Anatomy and Physiology
|
|
|
- Preston Caldwell
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies
2 !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on exercise to your standard lab experience. It is not intended to be used in lieu of the hands on lab time. In lab you will be tested on the actual lab specimens and not the pictures contained within this video presentation.
3 How to use this material Each specimen is illustrated in a two slide sequence. The first slide contains a fully labeled specimen. The second slide is missing the labels and asks you to supply them like a test circumstance. You can toggle back and forth between the two slides until you have mastered all the items. This presentation is patterned after material within your lab manual by Darrell Davies. Be sure to check with your instructor for any alterations specific to your course. This presentation is designed to better prepare you for lab quizzes, or Part I of the two part testing system in each lab unit. Other video material (A.D.A.M. and Histology) is accessed elsewhere. Those materials are for lab practicals, Part II of testing in each lab unit.
4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Funding for this presentation was obtained through an Innovations In Learning Technologies grant at KVCC. I wish to thank Marylan Hightree and Lynn Morrison for their technical assistance during development of this material. I also wish to thank Michelle VanderMeer for her work in developing the beta version of this presentation as her tutoring internship while working at the KVCC Learning Center.
5 Unit III lab exercises # Cardiovascular Lymphatic Respiratory
6 Human Heart Lab exercises #11 & 12
7 Life sized human heart Our enlarged model in lab
8 Lymph node (green dots) Anterior view heart Lymph vessel (green lines) R I G H T S I D E Base of heart Trachea Myocardium L E F T S I D E Apex of heart
9 (green dots) view heart (green lines) of heart of heart
10 Aorta Inferior vena cava Major venous sinus Apex Inferior view
11 view
12 Lt. Brachiocephalic v. Anterior view veins Base of heart Rt. Brachiocephalic v. Superior vena cava Rt. Internal jugular Rt. Subclavian v. Lt. Internal jugular Lt. Subclavian v.
13 view of heart
14 Rt. Common carotid Lt. common carotid Rt. Subclavian a. Brachiocephalic a. Anterior view arteries Aorta Base of heart Lt. subclavian a. Lt. pulmonary a. Pulmonary trunk
15 View of heart
16 Anterior view dissected heart Rt. atrium Lt. atrium Base Tricuspid valve Mitral valve Rt. ventricle Interventricular septum (hypertrophied) Apex Lt. ventricle Hypertrophied wall of lt. ventricle
17 view dissected heart ( ) of
18 Pulmonary semilunar valve Rt.at. Hypertorphied Interventricular septum Lt.at. Tricuspid valve Mitral / bicuspid valve
19 .... /
20 Respiratory Tree Lab exercise #13
21 Larynx Rt. primary / main stem bronchus Trachea Lt. primary / main stem bronchus Carina Respiratory tree rt. oblique view
22 / / Respiratory tree rt. oblique view
23 Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid ligament Thyroid cart. Adam s apple Cricothyroid ligament Thyroid gld. (rt. half) Trachea Cricoid cart.
24 (rt. half)
25 Rt. Primary / main stem bronchus Trachea Lt. primary / main stem bronchus 3 rt. Side secondary / lobar bronchi Carina 2 lt. side secondary / lobar bronchi 20 Tertiary bronchi (multicolored tubes)
26 / Trachea / / / (multicolored tubes)
27 Thyrohyoid ligament Epiglottis False vocal fold True vocal fold (vocal chord) Adam s apple Cricoid cart. c.c. Cricothyroid ligament Trachea Larynx midsagittal section
28 ( ) c.c. section
29 Larynx Lab exercise #13
30 Hyoid bone Epiglottis Arytenoid carts. Thyroid cart. Adam s apple Cricoid cart. Trachea Larynx anterior view
31 view
32 Epiglottis Glottis Thyroid cart. Arytenoid carts. Cricoid cart. Trachea Larynx Posterior view
33 view
34 A N T E R I O R Adam s apple Cricoid cart. Hyoid bone Epiglottis Thyroid cart. Trachea P O S T E R I O R Larynx lt. lateral view
35 Larynx view
36 Larynx superior view Hyoid bone Epiglottis Thyroid cart. Thyroid cart. True vocal folds / vocal chords Glottis Arytenoid carts.
