CHAPTER 4 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle CHAPTER CONTENTS STRUCTURE OF SKELETAL MUSCLE.......................................................................46
Oatis_CH04_045-068.qxd 4/18/07 2:21 PM Page 45 CHAPTER 4 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle CHAPTER CONTENTS STRUCTURE OF SKELETAL MUSCLE.......................................................................46
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis
 Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal
 Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper Extremity Pectoralis Major Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal Crest of greater tubercle (Lateral lip of bicipital groove)
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and
 A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins
 Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
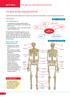 SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
SECTION A A general overview of the skeletal system is required, but will not be directly examined, so we include a general overview here. Introduction The skeletal system The appendicular skeletal system
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises
 Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Cardiac Rehab Program: Stretching Exercises Walk around the room, step side to side, ride a bike or walk on a treadmill for at least 5 minutes to warm up before doing these stretches. Stretch warm muscles
Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics
 2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
Hip and Trunk Exercise Program
 Hip and Trunk Exercise Program Hip and Pelvis Exercise Program Gluteus Medius and Minimus (Hip Abductors) Page 2 Lateral Hip Rotators Page 6 Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) and Illiotibial Band (ITB) Page 7 Lower
Hip and Trunk Exercise Program Hip and Pelvis Exercise Program Gluteus Medius and Minimus (Hip Abductors) Page 2 Lateral Hip Rotators Page 6 Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL) and Illiotibial Band (ITB) Page 7 Lower
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND
 Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
Muscle Energy Technique. Applied to the Shoulder
 Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Muscle Energy Technique Applied to the Shoulder MUSCLE ENERGY Theory Muscle energy technique is a manual therapy procedure which involves the voluntary contraction of a muscle in a precisely controlled
Myofit Massage Therapy Stretches for Cycling
 Guidelines for Stretching Always assume the stretch start position and comfortably apply the stretch as directed. Think Yoga - gently and slowly, no ballistic actions or bouncing at joint end range. Once
Guidelines for Stretching Always assume the stretch start position and comfortably apply the stretch as directed. Think Yoga - gently and slowly, no ballistic actions or bouncing at joint end range. Once
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function. Skeletal muscles act on bones to produce movement of the limb and to move (lift and carry) objects.
 ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Spine Conditioning Program Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain
 Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
Understanding back pain 1 The anatomy & physiology of back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse
 PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
Stretching in the Office
 Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
7Muscles. Major Themes. Chapter Objectives. Overview of Muscle 228. Structure of Skeletal Muscle Tissue 231. Muscle Energy 243
 7Muscles Major Themes Muscle cells shorten on command; no other cells do. There are three types of muscle cells: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily to produce body movements.
7Muscles Major Themes Muscle cells shorten on command; no other cells do. There are three types of muscle cells: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle contracts voluntarily to produce body movements.
Speed, Agility, Quickness Training
 Speed, Agility, Quickness Training Goal: To develop Speed, Agility, and Quickness (SAQ) and functional football strength for young football players through a consistent and safe format. Place the stations
Speed, Agility, Quickness Training Goal: To develop Speed, Agility, and Quickness (SAQ) and functional football strength for young football players through a consistent and safe format. Place the stations
11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions. Taft College Human Physiology
 11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Taft College Human Physiology Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Isotonic Contractions: Tension produced and overall shortening of the muscle as a load is
11 - Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Taft College Human Physiology Types Of Skeletal Muscle Contractions Isotonic Contractions: Tension produced and overall shortening of the muscle as a load is