37 view /
38 Lungs Lab exercise #13
39 view multicolored lung ( + ) lung ( + ) lung lung
40 Lungs anterior view 20 multicolored lung segments ( ) Lower lobe Upper lobe Middle lobe Apices M E D I A S T I N U M Upper lobe Lower lobe 5 lung lobes (3 + 2) Rt. lung Lt. lung
41 Sagittal Section Head Lab exercise #13
42 Frontal sinus Crista gali of ethmoid Hypophyseal fossa of sphenoid Superior concha Sphenoid sinus Middle concha Uvula Inferior concha Vestibule Hard palate (maxilla + palatine bones) Eustachian tube origin Head midsagittal section
43 of of ( + ) Head section
44 Frontal sinus Crista gali of ethmoid Cribriform plate of ethmoid Hypophyseal fossa of sphenoid Spenoid sinus External nare
45 of of of
46 Middle concha Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid) Inferior concha Eustachian tube origin Uvula Palatine tonsil Epiglottis Lingual tonsil
47 ( )
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Administrative. Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality
 CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
CHEST X-RAY Administrative Patient name Date compare with previous Position markers R-L, upright, supine Technical quality AP or PA ( with x-ray beam entering from back of patient, taken at 6 feet) Good
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
the Cardiovascular System
 5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant 8. Blood supply of lungs 9. Lymphatics of Lungs 10. Nerve supply of Lungs 11. Pleura 12.
 ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Cardiology. Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart.
 Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart. Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Page 1 CONTENT Introduction Page 3 How to use the ECG Self Learning package.page
Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart. Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Page 1 CONTENT Introduction Page 3 How to use the ECG Self Learning package.page
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System
 Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Respiratory System Questions
 1. Which of the following bones does NOT contain a paranasal sinus? a. Sphenoid b. Maxillary c. Ethmoid d. Nasal e. Frontal 2. Which of the following muscles contracts during quiet expiration? a. Diaphragm
1. Which of the following bones does NOT contain a paranasal sinus? a. Sphenoid b. Maxillary c. Ethmoid d. Nasal e. Frontal 2. Which of the following muscles contracts during quiet expiration? a. Diaphragm
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Anatomy of the Respiratory System. The Respiratory System. Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2.
 The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen
 RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
RACE I Rapid Assessment by Cardiac Echo Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre NIjmegen RACE Goal-directed study with specific questions Excludes Doppler ultrasound Perform 50
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Normal CT scan of the chest
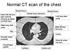 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION
 Pocket Guide To TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION Edited by Daniel G. Deschler, MD Terry Day, MD AAO HNS/F American Head and Neck Society Pocket Guide to NECK DISSECTION
Pocket Guide To TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION Edited by Daniel G. Deschler, MD Terry Day, MD AAO HNS/F American Head and Neck Society Pocket Guide to NECK DISSECTION
How To Teach An Integrated Ultrasound
 University of South Carolina School of Medicine Integrated Ultrasound Curriculum iusc Richard Hoppmann The Integrated Ultrasound Curriculum Initiated 2006 First (M1) and Second (M2) Year Medical Students
University of South Carolina School of Medicine Integrated Ultrasound Curriculum iusc Richard Hoppmann The Integrated Ultrasound Curriculum Initiated 2006 First (M1) and Second (M2) Year Medical Students
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
CHAPTER 19: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Fully explain the process (5 parts of) respiration. 2. Describe the significance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human cells. 3. Explain the structure and function of mucous membranes that
OBJECTIVES: 1. Fully explain the process (5 parts of) respiration. 2. Describe the significance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human cells. 3. Explain the structure and function of mucous membranes that
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human
 Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANIMAL SCIENCE 8646-B THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Respiration* is a physical process by which living organisms inhale oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere and then exhale carbon dioxide. The
ANIMAL SCIENCE 8646-B THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Respiration* is a physical process by which living organisms inhale oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere and then exhale carbon dioxide. The
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Question Bank Cardiology 2015. 143 157: Vignette multiple choice questions with answers
 Question Bank Cardiology 2015 Questions # s 1 127: Simple multiple choice questions 128 142: K-Type Questions 143 157: Vignette multiple choice questions with answers 1. A derivative of the intra-embryonic
Question Bank Cardiology 2015 Questions # s 1 127: Simple multiple choice questions 128 142: K-Type Questions 143 157: Vignette multiple choice questions with answers 1. A derivative of the intra-embryonic
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14
 Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY. Front and lateral view
 NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY Front and lateral view Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP How to obtain a good quality
NORMAL CHEST RADIOGRAPHY Front and lateral view Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) OFCP How to obtain a good quality
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAT DISSECTION UNIT
 CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
ENTERAL NUTRITION Policy/CPT ICD-10 ICD-10 Description ICD-9 ICD-9 Description EPA 870001100 N18.6 End stage renal disease 585.6 End stage renal disease EPA 870001101 C00.0 Malignant neoplasm of external
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve,
 Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
Questions FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008
 FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems
 Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Anatomy for Sport and Exercise
 Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
Unit 1: Anatomy for Sport and Exercise Unit code: M/600/0038 QCF Level 3: BTEC National Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose This unit explores the structure and function of the skeletal,
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Paramedic Resource Manual 2005
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP Paramedic Resource Manual 2005 SECOND EDITION Revised by Ontario Base Hospital Group Education Subcommittee Paramedic Resource Manual 2005 UPDATED BY Rob Theriault EMCA, RCT(Adv.),
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP Paramedic Resource Manual 2005 SECOND EDITION Revised by Ontario Base Hospital Group Education Subcommittee Paramedic Resource Manual 2005 UPDATED BY Rob Theriault EMCA, RCT(Adv.),
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
Changes to units must be approved by the appropriate committee/s. Unit guides should not be altered until notification of approval has been received.
 CHANGE UNIT OUTCOME/S COVER SHEET Changes to units must be approved by the appropriate committee/s. Unit guides should not be altered until notification of approval has been received. Medicine - the appropriate
CHANGE UNIT OUTCOME/S COVER SHEET Changes to units must be approved by the appropriate committee/s. Unit guides should not be altered until notification of approval has been received. Medicine - the appropriate
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
HISTORY. Questions: 1. What diagnosis is suggested by this history? 2. How do you explain her symptoms during pregnancy?
 HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
HISTORY 33-year-old woman. CHIEF COMPLAINT: months duration. Dyspnea, fatigue and nocturnal wheezing of six PRESENT ILLNESS: At ages 5 and 9, she had migratory arthritis. At age 29, in the third trimester
Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum
 Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum Philippe G. Dartevelle MARIE-LANNELONGUE HOSPITAL GUSTAVE ROUSSY INSTITUTE INSTITUTE OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY PARIS SUD UNIVERSITY Mediastinal Invasion Superior
Resection of Lung Cancer Invading the Mediastinum Philippe G. Dartevelle MARIE-LANNELONGUE HOSPITAL GUSTAVE ROUSSY INSTITUTE INSTITUTE OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY PARIS SUD UNIVERSITY Mediastinal Invasion Superior
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE
 RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter The Cardiovascular System: The Heart 663 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart WHY THIS MATTERS In this chapter, you will learn that The heart pumps blood through the pulmonary and systemic circuits
Chapter The Cardiovascular System: The Heart 663 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart WHY THIS MATTERS In this chapter, you will learn that The heart pumps blood through the pulmonary and systemic circuits
The heart walls and coronary circulation
 CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Heart Sounds & Murmurs
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Sounds & Murmurs Dr. Abeer A. Al-Masri MBBS, MSc, PhD Associate Professor Consultant Cardiovascular Physiologist Faculty of Medicine, KSU Detected over anterior chest wall
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book
 Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book Terms of Position and Direction 1. A section that separates the body in to right and left portions would be the A. Frontal section B. transverse
Emergency Medical Responder: Anatomy & Physiology Question Book Terms of Position and Direction 1. A section that separates the body in to right and left portions would be the A. Frontal section B. transverse
Syllabus for Biology 2402 Human Anatomy & Physiology 2 [This is a generic syllabus. Each instructor will give a syllabus customized for their course.
 Syllabus for Biology 2402 Human Anatomy & Physiology 2 [This is a generic syllabus. Each instructor will give a syllabus customized for their course.] Course Description Human Anatomy and Physiology II
Syllabus for Biology 2402 Human Anatomy & Physiology 2 [This is a generic syllabus. Each instructor will give a syllabus customized for their course.] Course Description Human Anatomy and Physiology II
Development of Simulation Tools Software
 Development of Simulation Tools Software Vincent Luboz Department of Biosurgery and Surgical Technology Imperial College London BSc VR Surgical Simulation Software Slide 1 Contents Virtual Reality VR Surgical
Development of Simulation Tools Software Vincent Luboz Department of Biosurgery and Surgical Technology Imperial College London BSc VR Surgical Simulation Software Slide 1 Contents Virtual Reality VR Surgical
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Activity 6.5 Crime investigation
 Purpose To explore the use of forensic techniques in an applied context. Body discovered A body has been discovered at a house in Redhill, Surrey. The body was found outside, near the house, and the immediate
Purpose To explore the use of forensic techniques in an applied context. Body discovered A body has been discovered at a house in Redhill, Surrey. The body was found outside, near the house, and the immediate
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Introduction to CV Pathophysiology. Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
 Introduction to CV Pathophysiology Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology 1. Basic Anatomy 2. Excitation Contraction Coupling
Introduction to CV Pathophysiology Munther K. Homoud, MD Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 Introduction to Cardiovascular Pathophysiology 1. Basic Anatomy 2. Excitation Contraction Coupling
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
